Distribution of the Riparian Salix Communities in and around Romanian Carpathians
Abstract
1. Introduction
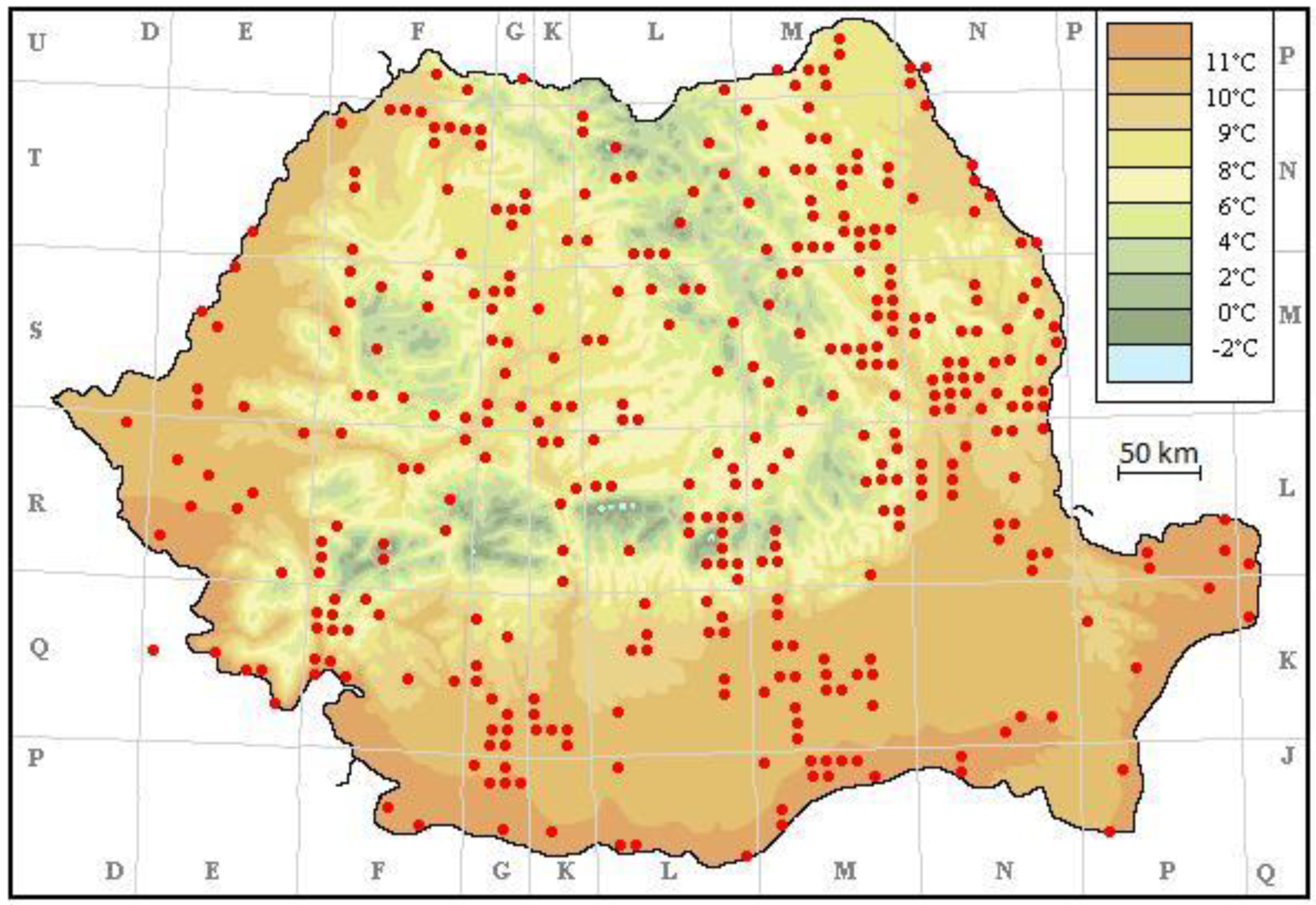
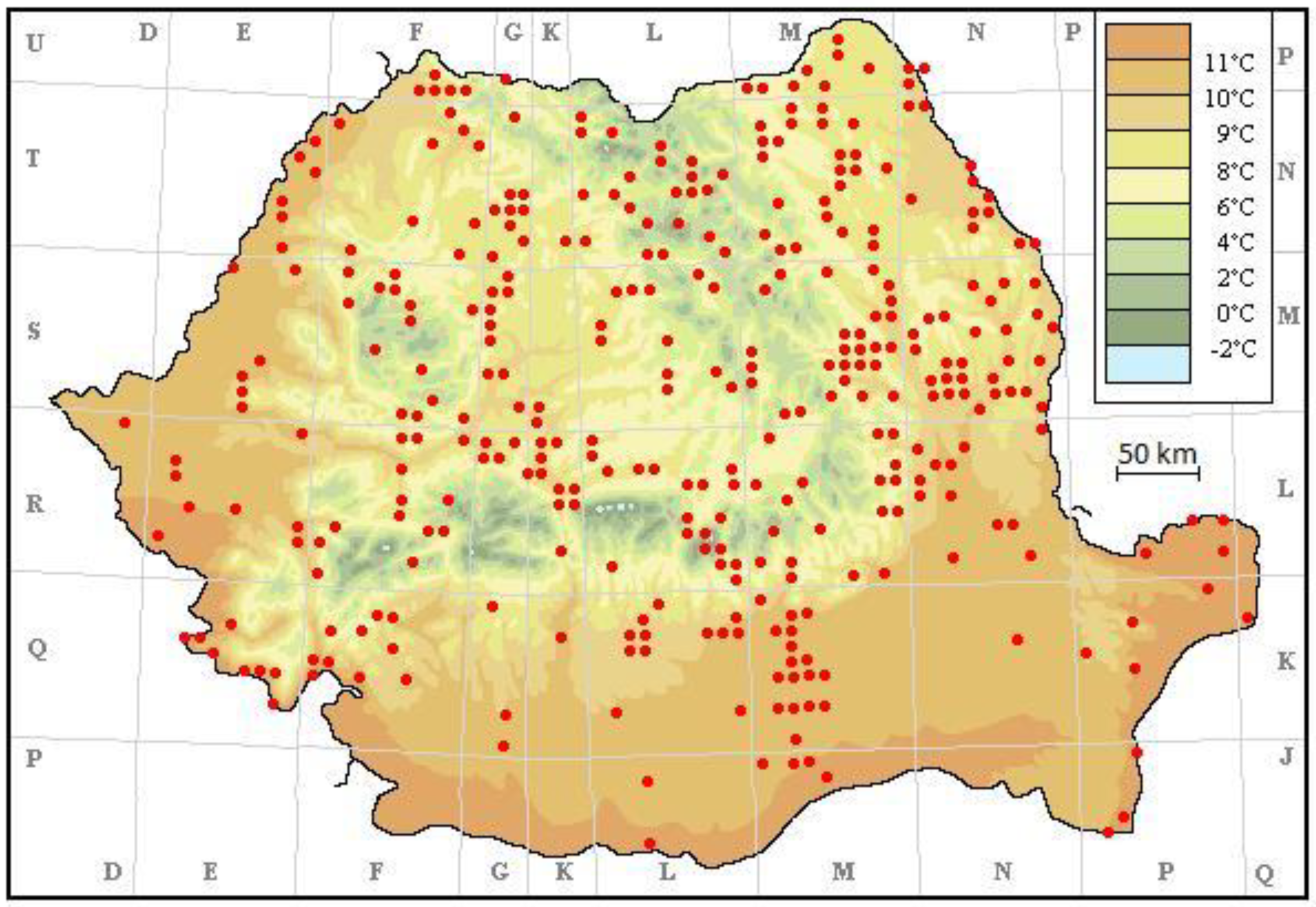
2. Material and Methods
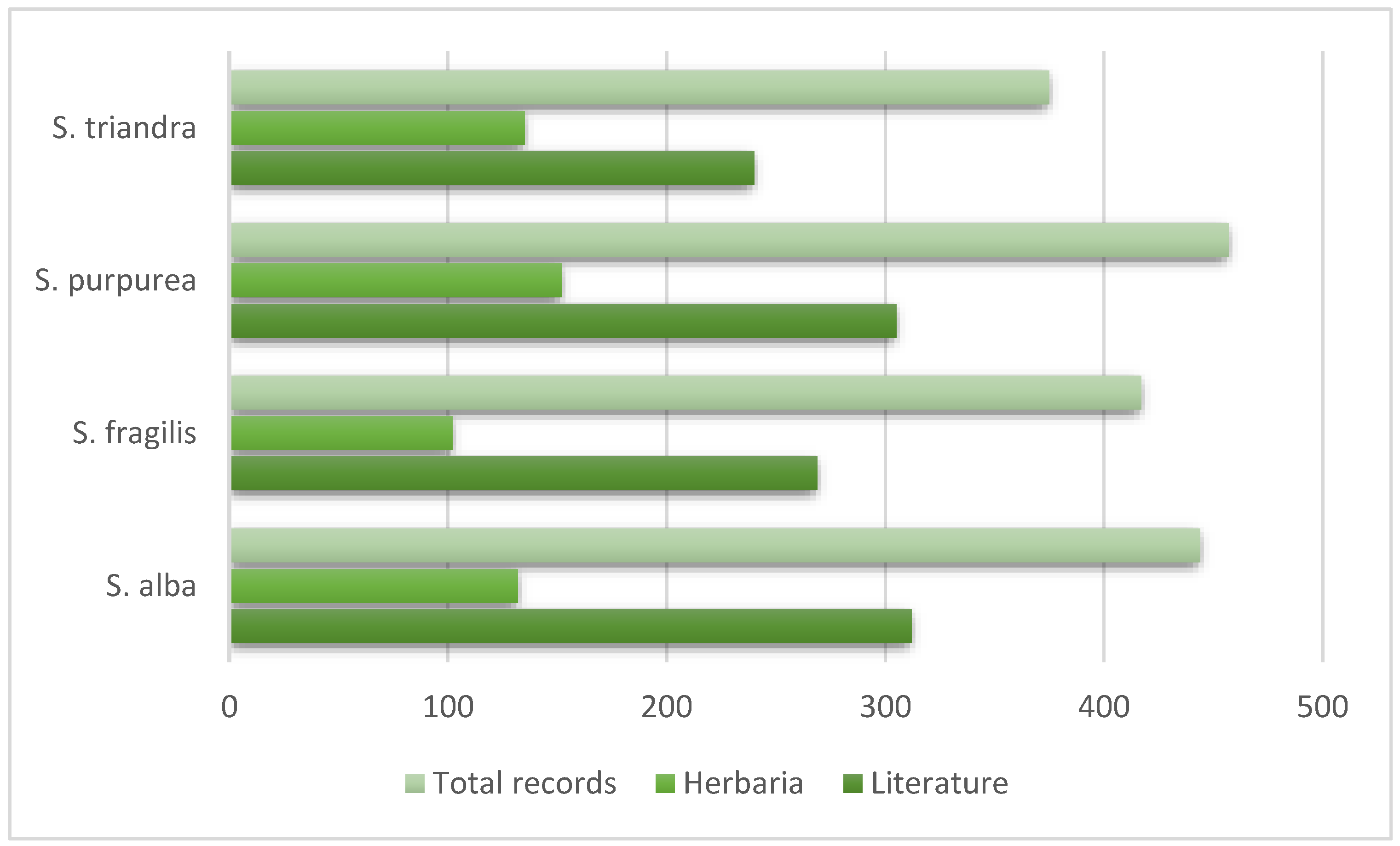
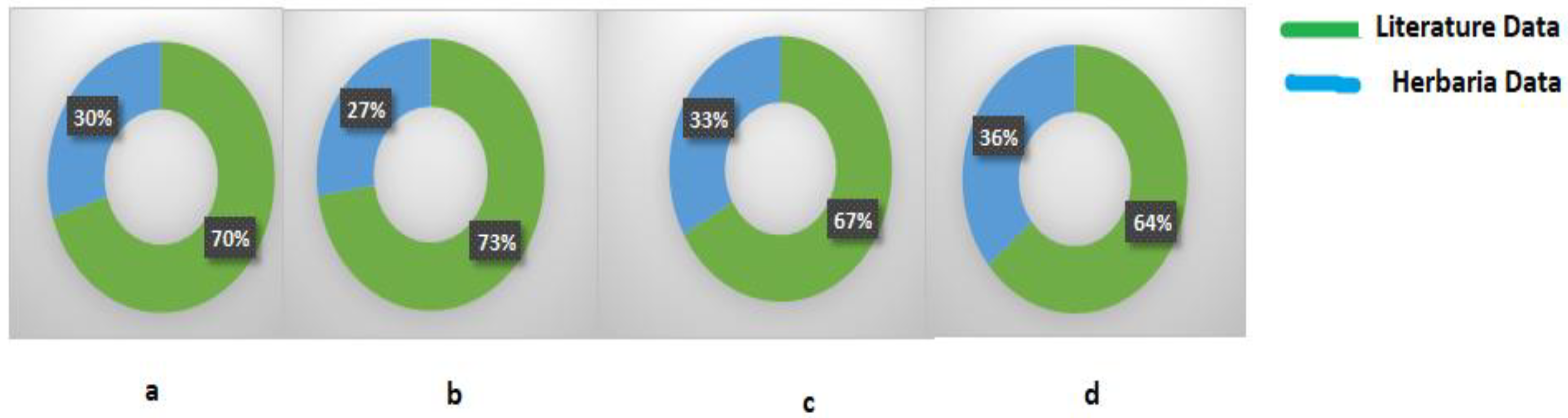
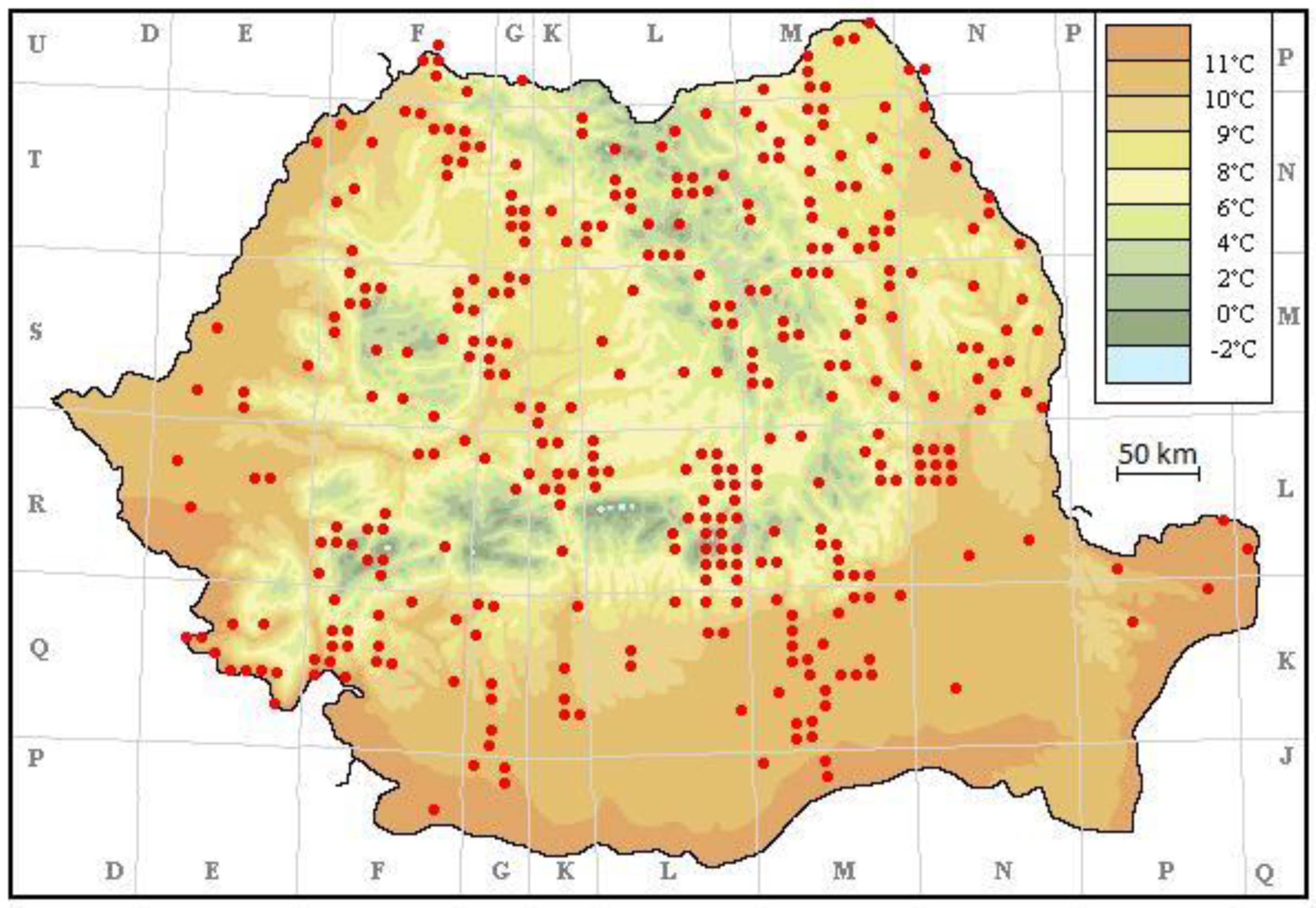
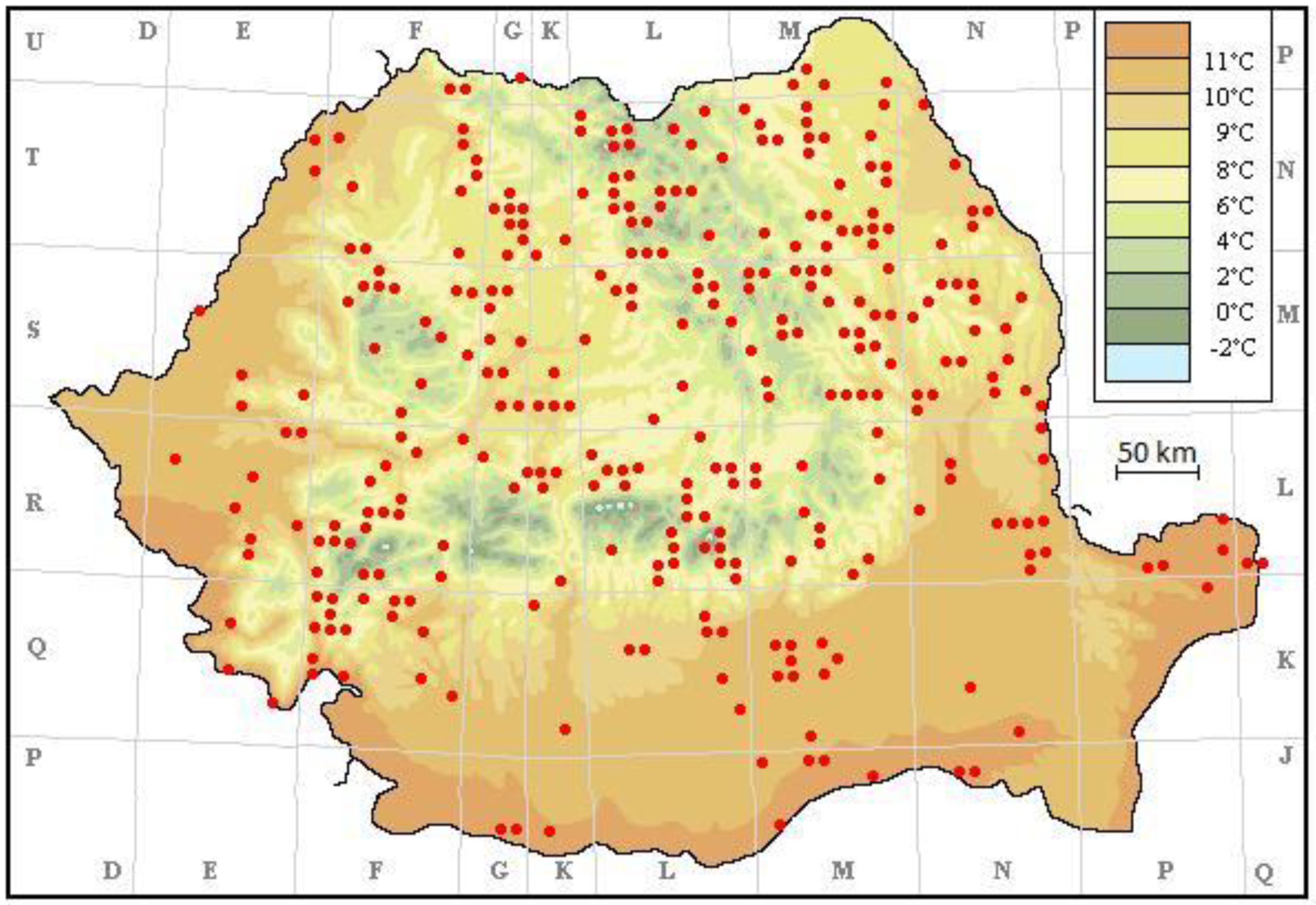
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Ecological Importance
4.2. Conservation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fremier, A.K.; Kiparsky, M.; Gmur, S.; Aycrigg, J.; Craig, R.K.; Svancara, L.K.; Goble, D.D.; Cosens, B.; Davis, F.W.; Scott, J.M. A riparian conservation network for ecological resilience. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 191, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiman, R.J.; Bilby, R.E.; Bisson, P.A. Riparian Ecology and Management in the Pacific Coastal Rain Forest. Bioscience 2000, 50, 996–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, W.W.; Gilbert, J.T.; Jensen, M.L.; Gilbert, J.D.; Hough-Snee, N.; McHugh, P.A.; Wheaton, J.M.; Bennett, S.N. Riparian vegetation as an indicator of riparian condition: Detecting departures from historic condition across the North American West. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfenstein, J.; Bauer, L.; Clalüna, A.; Bolliger, J.; Kienast, F. Landscape ecology meets landscape science. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.A.; Martin, C.O.; Fischenich, J.C. Riparian ecology and management in multi-land use watersheds. In International Conference on American Water Resources Association; American Water Resources Association: Middleburg, VA, USA, 2000; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Poff, N.L.; Allan, J.D.; Bain, M.B.; Karr, J.R.; Prestegaard, K.L.; Richter, B.D.; Sparks, R.E.; Stromberg, J.C. The natural flow regime. Bioscience 1997, 47, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.A.; Yang, Z.F.; Petts, G.E. A New Method to Assess the Flow Regime Alterations in Riverine Ecosystems. River Res. Appl. 2014, 31, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H.; Leng, G. Environmental flow assessment considering inter- and intra-annual streamflow variability under the context of non-stationarity. Water 2018, 10, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiman, R.J.; Decamps, H.; Pollock, M. The role of riparian corridors in maintaining regional biodiversity. Ecol. Appl. 1993, 3, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, J.C.; Vick, J.C.; Orr, B.K. Riparian vegetation dynamics on the Merced River. In California Riparian Systems: Processes and Floodplains Management, Ecology, and Restoration (2001 Riparian Habitat and Floodplains Conference Proceedings); University of California Press: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 302–314. [Google Scholar]
- Capon, S.; Chambers, L.E.; Mac Nally, R.; Naiman, R.J.; Davies, P.; Marshall, N.; Pittock, J.; Reid, M.; Capon, T.; Douglas, M.; et al. Riparian ecosystems in the 21st century: Hotspots for climate change adaptation? Ecosystems 2013, 16, 359–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.A. Riparian zone management in the Pacific Northwest: Who’s cutting what? Environ. Manag. 2000, 26, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzovkina, Y.A.; Quigley, M.F. Willows beyond wetlands: Uses of Salix L. species for environmental projects. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 162, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannone, N.; Guglielmin, M.; Casiraghi, C.; Malfasi, F. Salix shrub encroachment along a 1000 m elevation gradient triggers a major ecosystem change in the European Alps. Ecography 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roloff, A.; Korn, S.; Gillner, S. The Climate-Species-Matrix to select tree species for urban habitats considering climate change. Urban For. Urban Green. 2009, 8, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilloy, H.; González, E.; Muller, E.; Hughes, F.M.R.; Barsoum, N. Abrupt drops in water table level influence the development of Populus nigra and Salix alba seedlings of different ages. Wetlands 2011, 31, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.H.; Macdonald, S.E.; Henry, G.H. Sex-and habitat-specific responses of a high arctic willow, Salix arctica, to experimental climate change. Oikos 1999, 87, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.H.; Bay, C.; Nordenhäll, U. Effects of experimental warming on arctic willows (Salix spp.): A comparison of responses from the Canadian High Arctic, Alaskan Arctic, and Swedish Subarctic. Glob. Change Biol. 1997, 3, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, J.A.; Cortés, A.J.; Sedlacek, J.; Karrenberg, S.; van Kleunen, M.; Wipf, S.; Hoch, G.; Bossdorf, O.; Rixen, C. The snow and the willows: Earlier spring snowmelt reduces performance in the low-lying alpine shrub Salix