Black Coral Distribution in the Italian Seas: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Distribution Dataset and Methods
3. Results
3.1. The Distribution of Black Corals in the Italian Seas
3.2. Anthropogenic Impact
4. Discussion
Anthropogenic Factors Affecting Black Corals
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bo, M.; Bavestrello, G.; Canese, S.; Giusti, M.; Salvati, E.; Angiolillo, M.; Greco, S. Characteristics of a black coral meadow in the twilight zone of the central Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 397, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Canese, S.; Spaggiari, C.; Pusceddu, A.; Bertolino, M.; Angiolillo, M.; Giusti, M.; Loreto, M.F.; Salvati, E.; Greco, S.; et al. Deep Coral Oases in the South Tyrrhenian Sea. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Opresko, D.M.; Försterra, G.; Hofrichter, R. Orden Antipatharia (corales negros o espinosos). El Mar Mediterraneo (Fauna, Flora, Ecologia); Hofrichter, R., Ed.; Omega: Barcelona, Spain, 2004; pp. 506–509. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, M.; Canese, S.; Bavestrello, G. Discovering Mediterranean black coral forests: Parantipathes larix (Anthozoa: Hexacorallia) in the Tuscan Archipelago, Italy. Ital. J. Zool. 2013, 81, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bo, M.; Bavestrello, G. Mediterranean Black Coral Communities. In Mediterranean Cold-Water Corals: Past, Present and Future; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 249–251. [Google Scholar]
- Gori, A.; Bavestrello, G.; Grinyó, J.; Dominguez-Carrió, C.; Ambroso, S.; Bo, M. Animal forests in deep coastal bottoms and continental shelf of the Mediterranean Sea. In Marine Animal Forests: The Ecology of Benthic Biodiversity Hotspots; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 207–233. [Google Scholar]
- Chimienti, G.; De Padova, D.; Mossa, M.; Mastrototaro, F. A mesophotic black coral forest in the Adriatic Sea. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, M.; Numa, C.; Otero, M.D.M.; Orejas, C.; Garrabou, J.; Cerrano, C.; Kružić, P.; Antoniadou, C.; Aguilar, R.; Kipson, S.; et al. Overview of the Conservation Status of Mediterranean Anthozoa; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Deidun, A.; Tsounis, G.; Balzan, F.; Micallef, A. Records of black coral (Antipatharia) and red coral (Corallium rubrum) fishing activities in the Maltese Islands. Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2010, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Barucca, M.; Biscotti, M.A.; Brugler, M.R.; Canapa, A.; Canese, S.; Bavestrello, G. Phylogenetic relationships of Medi-terranean black corals (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Hexacorallia) and implications for classification within the order Antipatharia. Invertebr. Syst. 2018, 32, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opresko, D.M. Three new species of Leiopathes (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Antipatharia) from Southern Australia. Rec. Aust. Mus. 1998, 31, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Tursi, A.; Mastrototaro, F.; Matarrese, A.; Maiorano, P.; D’Onghia, G. Biodiversity of the white coral reefs in the Ionian Sea (Central Mediterranean). Chem. Ecol. 2004, 20, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taviani, M.; Freiwald, A.; Zibrowius, H. Deep Coral Growth in the Mediterranean Sea: An overview. Erlangen Earth Conference Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 137–156. [Google Scholar]
