Insights on the Existence of Ancient Glacial Refugee in the Northern Black/Azov Sea Lowland, with the Description of the First Stygobiotic Microcrustacean Species of the Genus Niphargus Schiödte, 1849 from the Mouth of the Don River
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
Phylogenetic Approach of Newly Discovered Species of the Genus Niphargus
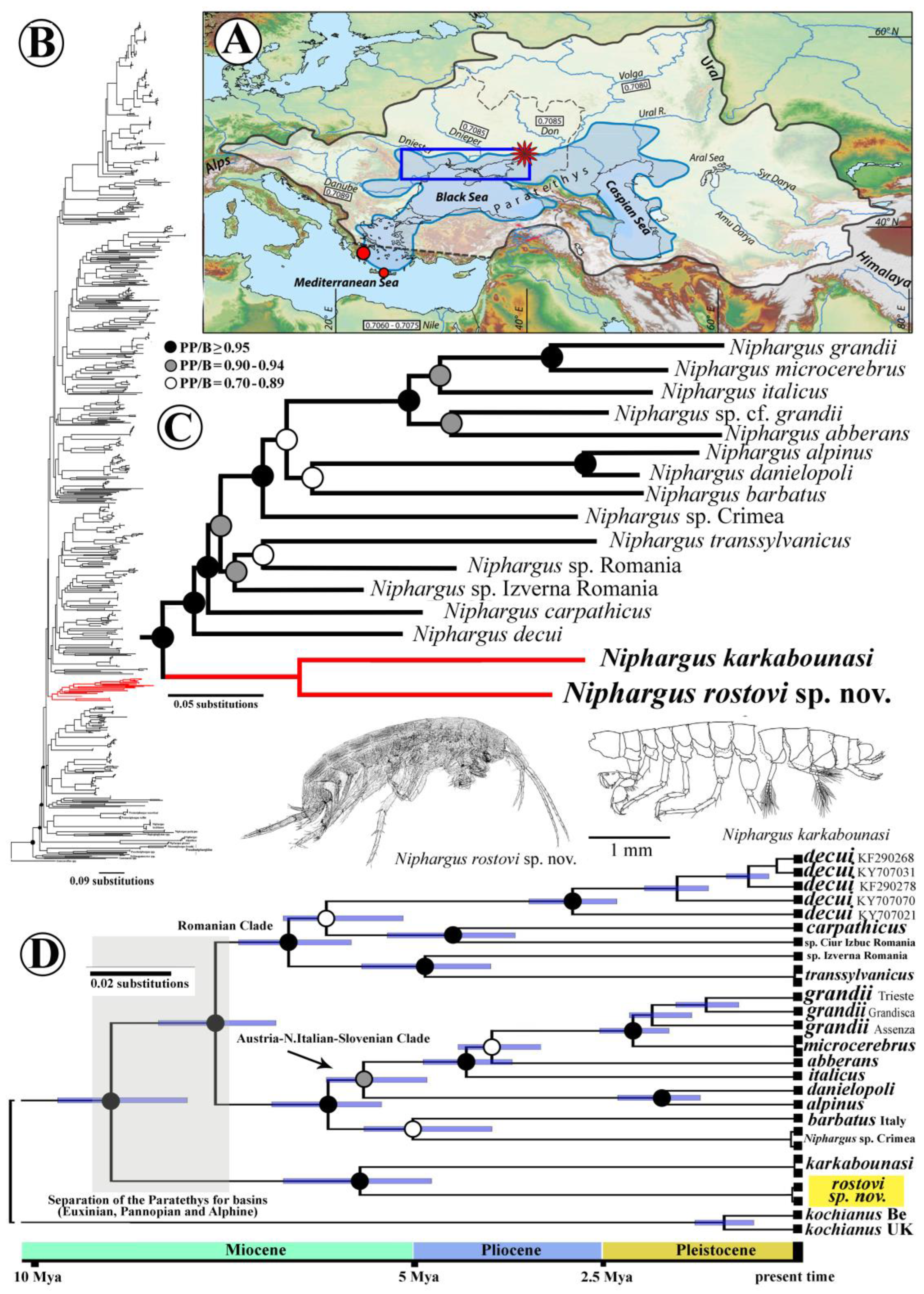
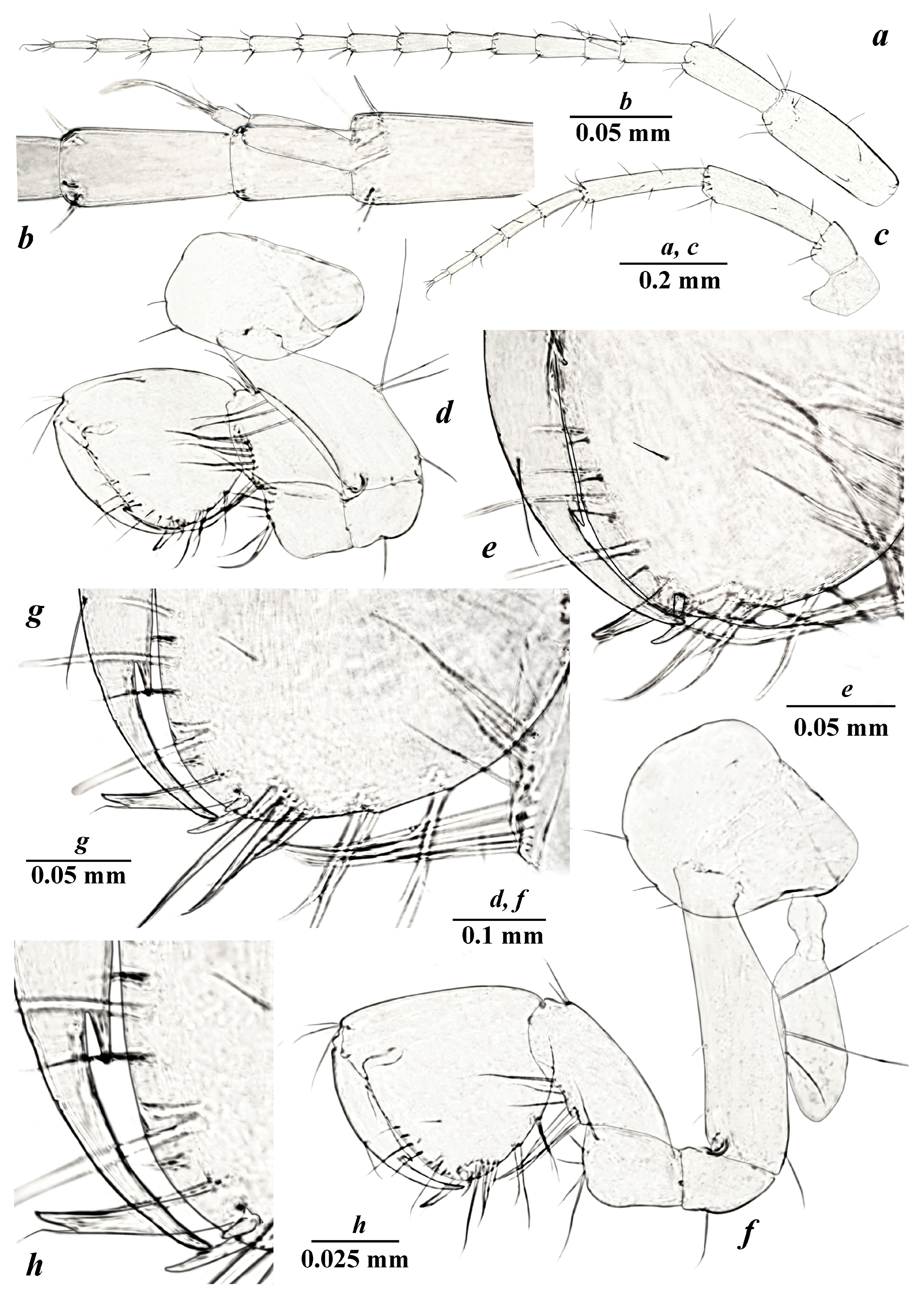
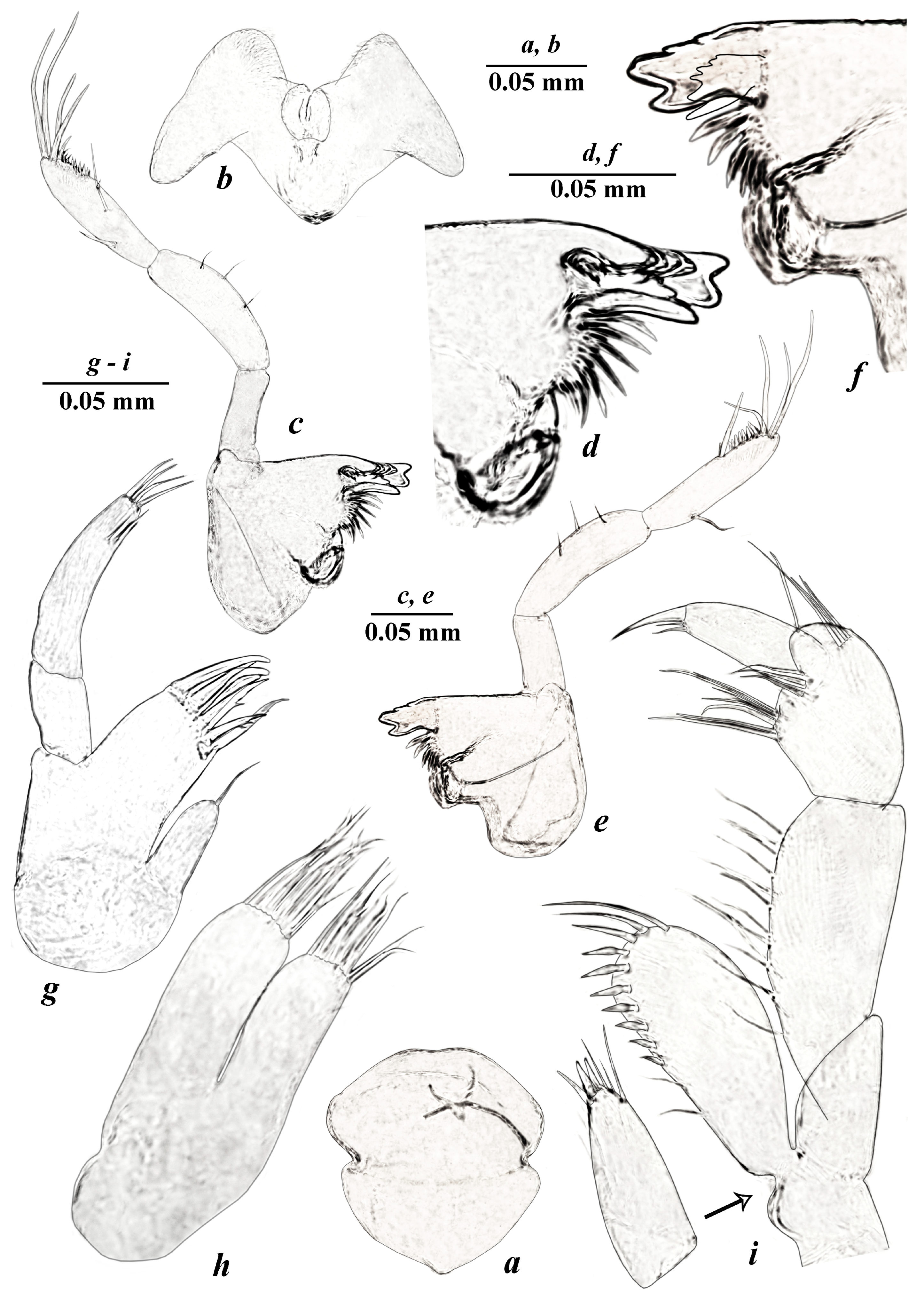
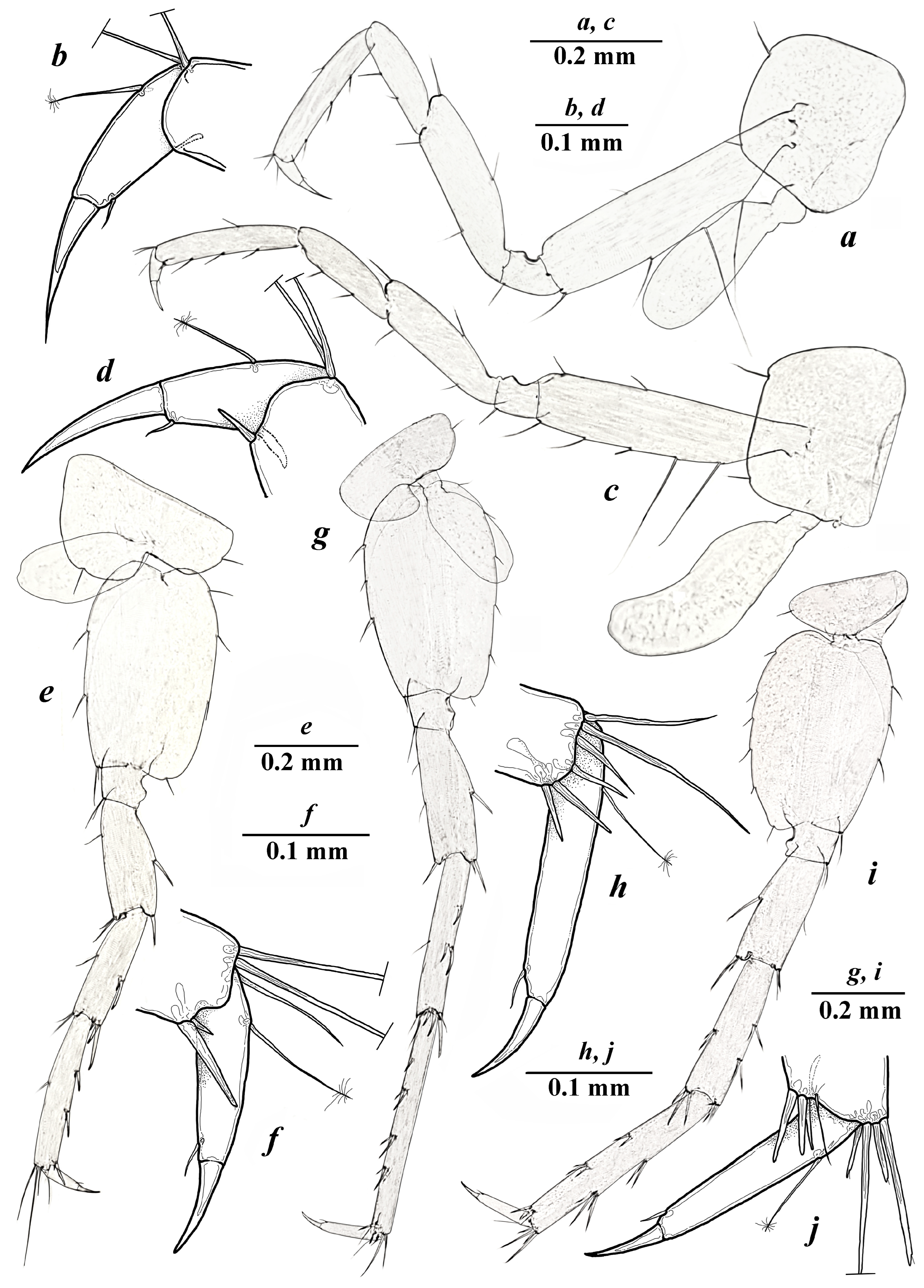
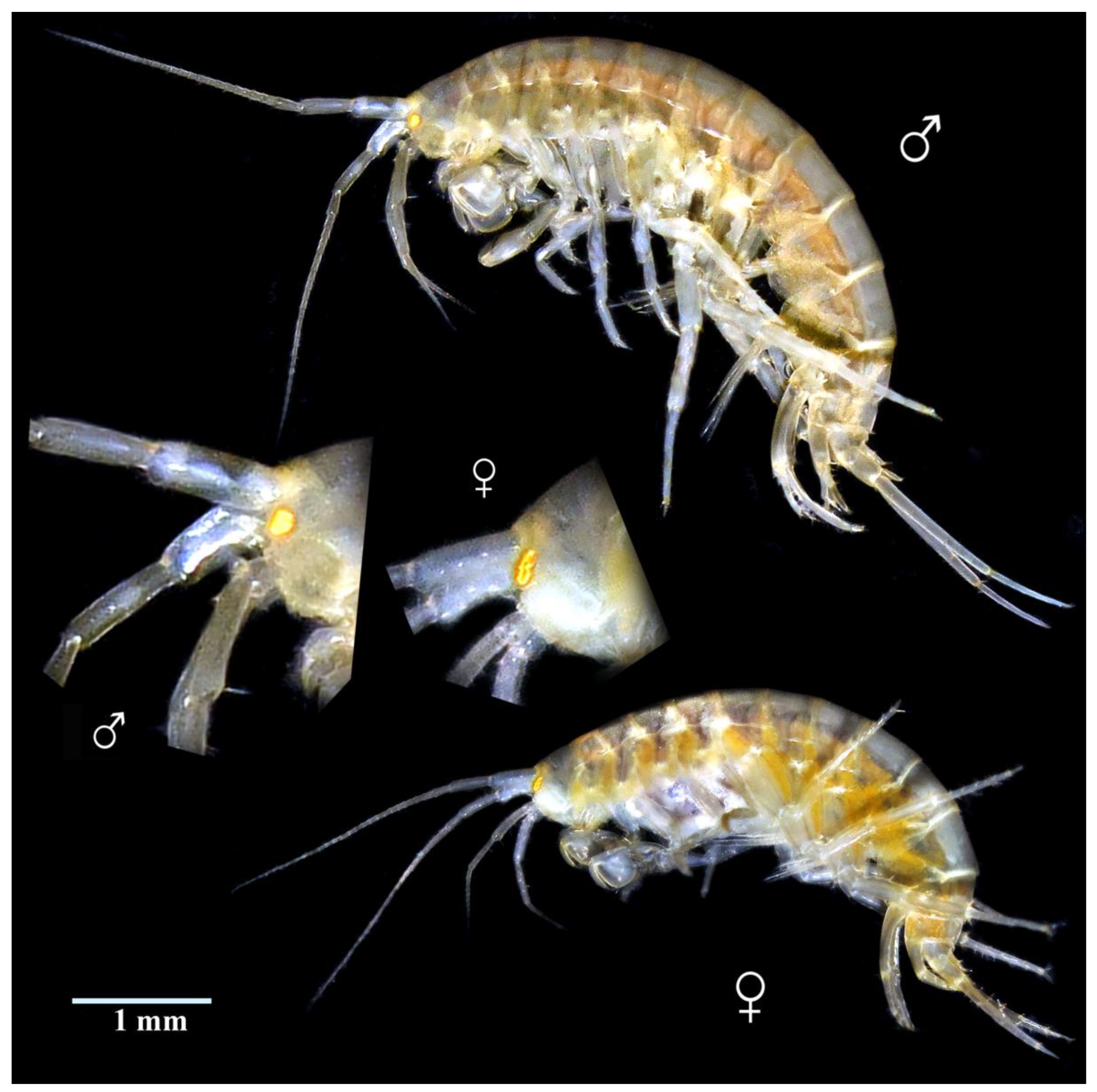
- Taxonomic part


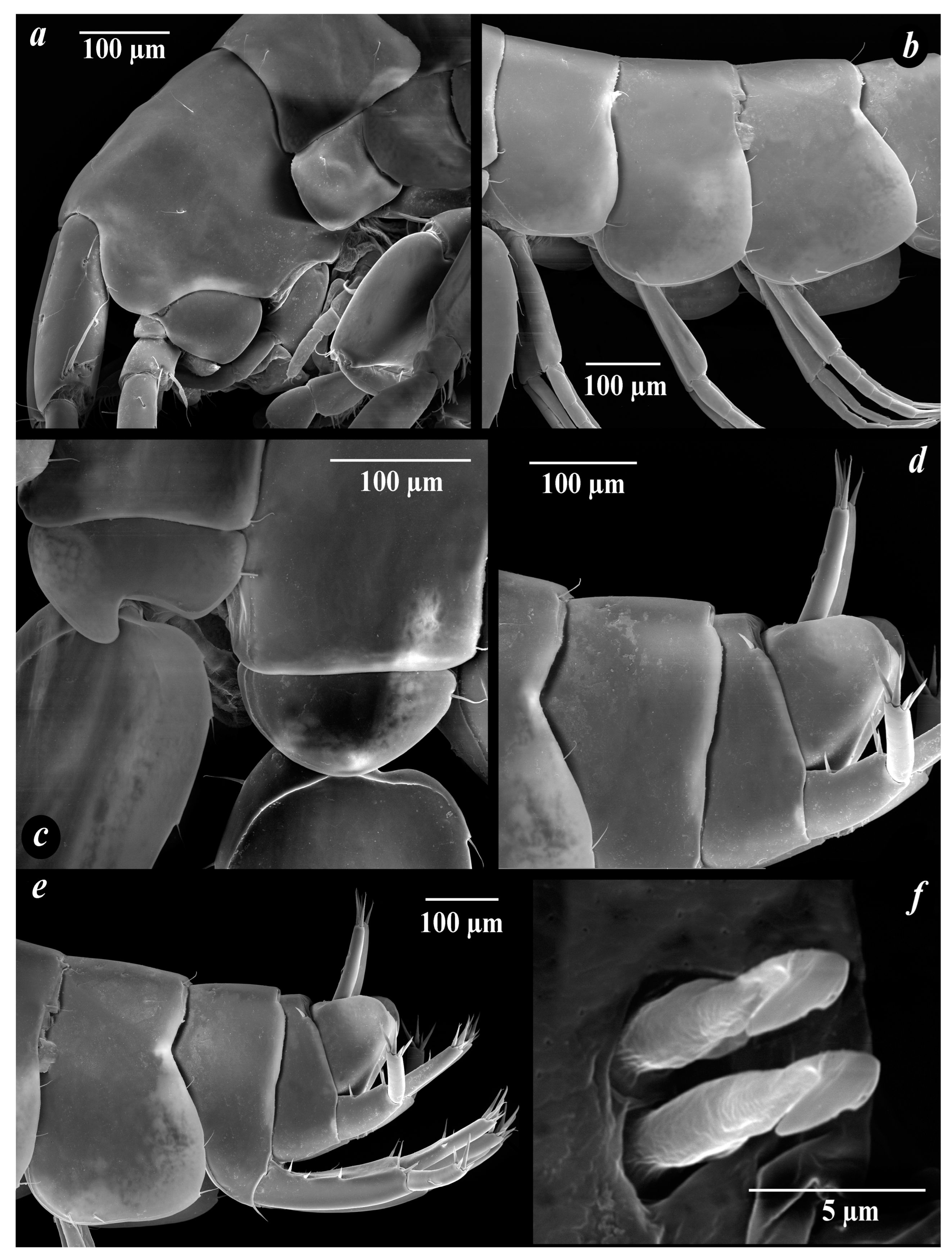
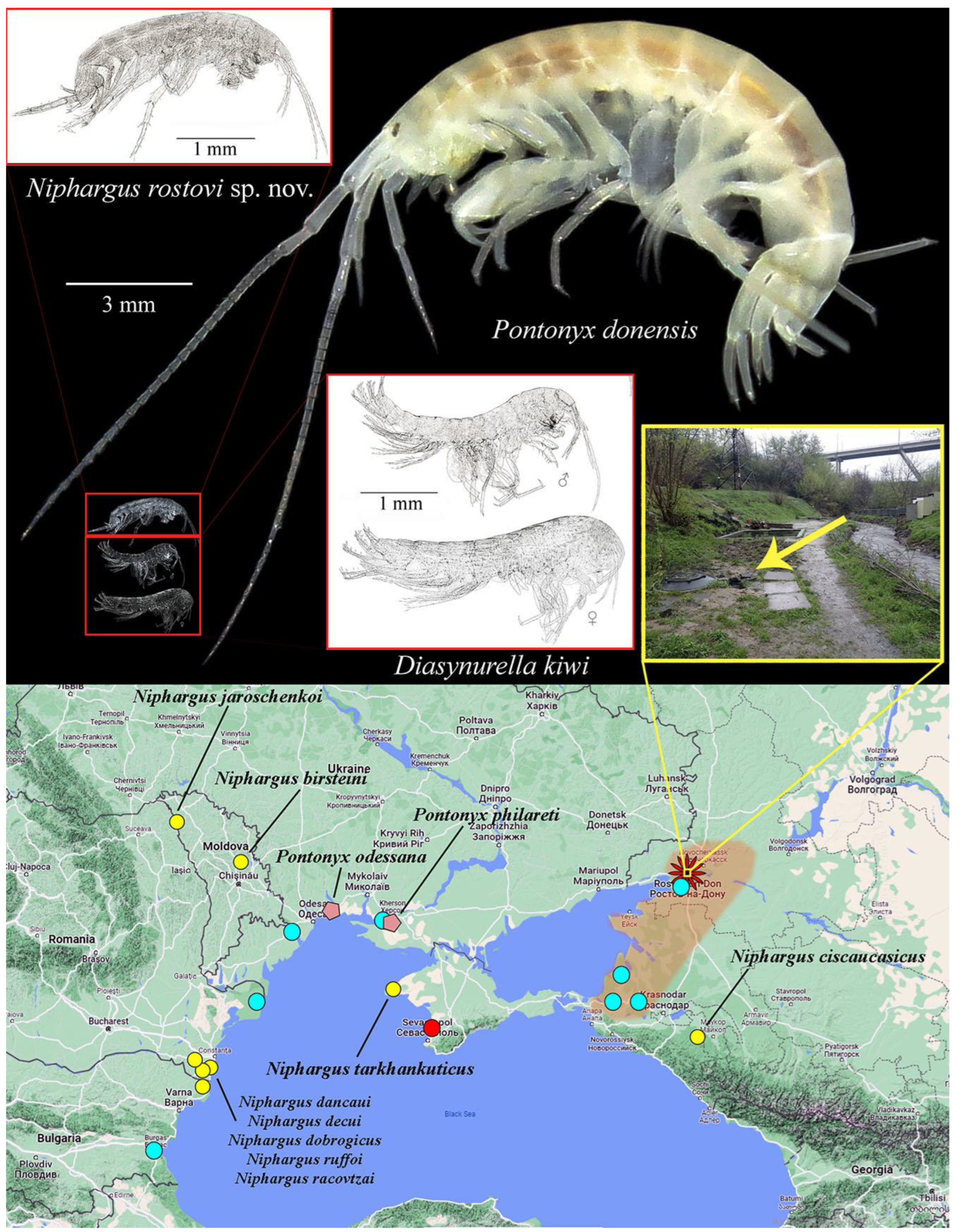
4. Discussion

| Species | Distribution | Lifestyle and Habitats | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRUSTACEA: AMPHIPODA | |||
| Synurella philareti Birštein, 1948 (=Pontonyx philareti) | Endemic, a spring in a mouth of Dnieper | stygobiotic, in springs | [130] |
| Pontonyx odessana (Sidorov and Kovtun, 2015) | Endemic, catacombs of Odessa | subterranean water reservoirs in the catacombs | [52] |
| Pontonyx donensis (Martynov, 1919) | Endemic, several springs in the Rostov-on-Don | stygobiotic, in springs | [48,56] |
| Diasynurella kiwi Marin and Palatov, 2023 | Endemic, a spring in the Rostov-on-Don | stygobiotic, in spring | [55] |
| Niphargus ciscaucasicus Marin and Palatov, 2019 | Endemic, Apsheronsk area | stygobiotic, inside well | [11] |
| Niphargus birsteini Dedyu, 1963 | Endemic, a spring in Pyatra village, Moldova | stygobiotic, in spring | [51] |
| Niphargus jaroschenkoi Dedyu, 1963 | Endemic, a spring in Novye Badrazi village, Moldova | stygobiotic, in spring | [51] |
| Niphargus tarkhankuticus Marin, Turbanov, Prokopov and Palatov, 2022 | Endemic, Tarkhankut Plain, Crimean Peninsula | stygobiotic, in wells | [9] |
| Niphargus dancaui Brad, Fišer, Flot and Sarbu, 2015 | Endemic, Movile Cave and surrounding area in Mangalia | sulphidic groundwater, caves | [97] |
| Niphargus dobrogicus Dancau, 1964 | Endemic, Doi Mai, Schitu and Vama Veche (Dobrogea) in Eastern Romania | sulphidic groundwater | [104,108] |
| Niphargus ruffoi (Karaman and Sarbu, 1993) | Endemic, Hagieni Spring near Mangalia | sulphidic groundwater | [106,108] |
| Niphargus racovitzai (Dancau, 1968) | Endemic, Movile Cave, Mangalia | sulphidic groundwater | [105,108] |
| Niphargus decui G. Karaman and Sarbu, 1995 | Endemic, in southern Dobrogea in Mangalia | stygobiotic, in well | [80,108] |
| Antrobathynella stammeri stammeri (Jakobi, 1954) | Endemic, Danilo-Ivanovka village, Zaporozhye region | stygobiotic, in spring | [131] |
| Bathynella natans ukrainica Monchenko, 1968 | Endemic, from the Chumshe spring in the vicinity of the village of Vladimirovka, Odessa region | stygobiotic, in spring | [131] |
| Niphargus potamophilus Birštein, 1954 | Sub-endemic, the Northern Black/Azov Sea Lowland | epigean, in ponds and other water reservoirs | [14,53,63] |
| Cryptorchestia cf. garbinii Ruffo, Tarocco and Latella, 2014 (a separate mitochondrial DNA (COI) lineage) | The Azov–Prikubanskaya Lowland | terrestrial, cryptic | pers. observ, in prep. |
| Pontogammarus cf. maeoticus (Sovinskij, 1894) (a separate mitochondrial DNA (COI) lineage) | Eastern Crimean Peninsula | free living, fresh water | [132] |
| INSECTA | |||
| Ecdyonurus dispar gratificus Martynov and Godunko, 2013 | Endemic to the Donetsk Ridge | fresh water, stream | [49] |
| Dorcadion spp. (ciscaucasicum-group, cinerarium-group) | Endemic or sub-endemic to Northern Black and Azov Sea Lowland | terrestrial | [133] |
| Colletes tardus Noskiewicz, 1936 | Kherson Province | terrestrial | [134] |
| Melitta budashkini Radchenko and Ivanov, 2012 | Cape Chauda, the Kerch Peninsula | terrestrial, xerophytic steppe | [135] |
| Andrena stepposa Osytshnjuk, 1977 | Donetsk region, Khomutovskaya steppe, valley of the Gruzsky Elanchik river, Kharkiv and Voronez regions | terrestrial | [136] |
| Strongylognathus arnoldii Radchenko, 1985 | Endemic, Tarkhankut Plain, Crimean Peninsula | terrestrial | [137,138] |
| Strongylognathus chelifer Radchenko, 1985 | Endemic, Kherson oblast, Askania-Nova | terrestrial | [102,103,138] |
| GASTROPODA | |||
| Elia novorossica nagolnica Balashov, 2013 | Endemic of Donetsk Upland | terrestrial | [139] |
| Clathrocaspia knipowitchi (Makarov, 1938) | Sub-endemic. In the Dnieper River near Kherson City, Don River and Caspian Sea | in rivers and freshwater parts of limans | [140,141] |
| Clathrocaspia stanislavi (Alexenko and Starobogatov, 1987) | Endemic, in the mouth of the Don river | in the stream of the river; probably crenobiotic [see 142] | [140,141,142] |
| Laevicaspia lincta (Milaschewitsch, 1908) | Sub-endemic, along the northern Black and Azov Sea coastal area | in fresh and brackish waterbodies | [141,142,143] |
| Laevicaspia ismailensis (Golikov and Starobogatov, 1966) | Endemic, along the northern Black and Azov Sea coastal area | in fresh and brackish waterbodies | [141,142,143] |
| Clessiniola variabilis (Eichwald, 1838) | Sub-endemic, northern Black and Azov Sea coastal area | in fresh and brackish waterbodies | [141,142,143] |
| Turricaspia chersonica Alexenko and Starobogatov, 1987 | Endemic, northern Black and Azov Sea coastal area | in fresh and brackish waterbodies | [141,142,143] |
| BIVALVIA | |||
| Anodonta anatina (a separate mitochondrial DNA (COI) lineage) | The Azov–Prikubanskaya Lowland | fresh water | [54] |
| Adacna fragilis Milaschewitsch, 1908 | Endemic, the northern Black Sea maritime area | fresh and brackish waterbodies | [141,144] |
