Particle Filter with Novel Nonlinear Error Model for Miniature Gyroscope-Based Measurement While Drilling Navigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. NNEM of the MGWD System
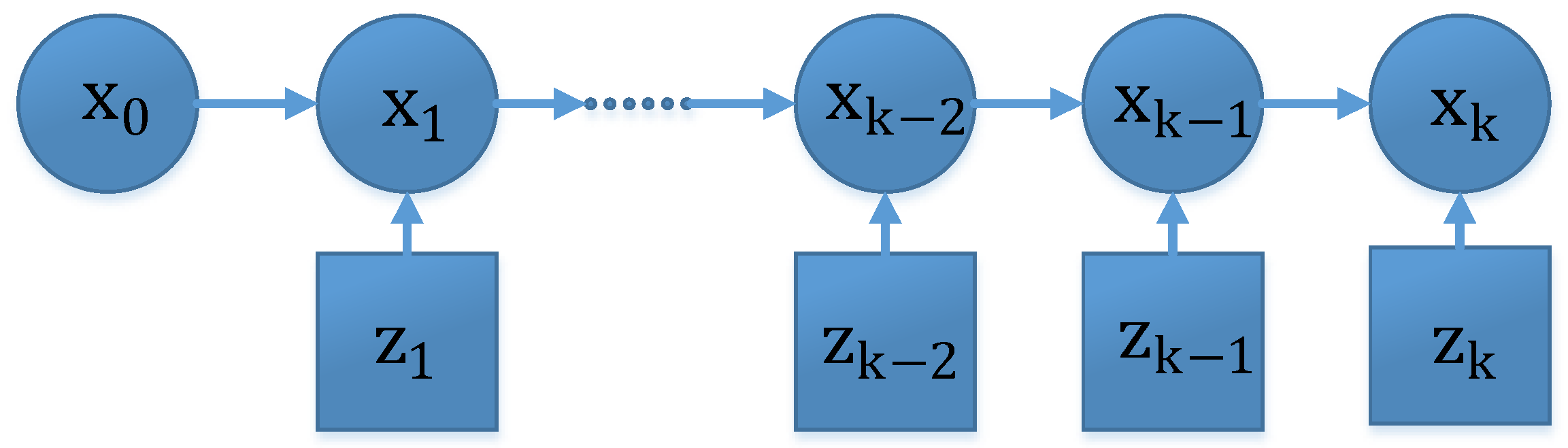
3. Recursive Bayesian Estimation
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
