Gaussian Process Based Bayesian Inference System for Intelligent Surface Measurement
Abstract
1. Introduction
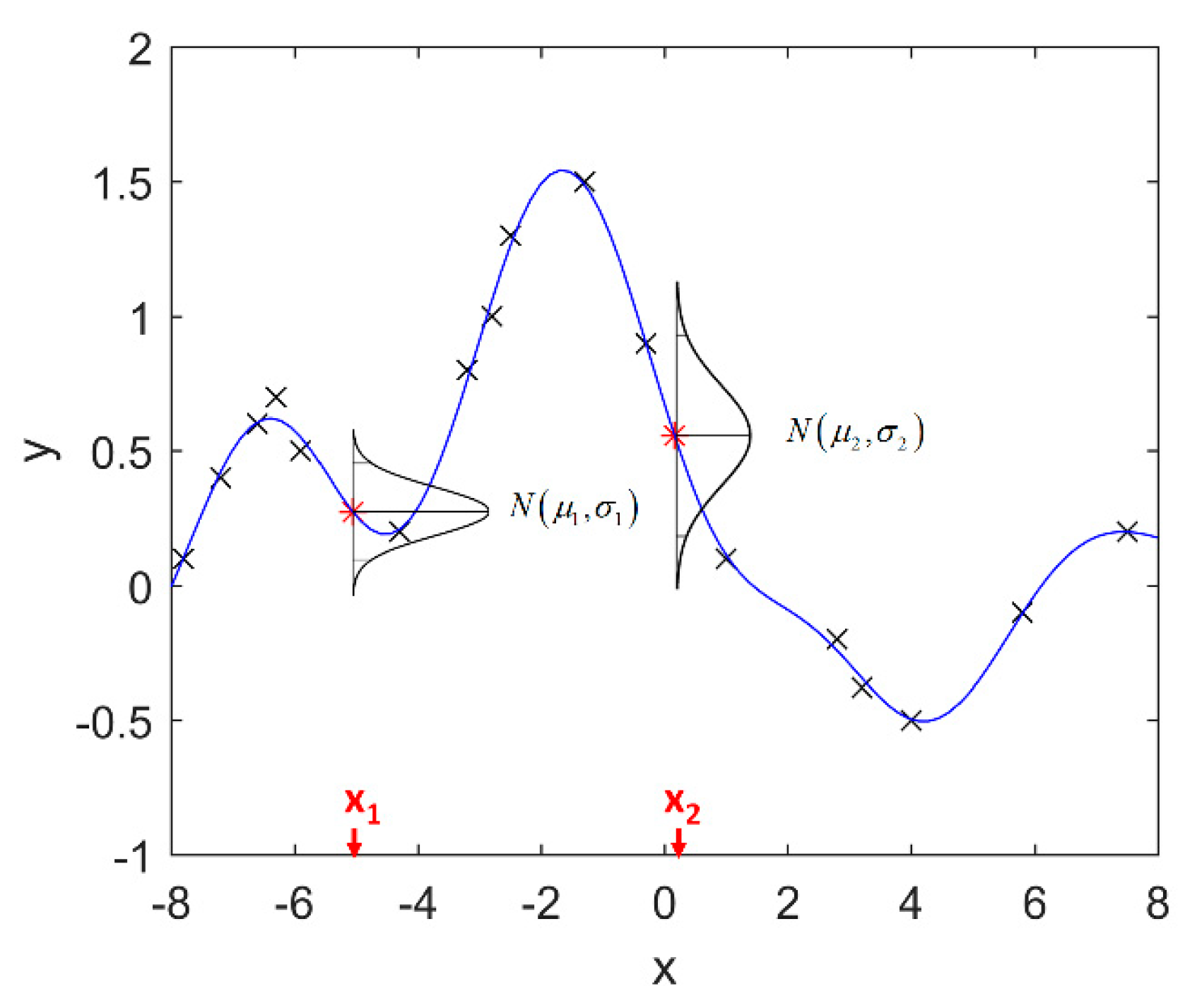
2. Preliminary
3. Gaussian Process Based Bayesian Inference System
3.1. System Configuration
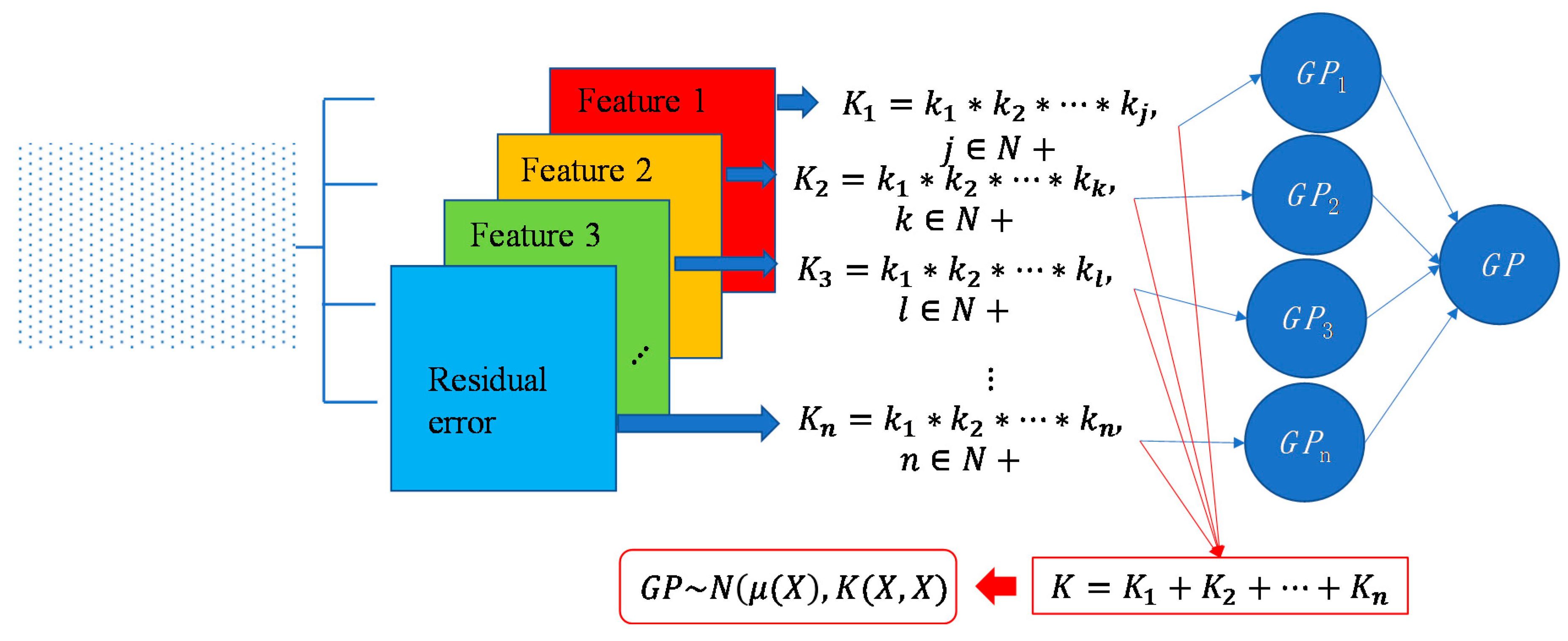
3.2. Design of Covariance Kernel via Multi-Feature Classification
3.3. Sampling Strategy Adaptation via Multi-Dataset Regression
4. Experimental Study
4.1. Computer Simulation on Surface Modelling
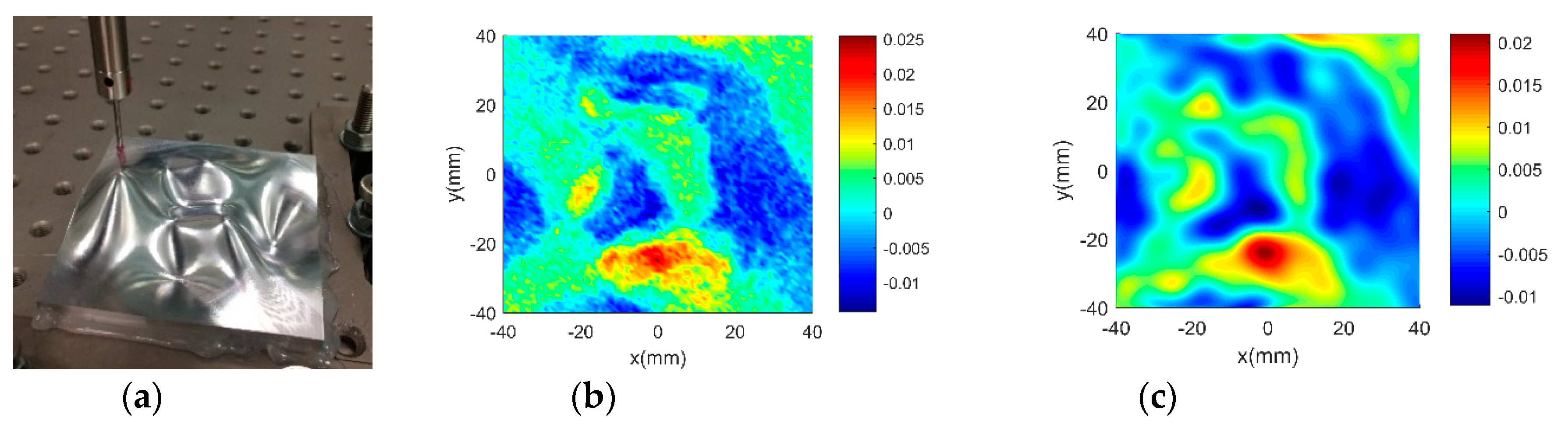
4.2. Actual Application on Multi-Sensor Instrument
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brinksmeier, E.; Schönemann, L. Generation of discontinuous microstructures by Diamond Micro Chiseling. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 63, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.J.; Whitehouse, D.J. Technological shifts in surface metrology. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 61, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, D.J. Surface geometry, miniaturization and metrology. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 370, 4042–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.Z.; Zhang, X.D.; Weckenmann, A. Manufacturing and measurement of freeform optics. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 62, 823–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, S.K. Multi-Scale Data Fusion for Surface Metrology. ProQuest Dissertations, The University of North Carolina at Charlotte, Charlotte, NC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Leach, R.K.; Boyd, R.D.; Burke, T.; Danzebrink, H.; Dirscherl, K.; Dziomba, T.; Gee, M.G.; Koenders, L.; Morazzani, V.; Pidduck, A.; Unger, W.E.S.; Yacoot, A. The European nanometrology landscape. Nanotechnology 2011, 2011. 22, 062001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckenmann, A.; Peggs, G.; Hoffmann, J. Probing systems for dimensional micro-and nano-metrology. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckenmann, A. Application of modern high resolution tactile sensors for micro-objects. Int. J. Precis. Technol. 2011, 2, 266–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISARA 400 Ultra Precision Coordinate Measuring Machine. Available online: http://www.ibspe.com/ibs_precision_engineering_uk/ibs_isara_400.html (access on 7 August 2018).
