Structure of Non-Indigenous Fouling Assemblages and Biocontamination Levels in Portuguese Recreational Marinas Under Different Salinity Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Sample Procedure
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
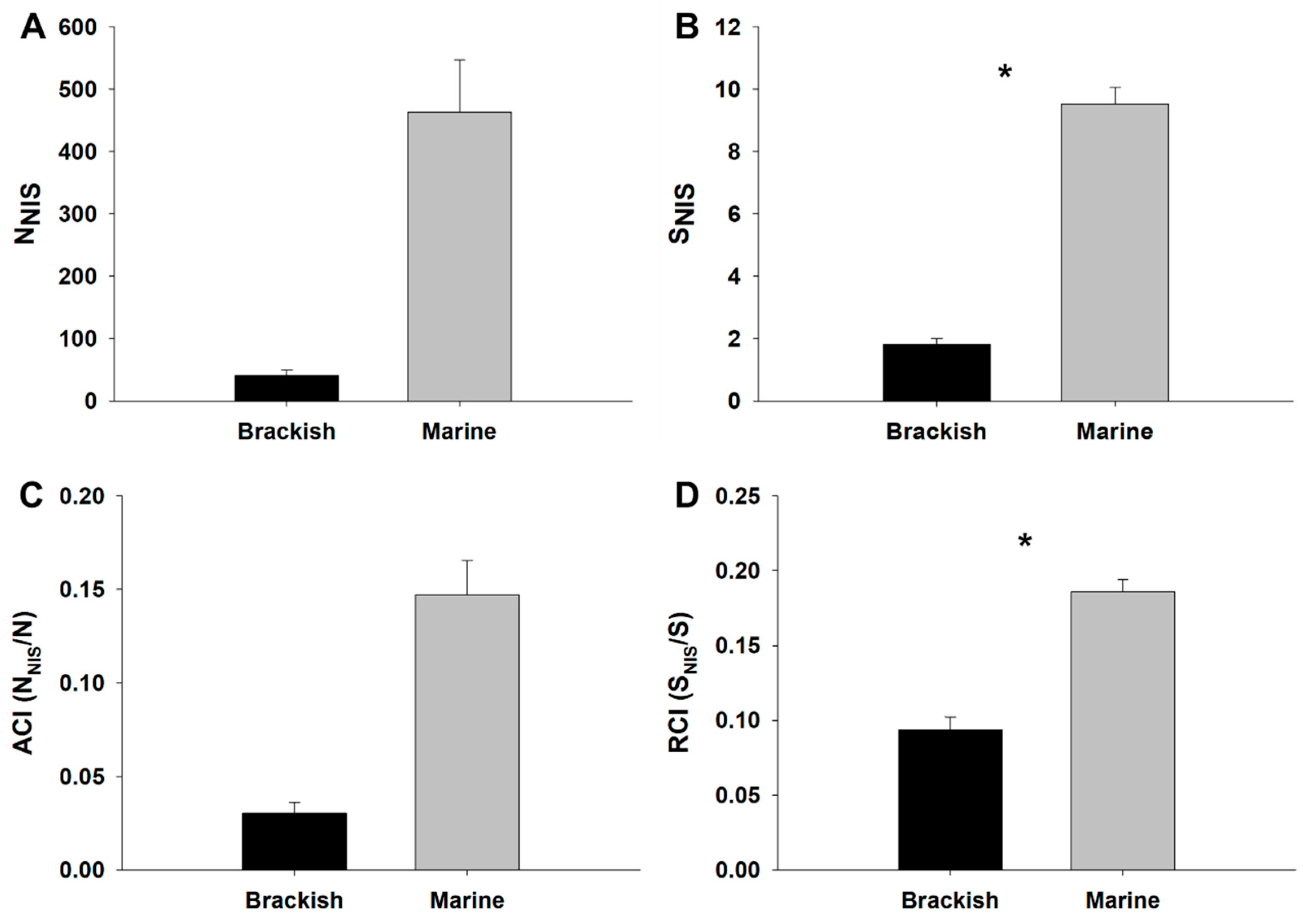
3.1. NIS Abundance, Richness and Biocontamination Levels
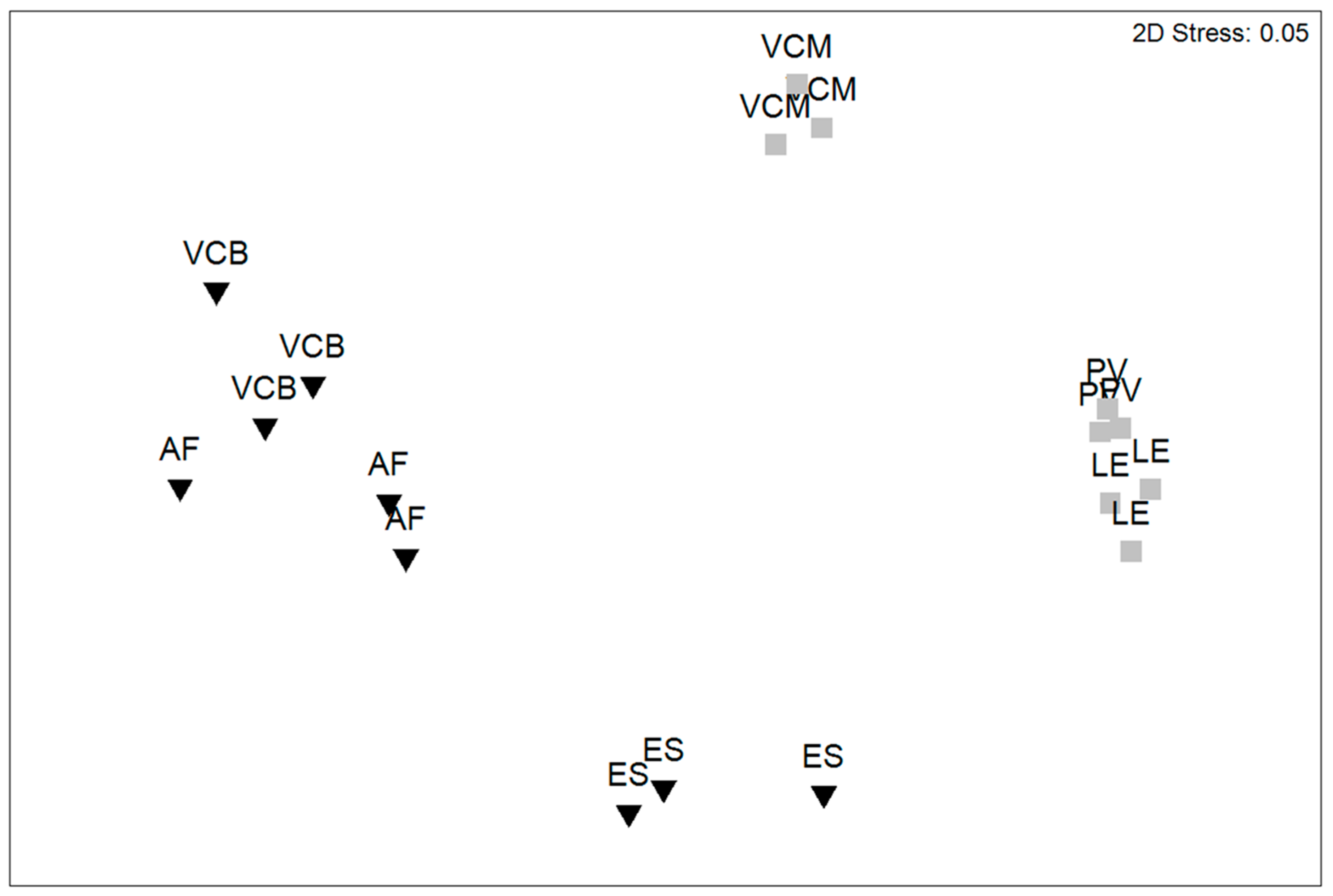
3.2. NIS Assemblage Structure
4. Discussion
4.1. NIS Assemblage Structure
4.2. Biocontamination Levels
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nikolaou, A.; Katsanevakis, S. Marine extinctions and their drivers. Reg. Environ. Change 2023, 23, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G.M.; Fofonoff, P.; Hines, A.H.; Grosholz, E.D. Non-indigenous species as stressors in estuarine and marine communities: Assessing invasion impacts and interactions. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 950–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olenin, S.; Alemany, F.; Cardoso, A.C.; Gollasch, S.; Goulletquer, P.; Lehtniemi, M.; McCollin, T.; Minchin, D.; Miossec, L.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A.; et al. Marine Strategy Framework Directive—Task Group 2. Non-Indigenous Species. EUR 24342; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2010; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebens, H.; Blackburn, T.M.; Dyer, E.E.; Genovesi, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Jeschke, J.M.; Pagad, S.; Pyšek, P.; Winter, M.; Arianoutsou, M.; et al. No saturation in the accumulation of alien species worldwide. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papacostas, K.J.; Rielly-Carroll, E.W.; Georgian, S.E.; Long, D.J.; Princiotta, S.D.; Quattrini, A.M.; Reutter, K.E.; Freestone, A.L. Biological mechanisms of marine invasions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 565, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, A.; Geraldi, N.R.; Lovelock, C.E.; Apostolaki, E.T.; Bennett, S.; Cebrian, J.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Marbà, N.; Martinetto, P.; Pandolfi, J.M.; et al. Global ecological impacts of marine exotic species. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haubrock, P.J.; Turbelin, A.J.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Novoa, A.; Taylor, N.G.; Angulo, E.; Ballesteros-Mejia, L.; Bodey, T.W.; Capinha, C.; Diagne, C.; et al. Economic costs of invasive alien species across Europe. In The Economic Costs of Biological Invasions Around the World; Zenni, R.D., McDermott, S., García-Berthou, E., Essl, F., Eds.; NeoBiota: Sophia, Bulgary, 2017; Volume 67, pp. 153–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyšek, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Simberloff, D.; Bacher, S.; Blackburn, T.M.; Carlton, J.T.; Dawson, W.; Essl, F.; Foxcroft, L.C.; Genovesi, P.; et al. Scientists’ warning on invasive alien species. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 1511–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberloff, D. Maintenance management and eradication of established aquatic invaders. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 2399–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojaveer, H.; Galil, B.S.; Carlton, J.T.; Alleway, H.; Goulletquer, P.; Lehtiniemi, M.; Marchini, A.; Miller, W.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A.; Peharda, M.; et al. Historical baselines in marine bioinvasions: Implications for policy and management. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, G.M.; Carlton, J.T.; Grosholz, E.D.; Hines, A.H. Global invasions of marine and estuarine habitats by non-indigenous species: Mechanisms, extent and consequences. Am. Zool. 1997, 37, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister, J.; Sievers, M.; Bush, F.; Bloecher, N. Biofouling in marine aquaculture: A review of recent research and developments. Biofouling 2019, 35, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Maritime Organization. 2023 Guidelines for the Control and Management of Ships’ Biofouling to Minimize the Transfer of Invasive Aquatic Species, 2024th ed.; International Maritime Organization Guidelines: London, UK, 2024; pp. 1–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke Murray, C.; Pakhomov, E.A.; Therriault, T.W. Recreational boating: A large unregulated vector transporting marine invasive species. Divers. Distrib. 