COI-Barcoding and Species Delimitation Assessment of Toad-Headed Agamas of the Genus Phrynocephalus (Agamidae, Squamata) Reveal Unrecognized Diversity in Central Eurasia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Taxon Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction, Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.4. Species Delimitation
2.5. Evaluation of Species Delimitation Results
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Characteristics
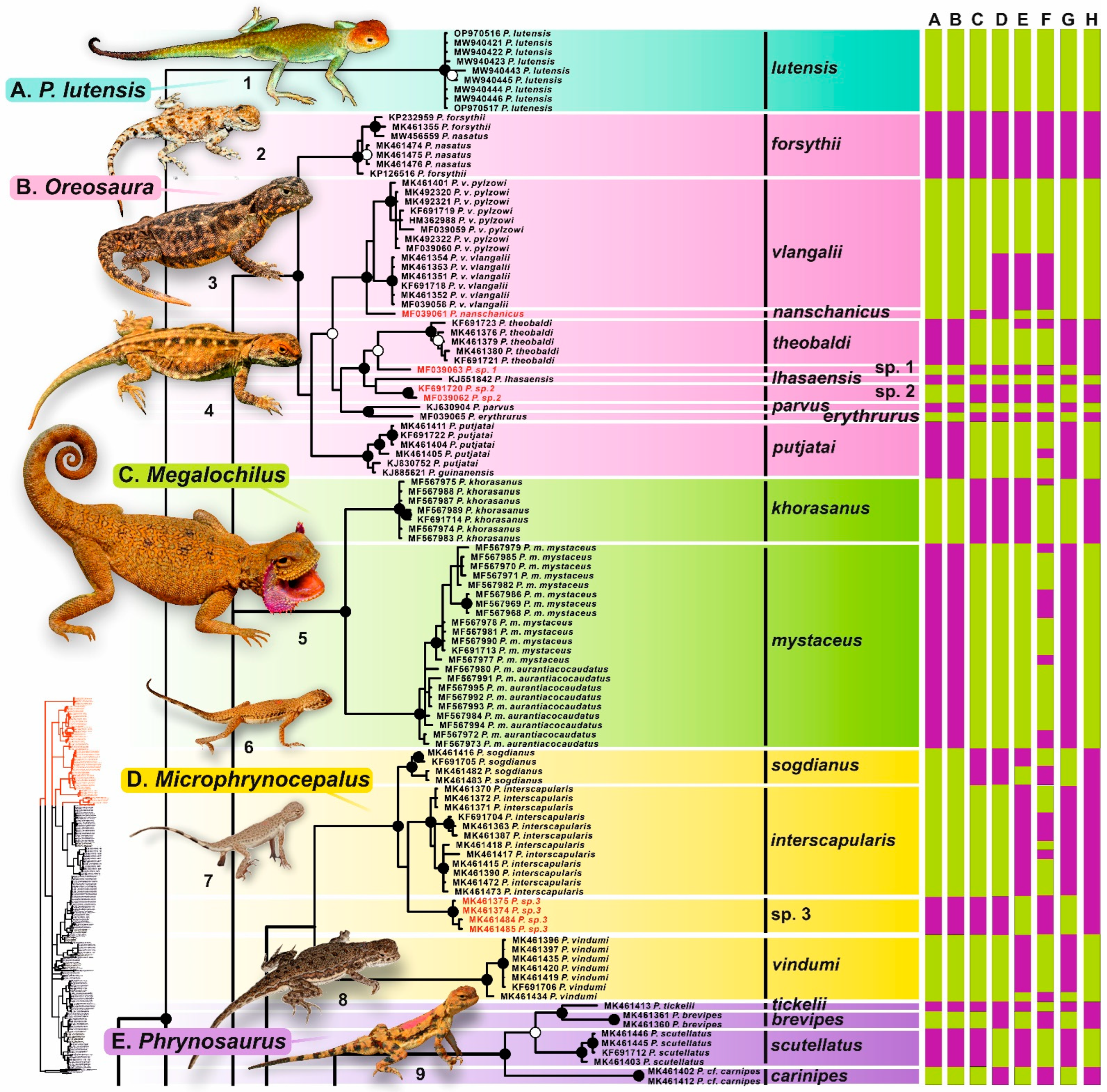
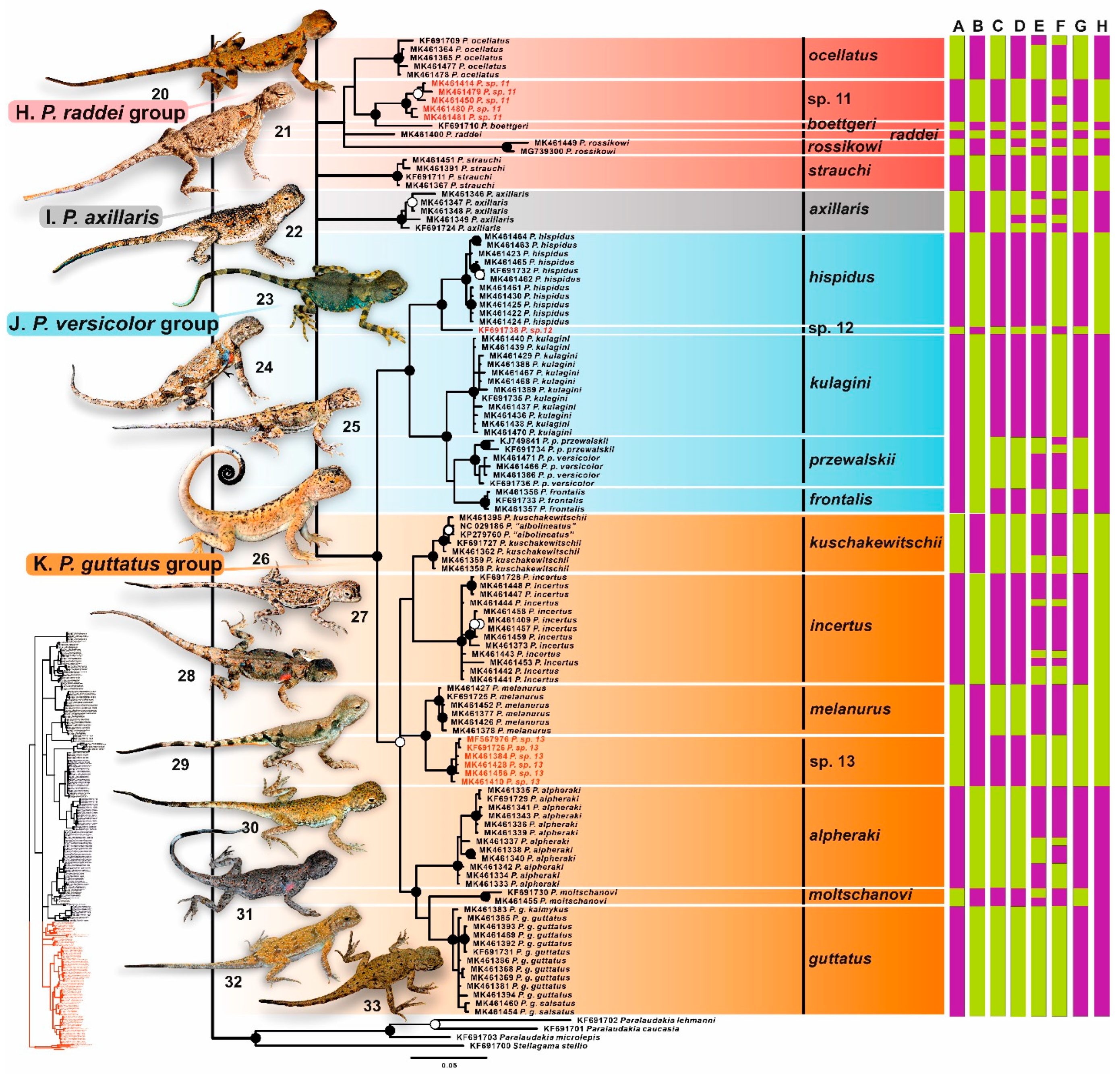
3.2. Phylogenetic Trees
3.3. Barcoding Gap
3.4. Species Delimitation
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparative Performance of Different Approaches to Species Delimitation
4.2. An Overview of the Phylogenetic Lineages and Taxonomic Implications
4.2.1. Phrynocephalus lutensis
4.2.2. Microphrynocephalus (Phrynocephalus interscapularis Species Group)
4.2.3. Phrynosaurus (Phrynocephalus scutellatus Species Group)
4.2.4. Phrynocephalus maculatus Species Group
4.2.5. Oreosaura (Phrynocephalus vlangalii Species Group)
4.2.6. Megalochilus (Phrynocephalus mystaceus Species Group)
4.2.7. Helioscopus (Phrynocephalus helioscopus Species Group)
4.2.8. Phrynocephalus raddei Species Group
4.2.9. Phrynocephalus axillaris
4.2.10. Phrynocephalus guttatus Species Group
4.2.11. Phrynocephalus przewalskii Species Group
4.2.12. Phrynocephalus Incertae Sedis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barabanov, A.V.; Ananjeva, N.B. Catalogue of the available scientific species-group names for lizards of the genus Phrynocephalus Kaup, 1825 (Reptilia, Sauria, Agamidae). Zootaxa 2007, 1399, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyeva, E.N.; Lebedev, V.S.; Dunayev, E.A.; Nazarov, R.A.; Bannikova, A.A.; Che, J.; Murphy, R.W.; Poyarkov, N.A. Cenozoic aridization in Central Eurasia shaped diversification of toad-headed agamas (Phrynocephalus; Agamidae, Reptilia). PeerJ. 2018, 6, e4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallas, P.S. Reise Durch Verschiedene Provinzen des Russischen Reichs. Bd. I; Kayserliche Academie der Wissenschaften: St. Petersburg, Russia, 1771; 540p. [Google Scholar]
- Macey, J.R.; Schulte, J.A.; Ananjeva, N.B.; Van Dyke, E.T.; Wang, Y.; Orlov, N.; Shafiei, S.; Robinson, M.D.; Dujsebayeva, T.; Freund, G.S.; et al. A molecular phylogenetic hypothesis for the Asian agamid lizard genus Phrynocephalus reveals discrete biogeographic clades implicated by plate tectonics. Zootaxa 2018, 4467, 1–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermuth, H. Liste der rezenten Amphibien und Reptilien. Agamidae. Tierreich 1967, 86, 127. [Google Scholar]
- Moody, S.M. Phylogenetic and Historical Biogeographical Relationships of the Genera in the Family Agamidae (Reptilia: Lacertilia). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1980; 373p. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Y. Partitioned Bayesian analyses, dispersal–vicariance analysis, and the biogeography of Chinese toad-headed lizards (Agamidae: Phrynocephalus): A re-evaluation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 45, 643–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, K.; Anderson, S. A new Iranian Phrynocephalus (Reptilia: Squamata: Agamidae) from the hottest place on earth and a key to the genus Phrynocephalus in southwestern Asia and Arabia. Zootaxa 2015, 3904, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uetz, P.; Freed, P.; Hošek, J. The Reptile Database. Available online: http://reptiledatabase.reptarium.cz (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Golubev, M.L. About the name Agama ocellata Lichtenstein in Eversmann, 1823 (Reptilia, Agamidae) with redescription of the types. Herpetol. Res. 1991, 1, 12–17, (In Russian with English summary). [Google Scholar]
- Dunayev, E.A. Nomenclature and distribution of toad-agams, Phrynocephalus (Reptilia, Agamidae) in Iliyskaya Hollow. Bull. Mosc. Soc. Nat. Biol. Ser. 1996, 101, 36–41, (In Russian with English summary). [Google Scholar]
