Microstructure Design for Fast Lifetime Measurements of Magnetic Tunneling Junctions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Statistics for the Measurement of the Lifetime
- Failure rate decreases with time. The population shows a certain degree of infant mortality, i.e., a fraction of the elements breaks shortly after the application of the stress agent. This regime is not desired for production since a large part of the sensor population will fail in an early stage.
- Failure rate increases with time. The behavior is dominated by aging. In addition, an initial time window exists for which the failure rate is negligible. This is the desired situation for applications since it allows the introduction of a guarantee time.
- Constant failure rate. Transition between the two previous cases. However, it may also be an indication of the existence of an external random agent dominating the behavior when this is always the case (e.g., a defective measurement setup generating peak voltages). The dependence of the lifetime on the stress agent strength allows to distinguish between both situations.
Measurement Time
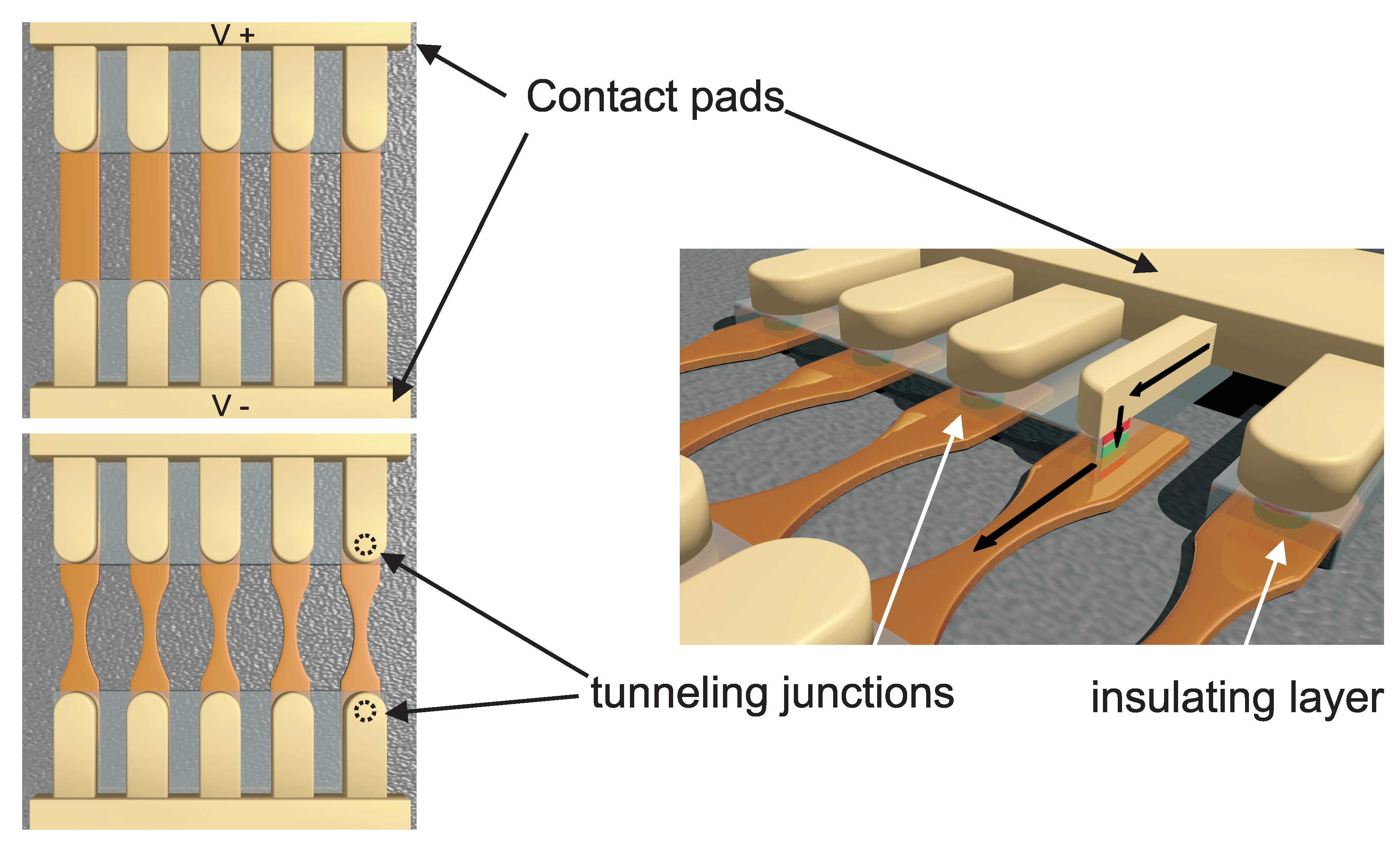
3. Description of the Microstructure Design
4. Results and Discussion
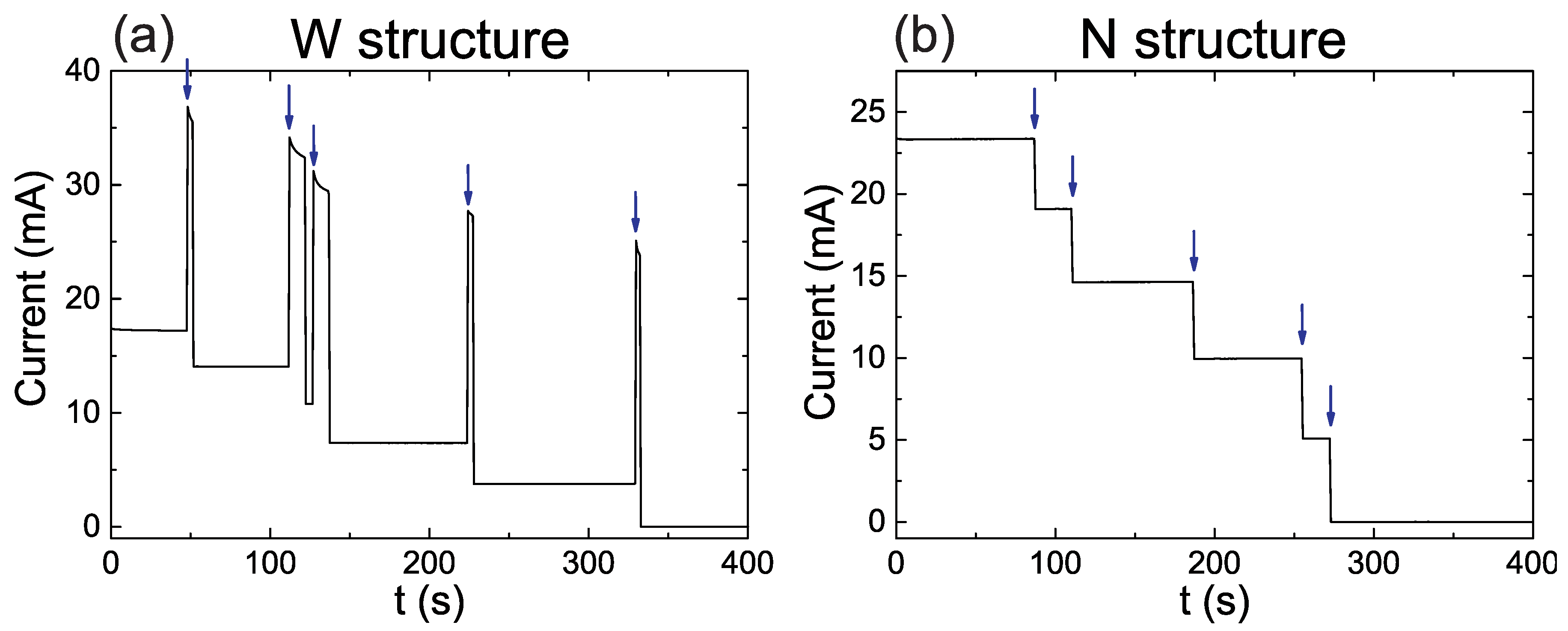
4.1. Single Measurements
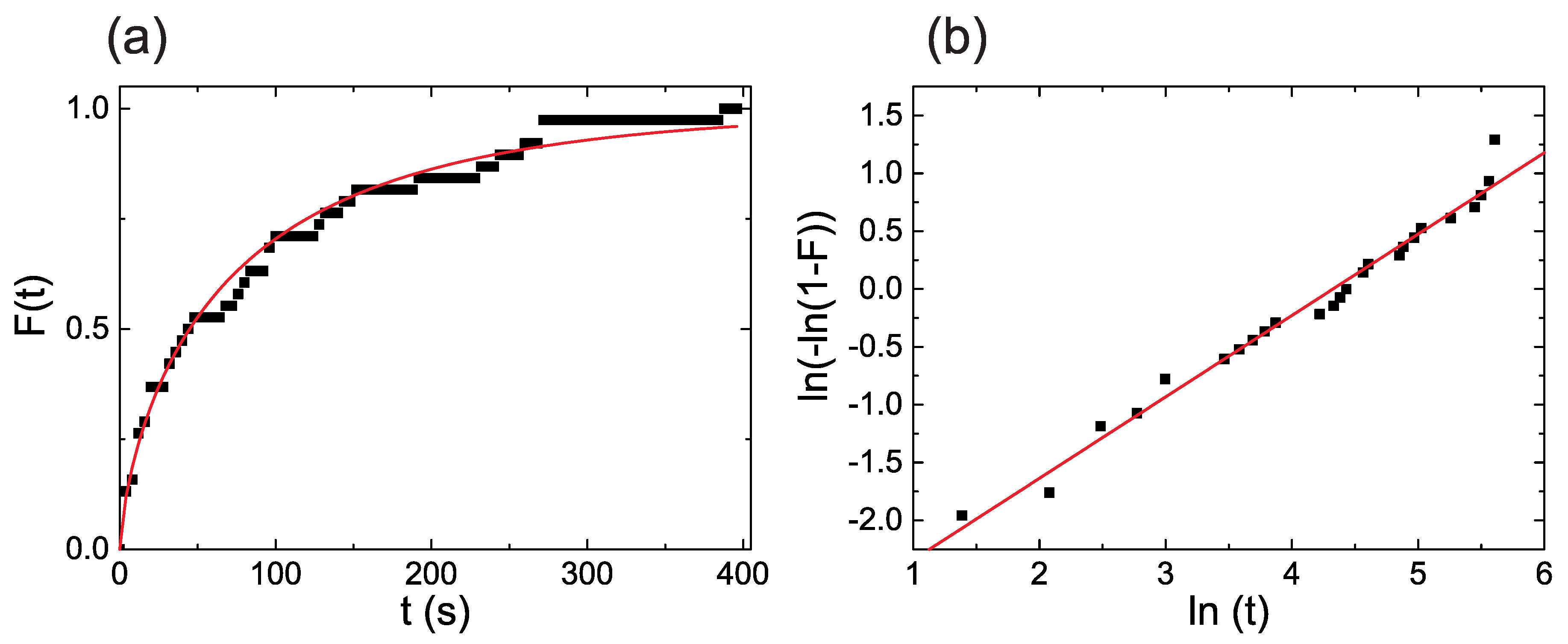
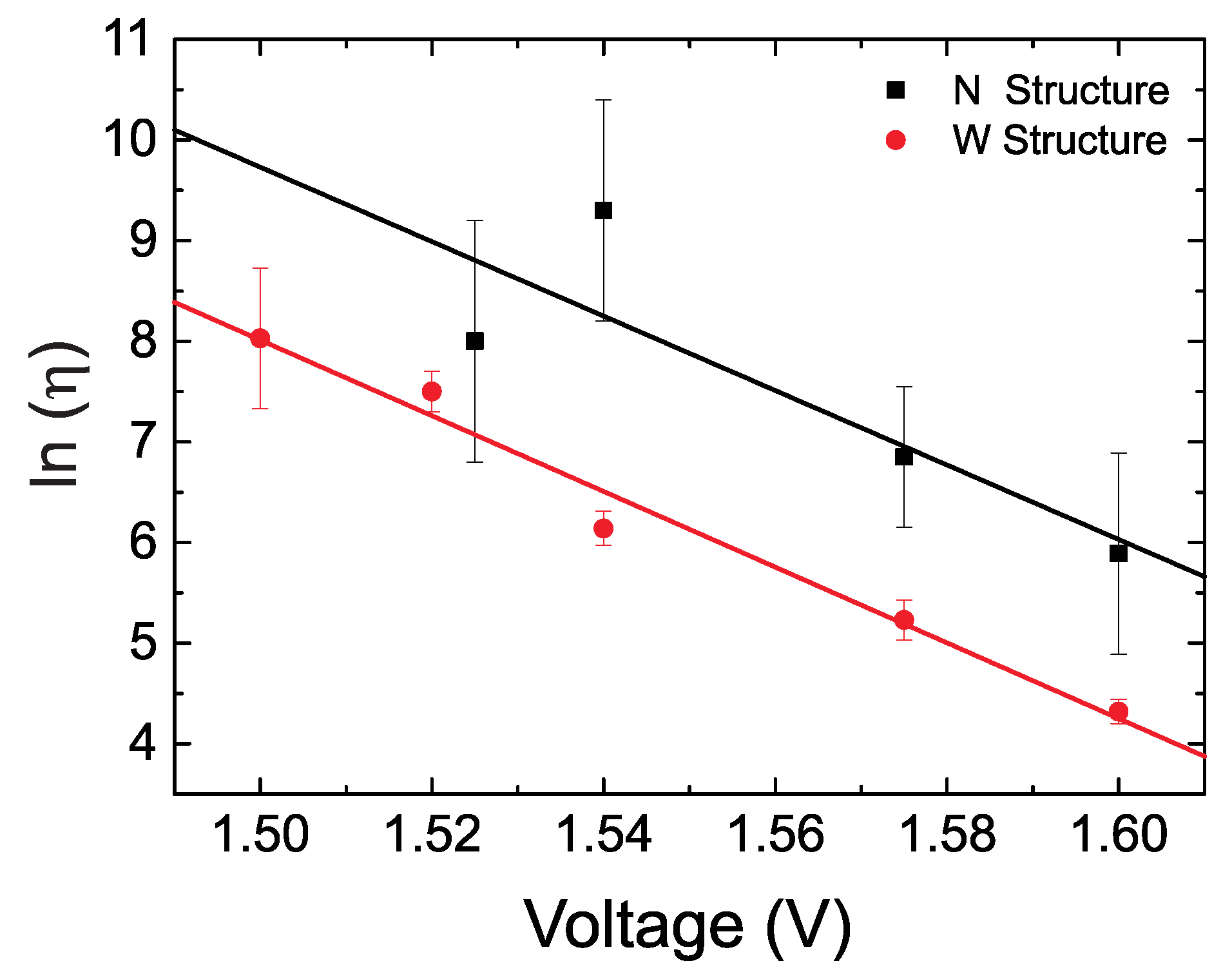
