Abstract
The synthesis and characterisation (UV-Vis, IR, HRESI-MS, 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopies, electrochemistry) is reported of the novel title material (1: alternatively named rac-1-(2′-benzothiazolyl)-2-ferrocenyl-2-propanol): a rare example of a ferrocenyl-benzothiazole hybrid species. Compound 1 is produced by the low temperature reaction of acetylferrocene (3) with a solution of the methyl anion derived via the deprotonation of 2-methyl-1,3-benzothiazole. The yield of 1 is moderate (34%) after purification and is an air and thermally stable solid under ambient conditions. Attempts to sublime 1, however, result in decomposition with one of the products being identified (NMR) as 3. The spectroscopic features of 1 are presented. Attempts to obtain suitable crystalline material of 1 for a single crystal X-ray diffraction study were unfortunately unsuccessful. Compound 1 also does not form stable coordination complexes with various metal salts (e.g., Ni[2+], Co[2+], etc.) under the conditions tested.
1. Introduction
Ferrocene and its many known derivatives have played a pivotal role in our understanding of organometallics [1,2] and the ferrocenyl functionality is routinely explored for its unique aspects and their influence on applications such as catalysis, ligand design, medicinal chemistry and materials science [3,4,5,6,7,8]. Benzothiazoles, a subclass of the azole heterocycles [9], have likewise found widespread use in drug development, and in novel organic and materials syntheses [10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. As part of our broader interest in both ferrocene [17,18] and azole-derivatives [19,20,21,22], we report herein the synthesis and characterisation of a rare hybrid example: that of rac-2-(2′-ferrocenyl-2′-hydroxy-n-propyl)-1,3-benzothiazole (i.e., 1). This material may also alternatively be named as rac-1-(2′-benzothiazolyl)-2-ferrocenyl-2-propanol.
2. Results and Discussion
The synthesis of the title material (i.e., 1) was carried out by the initial in situ formation of the methyl anion derived from 2-methyl-1,3-benzothiazole (2) using n-BuLi at low temperature (Scheme 1). The treatment of the solution of the resulting anion with acetylferrocene (3) at low temperature, followed by slow warming to room temperature (RT) afforded crude 1, which was thereafter isolated via extraction and subsequent recrystallization (see: Materials and Methods; Section 3.2).
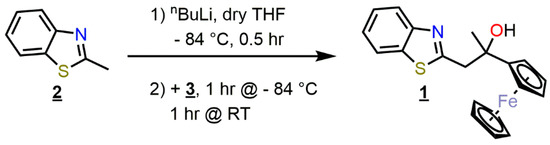
Scheme 1.
Schematic representation of the synthesis of 1 using azole 2 and acetylferrocene (3).
Compound 1 is an air-stable dark-orange coloured solid under ambient conditions; however, 1 is unstable over extended time periods when dissolved in chlorinated solvents (e.g., CHCl3, CH2Cl2) as these mixtures change colour to black and become opaque in nature. Sublimation of 1 in air also results in the decomposition of the compound [16]; one of the products of this process is identified (1H NMR) as acetylferrocene 3 (Scheme 1). Compound 1 is only slightly soluble in aromatic solvents and insoluble in saturated hydrocarbons.
Despite the many crystallographically characterised examples of CpFeCp–R (R ≠ H; Cp = η5-cyclopentadienyl) derivatives that have been previously reported (e.g., [17,18,23,24,25]), our attempts to obtain a material suitable for X-ray crystallographic characterisation of 1 were never forthcoming, despite a wide variety of methods employed [26,27,28]. Macroscopic crystals of 1 were invariably found to be multi-twinned species and hence did not yield crystallographic datasets of acceptable quality [29]. The spectroscopic and analytical (NMR, MS, m.p., etc.) features of 1, (found in Section 3.2 and in the Supplementary Materials associated with this manuscript) are, however, all fully consistent with the surmised formation of 1 as depicted in Scheme 1. The NMR characteristics, from both a 1H and 13C perspective, are perhaps best classified as routine and unsurprising [23,24,25]. The UV-Vis spectrum of 1 contains several absorbances that can be assigned to that of the benzothiazolyl unit [30,31,32,33,34] with a weaker d-d type transition in the visible region which is likely associated with the ferrocenyl moiety as previously described [35]. Infrared examination of 1 likewise reveals absorbances typical of this class of compounds [36,37,38,39]. Examination of 1 by cyclic voltammetry (CV) reveals two reversible redox processes with E½ values of 0.54 and 0.83 V (Figure S10); again these can be assigned to redox chemistry occurring in a localised fashion at the azoyl and ferrocenyl groups [23,24,25].