- Vafidis, D.; Koukouras, A. Antipatharia, Ceriantharia and Zoantharia (Hexacorallia, Anthozoa) of the Aegean Sea with a check list of the Mediterranean and Black Sea Species. Ann. Inst. Oceanogr. 1998, 74, 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Opresko, D.M. Redescription of Antipathes dichotoma Pallas, 1766 (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Antipatharia). Zool. Med. Leiden 2003, 77, 481–493. [Google Scholar]
- Morri, C.; Esposito, F.; Pessani, D. Checklist della flora e della fauna dei mari italiani (Parte I). Anthozoa Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2008, 15, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, M.; Tazioli, S.; Spanò, N.; Bavestrello, G. Antipathella subpinnata (Antipatharia, Myriopathidae) in Italian seas. Ital. J. Zool. 2008, 75, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danovaro, R.; Boero, F. Italian Seas. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 283–306. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C. Marine Biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Situation, Problems and Prospects for Future Research. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, F.; Tunesi, L.; Agardy, T. Zoning Marine Protected Areas through Spatial Multiple-Criteria Analysis: The Case of the Asinara Island National Marine Reserve of Italy. Conserv. Biol. 2002, 16, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzin, M.M.G.; Matterson, K.; Coppari, M.; Bavestrello, G.; Abbiati, M.; Costantini, F. Population genomic structure of the black coral Antipathella subpinnata in Mediterranean Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems. In Coral Reefs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Coppari, M.; Mestice, F.; Betti, F.; Bavestrello, G.; Castellano, L.; Bo, M. Fragmentation, re-attachment ability and growth rate of the Mediterranean black coral Antipathella subpinnata. Coral Reefs 2019, 38, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppari, M.; Ferrier-Pagès, C.; Castellano, M.; Massa, F.; Olivari, E.; Bavestrello, G.; Povero, P.; Bo, M. Seasonal variation of the stable C and N isotopic composition of the mesophotic black coral Antipathella subpinnata (Ellis & Solander, 1786). Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 233, 106520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Bava, S.; Canese, S.; Angiolillo, M.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Bavestrello, G. Fishing impact on deep Mediterranean rocky habitats as revealed by ROV investigation. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 171, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenpeace. I tesori sommersi del Canale di Sicilia. NO TRIVELLE TOUR 2012. 