Evaluation of Metabarcoding Primers for Analysis of Soil Nematode Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
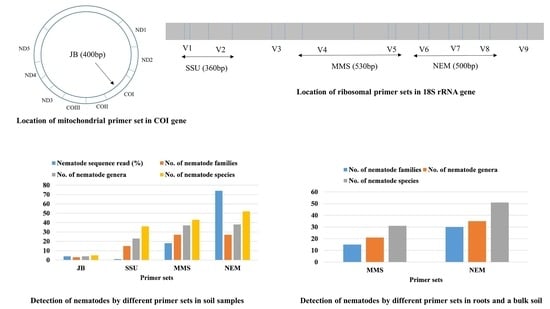
2.1. Primer Sets
2.2. Nematode Species, Mock Communities and Soil Samples
2.3. Root Samples
2.4. DNA Extraction, PCR and Sequencing Library Preparation
2.5. Sequence Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
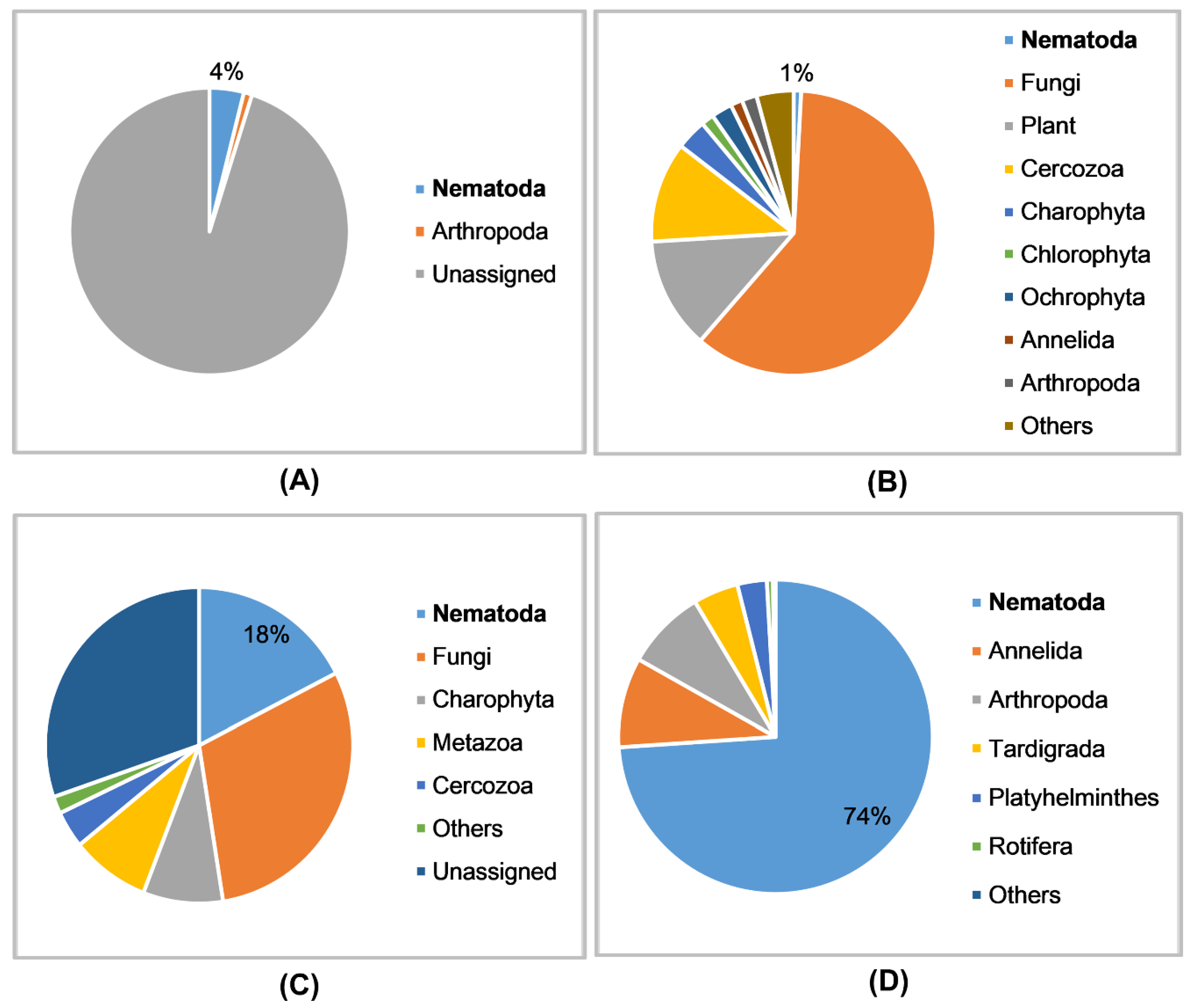
3.1. Data Characteristics
3.2. Individual Nematode Species
3.3. Mock Communities
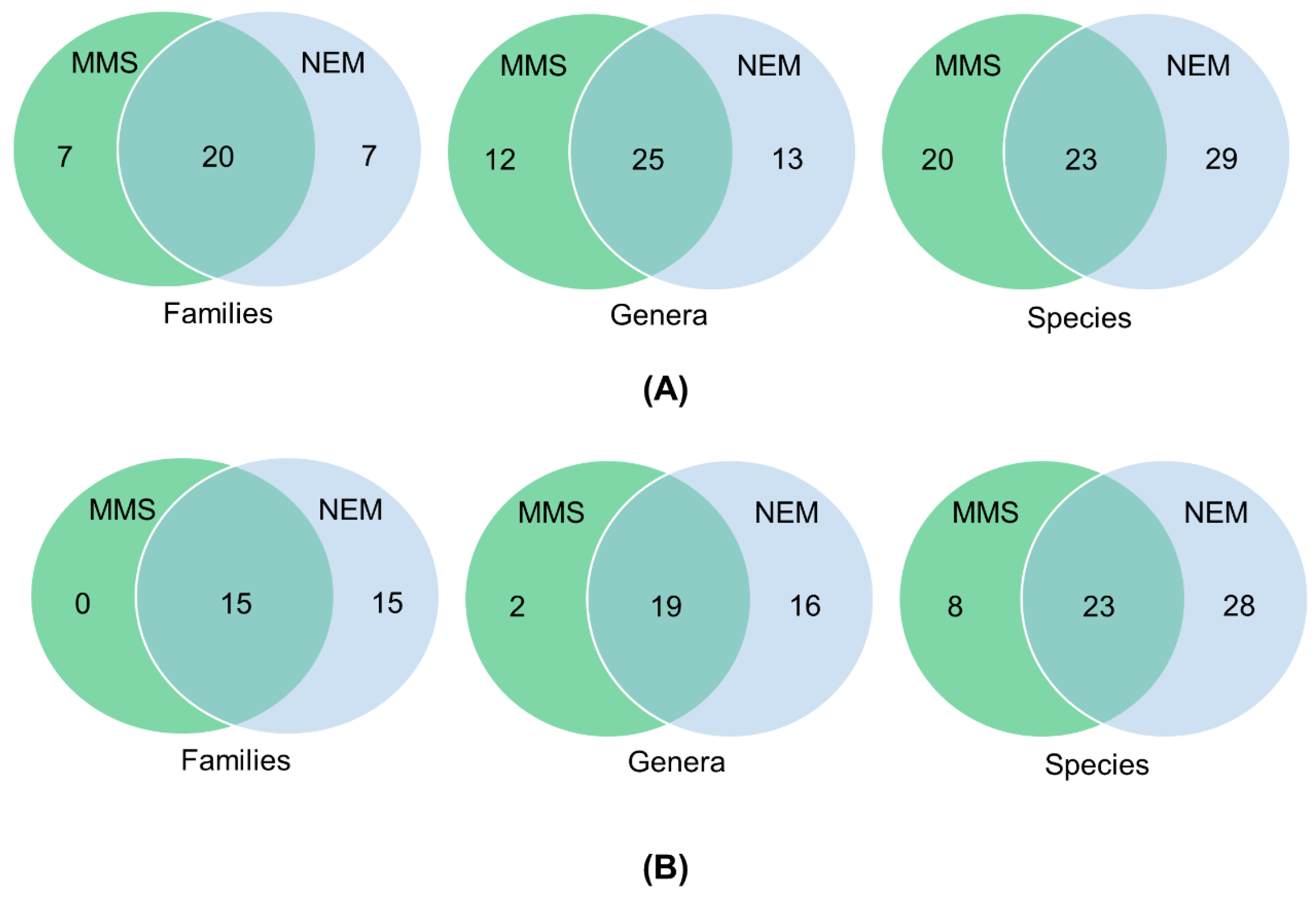
3.4. Detection of Nematodes in Soil Samples
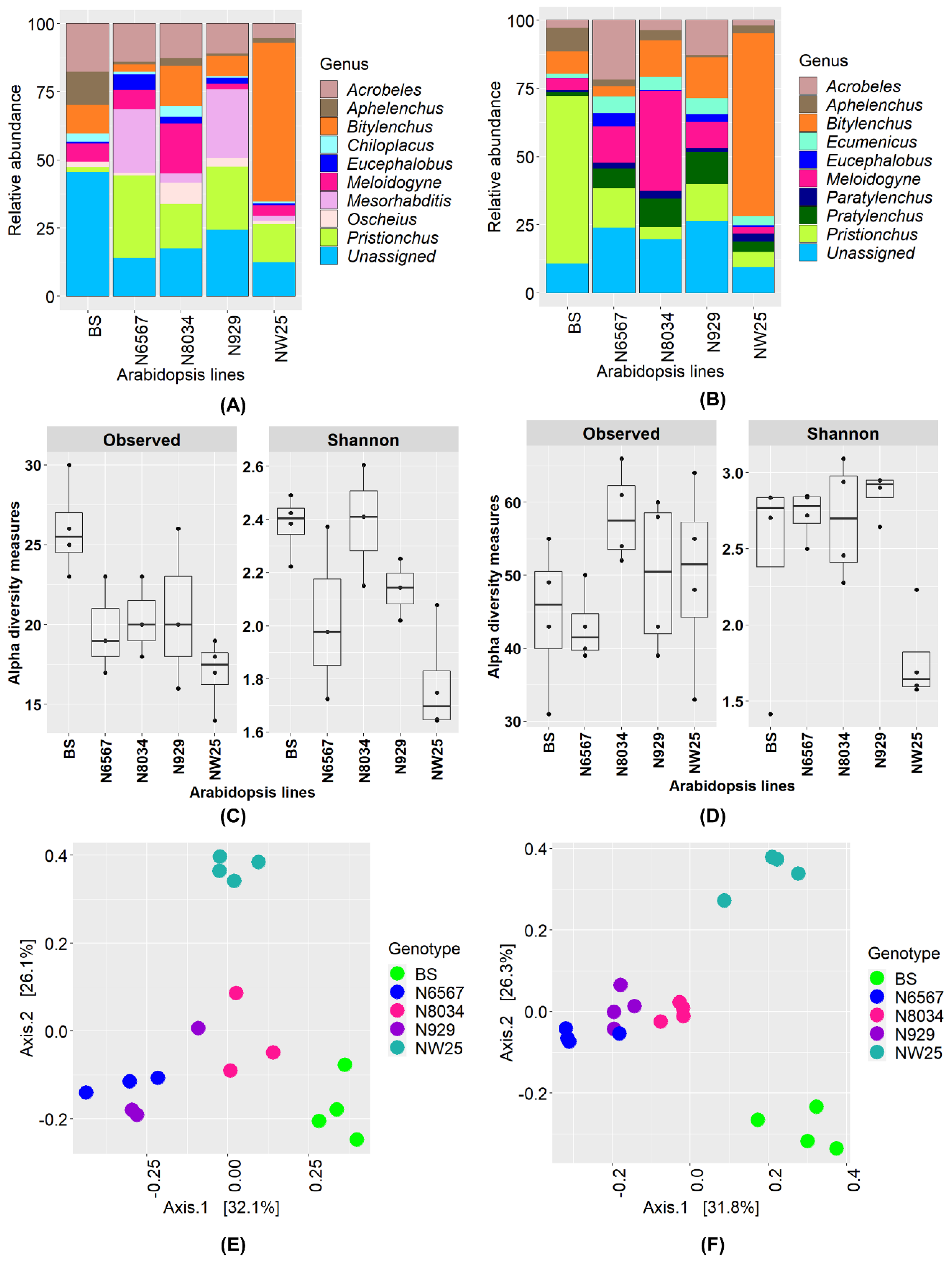
3.5. Nematode Communities in Root Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambshead, P.J.D.; Boucher, G. Marine nematode deep-sea biodiversity-hyperdiverse or hype? J. Biogeogr. 2003, 30, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hoogen, J.; Geisen, S.; Routh, D.; Ferris, H.; Traunspurger, W.; Wardle, D.A.; De Goede, R.G.M.; Adams, B.J.; Ahmad, W.; Andriuzzi, W.S.; et al. Soil nematode abundance and functional group composition at a global scale. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 572, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agatha, S.; Strüder-Kypke, M.C. Phylogeny of the order Choreotrichida (Ciliophora, Spirotricha, Oligotrichea) as inferred from morphology, ultrastructure, ontogenesis, and SSrRNA gene sequences. Eur. J. Protistol. 2007, 43, 37–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ley, P.; De Ley, I.T.; Morris, K.; Abebe, E.; Mundo-Ocampo, M.; Yoder, M.; Heras, J.; Waumann, D.; Rocha-Olivares, A.; Burr, A.J.; et al. An integrated approach to fast and informative morphological vouchering of nematodes for applications in molecular barcoding. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, M.; Astrin, J.; Borsch, T.; Burkhardt, U.; Grobe, P.; Hand, R.; Hausmann, A.; Hohberg, K.; Krogmann, L.; Lutz, M.; et al. How to tackle the molecular species inventory for an industrialized nation—Lessons from the first phase of the German Barcode of Life initiative GBOL (2012–2015). Genome 2016, 59, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abebe, E.; Mekete, T.; Thomas, W. A critique of current methods in nematode taxonomy. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 10, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaxter, M.; Mann, J.; Chapman, T.; Thomas, F.; Whitton, C.; Floyd, R.; Abebe, E. Defining operational taxonomic units using DNA barcode data. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holterman, M.; Holovachov, O.; Elsen, S.V.D.; Van Megen, H.; Bongers, T.; Bakker, J.; Helder, J. Small subunit ribosomal DNA-based phylogeny of basal Chromadoria (Nematoda) suggests that transitions from marine to terrestrial habitats (and vice versa) require relatively simple adaptations. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 48, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holterman, M.; Karssen, G.; Elsen, S.V.D.; Van Megen, H.; Bakker, J.; Helder, J. Small Subunit rDNA-Based Phylogeny of the Tylenchida Sheds Light on Relationships Among Some High-Impact Plant-Parasitic Nematodes and the Evolution of Plant Feeding. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiewnick, S.; Holterman, M.; Elsen, S.V.D.; Van Megen, H.; Frey, J.E.; Helder, J. Comparison of two short DNA barcoding loci (COI and COII) and two longer ribosomal DNA genes (SSU & LSU rRNA) for specimen identification among quarantine root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) and their close relatives. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 140, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, R.; Abebe, E.; Papert, A.; Blaxter, M. Molecular barcodes for soil nematode identification. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Ratnasingham, S.; De Waard, J.R. Barcoding animal life: Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoeckle, M. Taxonomy, DNA, and the Bar Code of Life. Bioscience 2003, 53, 796–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, M.S.; Yowell, C.A.; Courtney, C.H.; Dame, J.B. Substitution bias, rapid saturation, and the use of mtDNA for nematode systematics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRycke, S.; Remerie, T.; Vierstraete, A.; Backeljau, T.; Vanfleteren, J.; Vincx, M.; Moens, T. Mitochondrial DNA variation and cryptic speciation within the free-living marine nematode Pellioditis marina. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 300, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRycke, S.; Vanaverbeke, J.; Rigaux, A.; Backeljau, T.; Moens, T. Exploring the Use of Cytochrome Oxidase c Subunit 1 (COI) for DNA Barcoding of Free-Living Marine Nematodes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morise, H.; Miyazaki, E.; Yoshimitsu, S.; Eki, T. Profiling Nematode Communities in Unmanaged Flowerbed and Agricultural Field Soils in Japan by DNA Barcode Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, T.; Karssen, G.; Verhaeven, M.; Coyne, D.; Bert, W. Mitochondrial coding genome analysis of tropical root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne) supports haplotype based diagnostics and reveals evidence of recent reticulate evolution. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Monge, A.; Janssen, T.; Fang, Y.; Couvreur, M.; Karssen, G.; Bert, W. mtCOI successfully diagnoses the four main plant-parasitic Aphelenchoides species (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) and supports a multiple origin of plant-parasitism in this paraphyletic genus. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 148, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, T.; Karssen, G.; Orlando, V.; Subbotin, S.A.; Bert, W. Molecular characterization and species delimiting of plant-parasitic nematodes of the genus Pratylenchus from the penetrans group (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 117, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Back, M.A.; Prior, T.; Karssen, G.; Lawson, R.; Adams, I.; Sapp, M. Metabarcoding of soil nematodes: The importance of taxonomic coverage and availability of reference sequences in choosing suitable marker(s). Metabarcoding Metagenomics 2019, 3, 36408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, V.G.; Carvalho, G.R.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Johnson, H.F.; Neill, S.P.; Lambshead, J.D.; Thomas, W.K.; Power, D.; Creer, S. Metagenetic analysis of patterns of distribution and diversity of marine meiobenthic eukaryotes. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2014, 23, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porazinska, D.L.; Giblin-Davis, R.M.; Faller, L.; Farmerie, W.; Kanzaki, N.; Morris, K.; Powers, T.O.; Tucker, A.E.; Sung, W.; Thomas, W.K. Evaluating high-throughput sequencing as a method for metagenomic analysis of nematode diversity. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porazinska, D.L.; Sung, W.; Giblin-Davis, R.M.; Thomas, W.K. Reproducibility of read numbers in high-throughput sequencing analysis of nematode community composition and structure. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 10, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macheriotou, L.; Guilini, K.; Bezerra, T.N.; Tytgat, B.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nguyen, T.X.P.; Noppe, F.; Armenteros, M.; Boufahja, F.; Rigaux, A.; et al. Metabarcoding free-living marine nematodes using curated 18S and CO1 reference sequence databases for species-level taxonomic assignments. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 1211–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, J.; Kleinbölting, N.; Traunspurger, W. Comparison of morphological, DNA barcoding, and metabarcoding characterizations of freshwater nematode communities. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 2885–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waeyenberge, L.; De Sutter, N.; Viaene, N.; Haegeman, A. New Insights into Nematode DNA-metabarcoding as Revealed by the Characterization of Artificial and Spiked Nematode Communities. Diversity 2019, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, B.; De Groot, G.; Laros, I.; Stone, D.; Geisen, S. The need for standardisation: Exemplified by a description of the diversity, community structure and ecological indices of soil nematodes. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 87, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisen, S.; Snoek, L.B.; Hooven, F.C.T.; Duyts, H.; Kostenko, O.; Bloem, J.; Martens, H.; Quist, C.W.; Helder, J.A.; Van Der Putten, W.H. Integrating quantitative morphological and qualitative molecular methods to analyse soil nematode community responses to plant range expansion. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 1366–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebschull, J.M.; Zador, A.M. Sources of PCR-induced distortions in high-throughput sequencing data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, B.; Todd, T.C.; Herman, M.A. High-throughput amplicon sequencing of rRNA genes requires a copy number correction to accurately reflect the effects of management practices on soil nematode community structure. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 5456–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holovachov, O.; Haenel, Q.; Bourlat, S.J.; Jondelius, U. Taxonomy assignment approach determines the efficiency of identification of OTUs in marine nematodes. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenteros, M.; Rojas-Corzo, A.; Ruiz-Abierno, A.; DeRycke, S.; Backeljau, T.; Decraemer, W. Systematics and DNA barcoding of free-living marine nematodes with emphasis on tropical desmodorids using nuclear SSU rDNA and mitochondrial COI sequences. Nematology 2014, 16, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, S.W.J.; Velarde-Aguilar, M.G.; León-Règagnon, V.; Hebert, P.D.N. Advancing nematode barcoding: A primer cocktail for the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene from vertebrate parasitic nematodes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, R.; Nicolaisen, M. High-throughput