Novel Low-Cost Sensor for Human Bite Force Measurement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
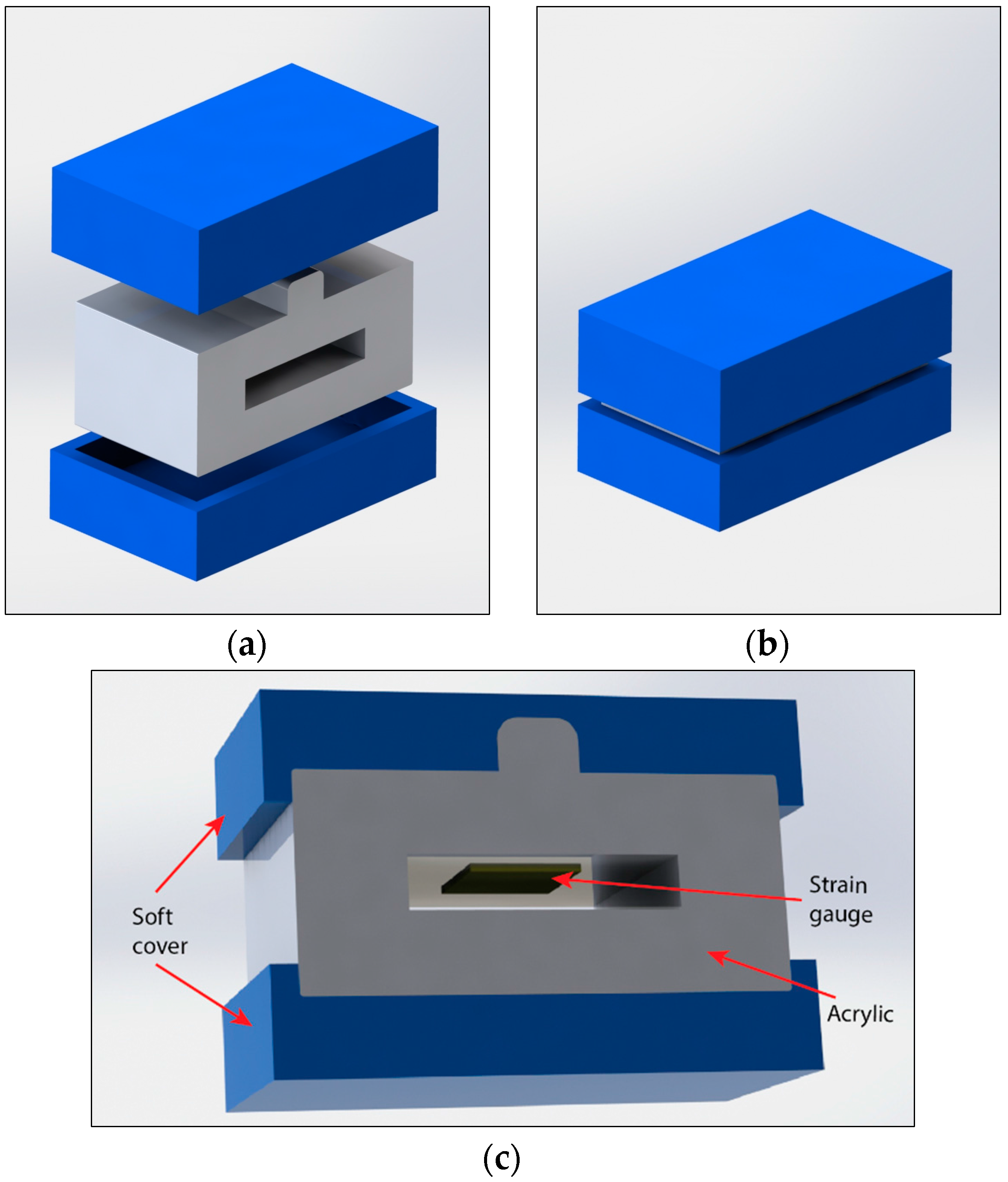
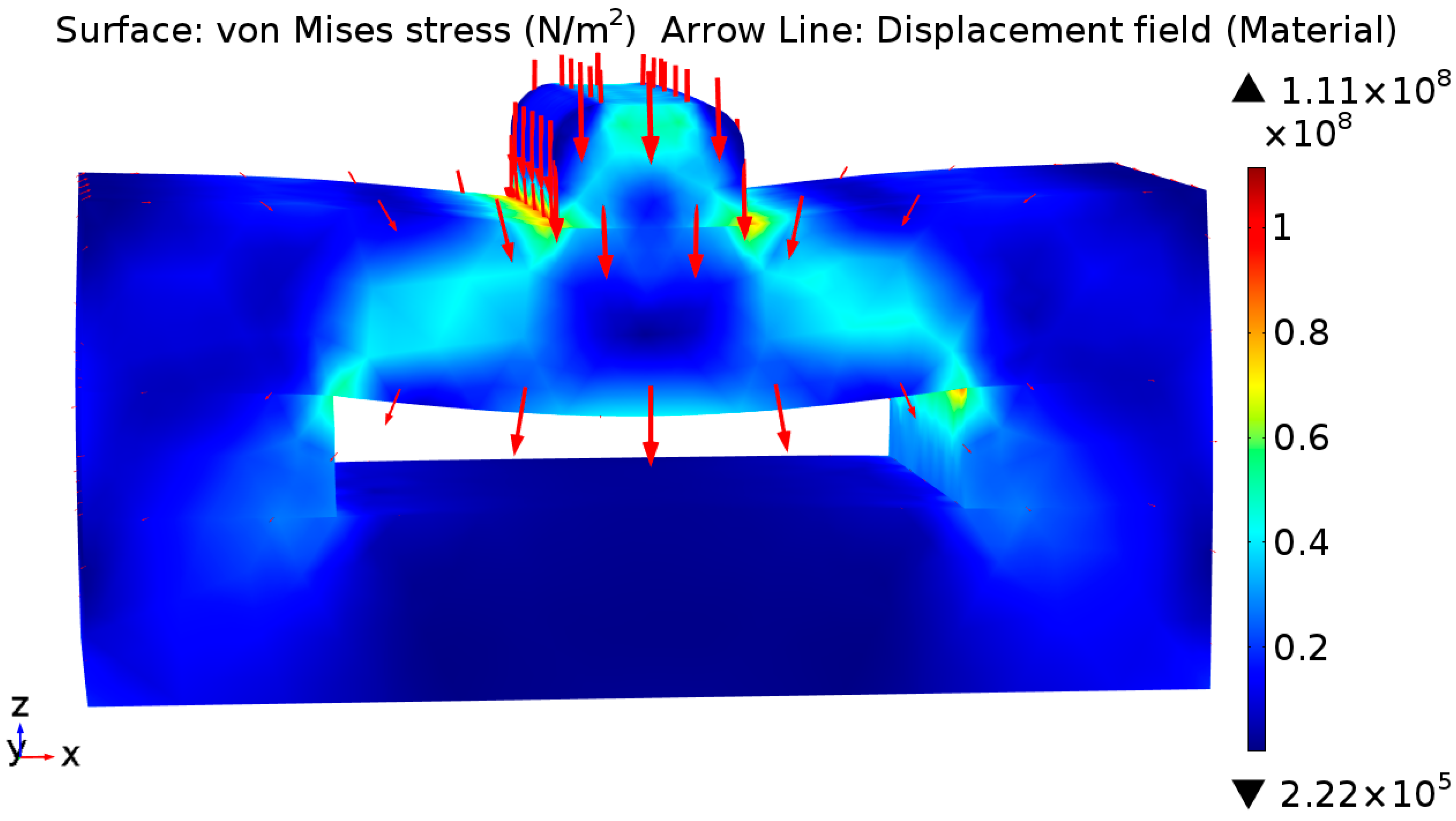
2. Design and Simulation
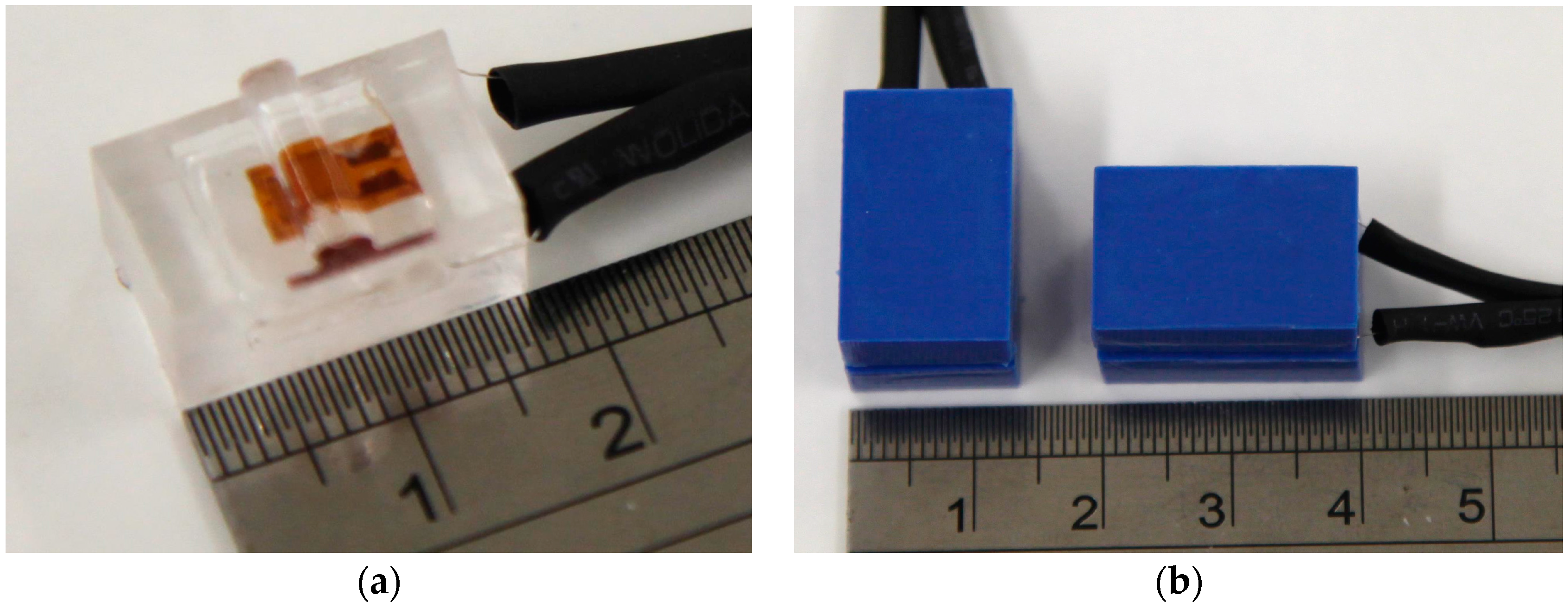
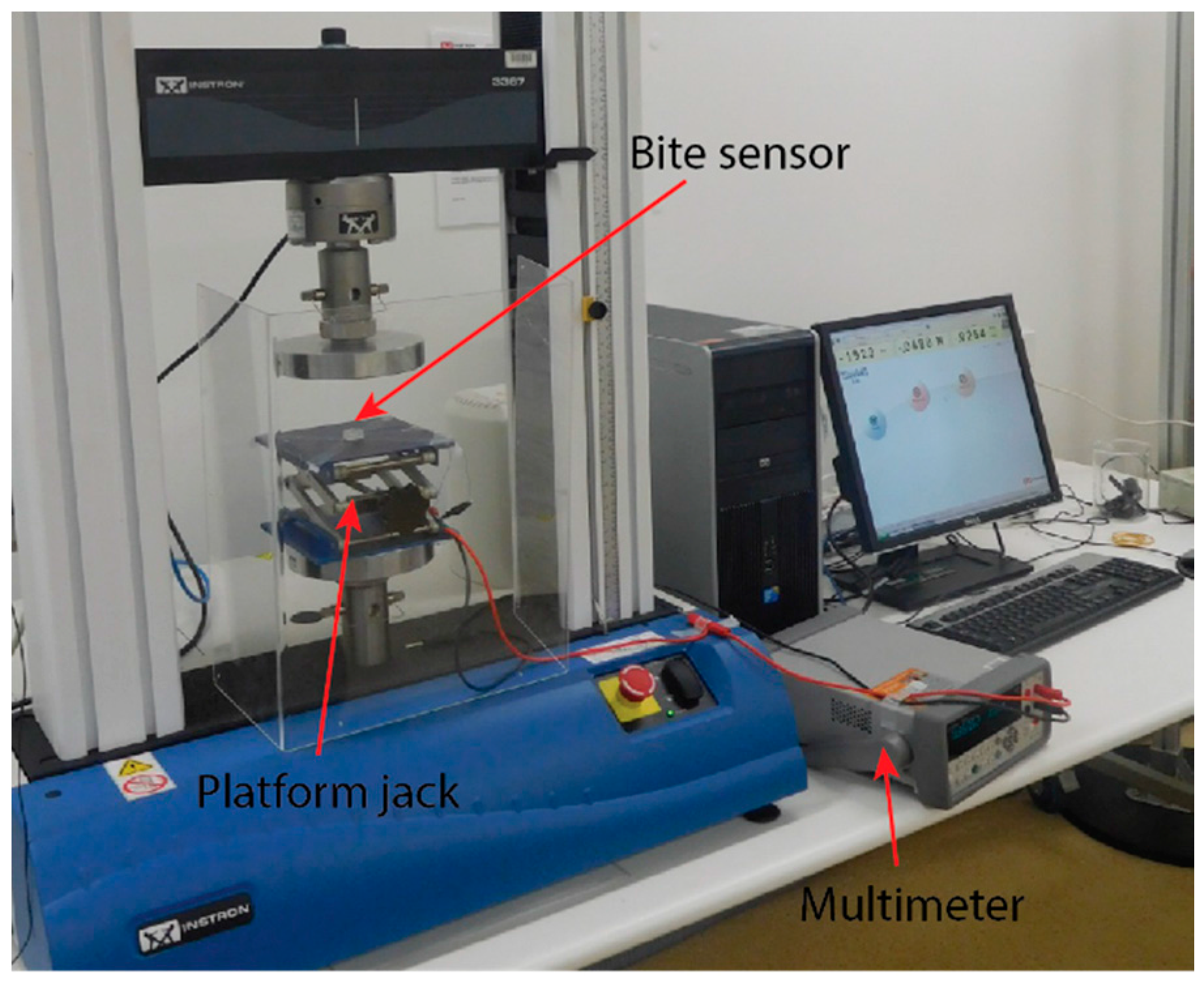
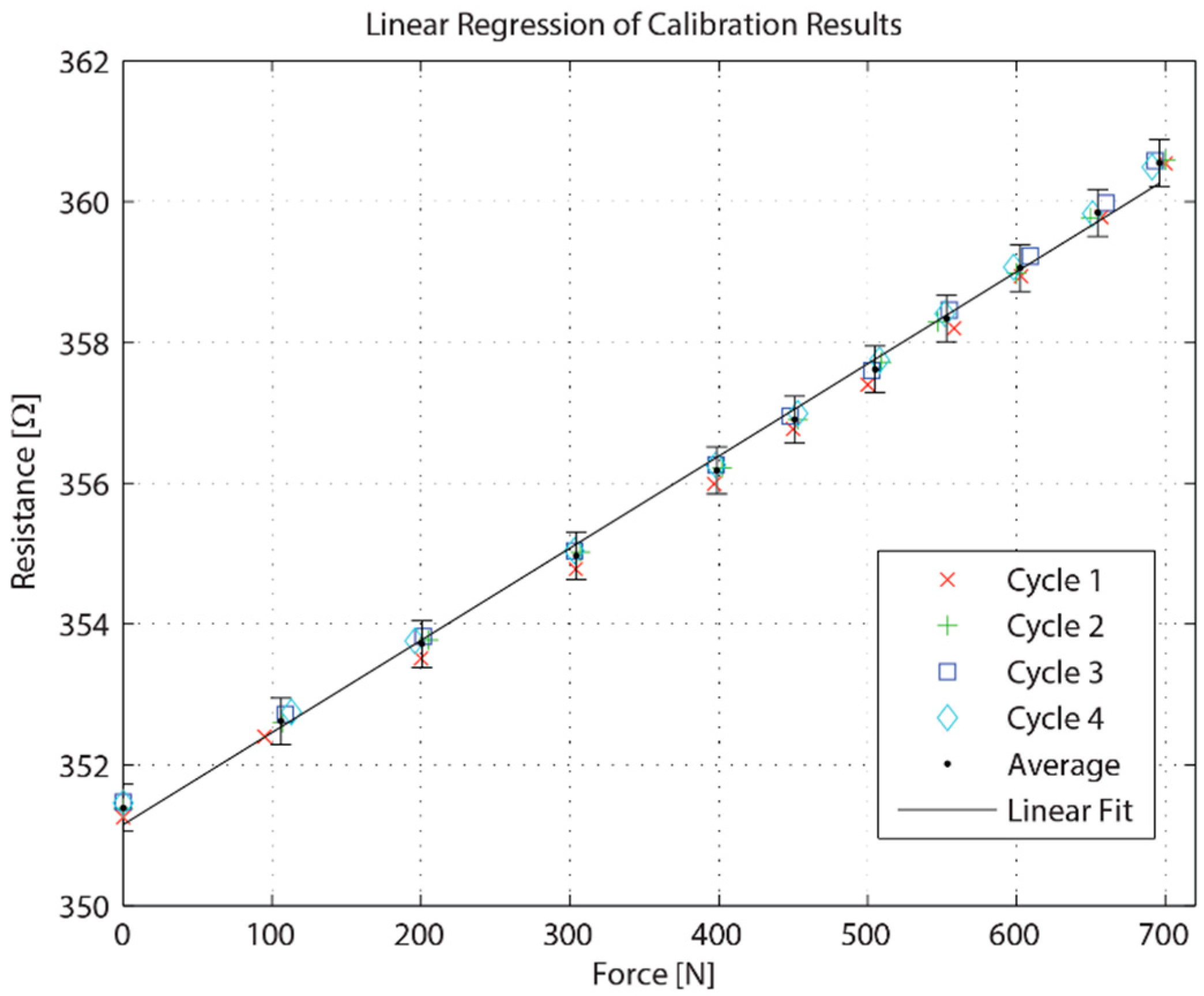
3. Fabrication and Calibration
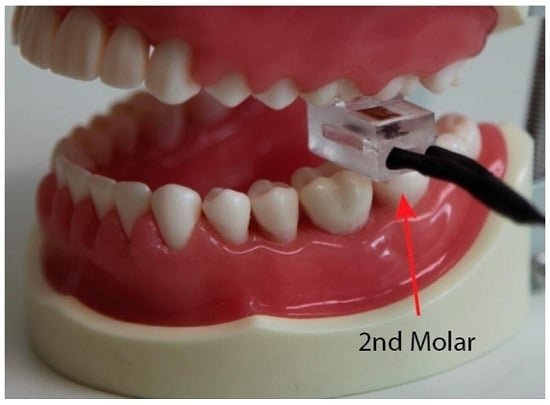