| Adacna colorata (Eichwald, 1829) | Sub-endemic, the northern Black Sea maritime area | fresh and brackish waterbodies | [141,144] |
| Hypanis plicata relicta (Milaschewitch, 1916) | Endemic, the northern Black Sea maritime area | fresh and brackish waterbodies | [141,144] |
| FISHES | |||
| Barbus kubanicus Berg, 1912 | Endemic of the Kuban River | fresh water | [11] |
| Sabanejewia maeotica Vasil’eva and Vasil’ev, 2023 | Endemic of the lower Don River | fresh water | [145] |
| Sabanejewia spp., Romanogobius spp., Alburnus spp., Leuciscus spp. (some species) | Local endemics of Ponto-Caspian Basin | fresh and brackish waters | [145,146,147] |
| MAMMALIA | |||
| Spalax arenarius Reshetnik, 1939 | The southern part of the left bank of the Dnieper River, opposite the city of Kherson | terrestrial, burrowing | [54,107,148] |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Horton, T.; Lowry, J.; De Broyer, C.; Bellan-Santini, D.; Coleman, C.O.; Corbari, L.; Costello, M.J.; Daneliya, M.; Dauvin, J.-C.; Fišer, C.; et al. World Amphipoda Database. Niphargus tatrensis Wrzesniovsky, 1888. World Register of Marine Species. 2023. Available online: http://marinespecies.org/amphipoda/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=546804 (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Väinölä, R.; Witt, J.D.S.; Grabowski, M.; Bradbury, J.H.; Jazdzewski, K.; Sket, B. Global diversity of amphipods (Amphipoda; Crustacea) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borko, Š.; Trontelj, P.; Seehausen, O.; Moškrič, A.; Fišer, C. A subterranean adaptive radiation of amphipods in Europe. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borko, Š.; Altermatt, F.; Zagmajster, M.; Fišer, C. A hotspot of groundwater amphipod diversity on a crossroad of evolutionary radiations. Divers. Distrib. 2022, 28, 2765–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendoš, M.; Delić, T.; Copilaș-Ciocianu, D.; Fišer, C. First insight into cryptic diversity of a Caucasian subterranean amphipod of the genus Niphargus (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Niphargidae). Zool. Anz. 2021, 290, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.; Krylenko, S.; Palatov, D. The Caucasian relicts: A new species of the genus Niphargus (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Niphargidae) from the Gelendzhik–Tuapse area of the Russian southwestern Caucasus. Zootaxa 2021, 4963, 483–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, G.S. New species of the subterranean genus Niphargus Schiödte, 1849 (Amphipoda, Gammaridea, Niphargidae) from Russia, N. krasnodarus sp. n. (Contribution to knowledge of Amphipoda 256). Biol. Serbica 2012, 34, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Turbanov, I.S.; Palatov, D.M.; Golovatch, S.I. The state of the art of biospeleology in Russia and other countries of the former Soviet Union: A review of the cave (endogean) invertebrate fauna. I. Introduction—Crustacea. Entomol. Rev. 2016, 96, 926–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.N.; Turbanov, I.; Prokopov, G.; Palatov, D.M. A New Species of the Genus Niphargus Schiödte, 1849 (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Niphargidae) from Groundwater Habitats of the Tarkhankut Upland, Crimean Peninsula. Diversity 2022, 14, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.N. Crustacean “cave fishes” from the Arabika karst massif (Abkhazia, Western Caucasus): New species of stygobiotic crustacean genera Xiphocaridinella and Niphargus from the Gegskaya Cave and adjacent area. Arthropoda Sel. 2019, 28, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.; Palatov, D. A new species of the genus Niphargus (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Niphargidae) from the southwestern part of the North Caucasus. Zool. Middle East 2019, 65, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.; Palatov, D. An occasional record of the amplexus in epigean Niphargus (Amphipoda: Niphargidae) from the Russian Western Caucasus. Zootaxa 2019, 4701, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, I.N. The Quaternary speciation in the Caucasus: A new cryptic species of stygobiotic amphipod of the genus Niphargus (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Niphargidae) from the Kumistavi (Prometheus) Cave, Western Georgia. Arthropoda Sel. 2020, 29, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatov, D.M.; Marin, I.N. Epigean (pond-dwelling) species of the genus Niphargus Schiödte, 1849 (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Niphargidae) from the coastal plains of the Black and Azov seas of the north- and south-western Caucasus. Invertebr. Zool. 2021, 18, 105–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.; Palatov, D. Cryptic refugee on the northern slope of the Greater Caucasian Ridge: Discovery of Niphargus (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Niphargidae) in the North Ossetia–Alania, North Caucasus, separated from its relatives in the late Miocene. Zool. Anz. 2021, 292, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, M.L. Extinction Vulnerability and Selectivity: Combining Ecological and Paleontological Views. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1997, 28, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInerney, C.E.; Maurice, L.; Robertson, A.L.; Knight, L.R.F.D.; Arnscheidt, J.; Venditti, C.; Dooley, J.S.G.; Mathers, T.; Matthijs, S.; Eriksson, K.; et al. The ancient Britons: Groundwater fauna survived extreme climate change over tens of millions of years across NW Europe. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, D.C.; Pipan, T. The Biology of Caves and Other Subterranean Habitats; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fišer, C.; Sket, B.; Stoch, F. Distribution of four narrowly endemic Niphargus species (Crustacea: Amphipoda) in the western Dinaric region with description of a new species. Zool. Anz. 2006, 245, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulquier, A.; Malard, F.; Lefébure, T.; Douady, C.J.; Gibert, J. The Imprint of Quaternary Glaciers on the Present-Day Distribution of the Obligate Groundwater Amphipod Niphargus virei (Niphargidae). J. Biogeogr. 2008, 35, 552–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trontelj, P.; Douady, C.J.; Fišer, C.; Gibert, J.; Gorički, Š.; Lefébure, T.; Sket, B.; Zakšek, V. A molecular test for cryptic diversity in ground water: How large are the ranges of macro-stygobionts? Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 727–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fišer, C. Niphargus: A model system for evolution and ecology. In Encyclopedia of Caves; Culver, D.C., White, W.B., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louwye, S.; Foubert, A.; Mertens, K.; Van Rooij, D. The IODP Expedition 307 Scientific Party. Integrated stratigraphy and palaeoecology of the lower and Middle Miocene of the Porcupine Basin. Geol. Mag. 2008, 145, 321–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachos, J.; Pagani, M.; Sloan, L.; Thomas, E.; Billups, K. Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present. Science 2001, 292, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, G.M. The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages. Nature 2000, 405, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, G.M. Ice ages: Their impact on species distributions and evolution. In Evolution on Planet Earth; Rothschild, L.J., Lister, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 339–361. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, G.M. The structure of biodiversity–insights from molecular phylogeography. Front. Zool. 2004, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provan, J.; Bennett, K.D. Phylogeographic insights into cryptic glacial refugia. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, T.; Bartlein, P.J. Global changes during the last 3 million years: Climatic controls and biotic response. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 1992, 23, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, P.E.; Volkova, V.S.; Webb, T., III; Guiot, J.; Andreev, A.A.; Bezusko, L.G.; Bezusko, T.V.; Bykova, G.V.; Dorofeyuk, N.I.; Kvavadze, E.V.; et al. Last glacial maximum biomes reconstructed from pollen and plant macrofossil data from northern Eurasia. J. Biogeogr. 2000, 27, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.R.; Lister, A.M. Cryptic northern refugia and the origins of the modern biota. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.R.; Lister, A.M.; Barnes, I.; Dalen, L. Refugia revisited: Individualistic responses of species in space and time. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2010, 277, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkhnishvili, D. Historical Biogeography of the Caucasus; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tarkhnishvili, D.; Gavashelishvili, A.; Mumladze, L. Palaeoclimatic models help to understand current distribution of Caucasian forest species. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2012, 105, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Fumagalli, L.; Wust-Saucy, A.G.; Cosson, J.F. Comparative phylogeography and postglacial colonization routes in Europe. Mol. Ecol. 1998, 7, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, T. Molecular biogeography of Europe: Pleistocene cycles and postglacial trends. Front. Zool. 2007, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, K.D.; Provan, J. What do we mean by ’refugia’? Quat. Sci. Rev. 2008, 27, 2449–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppel, G.; Van Niel, K.P.; Wardell-Johnson, G.W.; Yates, C.J.; Byrne, M.; Mucina, L.; Schut, A.G.T.; Hopper, S.D.; Franklin, S.E. Refugia: Identifying and understanding safe havens for biodiversity under climate change. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlík, P.; Marková, S.; Choleva, L.; Bogutskaya, N.G.; Ekmekçi, F.G.; Ivanova, P.P. Divergence with gene flow between Ponto-Caspian refugia in an anadromous cyprinid Rutilus frisii revealed by multiple gene phylogeography. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, G.F. Southern European glacial refugia: A tale of tales. Taxon 2011, 60, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, T.; Varga, Z. Extra-Mediterranean refugia: The rule and not the exception? Front. Zool. 2012, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, K.J.; Rudner, E.; Sümegi, P. The full-glacial forests of central and southeastern Europe. Quat. Res. 2000, 53, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrkjeeide, M.O.; Stenøien, H.K.; Flatberg, K.I.; Hassel, K. Glacial refugia and post-glacial colonization patterns in European bryophytes. Lindbergia 2014, 37, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eme, D.; Malard, F.; Konecny-Dupré, L.; Lefébure, T.; Douady, C.J. Bayesian phylogeographic inferences reveal contrasting colonization dynamics among European groundwater isopods. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 5685–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefébure, T.; Douady, C.J.; Gouy, M.; Trontelj, P.; Briolay, J.; Gibert, J. Phylogeography of a subterranean amphipod reveals cryptic diversity and dynamic evolution in extreme environments. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefébure, T.; Douady, C.J.; Malard, F.; Gibert, J. Testing dispersal and cryptic diversity in a widely distributed groundwater amphipod (Niphargus rhenorhodanensis). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2007, 42, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strayer, D.L. Limits to biological distributions in groundwater. In Groundwater Ecology; Gilbert, J., Danielopol, D.L., Stanford, J.A., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994; p. 310. [Google Scholar]
