EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interface for Decoding Motor Imagery Tasks within the Same Hand Using Choi-Williams Time-Frequency Distribution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. EEG Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
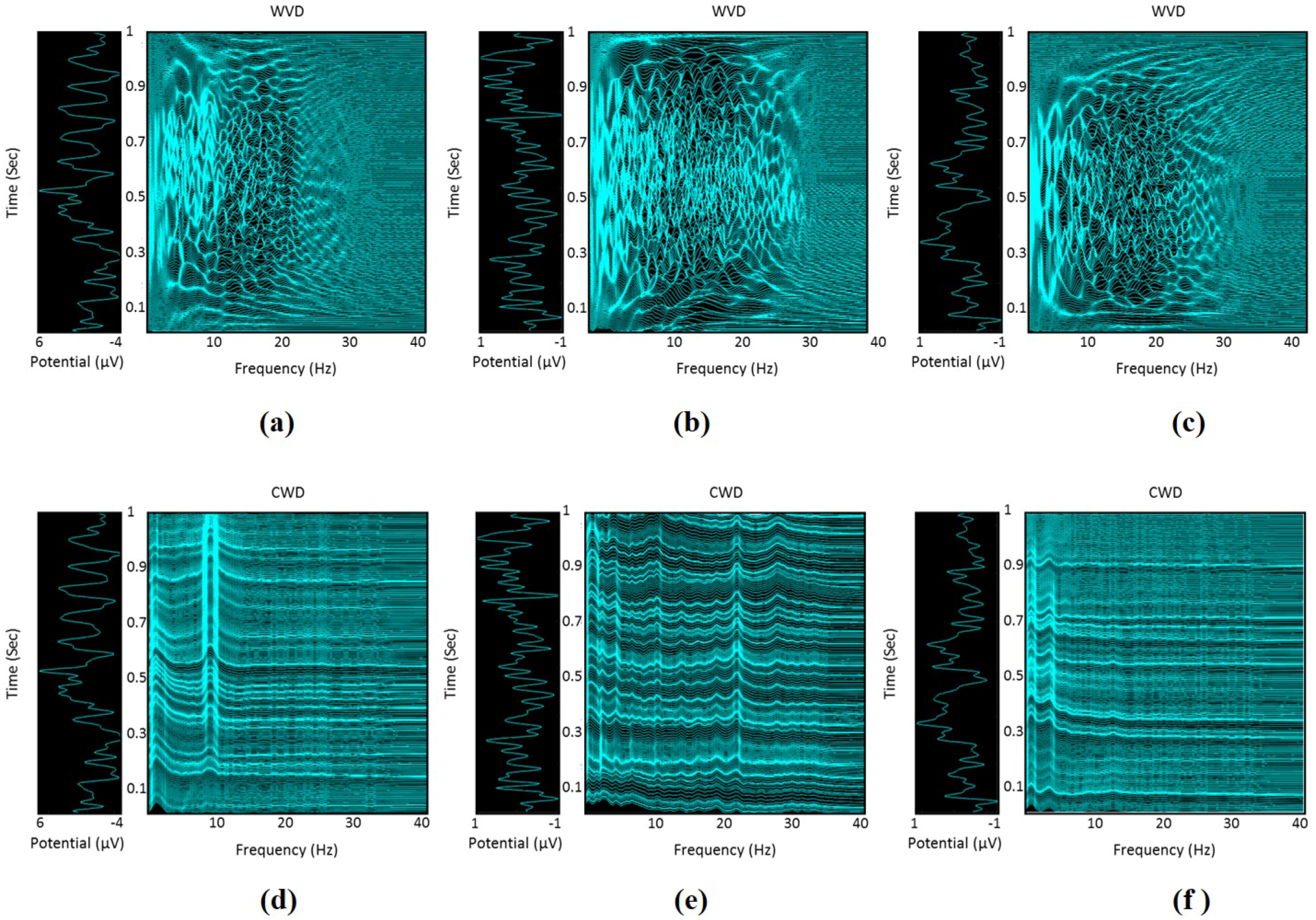
2.4. Time-Frequency Representation of EEG Signals
2.5. Time-Frequency Features
2.5.1. Log-Amplitude-Based Category
2.5.2. Amplitude-Based Category
2.5.3. Statistical-Based Category
2.5.4. Spectral-Based Category
2.5.5. Spectral Entropy-Based Category
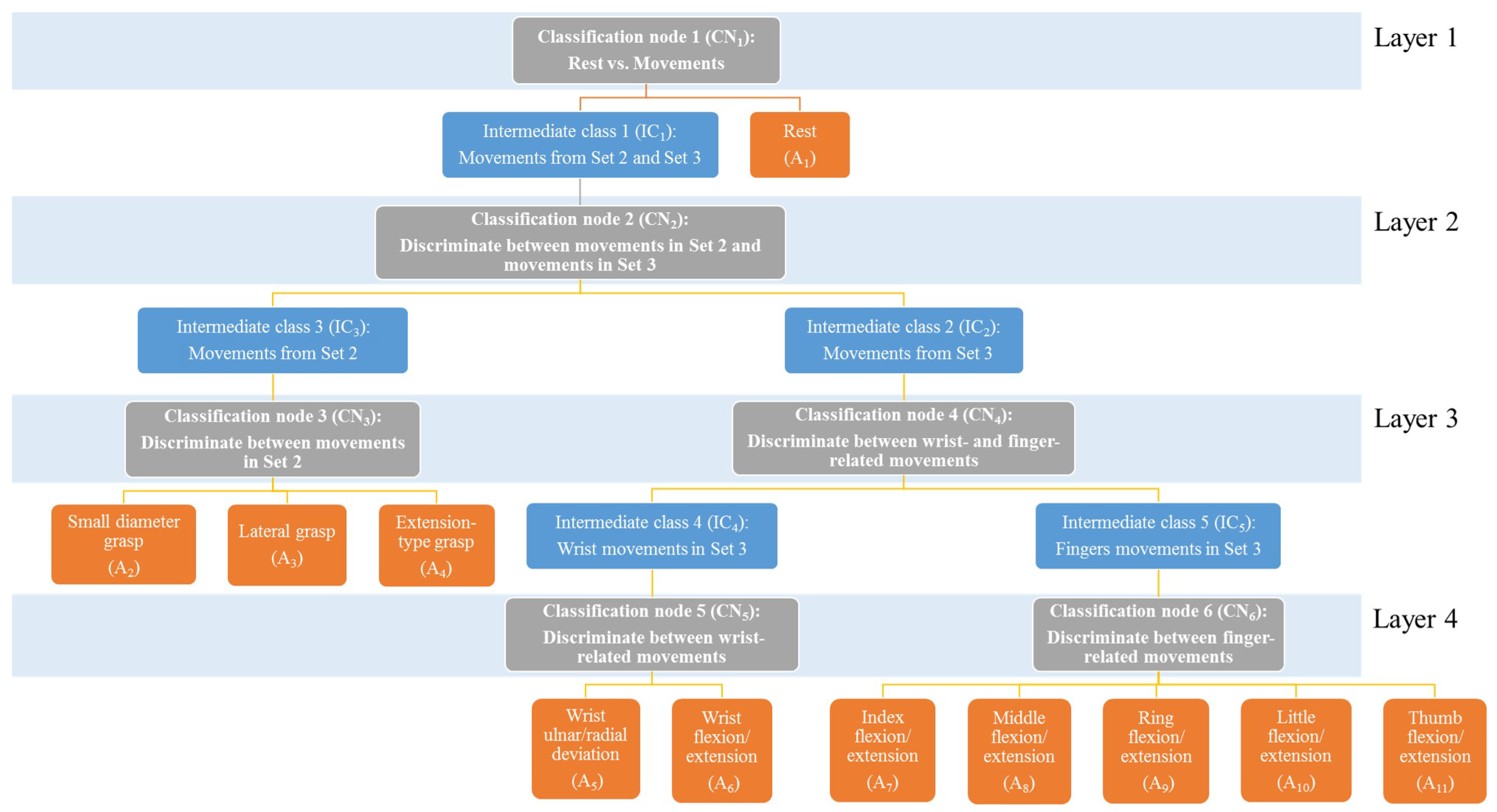
2.6. Classification of HMITs
2.7. Performance Evaluation Procedures and Metrics
3. Experimental Results
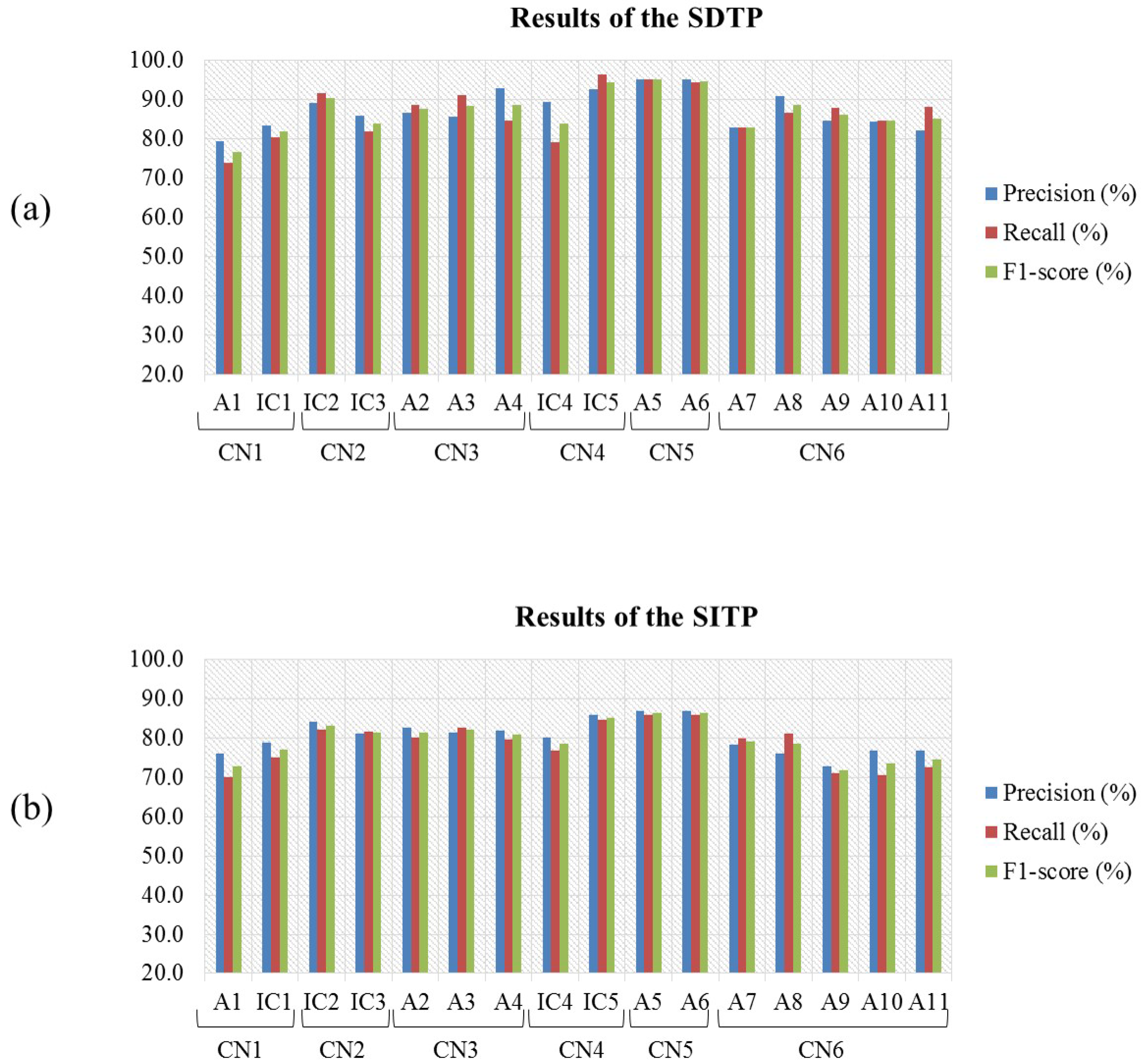
3.1. Evaluation Results of the Intact Subjects ()
3.1.1. Results of the Channel-Based Analysis
3.1.2. Results of the TFF-Based Analysis
3.2. Evaluation Results of the Amputated Subjects ()
3.2.1. Results of the Channel-Based Analysis
3.2.2. Results of the TFF-Based Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Channel-Based Analyses
4.2. TFF-Based Analyses
4.3. Comparison with Previous Approaches
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; McFarland, D.J.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Vaughan, T.M. Brain–computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbaumer, N. Breaking the silence: Brain–computer interfaces (BCI) for communication and motor control. Psychophysiology 2006, 43, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, J.J.; Krusienski, D.J.; Wolpaw, J.R. Brain-computer interfaces in medicine. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitaram, R.; Caria, A.; Veit, R.; Gaber, T.; Rota, G.; Kuebler, A.; Birbaumer, N. FMRI brain-computer interface: A tool for neuroscientific research and treatment. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2007, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuckovic, A.; Sepulveda, F. Delta band contribution in cue based single trial classification of real and imaginary wrist movements. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2008, 46, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, K.; Xiao, R.; Gonzalez, J.; Ding, L. Decoding individual finger movements from one hand using human EEG signals. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Wang, R.; Yu, D. Classification of four-class motor imagery employing single-channel electroencephalography. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, X.; Menon, C. EEG classification of different imaginary movements within the same limb. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelman, B.J.; Baxter, B.; He, B. EEG source imaging enhances the decoding of complex right-hand motor imagery tasks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafton, S.T.; Arbib, M.A.; Fadiga, L.; Rizzolatti, G. Localization of grasp representations in humans by positron emission tomography. Exp. Brain Res. 1996, 112, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Neuper, C.; Muller, G.R.; Obermaier, B.; Krausz, G.; Schlogl, A.; Scherer, R.; Graimann, B.; Keinrath, C.; Skliris, D.; et al. Graz-BCI: State of the art and clinical applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2003, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Ding, L.; He, B. Motor imagery classification by means of source analysis for brain–computer interface applications. J. Neural Eng. 2004, 1, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas-Alonso, L.F.; Gomez-Gil, J. Brain computer interfaces, a review. Sensors 2012, 12, 1211–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Yang, Q.; Wang, R.; Lin, P.; Gao, J.; Leng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H. A brain-computer interface based on a few-channel EEG-fNIRS bimodal system. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, R.; Tettamanti, A.; Gough, P.; Riboldi, E.; Marinoni, L.; Buccino, G. Action observation versus motor imagery in learning a complex motor task: A short review of literature and a kinematics study. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 540, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller-Putz, G.R.; Pfurtscheller, G. Control of an electrical prosthesis with an SSVEP-based BCI. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellers, E.W.; Vaughan, T.M.; Wolpaw, J.R. A brain-computer interface for long-term independent home use. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2010, 11, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donchin, E.; Spencer, K.M.; Wijesinghe, R. The mental prosthesis: Assessing the speed of a P300-based brain-computer interface. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 2000, 8, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Guger, C.; Müller, G.; Krausz, G.; Neuper, C. Brain oscillations control hand orthosis in a tetraplegic. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 292, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Sun, S.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, S. A brain-machine interface based on ERD/ERS for an upper-limb exoskeleton control. Sensors 2016, 16, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, R.; Muller, G.; Neuper, C.; Graimann, B.; Pfurtscheller, G. An asynchronously controlled EEG-based virtual keyboard: Improvement of the spelling rate. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeannerod, M. Mental imagery in the motor context. Neuropsychologia 1995, 33, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Neuper, C. Motor imagery and direct brain-computer communication. Proc. IEEE 2001, 89, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpaw, J.R.; McFarland, D.J. Control of a two-dimensional movement signal by a noninvasive brain-computer interface in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17849–17854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royer, A.S.; Doud, A.J.; Rose, M.L.; He, B. EEG control of a virtual helicopter in 3-dimensional space using intelligent control strategies. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2010, 18, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doud, A.J.; Lucas, J.P.; Pisansky, M.T.; He, B. Continuous three-dimensional control of a virtual helicopter using a motor imagery based brain-computer interface. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaFleur, K.; Cassady, K.; Doud, A.; Shades, K.; Rogin, E.; He, B. Quadcopter control in three-dimensional space using a noninvasive motor imagery-based brain–computer interface. J. Neural Eng. 2013, 10, 046003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Broek, S.P.; Reinders, F.; Donderwinkel, M.; Peters, M. Volume conduction effects in EEG and MEG. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 106, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbal, S.; Bereksi-Reguig, F. Time-frequency analysis of the first and the second heartbeat sounds. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 184, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boashash, B.; Azemi, G.; O’Toole, J.M. Time-frequency processing of nonstationary signals: Advanced TFD design to aid diagnosis with highlights from medical applications. IEEE Signal Process Mag. 2013, 30, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boashash, B.; Ouelha, S. Automatic signal abnormality detection using time-frequency features and machine learning: A newborn EEG seizure case study. Knowledge-Based Syst. 2016, 106, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Veluvolu, K.C. Time-frequency analysis of non-stationary biological signals with sparse linear regression based fourier linear combiner. Sensors 2017, 17, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quandt, F.; Reichert, C.; Hinrichs, H.; Heinze, H.J.; Knight, R.; Rieger, J.W. Single trial discrimination of individual finger movements on one hand: A combined MEG and EEG study. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 3316–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.M.; Gan, J.Q.; Sepulveda, F. Classifying mental tasks based on features of higher-order statistics from EEG signals in brain–computer interface. Inf. Sci. 2008, 178, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, M.; Gijsberts, A.; Castellini, C.; Caputo, B.; Hager, A.G.M.; Elsig, S.; Giatsidis, G.; Bassetto, F.; Müller, H. Electromyography data for non-invasive naturally-controlled robotic hand prostheses. Sci. Data 2014, 1, 140053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Wu, X.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X. A fully automated trial selection method for optimization of motor imagery based brain-computer interface. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, T.; Erdogmus, D.; Adami, A.; Pavel, M.; Mathan, S. Salient EEG channel selection in brain computer interfaces by mutual information maximization. In Proceedings of the IEEE 27th Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Shanghai, China, 1–4 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Herrero, G.; De Clercq, W.; Anwar, H.; Kara, O.; Egiazarian, K.; Van Huffel, S.; Van Paesschen, W. Automatic removal of ocular artifacts in the EEG without an EOG reference channel. In Proceedings of the IEEE 7th Nordic Signal Processing Symposium, Rejkjavik, Iceland, 7–9 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Castiglioni, P. Choi–williams distribution. In Encyclopedia of Biostatistics; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tzallas, A.T.; Tsipouras, M.G.; Fotiadis, D.I. Epileptic seizure detection in EEGs using time–frequency analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009, 13, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boubchir, L.; Al-Maadeed, S.; Bouridane, A. On the use of time-frequency features for detecting and classifying epileptic seizure activities in non-stationary EEG signals. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Boashash, B. Time-Frequency Signal Analysis and Processing: A Comprehensive Reference; Academic Press: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, L. Time-frequency distributions-a review. Proc. IEEE 1989, 77, 941–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L. Time-Frequency Analysis; Prentice Hall PTR: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero-Mosquera, C.; Trigueros, A.M.; Franco, J.I.; Navia-Vázquez, Á. New feature extraction approach for epileptic EEG signal detection using time-frequency distributions. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2010, 48, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, S.L. Hilbert Transforms in Signal Processing; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Boashash, B.; Azemi, G.; Khan, N.A. Principles of time–frequency feature extraction for change detection in non-stationary signals: Applications to newborn {EEG} abnormality detection. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claasen, T.; Mecklenbräuker, W. Time-frequency signal analysis. Philips J. Res. 1980, 35, 372–389. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.I.; Williams, W.J. Improved time-frequency representation of multicomponent signals using exponential kernels. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami, A.; Mendel, J.; Nikias, C. Higher-order spectra analysis (hosa) toolbox. Version 2000, 2. Available online: https://labcit.ligo.caltech.edu/ rana/mat/HOSA/ (accessed on 23 August 2017).
- Löfhede, J.; Thordstein, M.; Löfgren, N.; Flisberg, A.; Rosa-Zurera, M.; Kjellmer, I.; Lindecrantz, K. Automatic classification of background EEG activity in healthy and sick neonates. J. Neural Eng. 2010, 7, 016007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, B.; Faul, S.; Marnane, W.; Lightbody, G.; Korotchikova, I.; Boylan, G. A comparison of quantitative EEG features for neonatal seizure detection. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 1248–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, J.; Glover, J.R.; Ktonas, P.Y.; Kumar, A.T.; Mukherjee, A.; Karayiannis, N.B.; Frost, J.D., Jr.; Hrachovy, R.A.; Mizrahi, E.M. A multi-stage system for the automated detection of epileptic seizures in neonatal EEG. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. Publ. Am. Electroencephalogr. Soc. 2009, 26, 218. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, A.R.; Bashar, S.K.; Bhuiyan, M.I.H. On the classification of sleep states by means of statistical and spectral features from single channel electroencephalogram. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Kochi, India, 10–13 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, U.R.; Fujita, H.; Sudarshan, V.K.; Bhat, S.; Koh, J.E. Application of entropies for automated diagnosis of epilepsy using EEG signals: A review. Knowledge-Based Syst. 2015, 88, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Fujita, H.; Sudarshan, V.K.; Oh, S.L.; Adam, M.; Koh, J.E.; Tan, J.H.; Ghista, D.N.; Martis, R.J.; Chua, C.K.; et al. Automated detection and localization of myocardial infarction using electrocardiogram: A comparative study of different leads. Knowledge-Based Syst. 2016, 99, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, L. A measure of some time–frequency distributions concentration. Signal Process. 2001, 81, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, S.; Feldman, M.; Tomaszewski, J.; Shih, N.; Madabhushi, A. Cascaded multi-class pairwise classifier (CASCAMPA) for normal, cancerous, and cancer confounder classes in prostate histology. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Chicago, IL, USA, 30 March–2 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Granitto, P.M.; Rébola, A.; Cerviño, U.; Gasperi, F.; Biasoli, F.; Ceccatto, H.A. Cascade classifiers for multiclass problems. In Proceedings of the 7-th Argentine Symposium on Artificial Intelligence (ASAI), Rosario, Argentina, 29–30 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. On discriminative vs. generative classifiers: A comparison of logistic regression and naive bayes. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 2002, 2, 841–848. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, H.; Mao, Y.; Xiang, W.; Wang, Z. Recognition of human activities using SVM multi-class classifier. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreßel, U.H.G. Pairwise classification and support vector machines. In Advances in Kernel Methods; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 255–268. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.W.; Lin, C.J. A comparison of methods for multiclass support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2002, 13, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alam, S.S.; Bhuiyan, M.I.H. Detection of seizure and epilepsy using higher order statistics in the EMD domain. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 2013, 17, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alazrai, R.; Momani, M.; Daoud, M.I. Fall Detection for Elderly from Partially Observed Depth-Map Video Sequences Based on View-Invariant Human Activity Representation. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Allison, B.Z.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Cichocki, A. Optimized motor imagery paradigm based on imagining Chinese characters writing movement. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradberry, T.J.; Gentili, R.J.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L. Reconstructing three-dimensional hand movements from noninvasive electroencephalographic signals. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 3432–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makeig, S.; Kothe, C.; Mullen, T.; Bigdely-Shamlo, N.; Zhang, Z.; Kreutz-Delgado, K. Evolving signal processing for brain–computer interfaces. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 1567–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
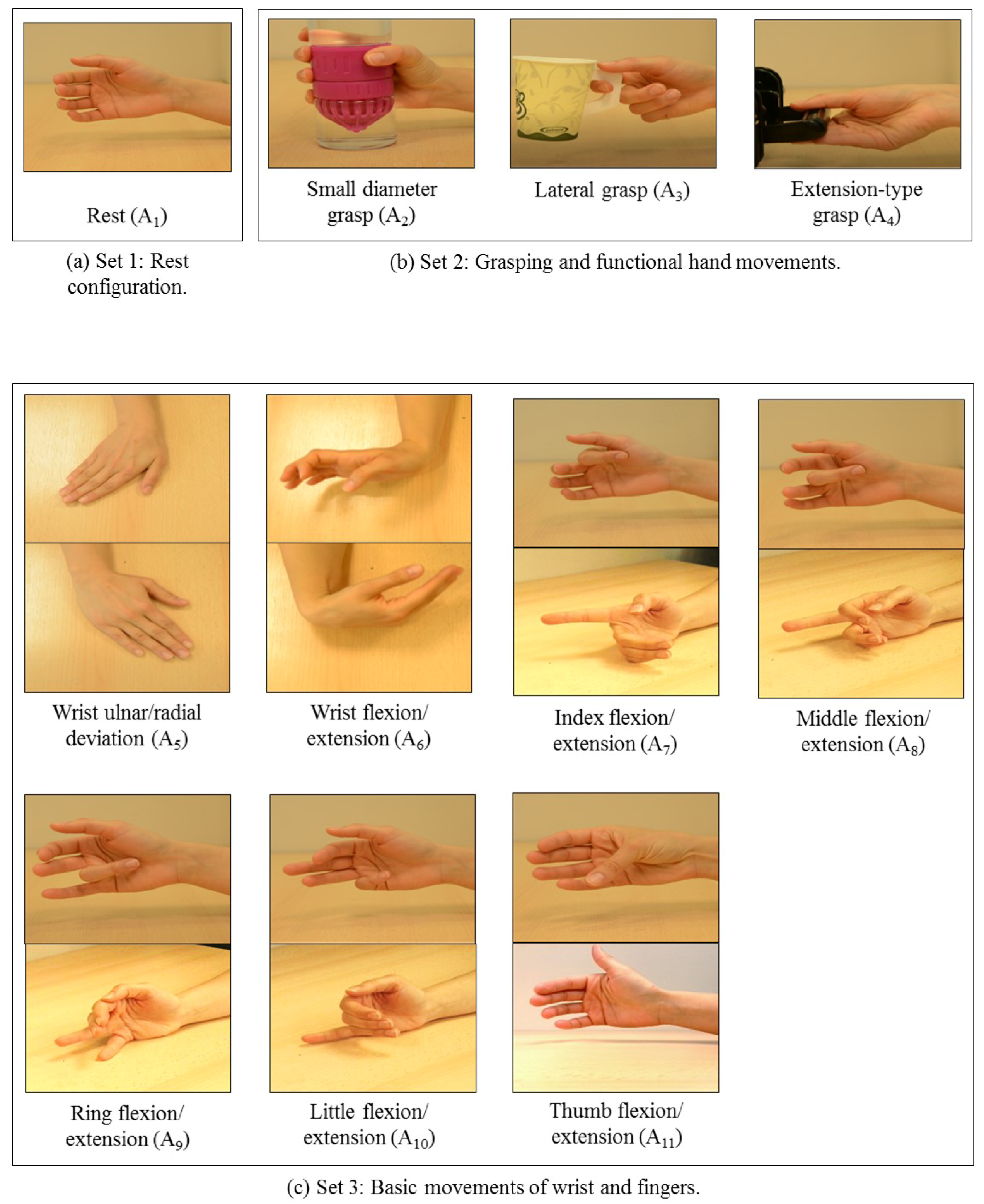


| Subject | Handedness | Amputated Hand | Years Since Amputation | Cause of Amputation | Prosthesis Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right hand | Left hand | 3.5 | Accident | Cosmetic | |
| Right hand | Right hand | 1.5 | Accident | None | |
| Left hand | Left hand | 4 | Accident | Myoelectric | |
| Right hand | Right hand | 5 | Accident | Cosmetic |
| Group Name | Comprised Electrodes |
|---|---|
| Broad bilateral () | , , , , , , , , , , |
| Left side () | , , , |
| Right side () | , , , |
| Narrow bilateral () | , , , , |
| Group of EEG Electrodes | Classification Layer | Classification Node | Results of the SDTP | Results of the SITP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRC | RCL | -Score | ACC | PRC | RCL | -Score | ACC | |||
| Layer 1 | 81.0 | 78.3 | 79.6 | 82.9 | 74.1 | 71.7 | 72.9 | 76.0 | ||
| Layer 2 | 83.5 | 82.3 | 82.9 | 83.7 | 66.5 | 65.4 | 65.9 | 72.0 | ||
| Layer 3 | 86.5 | 86.0 | 86.2 | 85.8 | 58.7 | 58.5 | 58.6 | 60.9 | ||
| 86.8 | 83.2 | 85.0 | 87.8 | 71.5 | 63.4 | 67.2 | 76.2 | |||
| Layer 4 | 91.0 | 90.9 | 91.0 | 90.7 | 68.8 | 68.7 | 68.7 | 69.7 | ||
| 77.9 | 76.6 | 77.2 | 76.9 | 45.6 | 45.5 | 45.6 | 51.9 | |||
| Overall average | 84.4 | 82.9 | 83.6 | 84.6 | 64.2 | 62.2 | 63.2 | 67.8 | ||
| Layer 1 | 77.4 | 72.1 | 74.7 | 77.2 | 70.3 | 67.0 | 68.6 | 73.1 | ||
| Layer 2 | 73.3 | 72.3 | 72.8 | 74.4 | 65.3 | 58.4 | 61.6 | 65.8 | ||
