Four in One: Cryptic Diversity in Geoffroy’s Side-Necked Turtle Phrynops geoffroanus (Schweigger 1812) (Testudines: Pleurodira: Chelidae) in Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
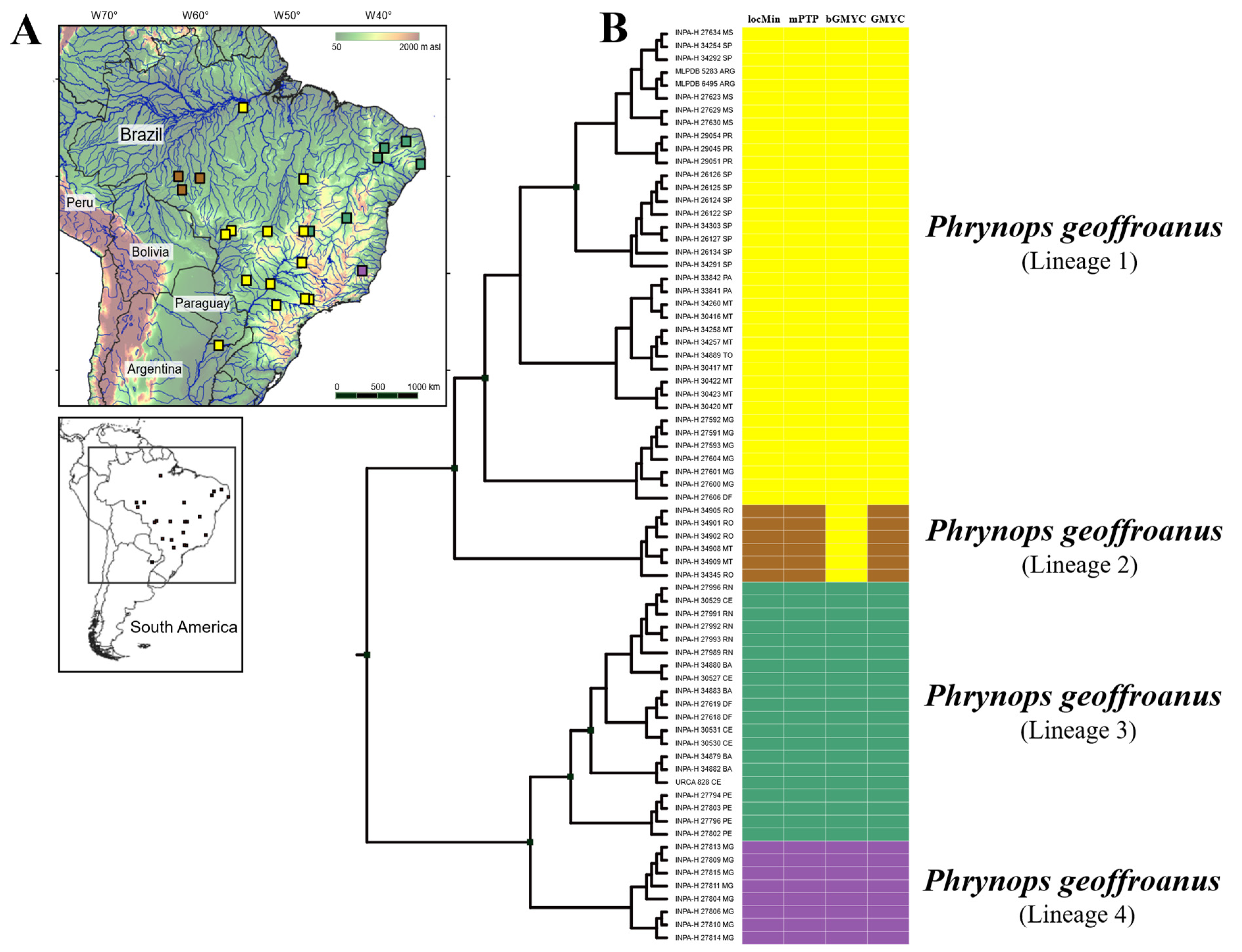
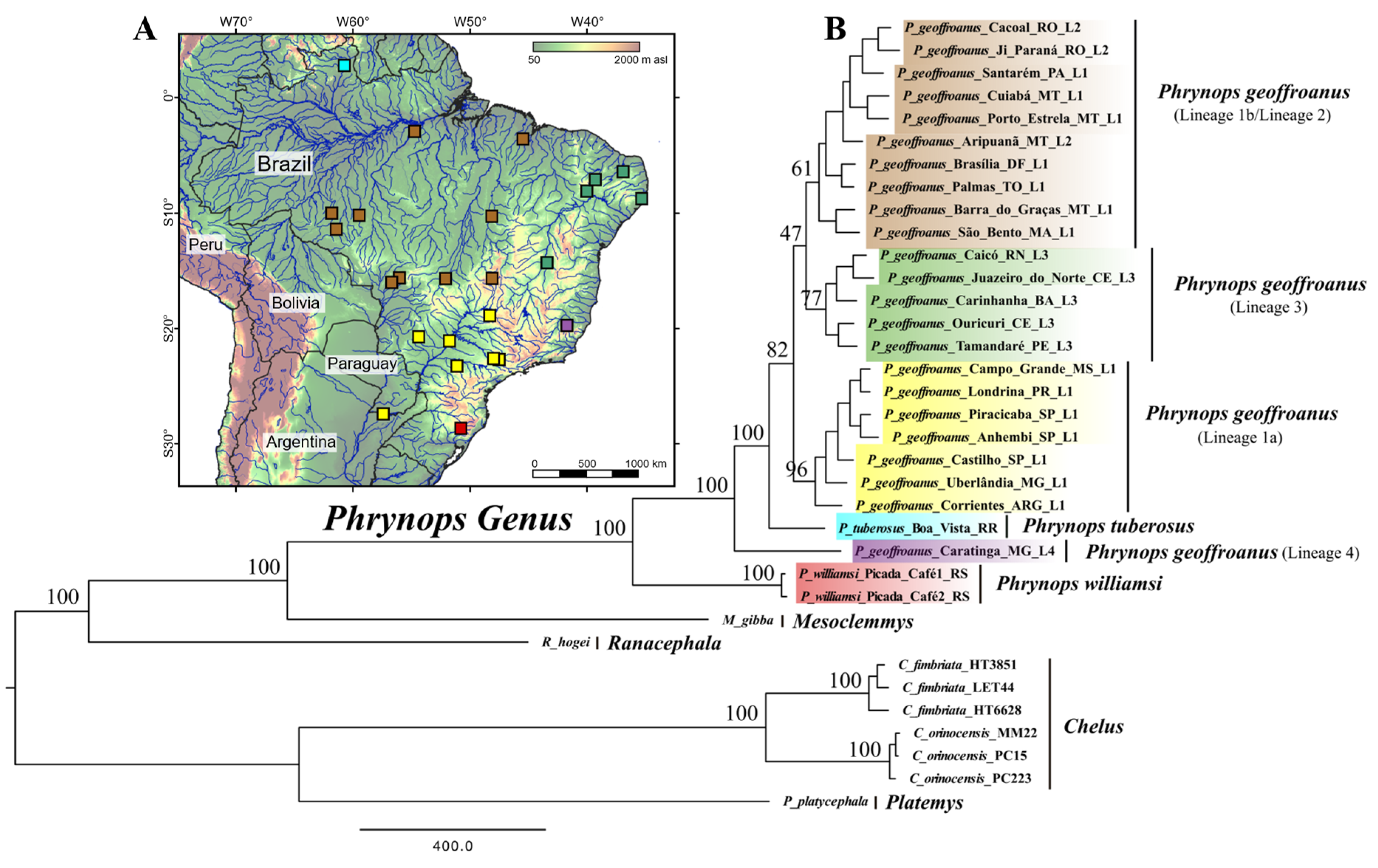
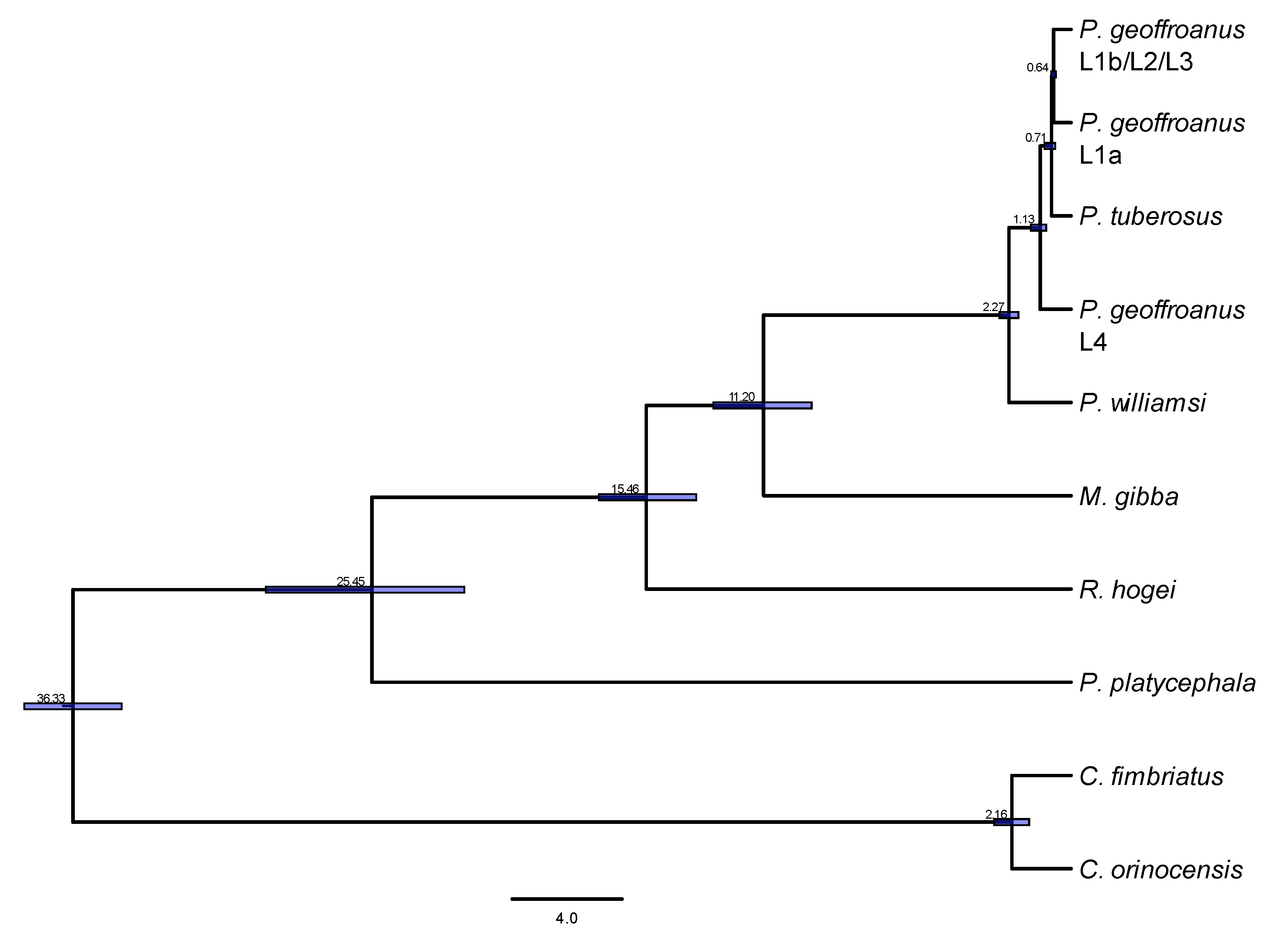
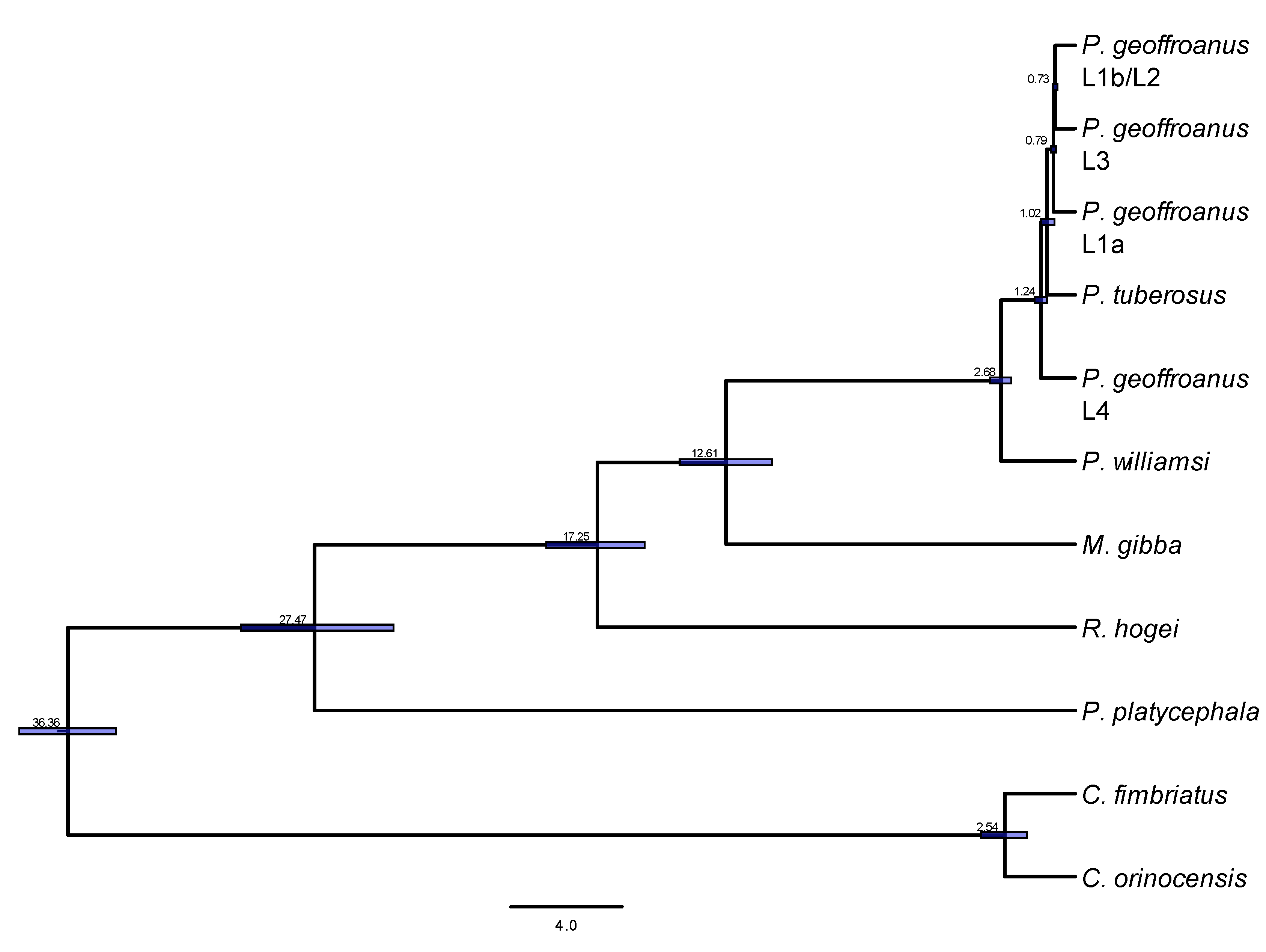
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Oliveira, D.P.; de Carvalho, V.T.; Hrbek, T. Cryptic diversity in the lizard genus Plica (Squamata): Phylogenetic diversity and Amazonian biogeography. Zool. Scr. 2016, 45, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, R.R.; Fouquet, A.; Ron, S.R.; Hernández-Ruz, E.J.; Melo-Sampaio, P.R.; Chaparro, J.C.; Vogt, R.C.; de Carvalho, V.T.; Pinheiro, L.; Ávila, R.W.; et al. A Pan-Amazonian species delimitation: High species diversity within the genus Amazophrynella (Anura: Bufonidae). PeerJ 2018, 6, e4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Machado, V.N.; Collins, R.A.; Ota, R.P.; Andrade, M.C.; Farias, I.P.; Hrbek, T. One thousand DNA barcodes of piranhas and pacus reveal geographic structure and unrecognised diversity in the Amazon. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehlmaier, C.; Zhang, X.; Georges, A.; Campbell, P.D.; Thomson, S.A.; Fritz, U. Mitogenomics of historical type specimens of Australasian turtles: Clarification of taxonomic confusion and old mitochondrial introgression. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friol, N.R. Revisão Taxonômica e Filogenia das Espécies Sul-Americanas de Chelidae (Testudines: Pleurodira). Ph.D. Thesis, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas-Ramírez, M.; Caballero, S.; Morales-Betancourt, M.A.; Lasso, C.A.; Amaya, L.; Martínez, J.G.; Viana, M.D.N.S.; Vogt, R.C.; Farias, I.P.; Hrbek, T.; et al. Genomic analyses reveal two species of the matamata (Testudines: Chelidae: Chelus spp.) and clarify their phylogeography. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 148, 106823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Queiroz, K. Species concepts and species delimitation. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roe, A.D.; Sperling, F.A.H. Population structure and species boundary delimitation of cryptic Dioryctria moths: An integrative approach. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 3617–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sites, J.W.; Marshall, J.C. Delimiting species: A Renaissance issue in systematic biology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vacher, J.