- Martynov, A.V. Sur ies Crustaces superieurs des environs du Rostov-sur-Don. Arb. Naturf. Ges. Don. Univ. 2019, 1, 39–53. [Google Scholar]
- Martynov, A.V.; Godunko, R.J. A new subspecies of the subgenus Ecdyonurus Eaton, 1868 (Ephemeroptera: Heptageniidae) from the East of Ukraine. Zootaxa 2013, 3666, 489–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birštein, J.A. Records of the Subterranean Amphipod Niphargus (Crustacea, Amphipoda) in the Lower Don Region and the Kuban Basin. Zool. Zhurnal 1954, 33, 1025–1031. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dedyu, I.I. On subterrestrian Amphipods (Crustacea) in the Moldavian SSR. Zool. Zhurnal 1963, 42, 206–215. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sidorov, D.A.; Kovtun, O.A. Synurella odessana sp. n. (Crustacea, Amphipoda, Crangonyctidae), first report of a subterranean amphipod from the catacombs of Odessa and its zoogeographic importance. Subterr. Biol. 2015, 15, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topachevskii, V.A. Fauna of the USSR: Mammals. Mole Rats, Spalacidae; Nauka Publishers: Leningrad, Russia, 1969; p. 248. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tomilova, A.A.; Lyubas, A.A.; Kondakov, A.V.; Vikhrev, I.V.; Gofarov, M.Y.; Kolosova, Y.S.; Vinarski, M.V.; Palatov, D.M.; Bolotov, I.N. Evidence for Plio-Pleistocene Duck Mussel Refugia in the Azov Sea River Basins. Diversity 2020, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatov, D.; Marin, I. Diversity of the Caucasian genus Diasynurella Behning, 1940 (Amphipoda: Crangonyctidae) with description of four new species. Arthropoda Sel. 2023, 32, 23–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.N.; Palatov, D.M. Diversity of the crangonyctid genus Pontonyx Palatov et Marin, 2021 (Amphipoda: Crangonyctidae) in the coastal habitats around the Black and Azov Seas, with the description of a new species from the southwestern Caucasus. Arthropoda Sel. 2023; 32, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, S.V.; Rogl, F.; Rozanov, A.Y.; Steininger, F.F.; Shcherba, I.G.; Kovac, M. Lithological-paleogeographic maps of Paratethys. Cour. Forsch. Inst. Senckenb. 2004, 250, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, S.V.; Shcherba, I.G.; Ilyina, L.B.; Nevesskaya, L.A.; Paramonova, N.P.; Khondkarian, S.O.; Magyar, I. Late Miocene to Pliocene palaeogeography of the Paratethys and its relation to the Mediterranean. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2006, 238, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krijgsman, W.; Grothe, A.; Andreetto, F.; Reichart, G.-J.; Wolthers, M.; van Baak, C.G.C.; Vasiliev, I.; Stoica, M.; Sangiorgi, F.; Middelburg, J.; et al. Paratethys pacing of the Messinian Salinity Crisis: Low salinity waters contributing to gypsum precipitation? Earth Plane. Sci. Let. 2020, 532, 116029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copilaş-Ciocianu, D.; Grabowski, M.; Pârvulescu, L.; Petrusek, A. Zoogeography of epigean freshwater Amphipoda (Crustacea) in Romania: Fragmented distributions and wide altitudinal variability. Zootaxa 2014, 3893, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copilaş-Ciocianu, D.; Fišer, C.; Borza, P.; Balázs, G.; Angyal, D.; Petrusek, A. Low intraspecific genetic divergence and weak niche differentiation despite wide ranges and extensive sympatry in two epigean Niphargus species (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2017, 181, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copilaş-Ciocianu, D.; Fišer, C.; Borza, P.; Petrusek, A. 2018. Is subterranean lifestyle reversible? Independent and recent large-scale dispersal into surface waters by two species of the groundwater amphipod genus Niphargus. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2018, 119, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morhun, H.; Son, M.O.; Rewicz, T.; Kazanavičiūtė, E.; Copilaş-Ciocianu, D. The first records of Niphargus hrabei and N. potamophilus in Ukraine and Bulgaria significantly enlarge the ranges of these species. Eur. Zool. J. 2022, 89, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, I.; de Leeuw, A.; Filipescu, S.; Krijgsman, W.; Kuiper, K.; Stoica, M.; Briceag, A. The age of the Sarmatian–Pannonian transition in the Transylvanian Basin (Central Paratethys). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2010, 297, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, I.; Stoica, M.; Grothe, A.; Lazarev, S.; Palcu, D.V.; van Baak, C.; Leeuw, A.D.; Sangiorgi, F.; Reichart, G.J.; Davies, G.R.; et al. Hydrological changes in restricted basins: Insights from strontium isotopes on late Miocene Pliocene connectivity of the Eastern Paratethys (Dacian Basin, Romania). Geochem. Geoph. Geosyst. 