Effectiveness of a Batteryless and Wireless Wearable Sensor System for Identifying Bed and Chair Exits in Healthy Older People
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Technological Intervention
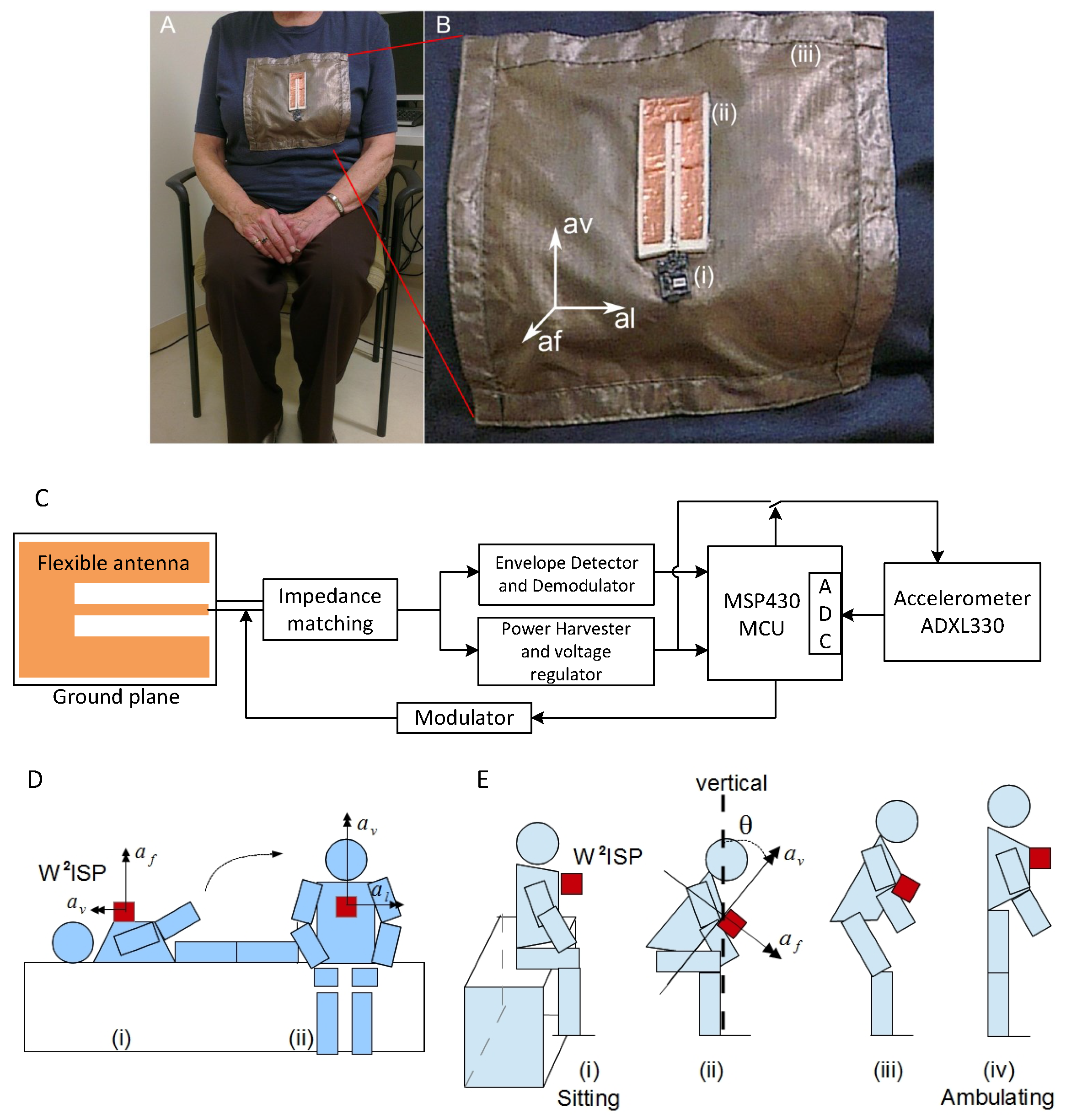
2.1. Sensor Technology
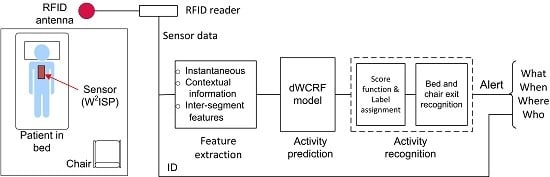
2.2. Bed and Chair Exit Recognition Approach
3. Methods
3.1. Data Collection
3.1.1. Study Participants
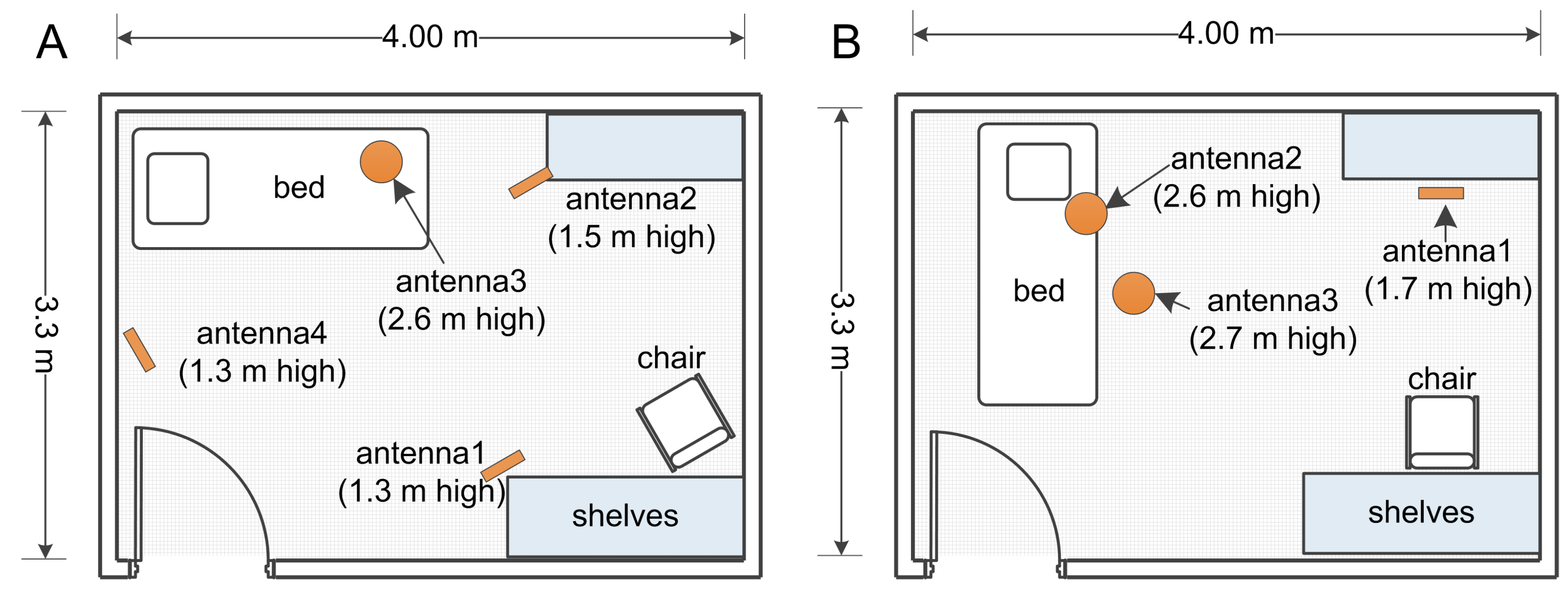
3.1.2. Clinical Setting and Procedure
3.2. Data Processing
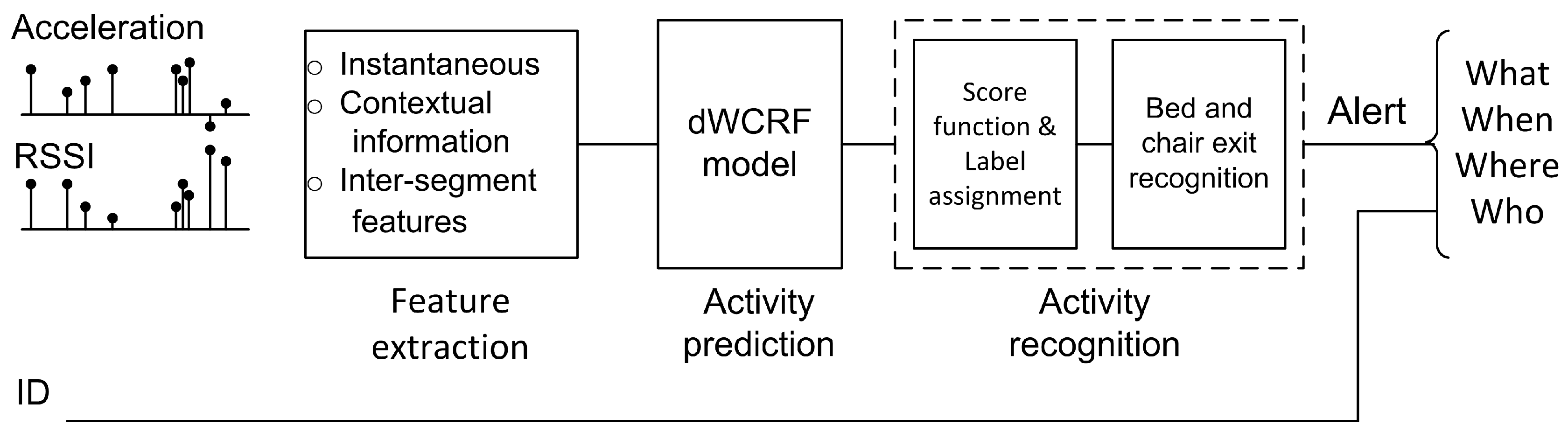
3.2.1. Feature Extraction
Instantaneous features:
Contextual information features:
- Importance of each antenna in collecting sensor observations given by the relative number of readings per antenna in the segment [41];
- Mutual information between bed and chair areas given by: , where is the indicator function and n the number of elements in the segment [41];
- IDs of antennas receiving maximum and minimum RSSI in segments;
- Displacement in the axis (Figure 3B), given by: ;
- Mean and standard deviation of acceleration readings , and ;
- Mean and standard deviation of RSSI for all antennas;
- Pearson correlation between pairs of acceleration axes;
- Standard deviation of variable frequency phase rate (VFPR) [40]; and
- Sum of modulus of constant frequency phase rate (CFPR) [40].
Inter-segment features:
- Difference of median, maximum and minimum of acceleration readings , and from consecutive segments; and
- Difference of median, maximum and minimum of RSSI per antenna from consecutive segments.
3.2.2. Activity Predictor
3.2.3. Bed and Chair Exit Recognition
3.2.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hitcho, E.B.; Krauss, M.J.; Birge, S.; Claiborne Dunagan, W.; Fischer, I.; Johnson, S.; Nast, P.A.; Costantinou, E.; Fraser, V.J. Characteristics and circumstances of falls in a hospital setting. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2004, 19, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassallo, M.; Amersey, R.A.; Sharma, J.C.; Allen, S.C. Falls on integrated medical wards. Gerontology 2000, 46, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, D.; Hopper, A.; Seed, P. Do hospital fall prevention programs work? A systematic review. