Abstract
Landraces are heterogeneous populations and their variability goes through continuous alterations because of physical, genetic, and epigenetic procedures exacerbated by the ongoing climatic changes. Appropriate stewardship of landrace diversity is pivotal to promote its longevity in a manner that is sustainable from the farming perspective. A seed multiplication procedure is presented based on the assumption that in order to improve effectiveness in resource use and increase seed productivity, landraces should comprise genotypes which minimize intra-species competition. These aforementioned genotypes should be of the “weak competitor” ideotype, which are selected so as to alleviate the interplant competition and reach as high as possible crop stand uniformity. Stand uniformity is essential to ensure the same growing conditions for each plant. Reduced intra-crop inequality and equal use of inputs by individual plants will optimize crop performance. Precisely, the “weak competitor” is most often of high yield potential due to a negative association between yielding and competitive ability. Therefore, the suggested procedure involves initial reproduction at nil-competition (widely spaced plants to preclude any plant-to-plant interference for inputs) where “off-type” and low yielding plants are omitted, followed by subsequent multiplication at dense stands. This may represent an effective cultural practice to improve also the landrace health status concerning seed-borne diseases in the absence of certification systems.
1. Introduction
The increased awareness of traditional crop varieties for specific market uses is driving interest in describing regionally adapted crop varieties, or landraces [1]. Landraces are dynamic populations of cultivated species characterized by genetic diversity, locally adapted and associated with traditional farming systems, and have a distinct identity that lacks formal crop improvement [2]. Domestication follows a multistep process in which initial domestication is followed by dispersal and subsequent selection for adaptation to new conditions of cultivation and environment [3]. Although landraces lag behind the commercial varieties in productivity [4], growers prefer them for cultivation under traditional low input agricultural systems thanks to higher yield stability. Their stability is due to the fact that regardless of the varying biotic and abiotic stress for each plant, one or more genotypes within the landrace population will yield satisfactorily [5].
Throughout centuries, farmers have been the major keepers of the genetic diversity that landraces offer [6]. Rarely any selection is carried out, and through removing the small and light seeds, it is hypothesized that farmers unwittingly select for large size seeds and for stress resistance and tolerance [5]. Maintenance breeding of landraces, if applied, means that “all true-to-type” genetic variation is transferred to the next generation. A major force of natural maintenance of landraces is stabilizing selection by which “off-type” plants or their capacity to reproduce are suppressed [5]. Therefore, this maintenance technique is more a rogueing rather than a real selection process. Nevertheless, landraces grown by farmers may lose their identity and healthiness in the long term. Contaminating and degrading forces, such as outcrossing, volunteer plants, physical admixture, as well as seed-borne diseases, are the root of this [7].
Genetic procedures precipitated by an ever-changing environment may accelerate the rate of landrace alteration for the worse. It is now well known that the genome is more flexible and plastic than previously assumed. The genome is dynamic and can modify itself in response to environmental pressure [8], and has inherent mechanisms to provide a continuing source of new genetic variability [9]. Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms generating de novo variation may result in the expansion of landrace diversity. Hence, the preferential and gradual proliferation of undesirable mutations at the expense of desirable constituent genotypes may lead to the landrace degeneration.
Seed represent a vehicle for several plant pathogens, viruses, bacteria, and fungi, contributing to their global dissemination. For example, more than 50 fungal pathogens have been reported to be seed-borne in rice (Oryza saliva L.) [10] among which 14 are of major importance [11]. Five out of the 26 viruses known to affect lentil (Lens culinaris L.) are also seed-borne [12]. Seed maintained by farmers carry seed-borne pathogens that reduce germination rate and transmit pathogens to plants, causing enormous crop losses [11,13]. A major impact of seed-borne diseases in wheat (Triticum sp.) is not only the yield reduction but also deterioration of the marketable grain quality [14]. Seed infections favor long-distance movement and the establishment of the disease in new regions [15]. For plant viruses, transmission by seed can provide long-term survival and be a significant epidemiological trait especially for viruses which are also transmitted by aphids [16]. A viable infected seed is a primary source of infection for further spread by insect vectors [12,17]. Consequently, the use of healthy seed is a major component of integrated production and promotes crop sustainability [16].
This review paper revolves around the landrace diversity evolving under natural selection and on account of the environmental forces exacerbated by the ongoing climatic changes. The issue is to establish a sustainable conservation breeding procedure to treat the landrace seed in a manner that keeps the desirable and expel the undesirable parts of the diversity. The main hypothesis is that (1) landrace cultivation should result in as far as possible uniform crop stand to increase efficiency in resource use; (2) uniform crop stand is attainable when the landrace constituent genotypes are of the “weak-competitor” ideotype so as to minimize the acquired intra-crop variation; (3) weak competitors are recognizable on the premise that they grow under the absence of intra-species competition; (4) due to an inverse relationship of yielding with competitive ability, maintenance of weak competitors, in reality, implies that high yielding genotypes are also kept. Hence, the paper ends up with a pilot scheme that entails the manipulation of landrace diversity through bulk selection under conditions approaching absolute absence of intra-species competition, with the aim of establishing continuous landrace adaptation to an ever-changing environment. Such a breeding strategy may expand landrace longevity and adoption by farmers reluctant to apply the traditional way of cultivation, while parallel cultivation of the landrace by traditional farmers would ensure the evolution of landrace by the natural selection process as well. It is necessary to clarify that the issue pertains to landraces grown primarily for grain since the further down documentation concerns grain/seed yield. Similar investigations for landraces of species cultivated for biomass (silage or hay) production are not available and future relevant research might be enlightening.