2011, 17, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floerl, O.; Inglis, G.J. Boat harbour design can exacerbate hull fouling. Austral Ecol. 2003, 28, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, N.K.; Dafforn, K.A.; Coleman, M.A.; Johnston, E.L. Environmental and ecological changes associated with a marina. Biofouling 2013, 29, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra-García, J.M.; Navarro-Barranco, C.; Martínez-Laiz, G.; Moreira, J.; Giráldez, I.; Morales, E.; Fernández-Romero, A.; Florido, M.; Ros, M. Assessing environmental pollution levels in marinas. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 144169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, S.D. Floating pontoons create novel habitats for subtidal epibiota. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 247, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulleri, F.; Chapman, M.G. The introduction of coastal infrastructure as a driver of change in marine environments. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 47, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, M.C.; Byers, J.E. Do artificial substrates favor nonindigenous fouling species over native species? J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 342, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafforn, K.A.; Johnston, E.L.; Glasby, T.M. Shallow moving structures promote marine invader dominance. Biofouling 2009, 25, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Laiz, G.; Ulman, A.; Ros, M.; Marchini, A. Is recreational boating a potential vector for non-indigenous peracarid crustaceans in the Mediterranean Sea? A combined biological and social approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempere-Valverde, J.; Castro-Cadenas, M.D.; Guerra-García, J.M.; Espinosa, F.; García-Gómez, J.C.; Ros, M. Buoys are non-indigenous fouling hotspots in marinas regardless of their environmental status and pressure. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, L.; Gomez-Agenjo, M.; Rayon-Viña, F.; Gyraitė, G.; Garcia-Vazquez, E. Alert calling in port areas: Marine litter as possible secondary dispersal vector for hitchhiking invasive species. J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 42, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempesti, J.; Langeneck, J.; Lardicci, C.; Maltagliati, F.; Castelli, A. Cut the rope: Short-term colonization of mooring lines by fouling community within the port of Livorno (Northern Tyrrhenian Sea, Western Mediterranean), focusing on alien species recruitment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 189, 106041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simkanin, C.; Davidson, I.C.; Dower, J.F.; Jamieson, G.; Therriault, T.W. Anthropogenic structures and the infiltration of natural benthos by invasive ascidians. Mar. Ecol. 2012, 33, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airoldi, L.; Turon, X.; Perkol-Finkel, S.; Rius, M. Corridors for aliens but not for natives: Effects of marine urban sprawl at a regional scale. Divers. Distrib. 2025, 21, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindegren, M.; Gabellini, A.P.; Munk, P.; Edelvang, K.; Hansen, F.T. Identifying key processes and drivers affecting the presence of non-indigenous marine species in coastal waters. Biol. Invasions 2022, 24, 2835–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebaane, S.; Freestone, A.L.; Des Pérez, A.; Sempere-Valverde, J.; Chainho, P.; Gama Monteiro, J.; Canning-Clode, J. Predation facilitates the abundance of biofouling non-indigenous species in estuarine marinas in NE Atlantic Portugal. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marraffini, M.L.; Geller, J.B. Species richness and interacting factors control invasibility of a marine community. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20150439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavira-O’Neill, K.; Guerra-García, J.M.; Moreira, J.; Ros, M. Mobile epifauna of the invasive bryozoan Tricellaria inopinata: Is there a potential invasional meltdown? Mar. Biodivers. 