- State estimation: once the posterior is obtained, the estimation of state and the covariance matrix of estimation error () are given by [45]:where is the estimation error and is the expectation of the random variables.
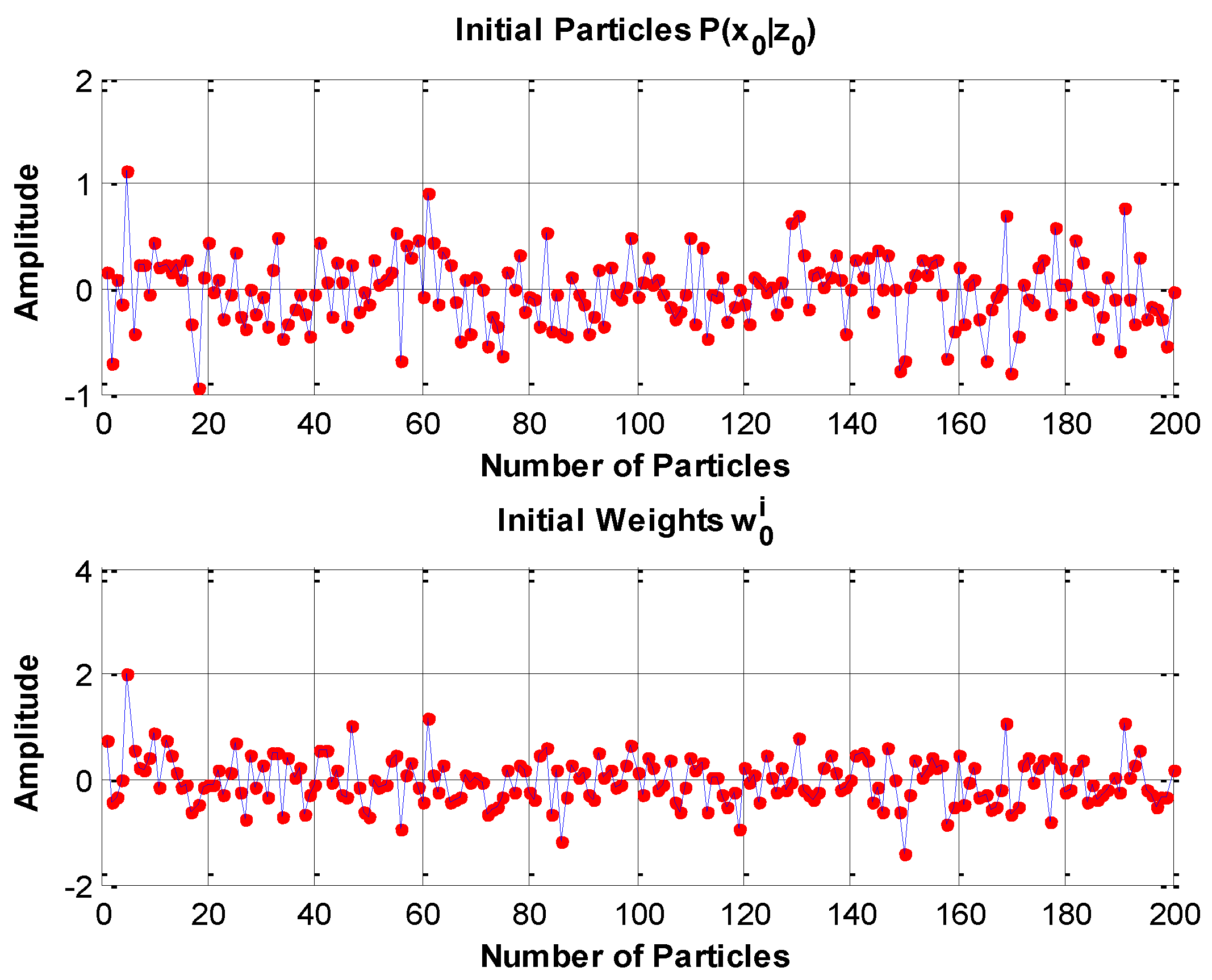
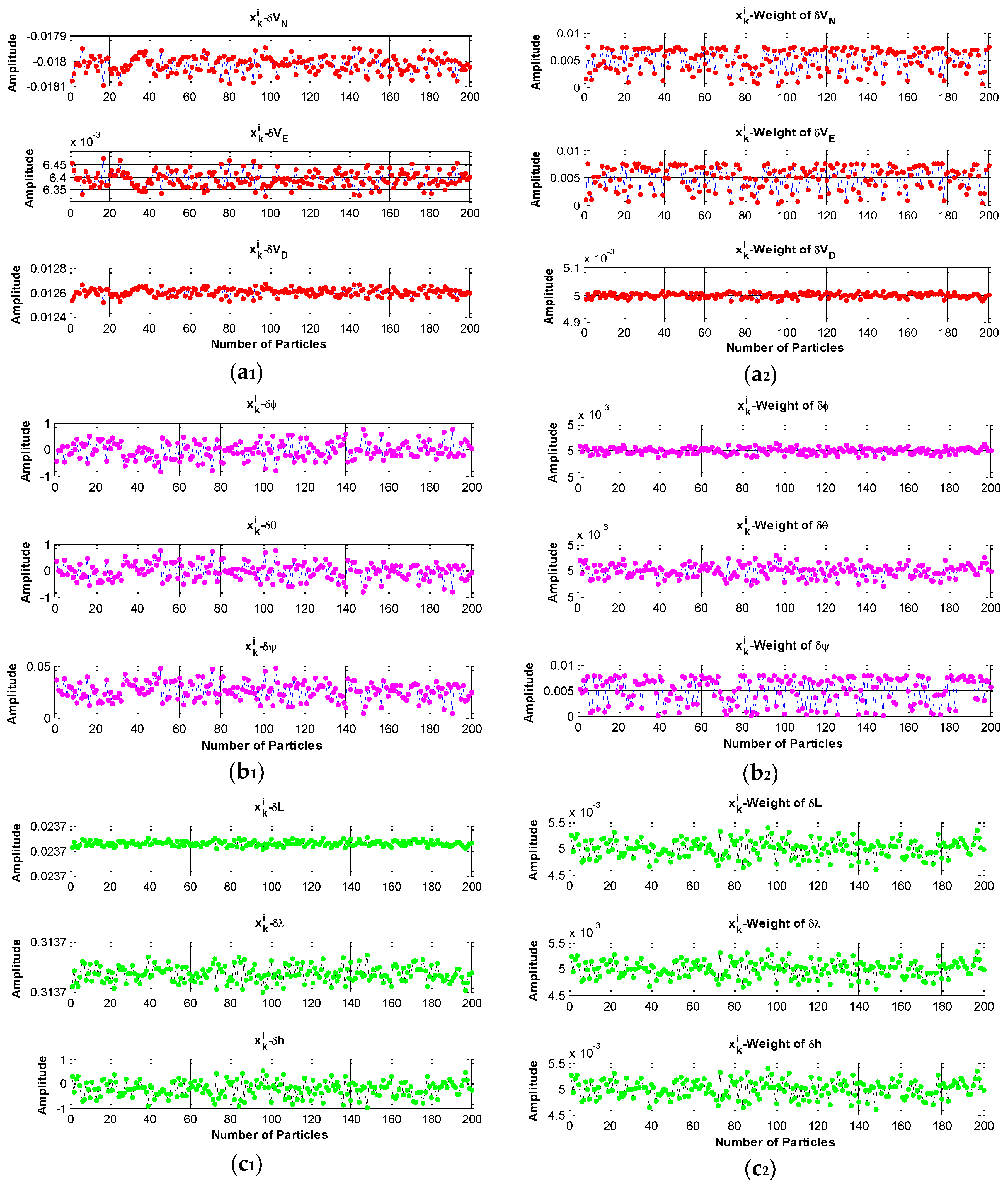
4. PF Algorithm
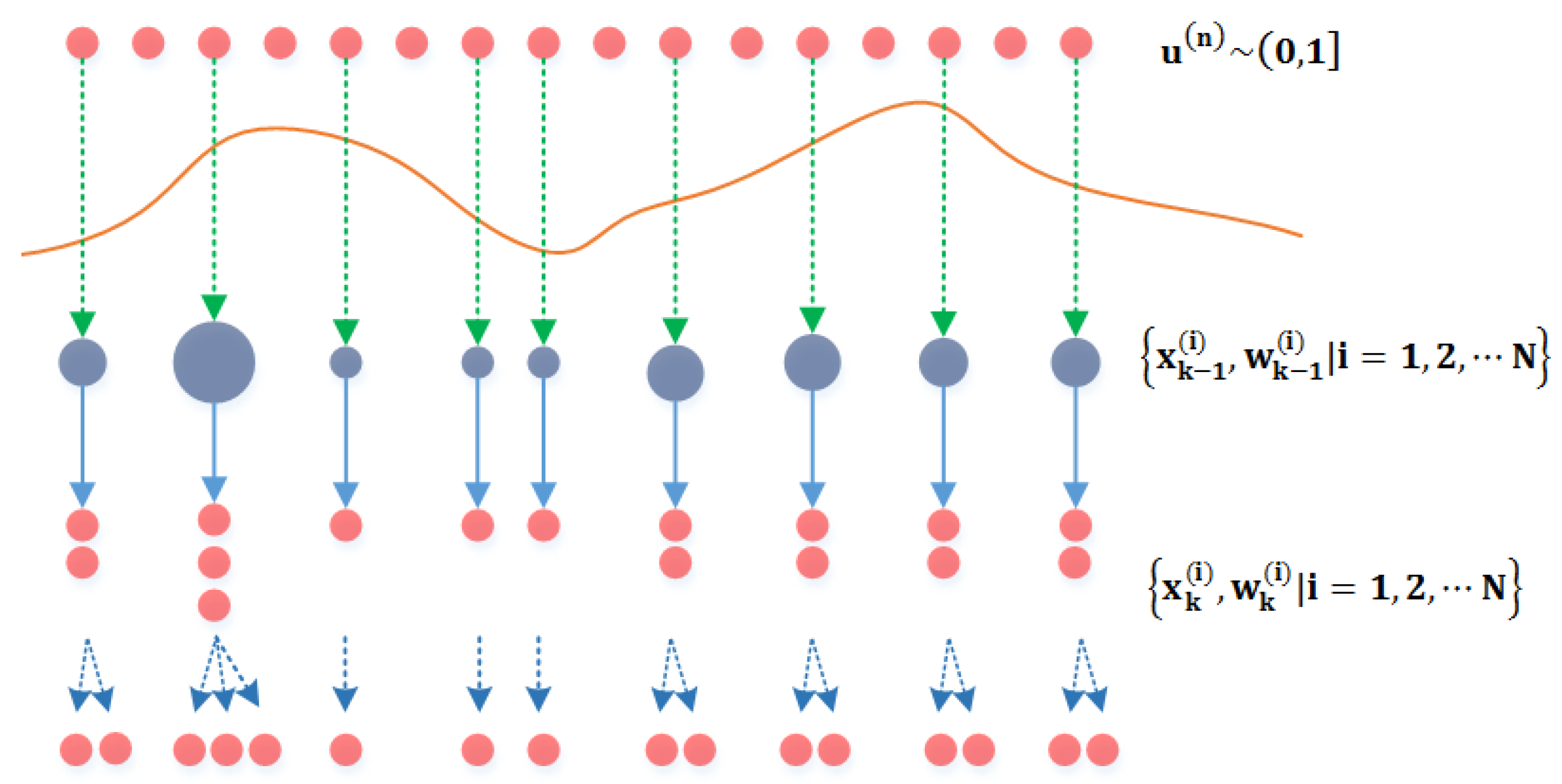
4.1. SIS Algorithm
4.2. Resampling Algorithm