- Schwenke, H.; Neuschaeferrube, U.; Pfeifer, T.; Kunzmann, H. Optical Methods for Dimensional Metrology in Production Engineering. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2002, 51, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, X.; Lu, W.; Hu, C.; Guo, X. Towards a traceable probe calibration method for white light interference based AFM. Precis. Eng. 2017, 51, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodhew, P.J.; Humphreys, J.; Beanland, R. Electron Microscopy and Analysis, 3rd ed.; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 9780748409686. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, W.; Lu, W.; Yu, N.; Chang, S. Improved zero-order fringe positioning algorithms in white light interference based atomic force microscopy. Optics Lasers Eng. 2018, 100, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, X.; Lu, W.; Guo, X. Influence of probe dynamic characteristics on the scanning speed for white light interference based AFM. Precis. Eng. 2017, 52, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yang, X.; Lu, W.; Yu, N.; Chen, L.; Zhou, L.; Chang, S. A Novel White Light Interference Based AFM Head. J. Lightwave Technol. 2017, 35, 3604–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GmbH, W.M. Multisensor Coordinate Metrology: Dimensional Measurement Using Optics, Probes, and X-ray Tomography. Available online: http://www.werthmesstechnik.de (accessed on 11 March 2018).
- GmbH, W.M. Modular Product Line. Available online: http://www.witec.de/products/ (accessed on 11 March 2018).
- Colosimo, B.M.; Pacella, M.; Senin, N. Multisensor data fusion via Gaussian process models for dimensional and geometric verification. Precis. Eng. 2015, 40, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, D.J.; Phillips, M.J. Sampling in a two-dimensional plane. J. Phys. A Gen. Phys. 1985, 18, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosimo, B.M.; Moroni, G.; Petrò, S. A tolerance interval based criterion for optimizing discrete point sampling strategies. Precis. Eng. 2010, 34, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Blunt, L.; Leach, R.K.; Scott, P.J. Intelligent sampling for the measurement of structured surfaces. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2012, 23, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Frosio, I.; Piuri, V.; Borghese, N.A. Automatic multiscale meshing through HRBF networks. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2005, 54, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.C.; Ming, C.L. Intelligent planning of CAD-directed inspection for coordinate measuring machines. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 1998, 11, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojadinovic, S.M.; Majstorovic, V.D.; Durakbasa, N.M.; Sibalija, T.V. Towards an intelligent approach for CMM inspection planning of prismatic parts. Measurement 2016, 92, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.; Aigrain, S. Gaussian processes for time-series modelling. Philos. Trans. 2012, 371, 20110550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galetto, M.; Mastrogiacomo, L.; Maisano, D.A.; Franceschini, F. Cooperative fusion of distributed multi-sensor LVM (Large Volume Metrology) systems. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 64, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besl, P.J.; Mckay, N.D. A Method for Registration of 3-D Shapes. IEEE Comput. Soc. 1992, 14, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Leach, R.K.; Jiang, X. Review of the mathematical foundations of data fusion techniques in surface metrology. Surf. Topograp. Metrol. Prop. 2015, 3, 023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.Z.G.; Wu, C.F.J. Bayesian Hierarchical Modeling for Integrating Low-Accuracy and High-Accuracy Experiments. Technometrics 2008, 50, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentzen, J.A.; Gravesen, J.; Anton, F.; Aanæs, H. Guide to Computational Geometry Processing. Foundations Algorithms, and Methods; Springer: London, UK, 2012; pp. 287–308. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, C.E.; Williams, C.K.I. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning. Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 69–106. ISBN 0-262-18253-X. [Google Scholar]
- Dumas, A.; Echard, B.; Gayton, N.; Rochat, O.; Dantan, J.Y.; Van Der Veen, S. AK-ILS: An Active learning method based on Kriging for the Inspection of Large Surfaces. Precis. Eng. 2013, 37, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldara, S.; Nuccio, S.; Spataro, C. Measurement uncertainty estimation of a virtual instrument. Proceesings of the 17th IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 1–4 May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevan, S. Data fusion with gaussian processes. Rob. Autonom. Syst. 2012, 60, 1528–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.J.; Cheung, C.F.; Kong, L.B.; Jiang, X.Q. Invariant Feature Pattern Based Form Characterization for the Measurement of Ultra-precision Freeform Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 4, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Geometric Characteristic | Base Function | Gp Prior | |
|---|---|---|---|
| WN | White noise |  |  |
| LIN | linearly varying amplitude | 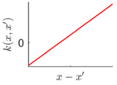 |  |
