Diversity of Freshwater Calanoid Copepods (Crustacea: Copepoda: Calanoida) in Southern Vietnam with an Updated Checklist for the Country
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collections
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Diversity of Calanoid Copepods in Southern Vietnam
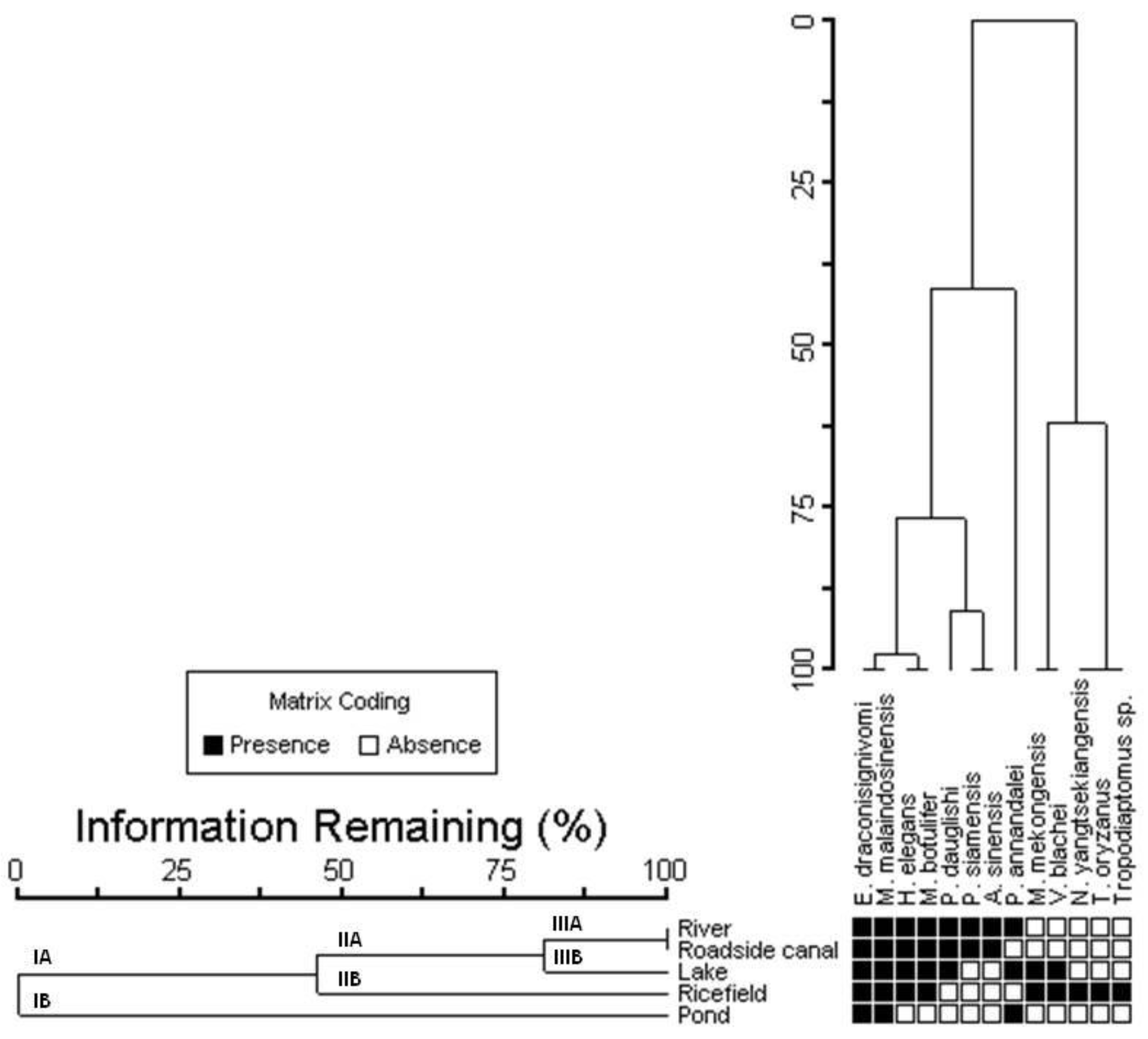
3.2. The Relationship between Calanoid Species and Environmental Variables
4. Discussion
4.1. Calanoid Copepod Diversity in Vietnam
4.2. The Relationship between Calanoid Species and Environmental Variables
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boxshall, G.A.; Defaye, D. Global diversity of copepods (Crustacea: Copepoda) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga Reddy, Y. Copepoda: Calanoida: Diaptomidae Key to the Genera Heliodiaptomus, Allodiaptomus, Neodiaptomus, Phyllodiaptomus, Eodiaptomus, Arctodiaptomus and Sinodiaptomus; SPB Academic: The Hague, Philippines, 1994; pp. 1–221. [Google Scholar]
- Sanoamuang, L.; Watiroyram, S. A new species of copepod (Copepoda: Calanoida) from the floodplain of the lower Mekong River Basin in Thailand and Cambodia, with an amended diagnosis of the genus Dentodiaptomus Shen & Tai, 1964. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2021, 69, 414–427. [Google Scholar]
- Brancelj, A.; Boonyanusith, C.; Watiroyram, S.; Sanoamuang, L. The groundwater-dwelling fauna in Southeast Asia. J. Limnol. 2013, 72, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz-Colmenares, M.E.; Soria, J.M.; Vicente, E. Can zooplankton species be used as indicators of trophic status and ecological potential reservoirs? Aquat. Ecol. 2021, 55, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxshall, G.A.; Halsey, S.H. An Introduction to Copepod Diversity; The Dorset Press: Dorchester, UK, 2004; pp. 1–655. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, T.C.; Boxshall, G. World of Copepods Database. Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org/copepoda/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=149688 (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Sanoamuang, L.; Dabseepai, P. Diversity, distribution, and habitat occurrence of the diaptomid copepods (Crustacea: Copepoda: Diaptomidae) in freshwater ecosystems of Thailand. Water 2021, 13, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.L.; Dang, N.T.; Ho, T.H. An annotated checklist of the family Diaptomidae Sars, 1903 (Copepoda, Calanoida) in Vietnam. Tap Chi Sinh Hoc. 2016, 38, 384–399. [Google Scholar]
