Adaptive Robust Unscented Kalman Filter via Fading Factor and Maximum Correntropy Criterion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fundamentals of the Proposed Filter
2.1. Maximum Correntropy Criterion
2.2. Cost Function of Adaptive Robust Kalman Filter
2.3. Formation of the Fading Factor
3. The New Adaptive Robust Unscented Kalman Filter
4. Simulation and Comparison
4.1. Radar Tracking System
4.2. Mars Entry Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Y. Consensus-Based Distributed Mixture Kalman Filter for Maneuvering Target Tracking in Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 8669–8681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumru, F.; Aka, T.; Altunta, E. Ballistic Target Tracking Using Multiple Model Kalman Filter with a Priori Ballistic Information. In Proceedings of the 25th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference, Antalya, Turkey, 15–18 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Prashant, G. Probabilistic Data AssociationFeedback Particle Filter for Multiple Target Tracking Applications. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2018, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E. A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems. Trans. ASME J. Basic Eng. 1960, 81, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.K.; Mba, D. Switching Kalman Filter for Failure Prognostic. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 52–53, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.G.; Teo, K.L.; Ahmed, N.U.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, W.Y. Optimal Fusion of Sensor Data for Kalman Filtering. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. A 2017, 14, 483–503. [Google Scholar]
- Psiaki, M. Kalman Filtering and Smoothing to Estimate Real Valued States and Integer Constants. J. Guidance Control. Dyn. 2010, 33, 1404–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroni, L. Kalman Filter for Attitude Determination of a CubeSat Using Low-cost Sensors. Comput. Appl. Math. 2017, 7–8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Deng, Z. Multi-sensor Optimal Information Fusion Kalman Filter. Automatica 2004, 40, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’ Anese, E.; Bazerque, J.A.; Giannakis, G.B. Group Sparse Lasso For Cognitive Network Sensing Robust to Model Uncertainties and Outliers. Phys. Commun. 2012, 5, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julier, S.; Uhlmann, J. Unscented Filtering and Nonlinear Estimation. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, R.; Wan, J. Iterated Unscented Kalman Filter for Passive Target Tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, 43, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasaratnam, I.; Haykin, S. Cubature Kalman Filters. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2009, 54, 1254–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, W. Strong Tracking Spherical Simplex-Radial Cubature Kalman Filter for Maneuvering Target Tracking. Sensors 2017, 17, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terejanu, G.; Singla, P.; Singh, T.; Scott, P. Adaptive Gaussian Sum Filter for Nonlinear Bayesian Estimation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2011, 56, 2151–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Wang, W.; Bai, L. Observation Noise Modeling Based Particle Filter: An Efficient Algorithm for Target Tracking in Glint Noise Environment. Neurocomputing 2015, 56, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, N.; Guo, J. Huber-Based Unscented Filtering and Its Application to Vision-Based Relative Navigation. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2010, 4, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durovic, Z.; Kovacevic, B. Robust Estimation with Unknown Noise Statistics. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1999, 44, 1292–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Sun, S. Robust Information Filter Based on Maximum Correntropy Criterion. J. Guidance Control Dyn. 2016, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlgaard, C.; Schaub, H. Adaptive Nonlinear Huber-Based Navigation for Rendezvous in Elliptical Orbit. J. Guidance Control Dyn. 2011, 34, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.; Mili, L. Robust Kalman Filter Based on a Generalized Maximum-Likelihood-Type Estimator. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Hu, B.; Chang, G.; Li, A. Multiple Outliers Suppression Derivative-Free Filter Based on Unscented Transformation. J. Guidance Control Dyn. 2015, 35, 1902–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, D.; de Souza, C.; Barbosa, K.; Trofino, A. Robust Linear H∞ Filter Design for a Class of Uncertain Nonlinear Systems: An LMI approach. SIAM J. Control. Optim. 2009, 48, 1452–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Zheng, W.; Sun, S. Adaptively Robust Unscented Kalman Filter for Tracking a Maneuvering Vehicle. J. Guidance Control Dyn. 2014, 37, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, H.; Xu, G. Adaptively Robust Filtering for Kinematic Geodetic Positioning. J. Geod. 2001, 75, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarinejadian, B.; Yousefi, M. Static Alignment of Inertial Navigation Systems Using an Adaptive Multiple Fading Factors Kalman Filter. Syst. Sci. Control. Eng. 2015, 3, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Wang, J. Adaptive Estimation of Multiple Fading Factors in Kalman Filter for Navigation Applications. GPS Solut. 2008, 12, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Frank, P. Strong Tracking Kalman Filtering of Nonlinear Time-Varying Stochastic Systems with Coloured Noise: Application to Parameter Estimation and Empirical Robustness Analysis. Int. J. Control 1996, 65, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, D.; Wu, M.; Hu, X. A Numerical Integration Perspective on Gaussian Filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 2910–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.S.; Cui, P.Y.; Zhu, S.Y. On the observability of Mars entry navigation using radiometric measurements. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Xia, Y.Q. Navigation Strategy with the Spacecraft Communications Blackout for Mars Entry. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 55, 1264–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
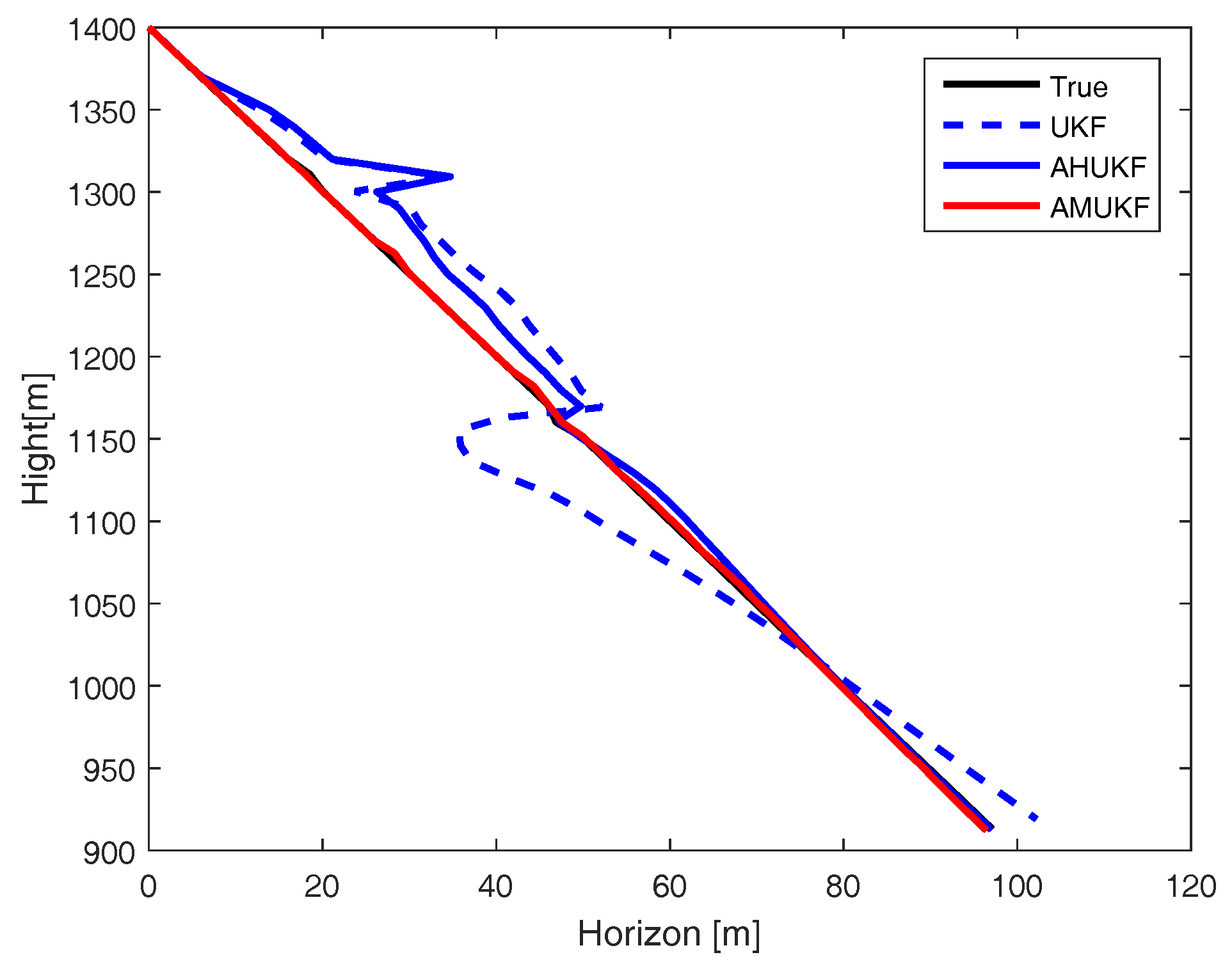
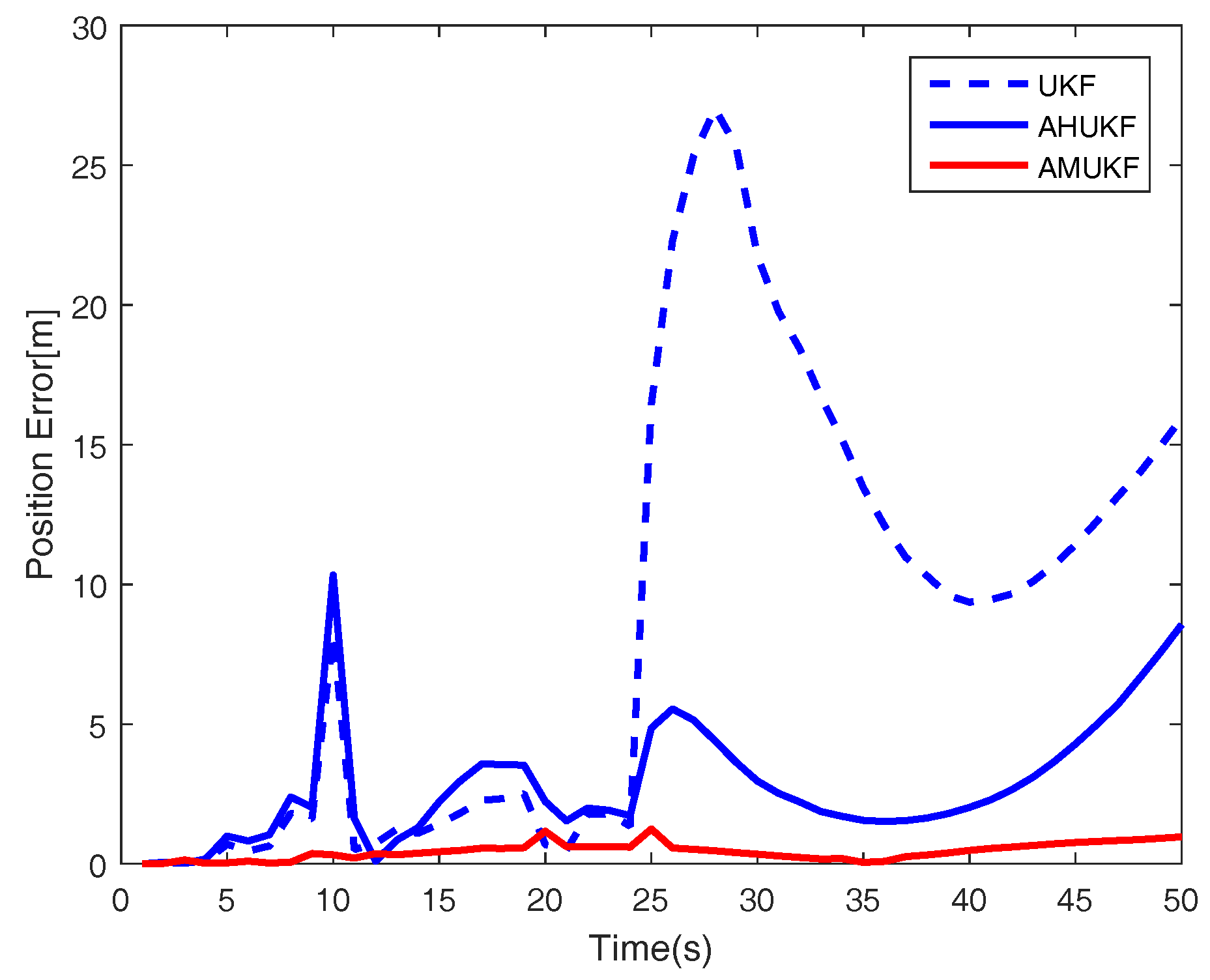



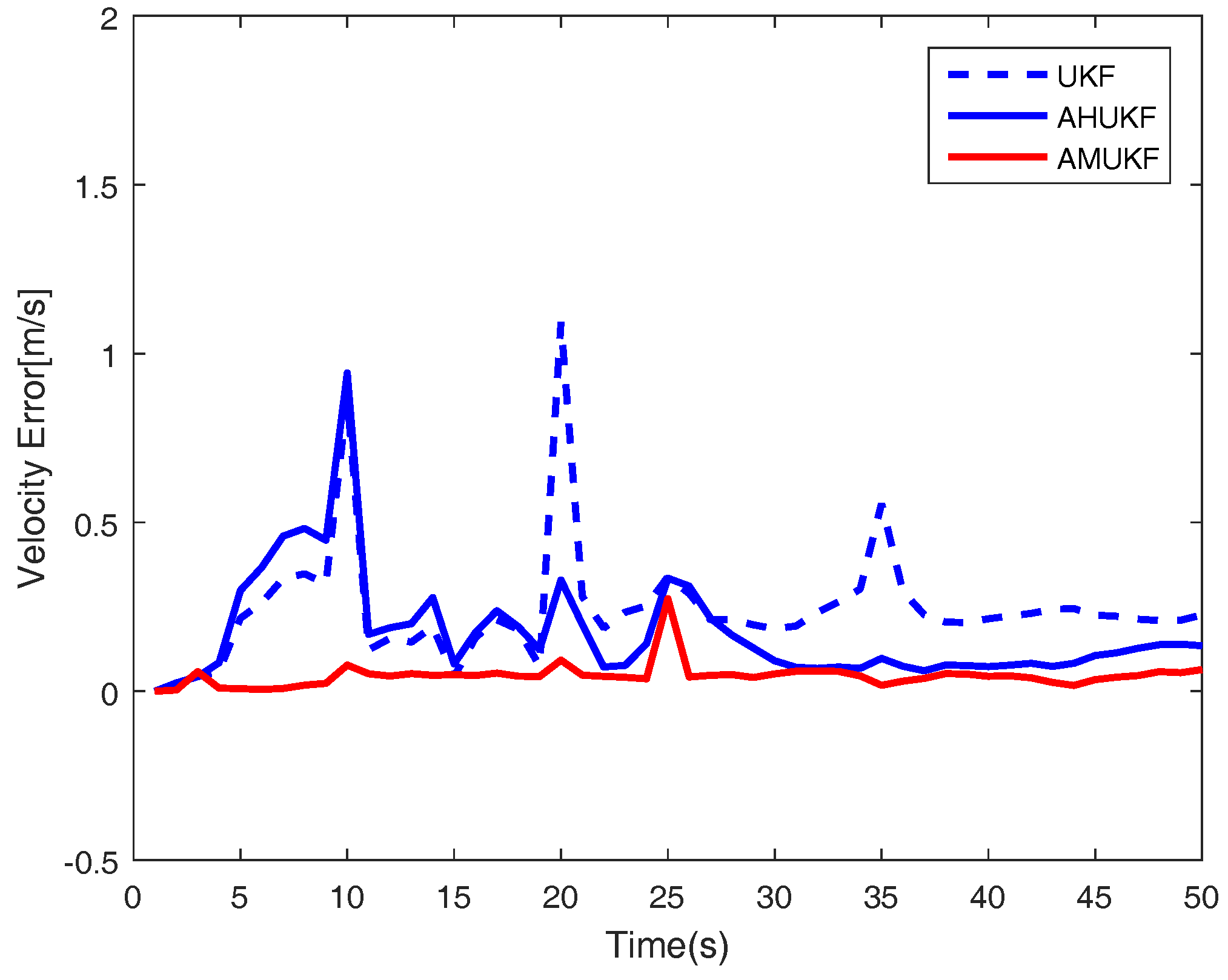


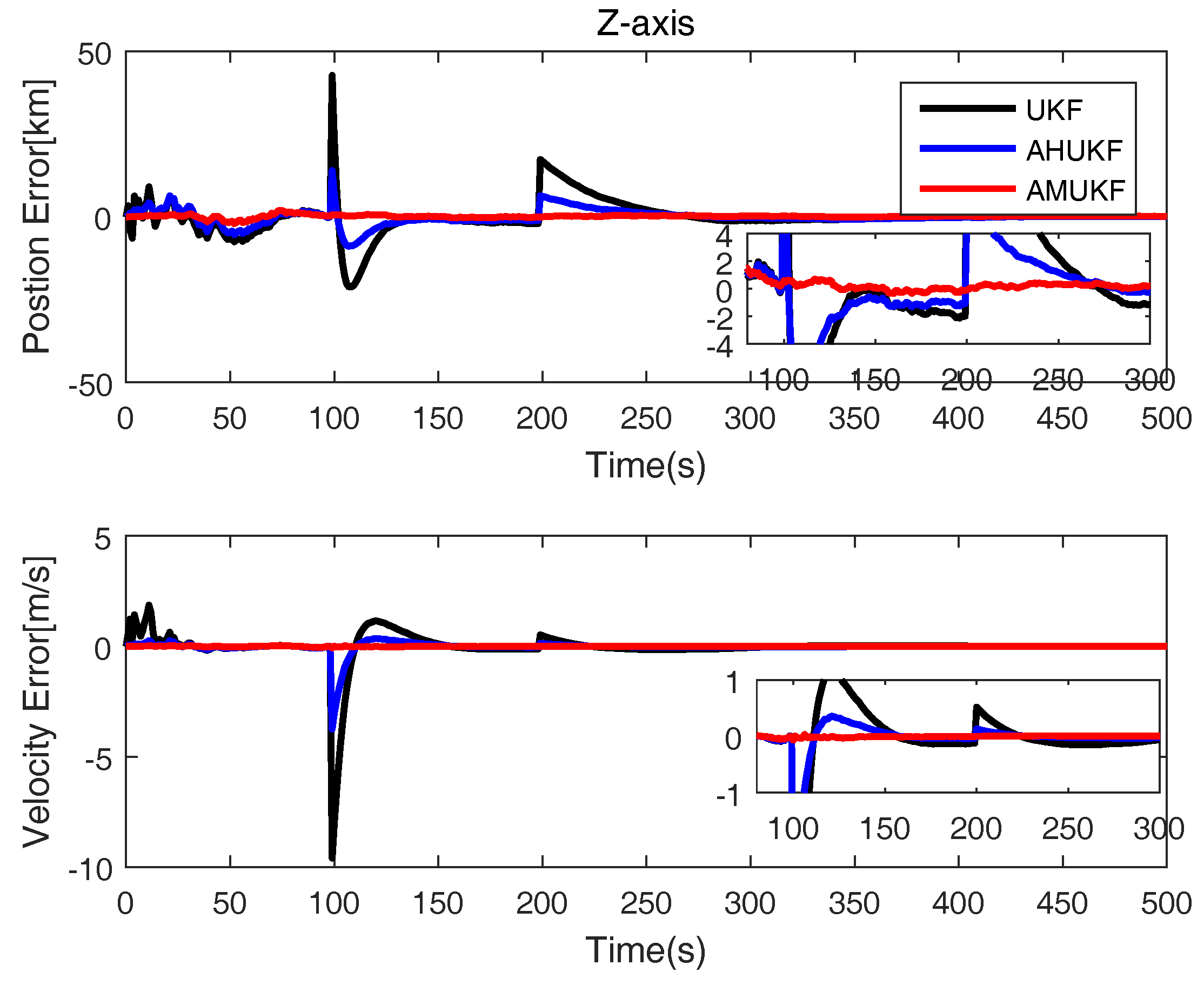
| First set = [0 m, 1400 m, 2 m/s, −10 m/s]. |
| . |
| Then iterate the follow, |
| for |
| Reformulate the augmented covariance |
| time update |
| Measurement update: |
| Calculate |
| end |
| where , , |
| , |
| and is a tune parameter. |
| More details about the selection of can be seen in [11,22]. |
