Origins of Six Species of Butterflies Migrating through Northeastern Mexico: New Insights from Stable Isotope (δ2H) Analyses and a Call for Documenting Butterfly Migrations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Sites
2.2. The Species
2.3. Stable Isotope Analyses
2.4. Assignment to Origin
3. Results
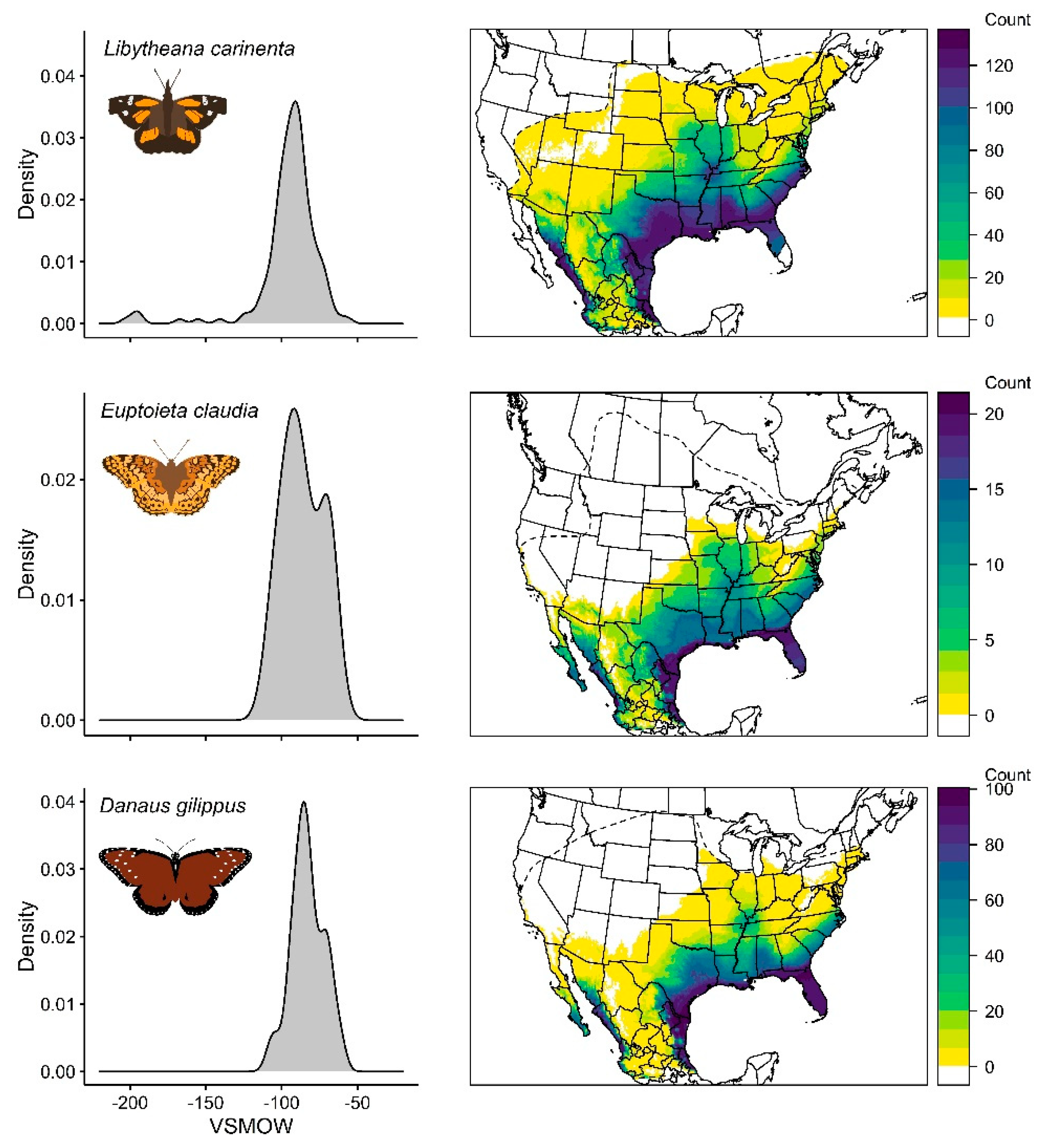
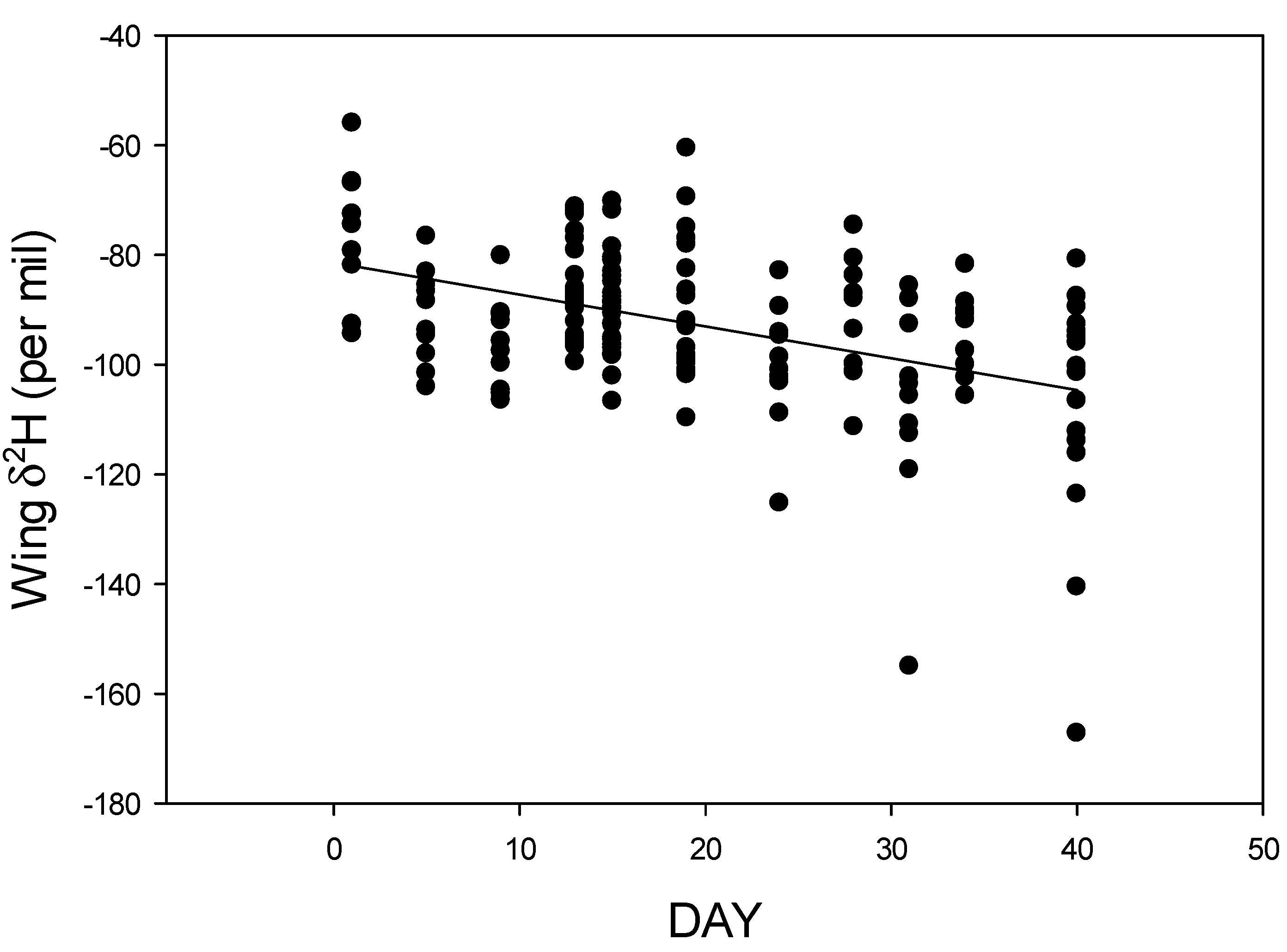
3.1. Libytheana Carinenta
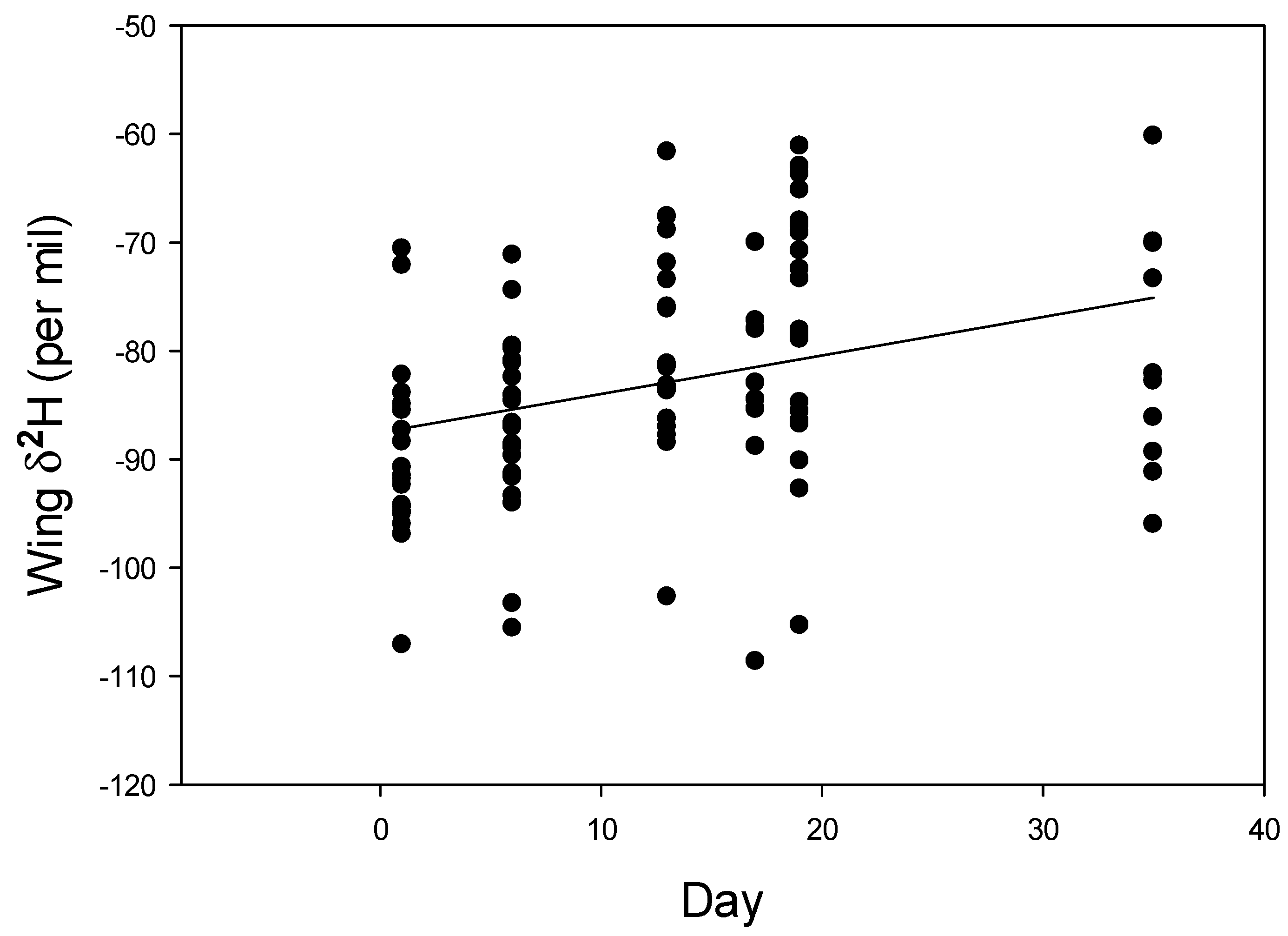
3.2. Euptoieta Claudia
3.3. Danaus Gilippus
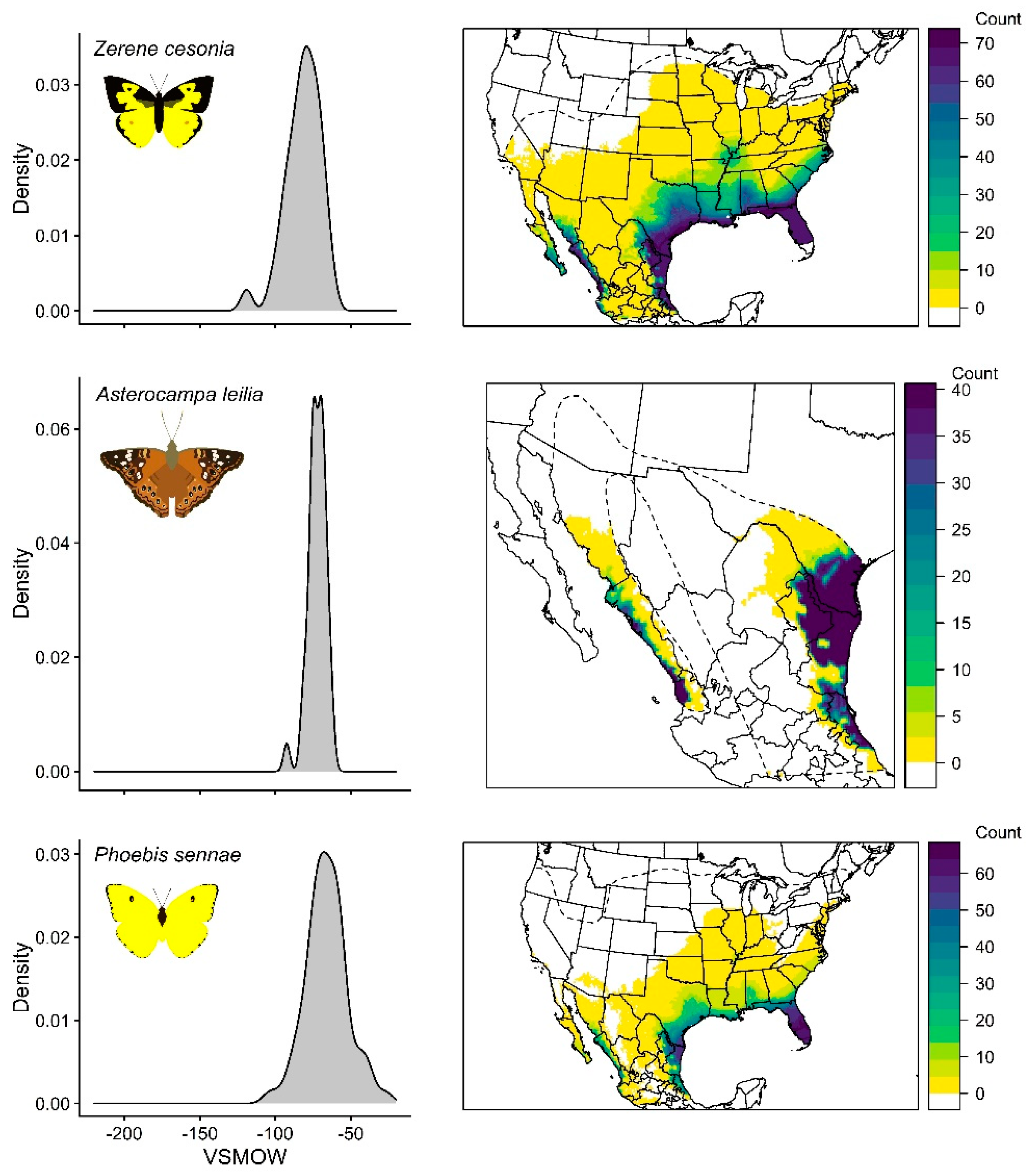
3.4. Zerene Cesonia
3.5. Asterocampa Leilia
3.6. Euptoieta Hegesia
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statements
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dingle, H. Migration: The Biology of Life on the Move, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; ISBN 0-19-964039-4. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, J.W.; Reynolds, D.R.; Wilson, K. Long-range seasonal migration in insects: Mechanisms, evolutionary drivers and ecological consequences. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, J.W.; Lim, K.S.; Reynolds, D.R. The significance of midsummer movements of Autographa gamma: Implications for a mechanistic understanding of orientation behavior in a migrant moth. Curr. Zool. 2013, 59, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanescu, C.; Soto, D.X.; Talavera, G.; Vila, R.; Hobson, K.A. Long-Distance autumn migration across the Sahara by painted lady butterflies: Exploiting resource pulses in the Tropical Savannah. Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20160561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.C. Do dragonflies migrate across the western Indian Ocean? J. Trop. Ecol. 2009, 25, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, K.A.; Anderson, R.C.; Soto, D.X.; Wassenaar, L.I. Isotopic evidence that dragonflies (Pantala Flavescens) migrating through the Maldives come from the northern Indian Subcontinent. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, K.A.; Jinguji, H.; Ichikawa, Y.; Kusack, J.W.; Anderson, R.C. Long-distance migration of the globe skimmer dragonfly to Japan revealed using stable hydrogen (δ2H) isotopes. Environ. Entomol. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikelski, M.; Moskowitz, D.; Adelman, J.S.; Cochran, J.; Wilcove, D.S.; May, M.L. Simple rules guide dragonfly migration. Biol. Lett. 2006, 2, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satterfield, D.A.; Sillett, T.S.; Chapman, J.W.; Altizer, S.; Marra, P.P. Seasonal insect migrations: Massive, influential, and overlooked. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 18, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Bayo, F.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G. Worldwide decline of the entomofauna: A review of its drivers. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 232, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.L.; Grames, E.M.; Forister, M.L.; Berenbaum, M.R.; Stopak, D. Insect decline in the anthropocene: Death by a thousand cuts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2023989118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Hedlund, J.; Reynolds, D.R.; Zhai, B.; Hu, G.; Chapman, J.W. The ‘migratory connectivity’ concept, and its applicability to insect migrants. Mov. Ecol. 2020, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srygley, R.B.; Dudley, R. Optimal strategies for insects migrating in the flight boundary layer: Mechanisms and consequences. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2008, 48, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.W.; Klaassen, R.H.; Drake, V.A.; Fossette, S.; Hays, G.C.; Metcalfe, J.D.; Reynolds, A.M.; Reynolds, D.R.; Alerstam, T. Animal orientation strategies for movement in flows. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, R861–R870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikelski, M.; Kays, R.W.; Kasdin, N.J.; Thorup, K.; Smith, J.A.; Swenson, G.W. Going wild: What a global small-animal tracking system could do for experimental biologists. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, E.S.; Kelly, J.F.; Contina, A.; Gabrielson, R.M.; MacCurdy, R.B.; Winkler, D.W. Advances in tracking small migratory birds: A technical review of light-level geolocation. J. Field Ornithol. 2013, 84, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.D.; Crewe, T.; Mackenzie, S.; Lepage, D.; Aubry, Y.; Crysler, Z.; Finney, G.; Francis, C.; Guglielmo, C.; Hamilton, D.; et al. The motus wildlife tracking system: A collaborative research network to enhance the understanding of wildlife movement. Avian Conserv. Ecol. 2017, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, K.A.; Norris, D.R.; Kardynal, K.J.; Yohannes, E. Animal migration: A context for using new techniques and approaches. In Tracking Animal Migration with Stable Isotopes; Hobson, K.A., Wassenaar, L.I., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–24. ISBN 978-0-12-814723-8. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, S.M.; Pitman, G.M.; Flockhart, D.T.T.; Norris, D.R. Radio-tracking reveals how wind and temperature influence the pace of daytime insect migration. Biol. Lett. 2019, 15, 20190327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, K.A.; Doward, K.; Kardynal, K.J.; McNeil, J.N. Inferring origins of migrating insects using isoscapes: A case study using the true armyworm, mythimna unipuncta, in North America. Ecol. Entomol. 2018, 43, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; West, J.B. Isoscapes for terrestrial migration research. In Tracking Animal Migration with Stable Isotopes, 2nd ed.; Hobson, K.A., Wassenaar, L.I., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 53–84. ISBN 978-0-12-814723-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wunder, M.B.; Norris, D.R. Design and analysis for isotope-based studies of migratory animals. In Tracking Animal Migration with Stable Isotopes; Hobson, K.A., Wassenaar, L.I., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 191–206. ISBN 978-0-12-814723-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hobson, K.A.