Abstract
Freshwater turtles comprise 81% of all chelonian species despite freshwater systems only occupying 1% of the earth’s surface, and they are commonly exploited as pets and food resources. This contact between humans and turtles may put both sides at risk of disease transmission. Additionally, human impact on ecosystems can cause disease outbreaks in turtle populations. In this review, we focused on disease agents affecting freshwater turtles, intending to contribute to conservation and public health efforts. We analysed 423 articles and noted a post-SARS-COVID-19 peak, with most research originating from Asia, North America, and Europe. Emydidae was the most frequently studied family, and there was also a bias towards adults, live specimens, and native species. Since most of the studied turtles were wild-caught, we recommend that captive turtles should also be thoroughly studied since they can transmit diseases to other turtles and humans. We registered 2104 potential disease-causing agents, with Platyhelminthes dominating within Animalia, while Proteobacteria dominated bacterial agents. Viruses’ representation was low, highlighting gaps in reptile virology. Fungi, Chromista, and Protozoa were also underrepresented, but this is changing with the development of molecular tools. This synthesis serves as a foundation for targeted health assessments, conservation strategies, and future research, essential to mitigate ecosystem and public health threats.
1. Introduction
Freshwater turtles (also called terrapins or pond turtles) are chelonian species that spend part or all of their life in freshwater [1]. Worldwide, there are more than 360 described species of chelonians [2], of which approximately 81% are freshwater species, so this group constitutes a large majority of chelonian diversity [1]. Similar to other groups, freshwater turtle species diversity is very high despite freshwater systems only occupying 1% of the planet. Freshwater turtles are present on all continents except in Antarctica, but not all families are evenly distributed throughout the globe [1].
Freshwater turtles are exploited by humans in a variety of ways. First of all, freshwater turtles are used as a food resource by some populations in Asia, South America, and Africa. Various human communities hunt, sell, and eat wild freshwater turtles, causing notable conservation impacts [3,4,5]. Turtles, along with other animals, are sold in wet markets for human consumption, which may pose a zoonotic transmission risk as diverse pathogens in the turtles may originate disease outbreaks [3]. Additionally, some freshwater turtles, particularly soft-shelled turtles, farm-raised to be sold for their meat, also have the potential to transmit diseases [6,7].
Freshwater turtles are also widely used as exotic pets. Chelonians are one of the most traded groups of vertebrates, with Geoemydidae, Testudinidae, and Emydidae being the most representative families [8]. These turtles may escape or be intentionally released from captivity [9], which affects the disease dynamics in native species and humans through the introduction of new diseases or by altering the richness and quantity of hosts, vectors, and disease-causing agents [10]. The Salmonella Lignieres, 1900 outbreaks in the United States which originated from small pet freshwater turtles, demonstrate how a disease that is at balance with its asymptomatic host can affect the human population [11].
Apart from food and pet ownership, freshwater turtles are also used in traditional medicine despite the lack of evidence on their efficacy [12,13]. These traditional medicine practices have serious implications for the conservation of wild chelonians [12,13], as well as in disease transmission dynamics both to turtles and to humans [14,15]. Finally, although less frequently, freshwater turtles are also used in magic/religious ceremonies and for ornamental purposes [12].
Anthropogenic changes to ecosystems may also have cascading effects on turtle populations. Zhang et al. [16] proposed that the increase in water temperature may have contributed to a massive outbreak of the Bellinger River Turtle virus, which caused major population declines. This demonstrates the importance of identifying and surveying disease-causing pathogens in freshwater turtles, even the ones that currently do not cause any evident disease or illness to humans or other animals.
The aim of this article was to review current knowledge regarding disease-causing agents such as parasites, fungi, bacteria, and viruses, reported from freshwater turtle hosts. This is essential information so that health assessment protocols, disease monitoring programs, conservation programs, and public health agents may direct their efforts to the most commonly identified pathogens to monitor and control the transmission of wildlife diseases. At the same time, we aim to identify knowledge gaps, both in terms of understudied host species, geographic regions, and parasite groups, which may be addressed in future studies.
2. Methods
In order to evaluate the diseases and parasites reported in freshwater chelonians, we conducted a literature search employing Google scholar, Scopus and Web of Science by combining the following search words: “freshwater turtle” AND “disease” AND “bacteria”; “freshwater turtle” AND “disease” AND “virus”; “freshwater turtle” AND “disease” AND “fungus”; “freshwater turtle” AND “disease” AND “fungi”; “freshwater turtle” AND “disease” AND “parasite”; “freshwater turtle” AND “disease” AND “protozoa”; “pond turtle” AND “disease” AND “bacteria”; “pond turtle” AND “disease” AND “virus”; “pond turtle” AND “disease” AND “fungus”; “pond turtle” AND “disease” AND “fungi”; “pond turtle” AND “disease” AND “parasite”; “pond turtle” AND “disease” AND “protozoa”; “terrapin” AND “disease” AND “bacteria”; “terrapin” AND “disease” AND “virus”; “terrapin” AND “disease” AND “fungus”; “terrapin” AND “disease” AND “fungi”; “terrapin” AND “disease” AND “parasite”; “terrapin” AND “disease” AND “protozoa”; “freshwater turtle” AND “parasite”; “freshwater turtle” AND “protozoa”; “pond turtle” AND “parasite”; “pond turtle” AND “protozoa”; “terrapin” AND “parasite”; “terrapin” AND “protozoa.
We retrieved all documents published until December 2023. Afterwards, we excluded all documents that were not published in peer-reviewed journals, written in English, and/or where the disease was not caused by parasites, fungi, bacteria, or viruses—for example, those caused by nutrition deficiency (Figure 1). From the remaining articles, we extracted the following data: year of publication, sampling location (continent and country), host, disease-causing agent, host age (juvenile, adult, or both), turtle state (dead, alive, or both), the presence or absence of symptoms, origin (wild or captive), and native or non-native host in that location. Regarding the symptoms, we classified them as present when at least one individual had symptoms. The host species were classified as native when a part of their natural distribution occurred in the country studied, even if in some cases they might be introduced in other areas of the country. In the retrieved articles, some of the information was not available; in such cases that information was classified as “unspecified”. After extracting all of this information, a second screening was performed where all articles that did not specify at least the host genus and/or the pathogen family were excluded, as well as the articles that did not confirm the infection or that did not include any freshwater chelonians (Figure 1).