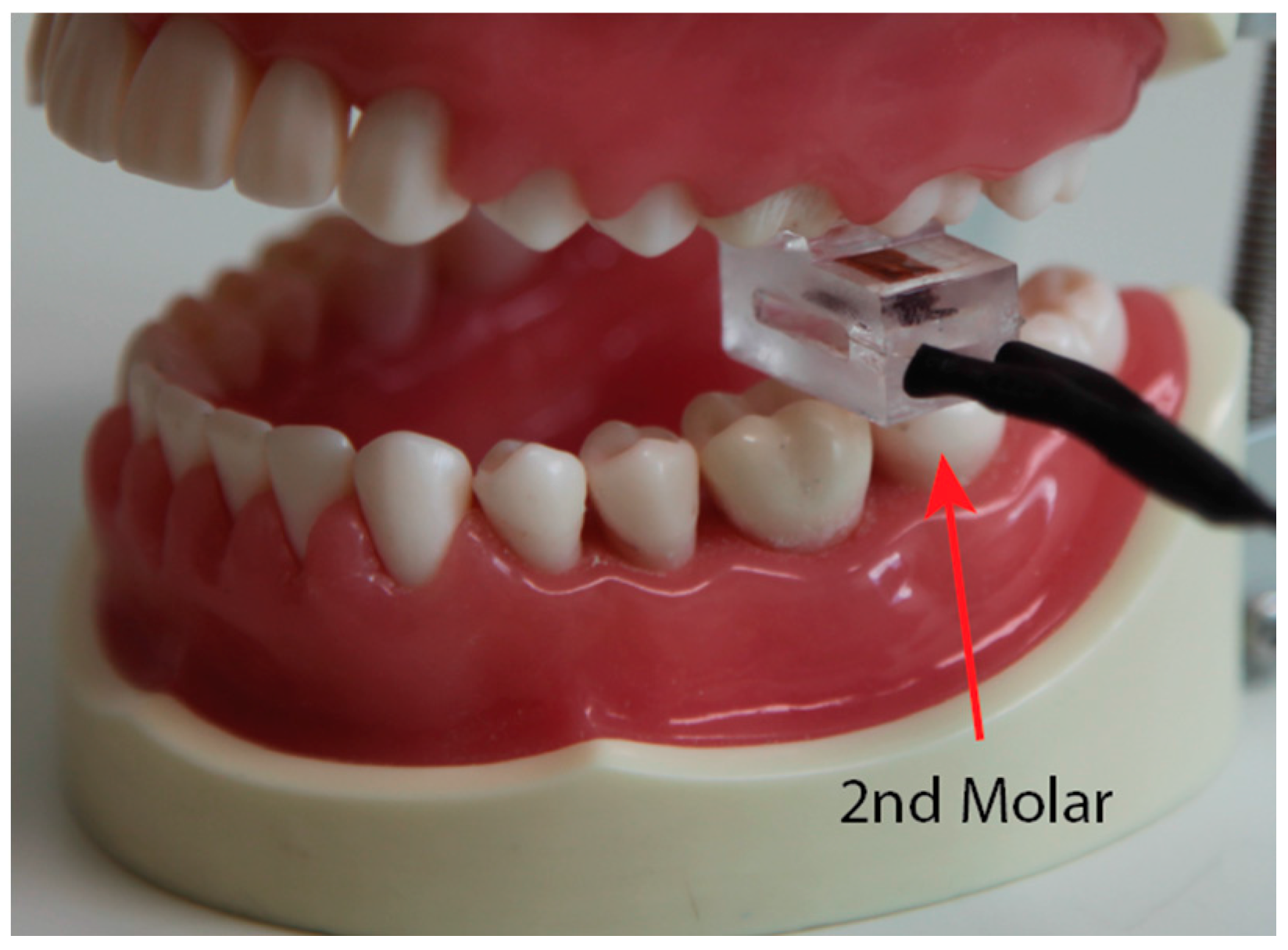
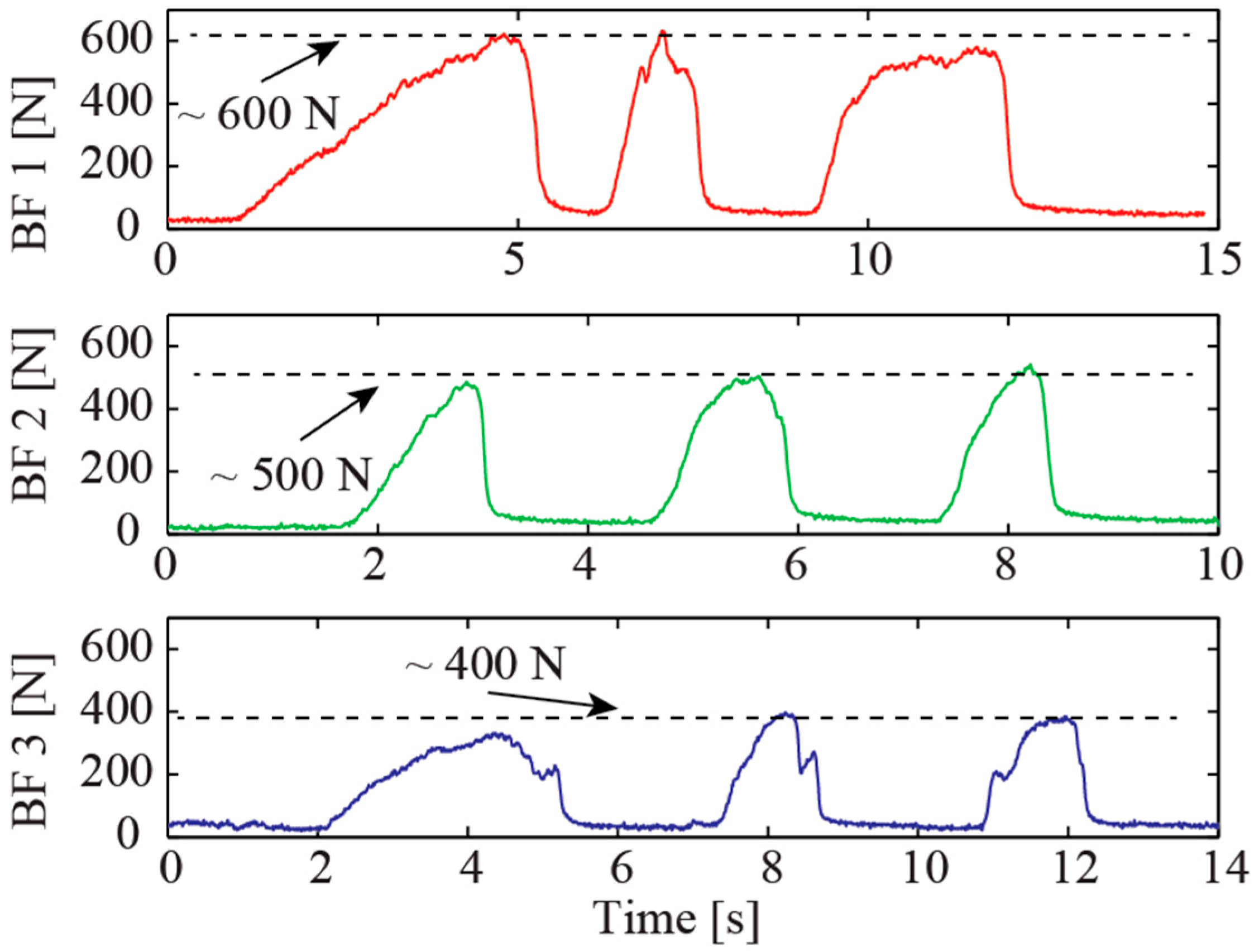
4. In Vivo Experimental Validation
- Fabrication (and structure)—simple: O (compact structure and easy to fabricate); complex: Δ (requires sophisticated processes, such as CNC machining); very complicated: X (time consuming process and bulky structure, such as hydraulic structures).