4.3. Roughing Strategy
5. Results and Discussion
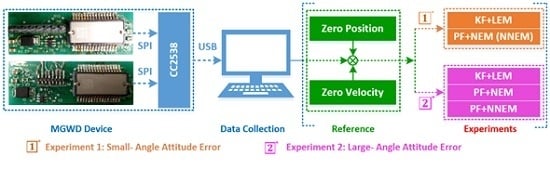
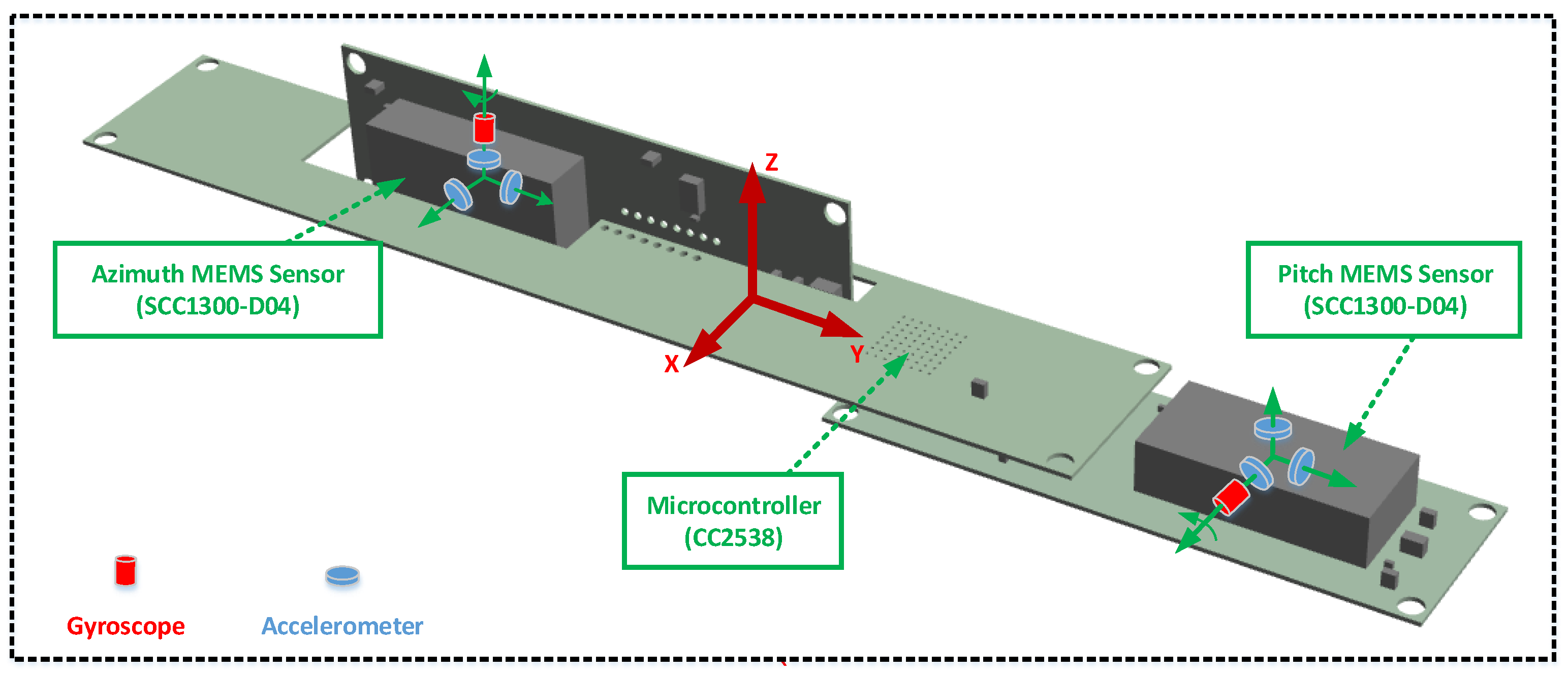
5.1. MGWD Device for Validation of Experimental Results
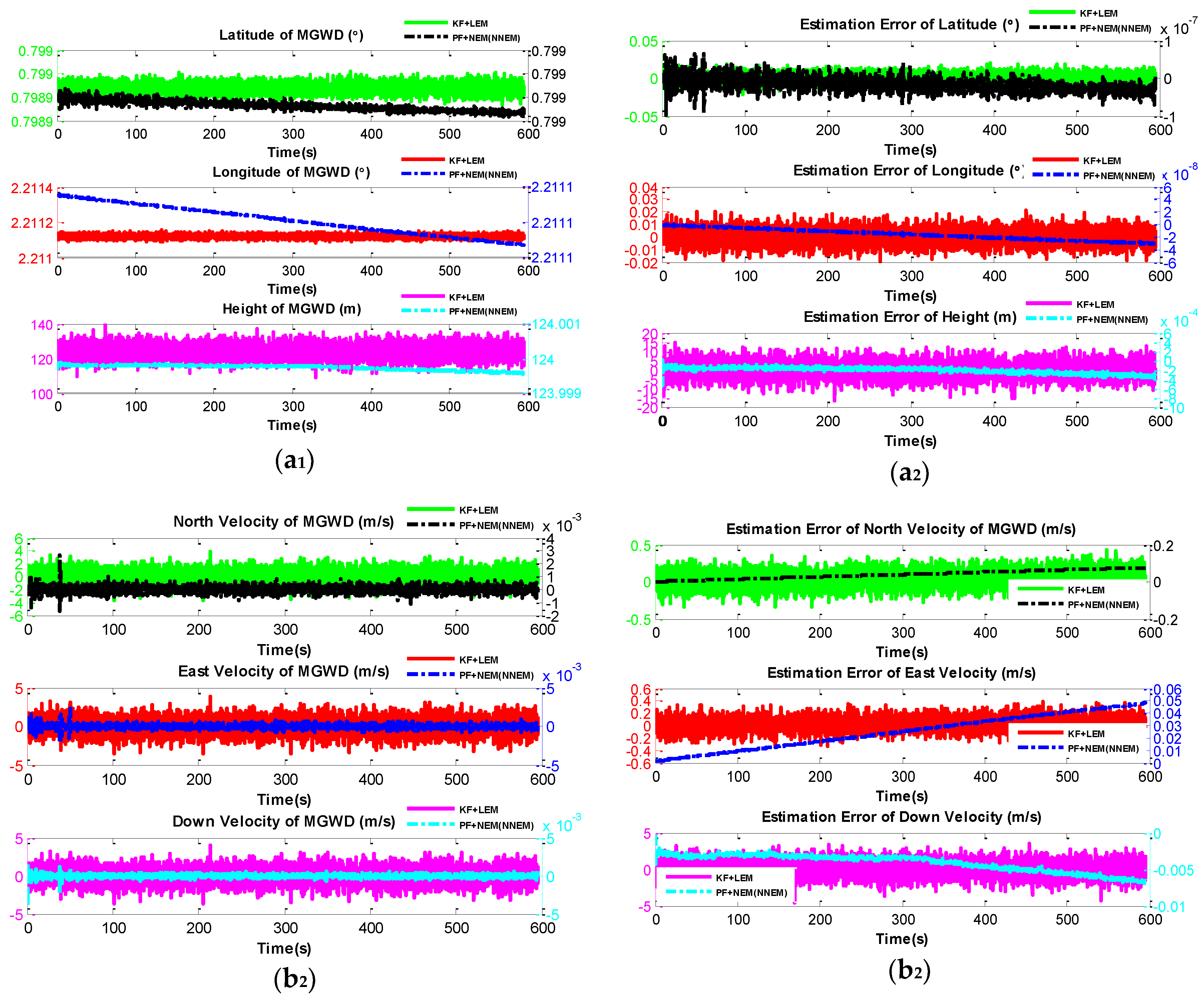
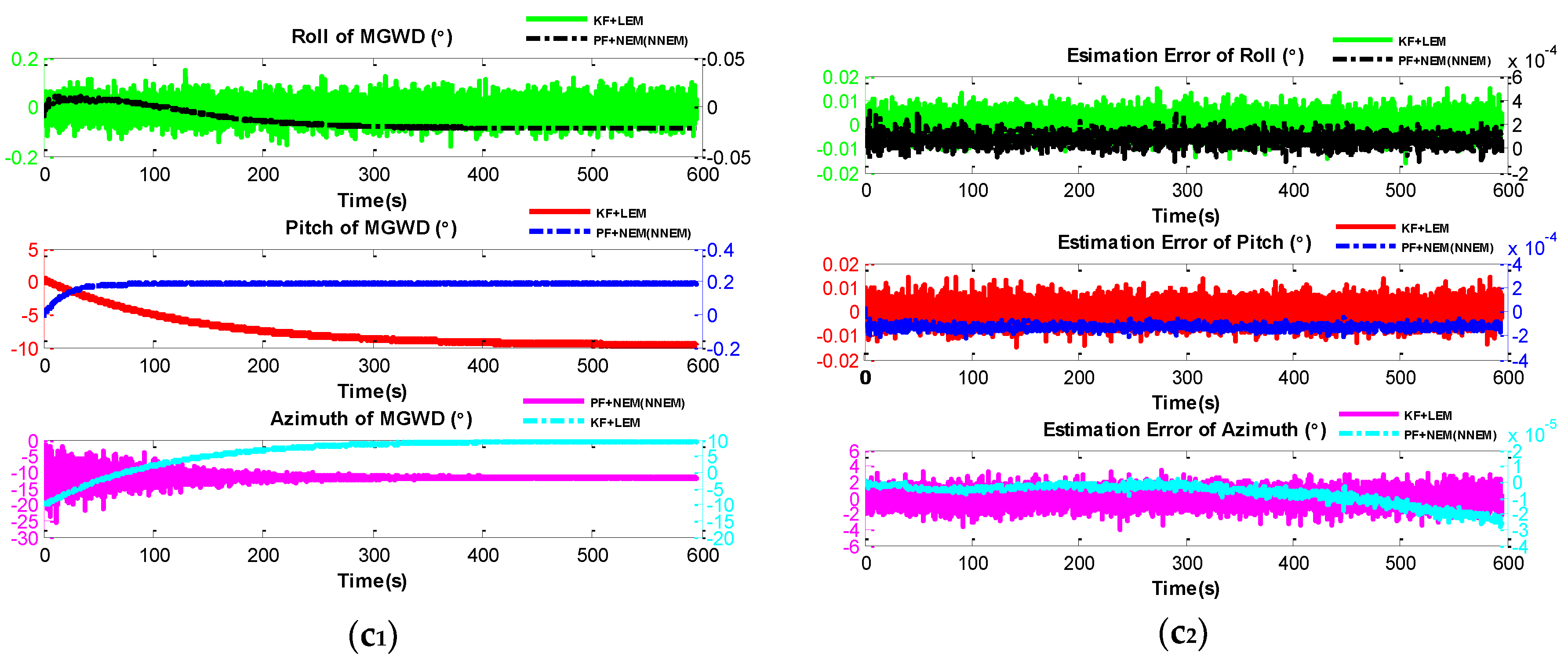
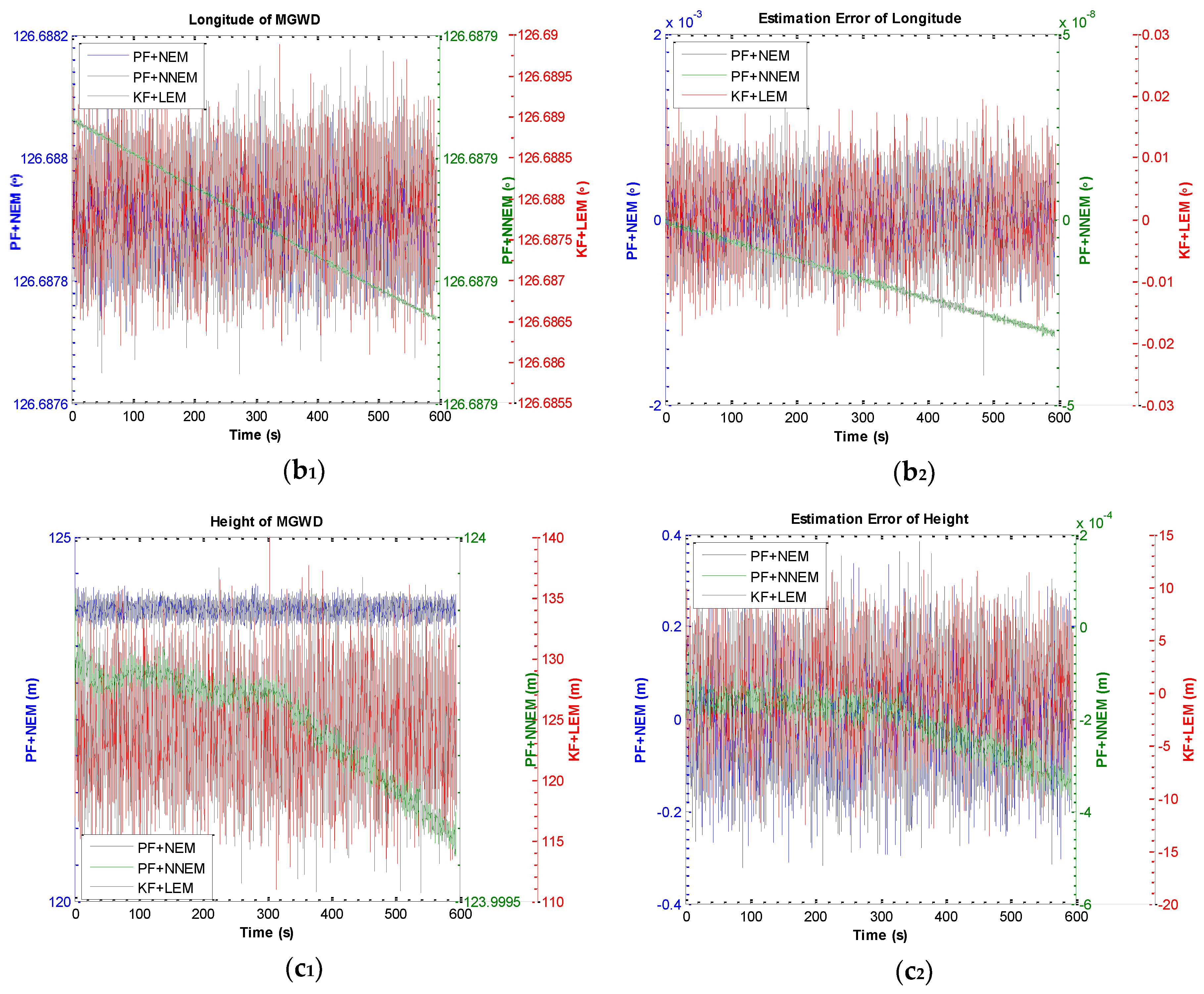
5.2. Experiment 1: Comparison of KF with LEM and PF with NEM under Small-Angle Attitude Error Condition
- Initial covariance matrix of system noise: R = diag([0.1,0.1, 0.1,0.1, 0.1, 0.1]);
- Initial covariance matrix of observation noise: Q = diag([0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1]);
- Initial position: latitude 126.6879; longitude 45.7776; height 124 m;
- Initial velocity: 0.
