Abstract
Nematode biodiversity is mostly unknown; while about 20,000 nematode species have been described, estimates for species diversity range from 0.1 to 100 million. The study of nematode diversity, like that of meiofaunal organisms in general, has been mostly based on morphology-based taxonomy, a time-consuming and costly task that requires well-trained specialists. This work represents the first study on the taxonomy of Mexican nematodes that integrates morphological and molecular data. We added eleven new records to the Mexican Caribbean nematode species list: Anticomidae sp.1, Catanema sp.1, Enoploides gryphus, Eurystomina sp.1, Haliplectus bickneri, Metachromadora sp.1, Odontophora bermudensis, Oncholaimus sp.1, Onyx litorale, Proplatycoma fleurdelis, and Pontonema cf. simile. We improved the COI database with 57 new sequences from 20 morphotypes. All COI sequences obtained in this work are new entries for the international genetic databases GenBank and BOLD. Among the studied sites, we report the most extensive species record (12 species) at Cozumel. DNA barcoding and species delineation methods supported the occurrence of 20 evolutionary independent entities and confirmed the high taxonomic resolution of the COI gene. Different approaches provided consistent results: ABGD and mPTP methods disentangled 20 entities, whereas Barcode Index Numbers (BINs) recovered 22 genetic species. Results support DNA barcoding being an efficient, fast, and low-cost method to integrate into morphological observations in order to address taxonomical shortfalls in meiofaunal organisms.
1. Introduction
Nematodes are hyper-diverse, abundant, and distributed worldwide [1]. Free-living species play critical ecological roles in benthic energy flow and contribute to the ecosystem by facilitating mineralization and nutrient cycling [2,3,4,5,6,7]. In the presence of high inputs of organic matter, their abundance increases, helping to regulate this resource. They are also a source of high-quality food for other animals [8,9,10,11]. Currently, about 20,000 nematode species—of which 6500 are marine benthic (= meiofaunal)—have been formally described [12,13], with estimates ranging between 0.1 and 100 million species [14]. The number of existing species is still uncertain because such estimates have been made at the local level, whereas little is known on a global scale. Gathering evidence of nematode diversity and distribution, increasing the record of marine nematodes species, especially in overlooked regions, is nowadays crucial [15].
Nematode taxonomy is an overlooked field of study in Mexico, with only about 119 genera and 183 species known for the country [16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. The majority of studies of marine nematodes in this region address ecological questions [17,18,19,20,21,23,24], whereas only five studies are focused on taxonomy [16,25,26,27]. For this reason, faunistic lists for nematodes in Mexico are at the family or genus level in most cases. The slow advance in the taxonomic knowledge of marine nematodes is due to technical difficulties. The identification of marine benthic nematodes is mostly based on morphological traits of male genital structures in mature individuals [28,29]. However, the occurrence of adult specimens is often rare. For this reason, nematode diversity is commonly disentangled to the family or genus level, especially in ecological studies. Morphology-based taxonomy is a time-consuming task that requires well-trained specialists who are becoming rare [30,31]. The use of morphological traits, in most cases, descriptive and potentially affected by convergent evolution and phenotypic plasticity, could also prevent an accurate quantification of the true nematode diversity [32,33,34]. Hence, there is an increasing need for methods that can rapidly and cost-effectively estimate nematode diversity in marine sediments. Molecular tools for taxonomic identification, delimitation of species, and an approach to the phylogeny hold the potential to overcome difficulties where morphological studies are painstakingly difficult and/or where the number of species far outweighs the availability of taxonomists. The identification of free-living marine nematodes is particularly difficult [35,36,37,38,39], and an integrated approach including genetic, morphological, and ideally, also ecological and behavioral data is needed [40].
Only one study conducted in Mexico (in Baja, CA, USA) [41] considered genetic tools to investigate the diversity of nematodes. Pereira and collaborators [41] revealed both a wide genetic diversity and geographic distribution of populations of Mesacanthion species. They used two molecular markers: 28S ribosomal rRNA gene and 18S, with 28S showing a better taxonomic resolution than 18S in delineating also cryptic species (similarly to [42]). The two markers did not show differences in the phylogenetic relationships among the investigated taxa, except for species of the genus Rhabdodemania [41].
In the Caribbean, two relevant studies have been conducted on the nematode fauna and none from Mexico [43,44]. In both studies, two molecular markers were considered: cytochrome oxidase subunit I (COI) and 18S ribosomal RNA gene (18S rRNA). Armenteros and collaborators [43] disentangled species of Desmodorid from Punta Francés, Cuba. They generated 34 sequences for COI across five genera and 27 sequences for 18S rRNA gene across six genera. Either marker could fully resolve the phylogenetic relationships of some lineages (i.e., within the subfamilies Desmodorinae and Spiriniinae). However, COI showed a better resolution than 18S among closely related and cryptic species. Macheriotou et al. [44] generated 18S and COI sequences from nematodes sampled in the equatorial North Pacific, Cuba, Italy (Panarea Island), Papua New Guinea, the Netherlands, Tunisia, and Vietnam. They generated 290 COI and 438 18S sequences; using reference databases for marine nematodes, they identified 39 OTUs (Operational Taxonomic Units with High Throughput Sequencing; HTS). Although the ribosomal marker outperformed the mitochondrial marker in terms of species and genus-level detections., they concluded that, for HTS technologies, it is urgent to continue creating high-quality taxon-specific reference sequence databases.
Free-living marine nematode species are poorly represented in public sequence databases. Limited availability of nematode reference sequences, especially from overlooked both localities and habitats such as the deep-sea, seagrass beds, and tropical coral reefs, hinders biogeographic patterns and characterization of ecosystems. Moreover, although DNA taxonomy is most successful when applied to fast-evolving genes such as the mitochondrial gene COI [42,45,46,47,48], genetic reference databases for nematodes mostly include nuclear markers such as 18S and 28S [36,43,48,49]. COI is poorly represented [44,47,50] because of the difficulty in amplifying this gene in a wide range of taxa within the phylum using ‘universal’ primers. Several studies regularly report low success in the amplification of COI and the necessity to design new specific primers to obtain a robust database [44,50,51]. The limited COI sequence datasets for marine nematodes prevent the establishment of an adequate understanding of intraspecific divergence.
