Assessment of Climate Change and Land Use Effects on Water Lily (Nymphaea L.) Habitat Suitability in South America
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
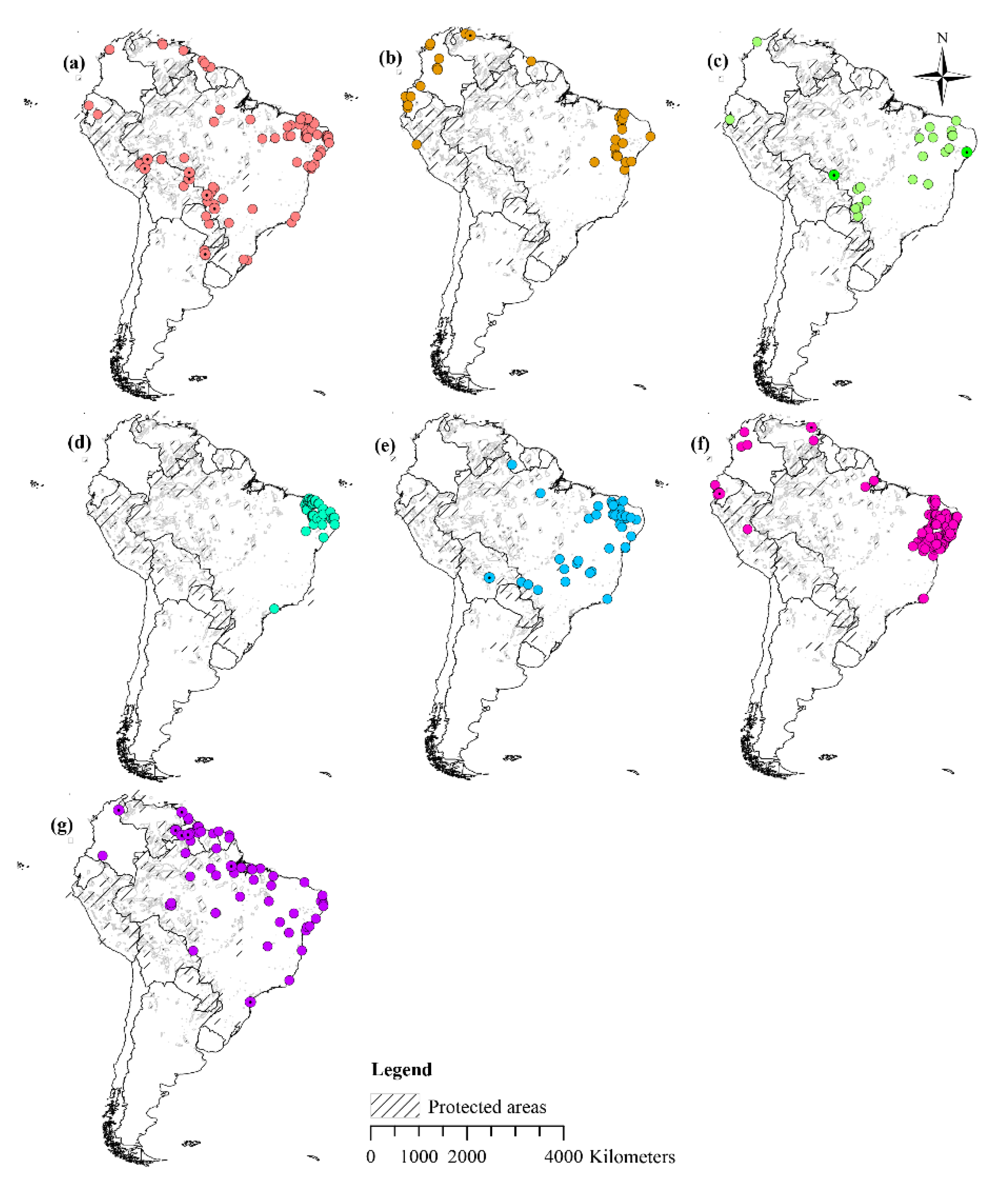
2.1. Species Occurrence Data
2.2. Environmental Data
2.3. Model Parameterization and Calibration
2.4. Predicting Current and Future Range Shifts
2.5. Species Conservation/Threat Area
3. Results
3.1. Variable Selection and Model Performance
3.2. Contribution of Variables
3.3. Current Potential Distribution