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2000, 48, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, S.; Rapp, K.; Rissmann, U.; Becker, C.; König, H.H. Cost of falls in old age: A systematic review. Osteoporos. Int. 2010, 21, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, V.; Abbott, R.; Whear, R.; Bethel, A.; Ukoumunne, O.; Thompson-Coon, J.; Stein, K. Multiple component interventions for preventing falls and fall-related injuries among older people: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, I.D.; Gillespie, L.D.; Robertson, M.C.; Murray, G.R.; Hill, K.D.; Cumming, R.G.; Kerse, N. Interventions for preventing falls in older people in care facilities and hospitals. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorr, R.I.; Chandler, A.M.; Mion, L.C.; Waters, T.M.; Liu, M.; Daniels, M.J.; Kessler, L.A.; Miller, S.T. Effects of an intervention to increase bed alarm use to prevent falls in hospitalized patients: A cluster randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahota, O.; Drummond, A.; Kendrick, D.; Grainge, M.J.; Vass, C.; Sach, T.; Gladman, J.; Avis, M. REFINE (REducing Falls in In-patieNt Elderly) using bed and bedside chair pressure sensors linked to radio-pagers in acute hospital care: A randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing 2014, 43, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong Shee, A.; Phillips, B.; Hill, K.; Dodd, K. Feasibility, Acceptability, and Effectiveness of an Electronic Sensor Bed/Chair Alarm in Reducing Falls in Patients With Cognitive Impairment in a Subacute Ward. J. Nurs. Care Qual. 2014, 29, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruyneel, M.; Libert, W.; Ninane, V. Detection of bed-exit events using a new wireless bed monitoring assistance. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2011, 80, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilbe, J.; Schulc, E.; Linder, B.; Them, C. Development and alarm threshold evaluation of a side rail integrated sensor technology for the prevention of falls. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2010, 79, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healey, F.; Monro, A.; Cockram, A.; Adams, V.; Heseltine, D. Using targeted risk factor reduction to prevent falls in older in-patients: A randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing 2004, 33, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demiris, G.; Hensel, B.K.; Skubic, M.; Rantz, M. Senior residents’ perceived need of and preferences for “smart home” sensor technologies. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care 2008, 24, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantelopoulos, A.; Bourbakis, N.G. A survey on wearable sensor-based systems for health monitoring and prognosis. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 2010, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, O.D.; Labrador, M.A. A survey on human activity recognition using wearable sensors. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 1192–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, B.; Aminian, K.; Paraschiv-Ionescu, A.; Loew, F.; Bula, C.J.; Robert, P. Ambulatory system for human motion analysis using a kinematic sensor: Monitoring of daily physical activity in the elderly. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 50, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfrey, A.; Bourke, A.K.; Ólaighin, G.M.; van de Ven, P.; Nelson, J. Activity classification using a single chest mounted tri-axial accelerometer. Med. Eng. Phys. 2011, 33, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Martín, D.; Pérez-López, C.; Samà, A.; Cabestany, J.; Català, A. A wearable inertial measurement unit for long-term monitoring in the dependency care area. Sensors 2013, 13, 14079–14104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodie, M.A.; Lord, S.R.; Coppens, M.J.; Annegarn, J.; Delbaere, K. Eight weeks remote monitoring using a freely worn device reveals unstable gait patterns in older fallers. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 2588–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, M.R.; Redmond, S.J.; Scalzi, M.E.; Lord, S.R.; Celler, B.G.; Lovell, N.H. Longitudinal falls-risk estimation using triaxial accelerometry. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwenk, M.; Hauer, K.; Zieschang, T.; Englert, S.; Mohler, J.; Najafi, B. Sensor-derived physical activity parameters can predict future falls in people with dementia. Gerontology 2014, 60, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Gu, T.; Tao, X.; Lu, J. A hierarchical approach to real-time activity recognition in body sensor networks. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2012, 8, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahoz, Y.S.; Labrador, M.A. Survey on fall detection and fall prevention using wearable and external sensors. Sensors 2014, 14, 19806–19842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, K.H.; Hetzer, K.; zu Schwabedissen, H.M.; Wiese, B.; Marschollek, M. Development and pilot study of a bed-exit alarm based on a body-worn accelerometer. Z. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2013, 46, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, J.H.M.; McGregor, A.H. Body-worn sensor design: What do patients and clinicians want? Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 39, 2299–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.C.; Hsu, Y.L. A review of accelerometry-based wearable motion detectors for physical activity monitoring. Sensors 2010, 10, 7772–7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranasinghe, D.C.; Shinmoto Torres, R.L.; Hill, K.; Visvanathan, R. Low cost and batteryless sensor-enabled radio frequency identification tag based approaches to identify patient bed entry and exit posture transitions. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinmoto Torres, R.L.; Ranasinghe, D.C.; Shi, Q.; Sample, A.P. Sensor enabled wearable RFID technology for mitigating the risk of falls near beds. In Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference on RFID, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 April–2 May 2013; pp. 191–198.
- Sample, A.P.; Yeager, D.J.; Powledge, P.S.; Smith, J.R. Design of a passively-powered, programmable sensing platform for UHF RFID systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on RFID, Grapevine, TX, USA, 26–28 March 2007; pp. 149–156.
- Kaufmann, T.; Ranasinghe, D.C.; Zhou, M.; Fumeaux, C. Wearable quarter-wave microstrip antenna for passive UHF RFID applications. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvanathan, R.; Ranasinghe, D.C.; Shinmoto Torres, R.L.; Hill, K. Framework for preventing falls in acute hospitals using passive sensor enabled radio frequency identification technology. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 5858–5862.
- Alemdar, H.; Ersoy, C. Wireless sensor networks for healthcare: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2688–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkenzeller, K. RFID Handbook: Fundamentals and Applications in Contactless Smart Cards, Radio Frequency Identification and Near-Field Communication; Wiley: West Sussex, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Swedberg, C. Group Health Reinvents Patient Care with RTLS. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6O7ywg1ps (accessed on 17 March 2014).
- Fry, E.A.; Lenert, L.A. MASCAL: RFID tracking of patients, staff and equipment to enhance hospital response to mass casualty events. In AMIA Annual Symposium Proceedings; American Medical Informatics Association: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2005; Volume 2005, pp. 261–265. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Wickramasinghe, A.; Ranasinghe, D.C. Investigating Sensor Data Retrieval Schemes for Multi-Sensor Passive RFID Tags. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on RFID, San Diego, CA, USA, 15–17 April 2015; pp. 158–165.