The main objectives of this study are to (i) improve our knowledge of the geographic distribution of meiofaunal nematodes in the Mexican Caribbean; (ii) contribute with new COI sequences to the public genetic databases; and, (iii) apply different delimitation models to test the taxonomic resolution of COI in marine nematodes. Integrating different species delineation models should prevent biased conclusions and disclose patterns of diversity and distribution [52]. We aim to disentangle nematode diversity by applying Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery (ABGD) [53], Barcode Index Number system (BINs) [54], and Poisson Tree Processes model (PTP) [55] on COI sequences.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nematode Sampling and Identification
Marine meiofaunal nematodes were collected in March and September 2011 from the intertidal zone in seven sites along the coast of Quintana Roo State, Mexico (Figure 1, Table 1). Four sediment samples were collected from each site using a Falcon corer (10 × 2 cm) [56]. Individuals were extracted by decantation in the field using two sieves (180 and 63 µm mesh) and fixed with DESS solution [57] or Formalin 10% [58]. In the laboratory, individuals were separated one-by-one and picked up under a stereomicroscope (NIKON SMZ-1). Then, nematodes specimens were individually transferred to temporary slides in a drop of MilliQ water covered by a coverslip and observed with an OLYMPUS BX51 microscope at different magnifications (10×, 40×, and 100×). Well-preserved specimens were identified morphologically and photographed with a camera (Canon G11). When was possible, more than one representative for each morphotype was subsequently selected for further molecular analyses. Morphological identification was carried out using available taxonomic keys for marine nematodes and comparison with original descriptions using several morphological parameters: length and maximum body width, size and position of setae, size and position of amphids, cuticle ornamentation, size and shape of spicula, presence of precloacal supplements, type and tail size and de Man’s ratios (a, b and c): a = body length/body width, b = body length/esophagus length and c= body length/tail length [59,60,61].
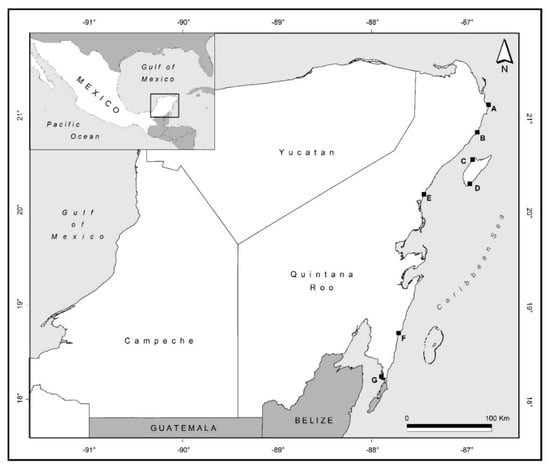
Figure 1.
Sampling localities from marine nematodes in the Mexican Caribbean. Site IDs (A, B, C, D, E, F, and G) are explained in Table 1.

Table 1.
List of sites where samples were collected. Coordinates are express in decimals *.
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and DNA Sequencing
Under the microscope, each selected nematode was removed from the temporary slide using a fine paintbrush, cut in pieces with a scalpel, and preserved in DESS. The DNA was extracted from single individual animals with a HotSHOT technique [62]. DNA was stored at 4 °C for further amplification of the COI gene. PCR reactions were performed in a final volume of 12.5 µL containing 6.25 µL of trehalose 10%, 2 µL of ddH20, 1.25 µL of 10X PCR Buffer, 0.625 µL of MgCl2 50 Mm, 0.125 µL of each primer (10 µM), 0.0625 µL of dNTPs (10 mM), 0.06 µL of Platinum® Taq Polymerase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), and 2.0 µL of DNA template [63]. We used two primer sets according to [64]: LC01490_t1 and HC02198_t1 (TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGTGGTCAACAAATCATAAAGATATTGG/ CAGGAAACAGCTATGACTAAACTTCAGGGTGACCAAAAAATCA); LC01490 and HC02198 (GGTCAACAAATCATAAAGATATTGG/ TAAACTTCAGGGTGACCAAAAAATCA). Thermocycler conditions, for both primer sets, were: 1 min at 94 °C, 5 cycles of 40 s at 94 °C, 40 s at 45 °C, and 1 min at 72 °C, followed by 35 cycles of 40 s at 94 °C, 40 s at 51 °C and 1 min at 72 °C, and a final extension of 5 min at 72 °C. PCR products were visualized on 2% agarose gels stained with ethidium bromide. Amplicons for LC01490_t1/LC01490_t1 were bidirectionally sequenced with M13F and M13R primers [65]; ABI 3730 capillary sequencer (ABI, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA, USA) using the BigDye© Terminator v.3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster, CA, USA). Sequences were obtained at the Canadian Centre for DNA Barcoding (CCDB) following standard protocols for high-volume samples [66].
2.3. Data Analysis
Sequences were assembled and edited with Codon Code Aligner v 3.0.3 software. The Clustal W program was used for the sequence alignment with default parameters. Phred score [67] was used to assess the quality of the sequences applying the following categories: no sequences = failed, mean Phred < 30 = low quality, 30 < mean Phred < 40 = medium quality, and mean Phred > 40 = high quality. Sequences with low quality and cross-contamination were removed for the analysis. COI sequences are available as part of the project FMN (Free-Living Marine Nematodes from Quintana Roo, Mexico) on Barcode of Life Data Systems (BOLD, www.boldsystems.org) [68].
Genetic divergence was calculated in MEGA v6 [69] using the Kimura two-parameter (K2P) distance model [70]. The presence of stop codons and indels was verified to discard any contaminants such as NUMTs (nuclear mitochondrial DNA segments) [71,72]. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) [73] and Identification Request, on GenBank and BOLD, respectively, were used to identify matches to the DNA sequences generated in this study.
2.4. Phylogenetic Tree Reconstruction and DNA Taxonomy
A Maximum-Likelihood (ML) tree was reconstructed in MEGA v6 software using 1000 bootstrap replications. The tree was reconstructed with sequences generated in this study and others retrieved from GenBank according to length, quality (stop codons presence), position (concerning barcoding region), and taxonomy (Accession numbers are in Supplement Table S1). The best-fitting substitution model was the General Time Reversible model with nonuniform evolutionary rates and invariant sites (GTR+G+I) and as chosen in MEGA. The COI sequence Bursaphelenchus sp. (order Tylenchina) was selected as the outgroup [74].