- Chaichareon, R. Diversity and Distribution of Freshwater Calanoid and Cyclopoid Copepods in Seven Provinces of Cambodia. Ph.D. Thesis, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sanoamuang, L.; Watiroyram, S. Allodiaptomus nongensis, a new diaptomid copepod (Copepoda: Calanoida) from a tributary of the Mekong River, with notes on its consumption by local people in Central Laos. J. Limnol. 2019, 78, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, R.P.; Lai, H.C. Crustacea: Copepoda, Calanoida. In Freshwater Invertebrates of the Malaysian Region; Yule, C.M., Sen, Y.H., Eds.; Academy of Sciences Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2014; pp. 254–266. [Google Scholar]
- Alekseev, V.R.; Haffner, D.G.; Vaillant, J.J.; Yusoff, F.M. Cyclopoid and calanoid copepod biodiversity in Indonesia. J. Limnol. 2013, 72, 245–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.L.D.; Pascual, J.A.F.; Dela Paz, E.S.P.; Rizo, E.Z.C.; Tordesillas, D.T.; Guinto, S.K.; Han, B.; Dumont, H.J.; Mamaril, A.C., Sr.; Papa, R.D.S. Annotated checklist and insular distribution of freshwater microcrustaceans (Copepoda: Calanoida & Cyclopoida; Cladocera: Anomopoda & Ctenopoda) in the Philippines. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2017, 65, 623–654. [Google Scholar]
- Wikipedia. Geography of Vietnam. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vietnam (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Shirota, A. The Plankton of South Viet Nam: Fresh Water and Marine Plankton; Overseas Technical Cooperation Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 1966; pp. 1–162. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, N.T.; Thai, T.B.; Pham, V.M. Classification of Freshwater Invertebrates in Northern of Vietnam; Science Publishing House: Ha Noi, Vietnam, 1980; pp. 1–573. [Google Scholar]
