“Lepidoptera Flies”, but Not Always…Interactions of Caterpillars and Chrysalis with Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
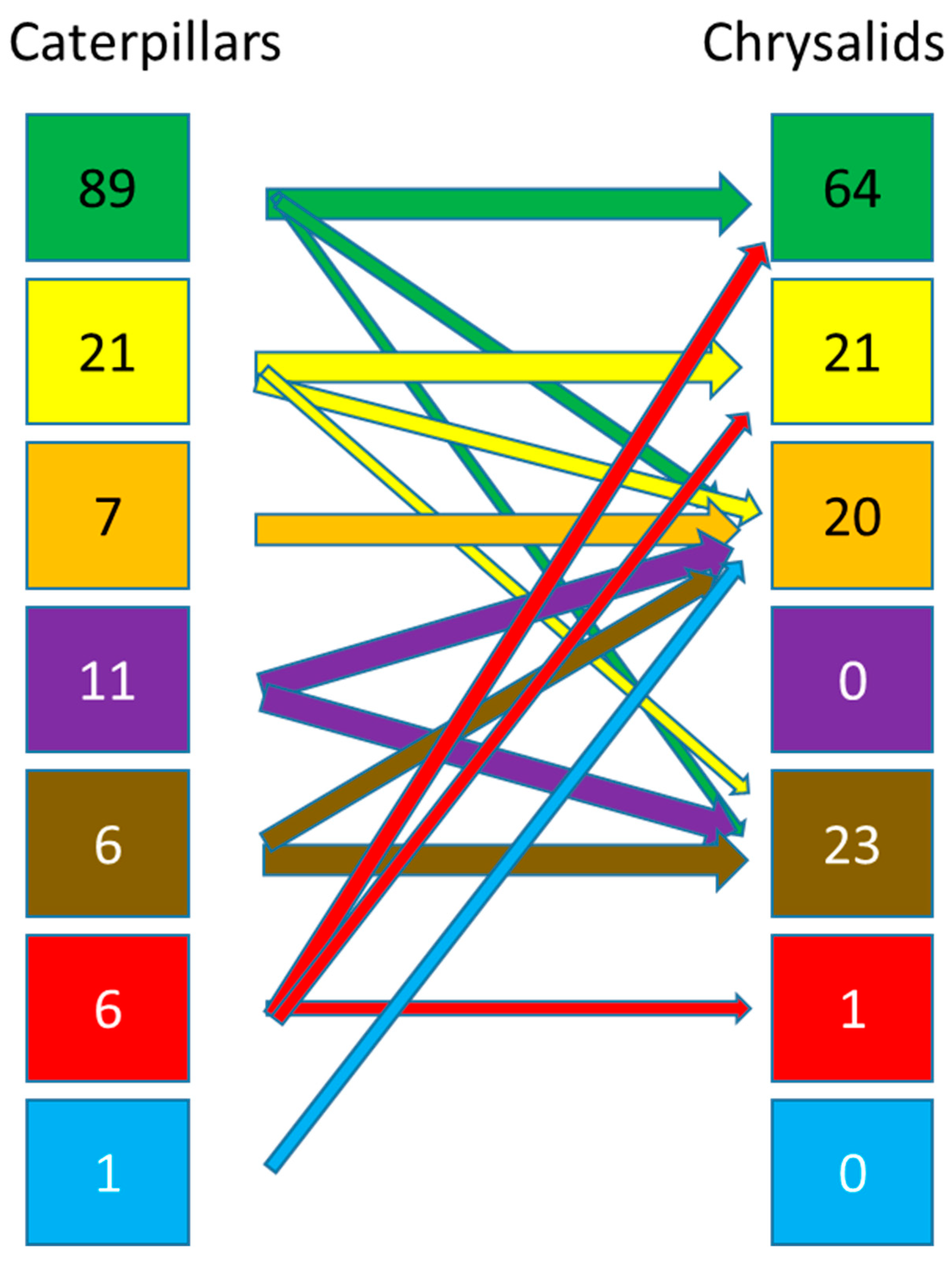
3.1. Generalities
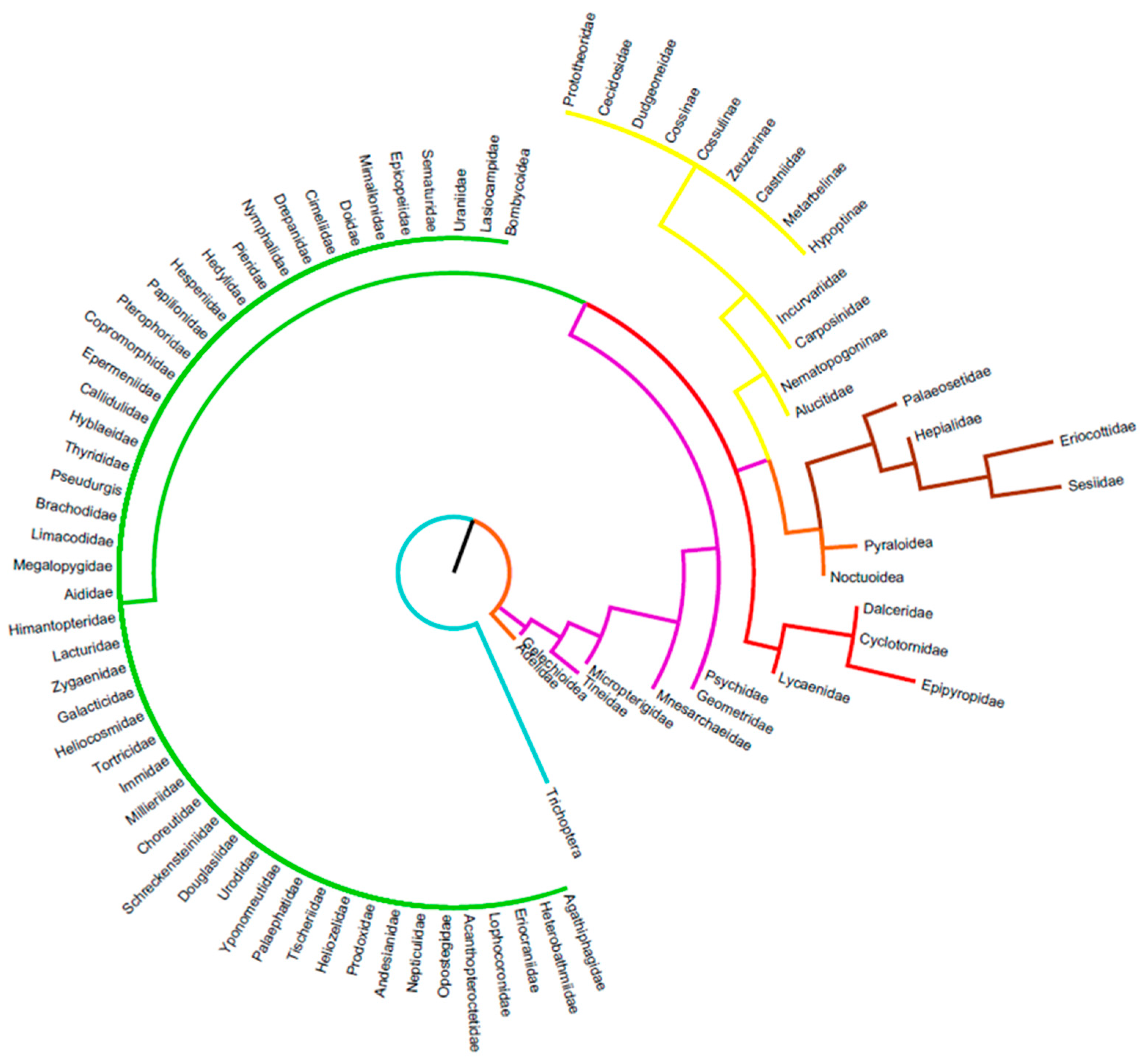
3.1.1. Caterpillars
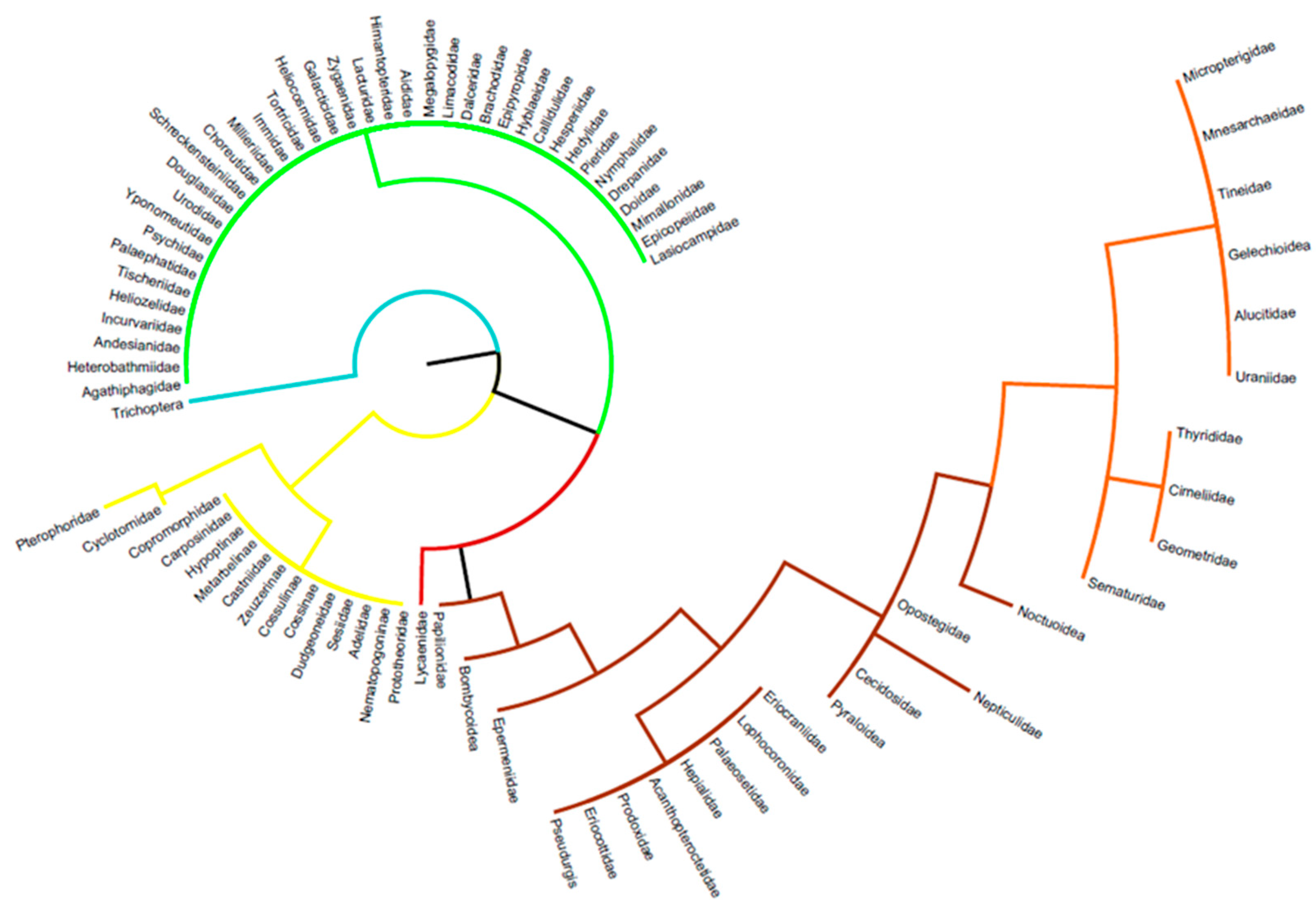
3.1.2. Chrysalids
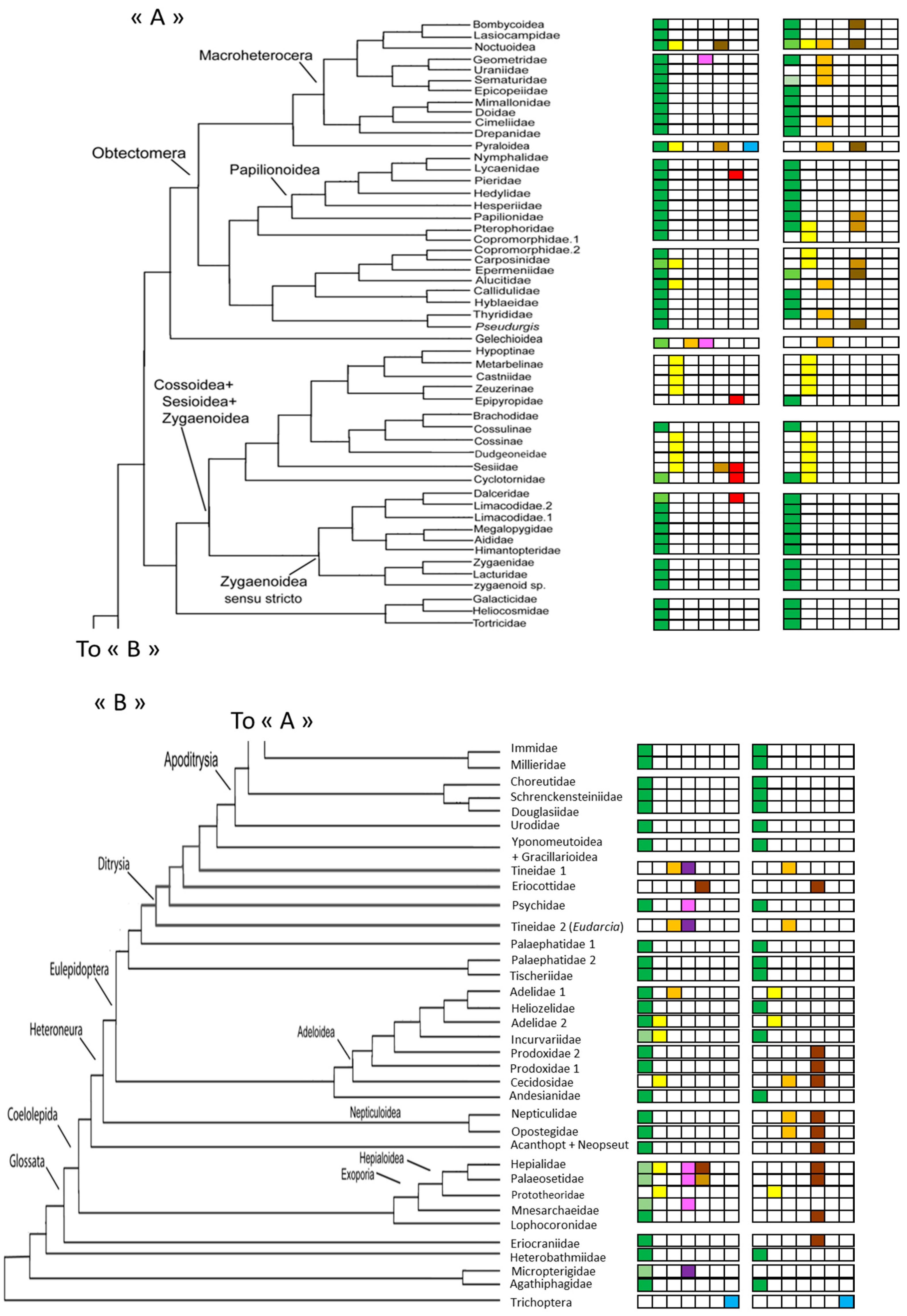
3.2. Details Subdivisions
3.2.1. Caterpillars
3.2.2. Chrysalids
3.3. Estimation of the Number of Species Having a Relationship with the Soil
4. Discussion
4.1. Caterpillars
4.2. Chrysalids
4.3. General Findings
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jabiol, B.; Brêthes, A.; Brun, J.J.; Ponge, J.F.; Toutain, F.; Zanella, A.; Aubert, M.; Bureau, F. Typologie des Formes d’Humus Forestières (Sous Climats Tempérés); Référentiel Pédologique 2008, Quae, Collection Savoir-Faire; Association Française pour l’Étude du Sol: Versailles, France, 2009; pp. 327–355. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, Y.; Shukla, V. Role of Earthworms in Soil Ecotoxicology Assessment Studies. In Trends in Technology for Agriculture, Food, Environment and Health; Agrobios International: Jodhpur, India, 2021; pp. 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, D.C.; Wall, D.H. Chapter 5—Soil Fauna: Occurrence, Biodiversity, and Roles in Ecosystem Function. In Soil Microbiology, Ecology and Biochemistry, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 111–149. [Google Scholar]
- Gobat, J.M.; Aragno, M.; Matthey, W. Le Sol Vivant: Bases de Pédologie, Biologie des Sols, 3rd ed.; PPUR Presses Polytechniques: Neuchatel, Switzerland, 2010; pp. 415–515. [Google Scholar]
- Decaëns, T.; Jiménez, J.J.; Gioia, C.; Measey, G.J.; Lavelle, P. The values of soil animals for conservation biology. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2006, 42, S23–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andujar, C.; Arribas, P.; Ruzicka, F.; Crampton-Platt, A.; Timmermans, M.J.T.N.; Vogler, A.P. Phylogenetic community ecology of soil biodisversity using mitochondrial metagenomics. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 3603–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavelle, P.; Decaëns, T.; Aubert, M.; Barot, S.; Blouin Bureau, M.F.; Margerie, P.; Mora, P.; Rossi, J.P. Soil invertebrates and ecosystem services. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2006, 42, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.; Prescott, C.E.; Abaker, W.E.A.; Augusto, L.; Cécillon, L.; Ferreira, G.W.D.; James, J.; Jandl, R.; Katzensteiner, K.; Laclau, J.P.; et al. Tamm Review: Influence of forest management activities on soil organic carbon stocks: A knowledge synthesis. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 466, 118127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuben, A. Nutrient availability and interactions between soil arthropods and microorganisms during decomposition of coniferous litter: A mesocosm study. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1991, 10, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstha, J.M.; Bell, R.T.; Launer, A.E.; Murphy, D.D. Soil arthropod abundance in coast redwood forest: Effect of selective timber harvest. Environ. Entomol. 1995, 24, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudacher, K.; Rennstam Rubbmark, O.; Birkhofer, K.; Malsher, G.; Sint, D.; Jonsson, M.; Traugott, M. Habitat heterogeneity induces rapid changes in the feeding behaviour of generalist arthropod predators. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.; Alemu, T.; Alemneh, T.; Pertoldi, C.; Bahrndorff, S. Thermal acclimation and adaptation across populations in a broadly distributed soil arthropod. Funct. Ecol. 2019, 33, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nieukerken, E.J.; Kaila, L.; Kitching, I.; Kristensen, N.P.; Lees, D.C.; Minet, J.; Mitter, C.; Mutanen, M.; Regier, J.C.; Simonsen, T.J.; et al. Order Lepidoptera Linnaeus, 1758. In Animal Biodiversity: An Outline of Higher Classification and Survey of Taxonomic Richness; Zhang, Z.Q., Ed.; Magnolia Press: Auckland, New Zealand, 2011; Volume 3148, pp. 212–221. [Google Scholar]
- Scoble, M.J. The Lepidoptera. Form, Function and Diversity; Natural History Museum Publications (RU); Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1992; pp. 1–404. [Google Scholar]
- Holzenthal, R.W. Tricoptera (Caddisflies). In Encyclopedia of Inland Waters; Likens, G.E., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 456–467. [Google Scholar]
- López-Carretero, A.; Díaz-Castelazo, C.; Boege, K.; Rico-Gray, V. Evaluating the spatio-temporal factors that structure network parameters of plant-herbivore interactions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.A.; Mitter, C.; Farrell, B. 20. Evolution of Larval Food Preferences in Lepidoptera. In Evolution, Systematics, and Biogeography; Kükenthal, W., Ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 403–422. [Google Scholar]