2018, 48, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-García, J.M.; Ruiz-Velasco, S.; Navarro-Barranco, C.; Moreira, J.; Angulo, G.; García-Domínguez, R.; Amengual, J.; Saenz-Arias, P.; López-Fé, C.M.; Martínez-Pita, I.; et al. Facilitation of macrofaunal assemblages in marinas by the habitat-forming invader Amathia verticillata (Bryozoa: Gymnolaemata) across a spatiotemporal scale. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 193, 106256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, E.A.; Almeida, A.C.; Nogueira, M.M.; Vieira, L.M. Effects of substratum type and orientation on the recruitment of bryozoans in an artificial area of the Western Atlantic. Biofouling 2023, 39, 748–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, N.; Bishop, M.; Bugnot, A.B.; Foster-Thorpe, C.; Herbert, B.; Hoet, A.S.; Mayer-Pinto, M.; Nakagawa, S.; Sherman, C.D.H.; Vozzo, M.L.; et al. Influence of habitat features on the colonisation of native and non-indigenous species. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 198, 106498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piola, R.F.; Johnston, E.L. Pollution reduces native diversity and increases invader dominance in marine hard-substrate communities. Divers. Distrib. 2008, 14, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, J.A.; Chang, A.L.; Ruiz, G.M. Aquatic pollution increases the relative success of invasive species. Biol. Invasions 2011, 13, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke Murray, C.; Gartner, H.; Gregr, E.J.; Chan, K.; Pakhomov, E.; Therriault, T.W. Spatial distribution of marine invasive species: Environmental, demographic and vector drivers. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, J.; Marchini, A.; Gazzola, F.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A. The influence of recreational boat traffic in the introduction of non-indigenous fouling species in three Ligurian marinas (Mediterranean Sea, Italy). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 303, 108810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, K.B.; Ng, C.S.L.; Wu, B.; Toh, T.C.; Cheo, P.R.; Tun, K.; Chou, L.M. Spatial variability of epibiotic assemblages on marina pontoons in Singapore. Urban Ecosyst. 2017, 20, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-García, J.M.; Navarro-Barranco, C.; Ros, M.; Sedano, F.; Espinar, R.; Fernández-Romero, A.; Martínez-Laiz, G.; Cuesta, J.A.; Giráldez, I.; Morales, E.; et al. Ecological quality assessement of marinas: An integrative approach combining biological and environmental data. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Velasco, S.; Ros, M.; Guerra-García, J.M. Estuarine versus coastal marinas: Influence of the habitat on the settlement of non-indigenous peracarids on the polychaete Sabella spallanzanii (Gmelin, 1791). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, H.; Keppel, E.; Chang, A.L.; Ruiz, G.M. Invasions in marine communities: Contrasting species richness and community composition across habitats and salinity. Estuaries Coast. 2018, 41, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, I.; Berecibar, E.; Castro, N.; Costa, J.L.; Frias, P.; Henriques, F.; Moreira, P.; Oliveira, P.M.; Silva, G.; Chainho, P. Assessment of the colonization and dispersal success of non-indigenous species introduced in recreational marinas along the estuarine gradient. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLusky, D.S.; Elliott, M. The Estuarine Ecosystem: Ecology, Threats and Management, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 1–216. [Google Scholar]
- Veiga, P.; Redondo, W.; Sousa-Pinto, I.; Rubal, M. Relationship between structure of macrobenthic assemblages and environmental variables in shallow sublittoral soft bottoms. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 129, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remane, A.; Schlieper, C. Biology of Brackish Water; Wiley Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 1–372. [Google Scholar]