2012. Available online: www.greenpeace.it (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Massi, D.; Vitale, S.; Titone, A.; Milisenda, G.; Gristina, M.; Fiorentino, F. Spatial distribution of the black coral Leiopathes glaberrima (Esper, 1788) (Antipatharia: Leiopathidae) in the Mediterranean: A prerequisite for protection of Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs). Eur. Zool. J. 2018, 85, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bo, M.; Bavestrello, G.; Canese, S.; Giusti, M.; Angiolillo, M.; Cerrano, C.; Salvati, E.; Greco, S. Coral assemblage off the Calabrian Coast (South Italy) with new observations on living colonies of Antipathes dichotoma. Ital. J. Zool. 2011, 78, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, R.; Pastor, X.; Garcia, S.; Marin, P.; Ubero, J. Importance of seamounts-like features for Mediterranean marine habitats and threatened species. Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Méditerr. 2013, 40, 716. [Google Scholar]
- Arena, P.; Li Greci, F. Indagine sulle condizioni faunistiche e sui rendimenti di pesca dei fondali batiali della Sicilia occidentale e della bordura settentrionale dei banchi della soglia Siculo-Tunisina. Quad. Lab. Tecnol. Pesca 1973, 1, 157–201. [Google Scholar]
- Santin, A.; Aguilar, R.; Akyol, O.; Begburs, C.R.; Benoit, L.; Chimienti, G.; Tiralongo, F. New records of rare species in the Mediterranean Sea (March 2021). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2021, 22, 199–217. [Google Scholar]
- Romagnoli, B.; Grasselli, F.; Costantini, F.; Abbiati, M.; Romagnoli, C.; Innangi, S.; Di Martino, G.; Tonielli, R. Evaluating the distribution of priority benthic habitats through a remotely operated vehicle to support conservation measures off Linosa Island (Sicily Channel, Mediterranean Sea). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Bavestrello, G. Distribuzione, Ecologia e conservazione dei coralli neri (Anthozoa, Antipatharia) del Mediterraneo; BMIB: Genova, Italy, 2013; p. 75. [Google Scholar]
- Ingrassia, M.; Macelloni, L.; Bosman, A.; Chiocci, F.L.; Cerrano, C.; Martorelli, E. Black coral (Anthozoa, Antipatharia) forest near the western Pontine Islands (Tyrrhenian Sea). Mar. Biodivers. 2016, 46, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaino, E.; Scoccia, F. Gamete spawning in Antipathella subpinnata (Anthozoa, Antipatharia): A structural and ultrastructural investigation. Zoomorphology 2010, 129, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiolillo, M.; Gori, A.; Canese, S.; Bo, M.; Priori, C.; Bavestrello, G.; Salvati, E.; Erra, F.; Greenacre, M.; Santangelo, G. Distribution and population structure of deep-dwelling red coral in the Northwest Mediterranean. Mar. Ecol. 2016, 37, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, M.; Innocenti, C.; Canese, S. Predicting suitable habitat for the gold coral Savalia savaglia (Bertoloni, 1819) (Cnidaria, Zoantharia) in the South Tyrrhenian Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 81, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onghia, G.; Calculli, C.; Capezzuto, F.; Carlucci, R.; Carluccio, A.; Maiorano, P.; Pollice, A.; Ricci, P.; Sion, L.; Tursi, A. New records of cold-water coral sites and fish fauna characterization of a potential network existing in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. 