Mapping Soil Salinity/Sodicity by using Landsat OLI Imagery and PLSR Algorithm over Semiarid West Jilin Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Descriptions
2.2. Data Sources and Pre-Processing
2.3. Random Forest to Classifying Land Cover
2.4. The PLSR
3. Results
3.1. Sensitivity of RS Variables to Soil EC and pH
3.2. The PLSR Models for Soil Salinity/Sodicity Retrieval
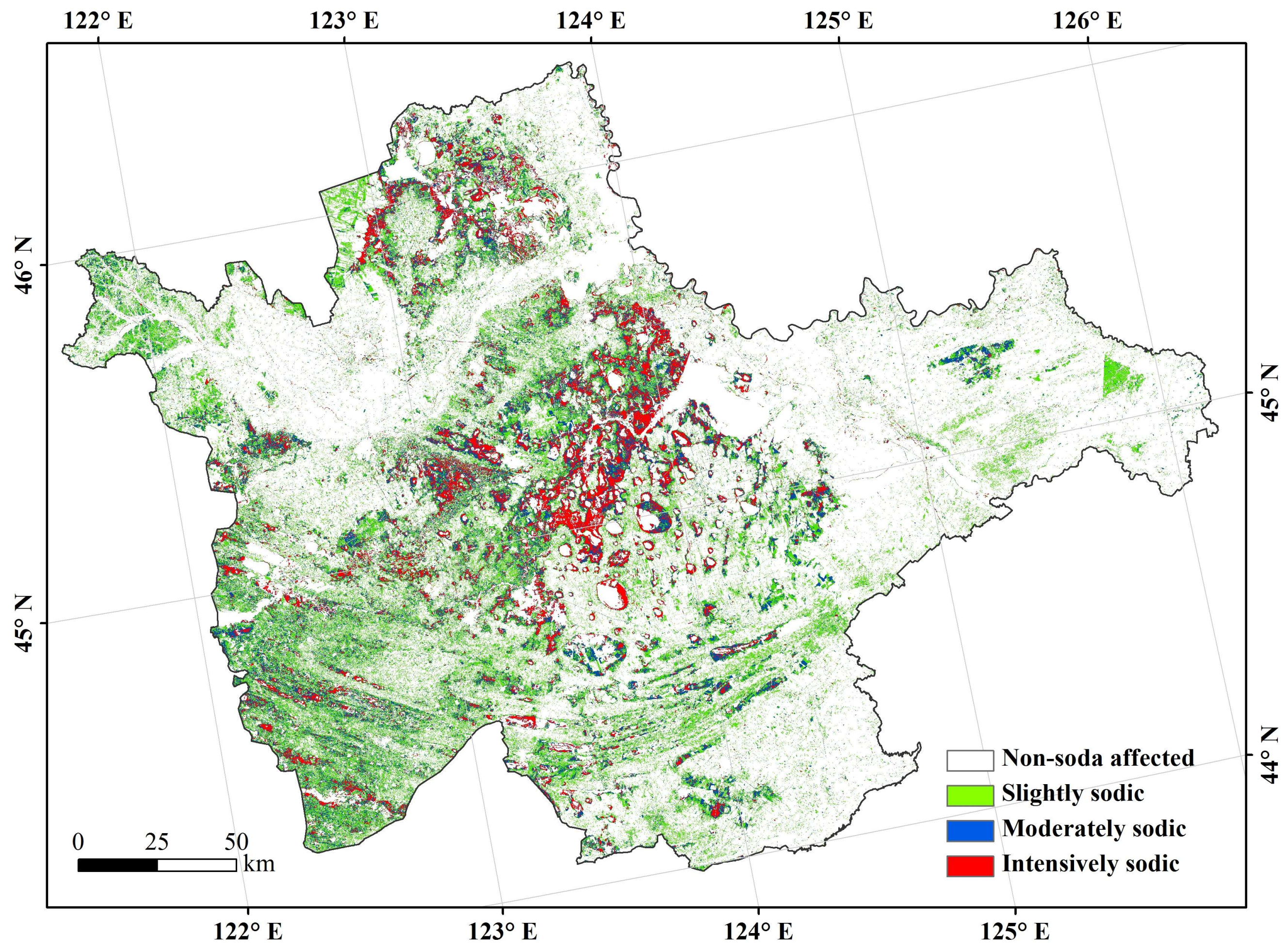
3.3. The Spatial Distributions of Soil Salinity and Sodicity
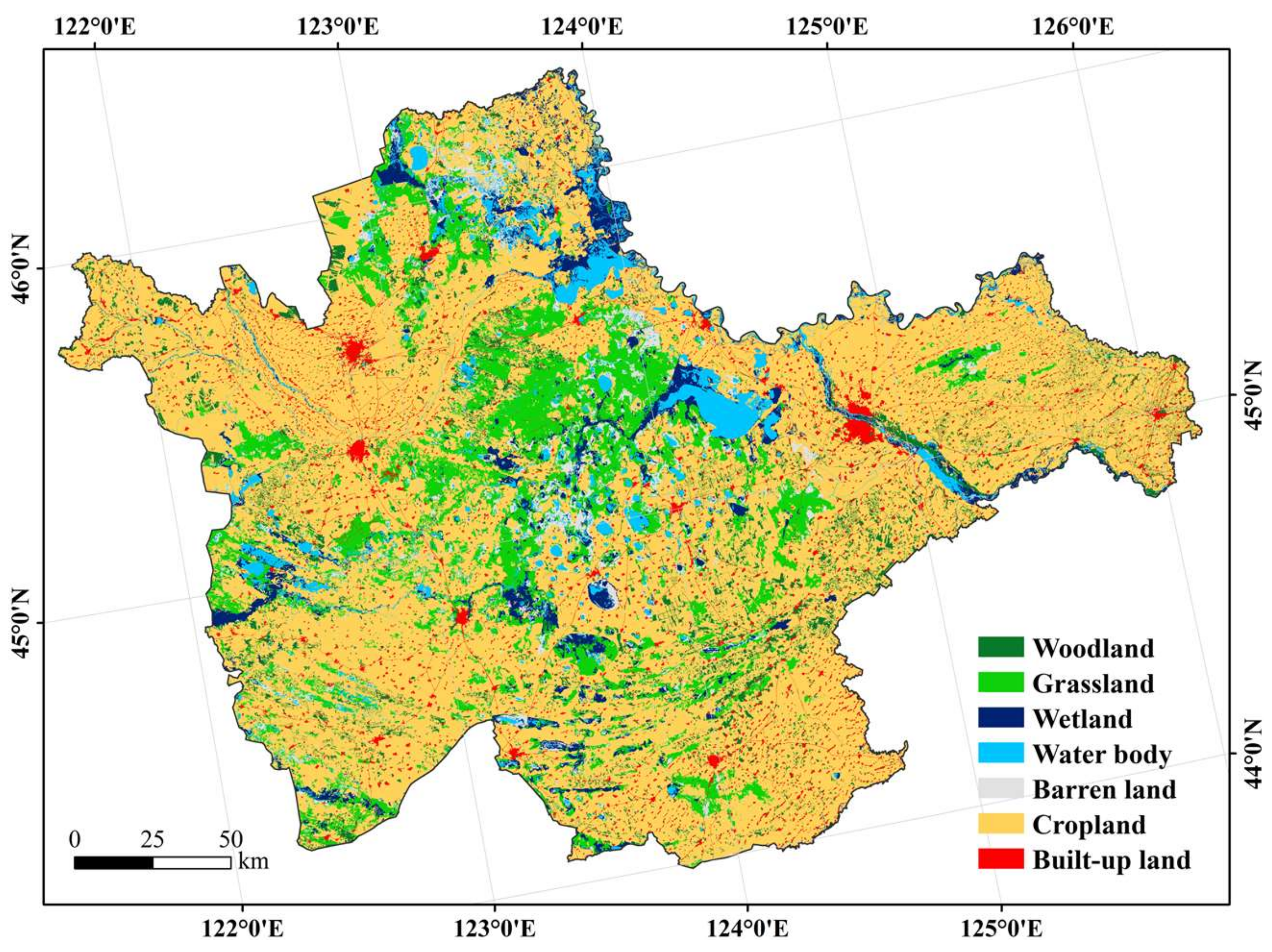
3.4. Land Cover Classifications
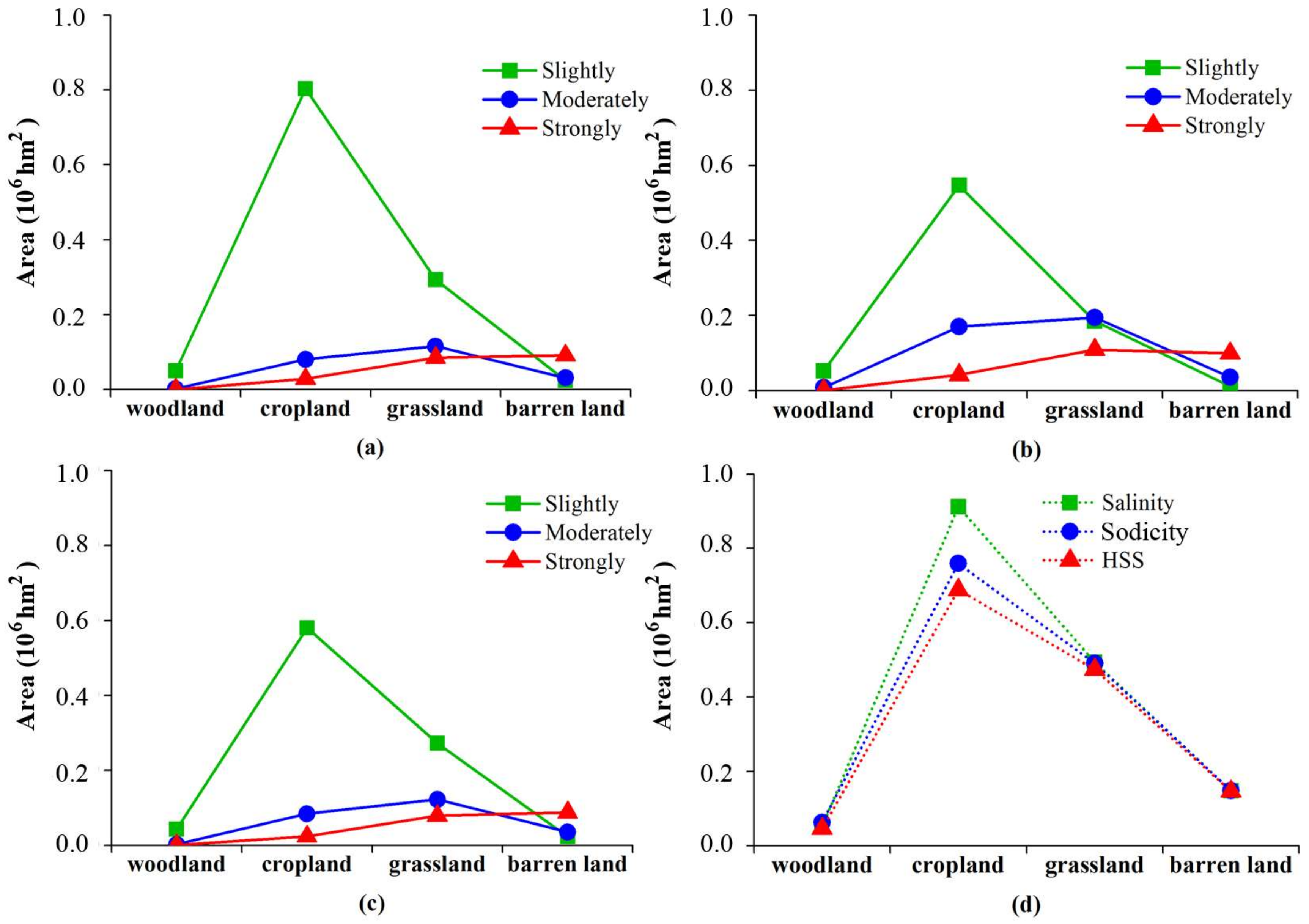
3.5. The Distribution of Soil Salinity/Sodicity with Land Cover
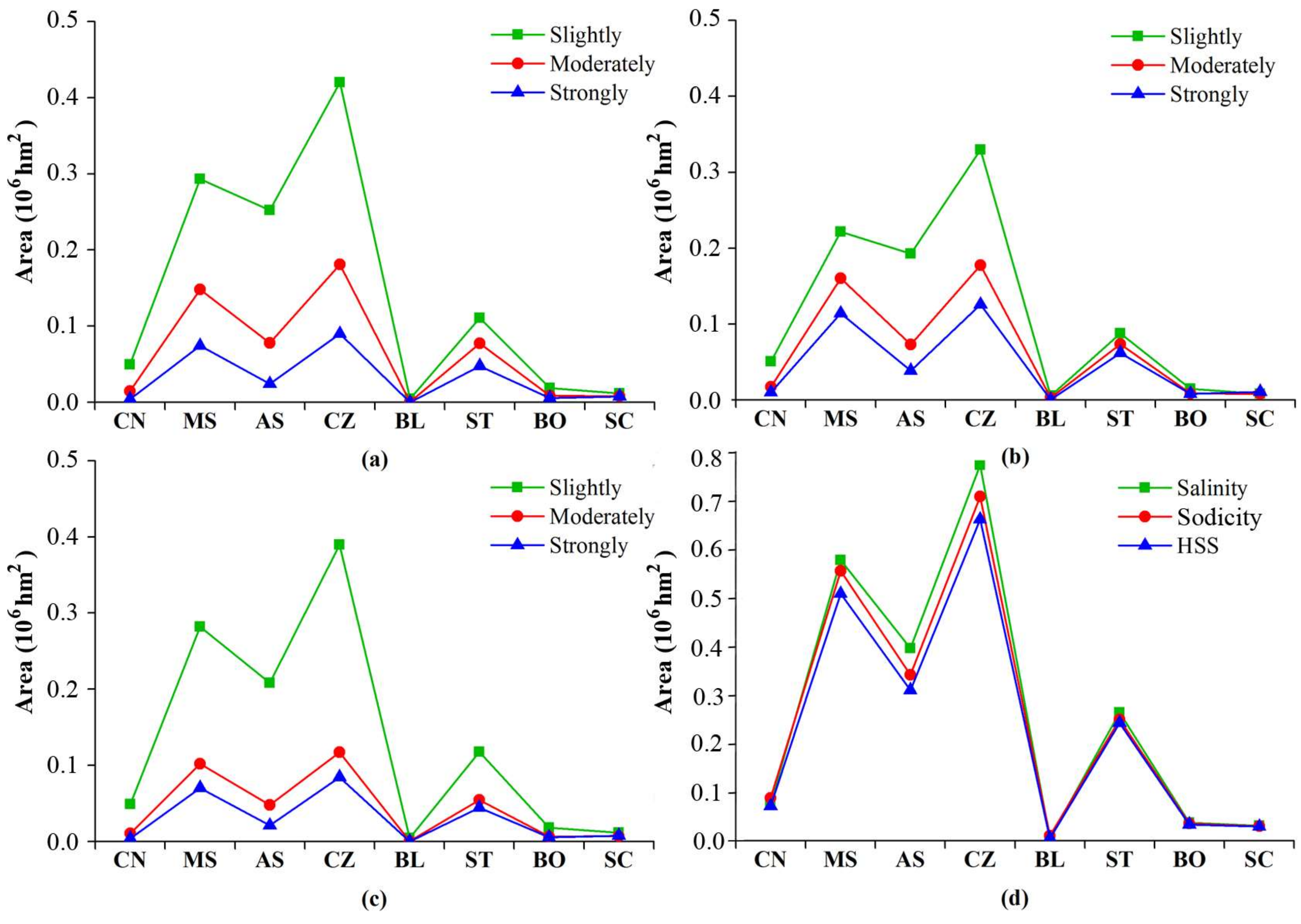
3.6. The Distribution of Soil Salinity/Sodicity with Soil Types
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, M.H. Practices of Irrigation & on-Farm Water Management; Ali, M.H., Ed.; Springer Science + Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 271–325. [Google Scholar]
- Bouaziz, M.; Matschullat, J.; Gloaguen, R. Improved remote sensing detection of soil salinity from a semi-arid climate in northeast Brazil. C. R. Geosci. 2011, 343, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidike, A.; Zhao, S.; Wen, Y. Estimating soil salinity in Pingluo county of China using Quickbird data and soil reflectance spectra. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.T. Discussion on ecological conservation strategy in western Songnen Plain. Syst. Sci. Compr. Stud. Agric. 2003, 19, 282–289. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.X.; Yang, J.F.; Liu, Q. Discussion on the problems of water environment ecologization in ecological housing district. Ecol. Environ. 2004, 13, 290–292. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Setia, R.; Lewis, M.; Marschner, P.; Raja Segaran, R.; Summers, D.; Chittleborough, D. Severity of salinity accurately detected and classified on a paddock scale with high resolution multispectral satellite imagery. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmappa, K.; Sharma, D.K.; Dagar, J.C.; Raju, R. Reclamation of salt-affected soils: Socioeconomic impact assessment. In Innovative Saline Agriculture; Dagar, J.C., Sharma, P.C., Sharma, D.K., Singh, A.K., Eds.; Springer Nature: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 489–505. [Google Scholar]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote sensing of soil salinity: Potentials and constraints. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, S.; Shanmugam, R.S. Multispectral and microwave remote sensing models to survey soil moisture and salinity. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Vincent, B.; Yang, J.; Bouarfa, S.; Vidal, A. Remote sensing monitoring of changes in soil salinity: A case study in Inner Mongolia, China. Sensors 2008, 8, 7035–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, R.P. Relating soil electrical conductivity to remote sensing and other soil properties for assessing soil salinity in northeast Thailand. Land Degrad. Dev. 2006, 17, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Minasny, B.; Sarmadian, F.; Malone, B.P. Digital mapping of soil salinity in Ardakan region, central Iran. Geoderma 2014, 213, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Liu, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, C. Analysis of salinization dynamics by remote sensing in Hetao Irrigation District of North China. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1952–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.; Menges, C.; Ahmad, W.; Zyl, J.J.V. The application of dielectric retrieval algorithms for maping soil salinity in tropical coastal environment using airborne polarimetric SAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 75, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allbed, A.; Kumar, L.; Aldakheel, Y.Y. Assessing soil salinity using soil salinity and vegetation indices derived from IKONS high-spatial resolution imageries: Applications in a date palm dominated region. Geoderma 2014, 230–231, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Tao, J.; Weng, Y. Soil salinity retrieval from advanced multi-spectral sensor with partial least square regression. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 488–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Wang, C.Z.; Zang, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Hao, Q.N.; Wu, Y.X. Remote sensing of soil alkalinity and salinity in the Wuyu’er-shuangyang River Basin, Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromham, L.; Saslis-Lagoudakis, C.H.; Bennett, T.H.; Flowers, T.J. Soil alkalinity and salt tolerance: Adapting to multiple stresses. Biol. Lett. 2013, 9, 20130566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, E. Possible role of soil alkalinity in plant breeding for salt-tolerance. Biol. Lett. 2013, 9, 20130566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Fang, N.F.; Zhang, P.C.; Shi, Z.H. Impacts of land use change on watershed streamflow and sediment yield: An assessment using hydrologic modelling and partial least squares regression. J. Hydrol. 