- Van Diggelen, A.D.; Montagna, P.A. Is salinity variability a benthic disturbance in estuaries? Estuaries Coast. 2016, 39, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, W.J. Exotic invaders of the meso-oligohaline zone of estuaries in the Netherlands: Why are there so many? Helgol. Meeresunters. 1999, 52, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paavola, M.; Olenin, S.; Leppäkoski, E. Are invasive species most successful in habitats of low native species richness across European brackish water seas? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 64, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehring, S. Four arguments why so many alien species settle into estuaries, with special reference to the German river Elbe. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2006, 60, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, F.; Barco, A.; Chen, Y.; Mirzajani, A.; Chan, F.T.; Lauringson, V.; Baltazar-Soares, M.; Zhan, A.; Bailey, S.A.; Javidpour, J.; et al. Is salinity an obstacle for biological invasions? Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 2708–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boets, P.; Lock, K.; Goethals, P.L. Assessing the importance of alien macro-Crustacea (Malacostraca) within macroinvertebrate assemblages in Belgian coastal harbours. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2012, 66, 75–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, V.; Giesler, R.J.; Wilson, A.M.W.; Nall, C.R.; Cook, E.J. Identifying the physical features of marina infrastructure associated with the presence of non-native species in the UK. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nall, C.R.; Guerin, A.J.; Cook, E.J. Rapid assessment of marine non-native species in northern Scotland and a synthesis of existing Scottish records. Aquat. Invasions 2015, 10, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtiniemi, M.; Ojaveer, H.; David, M.; Galil, B.; Gollasch, S.; McKenzie, C.; Minchin, D.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A.; Olenin, S.; Pederson, J. Dose of truth—Monitoring marine non-indigenous species to serve legislative requirements. Mar. Policy 2015, 54, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, M.; Keppel, E.; Marchini, A.; Repetto, M.F.; Ruiz, G.M.; Ferrario, J.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A. Monitoring non-indigenous species in port habitats: First application of a standardized North American protocol in the Mediterranean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 700730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Marine Environmental Policy (Marine Strategy Framework Directive). 2008. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2008/56/oj (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Convention on Biological Diversity. Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011–2020, Including Aichi Biodiversity Targets. Convention on Biological Diversity (Montreal). 2010. Available online: https://www.cbd.int/sp/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- European Union. Regulation (EU) Nº 1143/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 October 2014 on the Prevention and Management of the Introduction and Spread of Invasive Alien Species. 2014. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2014/1143/2019-12-14 (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Arbačiauskas, K.; Semenchenko, V.; Grabowski, M.; Leuven, R.S.E.W.; Paunović, M.; Son, M.O.; Csányi, B.; Gumuliauskaitė, S.; Konopacka, A.; Nehring, S.; et al. Assessment of biocontamination of benthic macroinvertebrate communities in European inland waterways. Aquat. Invasions 2008, 3, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, V.E.; Alexandrov, B.; Arbačiauskas, K.; Binimelis, R.; Copp, G.H.; Grabowski, M.; Lucy, F.; Leuven, R.S.E.W.; Nehring, S.; Paunović, M.; et al. Assessing the risks of aquatic species invasions via European inland waterways: From concepts to environmental indicators. IEAM 2009, 5, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çinar, M.E.; Bakir, K. ALien Biotic IndEX (ALEX)—A new index for assessing impacts of alien species on benthic communities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 87, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNeil, C.; Briffa, M.; Leuven, R.S.E.W.; Gell, F.R.; Selman, R. An appraisal of a biocontamination assessment method for freshwater macroinvertebrate assemblages; a practical way to measure a significant biological pressure? Hydrobiologia 