- Solovyeva, E.N.; Poyarkov, N.A.; Dunayev, E.A.; Nazarov, R.A.; Lebedev, V.S.; Bannikova, A.A. Phylogenetic relationships and subgeneric taxonomy of toad-headed agamas Phrynocephalus (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae) based on mitochondrial DNA sequence data. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2014, 455, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunayev, E.A.; Solovyeva, E.N.; Poyarkov, N.A. Taxonomy, Phylogeny and Distribution of Phrynocephalus (superspecies guttatus) (Reptilia: Agamidae). Curr. Stud. Herpetol. 2020, 20, 16–34. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunayev, E.A. History of study, taxonomy, distribution, and ecology of Phrynocephalus nasatus Golubev et Dunayev, 1995 (Reptilia: Agamidae). Russ. J. Herpetol. 2020, 27, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunayev, E.A.; Solovyeva, E.N.; Poyarkov, N.A. Systematics, phylogeny and evolution of Phrynocephalus (superspecies przewalskii) (Reptilia: Agamidae). Russ. J. Herpetol. 2021, 28, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wu, Y.; Ma, L.; Chen, Y.-J.; Ji, X. Genetic and morphological divergence among three closely related Phrynocephalus species (Agamidae). BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikov, D.; Melnikova, E.; Nazarov, R.; Rajabizadeh, M.; Al-Johany, A.; Amr, Z.S.; Ananjeva, N.B. Taxonomic revision of Phrynocephalus arabicus Anderson, 1984 complex with description of a new species from Ahvaz, south-western Iran. Russ. J. Herpetol. 2014, 21, 149–159. [Google Scholar]
- Melnikov, D.; Melnikova, E.; Nazarov, R.; Al-Johany, A.; Ananjeva, N. A new species of Phrynocephalus (Agamidae, Sauria) from Al Sharqiyah sands, Northeastern Oman, dedicated to the memory of Sako Tuniyev (1983–2015). Russ. J. Herpetol. 2015, 22, 301–309. [Google Scholar]
- Solovyeva, E.N.; Poyarkov, N.A.; Dunaev, E.A.; Duysebayeva, T.N.; Bannikova, A.A. Molecular differentiation and taxonomy of the sunwatcher toad headed agama species complex Phrynocephalus superspecies helioscopus (Pallas 1771) (Reptilia: Agamidae). Russ. J. Genet. 2015, 47, 842–856. [Google Scholar]
- Solovyeva, E.N.; Dunayev, E.A.; Poyarkov, N.A. Interspecific taxonomy of sunwatcher toadhead agama species complex (Phrynocephalus helioscopus, Squamata). Zool. Z. 2012, 91, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Solovyeva, E.N.; Dunayev, E.A.; Nazarov, R.A.; Radjabizadeh, M.; Poyarkov, N.A. Molecular and morphological differentiation of Secret Toad-headed agama, Phrynocephalus mystaceus, with the description of a new subspecies from Iran (Reptilia, Agamidae). ZooKeys 2018, 748, 97–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Ma, L.; Wang, Z. The complete mitochondrial genome of the toad-headed lizard, Phrynocephalus forsythii (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 3147–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.; Ma, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z. The complete mitochondrial genome of the toad-headed lizard, Phrynocephalus albolineatus (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2017, 28, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, D.; Chang, C. The complete mitochondrial genome of the color changeable toad-headed agama, Phrynocephalus versicolor (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2014, 27, 1121–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Jin, Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of the toad-headed lizard subspecies, Phrynocephalus theobaldi orientalis (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 559–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Liao, P.; Tong, H.; Jin, Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of the subspecies, Phrynocephalus erythrurus parva (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae), a toad-headed lizard dwell at highest elevations of any reptile in the world. Mitochondrial DNA Part A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 703–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.; Ratnasingham, S.; De Waard, J.R. Barcoding animal life: Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270 (Suppl. 1), S96–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System (www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, R.W.; Crawford, A.J.; Bauer, A.M.; Che, J.; Donnellan, S.C.; Fritz, U.; Haddad, C.F.B.; Nagy, Z.T.; Poyarkov, N.A.; Vences, M.; et al. Cold Code: The global initiative to DNA barcode amphibians and nonavian reptiles. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, A.J.; Lips, K.R.; Bermingham, E. Epidemic disease decimates amphibian abundance, species diversity, and evolutionary history in the highlands of central Panama. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13777–13782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begerow, D.; Nilsson, H.; Unterseher, M.; Maier, W. Current state and perspectives of fungal DNA barcoding and rapid identification procedures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puillandre, N.; Lambert, A.; Brouillet, S.; Acha, G. ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for primary species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieites, D.R.; Wollenberg, K.C.; Andreone, F.; Köhler, J.; Glaw, F.; Vences, M. Vast underestimation of Madagascar’s biodiversity evidenced by an integrative amphibian inventory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8267–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neigel, J.; Domingo, A.; Stake, J. DNA barcoding as a tool for coral reef conservation. Coral Reefs 2007, 26, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernooy, R.; Haribabu, E.; Muller, M.R.; Vogel, J.H.; Hebert, P.D.; Schindel, D.E.; Shimura, J.; Singer, G.A. Barcoding life to conserve biological diversity: Beyond the taxonomic imperative. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, A.J.; Cruz, C.; Griffith, E.; Ross, H.; Ibáñez, R.; Lips, K.R.; Driskell, A.C.; Bermingham, E.; Crump, P. DNA barcoding applied to ex situ tropical amphibian conservation programme reveals cryptic diversity in captive populations. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.A.; Poyarkov, N.A.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcoding: CO1 DNA barcoding amphibians: Take the chance, meet the challenge. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vences, M.; Nagy, Z.T.; Sonet, G.; Verheyen, E. DNA barcoding amphibians and reptiles. In DNA Barcodes; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 79–107. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, R.; Montero-Mendieta, S.; Simó-Riudalbas, M.; Sindaco, R.; Santos, X.; Fasola, M.; Llorente, G.; Razzetti, E.; Carranza, S. Unexpectedly high levels of cryptic diversity uncovered by a complete DNA barcoding of reptiles of the Socotra Archipelago. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Yang, C.; Ke, D. DNA barcoding and phylogenetic relationships in Anatidae. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2014, 27, 1042–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ruan, R. DNA barcodes and insights into the phylogenetic relationships of Corvidae (Aves: Passeriformes). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2018, 29, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Guan, L.; Wang, D.; Gan, X. DNA barcoding and evaluation of genetic diversity in Cyprinidae fish in the midstream of the Yangtze River. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 2702–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tizard, J.; Patel, S.; Waugh, J.; Tavares, E.; Bergmann, T.; Gill, B.; Norman, J.; Christidis, L.; Scofield, P.; Haddrath, O.; et al. DNA barcoding a unique avifauna: An important tool for evolution, systematics and conservation. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, Z.T.; Sonet, G.; Glaw, F.; Vences, M. First Large-scale DNA barcoding assessment of reptiles in the biodiversity hotspot of Madagascar, based on newly designed COI primers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, T.; Geissler, P.; Poyarkov, N.A.; Ihlow, F.; Galoyan, E.A.; Rödder, D.; Böhme, W. A new species of the genus Calotes Cuvier, 1817 (Squamata: Agamidae) from southern Vietnam. Zootaxa 2013, 3599, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, R.; Poyarkov, N.A.; Orlov, N.L.; Phung, T.M.; Nguyen, T.T.; Hoang, D.M.; Ziegler, T. Two new cryptic species of the Cyrtodactylus irregularis complex (Squamata: Gekkonidae) from southern Vietnam. Zootaxa 2012, 3302, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, R.A.; Poyarkov, N.A.; Orlov, N.L.; Nguyen, N.S.; Milto, K.D.; Martynov, A.A.; Konstantinov, E.L.; Chulisov, A.S. A review of Cyrtodactylus (Reptilia: Sauria: Geckonidae) fauna of Laos with description of four new species. Proc. Zool. Inst. RAS 2014, 318, 391–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neang, T.; Chan, S.; Poyarkov, N.A. A new species of smooth skink (Squamata: Scincidae: Scincella) from Cambodia. Zool. Res. 2018, 38, 214–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Macpherson, E.; Lambourdière, J.; Cruaud, C.; Boisselier-Dubayle, M.C.; Samadi, S. Barcoding type specimens helps to identify synonyms and an unnamed new species in Eumunida Smith, 1883 (Decapoda: Eumunididae). Invertebr. Syst. 2011, 25, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, N.M.; Carstens, B.C. Phylogenetic estimation error can decrease the accuracy of species delimitation: A Bayesian implementation of the general mixed Yule-coalescent model. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Salle, R.O. Species discovery versus species identification in DNA barcoding efforts: Response to Rubinoff. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 1545–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padial, J.M.; Miralles, A.; De la Riva, I.; Vences, M. The integrative future of taxonomy. Front. Zool. 2010, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiemers, M.; Fiedler, K. Does the DNA barcoding gap exist?—A case study in blue butterflies (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae). Front. Zool. 2007, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tingley, R.; Meiri, S.; Chapple, D.G. Addressing knowledge gaps in reptile conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 204(Part A), 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcoding of Life Project. Available online: www.boldsystems.org (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; 385p. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, N.V.; DeWaard, J.; Hebert, P.D.N. An inexpensive, automation friendly protocol for recovering high quality DNA. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisenko, A.V.; Lim, B.K.; Ivanova, N.V.; Hanner, R.H.; Hebert, P.D. DNA barcoding in surveys of small mammal communities: A field study in Suriname. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisenko, A.V.; Sones, J.E.; Hebert, P.D. The front-end logistics of DNA barcoding: Challenges and prospects. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruskop, S.V.; Borisenko, A.V.; Ivanova, N.V.; Lim, B.K.; Eger, J.L. Genetic diversity of northeastern Palaearctic bats as revealed by DNA barcodes. Acta Chiropterologica 2012, 14, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. In Nucleic Acids Symposium Series; Information Retrieval Ltd.: London, UK, 1999; pp. 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogeny. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Calcott, B.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Guindon, S. PartitionFinder: Combined selection of partitioning schemes and substitution models for phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. Tracer v1. 5. 2007. Available online: http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer (accessed on 3 July 2022).
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Hillis, D.M. Success of phylogenetic methods in the four-taxon case. Syst. Biol. 1993, 42, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ASAP: Assemble species by automatic partitioning. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kapli, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A. A General Species Delimitation Method with Applications to Phylogenetic Placements. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.K.; Leaché, A.D.; Burbrink, F.T.; McGuire, J.A.; Moritz, C. Coalescent-based species delimitation in an integrative taxonomy. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellicour, S.; Flot, J.F. Delimiting species-poor data sets using single molecular markers: A study of barcode gaps, haplowebs and GMYC. Syst. Biol. 2015, 64, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyer, P.A.; Seltzer, R.; Reiner-Brodetzki, T.; Hefetz, A. An integrative approach to untangling species delimitation in the Cataglyphis bicolor desert ant complex in Israel. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 115, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, M.T.; Wild, R.; Elliot, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Balke, M.; Inward, D.J.; Lees, D.C.; Ranaivosolo, R.; Eggleton, P.; Barraclough, T.G.; et al. Accelerated species inventory on Madagascar using coalescent-based models of species delineation. Syst. Biol. 2009, 58, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellicour, S.; Flot, J.F. The hitchhiker’s guide to single-locus species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.P.; Paulay, G. DNA barcoding: Error rates based on comprehensive sampling. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorin, V.A.; Solovyeva, E.N.; Hasan, M.; Okamiya, H.; Karunarathna, D.M.S.S.; Pawangkhanant, P.; de Silva, A.; Juthong, W.; Milto, K.D.; Nguyen, L.T.; et al. A little frog leaps a long way: Compounded colonizations of the Indian Subcontinent discovered in the tiny Oriental frog genus Microhyla (Amphibia: Microhylidae). PeerJ. 2020, 8, e9411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, J.; Barraclough, T.G.; Gomez-Zurita, J.; Cardoso, A.; Duran, D.P.; Hazell, S.; Kamoun, S.; Sumlin, W.D.; Vogler, A. Sequence-based species delimitation for the DNA taxonomy of undescribed insects. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, T.; Barraclough, T.G. Delimiting species using single-locus data and the Generalized Mixed Yule Coalescent approach: A revised method and evaluation on simulated data sets. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducasse, J.; Ung, V.; Lecointre, G.; Miralles, A. LIMES: A tool for comparing species partition. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2282–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, J.; Hale, J.; Mantziou, G.; Ananjeva, N.B.; Milto, K.; Clemann, N. Historical biogeography, phylogenetic relationships and intraspecific diversity of agamid lizards in the Central Asian deserts of Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2009, 53, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Hoelzele, A.R.; Papenfuss, T.J.; Zeng, X.; Ananjeva, N.B.; Zhang, Y. A phylogeny of Chinese species in the genus Phrynocephalus (Agamidae) inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 27, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabanov, A.M.; Ananjeva, N.B.; Papenfuss, T.J.; Wang, Y. A new name for Phrynocephalus theobaldi orientalis Wang, Papenfuss et Zeng, 1999. Russ. J. Herpetol. 2002, 9, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.T.; Brown, R. Partition number, rate priors and unreliable divergence times in Bayesian phylogenetic dating. Cladistics 2018, 34, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimipour, F.; Rastegar-Pouyani, N.; Rastegar Pouyani, E.; Hosseinian Yousefkhani, S.S.; Kamali, K. Molecular phylogenetic relationships within the Phrynocephalus maculatus–arabicus species complex (Sauria: Agamidae) in Iran. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2021, 59, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlick-Steiner, B.C.; Steiner, F.M.; Seifert, B.; Stauffer, C.; Christian, E.; Crozier, R.H. Integrative taxonomy: A multisource approach to exploring biodiversity. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Kuntner, M.; Bond, J.E.; Ono, H.; Liu, F.; Yu, L.; Li, D. A multi-tier species delimitation approach resolves conflicts in delineating the primitively segmented spider genus Heptathela endemic to Japanese islands. BioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babik, W.; Branicki, W.; Crnobrnja-Isailović, J.; Cogălniceanu, D.; Sas, I.; Olgun, K.; Poyarkov, N.A.; Garcia-París, M.; Arntzen, J.W. Phylogeography of two European newt species—Discordance between mtDNA and morphology. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2475–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renoult, J.P.; Geniez, P.; Bacquet, P.; Benoit, L.; Crochet, P.-A. Morphology and nuclear markers reveal extensive mitochondrial introgressions in the Iberian Wall Lizard species complex. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 4298–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leache, A.D.; Cole, C.J. Hybridization between multiple fence lizard lineages in an ecotone: Locally discordant variation in mitochondrial DNA, chromosomes, and morphology. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 1035–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toews, D.P.; Brelsford, A. The biogeography of mitochondrial and nuclear discordance in animals. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3907–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, J.A.; Linkem, C.W.; Koo, M.S.; Hutchison, D.W.; Lappin, A.K.; Orange, D.I.; Lemos-Espinal, J.; Riddle, B.R.; Jaeger, J.R. Mitochondrial introgression and incomplete lineage sorting through space and time: Phylogenetics of Crotaphytid lizards. Evolution 2007, 61, 2879–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.N.; Zhou, W.-W.; Le, T.-N.T.; Tran, A.-D.T.; Jin, J.-Q.; Vo, B.D.; Nguyen, L.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Hoang, D.D.; et al. Cytonuclear discordance, cryptic diversity, complex histories, and conservation needs in Vietnamese bent-toed geckos of the Cyrtodactylus irregularis species complex. Russ. J. Herpetol. 2017, 24, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher-Reid, M.C.; Wiens, J.J. What are the consequences of combining nuclear and mitochondrial data for phylogenetic analysis? Lessons from Plethodon salamanders and 13 other vertebrate clades. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunayev, E.A. Systematics and paleogeography: Conceptual synthesis by the example of Phrynocephalus (superspecies guttatus) (Reptilia: Agamidae). In Evolution and Systematics: Lamarck and Darwin in Modern Studies. Archiver of the Zoological Museum of Moscow State University; Sviridov, A.V., Shatalkin, A.I., Eds.; KMK Scientific Press: Moscow, Russia, 2009; Volume 50, pp. 274–298. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gozdzik, A.; Fu, J. Are toad-headed lizards Phrynocephalus przewalskii and frontalis (family Agamidae) the same species? Defining species boundaries with morphological and molecular data. Russ. J. Herpetol. 2009, 16, 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart, J.; Bi, K.E.; Gozdzik, A.; Fu, J. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite DNA loci in the toad-headed lizards, Phrynocephalus przewalskii complex. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2005, 5, 928–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquhart, J.; Wang, Y.; Fu, J. Historical vicariance and male-mediated gene flow in the toad-headed lizards Phrynocephalus przewalskii. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 3714–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubev, M.L.; Dunayev, E.A. Phrynocephalus nasatus (Reptilia, Agamidae), a new species of toad agama from Western China. Russ. J. Herpetol. 1995, 2, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Grummer, J.A.; Bryson, R.W.; Reeder, T.W. Species delimitation using Bayes factors: Simulations and application to the Sceloporus scalaris species group (Squamata: Phrynosomatidae). Syst. Biol. 2014, 63, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firkowski, C.R.; Bornschein, M.R.; Ribeiro, L.F.; Pie, M.R. Species delimitation, phylogeny and evolutionary demography of co-distributed, montane frogs in the southern Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 100, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pie, M.R.; Bornschein, M.R.; Ribeiro, L.F.; Faircloth, B.C.; McCormack, J.E. Phylogenomic species delimitation in microendemic frogs of the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 141, 106627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.O.; Brown, W.L. The subspecies concept and its taxonomic application. Syst. Zool. 1953, 2, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, D.R.; Hillis, D.M. Species in concept and practice: Herpetological applications. Herpetologica 1990, 46, 87–104. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, D.R.; Kluge, A.G.; Hillis, D.M. Species in contemporary herpetology: Comments on phylogenetic inference and taxonomy. Herpetol. Rev. 1992, 23, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kindler, C.; Fritz, U. Phylogeography and taxonomy of the barred grass snake (Natrix helvetica), with a discussion of the subspecies category in zoology. Vertebr. Zool. 2018, 68, 269–281. [Google Scholar]
- De Queiroz, K. An updated concept of subspecies resolves a dispute about the taxonomy of incompletely separated lineages. Herpetol. Rev. 2020, 51, 459–461. [Google Scholar]
- Hillis, D.M. New and not-so-new conceptualizations of species and subspecies: A reply to the “It’s species all the way down” view. Herpetol. Rev. 2021, 52, 49–50. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, T.L.; Chambers, E.A.; Matz, M.V.; Hillis, D.M. How mitonuclear discordance and geographic variation have confounded species boundaries in a widely studied snake. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 162, 107194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunayev, E.A. Phylogeny of lizards of Phrynocephalus genus (Reptilia: Agamidae): History of study and methodical approaches. In Voprosy Gerpetologii, Proceedings of the 3rd Meeting of the Nikolsky Herpetological Society, Pushchino, Russia, 9–13 October 2006; Zoological Institute: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2008; pp. 117–126. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Melnikov, D.; Melnikova, E.; Nazarov, R.; Rajabizadeh, M. Taxonomic revision of Phrynocephalus persicus De Filippi, 1863 complex with description of a new species from Zagros, southern Iran. Curr. Stud. Herpetol. 2013, 13, 34–46. [Google Scholar]
- Chernov, S.A. Reptiles—Reptilia. In The Animals of the USSR. Volume 2: The Desert Zone; Pavlovsky, E.N., Vinogradova, B.S., Eds.; USSR Academy of Sciences: Moscow-Leningrad, Russia, 1948; pp. 127–161. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein, H. Nomenclator Reptilium et Amphibiorum Musei Zoologici Berolinensis. Namenverzeichniss der in der zoologischen Sammlung der Koniglichen Universitat zu Berlin aufgestellten Arten von Reptilien und Amphibien nach ihren Ordnungen, Familien und Gattungen; Akademie der Wissenschaften: Berlin, Germany, 1856; 48p. [Google Scholar]