2016, 37, 1398–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlier, A.; Le Guilloux, E.; Olu, K.; Sarrazin, J.; Mastrototaro, F.; Taviani, M.; Clavier, J. Trophic relationships in a deep Med-iterranean cold-water coral bank (Santa Maria di Leuca, Ionian Sea). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 397, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrototaro, F.; D’Onghia, G.; Corriero, G.; Matarrese, A.; Maiorano, P.; Panetta, P.; Gherardi, M.; Longo, C.; Rosso, M.A.; Sciuto, F.; et al. Biodiversity of the white coral bank off Cape Santa Maria di Leuca (Mediterranean Sea): An update. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 412–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertino, A.; Savini, A.; Rosso, A.; Di Geronimo, I.; Mastrototaro, F.; Sanfilippo, R.; Gay, G.; Etiope, G. Benthic habitat characterization and distribution from two representative sites of the deep-water SML Coral Province (Mediterranean). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 380–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimienti, G.; Mastrototaro, F. Searching for black corals: The exploration of Tremiti islands MPA. Rapp. Comm. Mer. Médit. 2019, 42, 268. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, M.; Bavestrello, G.; Angiolillo, M.; Calcagnile, L.; Canese, S.; Cannas, R.; Cau, A.; D’Elia, M.; D’Oriano, F.; Follesa, M.C.; et al. Persistence of Pristine Deep-Sea Coral Gardens in the Mediterranean Sea (SW Sardinia). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cau, A.; Follesa, M.C.; Moccia, D.; Alvito, A.; Bo, M.; Angiolillo, M.; Canese, S.; Paliaga, E.M.; Orrù, P.E.; Sacco, F.; et al. Deepwater corals biodiversity along roche du large ecosystems with different habitat complexity along the south Sardinia continental margin (CW Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Biol. 2015, 162, 1865–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, A.; Rossi, S.; Linares, C.; Berganzo, E.; Orejas, C.; Dale, M.R.; Gili, J.-M. Size and spatial structure in deep versus shallow populations of the Mediterranean gorgonian Eunicella singularis (Cap de Creus, northwestern Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Biol. 2011, 158, 1721–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiolillo, M.; Canese, S. Deep Gorgonians and Corals of the Mediterranean Sea. In Corals in a Changing World; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tazioli, S.; Bo, M.; Boyer, M.; Rotinsulu, H.; Bavestrello, G. Ecological observations of some common antipatharian corals in the marine park of Bunaken (North Sulawesi, Indonesia). Zool. Stud. 2007, 46, 227–241. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, M.; Montgomery, A.D.; Opresko, D.M.; Wagner, D.; Bavestrello, G. Antipatharians of the Mesophotic Zone: Four Case Studies. In Coral Reefs of the Eastern Tropical Pacific; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 683–708. [Google Scholar]