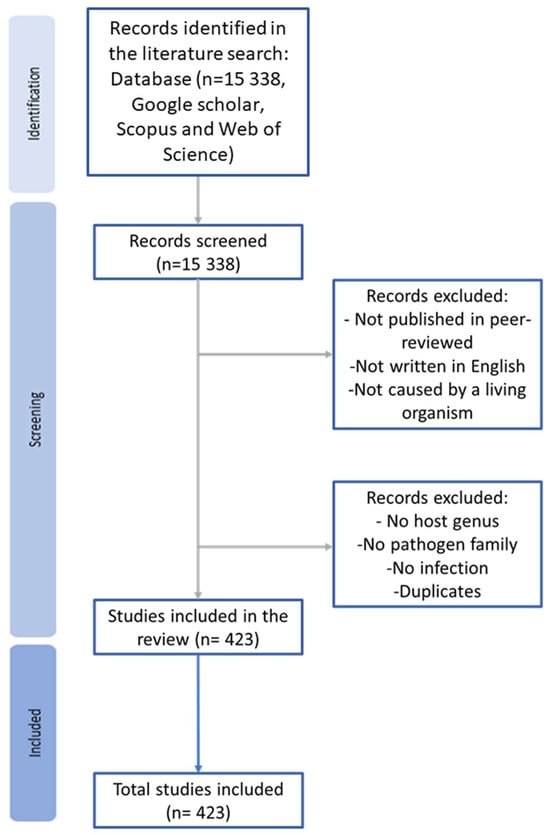
Figure 1.
The process of the literature review, which includes three different stages: identification, screening, and inclusion. At the identification stage, all Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science search results were gathered. Next, at the screening stage, all search results that did not meet the criteria were excluded. In the final analyses, only 423 were included.
We then completed and updated the taxonomic information using the Current ICTV Taxonomy Release (https://ictv.global/taxonomy, accessed on 8 January 2024) for viruses, the Global Catalogue of Microorganisms (https://gcm.wdcm.org/, accessed on 8 January 2024) for bacteria, the MycoBank (https://www.mycobank.org/, accessed on 9 January 2024) for fungus, and the Catalogue of Life (https://www.catalogueoflife.org/, accessed on 10 January 2024) for the remaining disease-causing agents. We also updated the taxonomic information of the freshwater chelonians following the Reptile Database (http://www.reptile-database.org/, accessed on 11 January 2024).
All calculations were made in Microsoft Excel®, statistical analysis was made in R version 4.2.2, and all figures and maps were produced in Datawrapper. The Wilcoxon signed-rank paired test was used to compare the number of native and non-native turtles for the families reported in the articles.
3. Timeline and Global Distribution
In total, we assessed 423 articles that included a positive infection in freshwater chelonian by virus, bacteria, fungus, and other parasites. Most records occurred after the turn of the century, especially after the SARS-COVID-19 outbreaks (Figure 2). The SARS-COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on the social and scientific perspective of wildlife’s role in the emergence of zoonotic diseases, which led to a notable increase in wildlife disease publications [17]. Despite the potential impact of the SARS-COVID-19 outbreak on disease research, others have found an increase in the number of scientific articles concerning wildlife disease, with particular emphasis on diseases affecting mammals [18]. Comparatively to mammals, the number of publications on reptile diseases remains low [18] although reptiles, and specifically freshwater turtles, are well-known sources of zoonotic diseases [19,20,21,22].
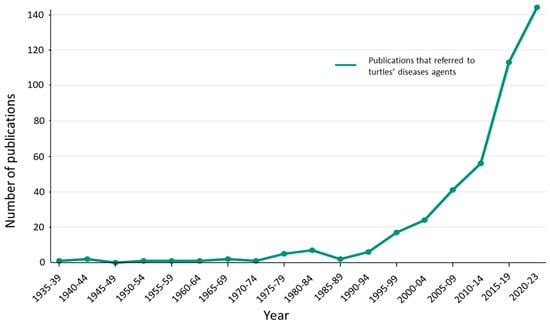
Figure 2.
Yearly distribution of publications involving disease agents in freshwater turtles.
From the 423 articles, we retrieved 558 locations across all continents except for Antarctica (Figure 3). The most represented continent was Asia (n = 136), followed by North America (n = 133) and Europe (n = 114). In contrast, the least represented continents were Oceania (n = 50) and Africa (n = 50). Although most records came from Asia, most countries have less than 10 studies, with the exception of China (n = 24), Malaysia (n = 24), India (n = 16), Vietnam (n=12), and Iran (n=11). On the North American continent, the majority of records were from the USA (n = 107). The studies involving turtles from Spain (n = 23), Italy (n = 17), France (n = 12), and Poland (n = 10) make up more than half of the records in Europe. This is consistent with other reviews on wildlife diseases, where most publications gathered were from Europe, North America, and Asia [23,24], as well as with the geographical areas where reptiles are most studied [25]. These geographical differences may be explained by the purchasing power parity, particularly by the North American and European countries, which allows some countries to invest in research [25].
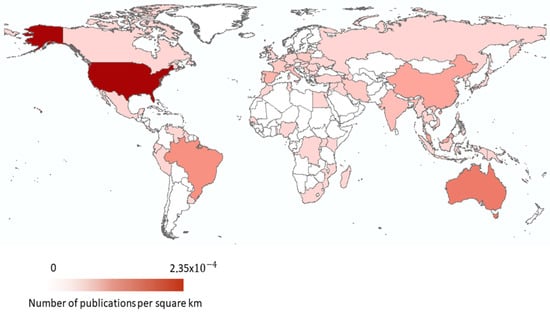
Figure 3.
World distribution of publications. The darker red represents a higher number of publications per square kilometer and the lighter red represents a lower number of publications per square kilometer. White-coloured countries did not have any publications.
4. Hosts
Of the 14 Testudines families [1,2,26], 11 families were present in this review, meaning that at least one member of each of these 11 families of freshwater turtles was present and that this review covered a significant diversity of the freshwater chelonian families [1]. When compared with other reptile groups, turtles have a higher number of published studies per species, and in general, the number of studies is positively associated with the species’ body mass and negatively associated with the year of the species description [25]. In our review, the most mentioned family was Emydidae (n = 865), while the least mentioned were Carettochelyidae (n = 8), Dermatemydidae (n = 8), and Platysternidae (n = 4) (Figure 4). Although the least mentioned families were those with the lowest number of described species [1,2,25] and there is a clear trend towards more references of disease agents associated with more species-diverse host families, there are exceptions. Following Uetz et al. [2], the most species-diverse family is Geoemydidae (71 species), followed by Chelidae (69 species), and then by Emydidae (58 species). In this review, the Emydidae family was mentioned 855 times, and the species with the greatest contributions were Trachemys scripta (Thunberg in Schoepff, 1792) (n = 313) and Emys orbicularis (Linnaeus, 1758) (n = 169) (Supplementary Materials S2). Trachemys scripta has been introduced in all continents (except for Antarctica) due to the pet trade [27], as well as trade for human consumption and religious reasons [28], and is often considered the most widely invasive reptile species in the world [29]. Host-switching of flatworm endoparasites from introduced T. scripta to native Mauremys leprosa (Schweigger, 1812) has already been identified in natural environments in the Mediterranean region [30]. Moreover, Demkowska-Kutrzepa et al. [31] identified that the helminth parasites co-introduced with T. scripta also infected M. leprosa and E. orbicularis. The increasing human contact with T. scripta and the knowledge that T. scripta transmits their parasites to native species [27] may explain the high number of publications that focus on their diseases. This review included 12 studies that show parasites that have been shared, or that have the potential to be shared, by T. scripta and native species such as E. orbicularis and M. leprosa (e.g., [32,33]). All but one study that referred to E. orbicularis were published after 2003, which may be due to the implementation of the Habitats Directive, which may have lagged in some countries [34,35]. Guedes et al. [25] also identified a positive association between IUCN threat status and the number of reptile studies. Nevertheless, E. orbicularis is not classified with any kind of threat status by the IUCN. The species E. orbicularis is one of the most widespread freshwater turtle species [36], which may also affect the number of published studies. The second most cited family was Geomydidae (Figure 4), in which the main contributors were species of the genus Mauremys (n = 155) (Supplementary Materials S2). This genus has a Palaearctic distribution [1], which includes 2 of the 3 continents with the largest number of studies (Europe and Asia). The family Chelidae is the third most represented family in our review (Figure 4), which, according to Uetz et al. [2], is the third most diverse family.