| Layer 3 | 74.2 | 73.7 | 73.9 | 73.6 | 49.3 | 49.4 | 49.4 | 49.3 | ||
| 76.7 | 69.0 | 72.6 | 79.1 | 70.1 | 52.5 | 60.1 | 72.8 | |||
| Layer 4 | 84.1 | 83.3 | 83.7 | 83.7 | 65.5 | 65.5 | 65.5 | 65.5 | ||
| 63.7 | 62.6 | 63.2 | 62.9 | 37.6 | 37.0 | 37.3 | 37.8 | |||
| Overall average | 74.9 | 72.2 | 73.5 | 75.1 | 59.7 | 55.0 | 57.1 | 60.7 | ||
| Layer 1 | 76.6 | 74.7 | 75.6 | 78.6 | 70.7 | 68.0 | 69.3 | 73.2 | ||
| Layer 2 | 73.0 | 71.7 | 72.3 | 73.7 | 61.9 | 57.2 | 59.5 | 63.6 | ||
| Layer 3 | 69.3 | 69.0 | 69.2 | 69.0 | 46.8 | 46.4 | 46.6 | 47.1 | ||
| 76.9 | 71.1 | 73.9 | 79.0 | 70.3 | 51.6 | 59.5 | 72.7 | |||
| Layer 4 | 83.9 | 83.1 | 83.5 | 83.2 | 60.4 | 60.5 | 60.4 | 60.4 | ||
| 59.6 | 58.6 | 59.1 | 59.4 | 34.4 | 34.1 | 34.3 | 35.0 | |||
| Overall average | 73.2 | 71.4 | 72.3 | 73.8 | 57.4 | 53.0 | 54.9 | 58.7 | ||
| Layer 1 | 75.6 | 72.1 | 73.8 | 76.6 | 67.3 | 64.4 | 65.8 | 70.1 | ||
| Layer 2 | 73.5 | 73.1 | 73.3 | 74.5 | 64.6 | 57.1 | 60.6 | 65.5 | ||
| Layer 3 | 71.7 | 71.3 | 71.5 | 70.8 | 49.6 | 49.3 | 49.5 | 50.1 | ||
| 78.5 | 70.8 | 74.5 | 80.1 | 70.2 | 52.9 | 60.3 | 71.2 | |||
| Layer 4 | 83.1 | 82.9 | 83.0 | 82.9 | 69.6 | 69.5 | 69.5 | 66.5 | ||
| 62.0 | 61.7 | 61.9 | 61.5 | 36.6 | 36.1 | 36.3 | 37.0 | |||
| Overall average | 74.1 | 72.0 | 73.0 | 74.4 | 59.6 | 54.9 | 57.0 | 60.1 | ||
| Category of TFFs | Classification Layer | Classification Node | Results of the SDTP | Results of the SITP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRC | RCL | -Score | ACC | PRC | RCL | -Score | ACC | |||
| Log-amplitude-based category () | Layer 1 | 81.4 | 77.1 | 79.2 | 85.1 | 77.4 | 72.6 | 74.9 | 76.6 | |
| Layer 2 | 87.6 | 86.8 | 87.2 | 87.8 | 82.6 | 81.8 | 82.2 | 81.7 | ||
| Layer 3 | 88.4 | 88.1 | 88.3 | 87.6 | 81.9 | 80.8 | 81.3 | 80.8 | ||
| 91.0 | 87.8 | 89.3 | 91.7 | 83.0 | 80.6 | 81.8 | 84.6 | |||
| Layer 4 | 95.1 | 94.7 | 94.9 | 94.9 | 86.9 | 85.9 | 86.3 | 86.9 | ||
| 85.0 | 86.0 | 85.5 | 85.5 | 76.2 | 75.1 | 75.6 | 74.4 | |||
| Overall average | 88.1 | 86.7 | 87.4 | 88.8 | 81.3 | 79.5 | 80.4 | 80.8 | ||
| Amplitude-based category () | Layer 1 | 78.8 | 76.3 | 77.5 | 80.5 | 72.7 | 69.2 | 70.9 | 70.0 | |
| Layer 2 | 79.6 | 78.3 | 78.9 | 80.2 | 72.2 | 70.0 | 71.1 | 62.1 | ||
| Layer 3 | 81.3 | 80.7 | 81.0 | 80.3 | 67.0 | 65.3 | 66.1 | 61.2 | ||
| 84.9 | 80.4 | 82.6 | 86.9 | 71.9 | 62.6 | 66.9 | 70.9 | |||
| Layer 4 | 89.6 | 89.9 | 89.7 | 89.8 | 71.7 | 70.4 | 71.1 | 68.4 | ||
| 71.2 | 71.0 | 71.1 | 71.5 | 59.8 | 56.2 | 57.9 | 53.4 | |||
| Overall average | 80.9 | 79.4 | 80.1 | 81.5 | 69.2 | 65.6 | 67.4 | 64.3 | ||
| Statistical-based category () | Layer 1 | 76.4 | 73.2 | 74.8 | 77.6 | 67.2 | 62.7 | 64.9 | 65.9 | |
| Layer 2 | 74.2 | 72.9 | 73.5 | 75.2 | 59.8 | 55.1 | 57.3 | 56.5 | ||
| Layer 3 | 72.7 | 72.6 | 72.6 | 72.5 | 46.3 | 46.0 | 46.2 | 51.5 | ||
| 75.7 | 71.6 | 73.6 | 79.3 | 65.8 | 52.4 | 58.3 | 57.7 | |||
| Layer 4 | 84.4 | 85.0 | 84.7 | 84.4 | 61.4 | 61.4 | 61.4 | 60.3 | ||
| 63.1 | 62.2 | 62.7 | 62.5 | 31.7 | 30.3 | 31.0 | 40.8 | |||
| Overall average | 74.4 | 72.9 | 73.6 | 75.2 | 55.4 | 51.3 | 53.2 | 55.4 | ||
| Spectral-based category () | Layer 1 | 79.5 | 80.3 | 79.9 | 83.1 | 72.9 | 70.1 | 71.5 | 72.3 | |
| Layer 2 | 85.4 | 85.0 | 85.2 | 86.0 | 73.5 | 72.6 | 73.0 | 71.1 | ||
| Layer 3 | 87.3 | 87.3 | 87.3 | 86.8 | 69.6 | 69.4 | 69.5 | 66.1 | ||
| 89.1 | 87.7 | 88.4 | 90.7 | 72.3 | 67.4 | 69.8 | 72.6 | |||
| Layer 4 | 91.3 | 90.6 | 91.0 | 92.8 | 80.4 | 80.3 | 80.3 | 79.1 | ||
| 81.9 | 82.4 | 82.1 | 82.4 | 60.3 | 59.4 | 59.9 | 57.8 | |||