herbacea. J. Ecol. 2016, 104, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bret-Harte, M.S.; Shaver, G.R.; Chapin, F.S., III. Primary and secondary stem growth in arctic shrubs: Implications for community response to environmental change. J. Ecol. 2002, 90, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myklestad, A.; Birks, H.J.B. A numerical analysis of the distribution patterns of Salix L. species in Europe. J. Biogeogr. 1993, 20, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanda, V.; Barabas, N.; Stefanut, S. Atlas Florae Romaniae. IV. Salix; Ion Borcea’ Press: Bacău, Romania, 2005; 172p, ISBN 973-86586-5-9. [Google Scholar]
- Avram, C.M.; Proorocu, M.; Mălinaș, A.; Mălinaș, C. The Effectiveness of Natura 2000 Network in Conserving Salix alba and Populus alba Galleries against Invasive Species: A Case Study of Mureșul Mijlociu—Cugir Site, Romania. Forests 2023, 14, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matenco, L.; Krézsek, C.; Merten, S.; Schmid, S.M.; Cloetingh, S.; Andriessen, P. Characteristics of collisional orogens with low topographic build-up: An example from the Carpathians. Terra Nova 2010, 22, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rãdoane, M.; Rãdoane, N.; Dumitriu, D. Geomorphological evolution of longitudinal river profiles in the Carpathians. Geomorphology 2003, 50, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Quick Guide to Using MGRS Coordinates. Available online: https://www.maptools.com/tutorials/mgrs/quick_guide (accessed on 17 December 2022).
- Ştefănuţ, S. The Hornwort and Liverwort Atlas of Romania; Edit. Ars Docendi—Universitatea din Bucureşti: Bucureşti, Romania, 2008; p. 510. ISBN 978-973-558-387-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bita-Nicolae, C. Distribution and Conservation Status of the Mountain Wetlands in the Romanian Carpathians. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun-Blanquet, J. Pflanzensoziologie: Grundzüge der Vegetationskunde, 3rd ed.; Springer: Vienna, Austria; New York, NY, USA, 1964; 631p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucina, L.; Bültmann, H.; Dierßen, K.; Theurillat, J.; Raus, T.; Čarni, A.; Šumberová, K.; Willner, W.; Dengler, J.; García, R.G.; et al. Vegetation of Europe: Hierarchical floristic classification system of vascular plant, bryophyte, lichen, and algal communities. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2016, 19, 3–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euro+MedPlantBase—The Information Resource for Euro-Mediterranean Plant Diversity. 