Abstract
Due to the remarkable ecological value of the Ross Sea, the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) adopted a large-scale Ross Sea region marine protected area (RSRMPA) in 2016. Since then, many CCAMLR Members have conducted research and monitoring in the region. In 2021, the U.S. Ross Sea science community convened a workshop to collate, synthesize, and coordinate U.S. research and monitoring in the RSRMPA. Here we present workshop results, including an extensive synthesis of the peer-reviewed literature related to the region during the period 2010–early 2021. From the synthesis, several things stand out. First, the quantity and breadth of U.S. Ross Sea research compares to a National Science Foundation Long Term Ecological Research project, especially involving McMurdo Sound. These studies are foundational in assessing effectiveness of the RSRMPA. Second, climate change and fishing remain the two factors most critical to changing ecosystem structure and function in the region. Third, studies that integrate ecological processes with physical oceanographic change continue to be needed, especially in a directed and coordinated research program, in order to effectively separate climate from fishing to explain trends among designated indicator species.
1. Introduction
The Ross Sea region marine protected area (RSRMPA), after several years of deliberations, was designated by CCAMLR (the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources) in 2016, coming into force in 2017 (via CCAMLR Conservation Measure 91-05) [1]. Halpern et al. [2] was helpful in summarizing global information up to 2003, and showed independently that the Ross Sea, at least during the last decade of the 20th century [3], was the least anthropogenically affected stretch of ocean on the planet. In a 2008 ‘bioregionalization’, CCAMLR also identified the Ross Sea shelf and slope as being important for inclusion in a network of MPAs [4]. CCAMLR agreed to adopt a system of MPAs, which now includes the RSRMPA and the South Orkney Islands Southern Shelf MPA (designated in 2009). The RSRMPA was established to be consistent with CCAMLR’s own articles of incorporation, having the goals of conserving marine living resources, maintaining ecosystem structure and function, protecting vital ecosystem processes and areas of ecological significance, and promoting scientific research (see Table 1). The MPA, which spans over 2 million km2 (including the area under the Ross and McMurdo ice shelves), is composed of three zones (Figure 1): a general protection zone (which is off limits to fishing with the exception of research fishing and in accordance with MPA objectives); a special research zone (where limited toothfish fishing is being allowed); and a krill research zone (where limited krill fishing would be allowed, if proposals are made).

Table 1.
Objectives of the Ross Sea region marine protected area (from CCAMLR Conservation Measure 91-05, paragraph 3).
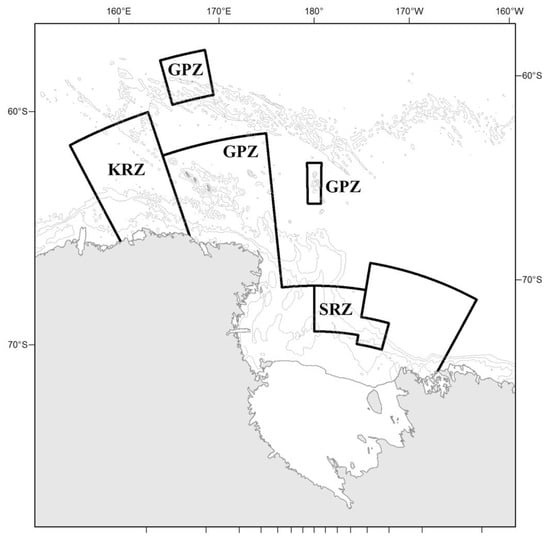
Figure 1.
Ross Sea region marine protected area (RSRMPA) boundaries (other than coastlines) in black, including management zones: General Protection Zone (GPZ; three areas), Special Research Zone (SRZ), and Krill Research Zone (KRZ).
Soon after the RSRMPA came into force, a Research and Monitoring Plan (RMP) was proposed [5] and endorsed by CCAMLR’s Scientific Committee (SC-CAMLR) ([6] para 5.45), though it has yet to be endorsed by CCAMLR. That would require all CCAMLR Member States to agree (i.e., a full consensus), which has not yet been achieved. The RSRMPA RMP lists 38 research and monitoring topics [5] (Table S1), and outlines priority elements relevant to the objectives of the MPA (see Table 4 in [5]). The RMP identifies key indicators (and ‘indicator species’) for evaluating ecosystem change and ultimately the effectiveness of the RSRMPA. These indicators are trends in: (i) numbers of breeding pairs of Adélie (Pygoscelis adelieae) and emperor penguins (Aptenodytes forsteri); (ii) numbers of pupping/breeding Weddell seals (Leptonychotes weddellii) and numbers of type-C killer whales (Orcinus orca); (iii) biomasses of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba), crystal krill (E. crystallorophias), Antarctic silverfish (Pleuragramma antarcticum), and Antarctic toothfish (Dissostichus mawsoni); and (iv) densities of benthic taxa that constitute vulnerable marine ecosystems. Thus, both the water column and benthic portions of the ecosystem are included. The two primary threats that might change ecosystem structure and function in the Ross Sea region are climate change and fishing. In this vein, overall, the goal of research and monitoring is to detect the effects of fisheries, and separate them from climate change, in any alteration of the Ross Sea ecosystem. Candidate baseline data for these indicators, including zone-specific estimates, were gathered, presented to SC-CAMLR, and added to the CCAMLR GIS database [7,8]. Since the RSRMPA came into force, several Member States have been actively pursuing research and monitoring in support of the MPA, and have prepared summary documents ([9] for New Zealand (NZ), [10] for Italy), including the United States (U.S.) [11].