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Taylor, O.R. Stable isotopes (ΔD and δ13C) Are geographic indicators of natal origins of monarch butterflies in Eastern North America. Oecologia 1999, 120, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, N.G.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Hobson, K.A.; Norris, D.R. Migratory connectivity of the monarch butterfly (Danaus Plexippus): Patterns of spring re-colonization in Eastern North America. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altizer, S.; Hobson, K.A.; Davis, A.K.; De Roode, J.C.; Wassenaar, L.I. Do healthy monarchs migrate farther? Tracking natal origins of parasitized vs. uninfected monarch butterflies overwintering in Mexico. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flockhart, D.T.T.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Martin, T.G.; Hobson, K.A.; Wunder, M.B.; Norris, D.R. Tracking multi-generational colonization of the breeding grounds by monarch butterflies in Eastern North America. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flockhart, D.T.T.; Fitz-gerald, B.; Brower, L.P.; Derbyshire, R.; Altizer, S.; Hobson, K.A.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Norris, D.R. Migration distance as a selective episode for wing morphology in a migratory insect. Mov. Ecol. 2017, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobson, K.A.; Kardynal, K.J.; Koehler, G. Expanding the isotopic toolbox to track monarch butterfly (Danaus Plexippus) origins and migration: On the utility of stable oxygen isotope (δ18O) measurements. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora Alvarez, B.X.; Carrera-Treviño, R.; Hobson, K.A. Mortality of monarch butterflies (Danaus Plexippus) at two highway crossing “Hotspots” during autumn migration in northeast Mexico. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fager, E.W. Migration notes from Mexico. Lepidoptera News 1952, 6, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Clench, H.K. Butterflies from Coahuila, Mexico. J. Lepidopterists’ Soc. 1968, 22, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Neck, R.W. Causal analysis of a migration of the snout butterfly, Libytheana Bachmanii Iarvata (Strecker) (Libytheidae). J. Lepidopterists’ Soc. 1983, 37, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Sada, M.L.; Madero, F.A. Guía de Mariposas de Nuevo León; Fondo Editorial de Nuevo Leon, UANL: Monterrey, Mexico, 2011; ISBN 607-7577-76-6. [Google Scholar]
- Brock, J.P.; Kaufman, K. Butterflies of North America, Hillstar Editions L.C.; Houghton Mifflin Harcourt: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, V.J. Mariposas Del Sureste de Coahuila, 1st ed.; Secretaria de Medio Ambiente de Coahuila: Coahuila, Mexico, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Glassberg, J. A Swift Guide to Butterflies of Mexico and Central America, 2nd ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2018; ISBN 1-4008-8986-3. [Google Scholar]
- Layberry, R.A.; Hall, P.W.; Lafontaine, J.D. The Butterflies of Canada; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1998; ISBN 0-8020-7881-8. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A.H. Some observations on butterfly migrations. Sci. Mon. 1931, 32, 150–155. [Google Scholar]
- Menchaca, A. Vive Ciudad Lluvia de Mariposas. 2012. Available online: https://www.elnorte.com/vida (accessed on 23 February 2021).
- Helfert, M.R. Migratory behavior of the snout butterfly, Libytheana Bachmanii Larvata (Strecker). Entomol. News 1972, 83, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, C.B. Insect migration. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1957, 2, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.J. Butterfly migrations in Florida: Seasonal patterns and long-term changes. Environ. Entomol. 2001, 30, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Walker, T.J. Butterfly migration in the boundary layer. J. Lepidopterists’ Soc. 1985, 37, 704–723. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, L.D.; Clench, H.K. Some aspects of mating behavior in butterflies. J. Lepidopterists’ Soc. 1968, 22, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, G.T. Phenology and diversity of a butterfly population in Southern Arizona. J. Lepidopterists’ Soc. 1978, 32, 207–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wassenaar, L.I.; Hobson, K.A. Comparative equilibration and online technique for determination of non-exchangeable hydrogen of keratins for use in animal migration studies. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2003, 39, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, D.; Koehler, G.; Wassenaar, L.; Hobson, K. Determination of stable hydrogen isotopic compositions of complex organic materials: Contrasting the role of exchangeable hydrogen and residual moisture. Rapid Comm. Mass Spectrom 2017, 31, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobson, K.A.; Wunder, M.B.; Van Wilgenburg, S.L.; Clark, R.G.; Wassenaar, L.I. A Method for investigating population declines of migratory birds using stable isotopes: Origins of harvested lesser scaup in North America. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wilgenburg, S.L.; Hobson, K.A.; Brewster, K.; Welker, J. Assessing dispersal in threatened migratory birds using stable hydrogen isotope (ΔD) analysis of feathers. Endanger. Species Res. 2012, 16, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wunder, M.B. Using isoscapes to model probability surfaces for determining geographic origins. In Isoscapes: Understanding Movement, Pattern, and Process on Earth through Isotope Mapping; West, J.B., Bowen, G.J., Dawson, T.E., Tu, K.P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 251–270. ISBN 978-90-481-3354-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, G.J.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Hobson, K.A. Global application of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes to wildlife forensics. Oecologia 2005, 143, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, G.J. Gridded Maps of the Isotopic Composition of Meteoric Waters; The University of Utah: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020.