2012. Available online: http://ww2.bgbm.org/EuroPlusMed/ (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- The Plant List Version 1.1. 2013. Available online: http://www.theplantlist.org/ (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Biță-Nicolae, C.; Sanda, V. Cormophlora of Romania: Spontaneous and Cultivated Cormophytes in Romania; Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrucken, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberg, H.H. Vegetation Ecology of Central Europe; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Dengler, J.; Jansen, F.; Chusova, O.; Hüllbusch, E.; Nobis, M.P.; Van Meerbeek, K.; Axmanová, I.; Bruun, H.H.; Chytrý, M.; Guarino, R.; et al. Ecological Indicator Values for Europe (EIVE) 1.0. Veg. Classif. Surv. 2023, 4, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microsoft Corporation. Microsoft Excel. 2018. Available online: https://office.microsoft.com/excel (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Past 4—The Past of the Future. Available online: https://www.nhm.uio.no/english/research/resources/past/ (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Argus, G.W. Salix (Salicaceae) distribution maps and a synopsis of their classification in North America, north of Mexico. Harv. Pap. Bot. 2007, 12, 335–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.J.; Chimner, R.A.; Merritt, D.M. Western Mountain Wetlands; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 313–328. [Google Scholar]
- Busch, D.E.; Smith, S.D. Mechanisms Associated With Decline of Woody Species in Riparian Ecosystems of the Southwestern U.S. Ecol. Monogr. 1995, 65, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.D.; He, L.; Hörandl, E. The evolutionary history, diversity, and ecology of willows (Salix L.) in the European Alps. Diversity 2021, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, D.M.; Shafroth, P.B. Edaphic, salinity, and stand structural trends in chronosequences of native and non-native dominated riparian forests along the Colorado River, USA. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 2665–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, V.B.; Stromberg, J.C.; Stutz, J.C. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with Populus–Salix stands in a semiarid riparian ecosystem. New Phytol. 