4.2. Weibull Plots and Extrapolation
5. Conclusions
6. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MTJ | Magnetic tunneling junction |
| GMR | Giant Magnetoresistance |
| TMR | Tunneling Magnetoresistance |
References
- Yamazaki, H.; Hirabayashi, H.; Oyama, N.; Sakai, M. Characteristics of TMR Angle Sensors. In Proceedings of the SENSOR+TEST Conferences, Nurenberg, Germany, 7–9 June 2011; pp. 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- TDK Corporation. Angle Sensors: TMR Angle Sensor with Digital Output; TDK Corporation: Tokyo, Japan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Data Sheet AAT001-10E TMR Angle Sensor NVE Corporation. Available online: www.nve.com/Downloads/AAT001.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2018).
- Wang, M.; Cai, W.; Cao, K.; Zhou, J.; Wrona, J.; Peng, S.; Yang, H.; Wei, J.; Kang, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Current-induced magnetization switching in atom-thick tungsten engineered perpendicular magnetic tunnel junctions with large tunnel magnetoresistance. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, M.N.; Islam, M.N. The Weibull distribution as a general model for forecasting technological change. Tech. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 1980, 18, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIST/SEMATECH e-Handbook of Statistical Methods. Available online: http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/ (accessed on 15 December 2018).