2010, 638, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempesti, J.; Langeneck, J.; Romani, L.; Garrido, M.; Lardicci, C.; Maltagliati, F.; Castelli, A. Harbour type and use destination shape fouling community and non-indigenous species assemblage: A study of three northern Tyrrhenian port systems (Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, W.G. The Comparison of Percentages in Matched Samples. Biometrika 1950, 37, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, A.J. Experiments in Ecology: Their Logical Design and Interpretation Using Analysis of Variances; Cambridge University Press: Sydney, Australia, 1997; pp. 1–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Somerfield, P.J.; Chapman, M.G. On resemblance measures for ecological studies, including taxonomic dissimilarities and a zero-adjusted Bray–Curtis coefficient for denuded assemblages. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 330, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Gorley, R.N.; Clarke, K.R. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2008; pp. 1–214. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. Distance-based tests for homogeneity of multivariate dispersions. Biometrics 2006, 62, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturrock, K.; Rocha, J. A multidimensional scaling stress evaluation table. Field Methods 2000, 12, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Austral. Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasby, T.M.; Connell, S.D.; Holloway, M.G.; Hewitt, C.L. Nonindigenous biota on artificial structures: Could habitat creation facilitate biological invasions? Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, J.C.; Viard, F.; González Sepúlveda, E.; Díaz, C.; Neira Hinojosa, J.; Pérez Araneda, K.; Silva, F.; Brante, A. Habitat type drives the distribution of non-indigenous species in fouling communities regardless of associated maritime traffic. Divers. Distrib. 2020, 26, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenz-Arias, P.; Navarro-Barranco, C.; Ros, M.; Moreira, J.; Guerra-García, J.M. Exploring biocontamination in associated macrofaunal assemblages in marinas: Soft bottoms vs artificial hard substrate. Where and what to look for? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Outinen, O.; Puntila-Dodd, R.; Barda, I.; Brzana, R.; Hegele-Drywa, J.; Kalnina, M.; Lindqvist, A.; Normant-Saremba, M.; Ścibik, M.; Strake, S.; et al. The role of marinas in the establishment and spread of non-indigenous species in Baltic Sea fouling communities. Biofouling 2021, 37, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chainho, P.; Costa, J.L.; Chaves, M.L.; Lane, M.F.; Dauer, D.M.; Costa, M.J. Seasonal and spatial patterns of distribution of subtidal benthic invertebrate communities in the Mondego River, Portugal—A poikilohaline estuary. In Marine Biodivers; Martens, K., Queiroga, H., Cunha, M.R., Moreira, M.H., Quintino, V., Rodrigues, A.M., Serôdio, J., Warwick, R.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubal, M.; Veiga, P.; Maldonado, C.; Torres, C.; Moreira, J. Population attributes and traits of Siphonaria pectinata (Mollusca: Siphonariidae) in range-edge and non range-edge populations at its Eastern Atlantic northern distribution boundary. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2015, 471, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ysebaert, T.; Meire, P.; Maes, D.; Buijs, J. The benthic macrofauna along the estuarine gradient of the Schelde estuary. Neth. J. Aquat. Ecol. 1993, 27, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, M.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; Guerra-García, J.M. Environmental factors modulating the extent of impact in coastal invasions: The case of a widespread invasive caprellid (Crustacea: Amphipoda) in the Iberian Peninsula. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 98, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, R.M.; Clarke, K.R. Increased variability as a symptom of stress in marine communities. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1993, 172, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, A.; Domínguez, J.; Novais, J.M.; Ramil, F. First record of Cordylophora caspia (Hydrozoa: Cnidaria) in the Tagus estuary, central Portugal. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2013, 6, e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyer, T.; Morais, P.; Amorim, K.; Leitão, F.; Martins, F.; Teodósio, M.A. On the presence of the Ponto-Caspian hydrozoan Cordylophora caspia (Pallas, 1771) in an Iberian estuary: Highlights on the introduction vectors and invasion routes. Bioinvasions Rec. 2017, 6, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Haaren, T.; Soors, J. Sinelobus stanfordi (Richardson, 1901): A new crustacean invader in Europe. Aquat. Invasions 2009, 4, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, J.; Reverter-Gil, O. Non-indigenous species of Bryozoa from anthropogenic habitats in the Bay of Cádiz (South Iberian Peninsula). Mar. Biodivers. 2024, 54, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamber, R.N. The marine fauna and flora of the Isles of Scilly. Tanaidacea (Crustacea: Peracarida). J. Nat. Hist. 2011, 45, 1801–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pasqua, M.; Bernarello, V.; Esquete, P.; Cornello, M.; Cacciatore, F.; Oselladore, F.; Ponis, E.; Boscolo Brusà, R. First records of the tanaid Species Zeuxo holdichi and Apseudopsis tridens (Crustacea: Peracarida) from the Venice Lagoon (Italy, Northern Adriatic Sea). Thalassas 2022, 38, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.R.; Sorbe, J.C.; Moreira, M.H. Spatial and seasonal changes of brackish peracaridan assemblages and their relation to some environmental variables in two tidal channels of the Ria de Aveiro (NW Portugal). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 190, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Esquete, P.; Moreira, J.; Troncoso, J.S. Peracarid assemblages of Zostera meadows in an estuarine ecosystem (O Grove inlet, NW Iberian Peninsula): Spatial distribution and seasonal variation. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2011, 65, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Foveau, A.; Pezy, J.P.; Bauxi, N.; Baffreau, A.; Bachelet, Q.; Chouquet, B.; Dancie, C.; Ruellet, T.; Dauvin, J.C. Range extension of the tanaidid Zeuxo holdichi (Bamber, 1990) along the northern coasts of France? Cah. Biol. Mar. 2018, 59, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederson, J.; Carlton, J.T.; Bastidas, C.; David, A.; Grady, S.; Green-Gavrielidis, L.; Hobbs, N.V.; Kennedy, C.; Knack, J.; McCuller, M.; et al. 2019 Rapid assessment survey of marine bioinvasions of Southern New England and New York, USA, with an overview of new records and range expansions. Bioinvasions Rec. 2021, 10, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter-Gil, O.; Souto, J. Watersiporidae (Bryozoa) in Iberian waters: An update on alien and native species. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverter-Gil, O.; Souto, J.; Fernández-Pulpeiro, E. Annotated checklist of recent marine Bryozoa from continental Portugal. NACC 2014, 21, 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Tempesti, J.; Langeneck, J.; Maltagliati, F.; Castelli, A. Macrobenthic fouling assemblages and NIS success in a Mediterranean port: The role of use destination. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, J.; Rosso, A.; Marchini, A.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A. Mediterranean non-indigenous bryozoans: An update and knowledge gaps. Biodivers. Conserv. 2018, 27, 2783–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, J.; Caronni, S.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A.; Marchini, A. Role of commercial harbours and recreational marinas in the spread of non-indigenous fouling species. Biofouling 2017, 33, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenz-Arias, P.; Navarro-Barranco, C.; Guerra-García, J.M. Influence of environmental factors and sessile biota on vagile epibionts: The case of amphipods in marinas across a regional scale. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2022, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerckhof, F.; Haelters, J.; Gollasch, S. Alien species in the marine and brackish ecosystem: The situation in Belgian waters. Aquat. Invasions 2007, 2, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydar. D. What is natural? The scale of cryptogenesis in the North Atlantic Ocean. Divers. distrib. 