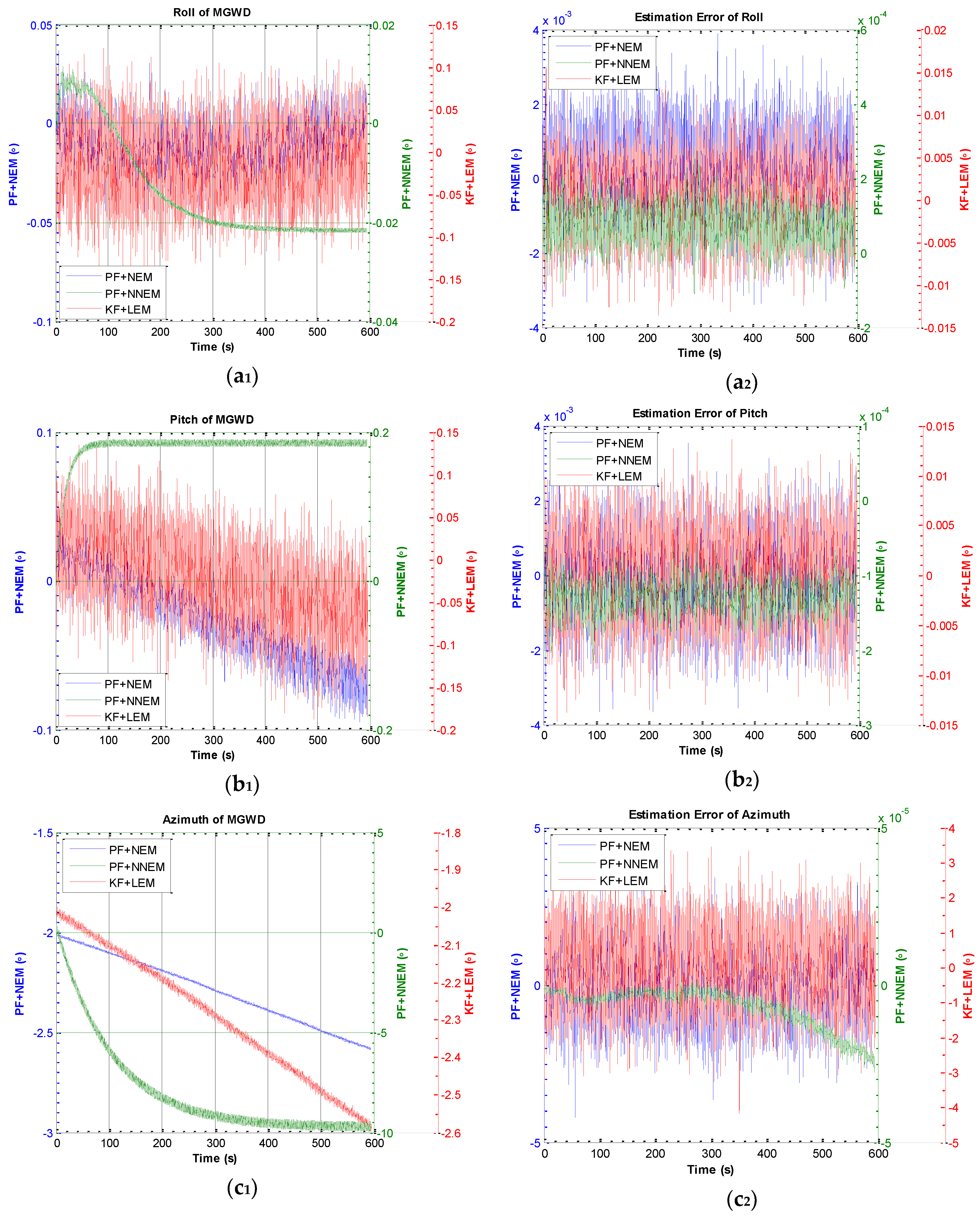
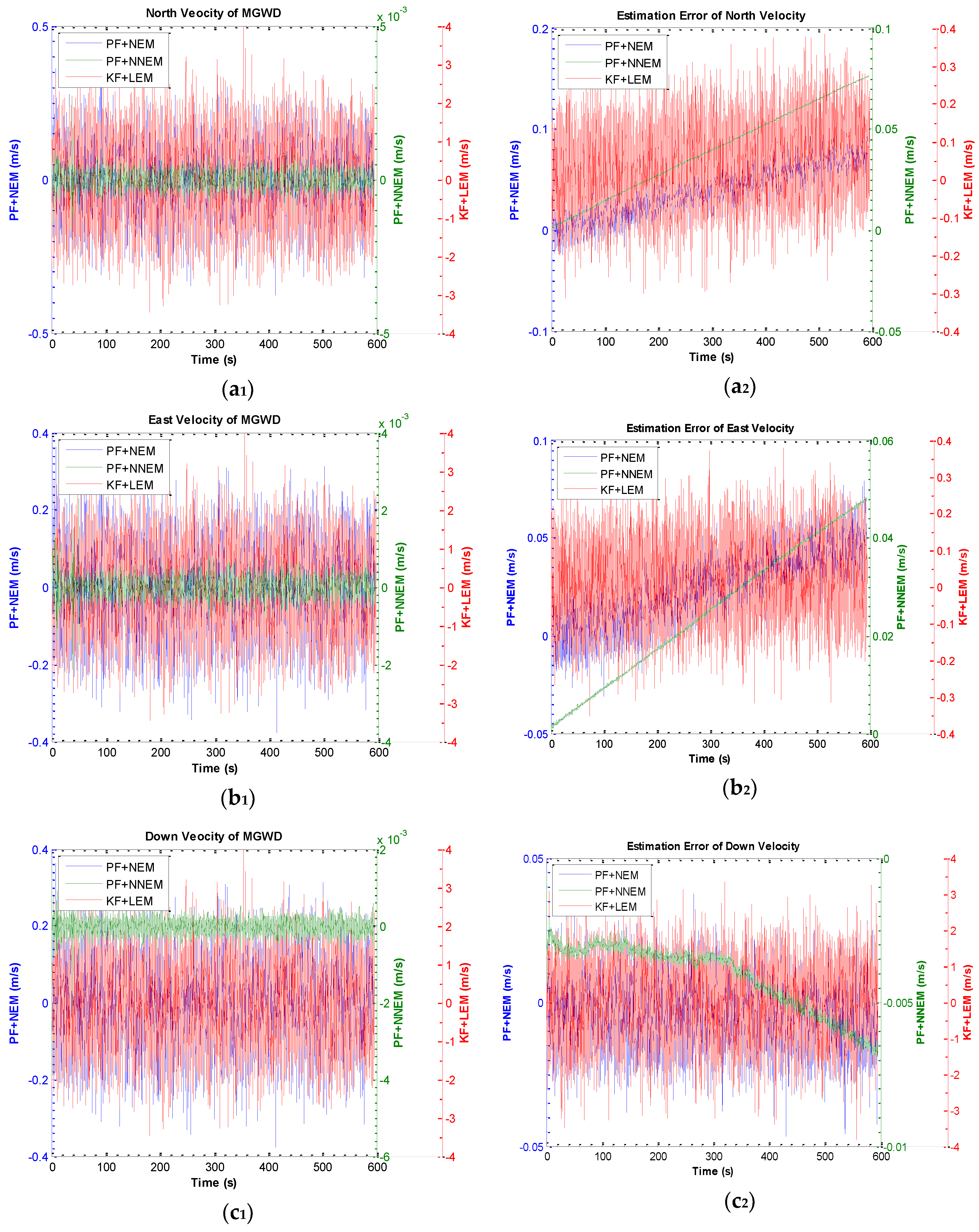
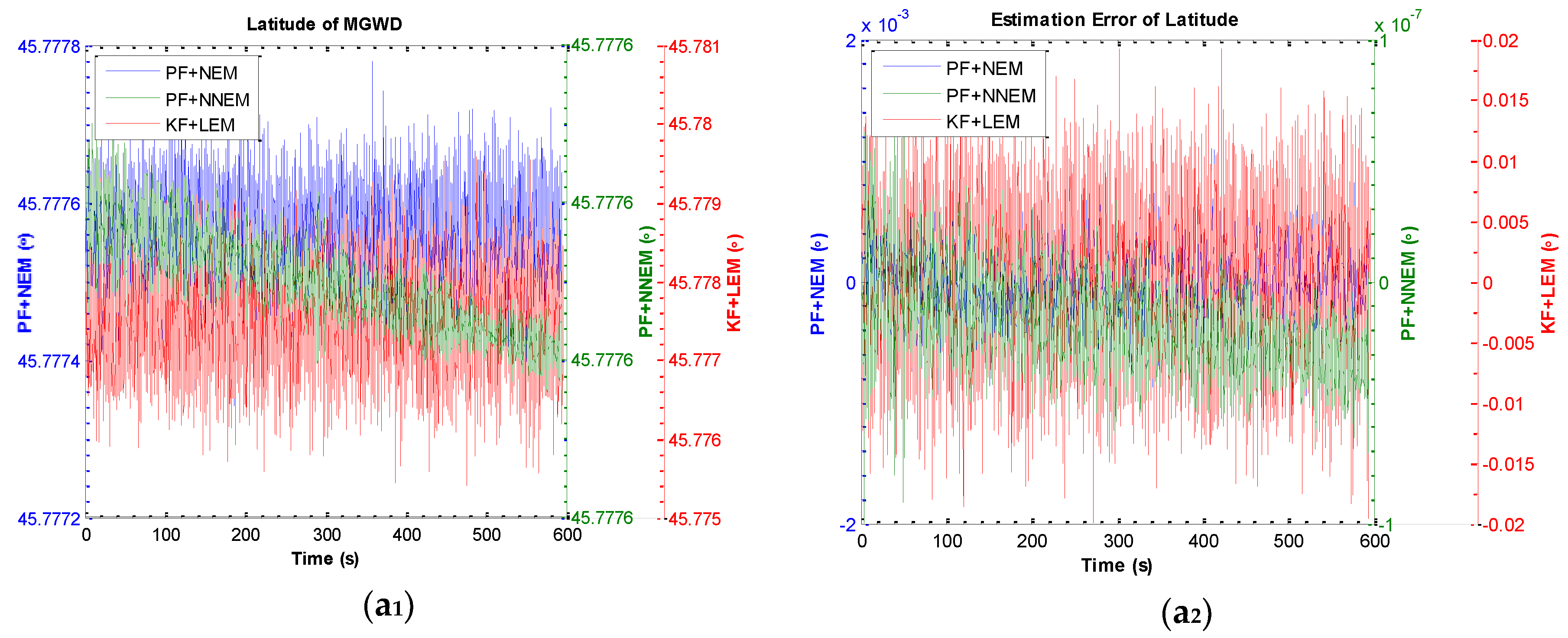
5.3. Experiment 2: Validation of the Performance of NNEM with Large-Angle Attitude Error
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- PetroWiki. Multilateral wells. Available online: http://petrowiki.org/Multilateral_wells (accessed on 20 December 2015).
- Longbotton, J.R.; Cox, D.C.; Gano, J.C.; Welch, W.R.; White, P.M.; Nivens, H.W.; Jacquier, R.C.; Holbrook, P.D.; Frreman, T.A.; Mills, D.H. Multilateral well drilling and completion method and apparatus. European Patent 1,249,574 B1, 27 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ledroz, A.G.; Pecht, E.; Cramer, D.; Mintchev, M.P. FOG-based navigation in downhole environment during horizontal drilling utilizing a complete inertial measurement unit: Directional measurement-while-drilling surveying. IEEE Trans. Instrum Meas. 2005, 54, 1997–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, S.; EI-Sayed, H.S.; Ismail, G.; Ohmer, H.; Stracke, M.; West, C.; Retnanto, A. Key issues in multilateral technology. Oil Field Rev. 1998, 10, 14–28. [Google Scholar]
- Matheson, E.; McElhinney, G.; Lee, R. The first use of gravity MWD in offshore drilling delivers reliable azimuth measurements in close proximity to sources of magnetic interference. In Proceedings of the IADC/SPE Drilling Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 2–4 March 2004.
- Torkildsen, T.; Edvardsen, I.; Fjogstad, A.; Saasen, A.; Amundsen, P.A.; Omland, T.H. Drilling fluid affects MWD magnetic azimuth and wellbore position. In Proceedings of the IADC/SPE Drilling Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 2–4 March 2004.