2. Materials and Methods
With the goal of collating, synthesizing, and working towards coordination of U.S. research and monitoring in the RSRMPA, as well as further satisfying CCAMLR’s request of Member States for reports of research activity (see above), the U.S. Ross Sea science community convened a virtual workshop on 26–27 April 2021 (see Supplementary Materials 1 and 2). The workshop included 51 participants representing active U.S. Ross Sea scientists as well as representatives of major U.S. science funding institutions (National Science Foundation (NSF) Office of Polar Programs, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), National Oceanic and Atmospheric Agency (NOAA), Pew Charitable Trusts, and Schmidt Ocean Institute). The array of participants was multi-disciplinary, with Ross Sea expertise spanning biophysical (weather, sea ice, physical oceanography, biological oceanography, and climate variability and modeling), forage species (silverfish, krill), mesopredators (toothfish, seals, penguins, whales), benthic invertebrate communities, pollution, and wildlife health (see Table 2 and Supplementary Material 2). The workshop goals were to identify, collate, assess, and synthesize research conducted by U.S. researchers in the Ross Sea since 2010, as seen to be relevant to the goals of the MPA (defined in CCAMLR Conservation Measure 91-05). This was done via participants’ summary presentations of research in their areas of expertise and gathering all published U.S. Ross Sea region research since 2010 (see Supplementary Material 1), as well as currently funded research (see Table S2). Organizers felt that the immense record of previous U.S. research relevant to ecosystem structure and function, and dating back to the International Geophysical Year (1959), had been adequately summarized by Smith et al. [12,13,14]. Further goals of the workshop were to discuss and identify gaps in RSRMPA research and monitoring, determine ways to fill those gaps, elucidate critical uncertainties regarding the Ross Sea ecosystem structure and dynamics, and develop ideas for coordination between ongoing and future research in the RSRMPA. Following the workshop, we assessed the compilation of peer-reviewed research and culled any papers not relevant to the Ross Sea or related to the objectives of the MPA in some way. We also assessed the papers according to which RSRMPA conservation objectives and RMP topics they addressed, respectively. Below, we provide a summary of our compilation of ongoing and peer-reviewed U.S. Ross Sea research, from 2010 to early-2021, of relevance to meeting the objectives and possible future updates of the RSRMPA and RMP. We also note critical uncertainties, data gaps, and actions the workshop participants consider necessary to address them.

Table 2.
Primary topics (and sub-topics) covered by U.S. researchers in the Ross Sea and number of published papers within each topical area (from 2010–April 2021).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Summary of Published Articles in the Context of the RSRMPA
We gathered 290 articles that were published by U.S. authors (lead or co-author) between 2010 and April 2021 that are relevant, if not directly applicable, to the Ross Sea or adjacent Southern Ocean bearing directly on the Ross Sea (see Supplementary Material 1). All of these papers contributed to the objectives of the RSRMPA in some ways (Figure 2; see Table 1 for full objectives), especially related to objectives i (conserving ecological structure and function) and iii (promoting research). Almost half were relevant to objective viii, which related to protecting coastal locations of particular importance. More than 100 in some way addressed v and vii, which related to protecting large-scale ecosystem processes and core foraging areas for top predators, respectively. A number of studies related to objective iv (representative benthic and pelagic environments), vi (core distributions of prey species), ix (areas important to toothfish, and x (vulnerable benthic habitats). None related to objective ii, which focused on providing a reference area for studying toothfish, or objective xi, which focused on studying krill in the Krill Research Zone specifically.
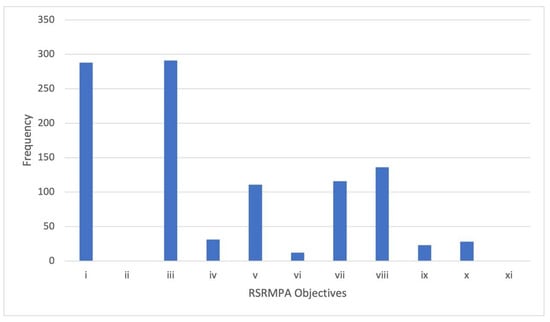
Figure 2.
Frequency of peer-reviewed papers (published between 2010–April 2021; see Supplementary Material 1 for full list of papers), authored or co-authored by U.S. researchers that related to specific objectives of the Ross Sea region marine protected area (RSRMPA) (See Table 1 above for objectives).
Research and monitoring topics specifically relevant to the objectives of the MPA, numbering 38 in total, are extensive (see Table S1), and the papers in our review contributed to multiple topics (Figure 3). More than half of the papers related to topic 3 (functional ecology), and a large number also focused on topic 2 (physical and biological changes), as well as topic 7 (effects of changes in prey on predators). Large numbers of papers also focused on topics 13 (productivity), 1 (biodiversity), 8 (toothfish relationship to predators), 10 (krill and silverfish), 4 (evolutionary biology), and 21 (benthic communities). A smaller number focused on topics 6 (trends in krill and silverfish related to physical drivers, climate change and fishery effects), 9 (toothfish distribution), 11 (toothfish ecology), 14 (toothfish recruitment), 15 (importance of areas under sea ice and ice shelves), 17 (movements and foraging of crabeater seals and emperor penguins in the eastern Ross Sea), 18 (demersal fish), and 19 (fishing effects on toothfish). Very few papers focused on 5, 12, 16, 20, 22, 28, 29, 30, 34, and 36 (see Table S1 for descriptions). Finally, no papers covered topics 23 to 27 (focused on the Balleny Islands region), 31 (drivers of seamount diversity), 32 (importance of benthos to toothfish), 33 (endemism on seamounts), 35, 37, and 38 (the latter three focused on the Krill Research Zone and northwestern Ross Sea region).