- Pichon, A.; Arvanitakis, L.; Roux, O.; Kirk, A.; Alauzet, C.; Bordat, D.; Legal, L. Genetic differentiation among various populations of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2006, 96, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legal, L.; Valet, M.; Dorado, O.; Jesus-Almonte, J.M.; Lopez, K.; Céréghino, R. Lepidoptera are relevant bioindicators of passive regeneration in tropical dry forests. Diversity 2020, 12, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enderlein, G. Beitrag zur Kenntnis der antarktischen Landarthropoden. Pringleoptera, eine neue Schmetterlingsgattung aus dem antarktischen Gebiet. Zool. Anz. 1905, 29, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- New, T.R. Are Lepidoptera an effective ‘umbrella group’ for biodiversity conservation? J. Insect Conserv. 1997, 1, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legal, L.; Dorado, O.; Machkour-M’Rabet, S.; Leberger, R.; Albre, J.; Mariano, N.A.; Gers, C. Ecological constraints and distribution of the primitive and enigmatic endemic Mexican butterfly Baronia brevicornis (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae). Can. Entomol. 2015, 147, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grehan, J.R.; Mielke, C.G. Evolutionary biogeography and tectonic history of the ghost moth families Hepialidae, Mnesarchaeidae, and Palaeosetidae in the Southwest Pacific (Lepidoptera: Exoporia). Zootaxa 2018, 4415, 243–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loof, A.; Schoofs, L. Calcitox-Metamorphosis in Insects: The Calcium (Ca2+)-Homeostasis System as the Integrated Primordial Receptor System for both Juvenile Hormone and Ecdysteroids. Life Excit. Biol. 2020, 7, 41–81. [Google Scholar]
- Common, I.F.B. Moths of Australia; Brill: Leyde, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 1–535. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, H.A. Lycaenid caterpillars (Lepidoptera, Lycaenidae) eating flowers of Dalea pennellii var. chilensis (Fabaceae) in the northern Chilean Andes. Rev. Bras. Entomol. 2014, 58, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brown, J.W. Patterns of Lepidoptera herbivory on conifers in the New World. J. Asia Pac. Biodivers. 2018, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, A.; Ehrlén, J. Caterpillar seed predators mediate shifts in selection on flowering phenology in their host plant. Ecology 2017, 98, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, B.; Fotouhi, K.; Mohtasebi, S.S.; Nasiri, A.; Goldansaaz, S.H. Detection of different densities of Ephestia kuehniella pest on white flour at different larvae instar by an electronic nose system. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2019, 84, 101522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naino-Jika, A.K.; Le Ru, B.; Capdevielle-Dulac, C.; Chardonnet, F.; Silvain, J.F. Population genetics of the Mediterranean corn borer (Sesamia nonagrioides) differs between wild and cultivated plants. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualini, E.; Natale, D. Zeuzera pyrina and Cossus cossus (Lepidoptera: Cossidae) control by pheromones: Four years advances in Italy. IOBC WPRS Bull. 1999, 22, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Nishida, K.; Robbins, R.K. One side makes you taller: A mushroom–eating butterfly caterpillar (Lycaenidae) in Costa Rica. Neotrop. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 15, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potocký, P.; Bartoňová, A.; Beneš, J.; Zapletal, M.; Konvička, M. Life-history traits of Central European moths: Gradients of variation and their association with rarity and threats. Insect Conserv. Divers. 2018, 11, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, L.L.; Kaminski, L.A.; Freitas, A.V. The tortoise caterpillar: Carnivory and armoured larval morphology of the metalmark butterfly Pachythone xanthe (Lepidoptera: Riodinidae). J. Nat. Hist. 2020, 54, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molleman, F. Puddling: From natural history to understanding how it affects fitness. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2010, 134, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legal, L.; Dorado, O.; Albre, J.; Bermudez-Torres, K.; Lopez, K. Mariposas Diurnas, Reserva de la Biosfera Sierra de Huautla, Estado de Morelos, México; Tropico Seco Ediciones: Cuernavaca, Mexico, 2017; pp. 1–330. [Google Scholar]
- Regier, J.C.; Mitter, C.; Kristensen, N.P.; Davis, D.R.; Van Nieukerken, E.J.; Rota, J.; Simonsen, T.J.; Mitter, K.T.; Kawahara, A.Y.; Yen, S.H.; et al. A molecular phylogeny for the oldest (nonditrysian) lineages of extant Lepidoptera, with implications for classification, comparative morphology and life-history evolution. Syst. Entomol. 2015, 40, 671–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP-Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony, Version 4.0b10; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001.
- Dumbleton, L. A new genus of seed-infesting micropterygid moths. Pac. Sci. 1952, 6, 17–29. [Google Scholar]
- Heppner, J.B. Valdivian Archaic Moths (Lepidoptera: Heterobathmiidae). In Encyclopedia of Entomology; Capinera, J.L., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 653. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, J.A. Chapter 151—Lepidoptera: Moths, Butterflies. In Encyclopedia of Insects, 2nd ed.; Resh, V.H., Cardé, R.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 559–587. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, E.S.; Kristensen, N.P. The Australian moth family Lophocoronidae and the basal phylogeny of the Lepidoptera Glossata. Invertebr. Taxon 1996, 10, 1199–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucheux, M.J. Antennal sensilla of male Lophocorona pediasia Common 1973 and their phylogenetic implications (Lepidoptera: Lophocoronidae). Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 2006, 42, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mey, W.; Léger, T.; Lien, V.V. Extant and fossil records of currently Australian primitive moths in South-East Asia and their biogeographic significance (Lepidoptera, Micropterigidae, Agatiphagidae, Lophocoronidae). Nota Lepidopterol. 2021, 44, 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minet, J. Proposal of an infraordinal name for the Acanthopteroctetidae (Lepidoptera). Bull. Soc. Entomol. France 2002, 107, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.R. Generic revision of the Opostegidae, with a synoptic catalog of the world’s species (Lepidoptera: Nepticuloidea). Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 1989, 478, 1–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nieukerken, E.J.; Doorenweerd, C.; Hoare, R.; Davis, D. Revised classification and catalogue of global Nepticulidae and Opostegidae (Lepidoptera, Nepticuloidea). ZooKeys 2016, 628, 65–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.M.; Lim, J.; Lee, B.W.; Byun, B.K. Three species of the genus Stigmella Schrank (Lepidoptera: Nepticulidae) feeding Quercus (Fagaceae) new to Korea. J. Asia Pac. Biodivers. 2020, 13, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.R.; Gentile, P. Andesianidae, a new family of monotrysian moths (Lepidoptera: Andesianoidea) from austral South America. Invertebr. Syst. 2003, 17, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, G.R.P.; Eltz, R.P.; Pase, R.B.; Silva, G.T.; Bordignon, S.A.L.; Mey, W.; Gonçalves, G.L. Cecidonius pampeanus, gen. et sp. n.: An overlooked and rare, new gall-inducing micromoth associated with Schinus in southern Brazil (Lepidoptera, Cecidosidae). ZooKeys 2017, 695, 37–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.R. A Revision of the Moths of the Subfamily Prodoxinae (Lepidoptera: Incurvariidae); Bulletin of the United States National Museum; Smithsonian Institution: Washington, DC, USA, 1967; Volume 255, pp. 1–170. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, J.A. Interrelationships of yuccas and yucca moths. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1992, 7, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellmyr, O.; Thompson, J.N.; Brown, J.; Harrison, R.G. Evolution of pollination and mutualism in the yucca moth lineage. Am. Nat. 1996, 148, 827–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppner, J.B. Leafcutter Moths (Lepidoptera: Incurvariidae). In Encyclopedia of Entomology; Capinera, J.L., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 656. [Google Scholar]
- Hirowatari, T.; Yagi, S.; Ohshima, I.; Huang, G.H.; Wang, M. Review of the genus Vespina (Lepidoptera, Incurvariidae) with two new species from China and Japan. Zootaxa 2021, 4927, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppner, J.B. Longhorned Fairy Moths (Lepidoptera: Adelidae). In Encyclopedia of Entomology; Capinera, J.L., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 2226. [Google Scholar]
- Van Nieukerken, E.J.; Eiseman, C.S. Splitting the leafmining shield-bearer moth genus Antispila Hübner (Lepidoptera, Heliozelidae): North American species with reduced venation placed in Aspilanta new genus, with a review of Heliozelid morphology. ZooKeys 2020, 957, 105–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stonis, J.R.; Diškus, A.; Remeikis, A.; Solis, M.A.; Katinas, L. Exotic-looking Neotropical Tischeriidae (Lepidoptera) and their host plants. ZooKeys 2020, 970, 117–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, D.R. A New Family of Monotrysian Moth from Austral South America (Lepidoptera: Palaephatidae), with a Phylogenetic Review of the Monotrysia; Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology; Smithsonian Institution: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; Volume 434, pp. 1–202. [Google Scholar]
- Heppner, J.B. Ermine Moths (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae). In Encyclopedia of Entomology; Capinera, J.L., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 1360–1361. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, J.C. Molecular Phylogenetics, Biodiversity and Life History Evolution of Yponomeutoidea (Lepidoptera: Ditrysia), with a Catalog and an Overview of the Lepidopteran Fossils. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Wang, S.X. First report of the family Urodidae from China, with descriptions of the immature stages of Wockia magna Sohn, 2014 (Lepidoptera: Urodoidea). SHILAP Rev. Lepidopterol. 2015, 43, 499–505. [Google Scholar]
- Poinar, G., Jr. A new genus of moths (Lepidoptera: Gracillarioidea: Douglasiidae) in Myanmar amber. Hist. Biol. 2019, 31, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, K.; Ctvrtecka, R.; Miller, S.E.; Rosati, M.E.; Molem, K.; Damas, K.; Gewa, B.; Novotny, V. Low host specificity and abundance of frugivorous Lepidoptera in the lowland rain forests of Papua New Guinea. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rota, J.; Aguiar, A.; Karsholt, O. Choreutidae of Madeira: Review of the known species and description of the male of Anthophila threnodes (Walsingham, 1910) (Lepidoptera). Nota Lepidopterol. 2014, 37, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, A.Y.; Plotkin, D.; Hamilton, C.A.; Gough, H.; St Laurent, R.; Owens, H.L.; Homziak, N.T.; Barber, J.B. Diel behavior in moths and butterflies: A synthesis of data illuminates the evolution of temporal activity. Org. Divers. Evol. 2018, 18, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppner, J.B. Imma Moths (Lepidoptera: Immidae). In Encyclopedia of Entomology; Capinera, J.L., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 1921. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.W.; Basset, Y.; Panmeng, M.; Putnaul, S.; Miller, S.E. Host records for Tortricidae (Lepidoptera) reared from seeds and fruits in a Thailand rainforest. Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 2019, 121, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basoalto, A.; Ramírez, C.C.; Lavandero, B.; Devotto, L.; Curkovic, T.; Franck, P.; Fuentes-Contreras, E. Population genetic structure of codling moth, Cydia pomonella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), in different localities and host plants in Chile. Insects 2020, 11, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, X.; Li, G. Effect of Different Host Plants on Growth, Development and Reproduction of Yellow Tortrix Moth Acleris fimbriana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Pak. J. Zool. 2021, 53, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagua, G.; Condamine, F.L.; Horak, M.; Zwick, A.; Sperling, F.A. Diversification shifts in leafroller moths linked to continental colonization and the rise of angiosperms. Cladistics 2017, 33, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, J.C.; Adamski, D. A New Species of Wockia Heinemann, 1890 (Lepidoptera: Urodidae) from Korea. Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 2008, 110, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Driesche, R.; LaForest, J.H.; Bargeron, C.T.; Reardon, R.C.; Herlihy, M. Forest Pest Insects in North America: A Photographic Guide; USDA Forest Service: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2013.
- Tremewan, W.G. A Bibliography of the Zygaenidae (Lepidoptera: Zygaenidae); Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 1–188. [Google Scholar]
- De Castro, E.C.; Musgrove, J.; Bak, S.; McMillan, W.O.; Jiggins, C.D. Phenotypic plasticity in chemical defence of butterflies allows usage of diverse host plants. Biol. Lett. 2021, 17, 20200863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveena, K.; Chinniah, C.; Shanthi, M. Cyanogenic glycosides and plant-herbivore interactions. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2021, 9, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, T.A.; Wagner, D.L.; Miller, S.E. A Revision of North American Lactura (Lepidoptera, Zygaenoidea, Lacturidae). ZooKeys 2019, 846, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niehuis, O.; Naumann, C.M.; Misof, B. Phylogenetic analysis of Zygaenoidea small-subunit rRNA structural variation implies initial oligophagy on cyanogenic host plants in larvae of the moth genus Zygaena (Insecta: Lepidoptera). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2006, 147, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symondson, W.O.; Holloway, J.D.; Goossens, B.; Müller, C.T. Bornean caterpillar (Lepidoptera) constructs cocoon from Vatica rassak (Dipterocarpaceae) resin containing multiple deterrent compounds. J. Nat. Hist. 2015, 49, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, A.; Corseuil, E.; Formentini, A.C. Lepidópteros de importância médica ocorrentes no Rio Grande do Sul. II. Aididae e Limacodidae. Biociencias 2005, 13, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Diniz, I.R.; Morais, H.C. Lepidopteran caterpillar fauna of cerrado host plants. Biodiv. Cons. 1997, 6, 817–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.W. Puss Caterpillar (Larva), Southern Flannel Moth (Adult), Megalopyge opercularis (JE Smith 1797), (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Zygaenoidea: Megalopygidae). EDIS. 2013. Available online: https://entnemdept.ufl.edu/creatures/misc/moths/puss.htm (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Wu, C.S.; Solovyev, A.V. A review of the genus Miresa Walker in China (Lepidoptera: Limacodidae). J Insect Sci. 2011, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stoepler, T.M.; Lill, J.T.; Murphy, S.M. Intraplant movement of generalist slug caterpillars (Limacodidae: Lepidoptera): Effects of host plant and light environment. Environ. Entomol. 2014, 43, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lin, R.J.; Braby, M.F.; Hsu, Y.F. Evolution and losses of spines in slug caterpillars (Lepidoptera: Limacodidae). Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 9827–9840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heppner, J.B. Mexican Lepidoptera biodiversity. Insecta Mundi 2002, 16, 171–190. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, S.H.; Robinson, G.S.; Quicke, D.L. The phylogenetic relationships of Chalcosiinae (Lepidoptera, Zygaenoidea, Zygaenidae). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2005, 143, 161–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovlev, R.V.; Sulak, H.; Witt, T.J. Preliminary list of Cossidae sensu str. (Lepidoptera, Cossoidea: Cossidae: Cossinae & Zeuzerinae) of the Republic of Angola with description of a new Strigocossus species. Zootaxa 2019, 4586, 445–460. [Google Scholar]
- Rishi, R.R.; Sundararaj, R. Incidence of bark feeding borer, Indarbela quadrinotata Walker (Lepidoptera: Cossidae) on Sonneratia apetala in the Mangroves of Maharashtra, India. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2021, 9, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Rodríguez, J.M. Three new registers of stem-borer insects in Terminalia ivorensis A. Chev. Rev. Mex. Cienc. For. 2017, 8, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bella, S.; Bartsch, D.; Laštůvka, Z. Bibliographic summary and new records of the Brachodidae and Sesiidae of Sicily, with an updated list and some comments on the distribution of Italian species (Lepidoptera, Cossoidea). Spixiana 2017, 40, 139–156. [Google Scholar]