| SE | Infinitely differentiable, offering smooth variations with a typical length scale |  |  |
| PER | With arbitrary roughness and period, suitable for periodic shape |  | 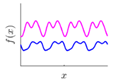 |
| MC | Finite times differentiable, suitable for different roughness with appropriate parameters |  |  |
| RQ | A mixture of SE with different length scales, more flexible with relatively more hyperparameters, suitable for smooth and multi-scaled shape | 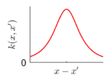 | 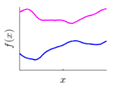 |
| NN | Rapid or large variations with non-stationary spatial correlation, suitable for the irregular surfaces with random features, such as the complex terrain | 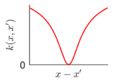 | 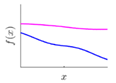 |
| PP | Finite continuously differentiable, suitable for large continuous or fast-changing shape |  | 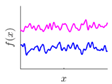 |
| Designed Complex Surfaces | Covariance Kernel Functions | Residual Maps |
|---|---|---|
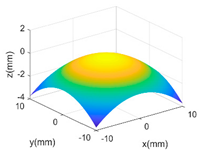 | SE | 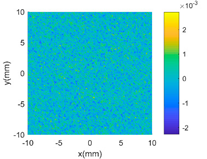 |
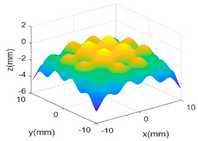 | SE + PER | 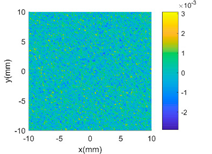 |
 | SE + PER + MC | 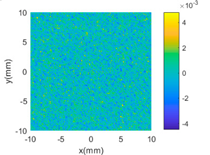 |
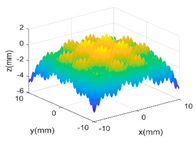 | SE + PER + PER |  |
| Measurement Strategy | Number of Points | RMS (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| Trigger probe dense measurement | 6456 | 5.9 |
| Laser scanner dense measurement | more than 40,000 | 11.2 |
| Trigger probe adaptive measurement | 493 | 5.7 |
| Multi-sensor adaptive measurement | 281 | 5.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, M.J.; Cheung, C.F.; Xiao, G.B. Gaussian Process Based Bayesian Inference System for Intelligent Surface Measurement. Sensors 2018, 18, 4069. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114069
Ren MJ, Cheung CF, Xiao GB. Gaussian Process Based Bayesian Inference System for Intelligent Surface Measurement. Sensors. 2018; 18(11):4069. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114069
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Ming Jun, Chi Fai Cheung, and Gao Bo Xiao. 2018. "Gaussian Process Based Bayesian Inference System for Intelligent Surface Measurement" Sensors 18, no. 11: 4069. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114069
APA StyleRen, M. J., Cheung, C. F., & Xiao, G. B. (2018). Gaussian Process Based Bayesian Inference System for Intelligent Surface Measurement. Sensors, 18(11), 4069. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114069