- Genin, A.; Dayton, P.K.; Lonsdale, P.F.; Spiess, F.N. Corals on seamount peaks provide evidence of current acceleration over deep-sea topography. Nat. Cell Biol. 1986, 322, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Di Camillo, C.G.; Addamo, A.M.; Valisano, L.; Bavestrello, G. Growth strategies of whip black corals (Cnidaria: An-tipatharia) in the Bunaken Marine Park (Celebes, Indonesia). Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2009, 2e54, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscock, K. Water movement. In Sublittoral Ecology. The Ecology of Shallow Sublittoral Benthos; Earll, R., Erwin, D.G., Eds.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1983; pp. 58–96. [Google Scholar]
- Coma, R.; Ribes, M.; Gili, J.-M.; Zabala, M. Seasonality in coastal benthic ecosystems. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2000, 15, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrano, C.; Bastari, A.; Calcinai, B.; Di Camillo, C.; Pica, D.; Puce, S.; Valisano, L.; Torsani, F. Temperate mesophotic ecosystems: Gaps and perspectives of an emerging conservation challenge for the Mediterranean Sea. Eur. Zool. J. 2019, 86, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, D.; Luck, D.G.; Toonen, R. The Biology and Ecology of Black Corals (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Hexacorallia: Antipatharia). Adv. Mar. Biol. 2012, 63, 67–132. [Google Scholar]
- Cairns, S.D. Deep-water corals: An overview with special reference to diversity and distribution of deep-water scleractinian corals. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2007, 81, 311–322. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, S.K.; Graham, N.A.J.; Polunin, N.V. Appraisal of visual assessments of habitat complexity and benthic composition on coral reefs. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.; Duineveld, G.C.A.; Lavaleye, M.S.S.; Bergman, M.J.N.; Van Haren, H.; Roberts, M. Downwelling and deep-water bottom currents as food supply mechanisms to the cold-water coral Lophelia pertusa (Scleractinia) at the Mingulay Reef Complex. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Etnoyer, P.J.; Wagner, D.; Fowle, H.A.; Poti, M.; Kinlan, B.; Georgian, S.E.; Cordes, E.E. Models of habitat suitability, size, and age-class structure for the deep-sea black coral Leiopathes glaberrima in the Gulf of Mexico. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2018, 150, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, R.H.; Wilson, E.O. The Theory Ofisland Biogeography; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1967; p. 224. [Google Scholar]
- De Clippele, L.H.; Huvenne, V.A.I.; Molodtsova, T.N.; Roberts, J.M. The Diversity and Ecological Role of Non-scleractinian Corals (Antipatharia and Alcyonacea) on Scleractinian Cold-Water Coral Mounds. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prouty, N.; Roark, E.; Buster, N.; Ross, S. Growth rate and age distribution of deep-sea black corals in the Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 423, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roark, E.B.; Guilderson, T.P.; Dunbar, R.B.; Fallon, S.; Mucciarone, D.A. Extreme longevity in proteinaceous deep-sea corals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5204–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortensen, P.; Buhl-Mortensen, L. Deep-water corals and their habitats in The Gully, a submarine canyon off Atlantic Canada. Erlangen Earth Conf. Ser. 2006, 247–277. [Google Scholar]