- Dyar, H.G. A lepidopterous larva on a leaf-hooper. (Epipyros barberiana n. sp.). Proc. Ent. Soc. Wash. 1902, 5, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, S.M. Natural Host Rearing and some Biological Aspects of the Leopard Moth Zeuzera pyrina L. (Lepidoptera: Cossidae) on Poplar Trees (Populus Sp.) (Malpighiales Salicaceae) in Egypt. J. Plant Prot. Pathol. 2019, 10, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.M.; López, G.B.; Huerta, P.J.P.; Miller, J.Y. A new genus of Castniinae (Lepidoptera Castniidae) with comments on comparative morphology and bionomics of its assigned species. Zootaxa 2019, 4668, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.A.; Williams, M.R.; Bishop, C.L.; Gamblin, T.; Fissioli, J.; Coppen, R.A. Notes on the biology, ecology, life history and conservation of the graceful sun-moth ‘Synemon gratiosa’ westwood, 1877 (Lepidoptera: Castniidae). Aust. Entomol. 2021, 48, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, J.I.; Crane, J.H.; Wasielewski, J.; Miller, J.Y.; Carrillo, D. Lepidoptera pests of sapodilla (Manilkara zapota (L.) van Royen) in south Florida, with some comments on life history and natural control. Insecta Mundi 2019, 0739, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Scaccini, D.; Ruzzier, E.; Daane, K.M. Givira ethela (Neumoegen and Dyar, 1893) (Lepidoptera: Cossidae), A Previously Unidentified Pest on Vitis vinifera (L.). Insects 2021, 12, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.S. Notes on Lepidoptera in the Eastern Cape Province (Part III). J. Entomol. Soc. S. Afr. 1954, 16, 166–167. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, A. Life history of Dysodia sica (Lepidoptera: Thyrididae) in Panama. Psyche 1980, 87, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, D.C. Morphology and behavior of the larva of Calindoea trifascialis (Lepidoptera: Thyrididae), a chemically defended retreat-building caterpillar from Vietnam. Zootaxa 2003, 225, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baksha, M.W.; Crawley, M.J. Relative preference of different host plants to teak defoliator, Hyblaea puera Cram. (Hyblaeidae: Lepidoptera) in Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. For. Sci. 1995, 24, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, S.H.; Wu, S. Biota Taiwanica: Calliduloidea, Callidulidae, Callidulinae; National Sun Yat-Sen University: Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 2009; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, G.R.P.; Pereira, C.M.; Becker, V.O.; Specht, A.; Gonçalves, G.L. A new cecidogenous species of many-plumed moth (Alucitidae) associated with Cordiera A. Rich. ex DC. (Rubiaceae) in the Brazilian Cerrado. Zoologia 2019, 36, e34604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaedike, R. New data on the taxonomy, distribution and host plants of Australian Epermeniidae (Lepidoptera: Epermenioidea). Zootaxa 2018, 4524, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Li, B.Y.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Cao, L.J.; Gong, Y.J.; Song, W.; Wei, S.J. Patterns of genetic variation among geographic and host-plant associated populations of the peach fruit moth Carposina sasakii (Lepidoptera: Carposinidae). BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Benedictis, J.A. On the taxonomic position of Ellabella Busck, with descriptions of the larva and pupa of E. bayensis (Lepidoptera: Copromorphidae). J. Res. Lepid. 1984, 23, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigot, L.; Etienne, J. Les Pterophoridae de l’île de la Guadeloupe (Lepidoptera). Bull. Soc. Entomol. France 2009, 114, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.S. Host-plant relationships in the Papilionidae (Lepidoptera): Parallel cladogenesis or colonization? Cladistics 1987, 3, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, J.; Legal, L.; Descimon, H.; Michel, F. Molecular phylogeny of swallowtail butterflies of the tribe Papilionini (Papilionidae, Lepidoptera). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1999, 12, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasuji, F. Egg size of skippers (Lepidoptera: Hesperiidae) in relation to their host specificity and to leaf toughness of host plants. Ecol. Res. 1987, 2, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, A.D.; Ogawa, J.R.; Brower, A.V.Z. Revised classification of the family Hesperiidae (Lepidoptera: Hesperioidea) based on combined molecular and morphological data. Syst. Entomol. 2009, 34, 467–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janz, N.; Nylin, S. Butterflies and plants: A phylogenetic study. Evolution 1998, 52, 486–502. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer-Paris, J.R.; Sanchez-Mercado, A.; Viloria, A.L.; Donaldson, J. Congruence and diversity of butterfly-host plant associations at higher taxonomic levels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, F.S.; Renwick, J.A.A. Host plant choice in Pieris butterflies. In Chemical Ecology of Insects 2; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 214–238. [Google Scholar]