To delimit evolutionary independent entities of marine nematode species and test the resolution of the sequenced COI gene, we applied three methods: (1) Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery (ABGD) [53] with the following parameters: relative gap (X) of 1.1, minimal intraspecific distance (Pmin) of 0.001, maximal intraspecific distance (Pmax) of 0.1, K2P [70] and JC69 (Jukes-Cantor) [75] as distance metrics, (2) Barcode Index Number (BIN) system [54], and (3) mPTP by selecting single-locus species delimitation with p-value 0.001 (http://mptp.h-its.org/#/tree) [55].
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Identification
A total of 30 morphotypes from 107 individuals were identified. The list of morphotypes and sampling locations is available in Table 2. The order Enoplida was represented by the highest number of morphotypes (11), followed by Desmodorida and Chromadorida (7), Monhysterida (3), Aerolaimida (1) and Plectida (Table 2). Families Desmodoridae and Chromadoridae were the best represented with five genera each and six and five species, respectively. Eighteen specimens, all morphological very similar, belonged to the Spirinia genus. However, based on de Man´s ratios (different proportions of bulb and tail sizes), we considered the presence of two distinct morphotypes: Spirinia sp.1 and S. sp.2 (Figure 2). Such morphological differences are supported by the results of integrative taxonomy (see below).

Table 2.
Morphotypes identified at the collection sites. Species are listed by nematode Order. The number of individuals and COI sequences analyzed in this study are indicated. Taxonomy classification is based on Nemys database (www.marinespecies.org) [12]. Sites are indicated as below: Cancún = A; Puerto Morelos= B; Cozumel, Playa Azul = C; Cozumel, Punta Sur = D; Tulum = E; Mahahual = F; and Xcalak = G.
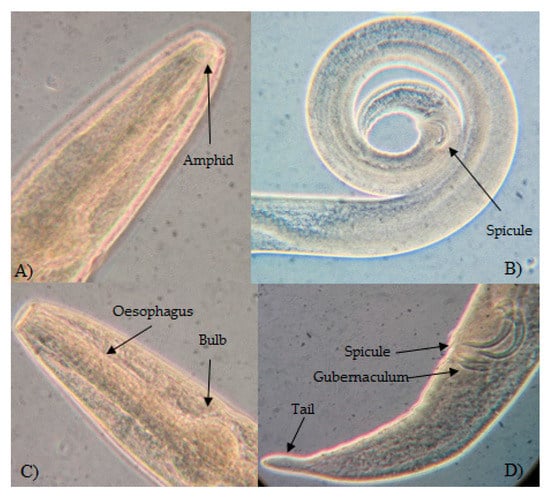
Figure 2.
Spirinia sp.2. Adult male. (A) Head showing circular amphid. (B) Posterior part of the body showing tail and spicule. (C) Anterior part of the body showing esophagus and esophageal bulb. (D) Posterior region showing spicule, gubernaculum, and tail shape.
In Tulum, one individual resembling the species Pontonema simile (Figure 3) was identified. This species was initially described by Southern as Oncholaimus similis [76] and redescribed by Filipjev [77] as P. simile. The Pontomema cf. simile reported in the present study had a shorter size (2100 µm) and a shorter spicule (32 µm) compared to the species described by Filipjev [77].
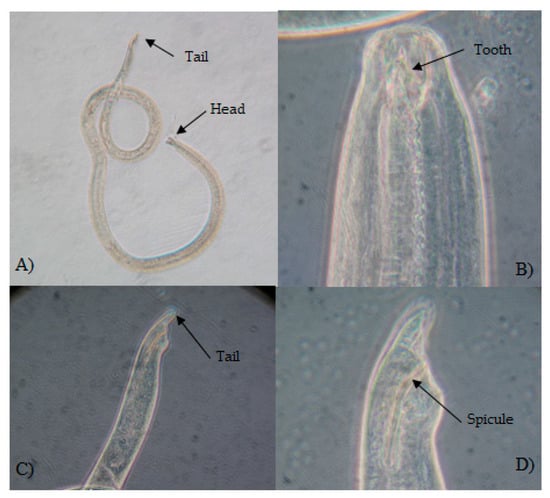
Figure 3.
Pontonema cf. simile (Southern, 1914) Filipjev, 1921. Collected in Tulum locality. Adult male. (A) Habitus. (B) Head showing dorsal tooth. (C) Tail short and rounded. (D) Posterior part of the body showing spicule and tail.
Among the sampled localities, Cozumel harbored the highest species richness (12 species), which all are new for this locality. From the other localities, we found fewer species but a greater abundance of individuals. Enoploides gryphus (Wieser & Hopper, 1967) is a new record for the Mexican Caribbean while Haliplectus bickneri (Chitwood, 1956), Proplatycoma fleurdelis (Hope, 1988), Pontonema cf. simile (Southern, 1914) Filipjev, 1921, Rhips sp.1, Epsilonema sp.1, Metachromadora sp.1, Spirinia sp.2, Odonthophora bermudensis (Jensen & Gerlach, 1976), Onyx litorale (Schulz, 1938), Epacanthion sp.1, Halalaimus sp.1, and Metaparoncholaimus sp.1, are new for Mexico.
3.2. Amplification and Sequencing
Overall, DNA amplification was successful for 67 individuals. However, sequences with low quality were discarded, and 57 sequences from 20 morphological species were considered (Table 2). Individuals of the species Actinonema sp.1, Epacanthion sp.1, Metaparoncholaimus sp.1, Odontophora bermudensis, Oncholaimus sp.1, Prochromadorella sp.1, and some specimens of chromadorids could not be sequenced (Table 2). All COI sequences produced in this study are new for the molecular databases GenBank and BOLD. According to Phred score [67], all sequences were of high quality (mean Phred > 40), longer than 500 bp (502–667 bp), and without internal stop codons. BLAST match values were between 71% and 85% with Nematoda. The mean genetic divergence was 0.43% and 26.45% for intraspecific and interspecific variation, respectively. In most cases, we observed a clear barcoding gap, although low interspecific variation was detected in a few cases (Figure 4). This study provides the first record of mtCOI sequence for Monoposthia mirabilis, Onyx litorale, Enoploides gryphus, Pontonema cf. simile, Proplatycoma fleurdelis, Xyala striata, and Haliplectus bickneri, and other higher-ranked taxa (Table 2).