2021, 22, e2020GC009369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avise, J.C. Molecular Markers, Natural History and Evolution; Chapman & Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1994; p. 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 from diverse metazoan. Mol. Mar Biol. Biotech. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA 7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to Estimate Maximum–Likelihood Phylogenies: Assessing the Performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouckaert, R.; Vaughan, T.G.; Barido-Sottani, J.; Duchêne, S.; Fourment, M.; Gavryushkina, A.; Heled, J.; Jones, G.; Kühnert, D.; De Maio, N.; et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. Beast 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntakis, A.; Anastasiadou, C.; Zakšek, V.; Fišer, C. Phylogeny and biogeography of three new species of Niphargus (Crustacea: Amphipoda) from Greece. Zool. Anz. 2015, 255, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borko, Š.; Collette, M.; Brad, T.; Zakšek, V.; Flot, J.-F.; Vaxevanopoulos, M.; Sarbu, S.M.; Fišer, C. Amphipods in a Greek cave with sulphidic and non-sulphidic water: Phylogenetically clustered and ecologically divergent. Syst. Biodivers. 2019, 17, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.; Stoch, F.; Knight, L.R.; Chauveau, C.; Flot, J.-F. The genus Microniphargus (Crustacea, Amphipoda): Evidence for three lineages distributed across northwestern Europe and transfer from Niphargidae to Pseudoniphargidae. Belg. J. Zool. 2021, 151, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy-Haim, T.; Simon-Blecher, N.; Frumkin, A.; Naaman, I.; Achituv, Y. Multiple transgressions and slow evolution shape the phylogeographic pattern of the blind cave-dwelling shrimp Typhlocaris. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copilaș-Ciocianu, D.; Petrusek, A. The southwestern Carpathians as an ancient centre of diversity of freshwater gammarid amphipods: Insights from the Gammarus fossarum species complex. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 3980–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krijgsman, W.; Stoica, M.; Hoyle, T.M.; Jorissen, E.L.; Lazarev, S.; Rausch, L.; Bista, D.; Alçiçek, M.C.; Ilgar, A.; van den Hoek Ostende, L.W.; et al. The myth of the Messinian Dardanelles: Late Miocene stratigraphy and palaeogeography of the ancient Aegean-Black Sea gateway. Palaeogeog. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2018, 560, 110033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krijgsman, W.; Palcu, D.V.; Andreetto, F.; Stoica, M.; Mandic, O. Changing seas in the late Miocene Northern Aegean: A Paratethyan approach to Mediterranean basin evolution. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 210, 103386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, G.S.; Sarbu, S. Niphargus decui n. sp. (Amphipoda, Gammaridea, Niphargidae), a new species from Romania. Trav. L’institut Spéologie Emile Racovitza 1995, 34, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Karaman, G.S. Contribution to the knowledge of the Amphipoda. Four new Niphargus species from Italy, N. duplus, N. stygocharis italicus, N. ruffoi and N. canui (Gammaridae). Vie Milieu 1976, 26, 21–50. [Google Scholar]
- Palatov, D.M.; Marin, I.N. When males and females belong to different genera: An interesting case of Synurella/Pontonyx (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Crangonyctidae) co-occurrence. Arthropoda Sel. 2021, 30, 443–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.N.; Palatov, D.M. The hidden diversity of the genus Lyurella Derzhavin, 1939 (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Crangonyctidae): Four new species from the subterranean habitats of the northwestern Caucasus, Russia. Zootaxa 2021, 5006, 127–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.N.; Palatov, D.M. Lifestyle switching and refugee availability are the main factors in the evolution and distribution of the genus Synurella Wrześniowski, 1877 (Amphipoda: Crangonyctidae). Arthropoda Sel. 2022, 31, 393–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjadze, S.; Asanidze, Z.; Gavashelishvili, A.; Soto-Adames, F.N. The hypogean invertebrate fauna of Georgia (Caucasus). Zool. Middle East 2019, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.; Badjadze, S.; Palatov, D. Diversity, taxonomy and phylogeny of the genus “Niphargus borutzkyi” ingroup (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Niphargidae) in Western Georgia, Caucasus. Zootaxa, 2023; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Naseka, A. Zoogeographical Freshwater Divisions of the Caucasus as a part of the West Asian Transitional Region. Proc. Zool. Inst. RAS 2010, 314, 469–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamaghani-Shishvan, M.; Esmaeili-Rineh, S. Two new species of groundwater amphipods of the genus Niphargus Schiödte, 1849 from northwestern Iran. Eur. J. Taxon. 2019, 546, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili-Rineh, S.; Mirghaffari, S.A. Niphargus hegmatanensis sp. nov. (Crustacea, Amphipoda, Niphargidae), a new species from subterranean freshwaters of western Iran. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2021, 20, 1049–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatilova, I.; Kokolashvili, I.M.; Bukhsianidze, M.G.; Koiava, K.P.; Maissuradze, L.S.; Bruch, A.A. Late Cenozoic Bioevents on the Territory of Georgia (Foraminifera and Pollen); Georgian National Museum: Tbilisi, Georgia, 2021; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Sękiewicz, K.; Danelia, I.; Farzaliyev, V.; Gholizadeh, H.; Iszkuło, G.; Naqinezhad, A.; Ramezani, E.; Thomas, P.A.; Tomaszewski, D.; Walas, Ł.; et al. Past climatic refugia and landscape resistance explain spatial genetic structure in Oriental beech in the South Caucasus. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatov, D.M.; Sokolova, A.M. Two new stygobiotic species of the genus Proasellus (Crustacea: Isopoda: Asellidae) from the North Caucasus. Invertebr. Zool. 2021, 18, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anistratenko, V.V.; Palatov, D.M.; Chertoprud, E.M.; Sitnikova, T.Y.; Anistratenko, O.Y.; Clewing, C.; Vinarski, M.V. Keyhole into a lost world: The First purely freshwater species of the Ponto-Caspian genus Clathrocaspia (Caenogastropoda: Hydrobiidae). Diversity 2022, 14, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marret, F.; Bradley, L.R.; Tarasov, P.E.; Ivanova, E.V.; Zenina, M.A.; Murdmaa, I.O. The Holocene history of the NE Black Sea and surrounding areas: An integrated record of marine and terrestrial palaeoenvironmental change. Holocene 2019, 29, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanina, T.A. Environmental Variability of the Ponto-Caspian and Mediterranean Basins during the Last Climatic Macrocycle. Geogr. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 13, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.; Krylenko, S.; Palatov, D. Euxinian relict amphipods of the Eastern Paratethys in the subterranean fauna of coastal habitats of the Northern Black Sea region. Invertebr. Zool. 2021, 18, 247–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brad, T.; Fišer, C.; Flot, J.-F.; Sarbu, S.M. Niphargus dancaui sp. nov. (Amphipoda, Niphargidae)—A new species thriving in sulfidic groundwaters in southeastern Romania. Eur. J. Taxon. 2015, 164, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Borgh, M.; Vasiliev, I.; Stoica, M.; Knežević, S.; Matenco, L.; Krijgsman, W.; Rundić, L.; Cloetingh, S. The isolation of the Pannonian basin (Central Paratethys): New constraints from magnetostratigraphy and biostratigraphy. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 103, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Borgh, M.; Stoica, M.; Donselaar, M.E.; Matenco, L.; Krijgsman, W. Miocene connectivity between the Central and Eastern Paratethys: Constraints from the western Dacian Basin. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2014, 412, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sworobowicz, L.; Mamos, T.; Grabowski, M.; Wysocka, A. Lasting through the ice age: The role of the proglacial refugia in the maintenance of genetic diversity, population growth, and high dispersal rate in a widespread freshwater crustacean. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 65, 1028–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukić, D.; Pinceel, T.; Marrone, F.; Mioduchowska, M.; Vad, C.F.; Brendonck, L.; Ptacnik, R.; Horvát, Z. Pleistocene allopatric differentiation followed by recent range expansion explains the distribution and molecular diversity of two congeneric crustacean species in the Palaearctic. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radchenko, A.G. Ants of the genus Strongylognathus (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of the USSR fauna. Zool. Zhurnal 1991, 70, 84–90. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Radchenko, A.G. Ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) of Ukraine; National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine: Kiev, Ukraine; I. I. Schmalhausen Institute of Zoology: Kiev, Ukraine, 2016; p. 496. [Google Scholar]
- Dancău, D. Noi contribuţii la studiul amfipodelor subterane Niphargus dobrogicus n. sp. Luc. Inst. Speol. Emil Racoviţă 1964, 3, 397–403. [Google Scholar]
- Dancău, D. Sur un nouvel Amphipode souterrain de Roumanie, Pontoniphargus racovitzai n. g., n. sp. Luc. Inst. Speol. Emil Racoviţă 1968, 7, 275–285. [Google Scholar]
- Karaman, G.S.; Sarbu, S. A new species of the genus Pontoniphargus Dancau, (Amphipoda, Gammaridea, Family Niphargidae) from Romania, P. ruffoi n. sp. Bolletino Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Verona 1993, 20, 569–582. [Google Scholar]
- Vorontsov, N.N.; Martynova, L.Y.; Fomichova, I.I. An electrophoretic comparison of the blood proteins in mole rats of the fauna of the USSR (Spalacinae, Rodentia). Zool. Zhurnal 1977, 56, 1207–1215. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Flot, J.-F.; Bauermeister, J.; Brad, T.; Hillebrand-Voiculescu, A.; Sarbu, S.M.; Dattagupta, S. Niphargus-Thiothrix associations may be widespread in sulphidic groundwater ecosystems: Evidence from southeastern Romania. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, S.; Lascu, C.; Brad, T. Dobrogea: Movile Cave; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 429–436. [Google Scholar]
- Brad, T.; Iepure, S.; Sarbu, S.M. The Chemoautotrophically Based Movile Cave Groundwater Ecosystem, a Hotspot of Subterranean Biodiversity. Diversity 2021, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, B.A.; Gandlin, A.A.; Simonov, E.S.; Levina, M.A.; Barmintseva, A.E.; Japoshvili, B.; Mugue, N.S.; Mumladze, L.; Mustafayev, N.J.; Pashkov, A.N.; et al. Phylogeny, phylogeography and hybridization of Caucasian barbels of the genus Barbus (Actinopterygii, Cyprinidae). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2019, 135, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselingh, F.P.; Neubauer, T.A.; Anistratenko, V.V.; Vinarski, M.V.; Yanina, T.A.; ter Poorten, J.J.; Kijashko, P.V.; Albrecht, C.; Anistratenko, O.Y.; D’Hont, A.; et al. Mollusc species from the Pontocaspian region—An expert opinion list. Zookeys 2019, 827, 31–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, C. A brief survey of the early Middle Pleistocene in Europe. In The Early Middle Pleistocene in Europe; Turner, C., Ed.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 295–317. [Google Scholar]