- Koubínová, D.; Dincă, V.; Dapporto, L.; Voda, R.; Suchan, T.; Vila, R.; Alvarez, N. Genomics of extreme ecological specialists: Multiple convergent evolution but no genetic divergence between ecotypes of Maculinea alcon butterflies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terblanche, R.F. Anoplolepis steingroeveri (Forel, 1894) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae), a new associated ant species record for myrmecophilous butterflies in Africa and new hostplant records for Crudaria (Wallengren, 1875) (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae: Aphnaeinae). Metamorphosis 2017, 28, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Carleial, S.; Maurel, N.; van Kleunen, M.; Stift, M. Oviposition by the Mountain Alcon Blue butterfly increases with host plant flower number and host ant abundance. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2018, 28, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsaki, N.; Ohata, M.; Sato, Y.; Rausher, M.D. Host Plant Choice Determined by Reproductive Interference between Closely Related Butterflies. Am. Nat. 2020, 196, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardman, J.E.; Smith, M. How important are olfactory cues for host-plant detection by migrating Danaus chrysippus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae, Danainae) in Cyprus? Entomol. Gaz. 2019, 70, 223–238. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, R.R.; Francini, R.B.; Habib, M.E.E.D.M.; Freitas, A.V.L. Seasonal Patterns of Host Plant Use in an Assemblage of Heliconiini Butterflies (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae) in a Neotropical forest. Neotrop. Entomol. 2021, 50, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, C.; Yack, J.E. Immature stages of the masked birch caterpillar, Drepana arcuata (Lepidoptera: Drepanidae) with comments on feeding and shelter building. J. Insect Sci. 2018, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, Y.M.; Baquero, A.I.; Farino, T.; Jiménez, R.E.; Petty, S.J. Aportaciones a la distribución, ecología e identificación de la oruga de Axia margarita (Hübner, 1813) en España (Lepidoptera: Cimeliidae). Bol. SEA 2018, 63, 297–300. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.S.; Wagner, D.L.; Opler, P.A.; Lafontaine, J.D. Fascicle 22.1A: Drepanoidea, Doidae; Noctuoidea, Notodontidae (Part): Pygaerinae, Notodontinae, Cerurinae, Phalerinae, Periergosinae, Dudusinae, Hemiceratinae. In The Moths of America North of Mexico; Wedge Entomological Research Foundation: Bakersfield, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–348. [Google Scholar]
- St Laurent, R.A.; Wagner, D.L.; Reeves, L.E.; Kawahara, A.Y. Notes on the larva and natural history of Lacosoma arizonicum Dyar (Mimallonoidea, Mimallonidae) with new host and parasitoid records. J. Lepid. Soc. 2017, 71, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Fan, X.L. First record of the genus Schistomitra Butler, 1881 (Lepidoptera, Epicopeiidae) from China, with the description of a new species. ZooKeys 2019, 878, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minet, J.; Scoble, M.J. The Drepanoid/Geometroid Assemblage. In Lepidoptera, Moths and Butterflies. Volume 1, Evolution, Systematics, and Biogeography. Handbook of Zoology, vol. IV, Arthropoda: Insecta, Part 35; Kristensen, N.P., Ed.; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 301–320. [Google Scholar]
- Cock, M.J.; Shaw, R.H. The biology of Epiplema albida (Hampson, 1891) (Lepidoptera, Uraniidae, Epipleminae) on Sri Lankan Privet, Ligustrum robustum (Roxb.) Blume subsp. walkeri (Decne.) PS Green (Oleaceae). Trop. Lepid. Res. 2017, 27, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kadej, M.; Zając, K.; Tarnawski, D. Oviposition site selection of a threatened moth Eriogaster catax (Lepidoptera: Lasiocampidae) in agricultural landscape—Implications for its conservation. J. Insect Conserv. 2018, 22, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raath, M.J.; Le Roux, P.C.; Veldtman, R.; Greve, M. Incorporating biotic interactions in the distribution models of African wild silk moths (Gonometa species, Lasiocampidae) using different representations of modelled host tree distributions. Aus. Ecol. 2018, 43, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, M.; Kiuchi, M. Effect of chilling of diapause pupa on adult emergence in the sweet potato hornworm, Agrius convolvuli (Linné) (Lepidoptera; Sphingidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1997, 32, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia, L.B.; Arnal, P.; Hallwachs, W.; Haxaire, J.; Janzen, D.; Kitching, I.J.; Rougerie, R. A global food plant dataset for wild silkmoths and hawkmoths and its use in documenting polyphagy of their caterpillars (Lepidoptera: Bombycoidea: Saturniidae, Sphingidae). Biodivers. Data J. 2020, 8, e60027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imada, Y.; Kawakita, A.; Makoto, K. Allopatric distribution and diversification without niche shift in a bryophyte-feeding basal moth lineage (Lepidoptera: Micropterigidae). Proc. R. Soc. B 2011, 278, 3026–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, G.W.; Kristensen, N.P. Mnesarchaeidae (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Hepialoidea). Fauna N. Z. 2019, 78. Available online: https://www.biotaxa.org/fnz/article/view/fnz.78 (accessed on 21 September 2021).