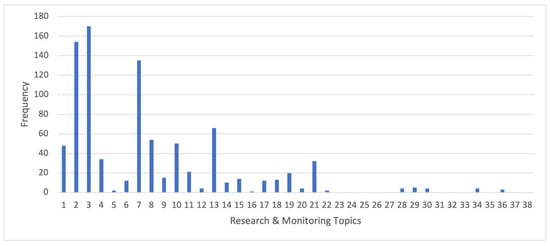
Figure 3.
Frequency of peer-reviewed papers (2010–April 2021; see Supplementary Materials 1 for full list of papers), authored or co-authored by U.S. researchers, which addressed specific research and monitoring topics as pertinent to the Ross Sea region marine protected area Research and Monitoring Plan (See Table S1 for list of topics).
Many of these publications were international collaborations. Collectively U.S. authors have published work with co-authors from 26 different Nation States, including 19 (of the 25) CCAMLR Member States.
3.2. Summary of United States Ross Sea Research
As demonstrated in these compilations, the U.S has a long history of marine research in the Ross Sea and surrounding waters akin to a de facto member of the NSF’s Long-Term Ecological Research (LTER) program, particularly for McMurdo Sound and immediately adjacent waters (see Supplementary Materials 1; for a directed literature review, see also [12,13,14,15,16]). The coastal weather has long been monitored at McMurdo Station and at a series of Automatic Weather Stations scattered around the Ross Sea periphery. Oceanographic structure of the Ross Sea has been elucidated, beginning in the 1960–1970s by surveys conducted by the USNS Eltanin, and continued by ocean sampling from U.S. Coast Guard icebreakers, important research platforms for a region covered extensively by sea ice for 9–10 months of the year (for summary see, e.g., [17]). The pace of U.S. ocean science in the Ross Sea increased with the acquisition of the R/V N.B. Palmer in 1992 and with increased international collaborations that made use of additional vessels. Subsequent and ongoing U.S. research identified decreasing Ross Sea salinity caused by upstream melt of ice shelves feeding into the adjacent Amundsen Sea and subsequently delivered to the Ross Sea via the coastal current; recently, ocean salinity decreases have (perhaps temporally) abated or even reversed (c.f., [18,19,20]). Investigations have documented the increased intrusion of warm Circumpolar Deep Water into the Ross Sea’s several submarine canyons [21], a phenomenon that has been well researched since the 1970s as part of the Ross Ice Shelf Project, which thus established a baseline. Finally, deployment of probes through holes drilled through the Ross Ice Shelf, as well as instrumented seals, have extended the spatial breadth of Ross Sea sampling, including both its physics and biota under the shelf (e.g., [22]).
The Ross Sea and adjacent ocean is one of the most heavily ice-covered areas in the Southern Ocean [23,24,25]. Sea ice dynamics are complex, and the greater Ross Sea region also has shown the strongest increase in sea ice with time of all Southern Ocean regions (1979–present). That is despite considerable seasonal to decadal variability, including several years recently of relative decrease in sea ice extent ([25] since recovered, C. Parkinson, pers. comm.). The dynamics of sea ice in the Ross Sea region have been of central interest. Since the late 1970s, with the development of microwave and visual sensors deployed on satellites, NASA-associated researchers have monitored the changing sea ice regime of the Ross Sea and surrounding ocean (references above). The relationship of annual and seasonal sea ice variability to fluctuations in decadal and long-term climate modes, such as the Southern Annular Mode, has been emphasized (e.g., [26]). Due to increasing winds—which U.S. researchers have monitored—sea ice extent, Ross Gyre speed, and also sea ice season have been increasing in the Ross Sea region (though sea ice season has been decreasing in coastal polynyas), unlike what is occurring in lower latitude portions of the Southern Ocean (e.g., [27,28]). These sea ice trends have important implications for altering the structure and dynamics of the Ross Sea ecosystem, including ocean access by air-breathing predators, primary productivity, and the numerical and functional relationships among higher trophic level species (e.g., [28,29]). Fast ice prevalence shows minimal discernable trend, though, at least in McMurdo Sound, the date of minimum fast ice extent has been occurring later and date of fast ice advance has been occurring earlier [30,31]. A slight reduction in fast ice seasonal persistence may be occurring in western McMurdo Sound [30].
Although dominated by sea ice (often snow-covered) that shields the ocean from sunlight, the Ross Sea is spectacularly productive, due largely to its latent and sensible heat polynyas [20,29]. U.S. research identified the processes that enhance the heightened productivity of polynya marginal ice zones (MIZ), a finding applicable to both polar regions [32]. Through water column sampling and remote sensing from satellites, the phytoplankton dynamics and productivity of the Ross Sea, which contribute as much as 28% to total Southern Ocean production [33], have been well studied by U.S. researchers (e.g., summary in [12,13]; see also [34]). This effort included decades of research on sea ice microbial communities (SIMCO) that preceded the time frame considered by our workshop, mostly within McMurdo Sound fast ice (e.g., [35]). Understanding SIMCO is especially important to the dominant sympagic portion of the Ross Sea ecosystem, as well as other directed programs (e.g., ROAVERRS, [36]).