-P.; Chave, J.; Ficetola, F.G.; Sommeria-Klein, G.; Tao, S.; Thébaud, C.; Blanc, M.; Camacho, A.; Cassimiro, J.; Colston, T.J.; et al. Large-scale DNA-based survey of frogs in Amazonia suggests a vast underestimation of species richness and endemism. J. Biogeogr. 2020, 47, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, W.W.; DeConto, R.; Wold, C.N.; Wilson, K.M.; Voigt, S.; Schulz, M.; Wold-Rossby, A.; Dullo, W.-C.; Ronov, A.B.; Balukhovsky, A.N.; et al. Alternative global cretaceous paleogeography. In The Evolution of Cretaceous Ocean/Climate Systems; Barrera, E., Johnson, C., Eds.; Geological Society of America Special Paper 332; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1999; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Huebinger, R.M.; Bickham, J.W.; Rhodin, A.G.J.; Mittermeier, R.A. Mitochondrial DNA corroborates taxonomy of the South American chelid turtles of the genera Platemys and Acanthochelys. Chelonian Conserv. Biol. 2013, 12, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, V.T.D.; Martínez, J.G.; Hernández-Rangel, S.M.; Astolfi-Filho, S.; Vogt, R.C.; Farias, I.P.; Hrbek, T. Giving IDs to turtles: SNP markers for assignment of individuals to lineages of the geographically structured Phrynops geoffroanus (Chelidae: Testudines). Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2017, 9, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão, M.; Colatreli, O.P.; de Fraga, R.; Kaefer, I.L.; Moravec, J.; Lima, A.P. High species richness of Scinax treefrogs (Hylidae) in a threatened Amazonian landscape revealed by an integrative approach. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehara, M.; Crawford, A.J.; Orrico, V.G.D.; Rodríguez, A.; Lötters, S.; Fouquet, A.; Barrientos, L.S.; Brusquetti, F.; De la Riva, I.; Ernst, R.; et al. High levels of diversity uncovered in a widespread nominal taxon: Continental phylogeography of the Neotropical tree frog Dendropsophus minutus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamblin, B.M.; Dutton, P.H.; Bjorndal, K.A.; Bolten, A.B.; Naro-Maciel, E.; Santos, A.J.B.; Bellini, C.B.; Marcovaldi, M.A.; Nairn, C.J. Deeper mitochondrial sequencing reveals cryptic diversity and structure in Brazilian Green Turtle rookeries. Chelonian Conserv. Biol. 2015, 14, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnizo, C.E.; Werneck, F.P.; Giugliano, L.G.; Santos, M.G.; Fenker, J.; Sousa, L.; D’Angiolella, A.B.; dos Santos, A.R.; Strüssmann, C.; Rodrigues, M.T.U.; et al. Cryptic lineages and diversification of an endemic anole lizard (Squamata, Dactyloidae) of the Cerrado hotspot. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 94, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faith, D.P.; Reed, C.A.; Hunter, J. Integrating phylogenetic diversity, complementarity, and endemism for conservation assessment. Conserv. Biol. 2004, 18, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; deWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pons, J.; Barraclough, T.G.; Gomez-Zurita, J.; Cardoso, A.; Duran, D.P.; Hazell, S.; Kamoun, S.; Sumlin, W.D.; Vogler, A.P. Sequence-based species delimitation for the DNA taxonomy of undescribed insects. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Rannala, B. Bayesian species delimitation using multilocus sequence data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9264–9269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bickford, D.P.; Lohman, D.J.; Sodhi, N.S.; Ng, P.K.L.; Meier, R.; Winker, K.; Ingram, K.K.; Das, I. Cryptic species as a window on diversity and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodin, A.G.J.; Stanford, C.B.; Dijk, P.P.V.; Eisemberg, C.C.; Luiselli, L.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Hudson, R.; Horne, B.D.; Goode, E.V.; Kuchling, G.; et al. Global Conservation Status of Turtles and Tortoises (Order Testudines). Chelonian Conserv. Biol. 2018, 17, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodin, A.G.J.; Iverson, J.B.; Bour, R.; Fritz, U.; Georges, A.; Shaffer, H.B.; van Dijk, P.P. Turtles of the World: Annotated Checklist and Atlas of Taxonomy, Synonymy, Distribution, and Conservation Status, 8th ed.; Chelonian Research Foundation & Turtle Conservancy: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781532350269. [Google Scholar]
- Moll, D.; Moll, E.O. The Ecology, Exploitation and Conservation of River Turtles; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; ISBN 0195102290. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijk, P.P.; Stuart, B.L.; Rhodin, A.G.J. Asian Turtle Trade: Proceedings of a Workshop on Conservation and Trade of Freshwater Turtles and Tortoises in Asia. Chelonian Res. Monogr. No. 2 2000, 2, 269. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons, J.W.; Scott, D.E.; Ryan, T.J.; Buhlmann, K.A.; Tuberville, T.D.; Metts, B.S.; Greene, J.L.; Mills, T.; Leiden, Y.; Poppy, S.; et al. The global decline of reptiles, Déjà Vu amphibians. Bioscience 2000, 50, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bour, R. Global diversity of turtles (Chelonii; Reptilia) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, F.D.L.; Campos, Z.; Hernández-Rangel, S.M.; Martínez, J.G.; Souza, B.C.; de Thoisy, B.; Botero-Arias, R.; Hrbek, T.; Farias, I.P. Delimitation of evolutionary units in Cuvier’s dwarf caiman, Paleosuchus palpebrosus (Cuvier, 1807): Insights from conservation of a broadly distributed species. Conserv. Genet. 