- Bao, L.; Intille, S.S. Activity Recognition from User-Annotated Acceleration Data. In Pervasive Computing; Ferscha, A., Mattern, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004; Volume 3001, pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nikitin, P.V.; Martinez, R.; Ramamurthy, S.; Leland, H.; Spiess, G.; Rao, K.V.S. Phase based spatial identification of UHF RFID tags. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on RFID, Orlando, FL, USA, 14–16 April 2010; pp. 102–109.
- Wickramasinghe, A.; Ranasinghe, D.C. Recognising activities in real-time using body worn passive sensors with sparse data streams: To interpolate or not to interpolate? In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking and Services (MOBIQUITOUS), Portugal, Coimbra, 22–24 July 2015.
- Li, H.; Ye, C.; Sample, A.P. IDSense: A human object interaction detection system based on passive UHF RFID. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Seoul, Korea, 18–23 April 2015; pp. 2555–2564.
- Shinmoto Torres, R.L.; Ranasinghe, D.C.; Shi, Q. Evaluation of wearable sensor tag data segmentation approaches for real-time activity classification in elderly. In Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking, and Services; Stojmenovic, I., Cheng, Z., Guo, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 131, pp. 384–395. [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty, J.D.; McCallum, A.; Pereira, F.C.N. Conditional random fields: Probabilistic models for segmenting and labeling sequence data. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Machine Learning; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Shinmoto Torres, R.L.; Ranasinghe, D.C.; Shi, Q.; van den Hengel, A. Learning from Imbalanced Multiclass Sequential Data Streams Using Dynamically Weighted Conditional Random Fields. Available online: http://xxx.lanl.gov/abs/arXiv:1603.03627 (accessed on 11 March 2016).
- Schmidt, M.; Swersky, K. crfChain, 2008. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6O9mlPgo4 (accessed on 18 March 2014).
- Yedidia, J.S.; Freeman, W.T.; Weiss, Y. Understanding belief propagation and its generalizations. In Exploring Artificial Intelligence in the New Millennium; Lakemeyer, G., Nebel, B., Eds.; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2003; pp. 239–236. [Google Scholar]
- Capezuti, E.; Brush, B.L.; Lane, S.; Rabinowitz, H.U.; Secic, M. Bed-exit alarm effectiveness. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2009, 49, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO/IEC 18000-6:2013—Information technology—Radio Frequency Identification for Item Management—Part 6: Parameters for Air Interface Communications at 860 MHz to 960 MHz General, 2013. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6ghl0sdLv (accessed on 31 January 2015).
- Dong, Y.; Wickramasinghe, A.; Xue, H.; Al-Sarawi, S.F.; Ranasinghe, D.C. A novel hybrid powered RFID sensor tag. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on RFID, San Diego, CA, USA, 15–17 April 2015; pp. 55–62.