The Ross Sea neritic biota is represented by both benthic and water column communities, and has long been a target of U.S. research in collaboration with NZ researchers (e.g., [37]). U.S. research first sampled by camera, in a grid of stations, the characteristics and diversity of benthic communities throughout the southwestern Ross Sea [38]. However, most researchers concentrated on shallow benthic communities on both coasts of McMurdo Sound, accessible from McMurdo Station, by using the fast ice as a platform without requiring vessel support. The Barry et al. [38] effort related benthic community composition to the degree of Particulate Organic Carbon that rains down from the high surface productivity, thus contributing to the carbon sequestration capacities of the Ross Sea [29,39]. That biotic community’s response to ocean–climate regime shifts, now a well-researched subject the world over, was first discovered during these efforts, and continues to be important in ongoing research (e.g., [40,41]). Extensive effort also has been made to investigate effects of pollutants emanating from McMurdo Station, and biotic responses to its recent amelioration [42,43,44].
In general, the water column biota, apart from phytoplankton, is not well researched in the Ross Sea, largely due to the infrequent availability of research vessels. U.S. researchers characterized the Ross Sea fish fauna early on and investigated interspecific interactions within the food web (e.g., [45,46]). Subsequently, most U.S. fish research has focused on physiology and genetics of fish (e.g., [47,48]), which has only indirect relevance to differentiating climate change effects from those of fishing in the alteration of food web structure and dynamics in the Ross Sea. A spin-off of the physiological research is the longest record of catch per unit effort of an Antarctic fish (toothfish), as a measure of prevalence, and subsequently the main target of Ross Sea fisheries [49]. These fish were a focus of physiological research, which required them being caught and then kept in aquaria. Most recent U.S. research on Ross Sea fish, and zooplankton, besides describing new species (e.g., [50]), has come from multiple-year studies of the diets of upper level predators (e.g., [51,52]). On some occasions, these efforts have been accompanied with acoustically equipped ocean buoyancy gliders to quantify the preyscape [53], and an acoustic survey of zooplankton, krill, and fish in McMurdo Sound using a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) deployed through the fast ice (e.g., [54]). In regard to krill, a modeling study by Davis et al. [55] summarized what is known, including work by other than U.S. researchers, in the Ross Sea.
The main upper trophic level predators of the Ross Sea—Weddell seals, killer whales, minke whales (Balaenoptera bonaerensis), Adélie penguins, and emperor penguins, which contribute disproportionately to world totals [12]—are the best known of anywhere south of the Antarctic Polar Front, with the U.S. contributing centrally to the effort. The only demographic studies—using marked, known-age, known-history individuals, extending for ~50 years for Weddell seals and ~25 years for Adélie penguins—were conducted at Ross Island and led by U.S. researchers (with NZ collaborators; see Supplementary Materials 1). Changes in demographic variables, as well as foraging dynamics and diet, have been measured against bio-physical processes in the surrounding ocean, as well as interspecific, competitive interactions, involving toothfish, penguins, seals, and whales (e.g., [51,53,54]). Included are activities throughout the polar year thanks to the advent of microtechnology and biologging (see Supplementary Materials 1).
As indicated above, the populations of Weddell seals, and the two penguin species, have been tracked closely by U.S. researchers for several decades (in collaboration with NZ scientists) using aerial surveys when possible [56,57]. In the case of the seals, many surveys have been conducted using snowmobiles [30,58]. Recently, this effort has been made easier through the use of high-resolution satellite imagery and aerial vehicle (e.g., drones) techniques pioneered and instituted by U.S. scientists [58,59,60,61]. The importance of such population monitoring is enhanced by coincident demographic and foraging behavior studies that indicate the possible causes and effects of observed changes in the sizes, age/sex compositions, and productivity of these indicators of systemic changes (e.g., [52,62,63]).
During the last two years, several initiatives have continued into 2021 and beyond, largely unaffected by the COVID-19 pandemic (see Table S2). At least 10 NSF-/NASA-supported satellite studies have been investigating sea ice dynamics and oceanographic factors affecting the Ross Sea, including four investigations of the Ross Gyre and three of Circumpolar Deep Water intrusions into canyons of the continental shelf. These broader areas of ocean research have had, and will continue to have, important implications for the Ross Sea biota. Monitoring of meteorological conditions, using remote stations, is also on-going. Three projects are investigating the productivity ‘hotspot’ in the Ross Sea across scales, including polynyas and primary productivity. Integrating into those efforts are seven projects focused on the demography and foraging ecology of the ‘indicator’ Adélie penguin, emperor penguin, and Weddell seal, including direct linkage to spatial aspects of their preyscape in the southern Ross Sea.
3.3. Workshop Summary
From the synthesis and workshop discussions, several things stand out. First, the sheer quantity and breadth of U.S. Ross Sea research compares in scope to a large, complex, and long-running de facto LTER program (in company with actual LTERs funded by the NSF Office of Polar Programs for McMurdo Dry Valleys and Palmer Station; see above), especially in and adjacent to McMurdo Sound. These studies will continue to be foundational in: (1) assessing and monitoring the effectiveness of the RSRMPA in differentiating the effects of climate change and fishing on the structure and dynamics of the Ross Sea regional food webs; and (2) determining how management of regional fisheries may need to be adapted to account for the population and ecosystem effects of climate change. The southwestern Ross Sea is especially well studied (again, see summaries in [12,13,14,16]), though critical uncertainties and gaps remain in understanding both fished and forage species—especially the distributions, interannual variations in abundance, and interactions of toothfish, krill, and silverfish, which are important to penguins and seals, in an ‘intraguild predation’ context (mesopredators compete for prey, and also eat each other; [64]). The eastern Ross Sea is much less studied, yet based on movement and spatial utilization of key ’indicator’ species (e.g., [15,65]), is emerging as a critical location for future research, especially along the shelf break (see [65,66,67,68]). Future field-based studies, and annual monitoring, of forage species are critically needed across the Ross Sea. Far more than the well-studied seals and penguins, critical uncertainties remain regarding the life history of Antarctic toothfish, another ‘indicator’ species. These include actual abundance; location, timing, and frequency of spawning; and dispersal of eggs, including the role of the Ross Gyre; location of post-larval and juvenile fish (also affected by Ross Gyre); proportions of adult fish migrating to spawning areas and returning; spawning ground residence time; recruitment; and population genetics. The impacts of climate change on the toothfish population, e.g., implications of variation in strength of the Ross Gyre [23,26] in transporting egg/larvae, remain largely unquantified. Without this kind of information, separating the ecosystem effects of fishing from those of climate will remain challenging. During the workshop, central questions were discussed (Table 3), which could provide research priorities for the U.S. Ross Sea research community going forward.