2. Crop Stand Variation and Resource Use Efficiency
Studies in crops such as rice, maize (Zea mays L.), and wheat have evidenced that optimal efficiency of resource use at the crop level is a matter of crop stand uniformity [18,19,20,21,22,23]. A negative correlation between the coefficient of variation (CV) for grain yield per plant and mean grain yield per area was found in a study including seven maize hybrids at two densities, a typical density of 8.4 plant/m2 and a low density of 2.5 plants/m2 [24]. In a review work, the relationship between the crop stand uniformity and grain yield of wheat was investigated [21]. In total, 362 trials were separated into two groups, the first included 142 variety trials and the second 220 trials concerning fertilizer, weed management, and tillage. Both groups revealed a significant negative correlation of yield per area with CV of plot-to-plot variability. Based upon the provided equations, with increasing CVs from the lowest to the highest values, yield declined more than 80%. The provided yield decline model was exponential and more drastic at lower CVs, thereby pinpointing the importance of crop stand uniformity. A similar pattern demonstrating the negative relationship between plant-to-plant variability for single plant yield and the per unit area grain yield was also depicted when six maize hybrids were grown across four environments [23]. In that study, the CV values ranged from about 15% up to 70%, and according to the provided equation the corresponding yields at these extreme CVs were 9000 and <4500 kg/ha, respectively, implying a >50% yield gap. Of note, just a one-fifth increase of the CV from the lowest value towards the highest value would cause half of the total yield gap, highlighting the importance of crop stand uniformity to optimize the crop performance. The above reverse association was also reported in another maize study when average grain yields were plotted against the CV from by-plants yields across the range of 46 transects harvested from 13 different sites [19]. A highly significant negative slope was observed, with the highest yields (≈15,500 kg/ha) at sites with the lowest CVs, and the lowest yields (≈2500 kg/ha) at sites with the highest CVs.
Theoretically, the highest crop productivity is expected when “justice” will prevail and individuals share the growth resources equally [25]. Without an adequate and uniform rice stand, optimum rough rice yields are difficult to attain [18]. Evidence has been presented that productivity optimizes in uniform stands, and contrarily, the larger the interplant differences in growth and development, the stronger the established intra-species competition and the less the yield per unit area [22,25]. This happens because the lower than average yields of some plants are undercompensated by the higher yields of others, implying inefficient resource use. Interestingly, high densities precipitate intra-crop inequality and stand uniformity is inversely connected with crowding. Two groups each of seven maize hybrids tested across densities [24] demonstrated a positive correlation of CV for single-plant grain yield with the number of plants per area (Figure 1). This connection has been reported for other agronomic traits as well (i.e., plant height, ear height, ear length) [26]. Hence, in an effort to establish as high of crop a stand uniformity as possible, it seems that in order to optimize resource use efficiency particular emphasis should be placed on varieties that yield adequately at relatively low densities.
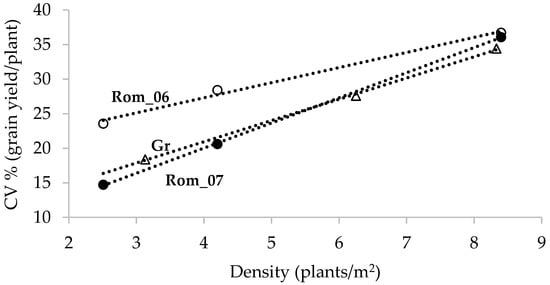
Figure 1.
The positive association of CV for single-plant grain yield with density depicted in two groups of seven hybrids, the first across two seasons (Rom_06, and Rom_07) and the second for a single season (Gr). Data from Tokatlidis et al. [24].
Since, by definition, minimal interference among plants excludes the presence of competitive advantages and disadvantages, it is implied that the principal property of a genotype is not the competitive but the yielding ability. In turn, it is self-evident that plants that occupy genetic competitive ability are prone to get an advantage and consume more inputs than their share. Hence, the crop that is comprised of a population devoid of “insatiable” individual genotypes is the only choice to optimize resource use efficiency, on the presupposition that these genotypes are of high yield potential and stability. A competitive ideotype does not maximize reproductive allocation in a population sense and a “communal” ideotype or “weak competitor” optimizes crop productivity [20]. Consequently, an ideal landrace should comprise genotypes that ensure the least possible intra-crop variation and inequality without compromising buffering ability against biotic and abiotic stresses.
3. Competitive vs. Yielding Ability
Genotype competitive and yielding ability are distinct agronomic traits, and their relationship is a determinant factor concerning degeneration of the landrace seed. Evidence of association in an inverse function has been reported in numerous studies [20,27,28,29,30,31]. A relative case study that verified this relationship was conducted in wheat by Fasoula [32] who applied selection within the variety “Siette Cerros”; six single-plant sister lines performed inversely when grown in the pure stand against the mixed stand. The negative association between the two traits is also supported by intercropping studies which involve different varieties of the same crop; a significant genotype by cropping system interaction occurs demonstrating that intercropping systems favor more genotypes that perform poorly as sole crops rather than those that are high performing when grown alone [33,34,35,36,37,38].
The hypothesis of a negative connection between yielding and competitive ability was investigated in two studies that considered landraces and their grain yield response to crowding. A genetically heterogeneous vetch (Vicia sativa L.) landrace was compared with a fairly homogeneous check (pure-line variety) across a range of six densities [39]. At intense crowding (25 plants/m2), the landrace lagged significantly behind the check by 29%; however, as density declined their gap was progressively bridged, while at the lowest crowding level (1.15 plants/m2) the landrace was superior by 32% (Figure 2a). This finding shows that in a genetically mixed stand, under intra-species competition strong competitor–low yielders prevail masking the yielding capacity of weak competitor–high yielders. As competition loosens, yielding capacity of high yielders is expressed relatively more and more until unfettered and fully expressed at nil-competition. The idea was verified in wheat as well [40]. Six landraces were tested against a homogeneous check variety at the typical farming density (≈450 plants/m2) for two trials (conventional and low-input conditions), as well as at nil-competition (1.15 plants/m2). Compared to the check, the average relative grain yield of the landraces was 53% at the dense stand and 120% at nil-competition. Figure 2b shows that landrace no 2 was the highest yielding in dense stand conditions (relative yield 64%) yet was the lowest yielding under nil-competition conditions (relative yield 91%); on the other extreme, landrace no 6 was the lowest yielding under dense stand conditions (64% below the check) yet was the highest yielding under nil-competition conditions (73% above the check), matching perfectly the speculation that yielding ability of individual genotypes might be suppressed by neighboring genotypes that possess genes for competitive ability. Tremendously discrepant behavior was found for landrace no 5 as well (i.e., a 38% inferiority under dense stand conditions turned into a 58% superiority under nil-competition conditions). These findings constitute a clear demonstration that intra-species competition might exert a high obstructive influence on high yielders to express their capacity. A similar influence was also evident in the case of inter-species competition in an intercropping study [37], where among 10 bean varieties two performed in an absolute discrepant manner when either grown as sole crop or intercropped with a maize hybrid. The one that was the lowest yielding when grown alone was the highest yielding when mixed with a maize hybrid (resulting in 75% more grain yield). On the other extreme, the highest yielding variety when grown under sole crop conditions (almost fourfold superior over the former) experienced a 78% grain yield reduction when intercropped (37% below the former).