sequencing of nematode communities from total soil DNA extractions. BMC Ecol. 2015, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadziavdic, K.; Lekang, K.; Lanzen, A.; Jonassen, I.; Thompson, E.M.; Troedsson, C. Characterization of the 18S rRNA Gene for Designing Universal Eukaryote Specific Primers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 87624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avó, A.P.; Daniell, T.J.; Neilson, R.; Oliveira, S.; Branco, J.; Adão, H. DNA Barcoding and Morphological Identification of Benthic Nematodes Assemblages of Estuarine Intertidal Sediments: Advances in Molecular Tools for Biodiversity Assessment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRycke, S.; Backeljau, T.; Vlaeminck, C.; Vierstraete, A.; Vanfleteren, J.; Vincx, M.; Moens, T. Spatiotemporal analysis of population genetic structure in Geomonhystera disjuncta (Nematoda, Monhysteridae) reveals high levels of molecular diversity. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 1799–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarova, S.S.; Malloch, G.; Oliveira, C.M.; Hübschen, J.; Neilson, R. Ribosomal and Mitochondrial DNA Analyses of Xiphinema americanum-Group Populations. J. Nematol. 2006, 38, 404–410. [Google Scholar]
- Sapkota, R.; Nicolaisen, M. Cropping history shapes fungal, oomycete and nematode communities in arable soils and affects cavity spot in carrot. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 257, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaxter, M.; De Ley, P.; Garey, J.R.; Liu, L.X.; Scheldeman, P.; Vierstraete, A.; Vanfleteren, J.R.; Mackey, L.Y.; Dorris, M.; Frisse, L.M.; et al. A molecular evolutionary framework for the phylum Nematoda. Nat. Cell Biol. 1998, 392, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudjordjie, E.N.; Sapkota, R.; Steffensen, S.K.; Fomsgaard, I.S.; Nicolaisen, M. Maize synthesized benzoxazinoids affect the host associated microbiome. Microbiome 2019, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treonis, A.M.; Unangst, S.K.; Kepler, R.M.; Buyer, J.S.; Cavigelli, M.A.; Mirsky, S.B.; Maul, J.E. Characterization of soil nematode communities in three cropping systems through morphological and DNA metabarcoding approaches. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deagle, B.E.; Jarman, S.N.; Coissac, E.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. DNA metabarcoding and the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I marker: Not a perfect match. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20140562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bik, H.; Sung, W.; De Ley, P.; Baldwin, J.G.; Sharma, J.; Rocha-Olivares, A.; Thomas, W.K. Metagenetic community analysis of microbial eukaryotes illuminates biogeographic patterns in deep-sea and shallow water sediments. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 21, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, E.; Giannico, R.; Montagna, M.; Turri, F.; Cremonesi, P.; Strozzi, F.; Leone, P.; Gandini, G.; Pizzi, F. A new primer set for DNA metabarcoding of soil Metazoa. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 77, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creer, S.; Fonseca, V.G.; Porazinska, D.L.; Giblin-Davis, R.M.; Sung, W.; Power, D.; Packer, M.; Carvalho, G.R.; Blaxter, M.; Lambshead, P.J.D.; et al. Ultrasequencing of the meiofaunal biosphere: Practice, pitfalls and promises. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Nematode Taxa | JB | SSU | MMS | NEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meloidogyne incognita | Genus | Not detected | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne arenaria | Genus | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne javanica | Genus | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne graminicola | Genus | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected |
| Meloidogyne ethiopica | Genus | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne inornata | Genus | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne ulmi | Genus | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne luci | Genus | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne hapla | Species | Genus | Species | Species |
| Meloidogyne enterolobii | Species | Not detected | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne chitwoodi | Species | Not detected | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne fallax | Genus | Not detected | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne minor | Genus | Species | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne naasi | Species | Not detected | Genus | Genus |
| Pratylenchus penetrans | Species | Not detected | Genus | Species |
| Pratylenchus spp. | Species | Not detected | Species | Species |
| Heterodera carotae | Not detected | Not detected | Genus | Family |
| Heterodera schachtii | Species | Species | Genus | Family |
| Belonolaimus longicaudatus | Not detected | Species | Species | Species |
| Bursaphelenchus mucronatus | Not detected | Not detected | Genus | Genus |