2013, 484, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawut, M.; Ghulam, A.; Tiyip, T.; Zhang, Y.-j.; Ding, J.-l.; Zhang, F.; Maimaitiyiming, M. Estimating soil sand content using thermal infrared spectra in arid lands. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 33, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udelhoven, T.; Emmerling, C.; Jarmer, T. Quantitative analysis of soil chemical properties with diffuse reflectance spectrometry and partial least-square regression: A feasibility study. Plant Soil 2003, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Zeng, S.L.; Gao, Y.; Ouyang, Z.T.; Li, B.; Fang, C.M.; Zhao, B. Using hyperspectral vegetation indices as a proxy to monitor soil salinity. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, L.J.; Forrester, S.T.; Rawson, A. The prediction of soil chemical and physical properties from mid-infrared spectroscopy and combined partial least-squares regression and neural networks (PLS-NN) analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2009, 97, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.; Wang, T.; Liao, J.; Li, S. Quantitative model based on field-derived spectral characteristics to estimate soil salinity in Minqin county, China. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Bai, Z.; Wei, S.; Yanfen, H.; Zongming, W.; Kaishan, S.; Dianwei, L.; Zhiming, L. Sandy desertification change and its driving forces in western Jilin Province, North China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, N.; Luo, L.; Li, X.; Ren, C.; Song, K.; Chen, J.M. Shrinkage and fragmentation of marshes in the west Songnen Plain, China, from 1954 to 2008 and its possible causes. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Mhaimeed, A.S.; Al-Shafie, W.M.; Ziadat, F.; Dhehibi, B.; Nangia, V.; De Pauw, E. Mapping soil salinity changes using remote sensing in central Iraq. Geoderma Reg. 2014, 2–3, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaoui, A.E.K.; Nicolas, H.; Walter, C. Detecting salinity hazards within a semiarid context by means of combining soil and remote-sensing data. Geoderma 2006, 134, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R.; Liu, H.Q.; Batchily, K.; van Leeuwen, W. A comparison of vegetation indices global set of TM images for EOS-MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 59, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhammadi, M.S.; Glenn, E.P. Detecting date palm trees health and vegetation greenness change on the eastern coast of the United Arab Emirates using SAVI. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1745–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.F.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Abarca-Hernandez, F.; Atkinson, P.M.; Jeganathan, C. Random forest classification of mediterranean land cover using multi-seasonal imagery and multi-seasonal texture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Chehata, N.; Mallet, C.; Boukir, S. Relevance of airborne lidar and multispectral image data for urban scene classification using Random Forests. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2011, 66, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wu, B.; Li, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zheng, H. An ecosysytem classification system based on reomte sensor information in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 219–226. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, B.; Li, X.; Xing, Q. Classification system of China land cover for carbon budget. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 7158–7166. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, S.; Buddenbaum, H.; Hill, J.; Kozak, J. Modeling and mapping of soil salinity with reflectance spectroscopy and landsat data using two quantitative methods (PLSR and ANN). Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10813–10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farifteh, J.; Van der Meer, F.; Atzberger, C.; Carranza, E.J.M. Quantitative analysis of salt-affected soil reflectance spectra: A comparison of two adaptive methods (PLSR and ANN). Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Gong, P.; Zhu, Z. A spectral index for estimating soil salinity in the yellow river delta region of China using EO-1 hyperion data. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirlas, V.; Benyamini, Y.; Marish, S.; Gotesman, M.; Fizik, E.; Agassi, M. Method for normalization of soil salinity data. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. ASCE 2003, 129, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S. Dryland Salinity-Introductory Extension Notes, 2nd ed.; Department of Conservation and Land Management: Perth, Australia, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.; Chen, X. Influence of atmospheric precipitation on soil leaching and desalinization in the North China plain. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2005, 42, 730–736. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Farifteh, J.; van der Meer, F.; van der Meijde, M.; Atzberger, C. Spectral characteristics of salt-affected soils: A laboratory experiment. Geoderma 2008, 145, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhag, M. Evaluation of different soil salinity mapping using remote sensing techniques in arid ecosystems, Saudi Arabia. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Pedreño, J.; Jordan, M.M.; Meléndez-Pastor, I.; Gómez, I.; Juan, P.; Mateu, J. Estimation of soil salinity in semi-arid land using a geostatistical model. Land Degrad. Dev. 2007, 18, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Kumar, S.; Saha, S.K. Hyperspectral satellite data in mapping salt-affected soils using linear spectral unmixing analysis. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2012, 40, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedetto, D.; Castrignano, A.; Diacono, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Ruggieri, S.; Tamborrino, R. Field partition by proximal and remote sensing data fusion. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 114, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldabaa, A.A.A.; Weindorf, D.C.; Chakraborty, S.; Sharma, A.; Li, B. Combination of proximal and remote sensing methods for rapid soil salinity quantification. Geoderma 2015, 239–240, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cemek, B.; Guler, M.; Kilic, K.; Demir, Y.; Arslan, H. Assessment of spatial variability in some soil properties as related to soil salinity and alkalinity in Bafra Plain in northern Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 124, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zornoza, R.; Acosta, J.A.; Bastida, F.; Domínguez, S.G.; Toledo, D.M.; Faz, A. Identification of sensitive indicators to assess the interrelationship between soil quality, management practices and human health. Soil 2015, 1, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaledian, Y.; Kiani, F.; Ebrahimi, S.; Brevik, E.C.; Aitkenhead-Peterson, J. Assessment and monitoring of soil degradation during land use change using multivariate analysis. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Zhao, G.; Chang, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, T.; Jia, J. Hyperspectral field estimation and remote-sensing inversion of salt content in coastal saline soils of the Yellow River Delta. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Spectral Index | Expression | Full Name | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | (NIR − Red)/(NIR + Red) | Normalized Differential Vegetation Index | Shrestha (2006) |