Table 3.
Central questions related to understanding, and thus facilitating the protection, of the Ross Sea ecosystem structure and function; most are inter-related. Based on review of literature (Supplementary Material 1), ongoing research (Table S2), and workshop discussion.
Second, the two general factors most critical to changing ecosystem structure and function in the Ross Sea are climate change and fishing. If there is adequate baseline information and appropriately structured monitoring, Adélie and emperor penguins, Weddell seals, and killer whales, all designated as ‘indicator species’ in the RMP, can show possible ecosystem changes caused by ongoing climate changes and/or fishing (see for instance, [56,69]). The aforementioned long-term U.S. supported penguin and seal studies in the southwestern Ross Sea meet both these conditions and, if continued, will provide useful information about the nature and possible causes of changes in population sizes and composition. Moreover, high-resolution satellite imagery and remote vehicles will mitigate lack of research vessels, but more importantly provide a larger scale context of population change. However, baseline and monitoring studies in sites elsewhere will also be of great value. These study sites should be included in the CCAMLR Ecosystem Monitoring Program (CEMP), similar to elsewhere in Antarctica (e.g., Scotia Sea, East Antarctica) where monitoring colonies of krill-dependent penguins and fur seals (Arctocephalus gazella) is prevalent [70,71]. This would help in informing if (and how) climate change and/or fishing is changing ecosystem structure and function in the Ross Sea, similar to how CEMP results are applied elsewhere in the Southern Ocean [71]. Fishing, in the context of climate change, needs to be better studied and monitored for its ecosystem impacts, including camera surveys of the benthos in the fishing areas. Additional field and monitoring studies on forage species (as noted above), benthic communities, and toothfish need to be conducted. Importantly, while the MPA has no capacity to protect the Ross Sea ecosystem from climate change, a well-executed RMP can separate fishing from climate effects, thus providing the scientific information needed to better manage towards enhancing the ecosystem’s resilience to anthropogenic, climate change influence.
Third, workshop participants highlighted a critical need for studies that integrate ecological processes with physical oceanographic change to facilitate a better understanding of alterations of Ross Sea ecology. Whether or not they are conducted by U.S. scientists remains to be seen, but certainly CCAMLR must play a role (see below). For example, physical processes are hypothesized to heavily influence biological processes (e.g., how Ross Sea toothfish utilize or cope with currents, e.g., Ross Gyre, during their spawning migrations and larval dispersal; see above), yet these are not well understood, nor are these connections defined in the RSRMPA RMP priority elements. In this vein, workshop participants believed the development of an integrated biophysical model that feeds into a comprehensive ecosystem model for the Ross Sea would help determine research and monitoring needs and priorities as well as help to interpret sparse observations and biophysical linkages. Such a coupled modelling system could then be used not only to better inform how the integrated system is currently functioning, but also how fishing and climate change may impact the Ross Sea ecosystem and how the MPA might better meet its objectives.
Finally, while LTER-equivalent research has been underway in McMurdo Sound and southwestern Ross Sea for decades (covering sea ice, weather, physical oceanography, biological oceanography, seal, and penguin population change, toothfish prevalence, and changes to the shallow benthic communities), the funding for this research is not stable, nor has the planning and execution of the various components been coordinated. Research in the U.S. Antarctic Program regarding the Ross Sea depends almost entirely on funding of unsolicited, peer-reviewed proposals by the NSF-Office of Polar Programs, supplemented with additional funding by NASA and other agencies. Workshop participants noted the need for more stable and long-term funding, including funding specifically aimed at determining whether the objectives of the RSRMPA are being met and, if not, what in the RMP or the MPA itself may improve RSRMPA outcomes. Multi-agency contributions and coordination will be essential. Participants also noted the need for more coordination among projects—which the workshop directly facilitated—as well as continued and more collaboration and coordination between other Member States doing research and monitoring in the RSRMPA. Overall, the U.S. Ross Sea science community was enthusiastic to contribute to research and monitoring of the RSRMPA, including contributing to the forthcoming MPA review.
Since the April 2021 workshop, at least 16 additional papers have been published (see Table S3), reflecting the ongoing contribution of U.S. scientists applicable to the RSRMPA. These include studies not only on topics core to previous Ross Sea work, providing further insights into productivity and upper trophic level predators, but also new insights into undersea fauna and tools for research and monitoring in the MPA (e.g., quantifying soundscapes). In 2022, the RSRMPA will undergo its first reporting period. This builds to 2027, when the MPA will come under formal review at CCAMLR. The work presented here, along with the research from other CCAMLR member states (e.g., NZ, Italy, and South Korea), will help provide a strong basis for assessing the effectiveness of the RSRMPA.