2006, 170, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poldini, L.; Vidali, M.; Ganis, P. Riparian Salix alba: Scrubs of the Po lowland (N-Italy) from an European perspective. Plant Biosyst. 2011, 145, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buma, B.; Bisbing, S.M.; Wiles, G.; Bidlack, A.L. 100 yr of primary succession highlights stochasticity and competition driving community establishment and stability. Ecology 2019, 100, e02885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, D. Production capacity of biomass of the floodpain community of Salix alba L. in southern Moravia. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2007, 55, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, M.N.; Albariño, R.; Villanueva, V.D. Invasive Salix fragilis alters benthic invertebrate communities and litter decomposition in northern Patagonian streams. Hydrobiologia 2013, 701, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewerentz, A.; Egger, G.; Householder, J.E.; Reid, B.; Braun, A.C.; Garófano-Gómez, V. Functional assessment of invasive Salix fragilis L. in north-western Patagonian flood plains: A comparative approach. Acta Oecol. 2019, 95, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ens, J.; Farrell, R.E.; Bélanger, N. Early effects of afforestation with willow (Salix purpurea, “Hotel”) on soil carbon and nutrient availability. Forests 2013, 4, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutier-Hurteau, B.; Turmel, M.-C.; Mercier, C.; Courchesne, F. The sequestration of trace elements by willow (Salix purpurea)—Which soil properties favor uptake and accumulation? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 4759–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silc, U. Vegetation of the class Salicetea purpureae in Dolenjska (SE Slovenia). Fitosociologia 2003, 40, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.-M.; Wang, L.-Y.; Li, S.-Y.; Zhou, J.-X.; Sun, Q.-X. Relationship between community type of wetland plants and site elevation on sandbars of the East Dongting Lake, China. For. Stud. China 2009, 11, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosner, E.; Schneider, S.; Lehmann, B.; Leyer, I. Hydrological prerequisites for optimum habitats of riparian Salix communities—Identifying suitable reforestation sites. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2011, 14, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, T.A.; Qaiser, K.N.; Khan, M.A. Growth and productivity of wicker willow (Salix triandra L.) plantation in Kashmir. Environ. Ecol. 2009, 27, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Saatkamp, A.; Falzon, N.; Argagnon, O.; Noble, V.; Dutoit, T.; Meineri, E. Calibrating ecological indicator values and niche width for a Mediterranean flora. Plant Biosyst. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, F.I. Temperature and the distribution of plant species. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1988, 42, 59–75. [Google Scholar]
- Fanelli, G.; Tescarollo, P.; Testi, A. Ecological indicators applied to urban and suburban floras. Ecol. Indic. 2006, 6, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J. Mapping Species Distributions: Spatial Inference and Prediction; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Riis, T.; Kelly-Quinn, M.; Aguiar, F.C.; Manolaki, P.; Bruno, D.; Bejarano, M.D.; Clerici, N.; Fernandes, M.R.; Franco, J.C.; Pettit, N.; et al. Global overview of ecosystem services provided by riparian vegetation. Bioscience 2020, 70, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparício, B.A.; Nunes, J.P.; Bernard-Jannin, L.; Dias, L.F.; Fonseca, A.; Ferreira, T. Modelling the role of ground-true riparian vegetation for providing regulating services in a Mediterranean watershed. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 11, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, J.; Xia, J.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, X.; Cai, W.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Dou, C. Distribution Pattern and Structure of Vascular Plant Communities in Riparian Areas and Their Response to Soil Factors: A Case Study of Baoan Lake, Hubei Province, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.R.; Jackson, R.D.; Boyd, C.S.; Tate, K.W. A scientific assessment of the effectiveness of riparian management practices. In Conservation Benefits of Rangeland Practices: Assessment, Recommendations, and Knowledge Gaps; American Water Resources Association: Middleburg, VA, USA, 2011; pp. 213–252. ISBN 1882132513. [Google Scholar]
- González, E.; Shafroth, P.B.; Lee, S.R.; Ostoja, S.M.; Brooks, M.L. Combined effects of biological control of an invasive shrub and fluvial processes on riparian vegetation dynamics. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 2339–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, C.; Jansson, R.; Kuglerová, L.; Lind, L.; Ström, L. Boreal riparian vegetation under climate change. Ecosystems 2012, 16, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivaes, R.; Rodríguez-González, P.M.; Albuquerque, A.