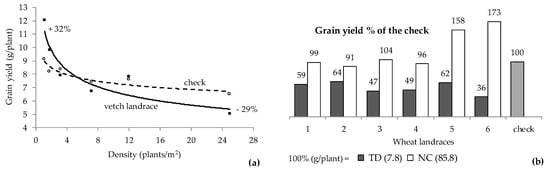
Figure 2.
The performance of heterogeneous landraces against respective homogeneous checks, (a) across a range of densities; and (b) at typical density (TD) and nil-competition (NC), indicate that high yielding genotypes involved in a landrace are expressed and detectable only at NC. Adapted from (a) Chatzoglou and Tokatlidis [39] and (b) Ninou et al. [40].
4. Mechanisms of New Variation
Varieties grown by farmers may lose their genetic identity and healthiness in the long term [41]. Contaminating and degrading forces, such as outcrossing, volunteer plants, physical admixture, natural selection, mutation, and seed-borne diseases, are at the root of this [7]. Eight years of natural selection increased seed weight in four populations derived from a composite cross of wheat [42]. On farm natural selection for four seasons led to discernible changes in agronomic, morphological, and phenological traits in lentil landraces [43]. Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms that generate de novo variation may also result in a considerable amount of new variation. Environmental forces, including those brought about by climatic changes, may accelerate the rate of genome alteration for the worse.
Landraces are dynamic populations undergoing several naturally occurring mutations that affect the per se diversity. Genomes are highly sensitive to unusual and unexpected events and can modify themselves in response to environmental forces [8]. Additional heterogeneity might stem from de novo generated variability due to spontaneous mutations [44,45], or novel recombination events stemming from genetic and epigenetic processes [46,47,48,49,50].
Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms leading to enhanced biodiversity are referred to as small-scale mutations in stances concerning nucleotide changes within genes, and large-scale mutations when pertaining to changes in the number of genes or the arrangement of the genes in a chromosome [49]. Active transposable elements are highly mutagenic and can cause changes at both the gene and genome level that exceed those of strong chemicals and radiation [51]. Some transposable elements expand genomes via duplications while others act in the “cut and paste” or the “gap repair” function [52]. The epigenetic mechanism of DNA methyliation, related to the activity of the transposon elements, is mounted at stress conditions, and methyliated cytosine could itself be mutagenic through spontaneous deamination to thymine [50]. Acetylation and deacetylation of histones can also cause modifications that affect gene expression, with transcription factors notably in response to biotic and abiotic stress stimuli [53]. The identification of small non-coding RNA molecules implicated in endogenous gene regulation and the control of invading genetic entities elevated additional epigenetic processes [50,54]. Such small RNA molecules, incorporated in RNA-complexes, take part in mRNA silencing. Specific histone modifications and the production of small RNAs have been directly correlated with DNA methyliation [55].
Gene pools have inherent mechanisms that provide a continuing source of new genetic variability thanks to genome plasticity [9]. Molecular biologists are finding that genomes undergo constant remodeling and restructuring via intragenic recombination, unequal crossing over, DNA methyliation, excision or insertion of transposable elements, gene duplication, genetic restoration, etc. [46,47,48,56,57]. Allele switching [58] and differential segregation of polymorphic chromosomal regions [59] have been reported as mechanisms of de novo variation. This additional knowledge reveals genomes have endogenous mechanisms to be flexible, plastic, and dynamic. It is thanks to such versatility that even small gene pools get novel genetic variability in response to stresses [50]. In flax (Linum usitatissimum) Cullis [46] discovered rapid modifications in the genome during plant developments under stress conditions that were associated with changes in gene expression. Recently, Lasky et al. [60], while working on sorghum landraces, reported that the environment explained a significant portion of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) variation and that genic SNPs were enriched for the environmental association.
Genetic variation stemming from physical and molecular procedures may expand the presently existing variation in landraces. Since wide variation may result in an uneven crop stand and unequal resource use among the individual plants in the farmer’s field, appropriate stewardship of landrace diversity, becomes imperative in order to mitigate crop inequalities. A conservation breeding scheme to remove undesirable genotypes and keep those that comprise a community of weak competitors is of paramount importance to optimize crop stand uniformity. Fortunately, such genotypes are of high yield efficiency when taking into account the negative relationship of yielding with competitive ability. Moreover, since high densities precipitate intra-crop inequality conservation breeding should also emphasize genotypes that better allow for cultivation at lower densities without compromising high productivity.
5. Stewardship of the Diversity
5.1. General Approach of Breeding at Nil-Competition
Natural selection may gradually lead to seed degradation and landrace degeneration from preferential and gradual proliferation of the strong competitors-low yielders at the expense to weak competitors-high yielders, due to the inverse connection of yielding with competitive ability [25,32,41]. Thus, the predominance of the strong competitors may also narrow the landrace variation for the worse. Annicchiarico and Piano [61] observed the occurrence of severe intra-species competition in white clover (Trifolium repens L.) landraces and found that under cultivation up to 90% of the individuals could be eliminated within a year of the crop cycle, resulting in a severe reduction of variation.
Genetic heterogeneity of landraces refers to the genetic variation from plant to plant. To investigate this variation, a specific condition that allows for the identification of differences among individual plants is a prerequisite. The ideal condition is when individual plants are grown widely apart so as to prevent any plant-to-plant interference for resources. In other words, to ensure that strong genetic competitive ability of an individual does not influence the growth and development of the neighboring plants. In fact, the regime does not represent absolute “justice” and it still involves acquired inequality due to an inevitable spatial heterogeneity. However, appropriate management may minimize this acquired inequality, and by assumption, the regime represents the absence of competition condition, referred as nil-competition regime [25].