- Dafaye, D. A new Tropodiaptomus (Copepoda, Calanoida, Diaptomidae, Diatominae) from Vietnam. Crustaceana 2002, 75, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, S.; Cho, N. A new species of Tortanus (Atortus) (Copepoda, Calanoida, Tortanidae) from the coastal waters of Nha trang, Vietnam. Crustaceana 2005, 78, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, T.H.; Tran, D.L.; Le, H.A. To add two species belonging to Diaptomidae family to the fauna of inland freshwater crustaceans (Calanoida: Copepoda) of Vietnam. Tap Chi Sinh Hoc. 2008, 30, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, D.D.; Nguyen, V.K.; Le, T.N.; Dang, N.T.; Ho, T.H. Identification Handbook of Freshwater Zooplankton of the Mekong River and Its Tributaries; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2015; pp. 1–207. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, H.C.; Fernando, C.H. Zoogeographical distribution of Southeast Asian freshwater Calanoida. Hydrobiologia 1980, 74, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanoamuang, L.; Watiroyram, S. Phyllodiaptomus (Phyllodiaptomus) roietensis, a new diaptomid copepod (Copepoda, Calanoida) from temporary waters in Thailand and Cambodia, with a key to the species. ZooKeys 2020, 911, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancelj, A. Hadodiaptomus dumonti n. gen., n. sp., a new freshwater stygobitic calanoid (Crustacea: Copepoda: Calanoida) from Vietnam (South Asia) and a new member of the subfamily Speodiaptominae Borutsky, 1962. Hydrobiologia 2005, 534, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.L.; Brancelj, A. Amended diagnosis of the genus Nannodiaptomus (Copepoda, Calanoida), based on redescription of N. phongnhaensis and description of a new species from caves in central Vietnam. Zootaxa 2017, 4221, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dumont, H.J.; Han, B.P.; Lin, Q. Updated checklist and distribution of the diaptomid copepods (Copepoda, Calanoida, Diaptomidae) of China. Crustaceana 2018, 91, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga Reddy, Y.R.; Sanoamuang, L.; Dumont, H.J. Amended delimitation of Mongolodiaptomus against Neodiaptomus and Allodiaptomus and redescription of the little known Mongolodiaptomus uenoi (Kikuchi, 1936) from Thailand (Copepoda: Calanoida: Diaptomidae). Hydrobiologia 2000, 418, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanoamuang, L.; Watiroyram, S. Mongolodiaptomus mekongensis, a new species of copepod (Copepoda, Calanoida, Diaptomidae) from temporary waters in the floodplain of the lower Mekong River Basin. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2018, 66, 782–796. [Google Scholar]