| Overall average | 85.7 | 85.5 | 85.6 | 87.0 | 71.5 | 69.9 | 70.7 | 69.8 | ||
| Spectral entropy-based category () | Layer 1 | 78.0 | 76.5 | 77.2 | 80.1 | 70.3 | 65.8 | 68.0 | 69.6 | |
| Layer 2 | 80.3 | 79.7 | 80.0 | 81.1 | 63.6 | 60.0 | 61.7 | 63.0 | ||
| Layer 3 | 81.7 | 81.3 | 81.5 | 81.1 | 56.0 | 56.0 | 56.0 | 55.4 | ||
| 84.5 | 81.8 | 83.1 | 86.6 | 63.1 | 56.7 | 59.7 | 76.5 | |||
| Layer 4 | 89.4 | 89.8 | 89.6 | 89.6 | 69.1 | 69.1 | 69.1 | 70.5 | ||
| 73.5 | 74.6 | 74.0 | 73.9 | 37.7 | 37.3 | 37.5 | 40.5 | |||
| Overall average | 81.2 | 80.6 | 80.9 | 82.1 | 60.0 | 57.5 | 58.7 | 62.6 | ||
| Group of EEG Electrodes | Classification Layer | Classification Node | Results of SDTP | Results of SITP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRC | RCL | -Score | ACC | PRC | RCL | -Score | ACC | |||
| Layer 1 | 79.7 | 77.3 | 78.5 | 80.5 | 74.3 | 72.7 | 73.5 | 75.1 | ||
| Layer 2 | 81.5 | 79.3 | 80.4 | 81.5 | 69.8 | 68.0 | 68.9 | 70.8 | ||
| Layer 3 | 85.2 | 84.6 | 84.9 | 84.6 | 76.8 | 76.5 | 76.6 | 76.4 | ||
| 88.8 | 86.0 | 87.3 | 89.1 | 77.0 | 74.9 | 75.9 | 81.7 | |||
| Layer 4 | 92.1 | 92.3 | 92.2 | 92.2 | 82.7 | 82.3 | 82.5 | 82.0 | ||
| 81.3 | 81.4 | 81.4 | 81.2 | 57.4 | 57.6 | 57.5 | 57.5 | |||
| Overall average | 84.8 | 83.5 | 84.1 | 84.8 | 73.0 | 72.0 | 72.5 | 73.9 | ||
| Layer 1 | 76.7 | 74.9 | 75.8 | 77.7 | 66.6 | 64.9 | 65.8 | 71.4 | ||
| Layer 2 | 77.5 | 76.8 | 77.2 | 78.4 | 65.0 | 58.9 | 61.8 | 64.0 | ||
| Layer 3 | 83.9 | 81.7 | 82.7 | 81.2 | 58.0 | 57.8 | 57.9 | 58.1 | ||
| 86.5 | 83.8 | 85.1 | 85.3 | 67.6 | 63.9 | 65.7 | 65.0 | |||
| Layer 4 | 85.0 | 85.8 | 85.4 | 84.7 | 77.7 | 78.1 | 77.9 | 77.9 | ||
| 72.1 | 72.6 | 72.3 | 73.5 | 45.7 | 44.4 | 45.0 | 45.6 | |||
| Overall average | 80.3 | 79.3 | 79.8 | 80.2 | 63.4 | 61.3 | 62.3 | 63.6 | ||
| Layer 1 | 77.0 | 75.9 | 76.5 | 78.7 | 68.4 | 67.3 | 67.8 | 70.0 | ||
| Layer 2 | 79.7 | 78.3 | 79.0 | 80.4 | 66.7 | 63.8 | 65.2 | 67.6 | ||
| Layer 3 | 85.2 | 83.3 | 84.3 | 83.8 | 62.2 | 62.4 | 62.3 | 62.2 | ||
| 85.5 | 84.4 | 85.0 | 85.2 | 70.0 | 59.0 | 64.0 | 67.6 | |||
| Layer 4 | 87.4 | 86.3 | 86.9 | 85.0 | 75.5 | 75.4 | 75.5 | 75.4 | ||
| 76.4 | 76.8 | 76.6 | 76.4 | 46.5 | 46.1 | 46.3 | 46.9 | |||
| Overall average | 81.9 | 80.9 | 81.4 | 81.6 | 64.9 | 62.3 | 63.5 | 64.9 | ||
| Layer 1 | 76.7 | 74.4 | 75.6 | 75.2 | 66.7 | 62.0 | 64.3 | 67.6 | ||
| Layer 2 | 80.7 | 79.1 | 79.9 | 80.7 | 66.2 | 62.5 | 64.3 | 67.7 | ||
| Layer 3 | 84.3 | 81.3 | 82.8 | 82.7 | 69.8 | 69.9 | 69.8 | 67.0 | ||
| 87.9 | 86.8 | 87.3 | 87.3 | 75.5 | 68.3 | 71.7 | 79.8 | |||
| Layer 4 | 90.5 | 90.7 | 90.6 | 89.1 | 70.6 | 70.3 | 70.5 | 70.5 | ||
| 78.1 | 77.1 | 77.6 | 77.7 | 53.0 | 52.1 | 52.5 | 52.2 | |||
| Overall average | 83.0 | 81.6 | 82.3 | 82.1 | 67.0 | 64.2 | 65.5 | 67.5 | ||
| Category of TFFs | Classification Layer | Classification Node | Results of the SDTP | Results of the SITP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRC | RCL | -Score | ACC | PRC | RCL | -Score | ACC | |||
| Log-amplitude-based category () | Layer 1 | 79.3 | 78.0 | 78.6 | 77.8 | 76.5 | 74.8 | 75.6 | 77.6 | |
| Layer 2 | 90.7 | 88.6 | 89.7 | 90.0 | 88.8 | 88.4 | 88.6 | 89.1 | ||
| Layer 3 | 93.0 | 93.0 | 93.0 | 93.1 | 90.7 | 90.5 | 90.6 | 90.6 | ||
| 93.6 | 91.7 | 92.7 | 94.6 | 92.4 | 85.5 | 88.8 | 90.5 | |||
| Layer 4 | 97.4 | 97.3 | 97.4 | 97.4 | 93.3 | 93.5 | 93.4 | 93.4 | ||
| 89.3 | 88.4 | 88.8 | 88.3 | 86.0 | 85.6 | 85.8 | 85.5 | |||
| Overall average | 90.5 | 89.5 | 90.0 | 90.2 | 87.9 | 86.4 | 87.1 | 87.8 | ||