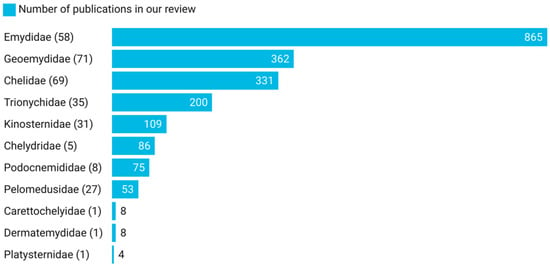
Figure 4.
Number of publications for each family of freshwater turtles and the total number of turtle species in each family according to Uetz et al. [2]. The total number of hosts is more than the total number of publications because several publications refer to more than one turtle species.
More than 50% of the studied freshwater turtles were wild-caught (Table 1), and these were mostly obtained from studies that were the first records of a specific parasite or from health assessment and disease prevalence of free-ranging chelonians. Such health assessment studies are a key component to evaluating wildlife disease in the “One Health” framework. The “One Health” approach highlights that the health of humans, animals, and ecosystems is linked and interdependent, so it proposes an interdisciplinary approach to address these issues [37]. Wildlife plays a critical role in the (re-)emergence of human and livestock diseases [37], and for this reason, wildlife disease surveillance has an important role in preventing and predicting disease outbreaks. On the other hand, the studies that incorporated captive freshwater turtles (n = 83) (Table 1) focused on a wider variety of research problems, such as microbiome, experimental infection, clinical diagnostics, antibiotic resistance, expression of heat shock proteins, health assessments, and more. The number of health assessment studies was considerably inferior in captivity than in the wild. Nevertheless, the risk imposed by freshwater turtles should not be neglected. Hossain and Heo [20] reviewed the bacteria transmitted by pet turtles and reported that the zoonotic risk is associated with unhygienic handling of the turtles and the poor hygiene of the terrarium. Some professions, such as zookeepers and veterinarians, carry a high risk of disease transmission from captive wildlife [38,39]. That being said, understanding the zoonotic potential of some diseases may require a disease surveillance methodology that incorporates both wild and captive specimens that were underrepresented in the available data (7.8%).

Table 1.
Summary table of the number of publications reporting turtle age, state, origin, and native/non-native status. The age groups were adults, juveniles, eggs, and adult and juvenile. Turtles were classified as alive when captured alive, dead when captured dead, and as “both” when dead and alive specimens were assessed. The origin was classified as “wild” when all animals were gathered from the environment, as “captive” when all animals were living in captivity, and as “both” when some animals came from the wild and others from captivity. Studies classified as “native” were conducted only with autochthonous species, as “non-native” when only allochthonous species were assessed, and as “both” when both allochthonous and autochthonous species were included. All studies without information about one of the variables were classified as “unspecified”.
In our review, 275 of 423 studies only sampled living freshwater turtles (Table 1), and of these, in 70 studies the turtles did not exhibit any symptoms. This suggests that many of the turtles may develop subclinical diseases characterised by the lack of symptoms. This was the case of frog virus 3 in a wild population of Chrysemys picta (Schneider,1783) and Chelydra serpentina (Linnaeus,1758) in Canada where, despite the virus’s presence, no sign of illness was detected [40]. In another study, three novel herpes viruses were detected in healthy populations of Glyptemys muhlenbergii (Schoepff,1801), Glyptemys insculpta (Le Conte, 1830), and Clemmys guttata (Schneider, 1792) [41]. Endemic diseases occur naturally in stable balance with the host, environment, and vector (in vector-borne diseases), which leads to the asymptomatic presence in their natural hosts [42]. Some anthropogenic factors may alter this stable balance and can cause an epidemic—such as increased interspecies contact, translocation of novel hosts, and introduction of new parasites [10,42]. Also, climate change influences the appearance of diseases outside their normal range due to the expansion of the host range and/or expansion of the free-living disease range [43]. All of the above can cause an epidemic from a subclinical disease and is one of the reasons to implement wildlife surveillance programs. Some of the studies employed an opportunistic sampling strategy, by incorporating dead individuals that were not euthanized. This type of study is essential to understand which diseases are causing mortality events. Nevertheless, not incorporating living animals does not allow for the comparison of the disease prevalence between dead and surviving turtles. In this review, only 31 studies analysed both living and dead turtles, which is a very low number.
Regarding the origin of the freshwater turtles, we found out that most studies (n = 343) evaluated native species (Table 1). The Wilcoxon signed-rank-paired test to compare the number of reported native and non-native turtles for each family resulted in highly significant differences (p = 0.00293) (Figure S3). We do not suggest that this reflects the pathogen loss in non-native species when outside of their native range, although this can happen [44]; it is simply a consequence of a higher number of studies with native species. This might be due to the conservation status of freshwater turtles. More than 53% of all the species of freshwater turtles are currently classified as having some kind of threat level or as extinct in the wild [45], and this percentage must be outdated because human pressure keeps increasing. On the other hand, the number of published studies focused on non-native turtles is much lower, and these publications only started after 2000. This reflects the increasing awareness of the impact of non-native species that began in the 1990s and resulted in, for example, EU legislation in 1997, Regulation 338/97, which banned the import of specific species, and later by Regulation 1143/2014, which defines the measures to prevent, minimize, and mitigate the introduction and spread of non-native species. Finally, studies involving both native and non-native species may allow for the detection of transmission patterns between the two types of species. Although, in most cases, only the transmission of parasites from non-native species to native ones is considered, native species may be a source of parasites to non-native species that may become alternative hosts and disease amplifiers in the ecosystem [10].