- Srinui, K.; Nishida, S.; Ohtsuka, S. A new species of Pseudodiaptomus (Crustacea, Copepoda, Calanoida, Pseudodiaptomidae) from the Prasae River Estuary, Gulf of Thailand. ZooKeys 2013, 338, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.G.; Huynh, T.H.N. Assessment of surface water quality and monitoring in southern Vietnam using multicriteria statistical approaches. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2022, 32, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.S.; Kumar, R.; Hsieh, C.W.; Kuo, A.Y.; Souissi, S.; Hsu, M.H.; Wu, J.T.; Liu, W.C.; Wang, C.F.; Chen, Q.C. Patterns of zooplankton distribution along the marine, estuarine, and riverine portions of the Danshuei ecosystem in northern Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 2010, 49, 335–352. [Google Scholar]
- Sanoamuang, L. Freshwater Zooplankton: Calanoid Copepods in Thailand; Klangnanatham Publishers: Khon Kaen, Thailand, 2002; pp. 1–159. [Google Scholar]
- Sivongxay, N. Species Diversity and Distribution of Calanoid and Cyclopoid Copepods from the central part of Lao People’s Democratic Republic. Ph.D. Thesis, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand, 2005. [Google Scholar]
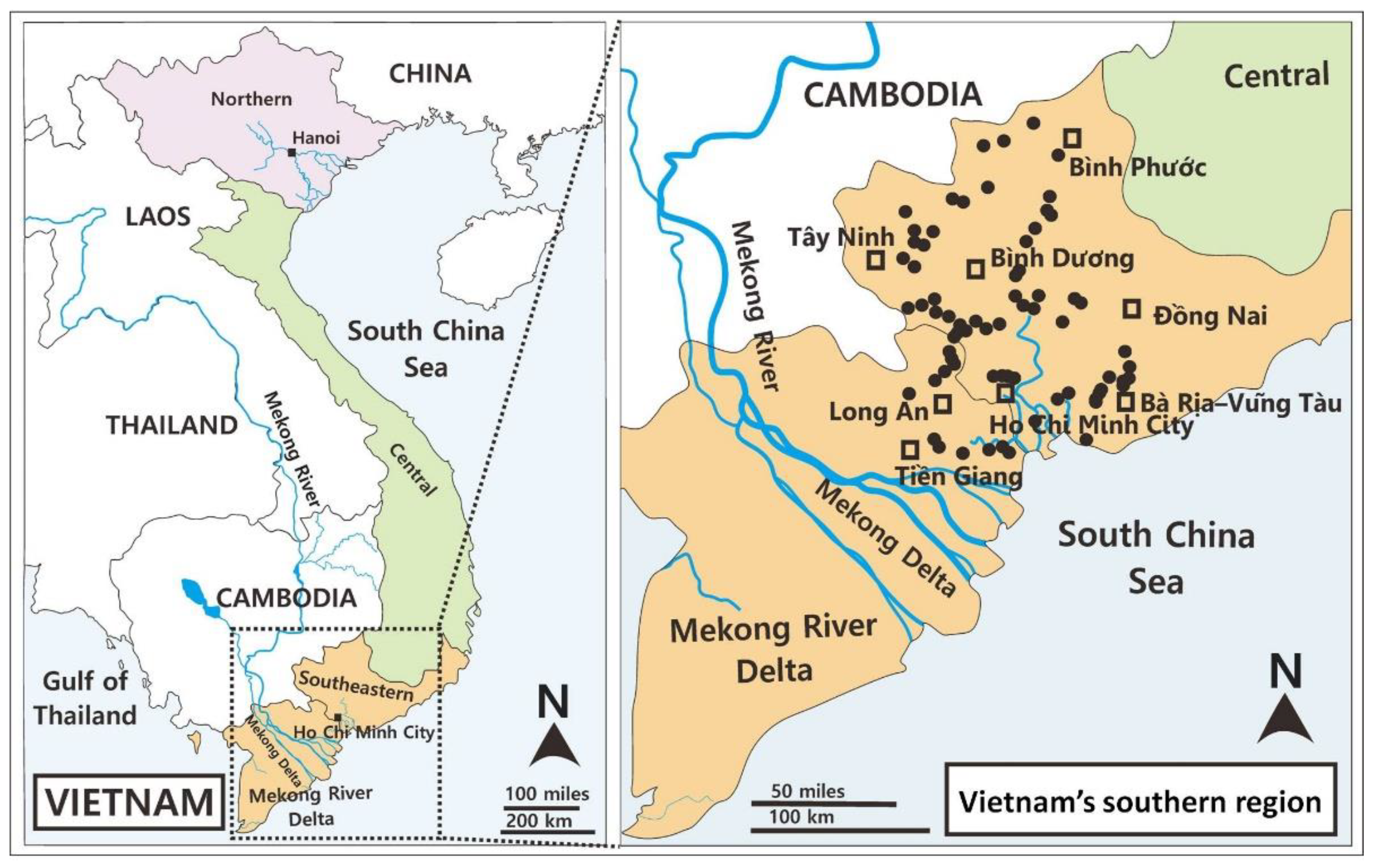

| Habitat Types | Number of Sites | Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | Altitude (m) | Province |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P, C, Ri, Rf | 15 | 10°39′–11°04′ | 106°20′–106°43′ | 5–18 | Ho Chi Minh City |
| L, P, Ri | 11 | 10°20′–10°43′ | 107°05′–107°18′ | 6–150 | Bà Rịa–Vũng Tàu |
| L, Ri | 7 | 10°58′–11°14′ | 106°38′–106°51′ | 9–47 | Bình Dương |
| L, Ri, Rf | 21 | 11°26′–11°58′ | 106°29′–106°58′ | 33–196 | Bình Phước |
| L | 5 | 10°46′–11°05′ | 106°59′–107°18′ | 36–189 | Đồng Nai |
| C, Ri, Rf | 7 | 10°45′–10°56′ | 106°22′–106°27′ | 7–11 | Long An |
| L, C, Ri, Rf | 13 | 11°06′–11°36′ | 106°10′–106°26′ | 11–43 | Tây Ninh |
| L, C, Ri, P | 8 | 10°21′–10°42′ | 106°19′–106°40′ | 4–23 | Tiền Giang |
| Total | 87 |
| Environmental Variables | Rainy Season | Dry Season |
|---|---|---|
| Water temperature (°C) | 27.00–35.1 | 26.5–33.4 |
| pH | 5.1–8.7 | 5.1–8.0 |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg L−1) | 1.3–10.0 | 1.9–10.6 |
| Conductivity (µS cm−1) | 11–1980 | 25–3980 |