- Chen, S.J.; Fumeaux, C.; Ranasinghe, D.C.; Kaufmann, T. Paired snap-on buttons connections for balanced antennas in wearable systems. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1498–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellomäki, T.; Virkki, J.; Merilampi, S.; Ukkonen, L. Towards Washable Wearable Antennas: A Comparison of Coating Materials for Screen-Printed Textile-Based UHF RFID Tags. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2012, 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpello, M.L.; Kazani, I.; Hertleer, C.; Rogier, H.; Vande Ginste, D. Stability and efficiency of screen-printed wearable and washable antennas. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 838–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

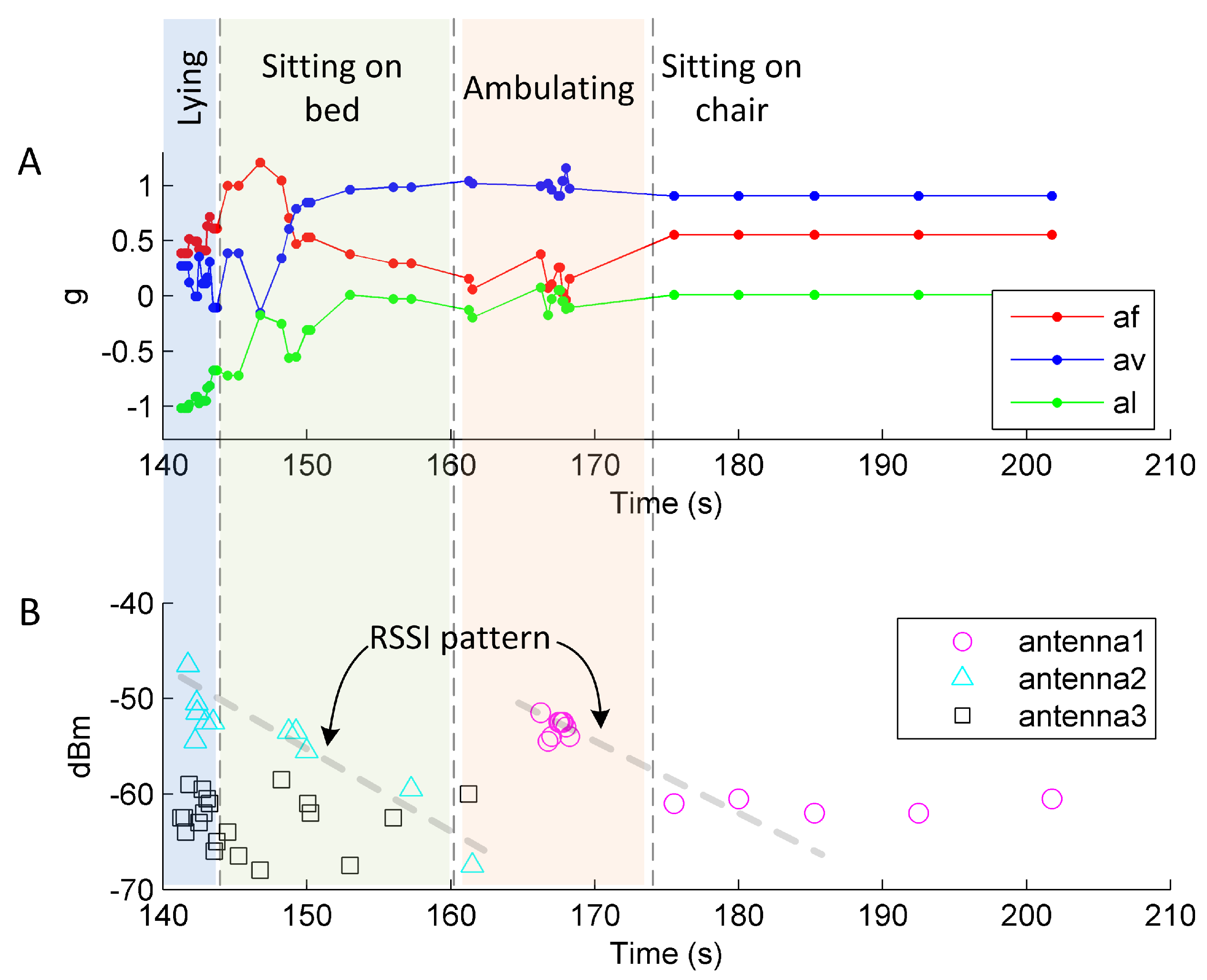
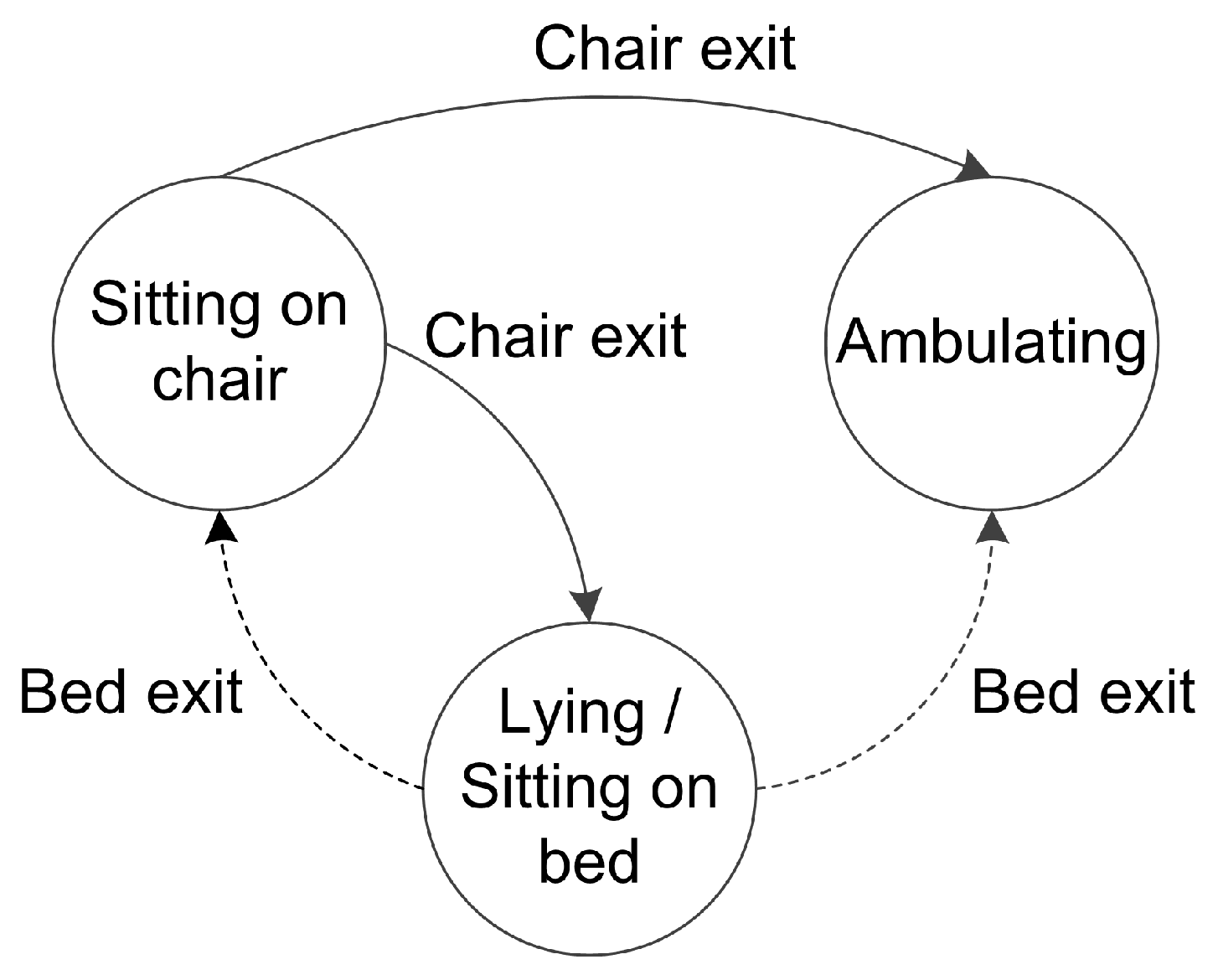
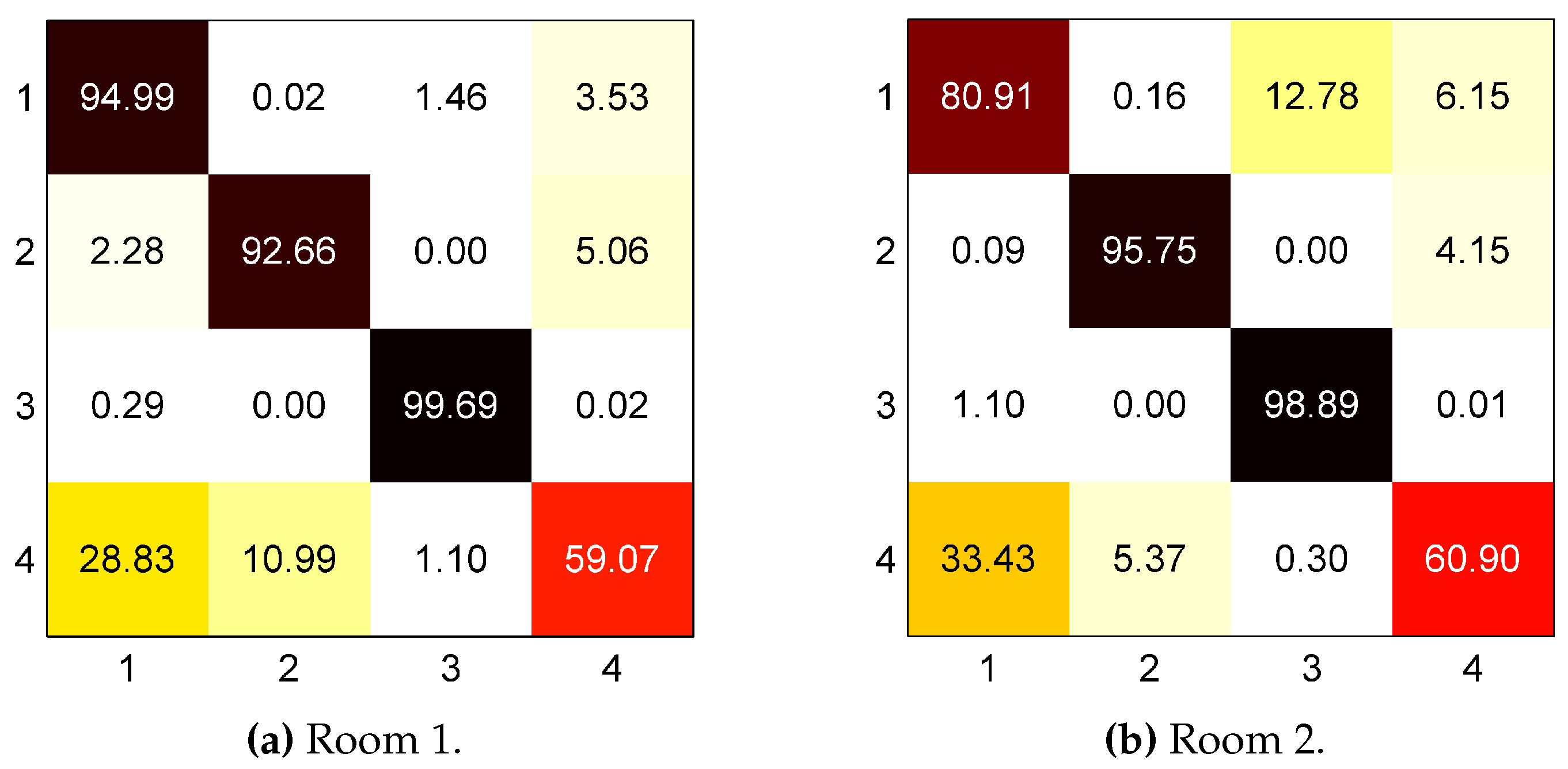
| Without Score Function | Using Score Function | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Room 1 (%) | Room 2 (%) | Room 1 (%) | Room 2 (%) | p-value (p) | ||
| Bed Exit | Recall | <0.001 | ||||
| Precision | ||||||
| F-score | <0.001 | |||||
| Chair Exit | Recall | <0.001 | ||||
| Precision | 0.68 | |||||
| F-score | 0.07 | |||||
| Room 1 (%) | Room 2 (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bed Exit | Recall | 72.64 ± 8.9 | 91.91 ± 9.7 |
| Precision | 43.22 ± 8.7 | 66.93 ± 13.1 | |
| F-score | 53.96 ± 5.84 | 76.40 ± 8.8 | |
| Chair Exit | Recall | 96.98 ± 4.9 | 61.75 ± 22.5 |
| Precision | 71.13 ± 21.8 | 63.99 ± 30.1 | |
| F-score | 80.51 ± 16.14 | 60.55 ± 24.3 |