In our review, most studies did not specify the age of the freshwater turtles, with only 118 (18.9%) of all studies identifying a specific age group (Table 1). When specified, adult freshwater turtles were the most common age group (n = 56), while eggs were the least referenced age group (n = 7) (Table 1). Interestingly, five of the studies where eggs were sampled, focused on fungal pathogens, specifically species of the genus Fusarium Link, 1809, and Emydomyces testavorans Woodburn, 2019. Martínez-Ríos et al. [46] found that Trachemys scripta eggs, either symptomatic or asymptomatic, can carry pathogens associated with STEF (sea turtle egg fusariosis) disease. STEF disease can cause high mortality in sea turtle eggs worldwide [47], and some recent studies show egg failure due to STEF disease in freshwater turtles, which may severely impact their conservation [48].
Most studies focused on the diseases present in adults or adults and juveniles, and most turtles were caught using traps since they were wild turtles (see paragraphs above). Independently of the trap type used, the capture rate for juveniles was lower than that for adults [49,50], which means that studies may not have been intentionally directed to adults. Despite the low capture rate, juveniles were still caught by the most conventional freshwater turtle sampling methodology, and accordingly, some studies include both adults and juveniles (n=41, 9.7%). Studies only directed to juveniles were mainly focused on viruses and bacteria and evaluated the pathogenicity, treatment, diagnosis, and microbiome, with a vast majority being conducted in captivity.
5. Disease Agents
A total of 2101 infections were reported, and across all agents, more than half belonged to Animalia (n = 1113) (Figure 5). Similarly, in their meta-analyses on the relationship between host body condition and parasite infection, Sánchez et al. [51] found that the majority of the parasites were from Animalia. On the contrary, in their review of long-term studies in wildlife diseases, Barroso et al. [18] identified viruses and bacteria as major pathogens. One of the differences between the above-described papers is the fact that Sánchez et al. [51] used a combination of (parisit*OR infect* OR disease*), and Barroso et al. [18] used ‘disease’ as a search word for the whole literature search. In our review, the number of papers increased from 219 to 423 when we removed the word ‘disease’ before ‘parasite’ and ‘protozoa’. These results referred, almost exclusively, to animal parasites, many of them not identified in the literature search performed before removing the word ‘disease’. According to Foufopoulos et al. [52], all disease-causing agents can be classified as parasites. On the other hand, pathogens are a subset of microparasites such as bacteria and viruses that have substantial detrimental effects on the hosts. The word ‘disease’ is more closely associated with pathogens than with other parasites, like leeches and ticks, which are often considered primarily in their role as vectors of diseases. Nevertheless, many microorganisms naturally form part of the healthy microbiome of the hosts as commensals or mutualists but do not cause any disease. Therefore, it is extremely important to refine and adapt search words, so that information from all spectra of infectious agents can be gathered in reviews. We propose that in the case of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, the word ‘disease’ should be added to the literature search to exclude papers that only describe the healthy/normal microbiome. On the other hand, when searching for parasites and protozoa, the word ‘disease’ should be excluded as a search word to make sure that all types of parasites are included in the review.
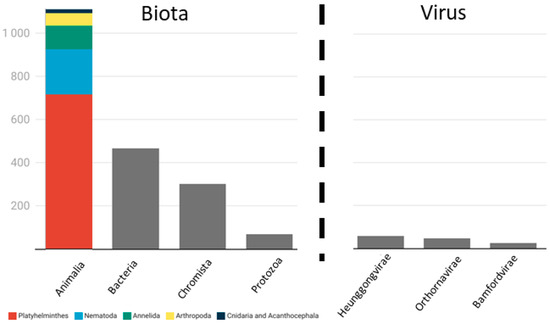
Figure 5.
Number of publications for each potential disease agent. The combined number of publications is higher than the total number of publications because many publications refer to more than one disease agent.
Animal parasites are often classified as macroparasites [51] although this group has both ectoparasites, such as leeches and ticks, and endoparasites, including roundworms and flatworms. The Platyhelminthes phylum was the most represented phylum of Animalia (n = 719), with the following classes present: Trematoda (n = 440), Monogenea (n = 272), and Cestoda (n = 5) (Supplementary Materials S2). According to a global estimate, platyhelminthes in reptiles represent 6% of the total diversity, with Trematoda being the predominant class [53], which is concordant with the results of this review. This number must be an underestimate due to the rate of newly described species, the high number of cryptic species, and the fact that major efforts to describe the platyhelminthes have been concentrated in developed countries where the platyhelminthes diversity is lower [53]. As in our review, Poulin et al. [54] identified Cestoda as the least studied. Among animal hosts, acanthocephalans and nematodes are the most mentioned helminth parasites due to their pathogenicity and zoonotic potential [54]. In this review, the second most reported phylum within Animalia was Nematoda (n = 201). Some estimates indicate that the Nematoda phylum is one of the most diverse of the Animalia [55]; nevertheless, three things must be taken into account extrapolating this information to the parasitic nematodes of animals, especially for freshwater turtles. First, the nematode diversity was calculated using all nematode species, which include free-living species [55]. The majority of nematode species are free-living [56], so the diversity of parasitic nematodes might not reflect the diversity of all nematode species. Second, many parasitic nematodes infect plant species with devastating ecological and economic consequences [57]. These plant parasites were also considered by Poulin and Morand [55]. Finally, amphibians and reptiles are underrepresented in studies that focus on nematodes. For instance, Cole and Viney [58], in their review of population genetics of parasitic nematodes of wild animals, only use lizard examples in the reptile section and do not include any chelonian examples in the aquatic animals section. The third and fourth most represented groups within Animalia were Annelida (n = 109) and Arthropoda (n = 57). From Arthropoda, only five families were present (Ixodidae, Sarcophagidae, Balanidae, Chelonibiidae, and Sebekidae), and from Annelida, four families were present (Erpobdellidae, Glossiphoniidae, Ozobranchidae, and Piscicolidae), so, for both phyla, all identified parasites were ectoparasites. Ectoparasites themselves have negative consequences for the hosts [59]. Many species of the Balanidae family are considered epizoic. Epizoic organisms use the surface of other organisms without any damage or harm [60]. Nevertheless, the presence of the species Amphibalanus eburneus (Gould,1841) and Amphibalanus improvisus (Darwin, 1854) may lead to erosion of the shell and vertebrae of the turtle, so they are considered parasites [60]. Additionally, ectoparasites can be vectors of other disease agents [61,62]. Particularly in freshwater turtles, leeches of the genus Placobdella Blanchard,1893, are a well-known vector for species of Haemogregarina Danilewsky, 1885, an obligate hemoparasite of reptiles [63,64].