| No | Species | Habitat Types | Provinces | Frequency (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permanent Waters | Temporary Waters | |||||||
| L | P | C | Ri | Rf | ||||
| Family Acartiidae Sars G.O., 1903 | ||||||||
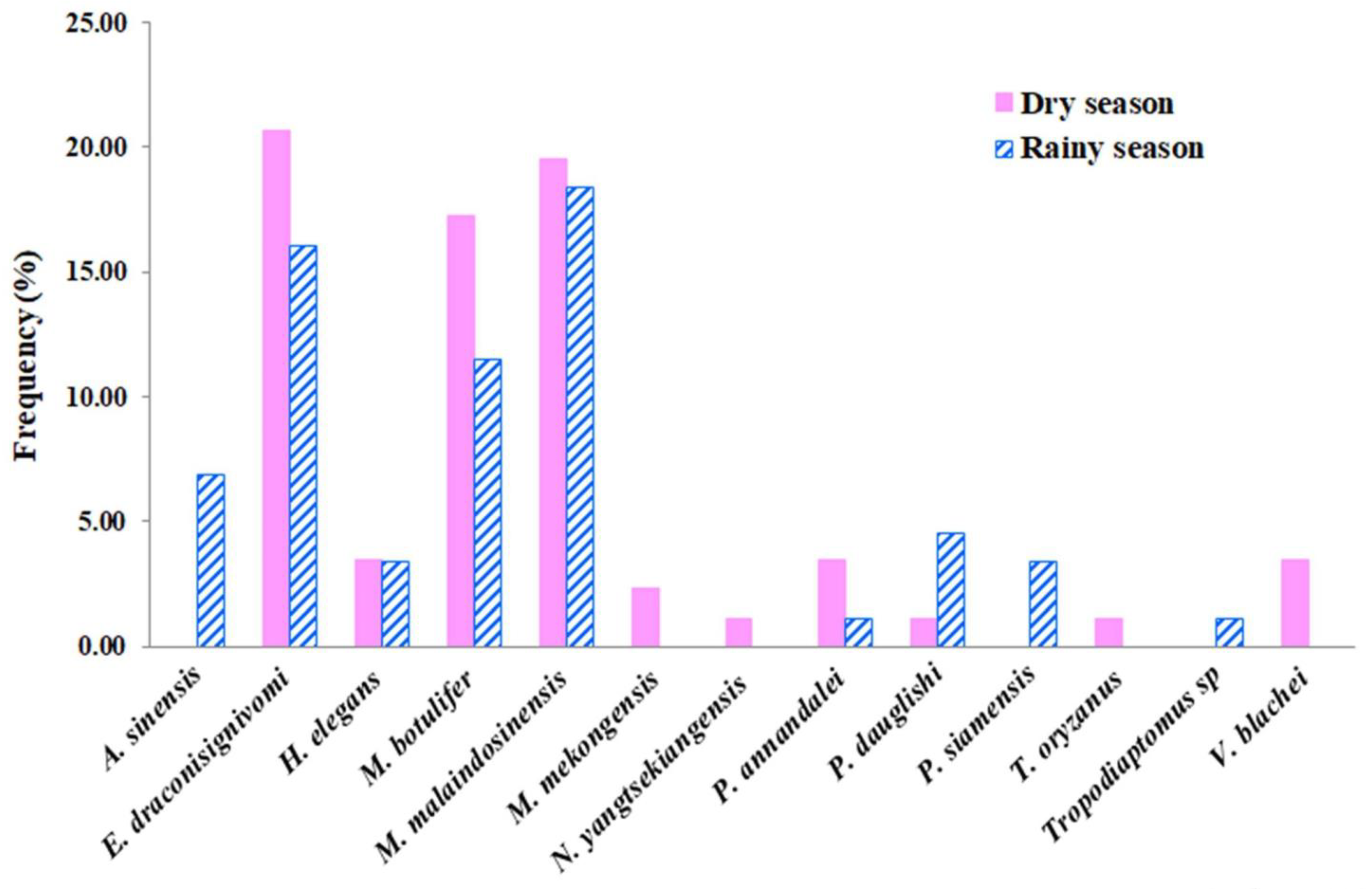
| 1 | AcartiellaSinensis Shen and Lee, 1963 | √ | √ | 1, 8 | 6.9 | |||
| Family Diaptomidae Baird, 1850 | ||||||||
| 2 | Eodiaptomus draconisignivomi Brehm, 1952 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 | 28.7 |
| 3 | Heliodiaptomus elegans Kiefer, 1935 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1, 4, 7 | 5.7 | |
| 4 | Mongolodiaptomus botulifer (Kiefer, 1974) | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 | 24.1 | |
| 5 | Mongolodiaptomus malaindosinensis (Lai and Fernando, 1978) * | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 | 28.7 |
| 6 | Mongolodiaptomus mekongensis Sanoamuang and Watiroyram, 2018 * | √ | √ | 4 | 2.3 | |||
| 7 | Neodiaptomus yangtsekiangensis Mashiko, 1951 | √ | 7 | 1.1 | ||||
| 8 | Tropodiaptomus oryzanus Kiefer, 1937 | √ | 4 | 1.1 | ||||
| 9 | Tropodiaptomus sp. | √ | 1 | 1.1 | ||||
| 10 | Vietodiaptomus blachei (Brehm, 1951) * | √ | √ | 4 | 3.4 | |||
| Family Pseudodiaptomidae Sars G.O., 1902 | ||||||||
| 11 | Pseudodiaptomus annandalei Sewell, 1919 | √ | √ | √ | 2 | 3.4 | ||
| 12 | Pseudodiaptomusdauglishi Sewell, 1932 | √ | √ | √ | 3, 5, 8 | 5.7 | ||
| 13 | Pseudodiaptomussiamensis Srinui, Nishida and Ohtsuka, 2013 * | √ | √ | 1 | 3.4 | |||
| Total | 8 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |||
| Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total variance in the species data: 0.7496 (a) Axis summary statistics and variance in species data | |||
| Eigenvalue | 0.430 | 0.207 | 0.102 |
| Variance in species data | |||
| % of variance explained | 57.4 | 27.6 | 13.7 |
| cumulative % explained | 57.4 | 84.9 | 98.6 |
| Pearson correlation, Spp–Envt | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| (b) Correlations of environmental parameters and canonical axes | |||
| Temperature | −0.766 | 0.190 | −0.060 |
| pH | −0.047 | 0.844 | 0.523 |
| Conductivity | 0.655 | 0.352 | −0.668 |
| DO | −0.391 | 0.782 | 0.485 |
| Species | This Study | Phan et al. (2015) [21] | Tran et al. (2016) [9] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family Acartiidae | ||||
| 1 | Acartiella sinensis Shen and Lee, 1963 | √ | √ | |
| Family Diaptomidae | ||||