- Cost—low: O (worldwide availability and simple fabrication); moderate: Δ (using commercially available sensors with non-complicated structures); high: X (complicated and time consuming processes, which may not be relevant to mass production).
- Measureable range (approximation in some cases)—>600: O; 300–600: Δ; <300: X.
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biswas, B.K.; Bag, S.; Pal, S. Biomechanical analysis of normal and implanted tooth using biting force measurement. IJE 2013, 4, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Alhowaish, L. Bite Force Evaluation in Children Following Dental Treatment. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Enkling, N.; Saftig, M.; Worni, A.; Mericske-Stern, R.; Schimmel, M. Chewing efficiency, bite force and oral health-related quality of life with narrow diameter implants—A prospective clinical study: Results after one year. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, S.; Bantleon, H.-P.; Hnat, W.P.; Freudenthaler, J.W.; Marcotte, M.R.; Johnson, B.E. A study of bite force, part 1: Relationship to various physical characteristics. Angle Orthod. 1995, 65, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kulloli, V.K.; Saidpatil, V.V. Design and development instrument to record biting force. IJSRP 2014, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; McAuliffe, P.; O’Connel, B.; Diamond, D.; Lau, K.T. Development of Bite Guard for Wireless Monitoring of Bruxism Using Pressure-Sensitive Polymer. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Body Sensor Networks, Singapore, 7–9 June 2010; pp. 109–116.