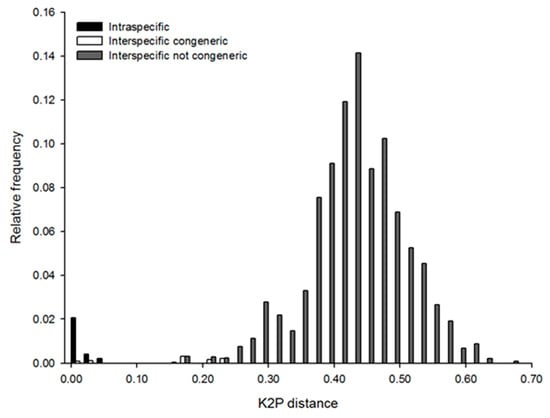
Figure 4.
Relative frequencies of Kimura two-parameter (K2P) distances in the COI sequences of marine nematodes analyzed in this study. Frequencies within species are marked in black, among congeneric species in white, and between species from different genera in grey.
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis and DNA Taxonomy
Maximum-likelihood analysis using the 57 COI sequences obtained in this work and an additional 70 [47,74,78,79] sequences from GenBank showed congruence between DNA barcode and morphological identification. Sequences were grouped in clusters represented by the morphological identity. The tree was supported in recent clades with bootstrap values >90% (Figure 5). The maximum genetic distance values were observed in Epsilonema sp.1 clade (4.02%) and Enoploides sp.2 (2.24%). The sequences of Spirinia sp.1 and S. sp.2, with interspecific divergence values of 7.7%, formed two distinct clades.
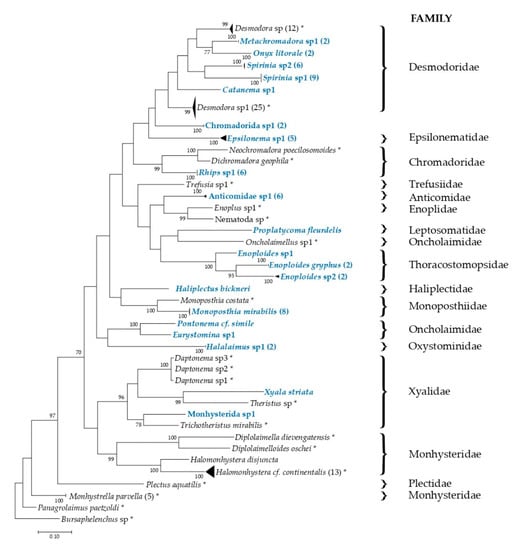
Figure 5.
Maximum-Likelihood tree reconstructed from COI DNA sequences based on GTR+G+I model. Sequences of marine nematodes from the present study are annotated according to their morphological identification. The 20 haplotypes generated in this study are highlighted in blue color. Numbers in parentheses refer to the number of specimens sequenced. Reference of 70 sequences obtained from GenBank are indicated with an asterisk. Accession numbers are in Supplementary Table S1. Higher taxa (families) are indicated behind the line. Classification is based on Nemys database in www.marinespecies.org [12]. Arely Martínez 2020 ©
To ascertain the number of entities, sequences obtained in this work were analyzed using three different methods: ABGD, mPTP, and BINs (Table 3). ABGD analysis with K2P showed 20 initial and 25 recursive partitions with prior maximal distances (PMD) of 0.0010; 20 initial and 21 recursive partitions with PMDs ranging from 0.0017 to 0.0028; and 20 initial and 20 recursive partitions with PMDs ranging from 0.0046 to 0.0129. With the JC69 model, the same results were observed (see Table 3). The mPTP method based on our phylogenetic tree recovered 20 evolutionary independent entities (p = 0.001). BINs split Enoploides sp.2 and Epsilonema sp.1: BOLD: AAU8181 (n = 1) and BOLD: AAU8183 (n = 1) for the first species, and BOLD: AAU8184 (n = 4); BOLD: AAV1242 (n = 1) for the second species. A total of 22 BINs were recovered. Interestingly, results obtained with integrative taxonomy supported that Spirinia sp.1 and S. sp.2 are two distinct species.

Table 3.
Evolutionary independent entities recovered from the COI sequences with the three different delimitation algorithms. Relative gap (X) of 1.1, minimal intraspecific distance (Pmin) of 0.001, maximal intraspecific distance (Pmax) of 0.1, K2P [70], and JC69 (Jukes-Cantor) [75] were selected as distance metrics. I = Initial partition, R= Recursive partition. EiEs = Evolutionary Independent Entities.
4. Discussion
4.1. Diversity and Distribution of Meiofaunal Marine Nematodes in Mexico
This study contributes to the current knowledge of the diversity and distribution of meiofaunal marine nematodes in Mexico. The faunistic information in Mexico, and Central America, in general, is traditionally scarce, reflecting the low number of taxonomic experts in the area [80]. Until now, a total of 183 species of marine nematodes are known for Mexico, of which seven have type locality in Mexico [16,22,26,81,82]. In the Mexican Caribbean specifically, there are few ecological and taxonomic studies focusing on marine nematodes [17,18,20] with Isla Mujeres and Banco Chinchorro being the most investigated localities. The Chromadorida order was the most represented in both sites [18,20]. Our results confirm the presence of Terschellingia longicaudata (de Man, 1907), Monoposthia mirabilis (Schulz, 1932), and Xyala striata (Cobb, 1920), all species that have been previously reported for Isla Mujeres [20].
This study adds twelve morphological records to the Mexican list of marine nematodes. Specifically, Haliplectus bickneri, Proplatycoma fleurdelis, Pontonema cf. simile, Rhips sp.1, Epsilonema sp.1, Metachromadora sp.1, Spirinia sp.2, Odonthophora bermudensis, Onyx litorale, Epacanthion sp.1, Halalaimus sp.1, and Metaparoncholaimus sp.1 are all new records for the country. Due to specimen immaturity and small sample size, it is necessary to collect additional specimens to obtain proper identification for some of the sampled taxa (e.g., Anticomid, chromadorid, and monhysterid).
The report of Desmodoridae taxon is particularly relevant. This family is globally represented with a high number of species (320 species) [80]. Nevertheless, genetic sequence records for this family are scarce compared with the number of species described [80]. Here, we add 20 COI new sequences from Desmodoridae taxa. However, species identification based only on morphology was particularly tricky due to the lack of well-defined diagnostic traits, weak taxonomic keys reference, and absence of updated databases, including species lists [43,47,80].