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Egger, G.; Ferreira, M.T. Riparian vegetation responses to altered flow regimes driven by climate change in Mediterranean rivers. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmel, H.; Weihs, P.; Leidinger, D.; Formayer, H.; Kalny, G.; Melcher, A. Can riparian vegetation shade mitigate the expected rise in stream temperatures due to climate change during heat waves in a human-impacted pre-alpine river? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 437–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, M.; McVicar, T.R.; Holland, K.L.; Daly, E. Riparian vegetation and geomorphological interactions in anabranching rivers: A global review. Ecohydrology 2022, 15, e2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourcade, Y. Comparing species distributions modelled from occurrence data and from expert-based range maps. Implication for predicting range shifts with climate change. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 36, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Nagy, J.; Fehérváry, I.; Vaszkó, C. Management of floodplain vegetation: The effect of invasive species on vegetation roughness and flood levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanović, N.; Kuzmanović, N.; Vukojičić, S.; Lakušić, D.; Jovanović, S. Floristic diversity, composition and invasibility of riparian habitats with Amorpha fruticosa: A case study from Belgrade (Southeast Europe). Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 24, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarghitan, M.; Oroian, S.; Tanase, C. Contributions to the study of the alien and invasive species in some protected areas in Mures County, Romani. Acta Horti Bot. Bucur. 2018, 45, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sanda, V.; Ollerer, K.; Burescu, P.; Fitocenozele din Romania, E. Ars Docendi; Universitatea Bucuresti: Bucharest, Romania, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schilling, K.E.; Mount, J.; Suttles, K.M.; McLellan, E.L.; Gassman, P.W.; White, M.J.; Arnold, J.G. An Approach for Prioritizing Natural Infrastructure Practices to Mitigate Flood and Nitrate Risks in the Mississippi-Atchafalaya River Basin. Land 2023, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State of Nature in the EU: Results from Reporting under the Nature Directives 2013–2018. Available online: www.eea.europa.eu/publications/state-of-nature-in-the-eu-2020 (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Bennett, A.F.; Nimmo, D.G.; Radford, J.Q. Riparian vegetation has disproportionate benefits for landscape-scale conservation of woodland birds in highly modified environments. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corkum, L.D. Conservation of running waters: Beyond riparian vegetation and species richness. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 1999, 9, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandžukovski, D.; Čarni, A.; Sotirovski, K. Interpretative Manual of European Riparian Forests and Shrublands; Ss Cyril and Methodius University in Skopje, Hans Em Faculty of Forest Sciences: Skopje, North Macedonia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Salinas, M.J.; Blanca, G.; Romero, A.T. Evaluating riparian vegetation in semi-arid Mediterranean watercourses in the south-eastern Iberian Peninsula. Environ. Conserv. 2000, 27, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| a | |||||||
| S. alba | S. fragilis | S. purpurea | S. triandra | ||||
| np | nw | np | nw | np | nw | np | nw |
| 6.5 | 3.1 | 6.7 | 2.5 | 6 | 4.7 | 6.7 | 2.8 |
| 7.2 | 4.3 | 6.4 | 2.9 | 5.1 | 5.9 | 5.1 | 5 |
| 7.9 | 3.9 | - | - | 7.9 | 3.5 | 7.5 | 3.2 |
| 5.8 | 5.8 | 4.5 | 2.8 | 7.8 | 4.3 | 7.5 | 4.4 |
| 4.8 | 3.7 | - | - | 4 | 3.6 | 3.9 | 3.6 |
| b | |||||||
| Salix | S. alba | S. fragilis | S. purpurea | S. triandra | |||
| M | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |||
| T | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |||
| R | 4 | 4 | 3.5 | 0 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bita-Nicolae, C. Distribution of the Riparian Salix Communities in and around Romanian Carpathians. Diversity 2023, 15, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030397
Bita-Nicolae C. Distribution of the Riparian Salix Communities in and around Romanian Carpathians. Diversity. 2023; 15(3):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030397
Chicago/Turabian StyleBita-Nicolae, Claudia. 2023. "Distribution of the Riparian Salix Communities in and around Romanian Carpathians" Diversity 15, no. 3: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030397
APA StyleBita-Nicolae, C. (2023). Distribution of the Riparian Salix Communities in and around Romanian Carpathians. Diversity, 15(3), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15030397