| DVI | NIR − Red | Differential Vegetation Index | Clevers et al. (1988) |
| EVI | NIR/Red | Enhanced Vegetation Index | Huete et al. (1997) |
| SAVI | (NIR − Red)/(NIR+Red + 0.5)1.5 | Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index | Bouaziz et al. (2011) |
| SI | Salinity Index | Bouaziz et al. (2011) | |
| SI2 | Salinity Index2 | Douaoui et al. (2006) | |
| SI3 | Salinity Index3 | Douaoui et al. (2006) | |
| SI4 | SWIR1/NIR | Salinity Index4 | Douaoui et al. (2006) |
| SRSI | Salinization Remote Sensing Index | Alhammadi et al. (2008) |
| EC | pH | Coastal | Red | Green | Blue | NIR | SWIR1 | SWIR2 | PAN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| pH | 0.703 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Coastal | 0.821 ** | 0.791 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Red | 0.810 ** | 0.805 ** | 0.988 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Green | 0.826 ** | 0.793 ** | 0.991 ** | 0.992 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Blue | 0.818 ** | 0.795 ** | 0.998 ** | 0.992 ** | 0.992 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| NIR | 0.348 ** | 0.068 ** | 0.294 ** | 0.245 * | 0.334 ** | 0.283 ** | 1 | - | - | - |
| SWIR1 | 0.704 ** | 0.788 ** | 0.912 ** | 0.944 ** | 0.925 ** | 0.923 ** | 0.160 * | 1 | - | - |
| SWIR2 | 0.738 ** | 0.791 ** | 0.939 ** | 0.967 ** | 0.948 ** | 0.948 ** | 0.143 * | 0.989 ** | 1 | - |
| PAN | 0.763 ** | 0.773 ** | 0.958 ** | 0.964 ** | 0.966 ** | 0.963 ** | 0.289 ** | 0.906 ** | 0.931 ** | 1 |
| EC | pH | SI | SI2 | SI3 | SI4 | SRSI | SAVI | NDVI | EVI | DVI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| pH | 0.703 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SI | 0.818 ** | 0.803 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SI2 | 0.722 ** | 0.507 ** | 0.770 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SI3 | 0.826 ** | 0.793 ** | 1.000 ** | 0.804 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SI4 | 0.472 ** | 0.704 ** | 0.731 ** | 0.209 * | 0.695 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| SRSI | 0.818 ** | 0.803 ** | 1.000 ** | 0.771 ** | 0.997 ** | 0.731 ** | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| SAVI | −0.665 ** | −0.814 ** | −0.931 ** | −0.467 ** | −0.888 ** | −0.920 ** | −0.912 ** | 1 | - | - | - |
| NDVI | −0.665 ** | −0.814 ** | −0.931 ** | −0.467 ** | −0.888 ** | −0.920 ** | −0.912 ** | 1.000 ** | 1 | - | - |
| EVI | −0.449 ** | −0.694 ** | −0.708 ** | −0.159 * | −0.677 ** | −0.877 ** | −0.708 ** | 0.889 ** | 0.889 ** | 1 | - |