We report for the first time meiofaunal nematode species from the Cozumel Island, namely Chromadorita sp.1, Catanema sp.1, Epsilonema sp.1, Epacanthion sp.1, Eurystomina sp.1, two species of Enoploides, Monoposthia mirabilis, Odontophora bermudensis, Onyx litorale, Proplatycoma fleurdelis, and Xyala striata. Cozumel was represented by the highest number of species, supporting that islands, with a high grade of endemism [83], are particularly relevant areas for the study of biodiversity also for meiofaunal species.
Regarding P. simile, specimens found in this work are very similar to the ones described by Southern, 1914 [76], due to comparable buccal cavities with a dorsal tooth, tail shapes, and spicules size. However, we hypothesize that the Mexican record may correspond to a new species for science. First, the original record was found in the intertidal zona of West Ireland, far away from our sample locality. Second, spicule size and total length are appreciably different in individuals from the two populations. Additional investigations comparing specimens from both localities are needed to support our hypothesis.
Individuals of Monoposthia mirabilis, Epsilonema sp.1, and Onyx litorale, were respectively represented by the same COI haplotypes even across different sampling sites, including Cozumel Island and continental sites such as Cancún, Puerto Morelos, Tulum, Mahahual, and Xcalak. This observation suggests that such species have a widespread distribution and a low genetic divergence within and among populations. Therefore, individuals of M. mirabilis reported for Isla Mujeres [20] and Onyx litorale for Cuba [80], could belong to the same, widely distributed, species.
4.2. COI Amplification
We recommend using HotSHOT technique to extract DNA from marine nematodes [62] because, at least in our study, it provided fairly good results. However, the amplification success rate was difficult (85.07%), confirming previous studies [44,47,79,84]. The problem lies in the high mitochondrial genome diversity among nematodes [85,86,87] and, consequently, a low success rate using universal primers as well as low availability of specific primers for the Nematoda group [47,88]. In five individuals, the length of COI sequences varied (approximately 150 bp) but these sequences were not found related to any nematode taxa at the rank of genus or family. Specifically, we consistently observed a low success of COI amplification for Epacanthion sp.1, Halalaimus sp.1, Prochromadorella sp.1, Proplatycoma fleurdelis, Odontophora bermudensis, and Oncholaimus sp.1, which highlights the need for new primers specifically designed for these taxa. COI sequences obtained by combining existing protocols developed for zooplankton eggs [62] and by Ivanova et al. for invertebrates [63], allowed us to obtain high-quality DNA barcodes and amplify the complete ‘barcode region’ (> 500 bp). Obtaining long sequences is particularly important; when COI sequences are amplified in a region without a definite barcoding gap (e.g., JB2/JB3) due to overlapping intra/inter-specific distances, the delineation of species boundaries could be unreliable [44,79,84]. Although not all the sequences could be assigned to a species-level taxon, our results will significantly help the taxonomic identification of nematodes in further studies and when high-throughput sequencing approach on environmental DNA is applied.
4.3. Integrative Taxonomy
COI sequences generated in this work contribute to increasing the record of public genetic repositories and are references for future studies focused on the patterns of diversity and distribution of marine nematodes. In meiofauna and particularly marine nematodes, taxonomic gaps may be compensated only with the integration of DNA and morphological-based taxonomy [31,46]. The combination of both approaches allows us to disentangle diversity at the species level. For example, the two Spirinias species showed different morphological traits. However, we could certainly assign them to different species only through integrative taxonomy. In fact, all specimens of Sprinia sp.1 were immature, although preliminary observations allowed to ascribe this species to either S. parasitifera or S. septentrionalis, both previously reported for Mexico [20,22]. Spirinia sp.2 was represented by several adult specimens. However, none of the morphometric measurements were sufficient to ascribe them to a known species. Spirinia sp.2 could be ascribed to S. amata or S. parasitifera because of the number of precloacal supplements; however, the larger size of spicules and larger total length size suggest similarities with S. inaurita. We do not discard the possibility that Spirinia sp.2 could belong to new species to science.
4.4. Application of Species Delineation Models to Disentangle Diversity
Our results confirm the advantage of disentangling species and estimating marine nematode diversity using the COI gene. Fast-evolving genes and relatively short genes such as mtCOI are not expected to resolve the phylogenetic relationships in the deeper nodes [39,89]. The use of a multiple-gene approach is needed to clarify the tree topology, thereby uncovering phylogeographic relationships and historical biogeography within the group [42]. However, as previous studies suggested, mtCOI can resolve relationships among closely related species [79] and, as suggested by Derycke et al. [47], we support that COI is a useful biomarker to disentangle the diversity of nematodes to the species level. The design of new primers for different taxonomic groups of marine nematodes and the increase of COI data sequences will advance our knowledge of the diversity in different ecosystems [84] as well as provide a better estimate of global species diversity [44].
Analytical methods ABGD and mPTP supported the presence of the 20 species identified morphologically. The ABGD method relies on user-selected parameters (distance model and a prior limit on intraspecific divergence). In our case, we took care not to select a high prior intraspecific divergence (P) to avoid combining all sequences in one single group [53]. For this reason, a prior value was set after analyzing the interspecific divergence values within our generated sequences. The value of 0.01 for prior intraspecific divergence showed the strongest congruence between groups recovered and species defined as proposed by Puillandre et al. [53]. Moreover, we obtained an equal number of groups after the third partition (P = 0.0046) with both models (K2P and JC9); this supports that the threshold for the barcoding gap in the sequences considered in this work is well-defined.
The BINs method showed a 90% match for the recovered evolutionary independent entities. Only Epsilonema sp.1 and Enoploides sp.2 were split into four BIN numbers. It is essential to consider that this method initially employs single linkage clustering, coupled with a 2.2% threshold to establish preliminary OTU boundaries [54]. If the threshold is higher than 2.2%, the method tends to separate a higher number of entities and overestimate diversity. Epsilonema sp.1 and Enoploides sp.2 both showed the highest intraspecific divergence values > 4% (4.02% and 2.24% respectively), although they are identical morphologically. Based on all the criteria, we recognized Epsilonema sp.1 and Enoploides sp.2 as a single species, concordantly to the results obtained by applying ABGD and mPTP methods. We should carefully consider the BIN numbers as a tool for disentangling nematode species until a more robust genetic database is developed.