- Purroy, A.; Requena, S.; Gili, J.M.; Canepa, A.; Sardá, R. Spatial assessment of artisanal fisheries and their potential impact on the seabed: The Cap de Creus regional case study (northwestern Mediterranean Sea). Sci. Mar. 2014, 78, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deidun, A.; Andaloro, F.; Bavestrello, G.; Canese, S.; Consoli, P.; Micallef, A.; Romeo, T.; Bo, M. First characterisation of aLeiopathes glaberrima(Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Antipatharia) forest in Maltese exploited fishing grounds. Ital. J. Zool. 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van De Water, J.A.; Coppari, M.; Enrichetti, F.; Ferrier-Pagès, C.; Bo, M. Local Conditions Influence the Prokaryotic Com-mu-nities Associated With the Mesophotic Black Coral Antipathella subpinnata. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onghia, G.; Mastrototara, F.; Matarrese, A.; Politou, C.-Y.; Mytilineou, C. Biodiversity of the Upper Slope Demersal Community in the Eastern Mediterranean: Preliminary Comparison Between Two Areas With and Without Trawl Fishing. J. Northwest Atl. Fish. Sci. 2003, 31, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrano, C.; Bavestrello, G.; Bianchi, C.N.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Bava, S.; Morganti, C.; Morri, C.; Picco, P.; Sara, G.; Schiaparelli, S.; et al. A catastrophic mass-mortality episode of gorgonians and other organisms in the Ligurian Sea (North-western Mediterranean), summer 1999. Ecol. Lett. 2000, 3, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
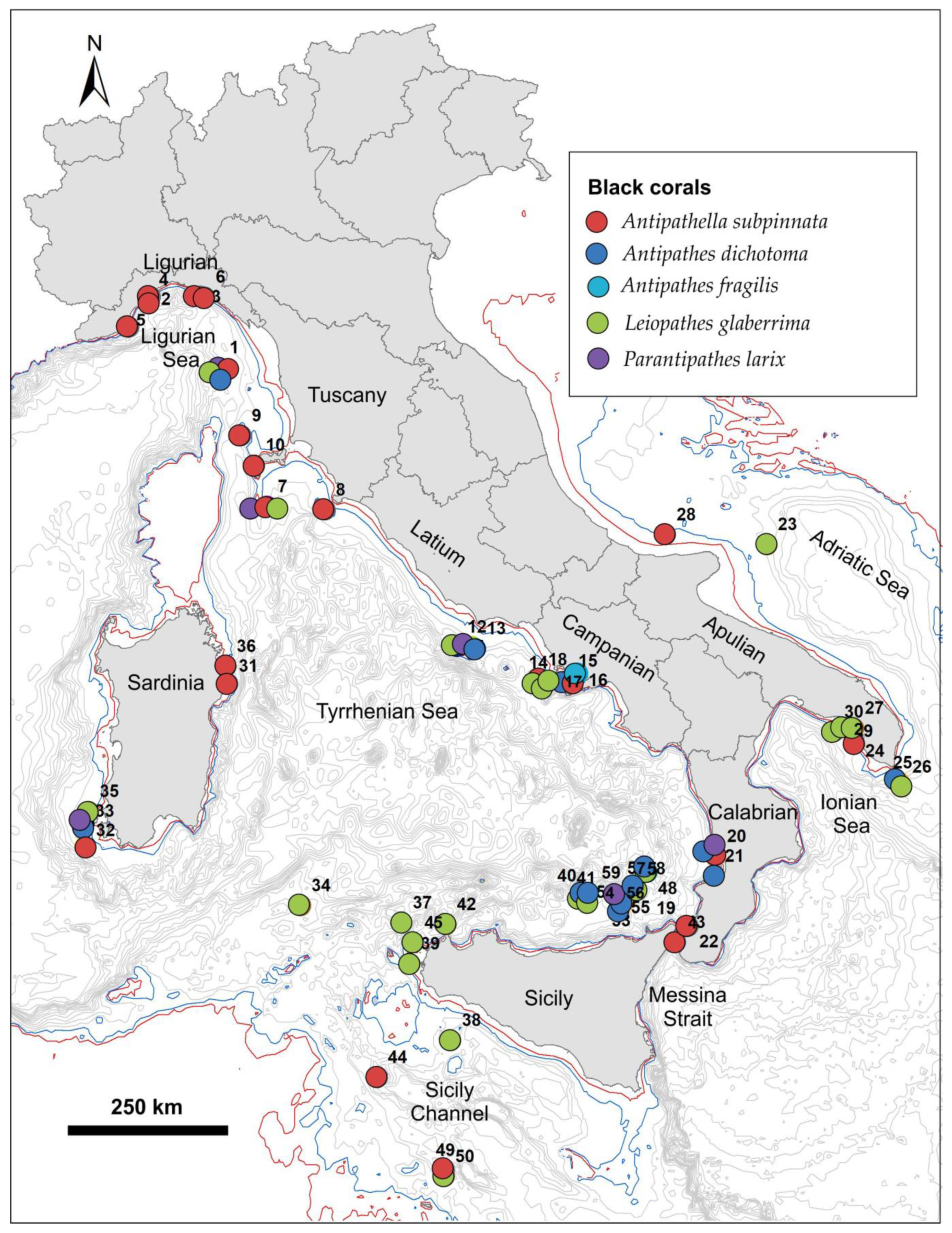
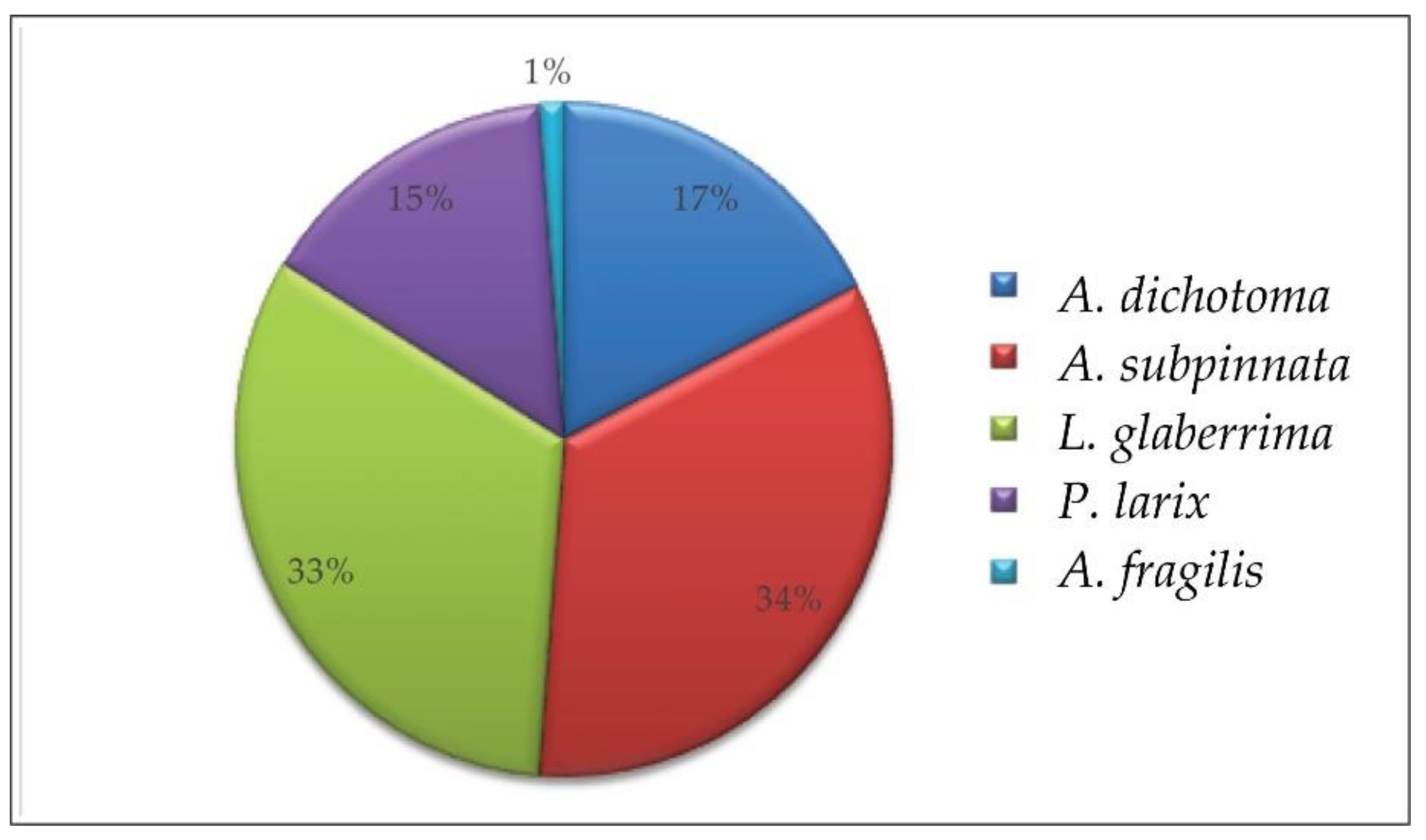
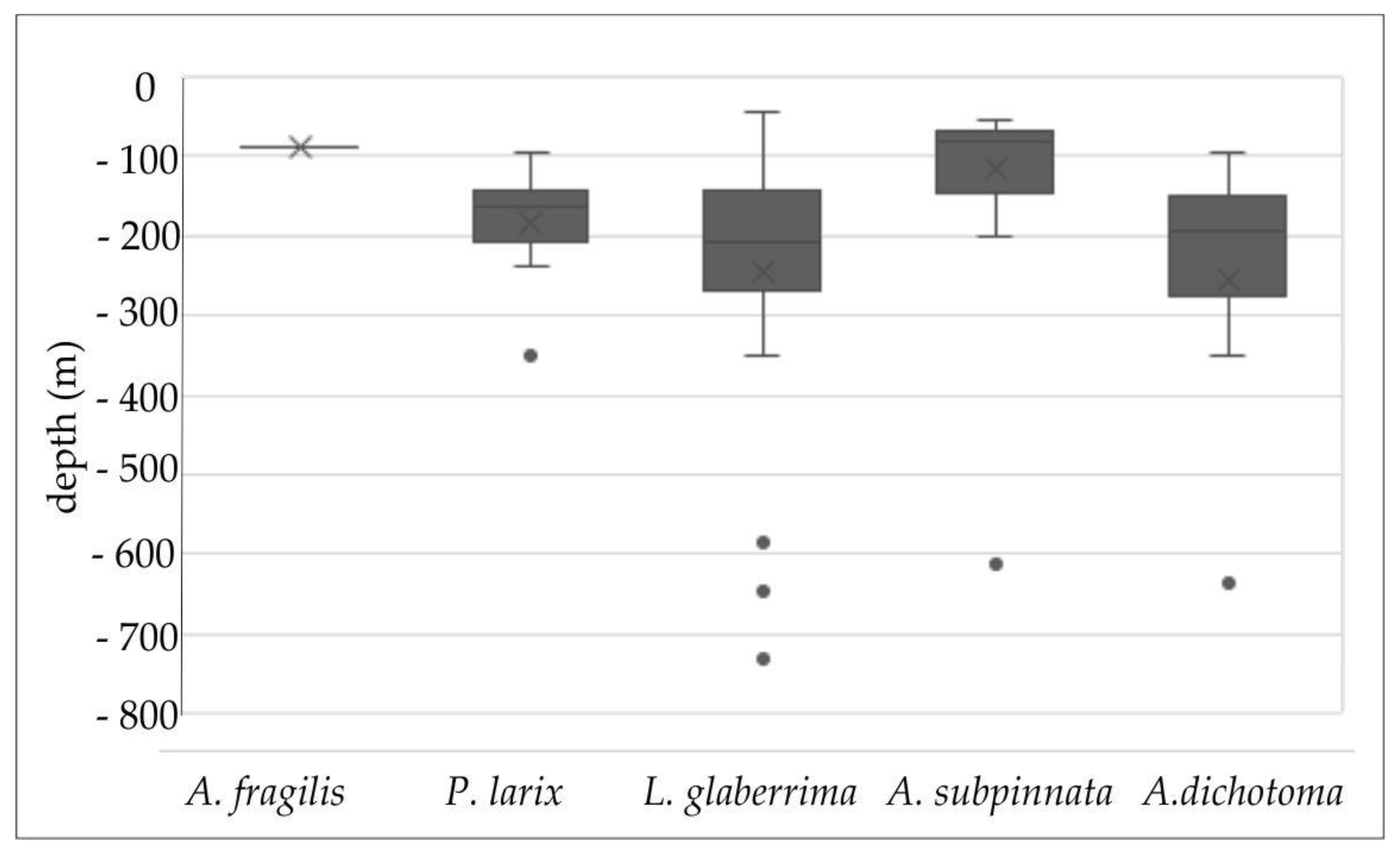

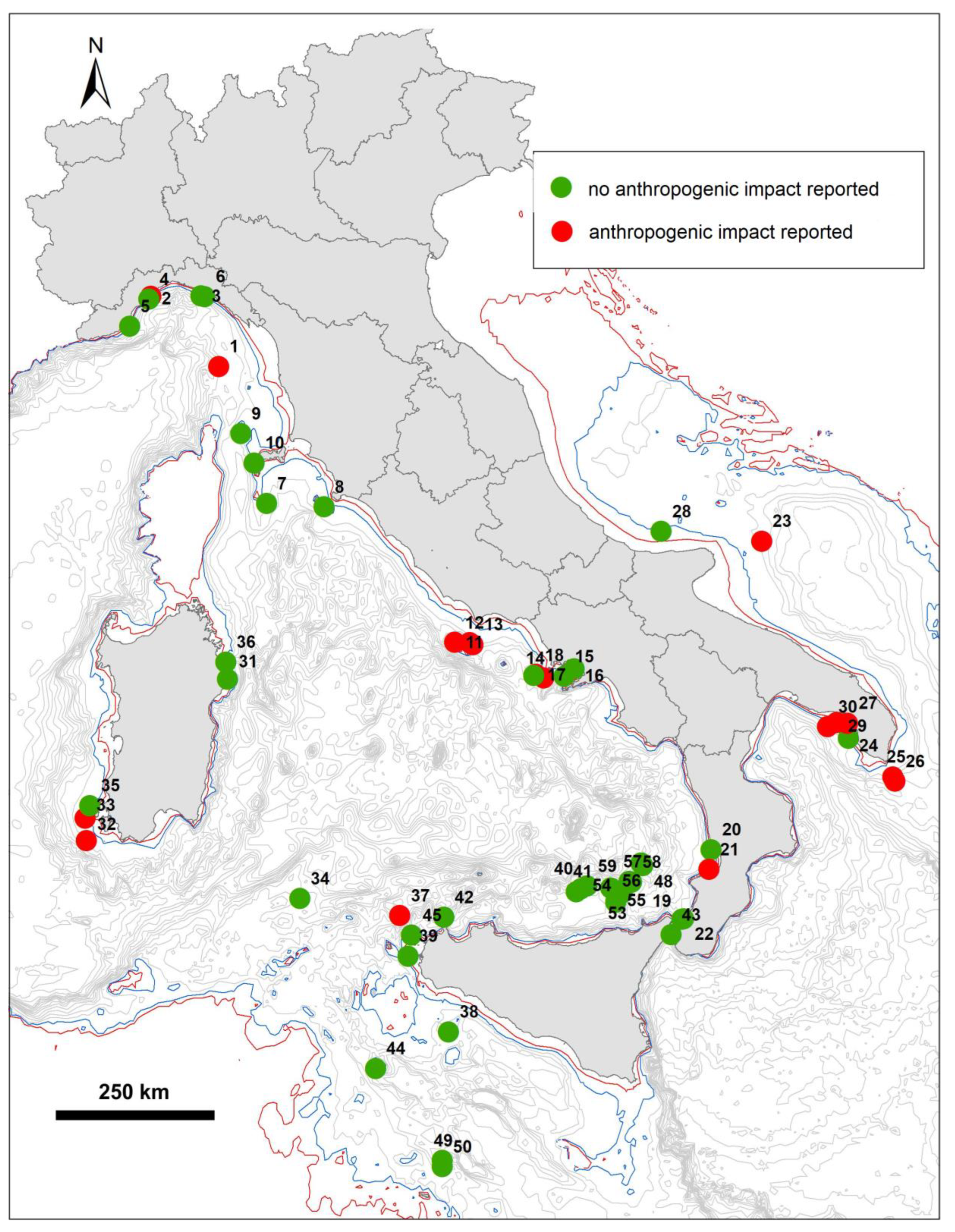
| Region | ID | Site | Sea | Coral | Min Depth | Max Depth | Setting | Substrate | Anthropogenic Impact | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligurian | 1 | Banco di S. Lucia | SE Ligurian Sea | AS, AD, LG, PL | 140 | 210 | Offshore banks and seamounts | Deep rocky banks | Fishing activity | [4,21] |
| Sicily | 2 | Mantice Shoal | Western Ligurian Sea | AS | 70 | 150 | Shelf edge and upper slope | Deep rocky banks | Fishing activity | [4] |
| 3 | Portofino Secca dell’Isuela | Ligurian Sea | AS | 56 | 60 | Shelf | Shoal | nd | [17,22,23] | |
| 4 | Bordighera | West Ligurian Sea | AS | 63 | 63 | Shelf | nd | nd | [22] | |
| 5 | Wreck Ravenna | Ligurian Sea | AS | 75 | 90 | Shelf | Rocky bottom | nd | [20] | |
| 6 | Punta Faro | Ligurian Sea | AS | 63 | 77 | Shelf | Shoal | nd | [23] | |
| 37 | Marco Bank | Western Sicily | LG | 240 | 260 | Offshore banks and seamounts | Deep rocky banks | Fishing activity | [24] | |
| 38 | Graham Shoal | Strait of Sicily | LG | 95 | 150 | Offshore banks and seamounts | Shoal | nd | [25] | |
| 39 | Favignana and Talbot Shoal | Strait of Sicily | LG | 100 | 100 | Offshore banks and seamounts | Shoal | nd | [26] | |