2012, 18, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chainho, P.; Fernandes, A.; Amorim, A.; Ávila, S.P.; Canning-Clode, J.; Castro, J.J.; Costa, A.C.; Costa, J.L.; Cruz, T.; Gollasch, S.; et al. Non-indigenous species in Portuguese coastal areas, coastal lagoons, estuaries and islands. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 167, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.R.; Andersen, P.; Andersen, N.R.; Bruhn, A.; Buur, H.; Carl, H.; Jakobsen, H.; Jaspers, C.; Lundgreen, K.; Nielsen, R.; et al. Reviewing introduction histories, pathways, invasiveness, and impact of non-indigenous in Danish marine waters. Diversity 2023, 15, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnasri-Afifi, I.; Zribi, I.; Abdelkader, N.; Charfi-Cheikhrouha, F.; Zakhama-Sraieb, R. Rapid assessment survey of non-indigenous and cryptogenic species in Tunisian marinas. BioInvasions Rec. 2024, 13, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryland, J.S.; Bishop, J.D.; De Blauwe, H.; El Nagar, A.; Minchin, D.; Wood, C.A.; Yunnie, A.L. Alien species of Bugula (Bryozoa) along the Atlantic coasts of Europe. Aquatic Invasions 2011, 6, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalhosa, P.; Souto, J.; Canning-Clode, J. Diversity of Bugulidae (Bryozoa, Cheilostomata) colonizing artificial substrates in the Madeira archipelago (NE Atlantic Ocean). Helgol. Mar. Res. 2017, 71, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrynda, P.E.J.; Fairall, V.R.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A.; d’Hondt, J.L. The distribution, origins and taxonomy of Tricellaria inopinata d’Hondt and Occhipinti Ambrogi, 1985, an invasive bryozoan new to the Atlantic. J. Nat. Hist. 2000, 34, 1993–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, E.; Richter, A. Non-indigenous species (NIS) of polychaetes (Annelida: Polychaeta) from the Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts of the Iberian Peninsula: An annotated checklist. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2017, 71, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, M.W. (1947) Establishment of an immigrant barnacle in British coastal waters. Nat. 1947, 159, 501–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, P.Y. Checklist of Cryptogenic and Alien Crustacea of the European Atlantic Coast. In In the Wrong Place—Alien Marine Crustaceans: Distribution, Biology and Impacts. Invading Nature; Galil, B., Clark, P., Carlton, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 345–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerckhof, F.; Cattrijsse, A. Exotic Cirripedia (Balanomorpha) from buoys off the Belgian coast. Mar. Biodivers. 2001, 31, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, G.I. A review of the amphipod genus Corophium, with notes on the British species. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1937, 21, 589–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revanales, T.; Guerra-García, J.M.; Ros, M. Colonization dynamics of potential stowaways inhabiting marinas: Lessons from caprellid crustaceans. Water 2022, 14, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, A.; Cardeccia, A. Alien amphipods in a sea of troubles: Cryptogenic species, unresolved taxonomy and overlooked introductions. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenetos, A.; Çinar, M.E.; Crocetta, F.; Golani, D.; Rosso, A.; Servello, G.; Shenkar, N.; Turon, X.; Verlaque, M. Uncertainties and validation of alien species catalogues: The Mediterranean as an example. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 191, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalhosa, P.; Gestoso, I.; Rocha, R.M.; Lambert, G.; Canning-Clode, J. Ascidian biodiversity in the shallow waters of the Madeira Archipelago: Fouling studies on artificial substrates and new records. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 43, 101672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.H.; Davis, M.E. Styela clava (Tunicata: Ascidiacea) - a new addition to the fauna of the Portuguese coast. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2005, 85, 403–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.H.; Lützen, J.; Davis, M.E. The spread of Styela clava Herdman, 1882 (Tunicata, Ascidiacea) in European waters. Aquat. Invasions 2007, 2, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