2018, 19, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.C. Amazon Turtles; Grafica Biblos SA: Lima, Peru, 2008; ISBN 6034017076. [Google Scholar]
- Roberto, I.J.; Bittencourt, P.S.; Muniz, F.D.L.; Hernández-Rangel, S.M.; Nóbrega, Y.C.; Ávila, R.W.; Souza, B.C.; Alvarez, G.; Miranda-Chumacero, G.; Campos, Z.; et al. Unexpected but unsurprising lineage diversity within the most widespread Neotropical crocodilian genus Caiman (Crocodylia, Alligatoridae). Syst. Biodivers. 2020, 18, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda-Almonacid, J.V.; Carr, J.L.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Rodríguez-Mahecha, J.V.; Mast, R.B.; Vogt, R.C.; Rhodin, A.G.J.; de La Ossa-Velásquez, J.; Rueda, J.N.; Mittermeier, C.G. Las Tortugas y los Cocodrilianos de los Países Andinos del Trópico; Editorial Panamericana, Formas e Impressos: Bogota, Colombia, 2007; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- McCord, W.P.; Joseph-Ouni, M.; Lamar, W.W. A taxonomic reevaluation of Phrynops (Testudines: Chelidae) with the description of two new genera and a new species of Batrachemys. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2001, 49, 715–764. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodin, A.G.J.; Mittermeier, R.A. Description of Phrynops williamsi, a new species of chelid turtle of the South American P. geoffroanus complex. In Advances in Herpetology and Evolutionary Biology. Essays in Honor of Ernest E. Williams; Rhodin, A.G.J., Miyata, K., Eds.; Museum of Comparative Zoology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1983; pp. 58–73. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, L.; Ferrara, C.R.; Vogt, R.C.; Guilhon, A.V. Nesting ecology and nest predation of Phrynops geoffroanus (Testudines, Chelidae) in the Guaporé River of the Brazilian and Bolivian Amazon. Chelonian Conserv. Biol. 2011, 10, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Springs Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Springs Harbor, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Palumbi, S.R. Nucleic acids II: The polymerase chain reaction. In Molecular Systematics; Hillis, D.M., Moritz, C., Mable, B.K., Eds.; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 205–247. [Google Scholar]