Under nil-competition conditions growth and seed production at the single-plant level reach their maximums. Differences between individuals also reach the maximum, thereby facilitating the detection of high yielding genotypes and single-plant selection [24,25,26,27,28,41]. More importantly, the negative relationship of yielding with competitive ability renders nil-competition indispensable for avoiding the selection of strong competitors at the expense of high yielders. Furthermore, a greater heritability of seed yield per plant under nil-competition conditions, rather than under dense stand conditions, constitutes a third favorable nil-competition element. Studies in winter rye (Secale cereale L.) [28] and maize [24,62] verified that nil-competition improves heritability by (i) minimizing the acquired variance that arises from nongenetic sources; and (ii) erasing the confounding impact of competition on the identification of the superior genotypes [25]. Hence, nil-competition is the optimal condition for seed stewardship to secure landrace conservation, particularly in crops cultivated for seed production.
The necessity to handle genetic heterogeneity with widely spaced plants brings the innovative honeycomb breeding model to the fore. The methodology was invented by Fasoulas [63], setting nil-competition as the first inviolable principle for suspending the role of competition in the evaluation and selection of single plants. Hence, the model appears ideal for sustaining landrace diversity. The method has been widely analyzed [25,27,64,65], thus, a brief description is given below that is adequate to serve this paper’s scope. Devoid of fallacious implications of competitive advantages and disadvantages, another important advantage pertaining to enhanced heritability refers to missing plants, a common issue in the field trials. Under competition, plants neighboring empty hill(s) gain acquired competitive advantage that may lead to biased evaluation and selection. Rather, at nil-competition, missing hills did not affect development or seed production of the neighbors so all the surviving plants are fairly considered for selection [24,41]. Thus, “off-type” and infected plants can be removed at very early stages and preclude pollination from plants to be discarded. Admittedly, the optimal interplant distance to ensure nil-competition is a matter of species per se and of intraspecies genotypes as well [24,41], and precise estimation for each crop requires further investigation. Nonetheless, on the basis of previous studies the interplant distance of 0.9 or 1 m is recommended for the majority of the crops (i.e., wheat, barley (Hordeum vulgare L.), rice, rye, Spanish vetchling (Lathyrus sp.), soybean [Glycine max (L) Merr.], common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.), vetch). In maize, nil-competition was approximated at higher distances [24,66]; however, that was for hybrids of high yield potential. For lentil (Lens culinaris), an interplant distance lower than 0.80 m has been reported to be large enough to reach nil-competition [67,68]. Nevertheless, experience on a particular crop is essential to decide on the interplant distance that ensures nil-competition.
Computer software is available (JMP.7) tailored to the honeycomb experimental pattern and these measures [69]. Placing each individual plant, , in the center of a ring (the moving circle illustrated in Figure 3) permits the use of the average yield of each replicate, , as a denominator, and the unitless to measure the relative plant yield efficiency devoid of the confounding effect of spatial heterogeneity. A range of 7–367, or even more, plants can be included in the ring [65,70] (i.e., the range of 7–367 is applicable in the software). In considering reasonable conditions for this procedure, a relatively big ring size is preferable in order to tackle the replicate heterogeneity due to landrace variation. The big size of the ring, beyond approaching a common control, offers the possibility to take into consideration plants of even the edge rows and avoid disqualification of any desirable genotype. Thus, the ring size of 109 shown in Figure 3 is a rational option. With interplant distance “d”, the area occupied per plant is [65]. Therefore, with single-plant hills spaced 1 m, the corresponding area per plant is 0.87 m2, and the area of the “109” circular control is about 95 m2, which is large enough to sample even huge levels of spatial heterogeneity [71]. Nevertheless, an even higher ring may be preferable in the case of a high ratio of missing plants in order to secure proper control for sampling the genetic heterogeneity.
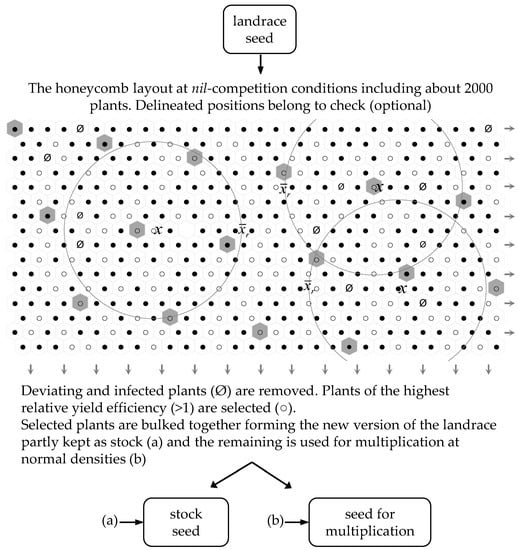
Figure 3.
A pilot scheme of the landrace bulk breeding involves the evaluation of about 2000 individual plants at an ultra-low density approaching nil-competition and the selection of 500–700 plants, ultimately culminating with upgraded seed to be used as stock (a) and the beginning of a multiplication round (b).
5.2. Bulk Selection to Replenish the Landrace Seed
The process carried out in adherence to isolation standards consists of a single-year selection phase. It aims to replenish the landrace seed, partly to be kept as stock, whereas the remaining is used to feed the multiplication rounds at normal densities. Thus, upgraded landrace seed would be available for cultivation purposes. The landrace seed is used to establish about 2000 plants in a honeycomb trial where single-plant hills are widely spaced to ensure nil-competition. As an option, the stock seed is used as the check so as to facilitate detection of the “off-type” plants. For example, in Figure 3 the check occupies the positions intended for entry 31 at the honeycomb design constructed for 31 entries. Deviating (“off-type”) plants and those with seed-borne diseases are removed as soon as they can be detected. The remaining plants are harvested separately and their seed yield is recorded. A large number of healthy plants of the landrace type are selected (including check plants), on the premise that their relative yield efficiency is above one (i.e., > 1). It is estimated from previous studies [67] that normally a proportion of 35%–45% of plants are able to yield an amount of seed () that exceeds the mean of the respective circle (). Hence, supposing that the number of finally harvested plants is 1500, a total of 500–700 plants will be selected and their seed will be mixed. Thanks to very high seed yield per plant, based on the rough estimations previously made by Tokatlidis [41], the produced seed is expected to be above 15, 25, 100, and 125 kg for lentil, wheat, maize, and common bean, respectively. Assuming that a small part is kept as seed stock, these values after the first densely multiplication become 500 kg for lentil and wheat, 1750 kg for common bean, and 2250 kg for maize. Of note, these yield levels were judged to be fairly poor, and much higher values might be closer to reality. For the multiplication phase under dense stand conditions, it is recommended that planting occur at slightly lower densities than normally used by farmers to accomplish good seed quality [7,41].