- Amundsen, P.A.; Ding, S.; Datta, B.K.; Torkildsen, T.; Saasen, A. Magnetic shielding during MWD azimuth measurements and wellbore positioning. Soc. Pet. Eng. 2008, 25, 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Noureldin, A.; Irvine-Halliday, D.; Mintchev, M.P. Accuracy limitations of FOG-based continuous measurement-while-drilling surveying instruments for horizontal wells. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2002, 51, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelmagd, N.; Tabler, H.; Irvine-Halliday, D.; Mintchev, M.P. Quantitative study of the applicability of fiber-optic gyroscopes for MWD borehole surveying. SPE J. 2000, 5, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureldin, A.; Tabler, H.; Irvine-Halliday, D.; Mintchev, M.P. A new borehole surveying technique for horizontal drilling processes using one fiber optic gyroscope and three accelerometers. In Proceedings of the IADC/SPE Drilling Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–25 February 2000.
- Estes, R.A.; Epplin, D.M. Development of a robust gyroscopic orientation tool for MWD operations. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical onference and Exhibition, Dallas, TX, USA, 1–4 October 2000.
- Li, T.; Yuan, G.; Lan, H.; Mintchev, M. Design and algorithm verification of a gyroscope-based inertial navigation system for small-diameter spaces in multilateral horizontal drilling applications. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1467–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britting, K.R. Inertial Navigation Systems; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1971; p. 249. [Google Scholar]
- Noureldin, A.; Karamat, T.B.; Georgy, J. Fundamentals of Inertial Navigation, Satellite-Based Positioning and Their Integration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; p. 314. [Google Scholar]
- Quinchia, A.G.; Falco, G.; Falletti, E.; Dovis, F.; Ferrer, C. A comparison between different error modeling of mems applied to GPS/INS integrated systems. Sensors 2013, 13, 9449–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barshan, B.; Durrant-Whyte, H.F. Inertial navigation systems for mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1995, 11, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherzinger, B. Inertial navigator error models for large heading uncertainty. In Proceedings of the IEEE Position Location and Navigation Symposium, Atlanta, GA, USA, 22–26 April 1996; pp. 477–484.
- Savage, P.G. Moving Base INS Alignment with Large Initial Heading Error; Strapdown Associates, Inc.: Maple Plain, MN, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Djurić, P.M.; Kotecha, J.H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Ghirmai, T.; Bugallo, M.F.; Miguez, J. Particle filtering: A review of the theory and how it can be used for solving problems in wireless communications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2003, 20, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureldin, A. New measurement-while-drilling surveying technique utilizing sets of fiber optic rotation sensors. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, E.-H. Accuracy improvement of low cost INS/GPS for land applications. Master‘s Thesis, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jurkov, A.S.; Cloutier, J.; Pecht, E.; Mintchev, M.P. Experimental feasibility of the in-drilling alignment method for inertial navigation in measurement-while-drilling. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 60, 1080–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintchev, M.P.; Pecht, E.; Cloutier, J.; Dzhurkov, A. In-drilling alignment. U.S. Patent 7,823,661 B2, 2 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhenhua, W. MEMS-based downhole inertial navigation systems for directional drilling applications. Master‘s Thesis, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhenhua, W.; Poscente, M.; Filip, D.; Dimanchev, M.; Mintchev, M. Rotary in-drilling alignment using an autonomous MEMS-based inertial measurement unit for measurement-while-drilling processes. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2013, 16, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Goshen-Meskin, D.; Bar-Itzhack, I.Y. Unified approach to inertial navigation system error modeling. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 1992, 15, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myeong-Jong, Y.; Heung-Won, P.; Chang-Bae, J.; Myeong-Jong, Y.; Heung-Won, P.; Chang-Bae, J. Equivalent nonlinear error models of strapdown inertial navigation system. In Proceedings of the Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 11–13 August 1997.
- Friedland, B. Analysis strapdown navigation using quaternions. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1978, 14, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, P.G. Mitigating Second Order Error Effects in Linear Kalman Filters Using Adaptive Process and Measurement Noise; Strapdown Associates, Inc.: Maple Plain, MN, USA, 2014; pp. 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yeon Fuh, J.; Yu Ping, L. On the rotation vector differential equation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1991, 27, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myeong-Jong, Y.; Jang Gyu, L.; Heung-Won, P. Comparison of SDINS in-flight alignment using equivalent error models. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1999, 35, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortz, J.E. A new mathematical formulation for strapdown inertial navigation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1971, AES-7, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, M.D. The kinematic equation for the rotation vector. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1993, 29, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, P.G. Strapdown Analytics; Strapdown Associates, Inc.: Maple Plain, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, J. Aided Navigation: GPS with High Rate Sensors, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, R.M. Applied Mathematics in Integrated Navigation Systems, 2nd ed.; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc.: Reston, VA, USA, 2003; pp. 106–107. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, D.O. A comparison of two approaches to pure-inertial and doppler-inertial error analysis. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1975, AES-11, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, K.P.; Wei, M. A framework for modelling kinematic measurements in gravity field applications. Bull. Géod. 1990, 64, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheimy, N. Inertial Techniques and INS/DGPS Integration (ENGO 623); Geomatics: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cappe, O.; Godsill, S.J.; Moulines, E. An overview of existing methods and recent advances in sequential monte carlo. IEEE Proc. 2007, 95, 899–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet, A.; Godsill, S.; Andrieu, C. On sequential monte carlo sampling methods for Bayesian filtering. Stat. Comput. 2000, 10, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoulis, A. Probability, Random Variables and Stochastic Processes; McGraw-Hill, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 637–638. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, N.J.; Salmond, D.J.; Smith, A.F.M. Novel approach to nonlinear/non-gaussian bayesian state estimation. IEE Proc. F Radar Signal Process. 1993, 140, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Corchado, J.M.; Bajo, J.; Sun, S.; Paz, J.F.D. Effectiveness of bayesian filters: An information fusion perspective. Inf. Sci. 2016, 329, 670–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, F.; Gunnarsson, F.; Bergman, N.; Forssell, U.; Jansson, J.; Karlsson, R.; Nordlund, P.J. Particle filters for positioning, navigation, and tracking. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S. Sequential monte carlo methods for dynamic systems. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1998, 93, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Ma, J. An improved particle filter for target tracking in sensor systems. Sensors 2007, 7, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Crassidis, J.L. Particle filtering for attitude estimation using a minimal local-error representation. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2010, 33, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storvik, G. Particle filters for state-space models with the presence of unknown static parameters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handschin, J.E.; Mayne, D.Q. Monte carlo techniques to estimate the conditional expectation in multi-stage non-linear filtering. Int. J. Contro 1969, 9, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handschin, J.E. Monte carlo techniques for prediction and filtering of non-linear stochastic processes. Automatica 1970, 6, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katja, N.; Koller-Meier, E.; Gool, L.V. An adaptive color-based particle filter. Image Vision Comput. 2003, 21, 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Haug, A.J. Introduction to Monte Carlo Methods; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, F. Particle filter theory and practice with positioning applications. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2010, 25, 53–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.; Thrun, S.; Burgard, W.; Dellaert, F. Particle Filters for Mobile Robot Localization; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 401–428. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, D. Optimal State Estimation: Kalman, H Infinity, and Nonlinear Approaches, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 400–403. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Bolic, M.; Djuric, P.M. Resampling methods for particle filtering: Classification, implementation, and strategies. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2015, 32, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, K.S.; Lee, S.J.; Flathman, D.P.; Roll, J.W.; Piercy, W. Sequential imputations and Bayesian missing data problems. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1994, 89, 278–288. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, G. Monte carlo and smoother for non-Gaussian nonlinear state space models. J. Comput. Gr. Stat. 1996, 5, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sileshi, B.G.; Ferrer, C.; Oliver, J. Particle filters and resampling techniques: Importance in computational complexity analysis. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Design and Architectures for Signal and Image Processing (DASIP), Cagliari, Italy, 8–10 October 2013; pp. 319–325.