- Konopacka, A.; Hupalo, K.; Rewicz, T.; Grabowski, M. Species inventory and distribution patterns of freshwater amphipods in Moldova. North-West. J. Zool. 2014, 10, 382–392. [Google Scholar]
- Dumnicka, E.; Galas, J. An overview of stygobiotic invertebrates of Poland based on published data. Subterr. Biol. 2017, 23, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumnicka, E.; Galas, J.; Najberek, K.; Urban, J. The influence of Pleistocene glaciations on the distribution of obligate aquatic subterranean invertebrate fauna in Poland. Zool. Anz. 2020, 286, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pociecha, A.; Karpowicz, M.; Namiotko, T.; Dumnicka, E.; Galas, J. Diversity of Groundwater Crustaceans in Wells in Various Geologic Formations of Southern Poland. Water 2021, 13, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.N.; Palatov, D.M. Volgonyx gen.n. and Pontonyx gen.n., two new genera of the family Crangonyctidae (Crustacea: Amphipoda) from the southeastern Europe. Arthropoda Sel. 2021, 30, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, G.M. Post-glacial re-colonization of European biota. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1999, 68, 87–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinenko, O.; Stümpel, N.; Mazanaeva, L.; Bakiev, A.; Shiryaev, K.; Pavlov, A.; Kotenko, T.; Kukushkin, O.; Chikin, Y.; Duisebayeva, T.; et al. Mitochondrial phylogeny shows multiple independent ecological transitions and northern dispersion despite of Pleistocene glaciations in meadow and steppe vipers (Vipera ursinii and Vipera renardi). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2015, 84, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandzik, D.; Jablonski, D.; Zinenko, O.; Kukushkin, O.V.; Moravec, J.; Gvoždík, V. Pleistocene extinctions and recent expansions in an anguid lizard of the genus Pseudopus. Zool. Scr. 2018, 47, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, E.; Keikhosravi, A.; Solhjouy-Fard, S.; Sheybak, F.; Schubart, C. Phylogeography of Potamon ibericum (Brachyura: Potamidae) identifies Quaternary glacial refugia within the Caucasus biodiversity hot spot. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 4749–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonski, D.; Kukushkin, O.V.; Avci, A.; Bunyatova, S.; Kumlutas, Y.; Ilgaz, C.; Polyakova, E.; Shiryaev, K.; Tuniyev, B.; Jandzik, D. The biogeography of Elaphe sauromates (Pallas, 1814), with a description of a new rat snake species. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, W.B.F.; Pitman, W.C., III; Major, C.O.; Shimkus, K.; Moskalenko, V.; Jones, G.A.; Dimitrov, P.; Gorür, N.; Sakinç, M.; Yüce, H. An abrupt drowning of the Black Sea shelf. Mar. Geol. 1997, 138, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, A.; Arz, H.W.; Lamy, F.; Wefer, G. Late glacial to Holocene paleoenvironmental evolution of the Black Sea, reconstructed with stable oxygen isotope records obtained on ostracod shells. Earth Plan. Sci. Lett. 2006, 241, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgievski, G.; Stanev, E.V. Paleo-evolution of the Black Sea watershed: Sea level and water transport through the Bosporus Straits as an indicator of the Lateglacial-Holocene transition. Clim. Dyn. 2006, 26, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federov, P.V. Postglacial transgression of the Black Sea. Int. Geol. Rev. 1971, 14, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanko-Hombach, V.; Yanina, T. Toward an understanding of human responses to environmental change in the Caspian-Black Sea-Mediterranean Corridors (IGCP 610 final report). Epis. J. Int. Geosci. 2019, 42, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanko-Homback, V.; Schnyukov, E.; Pasynkov, A.; Sorokin, V.; Kuprin, P.; Maslakov, N.; Montnenko, I.; Smyntyna, O. Geological and geomorphological factors and marine conditions of the Azov-Black Sea Basin and coastalistics as they determine prospecting for seabed prehistoric sites on the continental shelf. In Submerged Scapes of the European Continental Shelf: Quaternary Paleoenvironments; Flemming, N.C., Harff, J., Moura, D., Burgess, A., Bailey, G.N., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 431–478. [Google Scholar]
- Birštein, Y.A. The extent and distribution of the genus Synurella (Crustacea, Amphipoda). Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR Nov. Ser. 1948, 60, 701–704. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Monchenko, V.I. A new order of crustaceans (Crustacea, Bathynellacea) for the fauna of Ukraine with a description of a subspecies new to science. Vest. Zool. 1968, 4, 9–14. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nahavandi, N.; Ketmaier, V.; Plath, M.; Tiedemann, R. Diversification of Ponto-Caspian aquatic fauna: Morphology and molecules retrieve congruent evolutionary relationships in Pontogammarus maeoticus (Amphipoda: Pontogammaridae). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2013, 69, 1063–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarev, M.A. A revision of the taxonomic structure of Dorcadion cinerarium (Fabricius, 1787) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Stud. Rep. Dist. Mus. Prague-East. Taxon. Ser. 2011, 7, 255–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Kuhlmann, M. The bees of the genus Colletes Latreille 1802 of the Ukraine, with a key to species (Hymenoptera: Apoidea: Colletidae). Zootaxa 2012, 3488, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michez, D.; Kuhlmann, M.; Ivanov, S.P.; Radchenko, V.G. Description of four new species in the bee genus Melitta Kirby, 1802 (Hymenoptera: Melittidae). Zootaxa 2012, 3337, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, J.R.; Michez, D.; Nieto, A.; Patiny, S.; Radchenko, V.; Roberts, S. Andrena stepposa. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2013. e.T19198407A43114622. [CrossRef]