Within bacteria, the most reported phylum was Proteobacteria (n = 353), followed by Firmicutes (n = 33) and Bacteroidetes (n = 20) (Supplementary Materials S2). On the other hand, Fusobacteria was the least reported phylum, with only one example reported. The Proteobacteria phylum includes a variety of families, such as Aeromonadaceae, Brucellaceae, Pseudomonaceae, and Enterobactericeae. In this review, the latter family makes up more than half of Proteobacteria reports, which includes several zoonotic bacteria, such as species of Campylobacter Sebald and Veron, 1963 and Salmonella [65]. It is known that these potential disease agents can occur naturally in the host, only becoming pathogenic when the system’s natural balance is disturbed [42]. However, in captive pet reptiles (including turtles), the source of bacteria causing zoonotic diseases might not be the turtle itself but rather the water supply or the substrate of the terrarium where the reptile is held [66]. Environmental changes, such as pollutants, can also alter the normal microbiome and lead to the appearance of diseases caused by the increase or decrease of some bacteria taxa [67]. Even though the environmental microbiome may not influence the oral microbiome, the shell microbiome is extremely affected by the environmental microbiome [68], potentially causing the infection of human hosts through direct contact. Nevertheless, when compared with Python regius (Shaw, 1802) (Ball python), Acrantophis dumerili Jan, 1860 (Dumeril’s boa), and Eublepharis macularius (Blyth, 1854) (Leopard gecko), Trachemys scripta’s oral microbiome showed a higher bacterial diversity but not necessarily of pathogens, possibly associated with its wider, more omnivorous diet [69].
When it comes to viruses, a lack of appropriate detection and identification techniques and a greater focus on birds and mammals created a knowledge gap concerning reptile viruses [70] (Figure 6). Novel reptile viruses are being discovered every year, meaning that reptile virus diversity and, consequently, turtle virus diversity are underestimated [70]. It is clear that, in our review, viruses (n = 130, 6.2%) had a lower number of mentions when compared with Animalia (n = 1113, 52.9%) and Bacteria (n = 465, 22.1%).
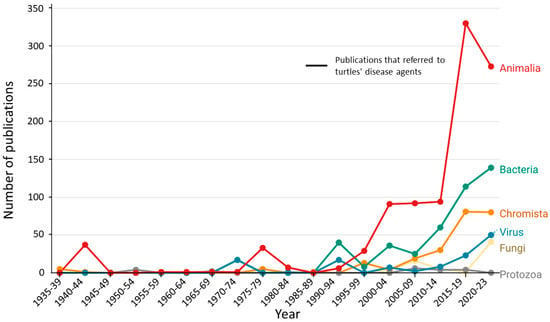
Figure 6.
Yearly distribution of the cited disease agents for each 5 years period (e.g., 1935–1939). The number of disease agents is higher than the total number of publications because many publications refer to more than one disease agent.
Fungi, Chromista, and Protozoa make up a small proportion of all reports of disease-causing agents (n = 393, 18.7%, Supplementary Materials S2), partly because the molecular tools needed for their identification have only recently been widely applied (Figure 6). Of these three groups, Chromista was the most mentioned group (n = 302), with Haemogregarinidae, Eimeriidae, and Plasmodiidae as the most widely reported families. Within Haemogregarinidae, the genera most mentioned were Haemogregarina (n = 160) and Hepatozoon Miller, 1908 (n = 5). In the other two families, the more widely reported genera were, respectively, Eimeria Schneider, 1875 (n = 100) and Haemoproteus Kruse, 1890 (n = 18). These hemoparasites are difficult to identify only using microscopy, and until recently, no ubiquitous molecular tool was available to identify them from a blood sample [71]. There are still unidentified forms of these parasites that can cause severe consequences for the hosts as, for example, in the case of the putative intranuclear coccidium that was recently identified in freshwater turtles using molecular tools [72]. This parasite has been associated with extensive symptoms and even death in terrestrial tortoises [73,74], but its impact on freshwater host species remains unknown. The most widely reported fungal parasites belonged to the genera Fusarium (n = 12) and Emydomyces (n = 26). These two genera cause emerging infectious diseases that severely impact freshwater turtle populations leading to their decline. Protozoa parasites were reported only twenty-three times, primarily represented by the genus Entamoeba Casagrandi and Barbagallo, 1897 (n = 11), and Trypanosoma Lühe, 1906 (n = 9).
Regarding the public health risk, in our review, we identified several potential zoonotic diseases that may be transmitted from freshwater turtles to humans. These include disease-causing agents such as species of the genera Salmonella, Leptospira, Klebsiella Trevisan, 1885, and Mycoplasma Nowak, 1929. Some have been documented to be transmitted from freshwater pet turtles to humans, such as Salmonella spp. [3], but many, despite the potential risk, have not been confirmed to be transmitted from freshwater turtles. Although direct contact with live freshwater turtles is the main infection route described, other infection routes should not be discarded, particularly due to the common use of freshwater turtles for food and religious rituals. Most of the articles that identified potential zoonotic diseases used captive or captive-raised turtles since these have the most contact with humans. Nonetheless, wild turtles may also carry zoonotic diseases [75,76]. For humans, these diseases may have very different outcomes, depending on the disease-causing agent itself and the human host. As an example, for Salmonella spp., the disease outcome is worse for children and the elderly [20].
6. Conclusions
In this review, we provide new insights into the agents of disease in freshwater chelonians. Identifying disease agents of freshwater turtles is of extreme importance not only from a conservation perspective but also from a public health perspective. Due to the variety of ways that freshwater turtles are used, their interaction with humans has increased and the potential to transmit zoonotic diseases has also increased.
We identified disease agents that include parasites, bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other pathogens. As with other animal groups, research on turtle diseases peaked after the COVID-19 pandemic. Nevertheless, reptile groups, specifically freshwater turtles, are still overlooked in wildlife disease research. Regarding global distribution, it follows the same pattern as other wildlife disease research, with more publications in Asia, North America, and Europe. However, the need for increased attention to understudied regions and host species is identified, emphasising the importance of filling knowledge gaps to develop effective health assessment protocols, disease monitoring programs, and conservation strategies.
The diversity of freshwater turtle families was covered in the study despite variations in the number of reported diseases and parasites for each family. Overall, the most diverse families were the ones with more disease agents reported. Trachemys scripta was the most studied species, which, due to its invasive status and its popularity as pets, can be a source of diseases to the native species and a source of zoonotic diseases to humans. To better understand, monitor, and evaluate disease dynamics, it is essential to incorporate both wild and captive populations. Only by incorporating this holistic “One Health” approach, we can properly minimize and mitigate disease transmission and risk. In our review, we also address the age, origin, and status of freshwater turtles studied, revealing a focus on adults and native species and a scarcity of studies involving both living and dead turtles. This prompts considerations for the design of future research to ensure a comprehensive understanding of disease prevalence and transmission dynamics. So, whenever possible, future studies should consider all age classes, native and non-native species, and both live and dead individuals.