| Filter | RMSE of x | RMSE of | RMSE of y | RMSE of |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UKF | 28.1 | 0.315 | 145 | 0.117 |
| AHUKF | 26.7 | 0.017 | 139 | 0.037 |
| AMUKF | 25.8 | 0.011 | 135 | 0.029 |
| Initial Setting | Notation | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Initial position | (−3.92 km, −3099.09 km, −1663.11 km) | |
| Initial velocity | (463.25 m/s, −1528.75 m/s, 5268.14 m/s) | |
| MSBs’ locations (1) | (875.35 km, −2914.43 km, −1509.77 km) | |
| MSBs’ locations (2) | (410.25 km, −2955.32 km, −1624.04 km) | |
| Vehicle mass | M | 2804 kg |
| Vehicle cross-section | s | 15.9 m |
| MRO | MEX | |
|---|---|---|
| semi-major axis a | km | km |
| eccentricity ratio e | rad | rad |
| argument of perigee | rad | rad |
| orbital inclination i | rad | rad |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Z.; Yin, L.; Huo, B.; Xia, Y. Adaptive Robust Unscented Kalman Filter via Fading Factor and Maximum Correntropy Criterion. Sensors 2018, 18, 2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082406
Deng Z, Yin L, Huo B, Xia Y. Adaptive Robust Unscented Kalman Filter via Fading Factor and Maximum Correntropy Criterion. Sensors. 2018; 18(8):2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082406
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Zhihong, Lijian Yin, Baoyu Huo, and Yuanqing Xia. 2018. "Adaptive Robust Unscented Kalman Filter via Fading Factor and Maximum Correntropy Criterion" Sensors 18, no. 8: 2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082406
APA StyleDeng, Z., Yin, L., Huo, B., & Xia, Y. (2018). Adaptive Robust Unscented Kalman Filter via Fading Factor and Maximum Correntropy Criterion. Sensors, 18(8), 2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082406