- RStudio Team RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2020.
- Hijmans, R.J. Raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling; R Package Version 33-13; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lamigueiro, O.P.; Hijmans, R. RasterVis. R Package Version 048; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pebesma, E.; Bivand, R. Classes and methods for Spatial Data in R. R. News 2005, 5, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pebesma, E. Simple features for R: Standardized support for spatial vector data. R. J. 2018, 10, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, G.B. A Migration of Klicogonia Castalia (Pieridae) in Northern Mexico. J. Lepidopterists’ Soc. 1971, 3, 124–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wassenaar, L.I.; Hobson, K.A. Natal origins of migratory monarch butterflies at wintering colonies in Mexico: New isotopic evidence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15436–15439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobson, K.A.; García-Rubio, O.R.; Carrera-Treviño, R.; Anparasan, L.; Kardynal, K.J.; Mcneil, J.; García-Serrano, E.; Mora Alvarez, B.X. Isotopic (δ2H) Analysis of stored lipids in migratory and overwintering monarch butterflies (Danaus Plexippus): Evidence for southern critical late-stage nectaring sites? Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 572140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, K.A.; Van Wilgenburg, S.L.; Faaborg, J.; Toms, J.D.; Rengifo, C.; Sosa, A.L.; Aubry, Y.; Brito Aguilar, R. Connecting breeding and wintering grounds of neotropical migrant songbirds using stable hydrogen isotopes: A call for an isotopic atlas of migratory connectivity: Isotopic atlas of connectivity. J. Field Ornithol. 2014, 85, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | N | Collection | δ2H (‰) Old Std | δ2H (‰) New Std |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. carinenta | 163 | 26 September to 4 November | −94.9±21.6a | −68.7±18.2 |
| E. claudia | 25 | 14 October to 20 November | −85.7±13.4b | −62.8±11.4 |
| D. gilippus | 100 | 14 October to 20 November | −82.9±10.7b | −59.6±9.1 |
| Z. cesonia | 73 | 26 September to 20 November | −81.1±11.4b | −58.5±9.7 |
| A. leilia | 38 | 8 October to 2 November | −70.42.5±6.3c | −50.9±5.4 |
| E. hegesia | 13 | 8 October to 4 November | −69.8±9.4c | −49.1±8.1 |
| P. sennae | 65 | 4 October to 20 November | −65.16.0±13.2c | −46.6±11.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hobson, K.A.; Kusack, J.W.; Mora-Alvarez, B.X. Origins of Six Species of Butterflies Migrating through Northeastern Mexico: New Insights from Stable Isotope (δ2H) Analyses and a Call for Documenting Butterfly Migrations. Diversity 2021, 13, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030102
Hobson KA, Kusack JW, Mora-Alvarez BX. Origins of Six Species of Butterflies Migrating through Northeastern Mexico: New Insights from Stable Isotope (δ2H) Analyses and a Call for Documenting Butterfly Migrations. Diversity. 2021; 13(3):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030102
Chicago/Turabian StyleHobson, Keith A., Jackson W. Kusack, and Blanca X. Mora-Alvarez. 2021. "Origins of Six Species of Butterflies Migrating through Northeastern Mexico: New Insights from Stable Isotope (δ2H) Analyses and a Call for Documenting Butterfly Migrations" Diversity 13, no. 3: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030102
APA StyleHobson, K. A., Kusack, J. W., & Mora-Alvarez, B. X. (2021). Origins of Six Species of Butterflies Migrating through Northeastern Mexico: New Insights from Stable Isotope (δ2H) Analyses and a Call for Documenting Butterfly Migrations. Diversity, 13(3), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030102