4. Conclusions
The Ross Sea is likely the most intensively studied and best known stretch of the Southern Ocean, including its physical and biotic processes (e.g., [12,13,14,16]), and relevant research continues based on unsolicited proposals, at least in regard to the U.S. effort. The key, in regard to effectiveness of the RSRMPA, is the degree to which the research can separate climate from fishing to explain trends in the indicator species designated. The likelihood of success would be heightened with a more directed program of research than what exists now.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/d14060447/s1, Supplementary Material 1, Supplementary Material 2, Table S1: Research and monitoring topics that are directly relevant to the Ross Sea region marine protected area (see Figure 1 for map), address core questions in the research and monitoring plan, and emphasize work throughout the geographic areas in the Ross Sea region (modified after Dunn et al., 2017), Table S2: Currently progressing Ross Sea projects relevant to the Ross Sea marine ecosystem (funded by NSF or NASA). Projects grouped according to topical areas., Table S3: Papers with U.S. authors focused on the Ross Sea published since the Ross Sea workshop (after April and through end of December 2021).
Author Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to all parts of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This workshop was supported in part by the Pew Charitable Trusts.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are available in this paper and appendices.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge all participants of the Ross Sea Region Marine Protected Area Research and Monitoring U.S. Workshop. We acknowledge Vasco Chavez-Molina and Sarah Becker for assistance with data synthesis. We further acknowledge the anonymous reviewers for their edits and comments which improved the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Brooks, C.M.; Crowder, L.B.; Osterblom, H.; Strong, A.L. Reaching consensus for conserving the global commons: The case of the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Conserv. Lett. 2020, 13, e12676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’Agrosa, C.; Bruno, J.F.; Casey, K.S.; Ebert, C.; Fox, H.E.; et al. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blight, L.K.; Ainley, D.G. Southern Ocean not so pristine. Science 2008, 321, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SC-CAMLR. Report of the Thirty-Seventh Meeting of the Scientific Committee; SC-CAMLR: Hobart, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, A.; Vacchi, M.; Watters, G.M. The Ross Sea Region Marine Protected Area Research and Monitoring Plan; SC-CAMLR-XXXVI/20; SC-CAMLR: Hobart, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- SC-CAMLR. Report of the XXXVI Meeting of the CAMLR Scientific Committee; SC-CAMLR: Hobart, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Delegation of the USA. Candidate Baseline Data for Ecosystem Indicators in the Ross Sea Region. Part A: Brief Presentation of Data; SC-CCAMLR-XXXVII/11; SC-CAMLR: Hobart, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Delegation of the USA. Candidate Baseline Data for Ecosystem Indicators in the Ross Sea Region. Part B: Discussion of the Data; SC-CCAMLR-XXXVII/BG/13; SC-CAMLR: Hobart, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pinkerton, M. New Zealand Research and Monitoring in the Ross Sea Region in Support of the Ross Sea Region Marine Protected Area: 2020 Update; SC-CAMLR-39/BG/32; SC-CAMLR: Hobart, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ghigliotti, L.; Azzaro, M.; Vacchi, M. Italy Research and Monitoring in the Ross Sea Region in Support of the Ross Sea Region Marine Protected Area: 2020 Update; SC-CAMLR-39/BG/53; SC-CAMLR: Hobart, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Delegation of the USA. Report on United States Research and Monitoring in Support of the Ross Sea Region Marine Protected Area; SC-CAMLR-39/BG/17; SC-CAMLR: Hobart, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.O.J.; Ainley, D.G.; Arrigo, K.R.; Dinniman, M.S. The oceanography and ecology of the Ross Sea. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 469–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.O.; Ainley, D.G.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Hofmann, E.E. The Ross Sea Continental Shelf: Regional Biogeochemical Cycles, Trophic Interactions, and Potential Future Changes. In Antarctic Ecosystems: An Extreme Environment in a Changing World, 1st ed.; Rogers, A.D., Johnston, N.M., Murphy, E.J., Clarke, A., Eds.; Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 213–242. [Google Scholar]
- Ainley, D.; Ballard, G.; Weller, J.B. Ross Sea Bioregionalization Part I; CCAMLR WG-EMM-10/11; CCAMLR: Hobart, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ballard, G.; Jongsomjit, D.; Ainley, D. Ross Sea Bioregionalization, Part II: Patterns of Co-Occurence of Mesopredators in an Intact Polar Ocean Ecosystem; CCAMLR WG-EMM-10/12; CCAMLR: Hobart, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, B.R.; Parker, S.; Pinkerton, M. Bioregionalisation and Spatial Ecosystem Processes in the Ross Sea Region; CCAMLR-WG-EMM-10/30; CCAMLR: Hobart, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, S. Observations of change in the Southern Ocean. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2006, 364, 1657–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvano, A.; Foppert, A.; Rintoul, S.R.; Holland, P.R.; Tamura, T.; Kimura, N.; Castagno, P.; Falco, P.; Budillon, G.; Haumann, F.A.; et al. Recent recovery of Antarctic Bottom Water formation in the Ross Sea driven by climate anomalies. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagno, P.; Falco, P.; Dinniman, M.S.; Spezie, G.; Budillon, G. Temporal variability of the Circumpolar Deep Water inflow onto the Ross Sea continental shelf. J. Mar. Syst. 2017, 166, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, S.S.; Giulivi, C.F.; Mele, P.A. Freshening of the Ross Sea During the Late 20th Century. Science 2002, 297, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinniman, M.S.; Klinck, J.M.; Smith, W.O. A model study of Circumpolar Deep Water on the West Antarctic Peninsula and Ross Sea continental shelves. Deep-Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2011, 58, 1508–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Complex life under the McMurdo Ice Shelf, and some speculations on food webs. Antarct. Sci. 2019, 31, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiso, J.C.; Kwok, R.; Martin, S.; Gordon, A.L. Variability and trends in sea ice extent and ice production in the Ross Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Pang, S.S.; Kacimi, S. Sea ice drift in the Southern Ocean: Regional patterns, variability, and trends. Elementa 2017, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, C.L. A 40-y record reveals gradual Antarctic sea ice increases followed by decreases at rates far exceeding the rates seen in the Arctic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 14414–14423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, R.; Comiso, J.C.; Lee, T.; Holland, P.R. Linked trends in the South Pacific sea ice edge and Southern Oscillation Index. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.W.J.; Solomon, S. Interpretation of Recent Southern Hemisphere Climate Change. Science. Science 2002, 296, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stammerjohn, S.; Massom, R.; Rind, D.; Martinson, D. Regions of rapid sea ice change: An inter-hemispheric seasonal comparison. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, K.R.; van Dijken, G.L.; Strong, A.L. Environmental controls of marine productivity hot spots around Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 5545–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainley, D.; Larue, M.A.; Stirling, I.; Stammerjohn, S.; Siniff, D.B. An apparent population decrease, or change in distribution, of Weddell seals along the Victoria Land coast. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2015, 31, 1338–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, A.D.; Massom, R.A.; Handcock, M.S.; Reid, P.; Ohshima, K.I.; Raphael, M.N.; Cartwright, J.; Klekociuk, A.R.; Wang, Z.; Porter-Smith, R. Eighteen-year record of circum-Antarctic landfast-sea-ice distribution allows detailed baseline charac-terisation and reveals trends and variability. Cryosphere 2021, 15, 5061–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.O.; Nelson, D.M. Phytoplankton Bloom Produced by a Receding Ice Edge in the Ross Sea: Spatial Coherence with the Density Field. Science 1985, 227, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, K.R.; Worthen, D.; Schnell, A.; Lizotte, M.P. Primary production in Southern Ocean waters. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 15587–15600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Smith, W.; Yu, X. Revisiting the Ocean Color Algorithms for Particulate Organic Carbon and Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in the Ross Sea. JGR Ocean. 2021, 126, e2021JC017749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SooHoo, J.B.; Palmisano, A.C.; Kottmeier, S.T.; Lizotte, M.P.; SooHoo, S.L.; Suhvan, C.W. Spectral light absorption and quantum yield of photosynthesis in sea ice microalgae and a bloom of Phaeocystis pouchetii from McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1987, 39, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditullio, G.R.; Dunbar, R.B. Biogeochemistry of the Ross Sea; Antarctic Research Series; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 78. [Google Scholar]
- Bullivant, J.S.; Dearborn, J.H. The Fauna of the Ross Sea. Part 5. General Accounts, Station Lists, and Benthic Ecology; New Zealand Oceanographic Institute Memoirs: Wellington, New Zealand, 1967; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, J.P.; Grebmeier, J.M.; Smith, J.; Dunbar, R. Oceanographic Versus Seafloor-Habitat Control of Benthic Megafaunal Communities in the S.W. Ross Sea, Antarctica; Antarctic Research Series; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 78. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.O.; Asper, V.; Tozzi, S.; Liu, X.; Stammerjohn, S.E. Surface layer variability in the Ross Sea, Antarctica as assessed by in situ fluorescence measurements. Prog. Oceanogr. 2011, 88, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayton, P.; Jarrell, S.; Kim, S.; Parnell, P.E.; Thursh, S.; Hammerstrom, K.; Leichter, J. Benthic responses to an Antarctic regime shift: food particle size and recruitment biology. Ecological Applications 2019, 29, e01823. [Google Scholar]
- Dayton, P. Interdecadal variation in an Antarctic sponge and its predators from oceanographic climate shifts. Science 1989, 245, 1484–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Hammerstom, K.K.; Conlan, K.E.; Thurber, A.R. Polar ecosystem dynamics: Recovery of communities from Organic enrichment in mcMurdo sound, antarctica. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2010, 50, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.A.; Klein, A.G.; Sweet, S.T.; Montagna, P.A.; Hyde, L.J.; Sericano, J.; Wade, T.L.; Kennicutt, M.C.; Beseres Pollack, J. Long-term changes in contamination and macrobenthic communities adjacent to McMurdo Station, Antarctica. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlan, K.E.; Kim, S.L.; Thurber, A.R.; Hendrycks, E. Benthic changes at McMurdo Station, Antarctica following local sewage treatment and regional iceberg-mediated productivity decline. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWitt, H.H. The character of the midwater fish fauna of the Ross Sea, Antarctica. In Antarctic Ecology; Holdgate, M.W., Ed.; Academic: London, UK, 1970; Volume 1, pp. 305–314. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, J.T. The Evolution of Neutrally Buoyant Notothenioid Fishes: Their Specializations and Potential Interactions in the Antarctic Marine Food Web. In Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985; pp. 430–436. [Google Scholar]