- Singh, S.; Utreja, A.K.; Sandhu, N.; Dhaliwal, Y.S. An innovative miniature bite force recorder. IJCPD 2011, 4, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dıraçoğlu, D.; Güçlü, B.; Alptekin, K.; Karan, A.; Aksoy, C. Maximal bite force measurement by the “istanbul bite force recorder”. J. PMR Sci. 2008, 3, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Bousdras, V.; Cunningham, J.; Ferguson-Pell, M.; Bamber, M.; Sindet-Pedersen, S.; Blunn, G.; Goodship, A. A novel approach to bite force measurements in a porcine model in vivo. IJOMS 2006, 35, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Martins, M.J.; Caramelo, F.J.; da Fonseca, J.A.R.; Nicolau, P.M.G. In vitro study on the sensibility and reproducibility of the new t-scan® III HD system. RPEMDCM 2014, 55, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarb, G.A.; Hobkirk, J.; Eckert, S.; Jacob, R. Prosthodontic Treatment for Edentulous Patients: Complete Dentures and Implant-Supported Prostheses, 13th ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Parle, D.; Desai, D.; Bansal, A. Estimation of individual bite force during normal occlusion using fea. In Proceedings of the Altair Technology Conference, Pune, India, 18–19 July 2013.
- Nelson, S.J. Wheeler’s Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Occlusion, 10th ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Koc, D.; Dogan, A.; Bek, B. Bite force and influential factors on bite force measurements: A literature review. Eur. J. Dent. 2010, 4, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tekscan. Force Sensors for Design. Available online: https://www.tekscan.com/sites/default/files/FLX-Force-Sensors-For-Design.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2016).
- Interlink. Applications of Force Sensing Technology. Available online: http://interlinkelectronics.com/whitepapers/whitepaper1.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2016).
- Interlink. Enhancing Medical Devices and Personal Healthcare Products with Force Sensing Technology. Available online: http://interlinkelectronics.com/whitepapers/whitepaper2.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2016).
- Flanagan, D.; Ilies, H.; O’brien, B.; McManus, A.; Larrow, B. Jaw bite force measurement device. JOI 2012, 38, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, P.W.; Lemen, C.A. Measuring bite force in small mammals with a piezo-resistive sensor. J. Mamm. 2008, 89, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Lantada, A.; González Bris, C.; Lafont Morgado, P.; Sanz Maudes, J. Novel system for bite-force sensing and monitoring based on magnetic near field communication. Sensors 2012, 12, 11544–11558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollinger, A.; Wanderley, M.M. Evaluation of commercial force-sensing resistors. In Proceedings of the International Conference on New Interfaces for Musical Expression, Paris, France, 4–8 June 2006.
- Roriz, P.; Carvalho, L.; Frazão, O.; Santos, J.L.; Simões, J.A. From conventional sensors to fibre optic sensors for strain and force measurements in biomechanics applications: A review. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, J.M.; Wataha, J.C. Dental Materials: Properties and Manipulation, 9th ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Van Noort, R.; Barbour, M.E. Introduction to Dental Materials, 4th ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Perspex® Technical Data Sheet. Available online: http://allplastics.com.au/component/docman/doc_download/382-allplastics-perspex-cell-cast-acrylic-technical-data-sheet-en?Itemid= (accessed on 8 March 2016).
- Ho, V.A.; Dao, D.V.; Sugiyama, S.; Hirai, S. Analysis of sliding of a soft fingertip embedded with a novel micro force/moment sensor: Simulation, experiment, and application. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 889–894.
- Dao, D.V.; Toriyama, T.; Wells, J.; Sugiyama, S. Six-degree of freedom micro force-moment sensor for application in geophysics. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 20–24 January 2002; pp. 312–315.