| 40 | Filicudi Aeolian islands | Tyrrhenian Sea | AD | 75 | 300 | Shelf edge and upper slope | Rocks encrusted by coralline algae | nd | [27,28] | |
| 41 | Filicudi Aeolian islands | Tyrrhenian Sea | LG | 300 | 300 | Deep areas | Rocky bottom | nd | [27,28] | |
| 42 | Cape San Vito Sicily | Tyrrhenian Sea | LG | 275 | 286 | Deep areas | nd | nd | [26,27] | |
| 43 | Messina Strait | Secche di Favazzina | AS | 55 | 70 | Rocky bottom | nd | [20] | ||
| 44 | Pantelleria | AS | 70 | 100 | Offshore banks and seamounts | nd | nd | [20] | ||
| 45 | Northern Levanzo Island | Tyrrhenian Sea | AS | 235 | 250 | Deep areas | nd | nd | [29] | |
| 46 | Stromboli | Tyrrhenian Sea | AS | 52 | 58 | Shelf | Rocky bottom | nd | [20] | |
| 47 | Stromboli | Tyrrhenian Sea | LG | 187 | 345 | Deep areas | Rocky bottom | nd | [30] | |
| 48 | NE Stromboli | Tyrrhenian Sea | AD, PL | 129,202 | 349, 202 | Shelf edge and upper slope | Rocky bottom | nd | [30] | |
| 49 | Linosa | Sicily channel | AS | 160 | 160 | Shelf | Bench terrace | nd | [31] | |
| 50 | Linosa | Sicily channel | LG | 200 | 200 | Shelf edge and upper slope | Bench terrace | nd | [31] | |
| 51 | NE Lipari | Tyrrhenian Sea | AS | 83 | 130 | Shelf | Rocks encrusted by coralline algae | nd | [30] | |
| 52 | NE Lipari | Tyrrhenian Sea | AS | 612 | 612 | Deep areas | Rocky bottom | nd | [30] | |
| 53 | NE Lipari | Tyrrhenian Sea | PL | 129 | 158 | Shelf | Rocks encrusted by coralline algae | nd | [30] | |
| 54 | NE Lipari | Tyrrhenian Sea | AD | 129 | 218 | Shelf edge and upper slope | Rocks encrusted by coralline algae | nd | [30] | |
| 55 | SW Lipari | Tyrrhenian Sea | AD | 207 | 298 | Shelf edge and upper slope | Rocky bottom | nd | [30] | |
| 56 | Salina | Tyrrhenian Sea | PL | 129 | 345 | Shelf edge and upper slope, deep areas | Rocky bottom | nd | [30] | |
| 57 | Panarea | Tyrrhenian Sea | LG | 187 | 345 | Deep areas | Vertical rocky walls | nd | [30] | |
| 58 | SE Panarea | Tyrrhenian Sea | AD, PL | 351,349 | 351,349 | Deep areas | Vertical rocky walls | nd | [30] | |
| 59 | NW Filicudi | Tyrrhenian Sea | AD, LG | 647 | 647 | Deep areas | Rocky bottom | nd | [30] | |
| Campanian | 14 | Vedove Shoal (Capri) | Tyrrhenian Sea | LG | 240 | 260 | Deep areas | Deep rocky banks | Lost garbage | [24] |
| 15 | Bay of Naples | Tyrrhenian Sea | AD, AS | 200 | 200 | Shelf edge and upper slope | Rocks encrusted by coralline algae | nd | [17,27] | |
| 16 | Naple Gulf | Tyrrhenian Sea | AF, AS | 80 | 100 | Shelf | Rocky bottom | nd | [17,32] | |
| 17 | Capri Island | Tyrrhenian Sea | AS | 70 | 70 | Shelf | Shoal | Fishing activity | [17,27] | |
| 18 | Capri Island | Tyrrhenian Sea | LG | 160 | 260 | Shelf edge and upper slope | Rocky bottom | nd | [17,27] | |
| Latium | 11 | Western Pontine Archipelago | Tyrrhenian sea | LG, PL | 194 | 220 | Offshore banks and seamounts | Rocky bottom | Fishing activity | [33] |
| 12 | Western Pontine Archipelago | Tyrrhenian sea | AD, LG, PL | 145 | 155 | Shelf edge and upper slope | Rocky bottom | Fishing activity | [33] | |
| 13 | Western Pontine Archipelago | Tyrrhenian sea | LG, PL | 130 | 138 | Shelf | Rocky bottom | Fishing activity and lost garbage | [33] | |