- Rahiamian, H.; Shafiei, S.; Rastegar Pouyani, N.; Rastegar Pouyani, E. Phylogenetic relationships of the gray-toad agama, Phrynocephalus scutellatus (Olivier, 1807), species complex from Iran. Zootaxa 2015, 3990, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier, G.A. Voyage dans l’Empire Ottoman, l’Egypte et al Perse; Agasse: Paris, France, 1807; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolsky, A.M. Reptiles and amphibians collected by N.A. Zarudnyi in Persia in 1903-1904. Annu. Musée Zool. Acad. Imp. Sci. St. Pétersb. 1907, 10, 260–301. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. Phylogeography of the Phrynocephalus vlangalii Species Complex in the Upper Reaches of the Yellow River Inferred from mtDNA ND4-tRNA(LEU) Segments. Asian Herpetol. Res. 2012, 3, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Brown, R.P.; Liu, N. Cladogenesis and phylogeography of the lizard Phrynocephalus vlangalii (Agamidae) on the Tibetan plateau. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 1971–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Zhu, L.; Wu, Q.N.; Hu, C.C.; Qu, Y.F.; Ji, X. Geological and climatic influences on population differentiation of the Phrynocephalus vlangalii species complex (Sauria: Agamidae) in the northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2022, 169, 107394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Brown, R. Morphological species and discordant mtDNA: A genomic analysis of Phrynocephalus lizard lineages on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 139, 106523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, Z.; Brown, R.P.; Liao, P.; Liu, N. Intraspecific lineages of the lizard Phrynocephalus putjatia from the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Impact of physical events on divergence and discordance between morphology and molecular markers. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 71, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blyth, E. Report of the Curator, Zoological Department. Proc. Asiat. Soc. Bengal 1863, 32, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, N.; Brown, R. The geography and timing of genetic divergence in the lizard Phrynocephalus theobaldi on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, N. Phylogeography of Phrynocephalus erythrurus from the Qiangtang Plateau of the Tibetan Plateau. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 54, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananjeva, N.B. On the validity of Megalochilus mystaceus (Pallas, 1776). In Systematics and Ecology of Amphibians and Reptiles; Ananjeva, N.B., Borkin, L.J., Eds.; Zoological Institute USSR Academy of Sciences: Leningrad, Russia, 1987; Volume 157, pp. 4–13. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Alekperov, A.M.; Galaeva, N.M. Pholidosis of Persian toad-headed agama Phrynocephalus helioscopus persicus De Filippi. Scientific proceedings of Azerbaijan University. Biol. Sci. 1975, 11, 54–57. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Alekperov, A.M. Amphibians and Reptiles of Azerbaijan; Elm Press: Baku, Azerbeijan, 1978; p. 264. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Manilo, V.V. Description of Karyotypes of Some Species and Subspecies of the Genus Phrynocephalus (Sauria, Agamidae) from Central Asia. Vestn. Zool. 2000, 34, 113–118. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Manilo, V.V. Cytogenetic review and evolution of karyotypes in the species of the genus Phrynocephalus Kaup, 1825 (Sauria, Agamidae) from the Eastern Palaearctic. Hamadryad 2001, 26, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Manilo, V.V.; Golubev, M.L. Karyotype information on some toad agamas of the Phrynocephalus species group (Sauria, Agamidae) of the former USSR. Asiat. Herpetol. Res. 1993, 5, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Szczerbak, N.N. Zoogeographic Analysis of Reptiles of Turkmenistan. In Biogeography and Ecology of Turkmenistan; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 307–328. [Google Scholar]
- Semenov, D.V.; Brushko, Z.K.; Kubykin, R.A.; Shenbrot, G.I. Taxonomic position and protective status of the round-headed lizard (Reptilia, Agamidae) in the territory of the USSR. Zool. Z. 1987, 66, 98–109, (In Russian with English Summary). [Google Scholar]
- Ananjeva, N.B.; Borkin, L.J.; Darevsky, I.S.; Orlov, N.L. Amphibians and Reptiles. Encyclopedia of the Nature in Russia; ABF: Moscow, Russia, 1998; p. 574. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ananjeva, N.B.; Orlov, N.L.; Khalikov, R.G.; Darevsky, I.S.; Ryabov, S.A.; Barabanov, A.V. The Reptiles of Northern Eurasia; Pensoft Publishers: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2006; p. 245. [Google Scholar]