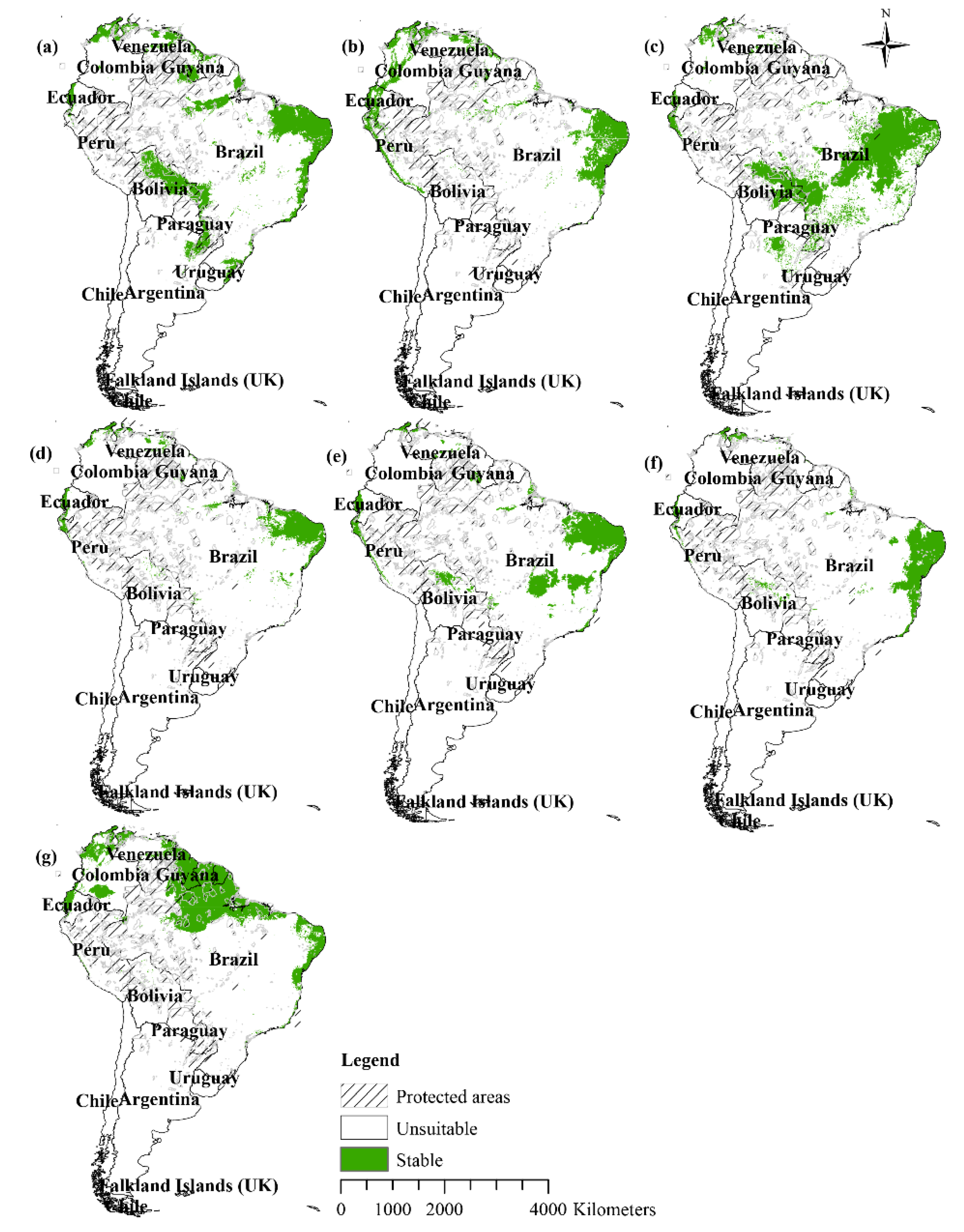
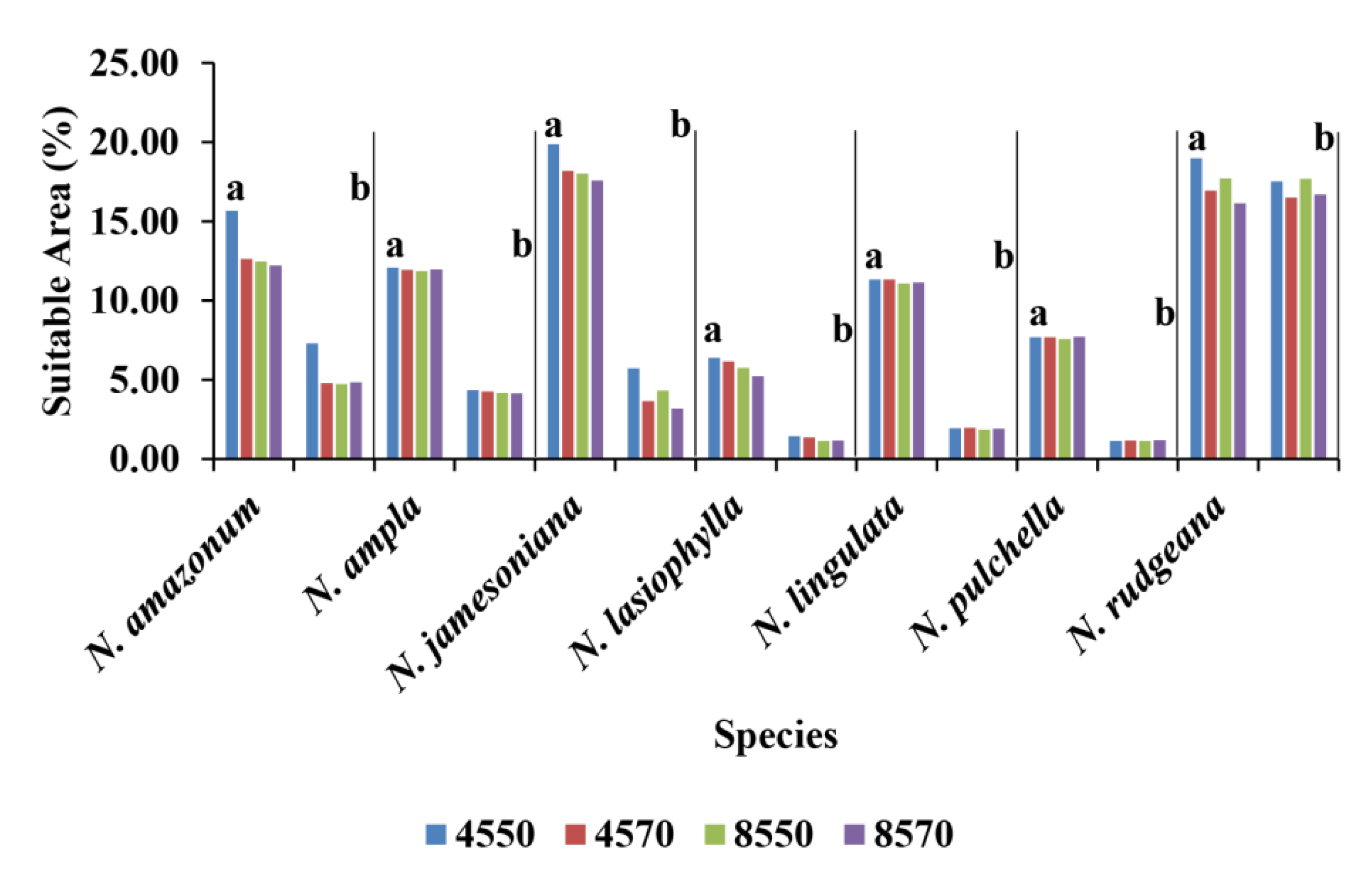
3.4. Future Distribution Changes
3.5. Land Use and the Distribution of Water Lilies
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chou, S.C.; Lyra, A.; Mourão, C.; Dereczynski, C.; Pilotto, I.; Gomes, J.; Bustamante, J.; Tavares, P.; Silva, A.; Rodrigues, D. Assessment of climate change over South America under RCP 4.5 and 8.5 downscaling scenarios. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2014, 3, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengo, J.; Nobre, C.; Tomasella, J.; Cardoso, M.; Oyama, M. Hydro-climatic and ecological behaviour of the drought of Amazonia in 2005. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Proc. Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 1773–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowbotham, J. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fifth Assessment Report: Review of Working Group I Contribution. 2014. Available online: https://publications.parliament.uk/ (accessed on 16 June 2022).