- Heppner, J.; Balcázar, L.M.A.; Wang, H.Y. Larval morphology of Ogygioses caliginosa from Taiwan (Lepidoptera: Palaeosetidae). Trop. Lep. 1995, 6, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Grehan, J. Larval feeding habits of the Hepialidae (Lepidoptera). J. Nat. Hist. 1989, 23, 803–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahola, M.; Davis, D.; Itämies, J.; Leinonen, R.; Mutanen, M. Description of immature stages of Nemophora bellela (Walker, 1863) (Lepidoptera: Adelidae). Entomol. Fenn. 2017, 28, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raman, A.; Suryanarayanan, T.S. Fungus–plant interaction influences plant-feeding insects. Fungal Ecol. 2017, 29, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, T. Diversity of saproxylic Lepidoptera. In Saproxylic Insects; Zoological Monographs; Ulyshen, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 319–338. [Google Scholar]
- Metz, M.A.; Davis, D.R.; Davis, M.M. A new species of Niditinea (Tineidae: Tineinae) with a preference for bird nests, and the known larval habitats of the species in the United States. Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 2018, 120, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgogne, J. Observations sur l’instinct des chenilles de Psychidae [Lep.]. Bull. Soc. Entomol. France 1949, 54, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppner, J.B. Old World Spiny-Winged Moths (Lepidoptera: Eriocottidae). In Encyclopedia of Entomology; Capinera, J.L., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 1358. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.K.; Sagliocco, J.L. Host-specificity of a root borer, Bembecia chrysidiformis [Lep.: Sesiidae], a potential control agent for Rumex sp. [Polygonaceae] in Australia. Entomophaga 1991, 36, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzese, D.J.; Wagner, D.L.; Harrison, T.; Jogesh, T.; Overson, R.P.; Wickett, N.J.; Skogen, K.A. Diversification in the microlepidopteran genus Mompha (Lepidoptera: Gelechioidea: Momphidae) is explained more by tissue specificity than host plant family. BioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirichenko, N.; Triberti, P.; Akulov, E.; Ponomarenko, M.; Gorokhova, S.; Sheiko, V.; Lopez-Vaamonde, C. Exploring species diversity and host plant associations of leaf-mining micromoths (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) in the Russian Far East using DNA barcoding. Zootaxa 2019, 4652, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sruoga, V.; Kaila, L.; Rocienė, A. The Elachistinae (Lepidoptera: Gelechioidea, Elachistidae) of Thailand, with description of eight new species. Eur. J. Taxon. 2019, 574, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabis, K. What is a moth doing under water? Ecology of aquatic and semi-aquatic Lepidoptera. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2018, 419, 42–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooker, J.F.; Giron, D. The evolution of endophagy in herbivorous insects. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 581816. [Google Scholar]
- Léger, T.; Mally, R.; Neinhuis, C.; Nuss, M. Refining the phylogeny of Crambidae with complete sampling of subfamilies (Lepidoptera, Pyraloidea). Zool. Scr. 2021, 50, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, S. Carnivorous caterpillars: The behaviour, biogeography and conservation of Eupithecia (Lepidoptera: Geometridae) in the Hawaiian islands. Geojournal 1983, 7, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodner, F.; Brehm, G.; Homeier, J.; Strutzenberger, P.; Fiedler, K. Caterpillars and host plant records for 59 species of Geometridae (Lepidoptera) from a montane rainforest in southern Ecuador. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strutzenberger, P.; Brehm, G.; Gottsberger, B.; Bodner, F.; Seifert, C.L.; Fiedler, K. Diversification rates, host plant shifts and an updated molecular phylogeny of Andean Eois moths (Lepidoptera: Geometridae). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, A.; Negrisolo, E.; Zilli, A.; Battisti, A.; Cerretti, P. A total evidence phylogeny for the processionary moths of the genus Thaumetopoea (Lepidoptera: Notodontidae: Thaumetopoeinae). Cladistics 2017, 33, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narem, D.M.; Meyer, M.H. Native prairie graminoid host plants of Minnesota and associated Lepidoptera: A literature review. J. Lepidop. Soc. 2017, 71, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighi, L.; Ranjbar Aghdam, H.; Imani, S.; Shojai, M. Age-stage two-sex life table analysis of Sesamia nonagrioides (Lep.: Noctuidae) reared on different host plants. Arch. Phytopathol. Pflanzenschutz 2017, 50, 438–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetzner, J.W., Jr.; Fetzner, J.J. Notes on the Life History of the Delicate Silver Y, Autographa pseudogamma (Grote, 1875) (Lepidoptera: Noctuoidea: Noctuidae: Plusiinae). Ann. Carnegie Mus. 2018, 85, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freina, J.J.; Mecenero, S.; Morton, A. Notes on the life history of Epitoxis namaqua de Freina & Mey, 2011 (Lepidoptera: Erebidae: Arctiinae: Syntomini). Metamorphosis 2020, 31, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Husain, A.; Hasan, W. New record of Common Owlet Moth Spirama helicina (Hubner, 1831) (Lepidoptera: Erebidae: Catocalinae) from Aligarh (Uttar Pradesh) with systematic account, distribution, host plants and biological control. Int. J. Agric. Appl. Sci. 2020, 1, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, P.Z.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W. A Novel Origin of Pteridivory among the New World Noctuoidea: Fern-Feeding “Litter Moths” (Erebidae: Herminiinae). Proc. Entomol. Soc. Wash. 2021, 123, 314–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A. Revision of Lepidoptera of Egypt, Superfamily Noctuoidea Part II: Erebidae, Nolidae and Euteliidae. Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 14, 59–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppner, J.B. Douglas Moths (Lepidoptera: Douglasiidae). In Encyclopedia of Entomology; Capinera, J.L., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 1241. [Google Scholar]