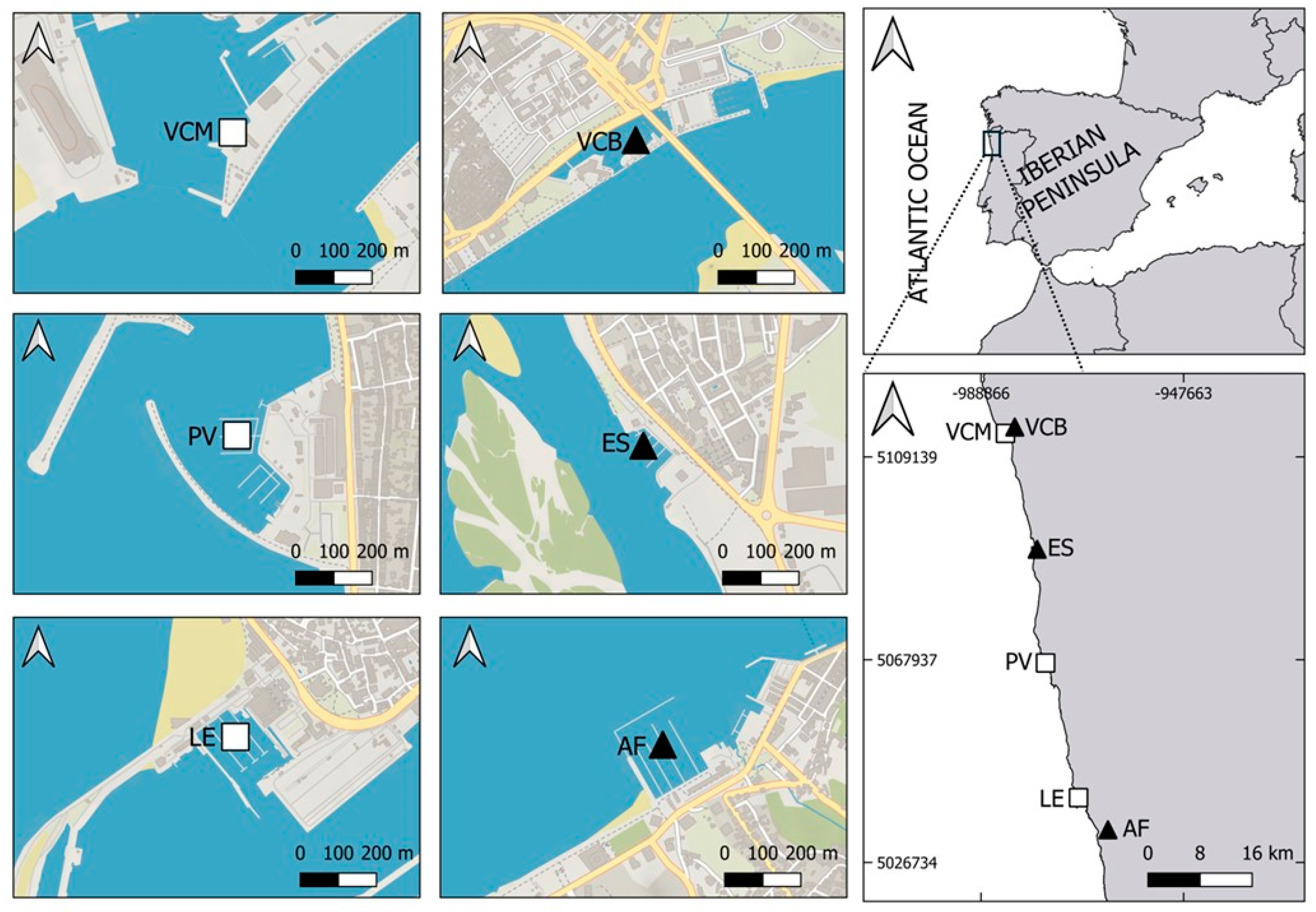

| Habitat | Marina | Coordinates | Salinity (psu) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brackish | Afurada | 41°08′32.7″ N 8°39′03.7″ W | 7.37–7.94 |
| Esposende | 41°31′37.2″ N 8°46′49.1″ W | 4.18–4.71 | |
| Viana do Castelo | 41°41′38.8″ N 8°49′17.9″ W | 19.05–20.12 | |
| Marine | Leça da Palmeira | 41°11′11.5″ N 8°42′18.0″ W | 31.9–32.7 |
| Póvoa do Varzim | 41°22′16.7″ N 8°45′54.0″ W | 34.4–34.6 | |
| Viana do Castelo | 41°41′06.4″ N 8°50′18.0″ W | 33.8–34.1 |
| Source of Variation | df | NNIS | SNIS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | F | MS | F | ||
| Habitat (Ha) | 1 | 3,211,000.34 | 2.77 | 1073.39 | 14.06 * |
| Marina (Ma)(Ha) | 4 | 1,160,390.30 | 27.98 *** | 76.36 | 30.38 *** |
| Site (Si) (Ha × Ma) | 12 | 41,466.57 | 0.58 | 2.51 | 1.86 |
| Residual | 54 | 71,242.75 | 1.35 | ||
| Total | 71 | ||||
| Transformation | none | ||||
| Cochran’s test | C = 0.67 | p < 0.01 | C = 0.23 | ns | |
| Source of Variation | df | ACI | RCI | SBCI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | F | MS | F | MS | F | ||
| Habitat (Ha) | 1 | 0.25 | 3.14 | 0.15 | 10.18 * | 25.68 | 20.78 * |
| Marina (Ma)(Ha) | 4 | 0.08 | 130.80 *** | 0.02 | 11.75 *** | 1.24 | 7.42 ** |
| Site (Si) (Ha × Ma) | 12 | <0.01 | 0.23 | <0.01 | 0.66 | 0.17 | 0.40 |
| Residual | 54 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.41 | |||
| Total | 71 | ||||||
| Transformation | none | none | none | ||||
| Cochran’s test | C = 0.31 | p < 0.05 | C = 0.28 | ns | C = 0.27 | ns | |
| Source of Variation | df | MS | Pseudo-F | Unique Permutations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Habitat (Ha) | 1 | 76,213 | 3.6041 * | 10 |
| Marina (Ma)(Ha) | 4 | 21,146 | 14.416 ** | 998 |
| Site (Si) (Ha × Ma) | 12 | 1466.8 | 2.3584 ** | 998 |
| Residual | 54 | 621.95 | ||
| Total | 71 |
| Species | Average Abundance | δi | δi% | δi/SD(δi) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marine | Brackish | ||||
| Zeuxo holdichi | 12.04 | 2.36 | 19.38 | 20.61 | 1.41 |
| Amathia gracillima | 4.99 | 0 | 11.4 | 12.13 | 2.37 |
| Apocorophium acutum | 5.71 | 0 | 9.2 | 9.79 | 1.18 |
| Watersipora subatra | 5.17 | 0.03 | 9.06 | 9.64 | 2.21 |
| Austrominius modestus | 2.29 | 0.23 | 6.73 | 7.15 | 0.94 |
| Monocorophium sextonae | 1.96 | 0 | 6.24 | 6.64 | 0.95 |
| Cordylophora caspia | 0 | 2.24 | 5.79 | 6.16 | 0.74 |
| Monocorophium acherusicum | 1.64 | 0.06 | 4.85 | 5.15 | 0.84 |
| Tricellaria inopinata | 2.66 | 0 | 4.5 | 4.79 | 0.91 |
| Diplosoma listerianum | 1.83 | 0 | 2.76 | 2.94 | 1.14 |
| Sinelobus stanfordi | 0 | 1.05 | 2.72 | 2.9 | 0.55 |
| Botryllus schlosseri | 1.62 | 0 | 2.62 | 2.79 | 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Gutiérrez, J.; Rubal, M.; Sampaio, L.; Moreira, J.; Ramil, F.; Sousa-Pinto, I.; Veiga, P. Structure of Non-Indigenous Fouling Assemblages and Biocontamination Levels in Portuguese Recreational Marinas Under Different Salinity Conditions. Diversity 2025, 17, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040245
Fernández-Gutiérrez J, Rubal M, Sampaio L, Moreira J, Ramil F, Sousa-Pinto I, Veiga P. Structure of Non-Indigenous Fouling Assemblages and Biocontamination Levels in Portuguese Recreational Marinas Under Different Salinity Conditions. Diversity. 2025; 17(4):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040245
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Gutiérrez, Jesús, Marcos Rubal, Leandro Sampaio, Juan Moreira, Fran Ramil, Isabel Sousa-Pinto, and Puri Veiga. 2025. "Structure of Non-Indigenous Fouling Assemblages and Biocontamination Levels in Portuguese Recreational Marinas Under Different Salinity Conditions" Diversity 17, no. 4: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040245
APA StyleFernández-Gutiérrez, J., Rubal, M., Sampaio, L., Moreira, J., Ramil, F., Sousa-Pinto, I., & Veiga, P. (2025). Structure of Non-Indigenous Fouling Assemblages and Biocontamination Levels in Portuguese Recreational Marinas Under Different Salinity Conditions. Diversity, 17(4), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040245