- Leiva, J. Assessment of climate change impacts on the water resources at the northern oases of Mendoza province, Argentina. In Global Change in Mountain Regions; Price, M.F., Ed.; Sapiens Publishing: Kirkmahoe, UK, 2006; pp. 81–83. [Google Scholar]
- Vuille, M.; Bradley, R.S.; Werner, M.; Keimig, F. 20th century climate change in the tropical Andes: Observations and model results. In Climate Variability and Change in High Elevation Regions: Past, Present & Future; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 75–99. [Google Scholar]
- Crimmins, S.M.; Dobrowski, S.Z.; Greenberg, J.A.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Mynsberge, A.R. Changes in climatic water balance drive downhill shifts in plant species’ optimum elevations. Science 2011, 331, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, K.H.; Vizy, E.K. Effects of twenty-first-century climate change on the Amazon rain forest. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 542–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchito, S.H.; Fernandez, J.P.R.; Pareja, D. Surrogate climate change scenario and projections with a regional climate model: Impact on the aridity in South America. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2014, 3, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, O.E.; Stuart Chapin, F.; Armesto, J.J.; Berlow, E.; Bloomfield, J.; Dirzo, R.; Huber-Sanwald, E.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jackson, R.B.; Kinzig, A. Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science 2000, 287, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsch, T.; Hilu, K.W.; Wiersema, J.H.; Löhne, C.; Barthlott, W.; Wilde, V. Phylogeny of Nymphaea (Nymphaeaceae): Evidence from substitutions and microstructural changes in the chloroplast trnT-trnF region. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2007, 168, 639–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Efremov, A.; Davidson, T.A.; Molina-Navarro, E.; Fidanza, K.; Betiol, T.C.C.; Chambers, P.; Grimaldo, J.T.; Martins, S.V.; Springuel, I. World distribution, diversity and endemism of aquatic macrophytes. Aquat. Bot. 2019, 158, 103127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalziell, E.L.; Lewandrowski, W.; Merritt, D.J. Increased salinity reduces seed germination and impacts upon seedling development in Nymphaea L. (Nymphaeaceae) from northern Australia’s freshwater wetlands. Aquat. Bot. 2020, 165, 103235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Singh, N.; Adit, A.; Kumaria, S.; Tandon, R.; Agarwal, M.; Jagannath, A.; Goel, S. Contrasting reproductive strategies of two Nymphaea species affect existing natural genetic diversity as assessed by microsatellite markers: Implications for conservation and wetlands restoration. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 773572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngarega, B.K.; Nzei, J.M.; Saina, J.K.; Halmy, M.W.A.; Chen, J.-M.; Li, Z.-Z. Mapping the habitat suitability of Ottelia species in Africa. Plant Divers. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzei, J.M.; Mwanzia, V.M.; Ngarega, B.K.; Musili, P.M.; Wang, Q.-F.; Chen, J.-M.; Li, Z.-Z. Ecological Niche Modeling of water Lily (Nymphaea L.) species in Australia under climate change to ascertain habitat suitability for conservation measures. Plants 2022, 11, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nzei, J.M.; Ngarega, B.K.; Mwanzia, V.M.; Musili, P.M.; Wang, Q.-F.; Chen, J.-M. The past, current, and future distribution modeling of four water lilies (Nymphaea) in Africa indicates varying suitable habitats and distribution in climate change. Aquat. Bot. 2021, 173, 103416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, S.G.; Hole, D.G.; Collingham, Y.C.; Hilton, G.; Rahbek, C.; Huntley, B. Assessing the impacts of future climate change on protected area networks: A method to simulate individual species’ responses. Environ. Manag. 