A New Elliptical Model for Device-Free Localization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Radio Tomographic Imaging
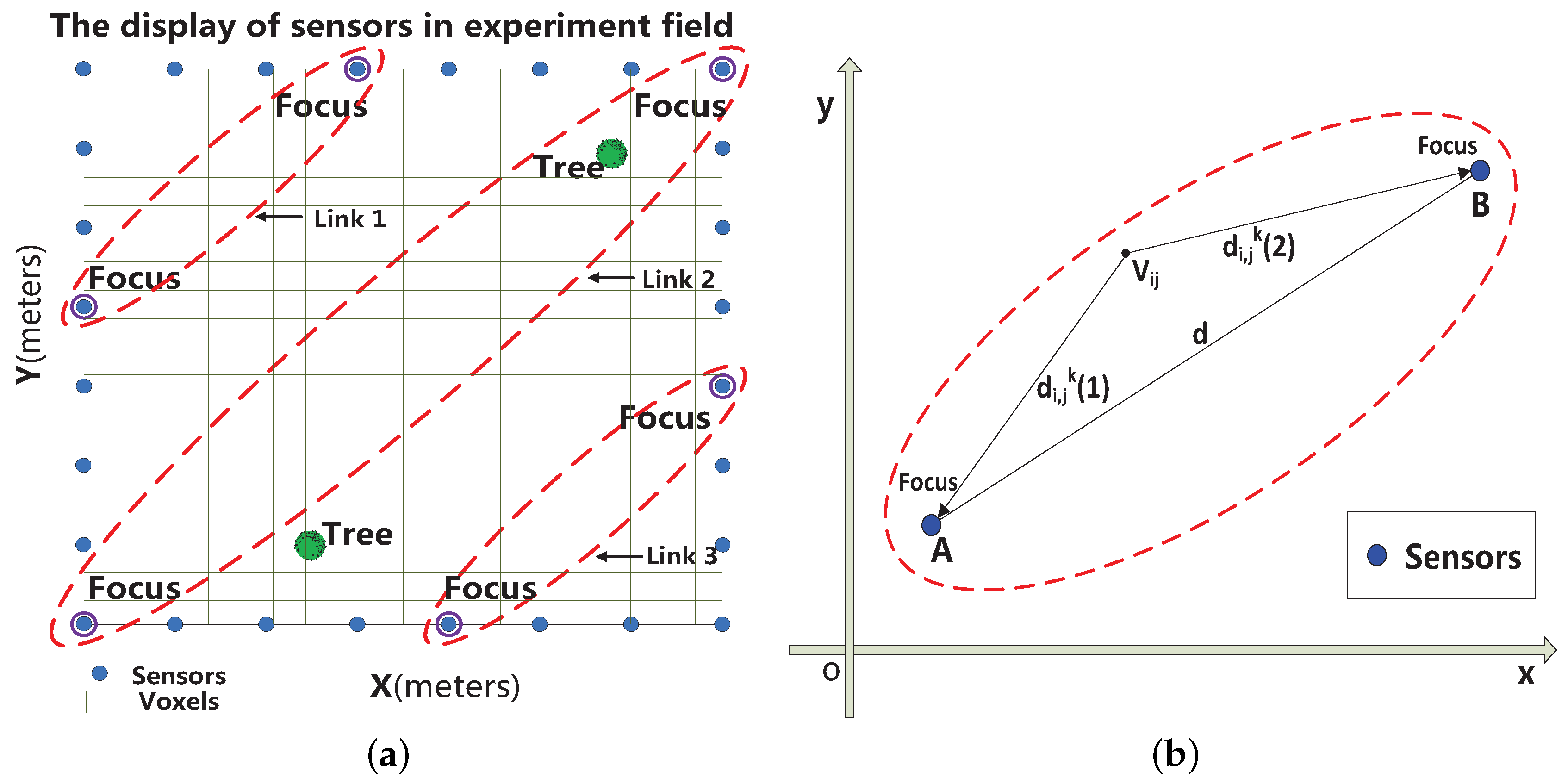
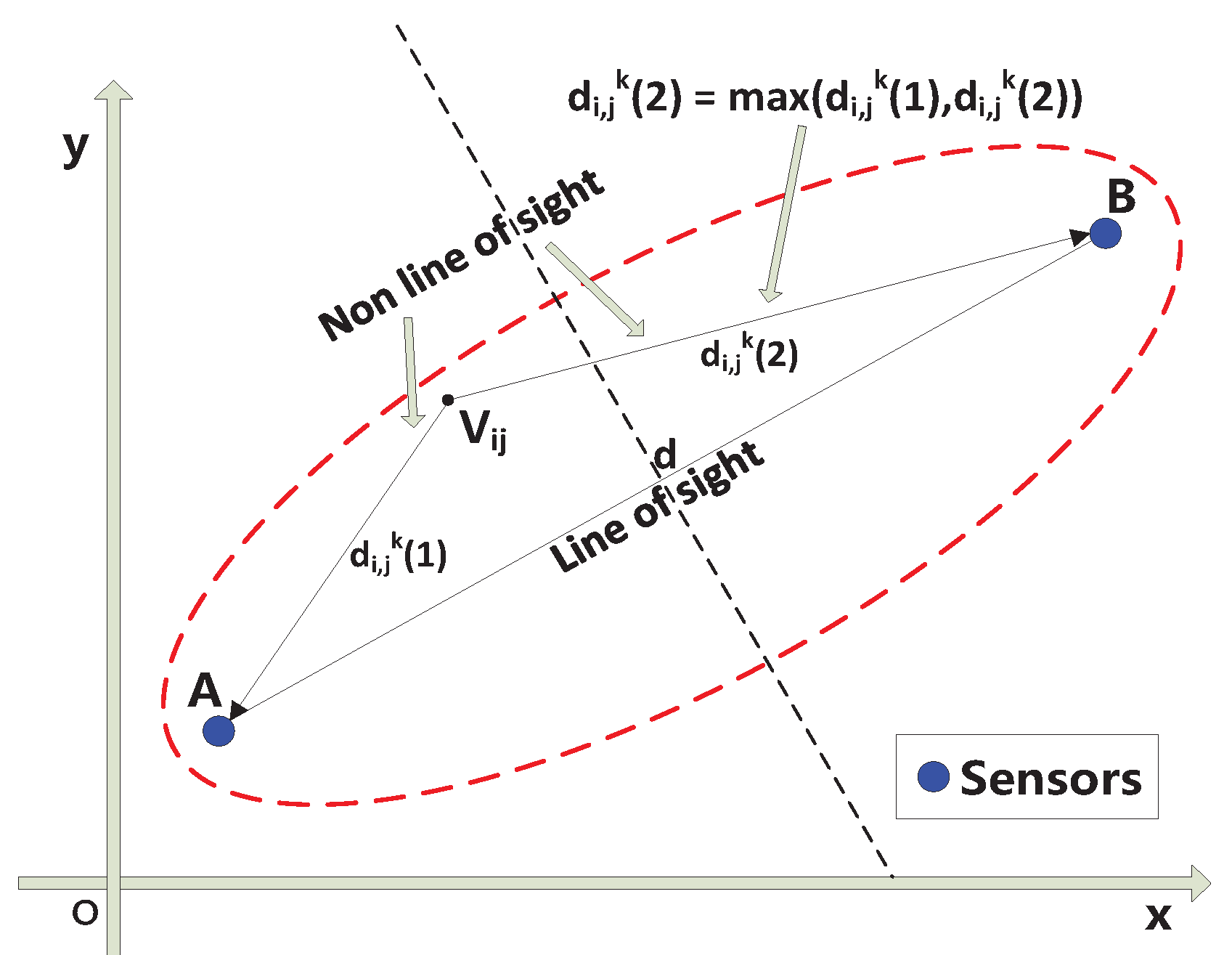
2.1. Elliptical Model
2.2. Image Reconstruction
3. Geometry-Based Elliptical Modeling
4. Sparse-Based Image Reconstruction
- Step 1
- To initialize the counter of iteration t = 1, the set of index Λ = Φ, the residual .
- Step 2
- Pointer to the atom .
- Step 3
- To set the index .
- Step 4
- New estimation of signals .
- Step 5
- New residual signals , .
- Step 6
- If t ≥ p, loop will be terminated. If t < p, Step 2 will restart.