- Cheung, K.P. Plasma Charging Damage; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Das, J.; Degraeve, R.; Roussel, P.; Groeseneken, G.; Borghs, G.; De Boeck, J. Area scaling and voltage dependence of time-to-breakdown in magnetic tunnel junctions. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Sok, J.; Cho, B.K.; Rhee, J.R.; Parkand, W.; Kim, T. Dielectric Characteristics of Magnetic Tunnel Junctions Using Amorphous CoNbZr Layers. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2005, 46, 1425. [Google Scholar]
- Conca, A.; Casper, F.; Paul, J.; Lehndorff, R.; Jakob, G.; Kläui, M.; Hillebrands, B.; Leven, B. Influence of the MgO barrier thickness on the lifetime characteristics of magnetic tunnelling junctions for sensors. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 225001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, T.; Chen, Q.; Beach, R.; Jan, G.; Horng, C.; Kula, W.; Torng, T.; Tong, R.; Zhong, T.; Tang, D.; et al. A Study of Write Margin of Spin Torque Transfer Magnetic Random Access Memory Technology. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, M.; Sin, K.; Funada, S.; Shi, X. Lifetime of magnetic tunnel junctions under voltage stress. In Proceedings of the International Magnetics Conference INTERMAG Europe, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 28 April–2 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sensitec. Available online: www.sensitec.com (accessed on 15 December 2018).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conca Parra, A.; Casper, F.; Paul, J.; Lehndorff, R.; Haupt, C.; Jakob, G.; Kläui, M.; Hillebrands, B. Microstructure Design for Fast Lifetime Measurements of Magnetic Tunneling Junctions. Sensors 2019, 19, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030583
Conca Parra A, Casper F, Paul J, Lehndorff R, Haupt C, Jakob G, Kläui M, Hillebrands B. Microstructure Design for Fast Lifetime Measurements of Magnetic Tunneling Junctions. Sensors. 2019; 19(3):583. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030583
Chicago/Turabian StyleConca Parra, Andrés, Frederick Casper, Johannes Paul, Ronald Lehndorff, Christian Haupt, Gerhard Jakob, Mathias Kläui, and Burkard Hillebrands. 2019. "Microstructure Design for Fast Lifetime Measurements of Magnetic Tunneling Junctions" Sensors 19, no. 3: 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030583
APA StyleConca Parra, A., Casper, F., Paul, J., Lehndorff, R., Haupt, C., Jakob, G., Kläui, M., & Hillebrands, B. (2019). Microstructure Design for Fast Lifetime Measurements of Magnetic Tunneling Junctions. Sensors, 19(3), 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030583