Two options for the procedure are suggested. The first involves continuous breeding where the bulk selection phase is established at the beginning of each multiplication round, followed by the seed reproduction phase for the number of seasons required to produce the seed amounts required (Figure 4a). Assuming that each breeding cycle upgrades the landrace, particularly for the self-pollinating species, the suggested number of 2000 established plants may gradually decrease to 1000 after two to three cycles accompanied by higher rates for selected plants. In cross-pollinators, in order to sample the relatively high variability originating from genotype segregation, a large number of established individuals is always imperative. This option might be exceptionally important for species severely suffering from seed-borne pathogens. Further, constant improvement of a landrace via the continuous procedure might expand it in commercial mechanized agriculture. In widely adopted landraces, the low multiplication rate (seed yield per seeding rate) of some crops (such as pulses and cereals) imposes massive seed reproduction that favors infection with seed-borne pathogens and genetic changes. Thus, a non-stop breeding procedure appears indispensable to alleviate these constraints. Landraces are usually cultivated in resource-poor smallholder farming systems. Resource-poor farmers may be unable to implement the continuous scenario and the second option can be applied, on an agricultural combination basis. In considering the periodic option, the bulk selection phase is established after several seasons of seed reproduction under dense stand conditions (Figure 4b). The precise number of years for practicing bulk breeding is tough to define depending on the species and the adoption rate of the landrace. Higher frequency for cross- rather than self-pollinating species is a reasonable choice. The rate of genetic changes may also differ among landraces with climatic and soil conditions during seed multiplication process, and may therefore represent determining factors. Traceable changes are certainly critical for a decision regarding the timing of a new round of periodic breeding. For instance, in widely adopted landraces higher rates of genetic changes may occur and frequent bulk breeding is more cost-effective.
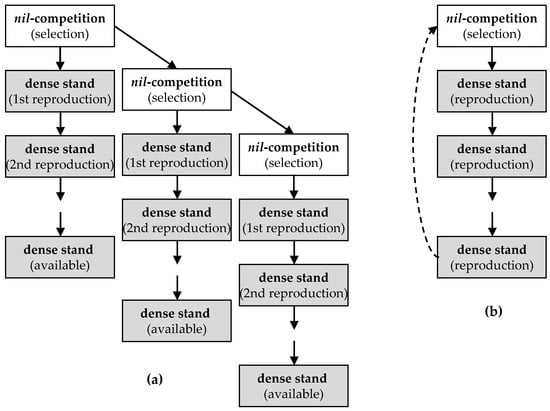
Figure 4.
Each multiplication round comprises a first starting phase of bulk breeding under nil-competition conditions followed by seed reproduction under dense stand conditions for the number of seasons required to satisfy the farmer’s demands. The procedure is (a) continuously suggested for landraces widely adopted and/or suffering from seed-borne diseases; or (b) suggested on a periodic basis with frequency depending on species and adoption rate of the landrace.
6. Discussion
Landraces are genetically heterogeneous with variability going through continuous changes because of physical, genetic, and epigenetic procedures. Ongoing climatic change is certain to exacerbate genome changes in response to environmental forces, and landraces that evolve via natural selection undergo considerable agronomic changes even within a few seasons of natural selection [42,43]. Thus, appropriate stewardship of landrace diversity is pivotal for promoting their longevity and improving yield and stress adaptation capacity in a manner that is sustainable from the farming perspective [72].
Contemporary landrace seed treatment under typical farming stand density conditions (under either natural selection or any maintenance breeding scheme) favor genotypes possessing genes for competitive ability. This condition implies two major disadvantages. Firstly, the prevailing strong competitors are usually low yielding genotypes due to the inverse connection between yielding and competitive ability [39,40]. Continuous seed reproduction under crowded conditions results in preferential and gradual proliferation of the strong competitors at the expense of the high yielders, leading to a gradual landrace degradation and variety degeneration [32,41,73]. Secondly, landraces that are comprised of a series of strong competitors are expected to exhibit high intra-crop variation, inversely connected with efficiency in resource use. Under typical farming conditions, spatial heterogeneity favors a number of plants to experience an early onset of growth, thereby providing them with an acquired advantage. In cases where these plants are “insatiable” thanks to their genetic competitive ability, they would be likely to take advantage of the circumstance to broaden their difference from the neighboring plants and thereby widen the intra-crop inequality. Therefore, the bulk selection at the beginning of the multiplication round appears fundamental to remove strong competitors so as to ensure that the landrace constituent individuals are of the “weak competitor” ideotype. A weak competitor optimizes reproductive allocation in a population sense and performs better compared to the competitive ideotype on the presupposition that the surrounding individuals are also weak competitors [20,30]. An improved landrace comprised of high yielding weak-competitor genotypes would be characterized by homeostasis, withstanding to acquired intra-crop inequality.
The current practice of propagation absolutely at crop densities creates a crucial barrier to deal with landrace genetic diversity. Intra-species competition plays a suspending role in identifying individual genotypes of high plant yield efficiency. To counteract the issue, the landrace seed need to be treated following a nil-competition regime that maximizes the phenotypic expression and differentiation [24,25,27,28,41], which is a prerequisite to identify the within-landrace genetic differences in order to remove inferior plants and to select the superior ones. Within a rye population of about 2000 plants either densely grown or under nil-competition conditions mass selection was applied at three selection pressures: the selection of 14.3%, 5.3%, and 1.6% of the highest yielding plants [28]. With intensifying pressure (by reducing the selection rate), the selection response increased under nil-competition conditions (4.1%, 5.4%, and 9.0%, respectively) while it declined (becoming even negative) under dense stand conditions (0.3%, −3.7%, and −5.2%, respectively), thereby highlighting the obstructive influence that intra-species competition exerts on genotypes of high yield potential.