2009, 43, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedo, M.N.; DeFries, R.S.; Morton, D.C.; Stickler, C.M.; Galford, G.L.; Shimabukuro, Y.E. Decoupling of deforestation and soy production in the southern Amazon during the late 2000s. PNAS 2012, 109, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, D.C.; DeFries, R.S.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Anderson, L.O.; Arai, E.; del Bon Espirito-Santo, F.; Freitas, R.; Morisette, J. Cropland expansion changes deforestation dynamics in the southern Brazilian Amazon. PNAS 2006, 103, 14637–14641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papeş, M.; Gaubert, P. Modelling ecological niches from low numbers of occurrences: Assessment of the conservation status of poorly known viverrids (Mammalia, Carnivora) across two continents. Divers. Distrib. 2007, 13, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Graham, C.H.; Anderson, R.P.; Dudík, M.; Ferrier, S.; Guisan, A.; Hijmans, R.J.; Huettmann, F.; Leathwick, J.R.; Lehmann, A. Novel methods improve prediction of species’ distributions from occurrence data. Ecography 2006, 29, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngarega, B.K.; Masocha, V.F.; Schneider, H. Forecasting the effects of bioclimatic characteristics and climate change on the potential distribution of Colophospermum mopane in southern Africa using Maximum Entropy (Maxent). Ecol. Inform. 2021, 65, 101419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Elith, J. On estimating probability of presence from use availability or presence background data. Ecology 2013, 94, 1409–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.-N.; Mbari, N.J.; Wang, S.-W.; Liu, B.; Mwangi, B.N.; Rasoarahona, J.R.; Xin, H.-P.; Zhou, Y.-D.; Wang, Q.-F. Modeling impacts of climate change on the potential distribution of six endemic baobab species in Madagascar. Plant Divers. 2021, 43, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend Peterson, A.; Papeş, M.; Eaton, M. Transferability and model evaluation in ecological niche modeling: A comparison of GARP and Maxent. Ecography 2007, 30, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, C.T.; Guilietti, A.M. Nymphaea vanildae (Nymphaeaceae): A new species from the Caatinga in Brazil. Phytotaxa 2013, 134, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, C.T.; Machado, I.C.; Giulietti, A.M. Nymphaeaceae of Brasil. SITIENTIBUS Série Ciências Biológicas 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello-Lammens, M.E.; Boria, R.A.; Radosavljevic, A.; Vilela, B.; Anderson, R.P. spThin: An R package for spatial thinning of species occurrence records for use in ecological niche models. Ecography 2015, 38, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esri, R. ArcGIS Desktop: Release 10; Environmental Systems Research Institute: Redlands, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Barve, N.; Barve, V.; Jiménez-Valverde, A.; Lira-Noriega, A.; Maher, S.P.; Peterson, A.T.; Soberón, J.; Villalobos, F. The crucial role of the accessible area in ecological niche modeling and species distribution modeling. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soberon, J.; Peterson, A.T. Interpretation of models of fundamental ecological niches and species’ distributional areas. Biodivers. Inform. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, L.E.; Medina-Vogel, G.; Peterson, A.T. Potential for spread of the white-nose fungus (Pseudogymnoascus destructans) in the Americas: Use of Maxent and NicheA to assure strict model transference. Geospat. Health 2014, 9, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, T.H. Checking bioclimatic variables that combine temperature and precipitation data before their use in species distribution models. Austral Ecol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014; Available online: www.r-project.org (accessed on 14 February 2019).