| Amplitude-based category () | Layer 1 | 72.3 | 71.6 | 72.0 | 74.8 | 71.8 | 69.0 | 70.4 | 74.0 | |
| Layer 2 | 84.7 | 82.3 | 83.5 | 84.0 | 77.6 | 73.9 | 75.7 | 76.7 | ||
| Layer 3 | 84.8 | 83.4 | 84.1 | 83.8 | 73.6 | 72.8 | 73.2 | 73.0 | ||
| 91.3 | 86.8 | 89.0 | 90.7 | 87.1 | 78.5 | 82.6 | 85.7 | |||
| Layer 4 | 85.3 | 84.9 | 85.1 | 84.9 | 85.4 | 86.2 | 85.8 | 85.2 | ||
| 72.7 | 72.8 | 72.8 | 72.3 | 62.9 | 61.7 | 62.3 | 61.6 | |||
| Overall average | 81.8 | 80.3 | 81.1 | 81.7 | 76.4 | 73.7 | 75.0 | 76.0 | ||
| Statistical-based category () | Layer 1 | 71.2 | 68.7 | 69.9 | 73.7 | 67.0 | 63.1 | 65.0 | 68.2 | |
| Layer 2 | 72.1 | 70.6 | 71.4 | 73.6 | 61.7 | 57.4 | 59.4 | 63.0 | ||
| Layer 3 | 74.4 | 74.0 | 74.2 | 74.6 | 52.6 | 51.4 | 52.0 | 51.3 | ||
| 78.7 | 78.6 | 78.7 | 82.9 | 67.7 | 63.3 | 65.4 | 74.0 | |||
| Layer 4 | 83.9 | 83.4 | 83.6 | 83.9 | 72.5 | 73.0 | 72.8 | 72.1 | ||
| 60.8 | 60.3 | 60.5 | 60.5 | 38.5 | 36.1 | 37.3 | 37.1 | |||
| Overall average | 73.5 | 72.6 | 73.1 | 74.9 | 60.0 | 57.4 | 58.7 | 61.0 | ||
| Spectral-based category () | Layer 1 | 76.4 | 75.1 | 75.7 | 75.6 | 74.4 | 70.8 | 72.6 | 74.7 | |
| Layer 2 | 85.6 | 84.5 | 85.0 | 85.5 | 77.8 | 76.8 | 77.3 | 78.3 | ||
| Layer 3 | 92.1 | 91.5 | 91.8 | 91.9 | 83.8 | 82.9 | 83.3 | 82.8 | ||
| 92.7 | 91.8 | 92.3 | 93.1 | 85.1 | 76.9 | 80.8 | 85.0 | |||
| Layer 4 | 92.7 | 92.7 | 92.7 | 92.8 | 87.4 | 87.6 | 87.5 | 87.7 | ||
| 87.5 | 86.5 | 87.0 | 86.9 | 70.2 | 69.9 | 70.1 | 70.4 | |||
| Overall average | 87.8 | 87.0 | 87.4 | 87.6 | 79.8 | 77.5 | 78.6 | 79.8 | ||
| Spectral entropy-based category () | Layer 1 | 75.4 | 72.3 | 73.8 | 77.5 | 69.1 | 66.7 | 67.9 | 71.8 | |
| Layer 2 | 76.7 | 75.4 | 76.1 | 77.6 | 65.4 | 63.0 | 64.2 | 66.4 | ||
| Layer 3 | 86.3 | 85.8 | 86.1 | 86.4 | 67.9 | 66.9 | 67.4 | 67.8 | ||
| 87.4 | 84.5 | 85.9 | 88.6 | 76.0 | 73.3 | 74.6 | 79.3 | |||
| Layer 4 | 88.8 | 89.3 | 89.0 | 88.6 | 82.4 | 82.3 | 82.4 | 82.8 | ||
| 77.2 | 76.7 | 77.0 | 76.4 | 51.3 | 51.0 | 51.2 | 51.3 | |||
| Overall average | 82.0 | 80.7 | 81.3 | 82.5 | 68.7 | 67.2 | 67.9 | 69.9 | ||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alazrai, R.; Alwanni, H.; Baslan, Y.; Alnuman, N.; Daoud, M.I. EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interface for Decoding Motor Imagery Tasks within the Same Hand Using Choi-Williams Time-Frequency Distribution. Sensors 2017, 17, 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17091937
Alazrai R, Alwanni H, Baslan Y, Alnuman N, Daoud MI. EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interface for Decoding Motor Imagery Tasks within the Same Hand Using Choi-Williams Time-Frequency Distribution. Sensors. 2017; 17(9):1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17091937
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlazrai, Rami, Hisham Alwanni, Yara Baslan, Nasim Alnuman, and Mohammad I. Daoud. 2017. "EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interface for Decoding Motor Imagery Tasks within the Same Hand Using Choi-Williams Time-Frequency Distribution" Sensors 17, no. 9: 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17091937
APA StyleAlazrai, R., Alwanni, H., Baslan, Y., Alnuman, N., & Daoud, M. I. (2017). EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interface for Decoding Motor Imagery Tasks within the Same Hand Using Choi-Williams Time-Frequency Distribution. Sensors, 17(9), 1937. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17091937