| DVI | −0.555 ** | −0.725 ** | −0.775 ** | −0.198 * | −0.736 ** | −0.912 ** | −0.775 ** | 0.935 ** | 0.935 ** | 0.909 ** | 1 |
| Transform | Imaging Feature | R2 | Expression | SD | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | Band | 0.706 | EC = 1.601Green − 3.093SWIR1 − 1.121 | 0.456 | 0.451 |
| Index | 0.704 | EC = 21.114NDVI + 5.411SI3 − 12.024 | 0.457 | 0.453 | |
| Hybrid | 0.706 | EC = 5.854SI3 − 3.093SWIR1 − 0.029 | 0.455 | 0.451 | |
| 1/r | Band | 0.646 | EC = − 45.758Blue − 1.031NIR + 2.670 | 0.501 | 0.527 |
| Index | 0.707 | EC = 8.506EVI − 11.121NDVI + 19.717 | 0.454 | 0.451 | |
| Hybrid | 0.712 | EC = 7.915EVI + 0.161Red − 2.236 | 0.45 | 0.446 | |
| er | Band | 0.717 | EC = 8.553Green − 1.969SWIR1 − 7.523 | 0.446 | 0.442 |
| Index | 0.711 | EC = 2.783SI3 − 3.165 | 0.45 | 0.448 | |
| Hybrid | 0.735 | EC = 14.090SI3 − 24.833Green + 13.174 | 0.432 | 0.429 | |
| log (r) | Band | 0.635 | EC = 9.244Green − 3.032Red + 4.557 | 0.507 | 0.503 |
| Index | 0.601 | EC = 1.692SI3 + 2.764SI2 + 2.549 | 0.53 | 0.525 | |
| Hybrid | 0.709 | EC = 20.220Green − 9.125SI + 8.066 | 0.452 | 0.449 | |
| 1/log(r) | Band | 0.726 | EC = − 2.052Green + 0.363SWIR1 − 1.969 | 0.432 | 0.435 |
| Index | 0.727 | EC = − 0.486SI3 − 0.450 | 0.437 | 0.435 | |
| Hybrid | 0.727 | EC = − 0.486SI3 − 0.450 | 0.437 | 0.435 | |
| 1/er | Band | 0.691 | EC = 4.634SWIR1 − 15.431Green + 9.478 | 0.467 | 0.462 |
| Index | 0.691 | EC = − 6.391SI3 − 7.701EVI + 3.169DVI + 8.618 | 0.469 | 0.463 | |
| Hybrid | 0.734 | EC = − 90.819Green + 43.953SI3 + 38.916 | 0.432 | 0.429 | |
| Sqrt(r) | Band | 0.675 | EC = 11.977Green − 3.844SWIR1 − 2.951 | 0.479 | 0.474 |
| Index | 0.682 | EC = 5.083SI3 + 7.866EVI − 3.338DVI − 4.727 | 0.474 | 0.469 | |
| Hybrid | 0.724 | EC = 58.351Green − 27.823SI3 − 13.214 | 0.441 | 0.437 |
| Transform | Imaging Feature | R2 | Expression | SD | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | Band | 0.666 | pH = 6.082Red − 1.743NIR + 8.156 | 0.573 | 0.568 |
| Index | 0.663 | pH = − 62.762NDVI + 41.701 | 0.575 | 0.571 | |
| Hybrid | 0.686 | pH = 3.753Green − 40.192NDVI + 28.970 | 0.557 | 0.551 | |
| 1/r | Band | 0.689 | pH = − 63.919Blue − 0.499NIR + 43.330 | 0.554 | 0.548 |
| Index | 0.691 | pH = 3.541SAVI − 0.346Red − 18.863 | 0.552 | 0.547 | |
| Hybrid | 0.694 | pH = 1.705SAVI − 1.348Coastal − 1.898 | 0.551 | 0.546 | |
| er | Band | 0.651 | pH = 4.442Red − 1.306NIR + 5.200 | 0.586 | 0.581 |
| Index | 0.682 | pH = − 155.862SAVI + 1.049SI3 + 183.862 | 0.56 | 0.56 | |
| Hybrid | 0.684 | pH = − 147.848SAVI + 2.551Green + 173.026 | 0.558 | 0.553 | |