- Gent, P.R.; Danabasoglu, G.; Donner, L.J.; Holland, M.M.; Hunke, E.C.; Jayne, S.R.; Lawrence, D.M.; Neale, R.B.; Rasch, P.J.; Vertenstein, M. The community climate system model version 4. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 4973–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, C.; Jones, R.; Lee, R.W.; Rowell, D. Selecting CMIP5 GCMs for downscaling over multiple regions. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 44, 3237–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscarella, R.; Galante, P.J.; Soley-Guardia, M.; Boria, R.A.; Kass, J.M.; Uriarte, M.; Anderson, R.P. ENM eval: An R package for conducting spatially independent evaluations and estimating optimal model complexity for Maxent ecological niche models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Dudík, M.; Schapire, R. Maxent Software for Modeling Species Niches and Distributions (Version 3.4.1). Available online: http.biodiversityinformatics.amnh.org/open_source/Maxent/ (accessed on 31 July 2017).
- Brown, J.L. SDM toolbox: A python-based GIS toolkit for landscape genetic, biogeographic and species distribution model analyses. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merow, C.; Smith, M.J.; Silander Jr, J.A. A practical guide to MaxEnt for modeling species’ distributions: What it does, and why inputs and settings matter. Ecography 2013, 36, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, M.A.; Morshed, N. Mapping disease transmission risk of Nipah virus in South and Southeast Asia. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; He, H.S.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, L.; Du, H.; Liu, K.; Zong, S. Predicting wetland distribution changes under climate change and human activities in a mid-and high-latitude region. Sustainability 2018, 10, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, G.R.; McMahon, M.J. Day and Night Temperature Differential (DIF) or the absence of far-red light alters cell elongation in celebrity white ‘Petunia. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2006, 131, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, J.C.; Phinn, S.; Butt, N.; McAlpine, C.A. The impact of climate change on the distribution of two threatened Dipterocarp trees. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 2238–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhne, C.; Yoo, M.-J.; Borsch, T.; Wiersema, J.; Wilde, V.; Bell, C.D.; Barthlott, W.; Soltis, D.E.; Soltis, P.S. Biogeography of Nymphaeales: Extant patterns and historical events. Taxon 2008, 57, 1123–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deininger, M.; Ward, B.M.; Novello, V.F.; Cruz, F.W. Late quaternary variations in the South American monsoon system as inferred by speleothems new perspectives using the SISAL database. Quaternary 2019, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corlett, R.T. Impacts of warming on tropical lowland rainforests. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2011, 26, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, G.M. Genetic consequences of climatic oscillations in the Quaternary. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Proc. Biol. Sci. 2004, 359, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, N.P.; Crow, G.E.; Wiersema, J.H. Nymphaea (Nymphaeaceae) in Bolivia: Notes on several species, three new country records, and a key to species. Rhodora 2001, 103, 326–331. [Google Scholar]