| Caenorhabditis elegans | Species | Species | Species | Species |
| Ditylenchus dipsaci | Not detected | Species | Species | Genus |
| Taxa in Mock Communities | JB | SSU | MMS | NEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meloidogyne incognita | Genus | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne arenaria | Genus | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne ethiopica | Genus | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne inornata | Genus | Not detected | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne ulmi | Genus | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne luci | Genus | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne hapla | Species | Not detected | Species | Species |
| Meloidogyne chitwoodi | Genus | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne fallax | Genus | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne minor | Not detected | Not detected | Genus | Genus |
| Meloidogyne naasi | Species | Genus | Genus | Genus |
| Pratylenchus penetrans | Species | Not detected | Not detected | Species |
| Heterodera carotae | Not detected | Genus | Genus | Family |
| Heterodera schachtii | Species | Genus | Species | Family |
| Belonolaimus longicaudatus | Not detected | Not detected | Species | Species |
| Caenorhabditis elegans | Species | Species | Species | Species |
| Globodera pallida | Species | Species | Species | Genus |
| Globodera rostochiensis | Species | Genus | Genus | Genus |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sikder, M.M.; Vestergård, M.; Sapkota, R.; Kyndt, T.; Nicolaisen, M. Evaluation of Metabarcoding Primers for Analysis of Soil Nematode Communities. Diversity 2020, 12, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100388
Sikder MM, Vestergård M, Sapkota R, Kyndt T, Nicolaisen M. Evaluation of Metabarcoding Primers for Analysis of Soil Nematode Communities. Diversity. 2020; 12(10):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100388
Chicago/Turabian StyleSikder, Md. Maniruzzaman, Mette Vestergård, Rumakanta Sapkota, Tina Kyndt, and Mogens Nicolaisen. 2020. "Evaluation of Metabarcoding Primers for Analysis of Soil Nematode Communities" Diversity 12, no. 10: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100388
APA StyleSikder, M. M., Vestergård, M., Sapkota, R., Kyndt, T., & Nicolaisen, M. (2020). Evaluation of Metabarcoding Primers for Analysis of Soil Nematode Communities. Diversity, 12(10), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100388