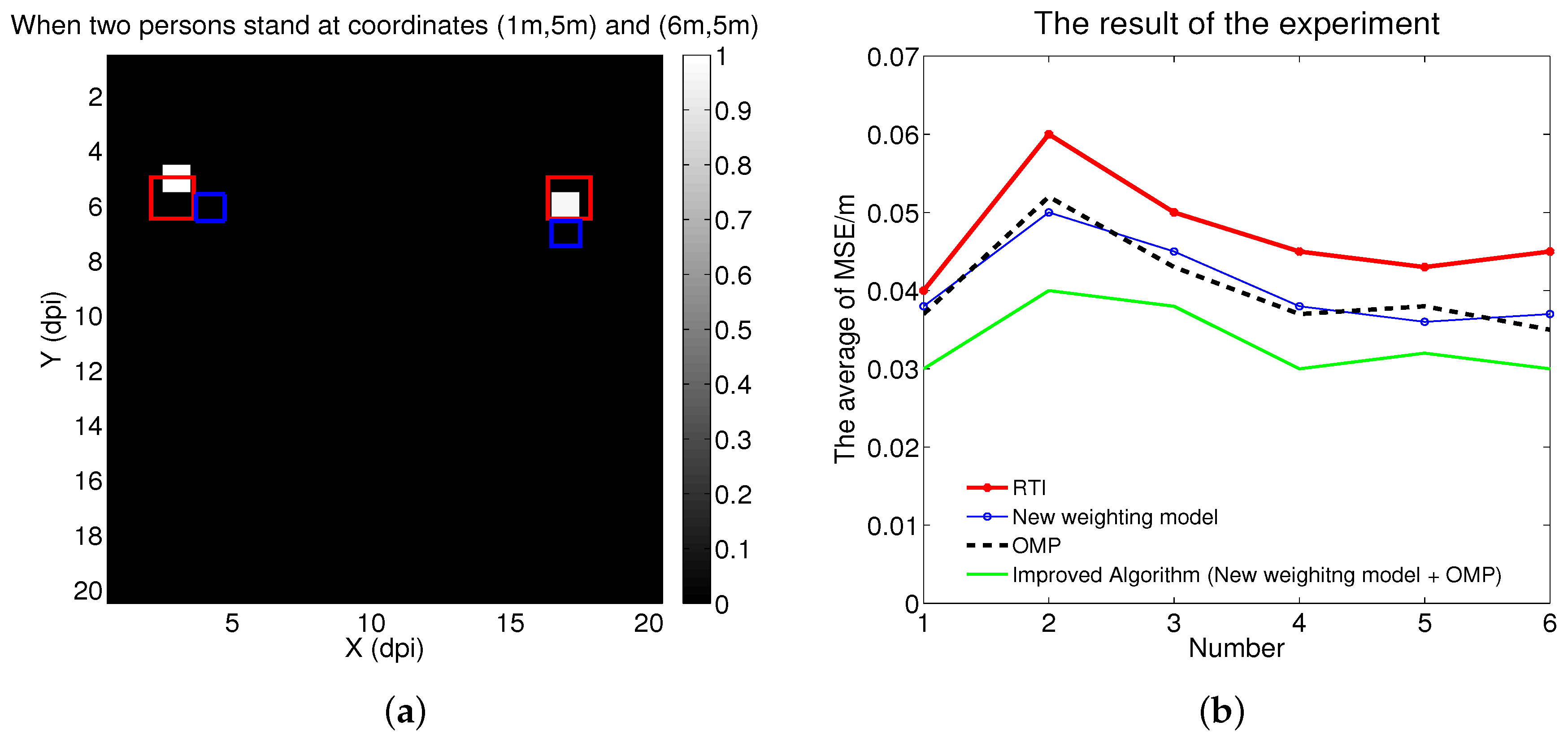
5. Experiment Results
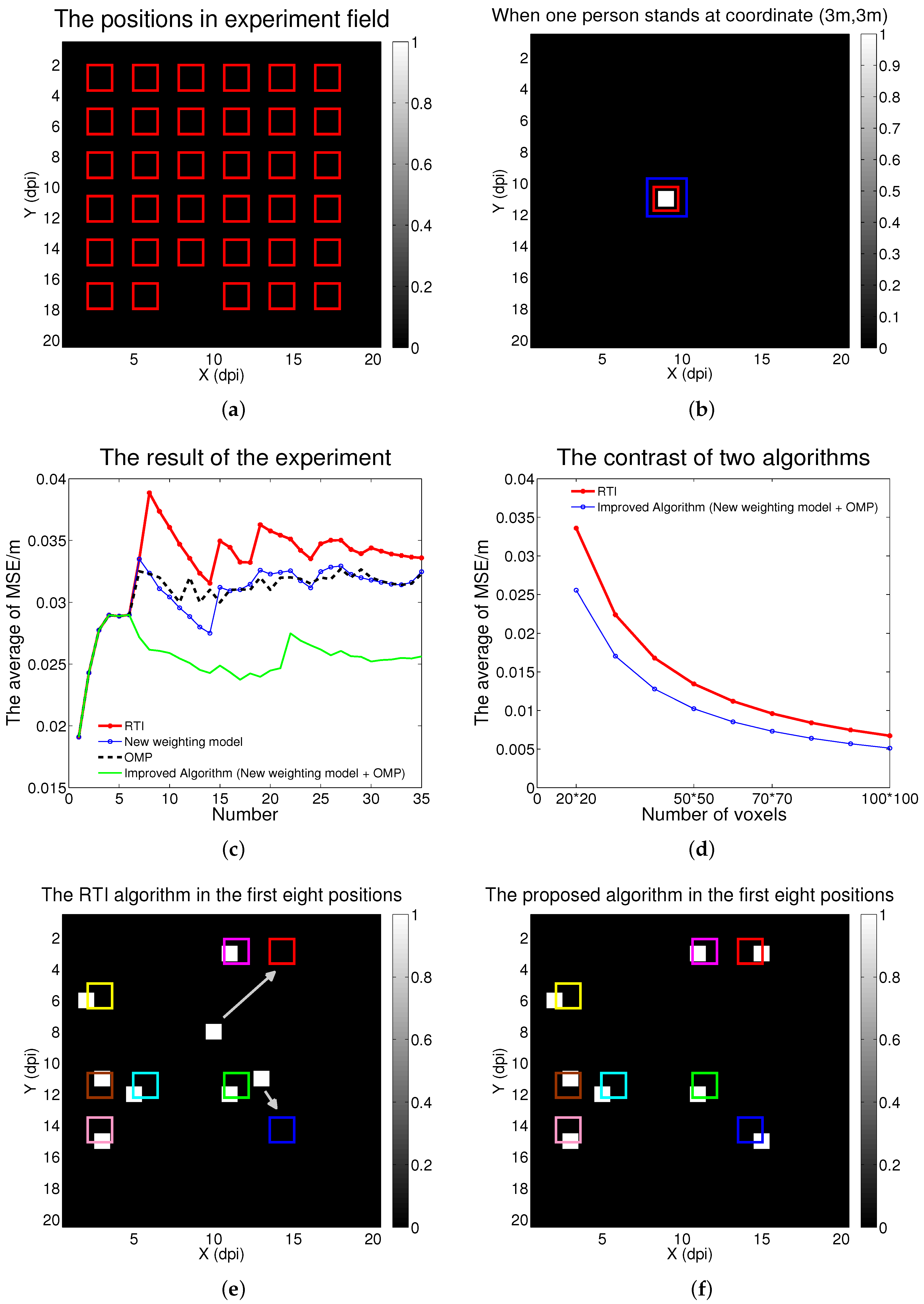
5.1. Description of Experiment
5.2. Experiment Result and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DFL | Device-free localization |
| WSN | Wireless sensor network |
| RTI | Radio tomographic imaging |
| OMP | Orthogonal matching pursuit |
| UWB | Ultra-wideband |
| NB | Narrow-band |
| RSS | Received signal strength |
| FP | Fingerprint |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| PF | Particle filter |
| CS | Compressed sensing |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| NOOLR | Nonlinear optimization approach with outlier link rejection |
| MSE | Mean-square error |
References
- Patwari, N.; Wilson, J. RF Sensor Networks for Device-Free Localization: Measurements, Models, and Algorithms. IEEE Proc. 2010, 98, 1961–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Long, H.; Xu, Q.; Lei, Q. A New RSSI-based Centroid Localization Algorithm by Use of Virtual Reference Tags. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Advanced Communications and Computation, IARIA, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–22 November, 2013.
- Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Bi, D. Collaborative target classification with multiagent system in wireless multimedia sensor networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Graz, Austria, 13–16 May 2012; pp. 2010–2015.