The suggested strategy, besides tackling the suspending role of intra-species competition on the highest yielding individuals, offers unique advantages to managing landrace diversity. It facilitates discerning and rogueing the deviating and disease carrying plants, and the weeds as well. It is also essential that the field should be free of volunteer plants. Plants with a seed-borne disease can be identified and removed at the very early stages. From this key topic perspective, seed treatment under nil-competition conditions is of great importance. In general, symptoms of the diseases are intensified and infected plants can be more easily recognized when plants are wide apart, contrary to the high densities that result in early canopy formation that shades over any infected source plant [16,74,75]. Therefore, nil-competition facilitates the discrimination between infected and healthy plants. Indeed, in a lentil landrace, the suggested procedure established for three successive cycles (selection of 100 out of 400–600 surviving plants) succeeded in purifying the seed stock from three initially identified seed-borne viruses and upgrading the landrace yielding capacity by 9% [67].
It is also noteworthy that, thanks to emphasizing the single-plant yielding capacity, selection under nil-competition conditions breeds varieties that are distinguished as density-independent [22,25,26,62,70]. The density-independent variety is capable of approaching its productivity plateau (attainable on the available resources) at wide and low threshold ranges of densities, notably at even lower densities than the typical densities that are currently required. Consequently, after several rounds of bulk breeding for the purpose of progressively improving plant yield efficiency, the optimum density of the landrace is certain to lower, which represents an added value for several reasons. Apart from the reduced required seeding rate, lower densities deintensify the plant-to-plant variation and intra-crop inequality (Figure 1), allowing them to better cope with their detrimental effects on resource uptake at both per plant and area level. Varieties of low optimum density are more effective in resource use and are more stable across the fluctuating environment; moreover, their use is also imperative for the approximation of the attainable yield based on the available resources [76]. Last but not least, cropping at lower densities is an inviolable rule particularly for low-input agriculture where the deficit in inputs render effectiveness in use of the utmost importance [77].
Landraces are assumed to be more dynamic than commercial varieties thanks to their extensive variability [2]. One could assume that the proposed new practice of seed stewardship may reduce the dynamic evolution of landraces because of the narrowing of their genetic variability. Precisely, the technique strives for the purification of landrace variability by removing the undesirable parts, and, moreover, actually strengthens the landrace dynamism. In addition to considering benefits, it may also present its own set of risks and uncertainties, such as the possibility of losing desirable traits. For example, fragrance in rice is connected with reduced yield under abiotic stress conditions [78]. If this is the case, the possibility of inverse association of grain yield with quality or other valuable characteristics should be taken into consideration in bulk selection performance.
7. Conclusions
Conclusively, the suggested procedure of seed management under nil-competition conditions offers unique advantages. The landrace is cured in considering both undesirable mutations and seed from seed-borne diseases. The landrace evolves towards a variety distinguished for homeostasis and density-independence, both essential for effective resource use, higher productivity, and over season stability. The option of seed storage under conditions (e.g., low temperatures) that keep the seed viable for long is not feasible for crops of low multiplication rate where huge storage space is needed [7]. In addition, it is not cost-effective in landraces because of the low adoption rate. This makes seed stewardship under nil-competition conditions the only way to cope with landrace diversity, not only as a non-stop procedure for landraces of wide adoption and/or suffering seed-borne diseases, but also to be periodically applied to be cost-effective in landraces with a low adoption rate. Within the framework of “landrace conservation”, sustainable seed management would be attained through the exploitation of adaptive responses to ever-changing biotic and abiotic agroecosystems, thereby promoting landrace adoption and sustainability. A strong interaction and association between the environment that the landraces have been developed and their genomic profile have been disclosed, thus the technique conducted in situ would maintain the appropriate genes of high adaptability [79]. The strategy can be easily applied by farmers, particularly those who are willing to work in cooperation and carry out the seed propagation process as a separate function.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the writing and editing of the review.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bota, J.; Conesa, M.A.; Ochogavia, J.M.; Medrano, H.; Francis, D.M.; Cifre, J. Characterization of a landrace collection for Tomàtiga de Ramellet (Solanum lycopersicum L.) from the Balearic Islands. Genet. Res. Crop Evol. 2014, 61, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, T.C.C.; Maxted, N.; Scholten, M.; Ford-Lloyd, B. Defining and identifying crop landraces. Plant Genet. Resour. 2005, 3, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gepts, P. A comparison between crop domestication, classical plant breeding, and genetic engineering. Crop Sci. 2002, 42, 1780–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouesnard, B.; Zanetto, A.; Welcker, C. Identification of adaptation traits to drought in collections of maize landraces from southern Europe and temperate regions. Euphytica 2016, 209, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeven, A.C. Traditional maintenance breeding of landraces: 2. Practical and theoretical considerations on maintenance of variation of landraces by farmers and gardeners. Euphytica 2002, 123, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsika-Sotiriou, M.; Mylonas, I.G.; Ninou, E.; Traka-Mavrona, E. The cultivation revival of a landrace: Pedigree and analytical breeding. Euphytica 2010, 176, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlevliet, J.E. How to maintain improved cultivars. Euphytica 2007, 153, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, B. The significance of the responses of the genome to challenge. Science 1984, 226, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmusson, D.C.; Phillips, R.L. Plant breeding progress and genetic diversity from de novo variation and elevated epistasis. Crop Sci. 1997, 37, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohana, D.C.; Prasad, P.; Vijaykumar, V.; Raveesha, K.A. Plant extract effect on seed-borne pathogenic fungi from seeds of paddy grown in Southern India. J. Plant Protection Res. 2011, 51, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Hossain, M.; Hassan, K.; Dash, C.K. Efficacy of different plant extract on reducing seed borne infection and increasing germination of collected rice seed sample. Univ. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 1, 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, S.G.; Larsen, R.; Makkouk, K.M.; Bashir, M. Virus diseases and their management. In The Lentil: Botany, Production and Uses; Erskine, W., Muehlbauer, F.J., Sarker, A., Sharma, B., Eds.; CAB International, Wallingford: Oxfordshire, UK, 2009; pp. 306–325. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, W.A.J.M.; Bateman, G.L. Fungal communities on roots of wheat and barley and effects of seed treatments containing fluquinconazole applied to control take-all. Plant Pathol. 2001, 50, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, D.; Rajesh, T.; Suting, E.G.; Debbarma, A. Detection of seed borne pathogens in wheat: Recent trends. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 500–507. [Google Scholar]