Our extensive analysis of disease-causing agents, including parasites, bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other pathogens, offers an informative resource for health assessments, disease monitoring, and conservation initiatives. Animalia had the most records for disease agents in freshwater turtles. In this kingdom, both endo- and ectoparasites were reported, although most were endoparasites. Among the endoparasites, the most recorded phylum was Platyhelminthes, followed by Nematoda. These phyla are highly diverse, which is consistent with the fact that they were the most represented ones. Within Animalia, ectoparasites were represented by Arthropoda and Annelida, and the latter may be vectors to disease-causing agents such as species of Haemogregarina. Bacteria were the second most recorded kingdom with Proteobacteria as the most reported phylum. Bacteria form part of the natural microbiome of reptiles, and their pathogenicity may be induced by environmental changes (both in the wild and in captivity). Reptile virus’ diversity may be high, but the focus on other viruses and the limited number of assessment techniques have compromised the knowledge about this group. Assessments of the remaining kingdoms (Fungi, Chromista, and Protozoa) make up a small proportion of all articles, but there has been a recent increase in studies, presumably reflecting the very recent development of appropriate molecular tools to identify these groups.
This review enhances our understanding of the complex interactions between freshwater turtles and disease-causing agents. It highlights the need for a concerted effort towards sustainable conservation and management practices, as well as the implementation of the “One Health” approach to reduce both human and animal diseases’ impact. Our findings underscore the urgency of addressing the various causes of freshwater turtle disease through health assessments and monitoring programs and of identifying key gaps in the current knowledge, as well as in research efforts, that should be used to improve future research in freshwater turtle diseases.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d16030171/s1. S1: List of references of the publications used in the review; S2: Systematic Review table. S3: Number of publications of native and non-native turtles for each family of freshwater turtles.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.R. and F.B.; methodology, J.R., R.X., D.J.H. and P.A.; formal analysis, J.R.; writing—original draft preparation, J.R.; writing—review and editing, R.X., D.J.H., F.B. and P.A.; supervision, R.X., D.J.H., F.B. and P.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study had the support of FCT through the strategic project UIDB/04292/2020 awarded to MARE and through project LA/P/0069/2020 granted to the Associated Laboratory ARNET. Raquel Xavier was supported by FCT under the Programa Operacional Potencial Humano—Quadro de Referência Estratégico, national funds from the European Social Fund and Portuguese Ministério da Educação e Ciência (2020.00854.CEECIND/CP1601/CT0001). The Foundation for Science and Technology supports Filipe Banha through an individual contract (CEEC/01896/2021).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bour, R. Global Diversity of Turtles (Chelonii; Reptilia) in Freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uetz, P.; Freed, P.; Reyes, F.; Aguilar, R.; Kudera, J.; Hošek, J. (Eds.) The Reptile Database. 2023. Available online: http://www.reptile-database.org/ (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Colon, V.A.; Lugsomya, K.; Lam, H.K.; Wahl, L.C.; Parkes, R.S.V.; Cormack, C.A.; Horlbog, J.A.; Stevens, M.; Stephan, R.; Magouras, I. Serotype Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Salmonella enterica Isolates from Freshwater Turtles Sold for Human Consumption in Wet Markets in Hong Kong. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 912693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, H.; McCormack, T.E.M.; Lo, H.; Nguyen, M.; Tapley, B. Hunting and Trade of Big-Headed Turtles (Platysternon megacephalum Gray 1831) in Two Protected Areas in Northern Vietnam. Herpetol. Notes 2021, 14, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Pezzuti, J.C.B.; Lima, J.P.; Da Silva, D.F.; Begossi, A. Uses and Taboos of Turtles and Tortoises Along Rio Negro, Amazon Basin. J. Ethnobiol. 2010, 30, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Public Health Risks Involved in the Human Consumption of Reptile Meat. EFSA J. 2007, 578, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnino, S.; Colin, P.; Dei-Cas, E.; Madsen, M.; McLauchlin, J.; Nöckler, K.; Prieto Maradona, M.; Tsigarida, E.; Vanopdenbosch, E.; Van Peteghem, C. Biological Risks Associated with Consumption of Reptile Products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 134, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, E.R.; Baker, S.E.; Macdonald, D.W. Global Trade in Exotic Pets 2006-2012: Exotic Pet Trade. Conserv. Biol. 2014, 28, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banha, F.; Diniz, A.; Anastácio, P.M. Patterns and Drivers of Aquarium Pet Discharge in the Wild. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.S.; Parker, I.M.; Gilbert, G.S.; Sofia Guerra, A.; Nunn, C.L. Introduced Species, Disease Ecology, and Biodiversity–Disease Relationships. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, S.; Tauxe, R.V.; Behravesh, C.B. Turtle-Associated Salmonellosis, United States, 2006–2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 22, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.R.; Vieira, W.L.; Santana, G.G. Reptiles Used in Traditional Folk Medicine: Conservation Implications. Biodivers. Conserv. 2008, 17, 2037–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-H.; Chang, H.-C.; Lue, K.-Y. Unregulated Trade in Turtle Shells for Chinese Traditional Medicine in East and Southeast Asia: The Case of Taiwan. Chelonian Conserv. Biol. 2009, 8, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.R.; Rosa, I.M. Biodiversity, Traditional Medicine and Public Health: Where Do They Meet? J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomedicine 2007, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friant, S.; Bonwitt, J.; Ayambem, W.A.; Ifebueme, N.M.; Alobi, A.O.; Otukpa, O.M.; Bennett, A.J.; Shea, C.; Rothman, J.M.; Goldberg, T.L.; et al. Zootherapy as a Potential Pathway for Zoonotic Spillover: A Mixed-Methods Study of the Use of Animal Products in Medicinal and Cultural Practices in Nigeria. One Health Outlook 2022, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Finlaison, D.S.; Frost, M.J.; Gestier, S.; Gu, X.; Hall, J.; Jenkins, C.; Parrish, K.; Read, A.J.; Srivastava, M.; et al. Identification of a Novel Nidovirus as a Potential Cause of Large Scale Mortalities in the Endangered Bellinger River Snapping Turtle (Myuchelys georgesi). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, W.; Ternova, L.; Parasnis, S.A.; Kovaleva, M.; Nagy, G.J. Climate Change and Zoonoses: A Review of Concepts, Definitions, and Bibliometrics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso, P.; Acevedo, P.; Vicente, J. The Importance of Long-term Studies on Wildlife Diseases and Their Interfaces with Humans and Domestic Animals: A Review. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1895–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Wimalasena, S.; Zoysa, M.; Heo, G.-J. Prevalence of Citrobacter Spp. From Pet Turtles and Their Environment. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2017, 26, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Heo, G.-J. Pet-Turtles: A Potential Source of Human Pathogenic Bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 3785–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, C.; Martín-Maldonado, B.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Sevilla-Navarro, S.; Lorenzo-Rebenaque, L.; Montoro-Dasi, L.; Manzanares, A.; Ayats, T.; Mencía-Gutiérrez, A.; Jordá, J.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistant Salmonella in Chelonians: Assessing Its Potential Risk in Zoological Institutions in Spain. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Modry, D.; Otranto, D. Zoonotic Parasites of Reptiles: A Crawling Threat. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, D.M.; Carver, S.; Jones, M.E.; Krkošek, M.; Skerratt, L.F. Emerging Infectious Diseases of Wildlife: A Critical Perspective. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiethoelter, A.K.; Beltrán-Alcrudo, D.; Kock, R.; Mor, S.M. Global Trends in Infectious Diseases at the Wildlife–Livestock Interface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9662–9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, J.J.M.; Moura, M.R.; Alexandre, F.; Diniz-Filho, J. Species out of Sight: Elucidating the Determinants of Research Effort in Global Reptiles. Ecography 2023, 2023, e06491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, J.B. A Review of Chelonian Type Specimens (Order Testudines). Megataxa 2022, 7, 1–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, R.A. (Ed.) A Handbook of Global Freshwater Invasive Species; Earthscan: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-84971-228-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay, N.F.; Ng, P.K.A.; O’Riordan, M.; Chou, L.M. The Red-Eared Slider (Trachemys scripta elegans) in Asia: A Review. In Biological Invaders in Inland Waters: Profiles, Distribution, and Threats; Gherardi, F., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, F. Alien Reptiles and Amphibians: A Scientific Compendium and Analysis; Invading Nature: Springer Series in Invasion Ecology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; ISBN 978-1-4020-8945-9. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, L.; Du Preez, L.; Bonneau, E.; Héritier, L.; Quintana, M.; Valdeón, A.; Sadaoui, A.; Kechemir-Issad, N.; Palacios, C.; Verneau, O. Parasite Host-Switching from the Invasive American Red-Eared Slider, Trachemys scripta elegans, to the Native Mediterranean Pond Turtle, Mauremys leprosa, in Natural Environments. Aquat. Invasions 2015, 10, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demkowska-Kutrzepa, M.; Studzińska, M.; Roczeń-Karczmarz, M.; Tomczuk, K.; Abbas, Z.; Różański, P. A Review of the Helminths Co-Introduced with Trachemys scripta elegans—A Threat to European Native Turtle Health. Amphib.-Reptil. 2018, 39, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Héritier, L.; Valdeón, A.; Sadaoui, A.; Gendre, T.; Ficheux, S.; Bouamer, S.; Kechemir-Issad, N.; Du Preez, L.; Palacios, C.; Verneau, O. Introduction and Invasion of the Red-Eared Slider and Its Parasites in Freshwater Ecosystems of Southern Europe: Risk Assessment for the European Pond Turtle in Wild Environments. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 1817–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verneau, O.; Palacios, C.; Platt, T.; Alday, M.; Billard, E.; Allienne, J.-F.; Basso, C.; Du Preez, L.H. Invasive Species Threat: Parasite Phylogenetics Reveals Patterns and Processes of Host-Switching between Non-Native and Native Captive Freshwater Turtles. Parasitology 2011, 138, 1778–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beunen, R. European Nature Conservation Legislation and Spatial Planning: For Better or for Worse? J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2006, 49, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, E.K.; Bowler, D.E.; Hof, C. European Habitats Directive Has Fostered Monitoring but Not Prevented Species Declines. Conserv. Lett. 2023, 16, e12948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velo-Antón, G.; Wink, M.; Schneeweiß, N.; Fritz, U. Native or Not? Tracing the Origin of Wild-Caught and Captive Freshwater Turtles in a Threatened and Widely Distributed Species (Emys orbicularis). Conserv. Genet. 2011, 12, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Mavingui, P.; Boetsch, G.; Boissier, J.; Darriet, F.; Duboz, P.; Fritsch, C.; Giraudoux, P.; Le Roux, F.; Morand, S.; et al. The One Health Concept: 10 Years Old and a Long Road Ahead. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, P.C.; Martínez-Nevado, E.; González, A.; Abelló-Poveda, M.T.; Fernández-Bellon, H.; De La Riva-Fraga, M.; Marquet, B.; Guéry, J.-P.; Knauf-Witzens, T.; Weigold, A.; et al. Intestinal Protists in Captive Non-Human Primates and Their Handlers in Six European Zoological Gardens. Molecular Evidence of Zoonotic Transmission. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 819887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.; Sharma, R.; Aulakh, R.S.; Gill, J.P.S.; Singh, B.B. Seroprevalence and Risk Factor Investigation for the Exposure of Toxoplasma Gondii among Veterinary Personnel in Punjab, India. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 80, 101739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstairs, S.J.; Kyle, C.J.; Vilaça, S.T. High Prevalence of Subclinical Frog Virus 3 Infection in Freshwater Turtles of Ontario, Canada. Virology 2020, 543, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossiboff, R.J.; Raphael, B.L.; Ammazzalorso, A.D.; Seimon, T.A.; Newton, A.L.; Chang, T.Y.; Zarate, B.; Whitlock, A.L.; McAloose, D. Three Novel Herpesviruses of Endangered Clemmys and Glyptemys Turtles. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deem, S.L.; Karesh, W.B.; Weisman, W. Putting Theory into Practice: Wildlife Health in Conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 15, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M.J.; Kutz, S.J.; Jenkins, E.; O’Hara, T.M. The Potential Impact of Climate Change on Infectious Diseases of Arctic Fauna. Int. J. Circumpolar Health 2005, 64, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torchin, M.E.; Lafferty, K.D.; Dobson, A.P.; McKenzie, V.J.; Kuris, A.M. Introduced Species and Their Missing Parasites. Nature 2003, 421, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodin, A.G.J.; Stanford, C.B.; Dijk, P.P.V.; Eisemberg, C.; Luiselli, L.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Hudson, R.; Horne, B.D.; Goode, E.V.; Kuchling, G.; et al. Global Conservation Status of Turtles and Tortoises (Order Testudines). Chelonian Conserv. Biol. 2018, 17, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ríos, M.; Martín-Torrijos, L.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J. The Invasive Alien Red-Eared Slider Turtle, Trachemys scripta, as a Carrier of STEF-Disease Pathogens. Fungal Biol. 2022, 126, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, C.W.; Sarmiento-Ramírez, J.M.; Short, D.P.G.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J.; O’Donnell, K.; Geiser, D.M. Unraveling the Ecology and Epidemiology of an Emerging Fungal Disease, Sea Turtle Egg Fusariosis (STEF). PLOS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranco, A.S.; Gillingham, M.A.F.; Wilhelm, K.; Torres, M.D.L.; Sommer, S.; Romo, D. Transcending Sea Turtles: First Report of Hatching Failure in Eggs of an Amazonian Freshwater Turtle with Symptoms of the Fungal Emerging Disease Fusariosis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e3282–e3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterrett, S.C.; Smith, L.L.; Schweitzer, S.H.; Maerz, J.C. An Assssment Of Two Methods For Sampling River Turtle Assemblages. Herpetol. Conserv. Biol. 2010, 5, 490–497. [Google Scholar]