- de Sousa, D.; Matias, L.Q. Synopsis of genus Nymphaea L. (Nymphaeaceae) in state of Ceará. Rev. Caatinga 2012, 25, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Langdon, J.G.; Lawler, J.J. Assessing the impacts of projected climate change on biodiversity in the protected areas of western North America. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Peepre, J. Economic Benefits of Protected Areas to Community and Tourism 2014, pp. 1–39. Available online: http://nbsapforum.net/sites/default/files/Economic%20Benefits%20of%20Protected%20Areas.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Rowland, E.L.; Fresco, N.; Reid, D.; Cooke, H.A. Examining climate-biome (“cliome”) shifts for Yukon and its protected areas. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2016, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, L.; Midgley, G.; Andelman, S.; Araújo, M.; Hughes, G.; Martinez-Meyer, E.; Pearson, R.; Williams, P. Protected area needs in a changing climate. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 5, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hole, D.G.; Willis, S.G.; Pain, D.J.; Fishpool, L.D.; Butchart, S.H.; Collingham, Y.C.; Rahbek, C.; Huntley, B. Projected impacts of climate change on a continent wide protected area network. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Jolly, I.; Sophocleous, M.; Zhang, L. Global impacts of conversions from natural to agricultural ecosystems on water resources: Quantity versus quality. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, M.T.; Costa, M.H.; Soares-Filho, B.S. The influence of historical and potential future deforestation on the stream flow of the Amazon river land surface processes and atmospheric feedbacks. J. Hydrol. 2009, 369, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, M.C. Accelerating extinction risk from climate change. Science 2015, 348, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butchart, S.H.; Clarke, M.; Smith, R.J.; Sykes, R.E.; Scharlemann, J.P.; Harfoot, M.; Buchanan, G.M.; Angulo, A.; Balmford, A.; Bertzky, B. Shortfalls and solutions for meeting national and global conservation area targets. Conserv. Lett. 2015, 8, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, K. Renting Biodiversity: The conservation concessions approach: With all the money we spend making conservation pay for itself, we could just pay for conservation. Conserv. Pract. 2003, 4, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable No. | Bioclimatic Variable | Code | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mean diurnal range (mean of monthly (max temp – min temp)) | bio2 | 1.7436 |
| 2 | Temperature seasonality (standard deviation × 100) | bio4 | 1.9289 |
| 3 | Maximum temperature of the warmest month | bio5 | 1.1728 |
| 4 | Precipitation of the wettest month | bio13 | 1.8567 |
| 5 | Precipitation seasonality (coefficient of variation) | bio15 | 1.4996 |
| 6 | Land use cover | dom_lu | 1.2866 |
| Species | Features Class | rm Value | Current Habitat Suitability (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N. amazonum | LQHP | 3.5 | 2,339,884 |
| N. ampla | LQ | 2.5 | 1,558,143 |
| N. jamesoniana | LQH | 4 | 2,790,903 |
| N. lasiophyla | LQH | 2 | 862,217 |
| N. lingulata | LQH | 4 | 1,341,940 |
| N. pulchella | LQH | 4 | 907,696.1 |
| N. rudgeana | LQH | 3.5 | 2,657,233 |
| RCP 4.5 | RCP 8.5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Current | 2050 | 2070 | 2050 | 2070 |
| N. amazonum | 0.847 ± 0.075 | 0.808 ± 0.116 | 0.803 ± 0.118 | 0.815 ± 0.115 | 0.811 ± 0.111 |
| N. ampla | 0.878 ± 0.081 | 0.887 ± 0.089 | 0.889 ± 0.090 | 0.891 ± 0.084 | 0.879 ± 0.085 |
| N. jamesoniana | 0.842 ± 0.083 | 0.859 ± 0.086 | 0.848 ± 0.096 | 0.848 ± 0.090 | 0.848 ± 0.094 |
| N. lasiophylla | 0.963 ± 0.036 | 0.954 ± 0.045 | 0.951 ± 0.049 | 0.953 ± 0.048 | 0.958 ± 0.035 |
| N. lingulata | 0.902 ± 0.036 | 0.890 ± 0.074 | 0.889 ± 0.075 | 0.891 ± 0.078 | 0.882 ± 0.087 |
| N. pulchella | 0.927 ± 0.025 | 0.936 ± 0.022 | 0.935 ± 0.021 | 0.938 ± 0.021 | 0.933 ± 0.023 |