- Pirzada, N.; Nayan, M.Y.; Hassan, F.S.M.F.; Khan, M.A. Device-free localization technique for indoor detection and tracking of human body: A survey. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 129, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, Y.; Wymeersch, H.; Meijerink, A.; Bentum, M.; Scanlon, W. Device-Free Person Detection and Ranging in UWB Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Sign. Process. 2014, 8, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.; Patwari, N. A Fade-Level Skew-Laplace Signal Strength Model for Device-Free Localization with Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 2012, 11, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, K.; Guo, X.; Wang, G. A real-time device-free localization system using correlated RSS measurements. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2013, 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsocchi, P.; Potortì, F.; Nepa, P. Device-free indoor localization for AAL applications. In Wireless Mobile Communication and Healthcare; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 361–368. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Huang, K.; Guo, Y.; Wang, G.; Guo, X. A Diffraction Based Modified Exponential Model for Device-Free Localization with RSS Measurements. In Intelligent Robotics and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 342–353. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, K.; Jiang, N.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, G. An Exponential-Rayleigh Model for RSS-Based Device-Free Localization and Tracking. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 2015, 14, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Song, B. Sequential Geometric Approach for Device-Free Localization with Outlier Link Rejection. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wu, C.; Shangguan, L.; Liu, Y. Omnidirectional Coverage for Device-Free Passive Human Detection. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2014, 25, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Ohtsuki, T. Signal Eigenvector-Based Device-Free Passive Localization Using Array Sensor. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deak, G.; Curran, K.; Condell, J.; Deak, D.; Kiedrowski, P. Support Vector Machine Classification in a Device-Free Passive Localisation (DFPL) Scenario. In Image Processing and Communications Challenges 4; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Cui, K.; Wu, Z.; Yin, L. Entropy-Based TOA Estimation and SVM-Based Ranging Error Mitigation in UWB Ranging Systems. Sensors 2015, 15, 11701–11724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Q.; Cheng, P.; Yu, Y.; Xin, K.; Wang, H. Lightweight Robust Device-Free Localization in Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5681–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Song, B.; Yu, X.; Chen, P. Nonlinear Optimization-Based Device-Free Localization with Outlier Link Rejection. Sensors 2015, 15, 8072–8087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.; Patwari, N. Radio Tomographic Imaging with Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 2010, 9, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltiokallio, O.; Bocca, M.; Patwari, N. A Fade Level-Based Spatial Model for Radio Tomographic Imaging. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 2014, 13, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Q.; Yu, Y.; Cheng, P.; Wu, L.; Wang, H. Robust Device-Free Wireless Localization Based on Differential RSS Measurements. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 5943–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savazzi, S.; Nicoli, M.; Carminati, F.; Riva, M. A Bayesian Approach to Device-Free Localization: Modeling and Experimental Assessment. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Sign. Process. 2014, 8, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Fang, D.; Wu, C.; Yang, Z.; Xing, T. Transferring Compressive-Sensing-Based Device-Free Localization Across Target Diversity. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 2397–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Q.; Wang, H.; Cheng, P.; Xin, K. Device-Free Localization With Multidimensional Wireless Link Information. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwari, N.; Agrawal, P. Effects of Correlated Shadowing: Connectivity, Localization, and RF Tomography. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, St. Louis, Missouri, USA, 22–24 April 2008; pp. 82–93.
- Kuang, R.; Song, H.; Wang, G. Target localization via correlated link inference. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Beijing, China, 7–10 August 2011; pp. 1010–1014.
- Rasool, I.; Kemp, A. Statistical analysis of wireless sensor network Gaussian range estimation errors. Wirel. Sensor Syst. IET 2013, 3, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deak, G.; Curran, K.; Condell, J. Evaluation of smoothing algorithms for a RSSI-based device-free passive localisation. In Image Processing and Communications Challenges 2; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 469–476. [Google Scholar]
- El-Kafrawy, K.; Youssef, M.; El-Keyi, A. Impact of the human motion on the variance of the received signal strength of wireless links. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Personal Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Toronto, Canada, 11–14 September 2011; pp. 1208–1212.