- Tesche, M.R.; Hodges, K.E. Unreliable Population Inferences from Common Trapping Practices for Freshwater Turtles. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2015, 3, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, C.A.; Becker, D.J.; Teitelbaum, C.S.; Barriga, P.; Brown, L.M.; Majewska, A.A.; Hall, R.J.; Altizer, S. On the Relationship between Body Condition and Parasite Infection in Wildlife: A Review and Meta-analysis. Ecol. Lett. 2018, 21, 1869–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foufopoulos, J.; Wobeser, G.A.; McCallum, H. Infectious Disease Ecology and Conservation, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2022; ISBN 978-0-19-958350-8. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, C.J.; Dallas, T.A.; Alexander, L.W.; Phelan, A.L.; Phillips, A.J. What Would It Take to Describe the Global Diversity of Parasites? Proc. R Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20201841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, R.; Presswell, B.; Bennett, J.; De Angeli Dutra, D.; Salloum, P.M. Biases in Parasite Biodiversity Research: Why Some Helminth Species Attract More Research than Others. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2023, 21, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulin, R.; Morand, S. The Diversity of Parasites. Q. Rev. Biol. 2000, 75, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abebe, E.; Decraemer, W.; Ley, P. Global Diversity of Nematodes (Nematoda) in Freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.T.; Haegeman, A.; Danchin, E.G.J.; Gaur, H.S.; Helder, J.; Jones, M.G.K.; Kikuchi, T.; Manzanilla-López, R.; Palomares-Rius, J.E.; Wesemael, W.M.L.; et al. Top 10 Plant-Parasitic Nematodes in Molecular Plant Pathology: Top 10 Plant-Parasitic Nematodes. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 946–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, R.; Viney, M. The Population Genetics of Parasitic Nematodes of Wild Animals. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitze, P.S.; Tschirren, B.; Richner, H. Life History and Fitness Consequences of Ectoparasites. J. Anim. Ecol. 2004, 73, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, R.E. Parasites in the Diamondback Terrapin, Malaclemys terrapin: A Review. J. Herpetol. Med. Surg. 2003, 13, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Ribeiro, S.R.; Castilho-Onofrio, V.; Marcili, A.; Simonato, B.B.; Latrofa, M.S.; Benelli, G.; Otranto, D.; Barros-Battesti, D.M. Molecular Detection of Vector-Borne Agents in Ectoparasites and Reptiles from Brazil. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Colella, V.; Lia, R.P.; Nguyen, V.L.; Barros-Battesti, D.M.; Iatta, R.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Otranto, D. Borrelia burgdorferi (Sensu Lato) in Ectoparasites and Reptiles in Southern Italy. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddall, M.E.; Desser, S.S. Transmission of Haemogregarina balli From Painted Turtles to Snapping Turtles Through the Leech Placobdella Ornata. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 1217–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verneau, O.; Melliti, S.; Kimdil, L.; El Mouden, E.H.; Achouri, M.S.; Rouag, R. Molecular Phylogenies of Leeches and Haemoparasites Infecting Freshwater Turtles in Aquatic Ecosystems of Northern Africa Suggest Phylogenetic Congruence between Placobdella costata Sensu Lato and Haemogregarina stepanowi Sensu Lato. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebicz, A.; Śliżewska, K. Campylobacteriosis, Salmonellosis, Yersiniosis, and Listeriosis as Zoonotic Foodborne Diseases: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2018, 15, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, D.-S.; Shin, G.-W.; Wendt, M.; Heo, G.-J. Prevalence of Salmonella Spp. in Pet Turtles and Their Environment. Lab. Anim. Res. 2016, 32, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, D.J.; Bissett, A.; Nilsson, S.; Bose, U.; Nelis, J.L.D.; Nahar, A.; Smith, M.; Gonzalez-Astudillo, V.; Braun, C.; Baddiley, B.; et al. Perturbation of the Gut Microbiome in Wild-Caught Freshwater Turtles (Emydura macquarii macquarii) Exposed to Elevated PFAS Levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, M.; Kedy, C.; Skalla, C. Consistent Patterns in 16S and 18S Microbial Diversity from the Shells of the Common and Widespread Red-Eared Slider Turtle (Trachemys scripta). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zancolli, G.; Mahsberg, D.; Sickel, W.; Keller, A. Reptiles as Reservoirs of Bacterial Infections: Real Threat or Methodological Bias? Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, E.F.; Russo, A.G.; Yan, G.J.H.; Mercer, L.K.; White, P.A. Revealing the Uncharacterised Diversity of Amphibian and Reptile Viruses. ISME Commun. 2022, 2, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, J.K.C.; Picelli, A.M.; Da Silva, M.R.L.; Valadão, R.M.; Hernández-Ruz, E.J.; Viana, L.A. Phylogenetic Analysis of Chelonian Hemogregarines Reveals Shared Species among the Amazonian Freshwater Turtle Podocnemis Spp. and Provides a Description of Two New Species of Haemogregarina. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laghzaoui, E.-M.; Perera, A.; Harris, D.J.; El Mouden, E.H. Characterization and Identification of Haemogregarine Hemoparasites (Apicomplexa: Adeleina: Hepatozoidae) in Natural Populations of Mauremys leprosa leprosa and M. leprosa saharica from Morocco. Syst. Parasitol. 2021, 98, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.G.; Watson, M.K. Diseases of the Reptile Renal System. Veterinary Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2020, 23, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reavill, D.R.; Schmidt, R.E. Urinary Tract Diseases of Reptiles. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2010, 19, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezzutto, D.; Barbero, R.; Canale, G.; Acutis, P.; Biolatti, C.; Dogliero, A.; Mitzy, M.; Francone, P.; Colzani, A.; Bergagna, S.; et al. Detection of Leptospira Spp. in Water Turtle (Trachemys scripta) Living in Ponds of Urban Parks. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.P.; Kawanami, A.E.; Silva, A.S.L.; Chung, D.G.; Werther, K. Detection of Leptospira Spp. in Wild Phrynops geoffroanus (Geoffroy’s Side-Necked Turtle) in Urban Environment. Acta Trop. 2016, 164, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).