| N. rudgeana | 0.814 ± 0.086 | 0.794 ± 0.083 | 0.800 ± 0.089 | 0.796 ± 0.089 | 0.806 ± 0.090 |
| RCP 4.5 | RCP 8.5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Variable | Current | 2050 | 2070 | 2050 | 2070 |
| N. amazonum | bio2 | 32.6 | 28.3 | 29.8 | 32.5 | 30.0 |
| bio4 | 17.6 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.4 | 2.7 | |
| bio5 | 16.1 | 15.3 | 11.6 | 12.2 | 12.0 | |
| bio13 | 9.5 | 19.5 | 18.8 | 20.4 | 20.6 | |
| bio15 | 4.3 | 9.8 | 12.7 | 10.4 | 11.3 | |
| dom_lu | 20.0 | 23.7 | 23.9 | 21.2 | 23.3 | |
| N. ampla | bio2 | 23.5 | 35.3 | 35.7 | 40.2 | 37.5 |
| bio4 | 17.8 | 13.5 | 13.8 | 12.2 | 15.2 | |
| bio5 | 0.0 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 3.8 | |
| bio13 | 25.8 | 20.3 | 20.2 | 15.9 | 15.9 | |
| bio15 | 8.3 | 10.5 | 9.5 | 11.2 | 8.6 | |
| dom_lu | 24.6 | 18.9 | 19.2 | 18.1 | 19.2 | |
| N. jamesoniana | bio2 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| bio4 | 18.6 | 6.4 | 6.8 | 3.9 | 4.5 | |
| bio5 | 29.1 | 16.6 | 14.3 | 12.6 | 8.9 | |
| bio13 | 2.8 | 20.9 | 17.0 | 22.7 | 21.1 | |
| bio15 | 19.3 | 21.3 | 23.5 | 23.2 | 25.1 | |
| dom_lu | 30.3 | 34.4 | 38.0 | 37.5 | 39.9 | |
| N. lasiophylla | bio2 | 24.9 | 27.3 | 26.6 | 30.5 | 31.1 |
| bio4 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.6 | |
| bio5 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 2.3 | |
| bio13 | 7.4 | 10.3 | 7.1 | 7.5 | 7.1 | |
| bio15 | 58.2 | 52.9 | 56.2 | 53.0 | 50.9 | |
| dom_lu | 8.4 | 8.3 | 8.6 | 7.7 | 8.0 | |
| N. lingulata | bio2 | 19.4 | 20.6 | 21.6 | 23.0 | 23.0 |
| bio4 | 9.8 | 4.9 | 4.1 | 4.9 | 3.3 | |
| bio5 | 4.9 | 3.8 | 3.1 | 1.8 | 1.2 | |
| bio13 | 1.8 | 6.9 | 6.2 | 6.0 | 5.7 | |
| bio15 | 43.0 | 41.0 | 42.5 | 40.5 | 42.2 | |
| dom_lu | 21.1 | 22.7 | 22.5 | 23.8 | 24.6 | |
| N. pulchella | bio2 | 27.5 | 27.9 | 29.9 | 31.7 | 30.5 |
| bio4 | 38.6 | 19.5 | 17.9 | 18.6 | 16.3 | |
| bio5 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 3.6 | 4.0 | 6.0 | |
| bio13 | 4.6 | 23.3 | 21.1 | 20.6 | 20.7 | |
| bio15 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 1.9 | |
| dom_lu | 25.6 | 24.4 | 25.2 | 23.4 | 24.6 | |
| N. rudgeana | bio2 | 70.0 | 66.7 | 61.1 | 62.3 | 60.1 |
| bio4 | 6.9 | 10.3 | 9.4 | 8.6 | 11.6 | |
| bio5 | 1.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 | |
| bio13 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.6 | |
| bio15 | 12.7 | 10.7 | 16.5 | 16.0 | 15.4 | |
| dom_lu | 8.8 | 11.8 | 12.7 | 12.6 | 12.2 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nzei, J.M.; Ngarega, B.K.; Mwanzia, V.M.; Kurauka, J.K.; Wang, Q.-F.; Chen, J.-M.; Li, Z.-Z.; Pan, C. Assessment of Climate Change and Land Use Effects on Water Lily (Nymphaea L.) Habitat Suitability in South America. Diversity 2022, 14, 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100830
Nzei JM, Ngarega BK, Mwanzia VM, Kurauka JK, Wang Q-F, Chen J-M, Li Z-Z, Pan C. Assessment of Climate Change and Land Use Effects on Water Lily (Nymphaea L.) Habitat Suitability in South America. Diversity. 2022; 14(10):830. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100830
Chicago/Turabian StyleNzei, John M., Boniface K. Ngarega, Virginia M. Mwanzia, Joseph K. Kurauka, Qing-Feng Wang, Jin-Ming Chen, Zhi-Zhong Li, and Cheng Pan. 2022. "Assessment of Climate Change and Land Use Effects on Water Lily (Nymphaea L.) Habitat Suitability in South America" Diversity 14, no. 10: 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100830
APA StyleNzei, J. M., Ngarega, B. K., Mwanzia, V. M., Kurauka, J. K., Wang, Q.-F., Chen, J.-M., Li, Z.-Z., & Pan, C. (2022). Assessment of Climate Change and Land Use Effects on Water Lily (Nymphaea L.) Habitat Suitability in South America. Diversity, 14(10), 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100830