- Borowiec, L. Catalogue of ants of Europe, the Mediterranean Basin and adjacent regions (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Genus 2014, 25, 1–340. [Google Scholar]
- Radchenko, A.G. Ants of the genus Strongylognathus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in the European part of the USSR. Zool. Zhurnal 1985, 64, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar]
- Balashov, I. Elia novorossica (Stylommatophora, Clausiliidae) in Ukraine: Description, habitats, conservation status, concomitant terrestrial molluscs. Ruthenica 2013, 23, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Anistratenko, V.V.; Neubauer, T.A.; Anistratenko, O.Y.; Kijashko, P.V.; Wesselingh, F.P. A revision of the Pontocaspian gastropods of the subfamily Caspiinae (Caenogastropoda: Hydrobiidae). Zootaxa 2021, 4933, 151–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinarski, M.V.; Kantor, Y.I. Analytical Catalogue of Fresh and Brackish Water Molluscs of Russia and Adjacent Countries; A.N. Severtsov Institute of Ecology and Evolution of RAS: Moscow, Russia, 2016; 544p. [Google Scholar]
- Golikov, A.N.; Starobogatov, Y.I. Ponto-Caspian gastropods in the Azov-Black Sea Basin. Zool. Zhurnal 1966, 45, 352–362. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gogaladze, A.; Son, M.O.; Lattuada, M.; Anistratenko, V.V.; Syomin, V.L.; Pavel, A.B.; Popa, O.P.; Popa, L.O.; ter Poorten, J.-J.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; et al. Decline of unique Pontocaspian biodiversity in the Black Sea Basin: A review. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 12923–12947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlato, O.; Starobogatov, Y.I.; Bivalvia, C. Guide for Identification of the Fauna of the Black and Azov Seas. Vol. 3. Freeliving Invertebrates. Arthropods (Other Than Crustaceans), Mollusks, Echinodermatans, Chaetognathans, Chordatans; Mordukhay-Boltovskoy, F.D., Ed.; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1972; pp. 178–249. [Google Scholar]
- Vasil’eva, E.; Vasil’ev, V.P. A New Species of Golden Loach (genus Sabanejewia, Cobitidae) from the Sea of Azov Basin. J. Ichthyol. 2023, 63, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasil’eva, E.D.; Solovyeva, E.N.; Vasil’eva, V.P. Molecular Phylogeny of the Spined Loach Genus Sabanejewia (Osteichthyes: Cobitidae) Revised. J. Ichthyol. 2022, 62, 812–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasil’eva, E.D. Fish of the Black Sea. The Determinant of Marine, Brackish, Euryhaline and Passable Species with Color Illustrations Collected by S.V. Bogorodsky; VNIRO Publishing House: Moscow, Russian, 2007; p. 238. [Google Scholar]
- Reshetnik, Y.G. On the systematics and geographical distribution of mole rats (Spalacidae) in the Ukrainian SSR. Rep. Zool. Mus. Kyiv. 1939, 23, 3–21. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
| Species | p-Distance ± SE |
|---|---|
| Niphargus karkabounasi | 0.135 ± 0.015 |
| Niphargus italicus | 0.211 ± 0.020 |
| Niphargus microcerebrus | 0.213 ± 0.018 |
| Niphargus abberans | 0.215 ± 0.019 |
| Niphargus grandii | 0.218 ± 0.018 |
| Niphargus decui | 0.222 ± 0.019 |
| Niphargus alpinus | 0.223 ± 0.019 |
| Niphargus carpathicus | 0.224 ± 0.019 |
| Niphargus danielopoli | 0.234 ± 0.020 |
| Niphargus transsylvanicus | 0.242 ± 0.021 |
| Niphargus barbatus | 0.270 ± 0.024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marin, I.N.; Palatov, D.M. Insights on the Existence of Ancient Glacial Refugee in the Northern Black/Azov Sea Lowland, with the Description of the First Stygobiotic Microcrustacean Species of the Genus Niphargus Schiödte, 1849 from the Mouth of the Don River. Diversity 2023, 15, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050682
Marin IN, Palatov DM. Insights on the Existence of Ancient Glacial Refugee in the Northern Black/Azov Sea Lowland, with the Description of the First Stygobiotic Microcrustacean Species of the Genus Niphargus Schiödte, 1849 from the Mouth of the Don River. Diversity. 2023; 15(5):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050682
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarin, Ivan N., and Dmitry M. Palatov. 2023. "Insights on the Existence of Ancient Glacial Refugee in the Northern Black/Azov Sea Lowland, with the Description of the First Stygobiotic Microcrustacean Species of the Genus Niphargus Schiödte, 1849 from the Mouth of the Don River" Diversity 15, no. 5: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050682
APA StyleMarin, I. N., & Palatov, D. M. (2023). Insights on the Existence of Ancient Glacial Refugee in the Northern Black/Azov Sea Lowland, with the Description of the First Stygobiotic Microcrustacean Species of the Genus Niphargus Schiödte, 1849 from the Mouth of the Don River. Diversity, 15(5), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050682