5. Conclusions
Our work contributes towards building a more robust taxonomic and genetic database of meiofaunal nematodes, as well as advancing our knowledge of nematode diversity and distribution. At present, DNA sequencing techniques have opened up new possibilities for taxonomic research in meiofaunal nematodes. However, barcode sequences from marine nematodes are underrepresented in light of the diversity of the phylum [34]. Our study combines classical morphology-based taxonomy with DNA sequences to successfully delimit 20 marine nematode species. Although a new set of primers should be designed for some species, our data support that the COI gene represents an excellent molecular marker to disentangle nematode diversity. Moreover, we validate and support the intraspecific distance value threshold of 5% for nematode species [43,47,84]. Lastly, our study reports new records from an unexplored region and contributes to understanding patterns of diversity and distribution of nematodes in Mexico and worldwide.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1424-2818/12/3/107/s1, Table S1: Records downloaded from GenBank and using for reconstructing the Maximum-likelihood tree.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M.-A. and F.L.; data curation, A.M.-A., A.D.J.-N., and F.L.; formal analysis, A.M.-A. and F.L.; funding acquisition, A.M.-A.; investigation, A.M.-A., A.D.J.-N., and F.L.; methodology, A.M.-A.; project administration, A.M.-A.; software, F.L.; validation, A.D.J.-N. and F.L.; writing – review & editing, A.M.A., A.D.J.-N., and F.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT) through the Red MEXBOL Project no. 271108.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jose Angel Cohuo, Mario Yescas, and Blanca Prado for assistance during fieldwork; Jessica Landeros and Josué Puc for their help during editing; Yareli Cota for nematodes mounts; Holger Weissenberger for elaborating the map; Ruth Gingold (sweepandmore.com) for proofreading earlier versions of the manuscript; and, finally, the Canadian Center of DNA Barcoding (CCBD) for support during the sequencing process.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Van Den Hoogen, J.; Geisen, S.; Routh, D.; Ferris, H.; Traunspurger, W.; Wardle, D.A.; de Goede, R.G.M.; Adams, B.J.; Ahmad, W.; Andriuzzi, W.S.; et al. Soil nematode abundance and functional group composition at a global scale. Nature 2019, 572, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heip, C.; Vincx, M.; Vranken, G. Ecolgy of marine nematodes. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1985, 23, 399–489. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeeren, H.; Vanreusel, A.; Vanhove, S. Species distribution within the free-living marine nematode genus Dichromadora in the Weddell Sea and adjacent areas. Deep. Res. Part II-Top. Stud. Ocean. 2004, 51, 1643–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufahja, F.; Vitiello, P.; Aissa, P. More than 35 years of studies on marine nematodes from Tunisia: A checklist of species and their distribution. Zootaxa 2014, 3786, 269–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, K.G.M.T.; Pattnaik, A.K.; Rastogi, G.; Bhadury, P. An inventory of free-living marine nematodes from Asia’s largest coastal lagoon, Chilika, India. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 23, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semprucci, F. Marine nematodes from the shallow subtidal coast of the Adriatic Sea: Species list and distribution. Int. J. Biodivers. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semprucci, F.; Balsamo, M.; Frontalini, F. La comunidad de nematodos de una laguna costera (Laguna de Varano, Italia meridional): Patrones de la ecología y la biodiversidad. Sci. Mar. 2014, 78, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, D.A.S.; Derycke, S.; Da Rocha, C.M.C.; Barbosa, D.F.; Decraemer, W.; Dos Santos, G.A.P. Spatiotemporal variation and sediment retention effects on nematode communities associated with Halimeda opuntia (Linnaeus) Lamouroux (1816) and Sargassum polyceratium Montagne (1837) seaweeds in a tropical phytal ecosystem. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diane, Z.M.; Gouvello, L.; Nel, R.; Harris, L.R.; Bezuidenhout, K. The response of sandy beach meiofauna to nutrients from sea turtle eggs. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2017, 487, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, S.L.; Hebert, P.D.N.; Burian, S.K.; Webb, J.M. Biological identifications of mayflies (Ephemeroptera) using DNA barcodes. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2006, 24, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaglia, S.; Nascimento, F.J.A.; Bartoli, M.; Klawonn, I.; Brüchert, V. Meiofauna increases bacterial denitrification in marine sediments. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Register of Marine Species. Available online: www.marinespecies.org (accessed on 13 January 2017).
- Hugot, J.P.; Baujard, P.; Morand, S. Biodiversity in helminths and nematodes as a field of study: An overview. Nematology 2001, 3, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambshead, P.J.D. Marine nematode biodiversity. In Nematology: Advances and perspectives Nematode Morphology, Physiology and Ecology; Chen, Z.X., Chen, S.Y., Dickson, D.W., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2004; pp. 436–467. [Google Scholar]
- Coomans, A. Present status and future of nematode systematics. Nematology 2002, 4, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Fernandez, D.; Lambshead, P.J.D. Revision of the genus Elzalia Gerlach, 1957 (Nematoda: Xyalidae) including three new species from an oil producing zone in the Gulf of Mexico, with a discussion of the sibling species problem. Bull. Br. Museum Natural Hist. Zool. Ser. 1990, 56, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- De Jesús-Navarrete, A.; Herrera-Gómez, J. Vertical distribution and feeding types of nematodes from Chetumal Bay, Quintana Roo, Mexico. Estuaries 2002, 25, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesús-Navarrete, A. Diversity of nematoda in a Caribbean atoll: Banco Chinchorro, Mexico. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2003, 73, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- De Jesús-Navarrete, A. Littoral free living nematode fauna of Socorro Island, Colima, Mexico. Hidrobiologica 2007, 17, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- De Jesús-Navarrete, A. Nematodos de los arrecifes de Isla Mujeres y Banco Chinchorro, Quintana Roo, México. Rev. Biol. Mar. Oceanogr. 2007, 42, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesús-Navarrete, A. Distribución, abundancia y diversidad de los nematodos (Phylum Nematoda) bénticos de la Sonda de Campeche, México. Enero 1987. Rev. Biol. Trop. 1993, 41, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Comision Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/conabio (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- De Jesús-Navarrete, A.; Herrera-Gómez, J. Nematofauna asociada a la zona urbana de la bahía de Chetumal, Quintana Roo, México. Rev. Biol. Trop. 1999, 47, 867–875. [Google Scholar]