- Pääbo, S. Amplifying ancient DNA. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innes, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Taberlet, P.; Meyer, A.; Bouvet, J. Unusual mitochondrial DNA polymorphism in two local populations of blue tit (Parus caeruleus). Mol. Ecol. 1992, 1, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, B.N.; Le, M.; McCord, W.P.; Iverson, J.B.; Georges, A.; Bergmann, T.; Amato, G.; DeSalle, R.; Naro-Maciel, E. Comparing and combining distance-based and character-based approaches for barcoding turtles. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinforma. Appl. Note 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peterson, B.K.; Weber, J.N.; Kay, E.H.; Fisher, H.S.; Hoekstra, H.E. Double digest RADseq: An inexpensive method for de novo SNP discovery and genotyping in model and non-model species. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eaton, D.A.R. PyRAD: Assembly of de novo RADseq loci for phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1844–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, J.; Mouden, C.; Suchan, T.; Alvarez, N.; Arrigo, N.; Riou, C.; Lemaitre, C.; Peterlongo, P. DiscoSnp-RAD: De novo detection of small variants for RAD-Seq population genomics. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chifman, J.; Kubatko, L.S. Quartet inference from SNP data under the coalescent model. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (and Other Methods), Beta Version 4b10 2002. Available online: https://paup.phylosolutions.com/ (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Bouckaert, R.R.; Vaughan, T.G.; Barido-Sottani, J.; Duchene, S.; Fourment, M.; Gavryushkina, A.; Heled, J.; Jones, G.; Kuhnert, D.; de Maio, N.; et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujisawa, T.; Barraclough, T.G. Delimiting species using single-locus data and the generalized mixed Yule coalescent approach: A revised method and evaluation on simulated data sets. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapli, P.; Lutteropp, S.; Zhang, J.; Kobert, K.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A.; Flouri, T. Multi-rate Poisson Tree Processes for single-locus species delimitation under Maximum Likelihood and Markov Chain Monte Carlo. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1630–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.D.J.; Collins, R.A.; Boyer, S.; Lefort, M.-C.; Malumbres-Olarte, J.; Vink, C.J.; Cruickshank, R.H. Spider: An R package for the analysis of species identity and evolution, with particular reference to DNA barcoding. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 562–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, N.M.; Carstens, B.C. Phylogenetic estimation error can decrease the accuracy of species delimitation: A Bayesian implementation of the general mixed Yule-coalescent model. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. [Google Scholar]