- Cziko, P.A.; Cheng, C.H.C. A new species of nototheniid (Perciformes: Notothenioidei) fish from McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Copeia 2006, 2006, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cziko, P.A.; DeVries, A.L.; Evans, C.W.; Cheng, C.-H.C. Antifreeze protein-induced superheating of ice inside Antarctic notothenioid fishes inhibits melting during summer warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14583–14588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainley, D.G.; Nur, N.; Eastman, J.T.; Ballard, G.; Parkinson, C.L.; Evans, C.W.; Devries, A.L. Decadal trends in abundance, size and condition of Antarctic toothfish in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, 1972-2011. Fish Fish. 2013, 14, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayton, P.K.; Hammerstrom, K. A hagfish at Salmon Bay, McMurdo Sound, Antarctica? Antarct. Sci. 2018, 30, 243–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainley, D.G.; Dugger, K.M.; Mesa, M.L.; Ballard, G.; Barton, K.J.; Jennings, S.; Karl, B.J.; Lescroël, A.; Lyver, P.O.B.; Schmidt, A.; et al. Post-fledging survival of Adélie penguins at multiple colonies: Chicks raised on fish do well. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 601, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, K.T. Seasonal habitat preference and foraging behavior of Weddell seals in the western Ross Sea, Antarctica. In Movement, Habitat, and Foraging Behavior of Weddell Seals (Leptonychotes Weddellii) in the Western Ross Sea, Antarctica; University of California: Santa Cruz, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ainley, D.G.; Ballard, G.; Jones, R.M.; Jongsomjit, D.; Pierce, S.D.; Smith, W.O., Jr.; Veloz, S. Trophic cascades in the western ross sea, antarctica: Revisited. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 534, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenz, B.T.; Ainley, D.G.; Daly, K.L.; Ballard, G.; Conlisk, E.; Elrod, M.L.; Kim, S.L. Drivers of concentrated predation in an Antarctic marginal-ice-zone food web. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.B.; Hofmann, E.E.; Klinck, J.M.; Piñones, A.; Dinniman, M.S. Distributions of krill and Antarctic silverfish and correlations with environmental variables in the western Ross Sea, Antarctica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 584, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyver, P.O.B.; Marron, M.; Barton, K.; Ainley, D.; Pollard, A.; Gordon, S.; McNeill, S.; Ballard, G.; Wilson, P. Trends in the breeding population of Adélie penguins in the Ross Sea, 1981–2012: A coincidence of climate and resource extraction effects. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kooyman, G.L.; Ponganis, P.J. Rise and fall of Ross Sea emperor penguin colony populations: 2000 to 2012. Antarct. Sci. 2017, 29, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainley, D.G.; Cziko, P.A.; Nur, N.; Rotella, J.J.; Eastman, J.T.; Larue, M.; Stirling, I.; Abrams, P.A. Further evidence that Antarctic toothfish are important to Weddell seals. Antarct. Sci. 2020, 33, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRue, M.A.; Lynch, H.J.; Lyver, P.O.B.; Barton, K.; Ainley, D.G.; Pollard, A.; Fraser, W.R.; Ballard, G. A method for estimating colony sizes of Adélie penguins using remote sensing imagery. Polar Biol. 2014, 37, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larue, M.; Iles, D.; Labrousse, S.; Salas, L.; Ballard, G.; Ainley, D.; Saenz, B. A possible Adélie penguin sub-colony on fast ice by Cape Crozier, Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 2019, 31, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRue, M.; Salas, L.; Nur, N.; Ainley, D.; Stammerjohn, S.; Pennycook, J.; Dozier, M.; Saints, J.; Stamatiou, K.; Barrington, L.; et al. Insights from the first global population estimate of Weddell seals in Antarctica. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabh3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.; Ballard, G.; Schmidt, A.; Schwager, M. Multidrone aerial surveys of penguin colonies in Antarctica. Sci. Robot. 2020, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappes, P.J.; Dugger, K.M.; Lescroël, A.; Ainley, D.G.; Ballard, G.; Barton, K.J.; Lyver, P.O.B.; Wilson, P.R. Age-related reproductive performance of the Adélie penguin, a long-lived seabird exhibiting similar outcomes regardless of individual life-history strategy. J. Anim. Ecol. 2021, 90, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltran, R.S.; Testa, J.W.; Burns, J.M. An agent-based bioenergetics model for predicting impacts of environmental change on a top marine predator, the Weddell seal. Ecol. Model. 2017, 351, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, K.T.; McDonald, B.I.; Kooyman, G.L. Habitat preference and dive behavior of non-breeding emperor penguins in the eastern Ross Sea, Antarctica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 593, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, G.; Jongsomjit, D.; Veloz, S.D.; Ainley, D.G. Coexistence of mesopredators in an intact polar ocean ecosystem: The basis for defining a Ross Sea marine protected area. Biol. Conserv. 2012, 156, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gearheart, G.; Kooyman, G.L.; Goetz, K.T.; McDonald, B.I. Migration front of post-moult emperor penguins. Polar Biol. 2013, 37, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainley, D.G.; O’Connor, E.F.; Boekelheide, R.J. The marine ecology of birds in the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Ornithol. Monogr. 1984, 32, 1–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainley, D.G.; Crockett, E.L.; Eastman, J.T.; Fraser, W.R.; Nur, N.; O’Brien, K.; Salas, L.A.; Siniff, D.B. How overfishing a large piscine mesopredator explains growth in Ross Sea penguin populations: A framework to better understand impacts of a controversial fishery. Ecol. Model. 2017, 349, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, D.J. The CCAMLR Ecosystem Monitoring Programme. Antarct. Sci. 1997, 9, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K.; Croxall, J.P.; Briggs, D.R.; Murphy, E.J. Antarctic ecosystem monitoring: Quantifying the response of ecosystem indicators to variability in Antarctic krill. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2005, 62, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).