- Donoho, D.L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropp, J.; Gilbert, A. Signal Recovery From Random Measurements Via Orthogonal Matching Pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2007, 53, 4655–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, M.A.; Wakin, M.B. Analysis of Orthogonal Matching Pursuit Using the Restricted Isometry Property. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2010, 56, 4395–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T. Sparse Recovery With Orthogonal Matching Pursuit Under RIP. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2011, 57, 6215–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.T.; Wang, L. Orthogonal Matching Pursuit for Sparse Signal Recovery With Noise. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2011, 57, 4680–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
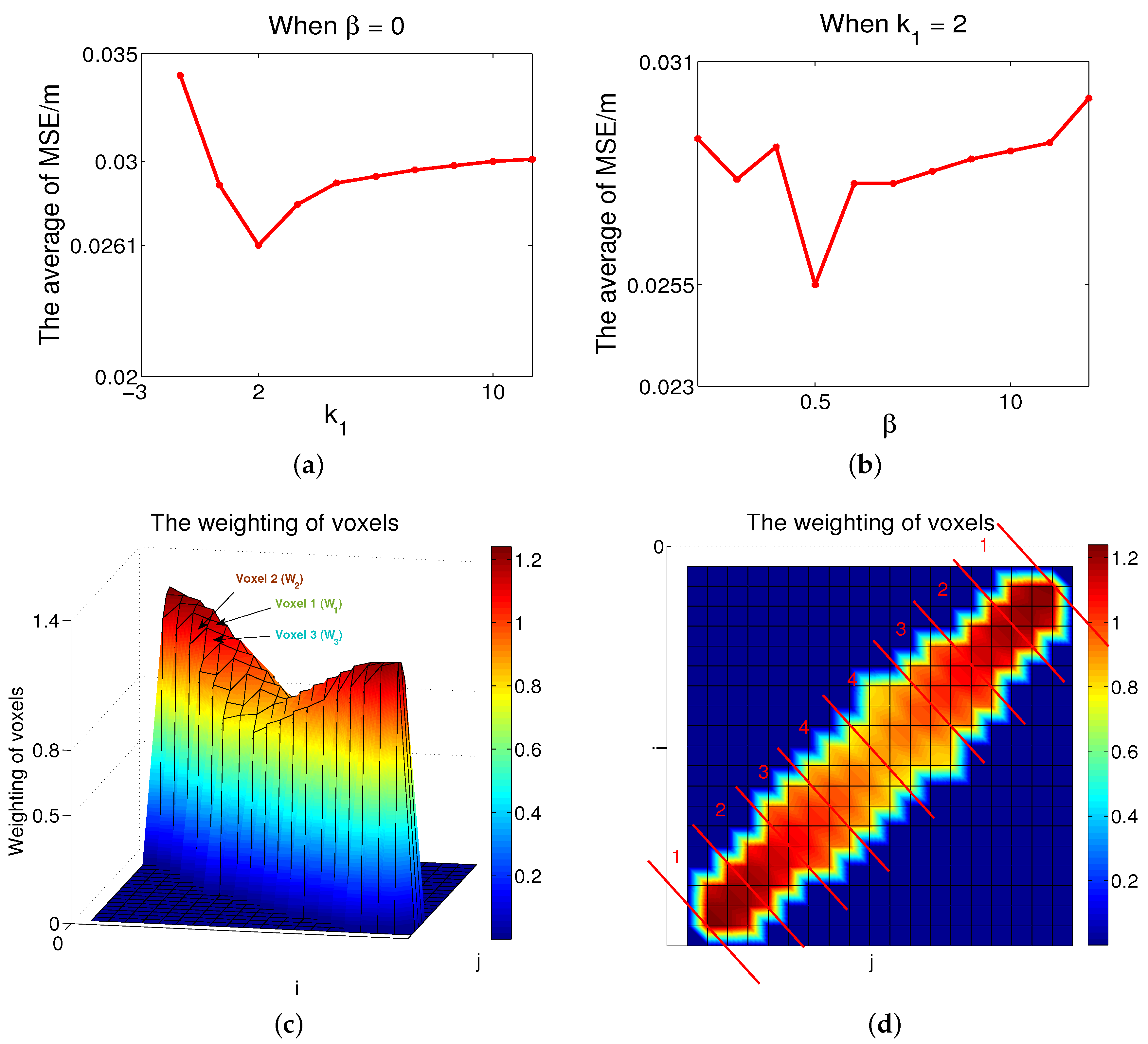
| Areas | The Range of Weightings |
|---|---|
| 1 | [1.12, 1.25] |
| 2 | [0.97, 1.08] |
| 3 | [0.75, 0.93] |
| 4 | [0.53, 0.70] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, Q.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H.; Tang, L. A New Elliptical Model for Device-Free Localization. Sensors 2016, 16, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040577
Lei Q, Zhang H, Sun H, Tang L. A New Elliptical Model for Device-Free Localization. Sensors. 2016; 16(4):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040577
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Qian, Haijian Zhang, Hong Sun, and Linling Tang. 2016. "A New Elliptical Model for Device-Free Localization" Sensors 16, no. 4: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040577
APA StyleLei, Q., Zhang, H., Sun, H., & Tang, L. (2016). A New Elliptical Model for Device-Free Localization. Sensors, 16(4), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040577