- Phan, H-.P.; Dao, D.V.; Nakamura, K.; Dimitrijev, S.; Nguyen, N.-T. The Piezoresistive Effect of SiC for MEMS Sensors at High Temperatures: A Review. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2015, 21, 1663–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.-P.; Dinh, T.; Kozeki, T.; Nguyen, T.-K.; Qamar, A.; Namazu, T.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Dao, D.V. The piezoresistive effect in top-down fabricated p-type 3C-SiC nanowires. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2016, 37, 1029–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, Y.; Iwasaki, L.; McCall, W., Jr.; Ohrbach, R.; Lozier, E.; Nickel, J. Reliability of electromyographic activity vs. bite-force from human masticatory muscles. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 119, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linsen, S.; Schmidt-Beer, U.; Fimmers, R.; Grüner, M.; Koeck, B. Craniomandibular pain, bite force, and oral health-related quality of life in patients with jaw resection. J. Pain Symp. Manag. 2009, 37, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaki, P.; Vieira, M.; Bommarito, S. Maximum bite force analysis in different age groups. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 18, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Varga, S.; Spalj, S.; Varga, M.L.; Milosevic, S.A.; Mestrovic, S.; Slaj, M. Maximum voluntary molar bite force in subjects with normal occlusion. Eur. J. Orthod. 2011, 33, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raadsheer, M.; Van Eijden, T.; Van Ginkel, F.; Prahl-Andersen, B. Contribution of jaw muscle size and craniofacial morphology to human bite force magnitude. J. Dent. Res. 1999, 78, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibrahim, A. The Measurement of Maximal Bite Force in Human Beings; University of Dundee: Dundee, Scotland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Banasr, F.H.; Alammari, M.R. A novel bio-sensor for registration of biting force in occlusally reactive single mandibular implant overdenture. Open J. Stomatol. 2013, 3, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, V.; Sforza, C.; Serrao, G.; Dellavia, C.; Tartaglia, G. Single tooth bite forces in healthy young adults. J. Oral Rehabil. 2004, 31, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, P.d.S.; Kogawa, E.M.; Lauris, J.R.P.; Conti, P.C.R. The influence of gender and bruxism on the human maximum bite force. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2006, 14, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdullah, M.M.; Saltaji, H.; Abou-Hamed, H.; Youssef, M. The relationship between molar bite force and incisor inclination: A prospective cross-sectional study. Int. Orthod. 2014, 12, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ref. | Sensing Principle | Sensor Material/Device Material | Max (N) | Mean (N) | Evaluation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fabrication (i) | Cost (ii) | Measure Range (iii) | |||||
| [1] | “specially designed transduction device” | - | 392 | 344.9 | - | - | Δ |
| [2] | Model 13 sub-miniature load cell | HSS, tool steel prongs | 323.3 | 180.6 | Δ | Δ | Δ |
| [4] | Pressure transducer (Omega PX300) | Pressurised rubber tube | 1280 | 814 | X | Δ | O |
| [5] | Strain gauge | 316 stainless steel fork | - | 615.8 | Δ | Δ | Δ |
| [6] | Custom piezoresistive composite | Conductive carbon black powder and PDMS embedded in acrylic splints | 120 range | - | Δ | Δ | X |
| [7] | Strain gauge | “high quality spring steel” | 668 | 606.8 | Δ | Δ | O |
| [8] | Model 13 sub-miniature load cell | 316L stainless steel, shaped like mouth guard | 146.7 | 101.01 | Δ | Δ | X |
| [30] | Tekscan FlexiForce | Stainless steel plates | - | 62.23 | Δ | Δ | O |
| [31] | “expansion measurement strips” | Hardened tool steel with chromium plating fork | 428.78 | 168.03 | Δ | Δ | O |
| [32] | Digital dynamometer (Kratos DDK/M) | - | - | 354.01 | - | - | - |
| [33] | Hydraulic pressure gauge | “vinyl material encased in disposable plastic tube” | 825.5 | 779 | X | - | O |
| [34] | 3-axis load cell (Kistler 9251A) | Acrylic plates | 888 | 545.7 | Δ | X | O |
| [35] | Pressure transducer (Omega PX309) | Water filled flexible synthetic tube with outer PVC tube and soft silicone tube coating | <1000 | 577 | X | X | O |
| [35] | Strain gauge | T-shaped metal with EVA sheet covers | <400 | 254 | Δ | Δ | Δ |
| [36] | Tekscan FlexiForce | Acrylic splints | - | 619.8 | O | Δ | O |
| [37] | Strain gauge (Occlusator) | Stainless steel | - | 306.07 | - | Δ | Δ |
| [38] | Digital dynamometer (Kratos IDDK) | - | 999.3 | 590 | - | Δ | O |
| [39] | Tekscan FlexiForce | Acrylic splints | - | 249.8 | O | Δ | O |
| This work | Strain gauge | Acrylic | 700 | - | O | O | O |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fastier-Wooller, J.; Phan, H.-P.; Dinh, T.; Nguyen, T.-K.; Cameron, A.; Öchsner, A.; Dao, D.V. Novel Low-Cost Sensor for Human Bite Force Measurement. Sensors 2016, 16, 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081244
Fastier-Wooller J, Phan H-P, Dinh T, Nguyen T-K, Cameron A, Öchsner A, Dao DV. Novel Low-Cost Sensor for Human Bite Force Measurement. Sensors. 2016; 16(8):1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081244
Chicago/Turabian StyleFastier-Wooller, Jarred, Hoang-Phuong Phan, Toan Dinh, Tuan-Khoa Nguyen, Andrew Cameron, Andreas Öchsner, and Dzung Viet Dao. 2016. "Novel Low-Cost Sensor for Human Bite Force Measurement" Sensors 16, no. 8: 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081244
APA StyleFastier-Wooller, J., Phan, H.-P., Dinh, T., Nguyen, T.-K., Cameron, A., Öchsner, A., & Dao, D. V. (2016). Novel Low-Cost Sensor for Human Bite Force Measurement. Sensors, 16(8), 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081244