- Gingold, R.; Mundo-Ocampo, M.; Holovachov, O.; Rocha-Olivares, A. The role of habitat heterogeneity in structuring the community of intertidal free-living marine nematodes. Mar. Biol. 2010, 157, 1741–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holovachov, O.; Tandingan De Ley, I.; Mundo-Ocampo, M.; Baldwin, J.G.; Rocha-Olivares, A.; De Ley, P. Nematodes from the Gulf of California. Part 1. The genera Ceramonema Cobb, 1920, Pselionema Cobb in Cobb, 1933 and Pterygonema Gerlach, 1954 (Nematoda: Ceramonematidae). Nematology 2008, 10, 347–373. [Google Scholar]
- Holovachov, O.; Mundo-Ocampo, M.; De Ley, I.T.; De Ley, P. Nematodes from the gulf of California. Part 2. Ceramonema nasobema sp. n. (nematoda: Ceramonematidae). Nematology 2008, 10, 835–844. [Google Scholar]
- Mundo-Ocampo, M.; Lambshead, P.J.D.; Debenham, N.; King, I.W.; De Ley, P.; Baldwin, J.G.; De Ley, I.T.; Rocha-Olivares, A.; Waumann, D.; Thomas, W.K.; et al. Biodiversity of littoral nematodes from two sites in the Gulf of California. Hydrobiologia 2007, 586, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ley, P. Lost in worm space: Phylogeny and morphology as road maps to nematode diversity. Nematology 2002, 2, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, T. Nematode molecular diagnostics: From bands to barcodes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2004, 42, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bik, H.M. Let’s rise up to unite taxonomy and technology. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leasi, F.; Sevigny, J.L.; Laflamme, E.M.; Artois, T.; Curini-Galletti, M.; de Jesus Navarrete, A.; Di Domenico, M.; Goetz, F.; Hall, J.A.; Hochberg, R.; et al. Biodiversity estimates and ecological interpretations of meiofaunal communities are biased by the taxonomic approach. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derycke, S.; Remerie, T.; Vierstraete, A.; Backeljau, T.; Vanfleteren, J.; Vincx, M.; Moens, T. Mitochondrial DNA variation and cryptic speciation within the free-living marine nematode Pellioditis marina. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 300, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ley, P.; Tandingan De Ley, I.; Morris, K.; Abebe, E.; Mundo-Ocampo, M.; Yoder, M.; Heras, J.; Waumann, D.; Rocha-Olivares, A.; Burr, A.H.J.; et al. An integrated approach to fast and informative morphological vouchering of nematodes for applications in molecular barcoding. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. B 2005, 360, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, N.R.R.; Da Silva, M.C.; Genevois, V.F.; Esteves, A.M.; De Ley, P.; Decraemer, W.; Rieger, T.T.; Dos Santos Correia, M.T. Marine nematode taxonomy in the age of DNA: The present and future of molecular tools to assess their biodiversity. Nematology 2010, 12, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Gregory, T.R. The promise of DNA barcoding for taxonomy. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadury, P.; Austen, M.C.; Bilton, D.T.; Lambshead, P.J.D.; Rogers, A.D.; Smerdon, G.R. Development and evaluation of a DNA-barcoding approach for the rapid identification of nematodes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 320, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadury, P.; Austen, M.C. Barcoding marine nematodes: An improved set of nematode 18S rRNA primers to overcome eukaryotic co-interference. Hydrobiologia 2010, 641, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaneto, D.; Flot, J.F.; Tang, C.Q. Guidelines for DNA taxonomy, with a focus on the meiofauna. Mar. Biodiv. 2015, 45, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaxter, M.L. The promise of a DNA taxonomy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2004, 359, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayrat, B. Towards integrative taxonomy? Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2005, 85, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.J.; Fonseca, G.; Mundo-Ocampo, M.; Guilherme, B.C.; Rocha-Olivares, A. Diversity of free-living marine nematodes (Enoplida) from Baja California assessed by integrative taxonomy. Mar. Biol. 2010, 157, 1665–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leasi, F.; Andrade, S.C.D.S.; Norenburg, J. At least some meiofaunal species are not everywhere. Indication of geographic, ecological and geological barriers affecting the dispersion of species of Ototyphlonemertes (Nemertea, Hoplonemertea). Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 1381–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenteros, M.; Rojas-Corzo, A.; Ruiz-Abierno, A.; Derycke, S.; Backeljau, T.; Decraemer, W. Systematics and DNA barcoding of free-living marine nematodes with emphasis on tropical desmodorids using nuclear SSU rDNA and mitochondrial COI sequences. Nematology 2014, 16, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macheriotou, L.; Guilini, K.; Bezerra, T.N.; Tytgat, B.; Nguyen, D.T.; Phuong Nguyen, T.X.; Noppe, F.; Armenteros, M.; Boufahja, F.; Rigaux, A.; et al. Metabarcoding free-living marine nematodes using curated 18S and CO1 reference sequence databases for species-level taxonomic assignments. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 1211–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, S.; Alcántara-Rodríguez, J.A.; Ciros-Pérez, J.; Gómez, A.; Hagiwara, A.; Galindo, K.H.; Jersabek, C.D.; Malekzadeh-Viayeh, R.; Leasi, F.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Fifteen species in one: Deciphering the Brachionus plicatilis species complex (Rotifera, Monogononta) through DNA taxonomy. Hydrobiologia 2017, 796, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Q.; Leasi, F.; Obertegger, U.; Kieneke, A.; Barraclough, T.G.; Fontaneto, D. The widely used small subunit 18S rDNA molecule greatly underestimates true diversity in biodiversity surveys of the meiofauna. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16208–16212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derycke, S.; Vanaverbeke, J.; Rigaux, A.; Backeljau, T.; Moens, T. Exploring the use of cytochrome oxidase c subunit 1 (COI) for DNA barcoding of free-living marine nematodes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadury, P.; Austen, M.C.; Bilton, D.T.; Lambshead, P.J.D.; Rogers, A.D.; Smerdon, G.R. Evaluation of combined morphological and molecular techniques for marine nematode (Terschellingia spp.) identification. Mar. Biol. 2008, 154, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, R.; Abebe, E.; Papert, A.; Blaxter, M. Molecular barcodes for soil nematodes identification. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derycke, S.; De Ley, P.; Tandingan De Ley, I.; Holovachov, O.; Rigaux, A.; Moens, T. Linking DNA sequences to morphology: Cryptic diversity and population genetic structure in the marine nematode Thoracostoma trachygaster (Nematoda, Leptosomatidae). Zool. Scr. 2010, 39, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Ratnasingham, S.; DeWaard, J.R. Barcoding animal life: Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. B 2003, 270, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekkonen, M.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcode-based delineation of putative species: Efficient start for taxonomic workflows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Lambert, A.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for primary species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. A DNA-Based Registry for All Animal Species: The Barcode Index Number (BIN) System. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kapli, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A. A general species delimitation method with applications to phylogenetic placements. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traunspurger, W. The biology and ecology of lotic nematodes. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 44, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, M.; Tandingan De Ley, I.; King, I.W.; Mundo-Ocampo, M.; Mann, J.; Blaxter, M.; Poiras, L.; De Ley, P. DESS: A versatile solution for preserving morphology and extractable DNA of nematodes. Nematology 2006, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerfield, P.J.; Warwick, R.M.; Moens, T. Meiofauna Techniques. In Methods for the study of marine benthos; Wiley Online Books: Chichester, UK, 2005; pp. 229–272. ISBN 9780470995129. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, H.M.; Warwick, R.M. Freeliving Marine Nematodes. Part 1: British Enoplids. Pictorial Key to World Genera and Notes for the Identification of British Species; Cambridge University Press, for the Linnean Society of London and the Estuarine and Brackish-water Sciences Association: Cambridge, UK, 1983; ISBN 0521254221. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, H.M.; Warwick, R.M. Free Livng Marine Nematodes: Part II British Chromadorids. Pictoral Key to World Genera and Notes for the Identification of British Species. Synopses of the British Fauna; Brill, E.J., Backhuys, W., Eds.; Linnean Society of London and the Estuarine and Brackish-water Sciences Association: Leiden, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Warwick, R.M.; Platt, H.M.; Somerfield, P.J. Free Living Marine Nematodes: Pictorial Key to World Genera and Notes for the Identification of British Species. Part III, Monhysterids; Bames, R.S.K., Crothers, J.H., Eds.; Linnean Society of London and the Estuarine and Coastal Sciences Association by Field Studies Council: Dorchester, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Montero-Pau, J.; Gómez, A.; Muñoz, J. Application of an inexpensive and high-throughput genomic DNA extraction method for the molecular ecology of zooplanktonic diapausing eggs. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2008, 6, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.V.; Grainger, C. Increased DNA barcode recovery using Platinum taq. CCDB Adv.: Methods Release 2006, 2, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Hajibabaei, M.; DeWaard, J.R.; Ivanova, N.V.; Ratnasingham, S.; Dooh, R.T.; Kirk, S.L.; Mackie, P.M.; Hebert, P.D.N. Critical factors for assembling a high volume of DNA barcodes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2005, 360, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.V.; Dewaard, J.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. An inexpensive, automation-friendly protocol for recovering high-quality DNA. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, B.; Green, P. Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res. 1998, 8, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System (www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richly, E.; Leister, D. NUMTs in sequenced eukaryotic genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Buhay, J.E.; Whiting, M.F.; Crandall, K.A. Many species in one: DNA barcoding overestimates the number of species when nuclear mitochondrial pseudogenes are coamplified. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13486–13491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.; Madden, T.; Schaffer, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D. Gapped blast and psi-blast: A new generation of protein database search programs. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazir, C.; Giblin-Davis, R.M.; Keskin, N.; Ye, W.; Hazir, S.; Scheuhl, E.; Thomas, W.K. Diversity and distribution of nematodes associated with wild bees in Turkey. Nematology 2010, 12, 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Jukes, T.H.; Cantor, C. Evolution of Protein Molecules. In Mammalian Protein Metabolism; Munro, H.N.E., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 21–132. [Google Scholar]
- Southern, R. Nemathelmaia, Kinorhyncha, and Chaetognatha. Proc. R. Irish Acad. 1914, 31, 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Filipjev, I.N. Free-living marine nematodes of the Sevastopol area. Trudy Osob. Zool. Lab. Sebastop. Biol. Sta. 1921, II, 351–614. [Google Scholar]
- Velasco-Castrillón, A.; Stevens, M.I. Morphological and molecular diversity at a regional scale: A step closer to understanding Antarctic nematode biogeography. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauquier, F.; Leliaert, F.; Rigaux, A.; Derycke, S.; Vanreusel, A. Distinct genetic differentiation and species diversification within two marine nematodes with different habitat preference in Antarctic sediments. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenteros, M.; Ruiz-Abierno, A.; Decraemer, W. Revision of Desmodorinae and Spiriniinae (Nematoda: Desmodoridae) with redescription of eight known species. Eur. J. Taxon. 2014, 96, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Fernandez, D.; Decraemer, W. Cheironchus paravorax n. sp. and Cheironchus vorax Cobb, 1917 from the Campeche Sound, an oil producing zone in the Gulf of Mexico (Nemata: Selachinematidae). Bull. l’Institut R. des Sci. Nat. Belgique 1993, 63, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Holovachov, O.; De Ley, I.T.; Mundo-Ocamnpo, M.; Gingold, R.; De Ley, P. Nematodes from the Gulf of California. Part 3. Three new species of the genus Diplopeltoides Gerlach, 1962 (Nematoda: Diplopeltoididae) with overviews of the genera Diplopeltis Gerlach, 1962 and Diplopeltula Gerlach, 1950. Russ. J. Nematol. 2009, 17, 43–57. [Google Scholar]
- Witt, C.C.; Maliakal-Witt, S. Why are diversity and endemism Linked on islands? Ecography 2007, 30, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avó, A.P.; Daniell, T.J.; Neilson, R.; Oliveira, S.; Branco, J.; Adão, H. DNA Barcoding and morphological identification of benthic nematodes assemblages of estuarine intertidal sediments: Advances in molecular tools for biodiversity assessment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okimoto, R.; Macfarlene, J.L.; Clary, D.O.; Wolstenholme, D.R. The mitochondrial genomes of two nematodes, Caenorhabditis elegans and Ascaris suum. Genetics 1992, 130, 471–498. [Google Scholar]
- Ekrem, T.; Willassen, E.; Stur, E. A comprehensive DNA sequence library is essential for identification with DNA barcodes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 43, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsasser, S.C.; Floyd, R.; Hebert, P.D.N.; Schulte-Hostedde, A.I. Species identification of North American guinea worms (Nematoda: Dracunculus) with DNA barcoding. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, S.W.J.; Velarde-Aguilar, M.G.; León-Règagnon, V.; Hebert, P.D.N. Advancing nematode barcoding: A primer cocktail for the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene from vertebrate parasitic nematodes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leasi, F.; Norenburg, J.L. The necessity of DNA taxonomy to reveal cryptic diversity and spatial distribution of meiofauna, with a focus on nemertea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).