| 2 | Allodiaptomus mieni Dang and Ho, 1985 | √ | √ | |
| 3 | A. raoi Kiefer, 1936 | √ | √ | |
| 4 | A. specillodactylus Shen and Tai, 1964 | √ | ||
| 5 | Dentodiaptomus javanus (Grochmalicki, 1915) | √ | ||
| 6 | Dolodiaptomus spinicaudatus Shen and Tai, 1964 | √ | ||
| 7 | Eodiaptomus draconisignivomi Brehm, 1952 | √ | √ | √ |
| 8 | Hadodiaptomus dumonti Brancelj, 2005 | √ | ||
| 9 | Heliodiaptomus elegans Kiefer, 1935 | √ | √ | √ |
| 10 | H. falxus Shen and Tai, 1964 | √ | ||
| 11 | Mongolodiaptomus birulai (Rylov, 1923) | √ | ||
| 12 | M. botulifer (Kiefer, 1974) | √ | √ | √ |
| 13 | M. calcarus Shen and Tai, 1965 | √ | ||
| 14 | M. gladiolus (Shen and Lee, 1963) | √ | √ | |
| 15 | M. malaindosinensis (Lai and Fernando, 1978) | √ | ||
| 16 | M. mekongensis Sanoamuang and Watiroyram, 2018 | √ | ||
| 17 | M. pectinidactylus (Shen and Tai, 1964) | √ | ||
| 18 | M. uenoi (Kikuchi, 1936) | √ | ||
| 19 | Mongolodiaptomus sp. 1 | √ | ||
| 20 | Mongolodiaptomus sp. 2 | √ | ||
| 21 | Nannodiaptomus phongnhaensis Dang and Ho, 2001 | √ | ||
| 22 | Neodiaptomus curvispinosus Dang and Ho, 2001 | √ | ||
| 23 | N. schmackeri (Poppe and Richard, 1892) | √ | ||
| 24 | N. vietnamensis Dang and Ho, 1998 | √ | ||
| 25 | N. yangtsekiangensis Mashiko, 1951 | √ | √ | √ |
| 26 | Phyllodiaptomus tunguidus Shen and Tai, 1964 | √ | ||
| 27 | Sinodiaptomus sarsi (Rylov, 1923) | √ | ||
| 28 | Tropodiaptomus foresti Defaye, 2002 | √ | ||
| 29 | T. oryzanus Kiefer, 1937 | √ | √ | √ |
| 30 | T. vicinus (Kiefer, 1930) | √ | √ | |
| 31 | Tropodiaptomus sp. | √ | ||
| 32 | Vietodiaptomus blachei (Brehm, 1951) | √ | ||
| 33 | V. hatinhensis Dang, 1977 | √ | √ | |
| 34 | V. tridentatus Dang and Ho, 1985 | √ | √ | |
| Family Pseudodiaptomidae | ||||
| 35 | Pseudodiaptomus annandelei Sewell, 1919 | √ | √ | |
| 36 | P. dauglishi Sewell, 1932 | √ | √ | |
| 37 | P. incisus Shen and Lee, 1963 | √ | ||
| 38 | P. inopinus Burckhardt, 1913 | √ | ||
| 39 | P. siamensis Srinui, Nishida and Ohtsuka, 2013 | √ | ||
| 40 | P. trihamatus Wright, 1937 | √ |
| Country | Number of Species | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Thailand | 42 | Sanoamuang and Dabseepai, 2021 [8] |
| Vietnam | 33 | Tran et al., 2016 [9]; this study |
| Cambodia | 24 | Chaichareon, 2011 [10] |
| Laos | 19 | Sanoamuang and Watiroyram, 2019 [11] |