| Tuscany | 7 | Montecristo Natural reserve | Tyrrhenian sea | AS, PL, LG | 108 | 200 | Shelf edge and upper slope | Shoal | nd | [4] |
| 8 | Mezzo Canale | Tyrrhenian Sea | AS | 70 | 70 | Shelf | nd | nd | [34] | |
| 9 | Capraia Island | Tyrrhenian Sea | AS | 75 | 90 | Shelf | Rocky bottom | nd | [17] | |
| 10 | Elba | Tyrrhenian Sea | AS | 60 | 94 | Shelf | Rocks encrusted by coralline algae | nd | [35] | |
| Calabrian | 19 | Scilla | Tyrrhenian Sea | AS | 50 | 100 | Shelf | Rocky bottom | nd | [1] |
| 20 | Golfo di S. Eufemia | Tyrrhenian Sea | AD PL AS | 70 | 120 | Shelf | Shoal | nd | [2] | |
| 21 | Vibo Marina | Tyrrhenian Sea | AD | 90 | 132 | Shelf | Shoal | Fishing activity | [27] | |
| 22 | Favazzina | Tyrrhenian sea northern border Messina Strait | AS | 62 | 72 | Shelf | Rocky bottom | nd | [36] | |
| Apulia | 23 | Vieste | Adriatic sea | LG | 350 | 350 | Deep areas | Rocky bottom | Fishing activity | [37] |
| 24 | Gallipoli | Adriatic sea | AS | 70 | 70 | Shelf | Rocky bottom | nd | [17] | |
| 25 | S. Maria di Leuca | Ionian Sea | LG | 671 | 790 | Deep areas | Rocky bottom | Fishing activity | [12,27,38,39] | |
| 26 | S. Maria di Leuca | Ionian Sea | AD | 630 | 640 | Deep areas | Rocky bottom | Fishing activity | [39,40] | |
| 27 | Torre Inserraglio | Ionian Sea | LG | 45 | 45 | Shelf | nd | Fishing activity | [37] | |
| 28 | Tremiti Islands | Adriatic Sea | AS | 51 | 80 | Shelf | nd | nd | [7,34,41] | |
| 29 | Porto cesareo | Ionian sea | LG | 100 | 236 | Shelf edge and upper slope | Rocky bottom | Fishing activity | [37] | |
| 30 | Porto cesareo | Ionian sea | LG | 50 | 50 | Shelf | Rocky bottom | Fishing activity | [37] | |
| 31 | Capo Comino | Eastern coasts of Sardinia | AS | 54 | 54 | Shelf | nd | nd | [17] | |
| Sardinia | 32 | SW coasts of Sardinia | Western Mediterranean Sea | AD, PL, LG | 210 | 210 | Shelf edge and upper slope | Shoal | Fishing activity | [42] |
| 33 | Rocky pinnacles off Carloforte | Sardinian Sea | AD, AS, LG, PL | 120 | 170 | Shelf edge and upper slope | Rocky bottom | Fishing activity and lost gabage | [43] | |
| 34 | Northern edge of Skerki Bank | Sardinian Channel | LG | 520 | 650 | Deep areas | nd | nd | [29] | |
| 35 | Western Carloforte Island | Sardinian Sea | LG | 70 | 130 | Shelf | nd | nd | [35] | |
| 36 | Posada canyon | Sardinian Sea | AS | 152 | 156 | Deep areas | nd | nd | [21] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ingrassia, M.; Di Bella, L. Black Coral Distribution in the Italian Seas: A Review. Diversity 2021, 13, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13070334
Ingrassia M, Di Bella L. Black Coral Distribution in the Italian Seas: A Review. Diversity. 2021; 13(7):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13070334
Chicago/Turabian StyleIngrassia, Michela, and Letizia Di Bella. 2021. "Black Coral Distribution in the Italian Seas: A Review" Diversity 13, no. 7: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13070334
APA StyleIngrassia, M., & Di Bella, L. (2021). Black Coral Distribution in the Italian Seas: A Review. Diversity, 13(7), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13070334