- Elmer, W.H. Seeds as vehicles for pathogen importation. Biol. Invasions 2002, 3, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.A.C. Using epidemiological information to develop effective integrated virus disease management strategies. Virus Res. 2004, 100, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutts, B.A.; Prince, R.T.; Jones, R.A.C. Quantifying effects of seedborne inoculum on virus spread, yield losses, and seed infection in the Pea seed-borne mosaic virus-field pea pathosystem. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravois, K.A.; Helms, R.S. Seeding rate effects on rough rice yield, head rice, and total milled rice. Agron. J. 1996, 88, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.L.; Hodgen, P.J.; Freeman, K.W.; Melchiori, R.; Arnall, D.B.; Teal, R.K.; Mullen, R.W.; Desta, K.; Phillips, S.B.; Solie, J.B.; et al. Plant-to-plant variability in corn product ion. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.Y.; Wang, G.X.; Yang, H.M.; Wei, X.P. Effect of water deficits on within-plot variability in growth and grain yield of spring wheat in northwest China. Field Crops Res. 2003, 80, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.L.; Payton, M.E.; Raun, W.R. Relationships between mean yield, coefficient of variation, mean square error, and plot size in wheat field experiments. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1999, 30, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatlidis, I.S.; Koutroubas, S.D. A review study of the maize hybrids’ dependence on high plant populations and its implications on crop yield stability. Field Crops Res. 2004, 88, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollenaar, M.; Wu, J. Yield improvement in temperate maize is attributable to greater stress tolerance. Crop Sci. 1999, 39, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatlidis, I.S.; Has, V.; Mylonas, I.; Has, I.; Evgenidis, G.; Melidis, V.; Copandean, A.; Ninou, E. Density effects on environmental variance and expected response to selection in maize (Zea mays L.). Euphytica 2010, 174, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasoula, V.A.; Tokatlidis, I.S. Development of crop cultivars by honeycomb breeding. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatlidis, I.S.; Koutsika-Sotiriou, M.; Tamoutsidis, E. Benefits from using maize density-independent hybrids. Maydica 2005, 50, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Fasoula, D.A.; Fasoula, V.A. Competitive ability and plant breeding. Plant Breed. Rev. 1997, 14, 89–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakou, D.T.; Fasoulas, A.C. Effects of competition and selection pressure on yield response in winter rye (Secale cereale L.). Euphytica 1985, 34, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M.P.; Acevedo, E.; Sayre, K.D.; Fischer, R.A. Yield potential in modern wheat cultivars: Its association with a less competitive ideotype. Field Crops Res. 1994, 37, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedgley, R.H. An appraisal of the Donald ideotype after 21 years. Field Crops Res. 1991, 26, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.B.; Schaalje, G.B.; Grant, M.N. Height, competition and yield potential in winter wheat. Euphytica 1994, 74, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasoula, D.A. Correlations between auto-, allo- and nill-competition and their implications in plant breeding. Euphytica 1990, 50, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atuahene-Amankwa, G.; Beatie, A.D.; Michaels, T.E.; Falk, D.E. Cropping system evaluation and selection of common bean genotypes for a maize/bean intercrop. Afr. Crop Sci. J. 2004, 12, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeyehu, S.; Simane, B.; Kirkby, R. Genotype x cropping system interaction in climbing beans (Phaseoulus vulgaris L.) grown as sole crop and in association with maize (Zea mays L.). Eur. J. Agron. 2006, 24, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Jenssen, E.S. Evaluating pea and barley cultivars for complementary in intercropping at different levels of soil N availability. Field Crops Res. 2001, 72, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, N.; Smith, M.E. Uncovering corn adaptation to intercrop with bean by selecting for system yield in the intercrop environment. J. Sustain. Agric. 2004, 24, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santalla, M.; Rodiño, A.P.; Casquero, P.A.; de Ron, A.M. Interactions of bush bean intercropped with field and sweet maize. Eur. J. Agron. 2001, 15, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefera, T.; Tana, T. Agronomic performance of sorghum and groundnut cultivars in sole and intercrop cultivation under semiarid conditions. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2002, 188, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzoglou, T.; Tokatlidis, I.S. Decision on germplasm choice to apply breeding within a local population of common vetch is affected by crowding. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 10, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninou, E.G.; Mylonas, I.G.; Tsivelikas, A.; Ralli, P.; Dordas, C.; Tokatlidis, I.S. Wheat landraces are better qualified as potential gene pools at ultraspaced rather than densely grown conditions. Sci. World J. 2014, 957472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokatlidis, I.S. Conservation breeding of elite cultivars. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 2417–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldringer, I.; Paillard, S.; Enjalbert, J.; David, J.L.; Brabant, P. Divergent evolution of wheat populations conducted under recurrent selection and dynamic management. Agronomie 1998, 18, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horneburg, B.; Becker, H.C. Crop Adaptation in On-Farm Management by genesand Conscious Selection: A Case Study with Lentil. Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossowski, S.; Schneeberger, K.; Lucas-Lledó, J.I.; Warthmann, N.; Clark, R.M.; Shaw, R.G.; Weigel, D.; Lynch, M. The rate and molecular spectrum of spontaneous mutations in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 2010, 327, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, R.G.; Byers, D.L.; Darmo, E. Spontaneous mutational effects on reproductive traits of Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 2000, 155, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cullis, C.A. Mechanisms and control of rapid genomic change in flax. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgante, M.; Brunner, S.; Pea, G.; Fengler, K.; Zuccolo, A.; Rafalski, A. Gene duplication and exon shuffling by helitron-like transposons generate intraspecies diversity in maize. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, P.A. Longevity of active transposons in corn breeding populations. Maydica 2008, 53, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Sinapidou, E.; Tokatlidis, I.S. Genetic mechanisms enhancing plant biodiversity. In Genetics, Biofuels and Local Farming System, Sustainable Agriculture Reviews; Lichtfouse, E., Ed.; Springer: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Volume 7, pp. 51–83. [Google Scholar]