| Room 1 | Room 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bed Exit | Mean±STD | 2.63 ± 4.08 s | 3.22 ± 6.05 s |
| Median | 1.20 s | 1.25 s | |
| Chair Exit | Mean±STD | 1.93 ± 2.55 s | 2.15 ± 1.56 s |
| Median | 1.13 s | 0.00 s |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shinmoto Torres, R.L.; Visvanathan, R.; Hoskins, S.; Van den Hengel, A.; Ranasinghe, D.C. Effectiveness of a Batteryless and Wireless Wearable Sensor System for Identifying Bed and Chair Exits in Healthy Older People. Sensors 2016, 16, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040546
Shinmoto Torres RL, Visvanathan R, Hoskins S, Van den Hengel A, Ranasinghe DC. Effectiveness of a Batteryless and Wireless Wearable Sensor System for Identifying Bed and Chair Exits in Healthy Older People. Sensors. 2016; 16(4):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040546
Chicago/Turabian StyleShinmoto Torres, Roberto Luis, Renuka Visvanathan, Stephen Hoskins, Anton Van den Hengel, and Damith C. Ranasinghe. 2016. "Effectiveness of a Batteryless and Wireless Wearable Sensor System for Identifying Bed and Chair Exits in Healthy Older People" Sensors 16, no. 4: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040546
APA StyleShinmoto Torres, R. L., Visvanathan, R., Hoskins, S., Van den Hengel, A., & Ranasinghe, D. C. (2016). Effectiveness of a Batteryless and Wireless Wearable Sensor System for Identifying Bed and Chair Exits in Healthy Older People. Sensors, 16(4), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040546