| log (r) | Band | 0.689 | pH = 3.466Blue + 11.968 | 0.552 | 0.548 |
| Index | 0.682 | pH = 2.761SI + 10.582 | 0.558 | 0.554 | |
| Hybrid | 0.689 | pH = 3.466Blue + 11.968 | 0.552 | 0.548 | |
| 1/log(r) | Band | 0.653 | pH = − 2.287Blue + 0.229NIR + 6.866 | 0.584 | 0.579 |
| Index | 0.677 | pH = 493.206SAVI − 44.705NDVI + 394.719 | 0.564 | 0.559 | |
| Hybrid | 0.691 | pH = 41.952SAVI − 0.559Green + 54.273 | 0.560 | 0.555 | |
| 1/er | Band | 0.678 | pH = − 8.159Red + 2.137NIR + 13.922 | 0.564 | 0.558 |
| Index | 0.688 | pH = 129.434SAVI − 3.412SRSI − 102.821 | 0.554 | 0.549 | |
| Hybrid | 0.688 | pH = 129.434SAVI − 3.412SRSI − 102.821 | 0.554 | 0.549 | |
| Sqrt(r) | Band | 0.678 | pH = 6.139Red + 5.851 | 0.561 | 0.558 |
| Index | 0.681 | pH = 4.617SRSI + 6.529 | 0.558 | 0.555 | |
| Hybrid | 0.689 | pH = 4.718SRSI − 1.647NIR + 7.643 | 0.553 | 0.548 |
| Level | Range of EC and pH |
|---|---|
| Unaffected | pH < 8.5 or EC < 0.2 mS/cm |
| Slightly affected | 0.2 mS/cm < EC < 0.4 mS/cm and 8.5 < pH < 9.0; 0.4 mS/cm < EC < 0.8 mS/cm and 8.5 < pH < 9.0; 0.2 mS/cm < EC < 0.4 mS/cm and 9.0 < pH < 9.5; |
| Moderately affected | 0.4 mS/cm < EC < 0.8 mS/cm and9.0 < pH < 9.5; EC > 0.8 mS/cm and 8.5 < pH < 9.0; 0.2 mS/cm < EC < 0.4 mS/cm and pH > 9.5; |
| Intensively affected | 0.8 mS/cm < EC and pH > 9.5; 0.4 mS/cm < EC < 0.8 mS/cm and pH > 9.5; 0.8 mS/cm < EC and 9.0 < pH < 9.5; |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Liu, M.; Du, B.; Wang, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhang, B. Mapping Soil Salinity/Sodicity by using Landsat OLI Imagery and PLSR Algorithm over Semiarid West Jilin Province, China. Sensors 2018, 18, 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041048
Yu H, Liu M, Du B, Wang Z, Hu L, Zhang B. Mapping Soil Salinity/Sodicity by using Landsat OLI Imagery and PLSR Algorithm over Semiarid West Jilin Province, China. Sensors. 2018; 18(4):1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041048
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Hao, Mingyue Liu, Baojia Du, Zongming Wang, Liangjun Hu, and Bai Zhang. 2018. "Mapping Soil Salinity/Sodicity by using Landsat OLI Imagery and PLSR Algorithm over Semiarid West Jilin Province, China" Sensors 18, no. 4: 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041048
APA StyleYu, H., Liu, M., Du, B., Wang, Z., Hu, L., & Zhang, B. (2018). Mapping Soil Salinity/Sodicity by using Landsat OLI Imagery and PLSR Algorithm over Semiarid West Jilin Province, China. Sensors, 18(4), 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041048