- Schliep, K.P. phangorn: Phylogenetic analysis in R. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 592–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kass, R.E.; Raftery, A.E. Bayes factors. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 773–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomson, R.C.; Spinks, P.Q.; Shaffer, H.B. A global phylogeny of turtles reveals a burst of climate-associated diversification on continental margins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2012215118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1.4.4. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/rambaut/figtree/releases/tag/v1.4.4 (accessed on 10 August 2020).
- Atchley, W.R.; Gaskins, C.T.; Anderson, D. Statistical properties of ratios. I. empirical results. Syst. Zool. 1976, 25, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombart, T.; Devillard, S.; Balloux, F. Discriminant analysis of principal components: A new method for the analysis of genetically structured populations. BMC Genet. 2010, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fouquet, A.; Gilles, A.; Vences, M.; Marty, C.; Blanc, M.; Gemmell, N.J. Underestimation of species richness in neotropical frogs revealed by mtDNA analyses. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, E.P.; Kaefer, I.L.; da Silva Nunes, M.; Lima, A.P.; Farias, I.P. Hidden diversity within the broadly distributed Amazonian giant monkey frog (Phyllomedusa bicolor: Phyllomedusidae). Amphibia-Reptilia 2020, 41, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrbek, T.; da Silva, V.M.F.; Dutra, N.; Gravena, W.; Martin, A.R.; Farias, I.P. A new species of river dolphin from Brazil or: How little do we know our biodiversity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e0083623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ippi, S.; Flores-Villela, O. Las tortugas neotropicales y sus areas de endemismo. Acta Zool. Mex. 2001, 84, 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, F.L. Geographical distribution patterns of South American side-necked turtles (Chelidae). Rev. Esp. Herpetol. 