- Barts, M.; Wilms, T. Die Agamen der Welt. Draco 2003, 4, 4–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, J. Cladogenesis and vicariance patterns in the toad-headed lizard Phrynocephalus versicolor species complex. Copeia 2004, 2, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.T.; Brown, R. Species history and divergence times of viviparous and oviparous Chinese toad-headed sand lizards (Phrynocephalus) on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 68, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauch, A.A. Part III. Reptilia and Amphibia. In Mongolia and the Tangut Lands, a Three-Year Journey in Eastern High Asia. Vol. II, Reptiles and Amphibians; Przevalsky, N.M., Ed.; Imperial Russian Geographical Society: St. Petersburg, Russia, 1876; pp. 1–55. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Alcock, A.W.; Finn, F. An account of the Reptilia collected by Dr. F. Maynard, Captain, A.H. McMahon, C.I.E., and the members of the Afghan–Baluch Boundary Comission of 1896. J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal 1897, 65, 550–566. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchener, A.C.; Machado, F.A.; Hayssen, V.; Moehlman, P.D.; Viranta, S.; Esselstyn, J. Consequences of the misidentification of museum specimens: The taxonomic status of Canis lupaster soudanicus. J. Mammology 2020, 101, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E.A.; Hebert, P.D. Assessing DNA barcodes for species identification in North American reptiles and amphibians in natural history collections. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, D.G.; Ibáñez, R.; Jaramillo, C.A.; Crawford, A.J.; Ray, J.M.; Gotte, S.W.; Jacobs, J.F.; Wynn, A.H.; Gonzalez-Porter, G.P.; McDiarmid, R.W.; et al. DNA barcoding of the National Museum of Natural History reptile tissue holdings raises concerns about the use of natural history collections and the responsibilities of scientists in the molecular age. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Xu, R. Phrynocephalus nasatus Mitochondrion, Complete Genome. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/MW456559.1 (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Chen, D.; Zhou, T.; Guo, X. The complete mitochondrial genome of Phrynocephalus forsythii (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae), a toad-headed agama endemic to the Taklamakan Desert. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 4046–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Jin, Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of an agama, Phrynocephalus putjatia (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae). Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 1028–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Chen, W.; Jin, Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of Phrynocephalus guinanensis (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae). Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2016, 27, 1103–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.F.; Xia, Y.; Penga, R.; Mo, B.H.; Li, L.; Zenga, X.M. Authentication of Chinese crude drug gecko by DNA barcoding. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solovyeva, E.N.; Dunayev, E.A.; Nazarov, R.A.; Bondarenko, D.A.; Poyarkov, N.A. COI-Barcoding and Species Delimitation Assessment of Toad-Headed Agamas of the Genus Phrynocephalus (Agamidae, Squamata) Reveal Unrecognized Diversity in Central Eurasia. Diversity 2023, 15, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020149
Solovyeva EN, Dunayev EA, Nazarov RA, Bondarenko DA, Poyarkov NA. COI-Barcoding and Species Delimitation Assessment of Toad-Headed Agamas of the Genus Phrynocephalus (Agamidae, Squamata) Reveal Unrecognized Diversity in Central Eurasia. Diversity. 2023; 15(2):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020149
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolovyeva, Evgeniya N., Evgeniy A. Dunayev, Roman A. Nazarov, Dmitriy A. Bondarenko, and Nikolay A. Poyarkov. 2023. "COI-Barcoding and Species Delimitation Assessment of Toad-Headed Agamas of the Genus Phrynocephalus (Agamidae, Squamata) Reveal Unrecognized Diversity in Central Eurasia" Diversity 15, no. 2: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020149
APA StyleSolovyeva, E. N., Dunayev, E. A., Nazarov, R. A., Bondarenko, D. A., & Poyarkov, N. A. (2023). COI-Barcoding and Species Delimitation Assessment of Toad-Headed Agamas of the Genus Phrynocephalus (Agamidae, Squamata) Reveal Unrecognized Diversity in Central Eurasia. Diversity, 15(2), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020149