| Indonesia | 17 | Alekseev et al., 2013 [13] |
| Malaysia and Singapore | 12 | Lim and Lai, 2014 [12] |
| Philippines | 8 | Lopez et al., 2017 [14] |
| Distributional Regions | Number of Species | List of Species |
|---|---|---|
| Vietnam only; potentially endemic species | 7 | Allodiaptomus mieni, Hadodiaptomus dumonti, Nannodiaptomus phongnhaensis, Vietodiaptomus hatinhensis, Neodiaptomus curvispinosus, N. vietnamensis, Tropodiaptomus foresti |
| Vietnam and South China only | 4 | Allodiaptomus specillodactylus, Dolodiaptomus spinicaudatus, Heliodiaptomus falxus, Mongolodiaptomus gladiolus |
| Vietnam and Laos only | 1 | Vietodiaptomus tridentatus |
| Lower Mekong River Basin | 2 | Eodiaptomus draconisignivomi, Mongolodiaptomus mekongensis |
| Southeast Asia | 3 | Mongolodiaptomus botulifer, M. malaindosinensis, Vietodiaptomus blachei |
| Southeast Asia and East Asia | 10 | Allodiaptomus raoi, Dentodiaptomus javanus, Mongolodiaptomus birulai, M. calcarus, M. pectinidactylus, M. uenoi, Neodiaptomus yangtsekiangensis, Phyllodiaptomus tunguidus, Sinodiaptomus sarsi, Tropodiaptomus oryzanus |
| Southeast Asia, East and South Asia | 3 | Heliodiaptomus elegans, Neodiaptomus schmackeri, Tropodiaptomus vicinus |
| Total | 30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boonmak, P.; Sanoamuang, L. Diversity of Freshwater Calanoid Copepods (Crustacea: Copepoda: Calanoida) in Southern Vietnam with an Updated Checklist for the Country. Diversity 2022, 14, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14070523
Boonmak P, Sanoamuang L. Diversity of Freshwater Calanoid Copepods (Crustacea: Copepoda: Calanoida) in Southern Vietnam with an Updated Checklist for the Country. Diversity. 2022; 14(7):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14070523
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoonmak, Phuttaphannee, and Laorsri Sanoamuang. 2022. "Diversity of Freshwater Calanoid Copepods (Crustacea: Copepoda: Calanoida) in Southern Vietnam with an Updated Checklist for the Country" Diversity 14, no. 7: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14070523
APA StyleBoonmak, P., & Sanoamuang, L. (2022). Diversity of Freshwater Calanoid Copepods (Crustacea: Copepoda: Calanoida) in Southern Vietnam with an Updated Checklist for the Country. Diversity, 14(7), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14070523