2005, 19, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas-Ramírez, M.; del Valle, C.; Ceballos, C.P.; Fritz, U. Trachemys medemi n. sp. from northwestern Colombia turns the biogeography of South American slider turtles upside down. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2017, 55, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Pires, T.C.S. Lizards of Brazilian Amazonia (Reptilia: Squamata). Zool. Verh. 1995, 299, 1–709. [Google Scholar]
- Gamble, T.; Simons, A.M.; Colli, G.R.; Vitt, L.J. Tertiary climate change and the diversification of the Amazonian gecko genus Gonatodes (Sphaerodactylidae, Squamata). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 46, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miralles, A.; Carranza, S. Systematics and biogeography of the Neotropical genus Mabuya, with special emphasis on the Amazonian skink Mabuya nigropunctata (Reptilia, Scincidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 54, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, A.; Pyron, R.A.; Peñafiel, N.; Romero-Barreto, P.; Culebras, J.; Bustamante, L.; Yánez-Muñoz, M.H.; Guayasamin, J.M. Comparative phylogeography reveals cryptic diversity and repeated patterns of cladogenesis for amphibians and reptiles in northwestern Ecuador. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa-Araújo, R.; Silva-Jr, J.S.; Boubli, J.P.; Rossi, R.V.; Canale, G.R.; Melo, F.R.; Bertuol, F.; Silva, F.E.; Silva, D.A.; Nash, S.D.; et al. An integrative analysis uncovers a new, pseudo-cryptic species of Amazonian marmoset (Primates: Callitrichidae: Mico) from the arc of deforestation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, G.P.; Röhe, F.; Bertuol, F.; Lima, I.J.; Polo, É.M.; Valsechi, J.; dos Santos, T.C.M.; Ennes, F.; Sampaio, R.; Nash, S.D.; et al. Taxonomic review of Saguinus mystax (Spix, 1823) (Primates, Callitrichinae), and description of a new species. PeerJ 2022. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Wermuth, H.; Mertens, R. Liste der rezenten Amphibien und Reptilien: Testudines, Crocodylia, Rhynchocephalia. Tierreich 1977, 100, 1–174. [Google Scholar]

| Method | Point_Estimate | CI_95 | CI_Median | CI_Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bGMYC | 3 | 2–6 | 3 | 3 |
| GMYC | 4 | 2–15 | 4 | 4 |
| locMin | 4 | 3–9 | 4 | 4 |
| mPTP | 4 | 2–14 | 4 | 4 |
| Hypothesis | Marginal Likelihood | Bayes Factor |
|---|---|---|
| One species (P. tuberosus + P. geoffroanus) | −198,684.3200 | 27,547.000 |
| Two species–current taxonomy (P. tuberosus, P. geoffroanus) | −190,849.6367 | 11,877.640 |