- Beadle, E.R.; Djuric, P.M. A fast-weighted bayesian bootstrap filter for nonlinear model state estimation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1997, 33, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

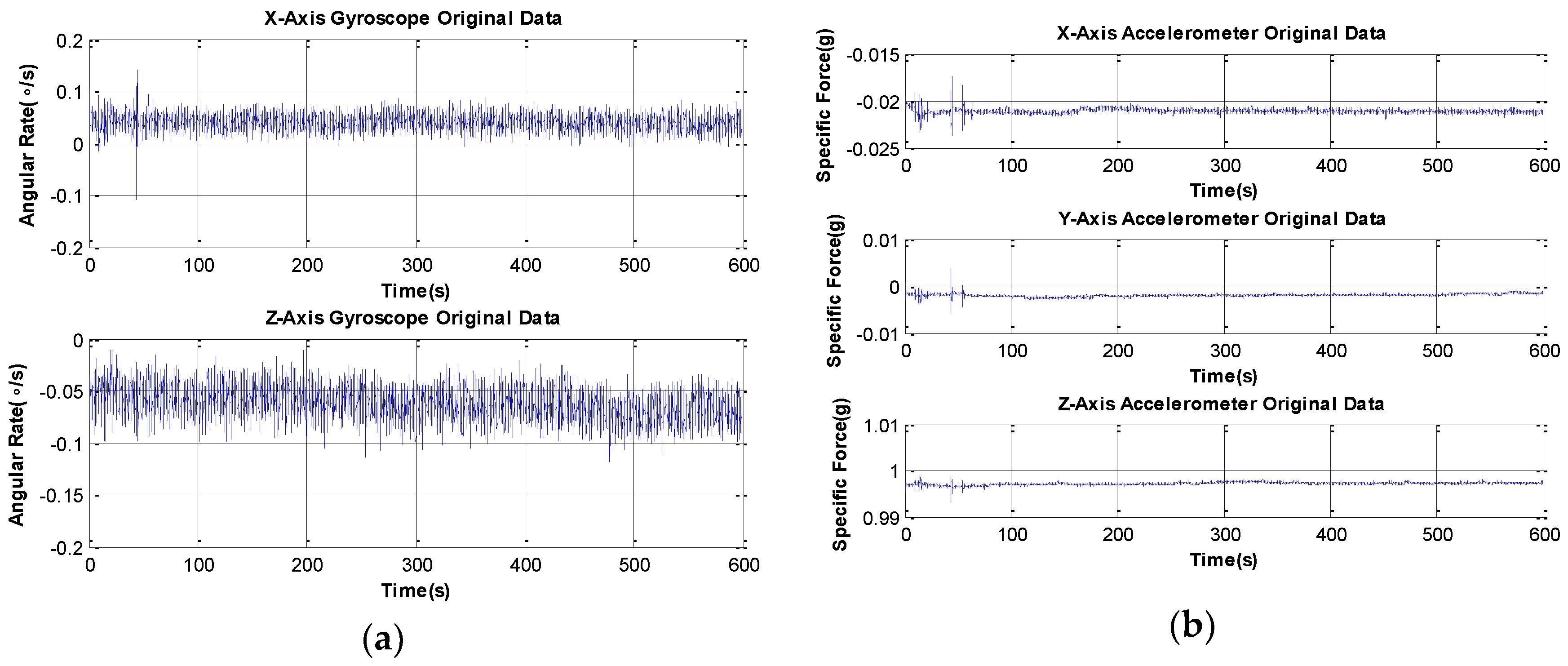

| Parameters | Gyroscope | Parameters | Accelerometer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Offset Short Term Instability | <2.1 °/h | Offset Error | ±70 mg |
| Angular Random Walk | 0.86 °/ | Linearity Error | ±40 mg |
| Noise Density | 0.02 (°/s/ | Noise | 5 ~ 7 mg |
| Temperature | −40 ~ +125 °C | Temperature | −40 ~ +125 °C |
| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processor | ARM Cortex-M3 | Debugging | cJTAG and JTAG |
| Frequency | 24 MHz | RF | 2.4 GHz IEEE 802.15.4 Transceiver |
| Peripherals | USB/I2C/SSI/UART | Size | 8 mm 8 mm |
| Temperature | −40 ~ +125 °C | Voltage | 2 V ~ 3.6 V |
| Parameters | PFNNEM | PFNEM | KF + LEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 45.777664 | 45.777613 | 45.777935 | |
| 126.687953 | 126.687934 | 126.688326 | |
| 123.999686 m | 123.652484 m | 120.945752 vm | |
| 0.002984 m/s | 0.0197424 m/s | 0.983472 m/s | |
| −0.000019 m/s | −0.234530 m/s | 1.342358 m/s | |
| 0.005637 m/s | 0.287584 m/s | 1.846332 m/s | |
| −0.021976 | −0.034748 | −0.053672 | |
| 0.184392 | −0.068584 | −0.026478 | |
| −9.893302 | −2.527547 | −2.599384 | |
| −0.362394 × 10−7 | −0.000014 | −0.000238 | |
| −0.457395 × 10−8 | −0.000106° | −0.000056 | |
| −0.000348 m | −0.196528 m | −8.872501 m | |
| 0.075922 m/s | 0.128473 m/s | 0.248382 m/s | |
| 0.048975 m/s | 0.056483 m/s | 0.287349 m/s | |
| −0.00648 m/s | −0.039320 m/s | 0.877265 m/s | |
| −0.000464 | 0.003502 | 0.004882 | |
| 0.000353 | 0.004528 | 0.005216 | |
| −0.000025 | 2.459532 | 1.879347 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Yuan, G.; Li, W. Particle Filter with Novel Nonlinear Error Model for Miniature Gyroscope-Based Measurement While Drilling Navigation. Sensors 2016, 16, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030371
Li T, Yuan G, Li W. Particle Filter with Novel Nonlinear Error Model for Miniature Gyroscope-Based Measurement While Drilling Navigation. Sensors. 2016; 16(3):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030371
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tao, Gannan Yuan, and Wang Li. 2016. "Particle Filter with Novel Nonlinear Error Model for Miniature Gyroscope-Based Measurement While Drilling Navigation" Sensors 16, no. 3: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030371
APA StyleLi, T., Yuan, G., & Li, W. (2016). Particle Filter with Novel Nonlinear Error Model for Miniature Gyroscope-Based Measurement While Drilling Navigation. Sensors, 16(3), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030371