- Muttkowski, R.A. Studies on the blood of insects III. The coagulation and clotting of insect blood. Bull. Brooklyn Entomol. Soc. 1924, 19, 128–144. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Sun, S.; Tan, H.; Qin, C.; Ji, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X. Chlorantraniliprole against the black cutworm Agrotis ipsilon (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): From biochemical/physiological to demographic responses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melguizo-Ruiz, N.; Jiménez-Navarro, G.; De Mas, E.; Pato, J.; Scheu, S.; Austin, A.T.; Wise, D.H.; Moya-Laraño, J. Field exclusion of large soil predators impacts lower trophic levels and decreases leaf-litter decomposition in dry forests. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, W.J.; Sanderman, J.; Melillo, J.M. Decreased soil organic matter in a long term soil warming experiment lowers soil water holding capacity and affects soil thermal and hydrological buffering. JGR Biogeosci. 2020, 125, e2019JG005158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.; Jiang, Q.; Aramwit, P.; Reddy, N. Litter to leaf: The unexplored potential of silk byproducts. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deharveng, L.; Dalens, H.; Drugmand, D.; Simon-Benito, J.C.; Da Gama, M.M.; Sousa, P.; Gers, C.; Bedos, A. Endemism mapping and biodiversity conservation in western Europe: An Arthropod perspective. Belg. J. Entomol. 2000, 2, 59–75. [Google Scholar]
- Barragán-Fonseca, K.Y.; Nurfikari, A.; Van De Zande, E.M.; Wantulla, M.; Van Loon, J.J.; De Boer, W.; Dicke, M. Insect frass and exuviae to promote plant growth and health. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number of Species | Caterpillars | % per Family | Chrysalids | % per Family | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Litter/Fungi | Roots | Litter | Soil | ||||
| Micropterigidae | 140 | 140 | 0 | 100 | 140 | 0 | 100 |
| Eriocraniidae | 29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 100 |
| Lophocoronidae | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 100 |
| Mnesarchaeidae | 14 | 14 | 0 | 100 | 14 | 0 | 100 |
| Palaeosetidae | 7 | 3 | 4 | 100 | 0 | 7 | 100 |
| Hepialidae | 400 | 0 | 200 | 50 | 0 | 200 | 50 |
| Acanthopteroctetidae | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 100 |
| Opostegidae | 200 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 200 | 0 | 100 |
| Adelidae | 300 | 100 | 0 | 33 | 100 | 0 | 33 |
| Nepticulidae | 862 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 862 | 0 | 100 |
| Cecidosidae | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 100 |
| Prodoxidae | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 |
| Tineidae | 3000 | 1000 | 0 | 33 | 1000 | 500 | 50 |
| Psychidae | 1000 | 600 | 0 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Eriocottidae | 210 | 0 | 200 | 95 | 0 | 200 | 95 |
| Sesiidae | 1000 | 0 | 150 | 15 | 0 | 150 | 15 |
| Gelechioidea | 4750 | 1000 | 500 | 32 | 3000 | 0 | 63 |
| Pseudurgis | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 100 |
| Thyrididae | 750 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 750 | 0 | 100 |
| Alucitidae | 250 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 250 | 0 | 100 |
| Epermeniidae | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 |
| Carposinidae | 290 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 290 | 100 |
| Pterophoridae | 1300 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 700 | 54 |
| Papilionidea | 600 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Pyraloidea | 8000 | 1500 | 0 | 19 | 2500 | 1500 | 50 |
| Cimeliidae | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 100 |
| Sematuridae | 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 10 | 100 |
| Uraniidae | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90 | 0 | 90 |
| Geometridae | 15,000 | 2000 | 0 | 13 | 6000 | 2000 | 53 |
| Noctuoidea | 20,000 | 3000 | 1500 | 22.5 | 1000 | 12,000 | 65 |
| Bombycoidea | 6000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1500 | 25 |
| Total species | 64,484 | 9357 | 2554 | 18.5 | 15,947 | 19,318 | 54.7 |
| base 157,000 species | 41% | 6% | 2% | 10% | 12% | ||
| 7.60% | 22.70% | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Legal, L. “Lepidoptera Flies”, but Not Always…Interactions of Caterpillars and Chrysalis with Soil. Diversity 2023, 15, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010027
Legal L. “Lepidoptera Flies”, but Not Always…Interactions of Caterpillars and Chrysalis with Soil. Diversity. 2023; 15(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleLegal, Luc. 2023. "“Lepidoptera Flies”, but Not Always…Interactions of Caterpillars and Chrysalis with Soil" Diversity 15, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010027
APA StyleLegal, L. (2023). “Lepidoptera Flies”, but Not Always…Interactions of Caterpillars and Chrysalis with Soil. Diversity, 15(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010027