| Three species–SVDQuartet topology (P. tuberosus, P. geoffroanus L4, P. geoffroanus L1a + L1b + L2 + L3) | −185,023.1492 | 224.663 |
| Four species–SVDQuartet topology (P. tuberosus, P. geoffroanus L4, P. geoffroanus L1a, P. geoffroanus L1b + L2 + L3) | −184,910.8179 | |
| Four species–alternate SLSD topology (P. tuberosus, P. geoffroanus L4, P. geoffroanus L3, P. geoffroanus L1a + L1b + L2) | −185,045.3345 | 269.033 |
| Five species–best SLSD topology (P. tuberosus, P. geoffroanus L4, P. geoffroanus L3, P. geoffroanus L2, P. geoffroanus L1a + L1b) | −185,649.9732 | 1478.311 |
| Five species–SVDQuartet topology (P. tuberosus, P. geoffroanus L4, P. geoffroanus L1a, P. geoffroanus L3, P. geoffroanus L1a + L2) | −184,916.6384 | 11.641 |
| Six species–SVDQuartet + SLSD topology (P. tuberosus, P. geoffroanus L4, P. geoffroanus L1a, P. geoffroanus L3, P. geoffroanus L1a, P. geoffroanus L2) | −185,173.1499 | 524.664 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Carvalho, V.T.; Vogt, R.C.; Rojas, R.R.; Nunes, M.d.S.; de Fraga, R.; Ávila, R.W.; Rhodin, A.G.J.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Hrbek, T.; Farias, I.P. Four in One: Cryptic Diversity in Geoffroy’s Side-Necked Turtle Phrynops geoffroanus (Schweigger 1812) (Testudines: Pleurodira: Chelidae) in Brazil. Diversity 2022, 14, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050360
de Carvalho VT, Vogt RC, Rojas RR, Nunes MdS, de Fraga R, Ávila RW, Rhodin AGJ, Mittermeier RA, Hrbek T, Farias IP. Four in One: Cryptic Diversity in Geoffroy’s Side-Necked Turtle Phrynops geoffroanus (Schweigger 1812) (Testudines: Pleurodira: Chelidae) in Brazil. Diversity. 2022; 14(5):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050360
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Carvalho, Vinicius Tadeu, Richard C. Vogt, Rommel R. Rojas, Mário da Silva Nunes, Rafael de Fraga, Robson W. Ávila, Anders G. J. Rhodin, Russell A. Mittermeier, Tomas Hrbek, and Izeni Pires Farias. 2022. "Four in One: Cryptic Diversity in Geoffroy’s Side-Necked Turtle Phrynops geoffroanus (Schweigger 1812) (Testudines: Pleurodira: Chelidae) in Brazil" Diversity 14, no. 5: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050360
APA Stylede Carvalho, V. T., Vogt, R. C., Rojas, R. R., Nunes, M. d. S., de Fraga, R., Ávila, R. W., Rhodin, A. G. J., Mittermeier, R. A., Hrbek, T., & Farias, I. P. (2022). Four in One: Cryptic Diversity in Geoffroy’s Side-Necked Turtle Phrynops geoffroanus (Schweigger 1812) (Testudines: Pleurodira: Chelidae) in Brazil. Diversity, 14(5), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050360