- Tsaftaris, A.S.; Polidoros, A.N.; Kapazoglou, A.; Tani, E.; Kovaćevic, N.M. Epigenetics and Plant Breeding. Plant Breed. Rev. 2008, 30, 49–176. [Google Scholar]
- Kidwell, M.G.; Lisch, D. Transposable elements as sources of genomic variation. In Mobile DNA II; Craig, N.L., Craigie, R., Gellert, M., Lambowitz, A.M., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 59–90. [Google Scholar]
- Slotkin, R.K.; Martienssen, R. Transposable elements and the epigenetic regulation of the genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnusamy, V.; Zhu, J.-K. Epigenetic regulation of stress responses in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, R.; O’Malley, R.C.; Tonti-Filippini, J.; Gregory, B.D.; Berry, C.C.; Millar, A.H.; Ecker, J.R. Highly integrated single-base resolution maps of the epigenome in Arabidopsis. Cell 2008, 133, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lolle, S.; Victor, J.L.; Young, J.M.; Pruitt, R.E. Genome-wide non-mendelian inheritance of etra-genomic information in Arabidopsis. Nature 2005, 434, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, N.M.; Stupar, R.M. Allelic variation and heterosis in maize: How do two halves make more than a whole? Genome Res. 2007, 17, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, K.; Boelter, J.; Lolle, S.; Hopkins, M.; Goggi, S.; Palmer, R.G.; Sandhu, D. Evaluation of spontaneous generation of allelic variation in soybean in response to sexual hybridization and stress. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 95, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haun, W.J.; Hyten, D.L.; Xu, W.W.; Gerhardt, D.J.; Albert, T.J.; Richmond, T.; Jeddeloh, J.A.; Jia, G.; Springer, N.M.; Vance, C.P.; et al. The composition and origins of genomic variation among individuals of the soybean reference cultivar Williams 82. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasky, J.R.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Ramu, P.; Deshpande, S.; Hash, C.T.; Bonnette, J.; Juenger, T.E.; Hyma, K.; Acharya, C.; Mitchell, S.E.; et al. Genome-environment associations in sorghum landraces predict adaptive traits. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annicchiarico, P.; Piano, E. Effect of selection under cultivation on morphological traits and yields of Ladino white clover landraces. Genet. Res. Crop Evol. 1997, 44, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatlidis, I.S.; Dordas, C.; Papathanasiou, F.; Papadopoulos, I.; Pankou, C.; Gekas, F.; Ninou, E.; Mylonas, I.; Tzantarmas, C.; Petrevska, J.K.; et al. Improved plant yield efficiency is essential for maize rainfed production. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaftaris, A.S. Apostolos Fasoulas, a laudation. Maydica 2005, 50, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fasoulas, A.C. A moving block evaluation technique for improving the efficiency of pedigree selection. Euphytica 1987, 36, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasoulas, A.C.; Fasoula, V.A. Honeycomb selection designs. Plant Breed. Rev. 1995, 13, 87–139. [Google Scholar]
- Tollenaar, M. Is low plant density a stress in maize? Maydica 1992, 37, 305–311. [Google Scholar]
- Kargiotidou, A.; Chatzivassiliou, E.; Tzantarmas, C.; Tokatlidis, I.S. Seed propagation at low density facilitated the selection of healthy plants to produce seeds with a reduced virus load in a lentil landrace. Seed Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachostergios, N.D.; Lithourgidis, A.S.; Roupakias, D.G. Effectiveness of single-plant selection at low density under organic environment: A field study with lentil. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauromoustakos, A.; Fasoula, V.A.; Thompson, K. Honeycomb designs computing and analysis. In Proceedings of the ENAR Spring Meeting, International Biometric Society, Eastern North American Region, Tampa, FL, USA, 26–29 March 2006; p. 63.
- Fasoula, V.A. Prognostic breeding: A new paradigm for crop improvement. Plant Breed. Rev. 2013, 37, 297–347. [Google Scholar]
- Kargiotidou, A.; Vlachostergios, D.N.; Tzantarmas, C.; Mylonas, I.; Foti, C.; Menexes, G.; Polidoros, A.; Tokatlidis, I.S. Addressing huge spatial heterogeneity induced by virus infections in lentil breeding trials. J. Biol. Res. Thessalon. 2016, 23, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, S.L.; Ceccarelli, S.; Blair, M.W.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Are, A.K.; Rodomiro, O. Landrace germplasm for improving yield and abiotic stress adaptation. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, A.C.; Akar, T.; Baresel, J.P.; Bebeli, P.J.; Bettencourt, E.; Bladenopoulos, K.V.; Czembor, J.H.; Fasoula, D.A.; Katsiotis, A.; Koutis, K.; et al. Cereal landraces for sustainable agriculture. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 237–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzamanidis, S.T.; Lithourgidis, A.S.; Roupakias, D.G. Plant density effect on the individual plant to plant yield variability expressed as coefficient of variation in barley. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2009, 7, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkouk, K.M.; Kumari, S.G. Epidemiology and integrated management of persistently transmitted aphid-borne viruses of legume and cereal crops in West Asia and North Africa. Virus Res. 2009, 141, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokatlidis, I.S. Addressing the yield by density interaction is a prerequisite to bridge the yield gap of rainfed wheat. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2014, 165, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, B.; Araya, H.; Berhe, T.; Edwards, S.; Gujja, B.; Khadka, R.B.; Koma, Y.S.; Sen, D.; Sharif, A.; Styger, E.; Uphoff, N.; et al. The system of crop intensification: Reports from the field on improving agricultural production, food security, and resilience to climate change for multiple crops. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, T.L.; Waters, D.L.; Brooks, L.O.; Henry, R.J. Fragrance in rice (Oryza sativa) is associated with reduced yield under salt treatment. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 68, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, B.S.; Dua, R.P.; Brahmi, P.; Bisht, I.S. On farm conservation of plant genetic resources for food and agriculture. Curr. Sci. 2014, 87, 557–559. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).