As we have a long-standing interest in the coordination chemistry of azoles (e.g., [19,20,21,22]), we have also investigated the potential of 1 to act as a ligand to transition metal centres. Benzothiazoles are well-known to form complexes, via N-atom binding interactions, to a variety of electrophilic centres such as Ni(2+), Pd(2+), U(6+), etc. [40,41,42,43,44,45,46]. We further envisioned that de-protonation of the –OH group of 1, followed by the addition of such metal centres, would allow for possible κ2-N,O-chelation as has been observed for related species [19,20,21,22]. Disappointingly, the treatment of solutions of 1 with t-BuOK, followed by the addition of metal salts (i.e., CoBr2·6H2O; Zn(OAc)2; Cu(NO3)2·2.5H2O; NiBr2·3H2O), did not yield any isolable metal complexes and only extensive decomposition, or partial recovery of 1, were the results.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
All reagents, solvents and deuterated solvents were obtained from commercially available sources. Dry solvents were dispensed from an Mbraun solvent purification system (MBraun, Stratham, NH, USA) immediately before use. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic measurements (1H: 400 MHz; 13C{1H}: 101 MHz) were carried out using a Bruker Avance II AC-400 MHz spectrometer (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) operating at 300K in the specified deuterated solvent as described. Abbreviations used in the 1H NMR line listings are as follows: ABq = AB quartet, ArH = aryl H-atom, br-s = broad singlet, CpH = H-atom on the mono-substituted cyclopentadienyl group, d = doublet, m = multiplet, q = quartet, s = singlet and t = triplet. Infrared spectroscopy was performed on an Agilent Cary 630 FTIR Spectrometer (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) in open air. The CV data were collected using a MetrOhm Autolab Type II potentiostat/galvanostat (Metrohm AUTOLAB BV, Utrecht, The Netherlands). The solvent (CH2Cl2) was degassed prior to analysis by CV. UV-Vis absorption profiles were collected using an Agilent Cary 60 UV-vis spectrometer (cuvette path length = 1 cm). Molar extinction coefficients were calculated using the Beer-Lambert law. Melting point measurements were determined with a BUCHI 565 melting point apparatus (Büchi Labortechnik AG, Flawil, Switzerland) in triplicate under ambient conditions. High resolution ESI mass spectrometry (HRESI-MS) was performed at the University of Toronto at the AIMS facility using electrospray ionization with positive polarity.
3.2. Synthesis of rac-2-(2′-Ferrocenyl-2′-hydroxy-n-propyl)-1,3-benzothiazole (1)
A three-neck round-bottomed flask containing dry THF (20 mL) and 2 (1.5 mL; 1.76 g: 11.8 mmol) was cooled to −84 °C (EtOAc/N2 [l] bath). Once appropriately chilled, n-BuLi (11 mL; 1.0 M in hexanes: 11 mmol) was added dropwise over a period of 10 min. The mixture was then stirred for 30 min. Then, 3 (2.82 g: 12.4 mmol), dissolved in dry THF (20 mL), was added dropwise over a period of 10 min. The contents of the reaction flask were then stirred at −84 °C for 1 h and left to warm slowly to RT; it was thereafter stirred for an additional hour. The resulting mixture was then poured into ice water (~100 mL) and the liquids added into a separatory funnel. The organic constituents were extracted with diethyl ether (50 mL × 2) and the combined organic phase was dried (MgSO4), filtered and evaporated via rotary evaporation. The resulting waxy solid was recrystallised with a 1:4 solvent mixture of toluene and hexanes. A dark orange coloured air-stable powder was thereafter recovered by vacuum filtration (Yield 1.39 g: 34%). The m.p. (uncorrected) of this solid was found to be 98.0 ± 0.1 °C. HRESI-MS calcd for C20H20NOSFe+: 378.0610; found 378.0600. UV-Vis (nm, [log ε]: MeCN): 207 [5.06], 214 [5.05], 259 [4.20], 269 [4.05], 438 [2.24]. Selected FT-IR ν (cm−1): 3403, 3089, 2978, 1632, 1438, 1315, 1170, 1103, 998, 760, 693. 1H NMR (C6D6), δ: 1.56 (s, 3H, –CH3), 3.30 (ABq, 2JH-H = 14.5 Hz, 2H, –CH2–), 3.84-3.86 (m, 1H, CpH), 3.87-3.89 (m, 1H, CpH), 3.91-3.92 (m, 1H, CpH), 3.93 (br-s, 1H, –OH), 4.04 (s, 5H, C5H5), 4.08-4.09 (m, 1H, CpH), 6.97-7.01 (m, 1H, ArH), 7.11-7.15 (m, 1H, ArH), 7.41-7.43 (m, 1H, ArH), 7.97-8.00 (m, 1H, ArH). 1H NMR (dmso-d6), δ: 1.49 (s, 3H, –CH3), 3.42 (m, 2H, –CH2–), 4.10 (t, 3JH-H = 1.9 Hz, 1H, CpH), 4.14 (q, 3JH-H = 1.9 Hz, 1H, CpH), 4.21 (s, 5H, C5H5), 4.23-4.24 (m, 1H, CpH), 5.05 (s, 1H, –OH), 7.36-7.40 (m, 1H, ArH), 7.43-7.47 (m, 1H, ArH), 7.92-7.94 (m, 1H, ArH), 8.01-8.03 (m, 1H, ArH). 13C NMR (dmso-d6), δ: 27.8, 48.6, 65.5, 65.8, 67.0, 67.1, 68.4, 69.7, 98.2, 121.8, 122.1, 124.7, 125.7, 135.7, 152.0, 168.1.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online. Figure S1. Copies of 1H NMR spectra of compound 1 (C6D6 and dmso-d6); Figure S2. Copy of 13C NMR spectra of 1 (dmso-d6); Figure S3. Copy of HRESI-MS spectrum of 1; Figure S4. Copy of FT-IR spectrum of 1; Figures S5–S8. Copies of UV-Vis spectra (MeCN solution) of 1; Figure S9. Copy of cyclic voltammogram (0.1 M MeCN) of 1. Figure S10. Copy of CV of 1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.L.M. and R.A.G.; methodology, M.G.Z., K.L.M. and R.A.G.; validation, M.G.Z., K.L.M. and R.A.G.; formal analysis, M.G.Z., K.L.M. and R.A.G.; investigation, M.G.Z., K.L.M. and R.A.G.; resources, R.A.G.; data curation, M.G.Z. and K.L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.G.Z., K.L.M. and R.A.G.; writing—review and editing, R.A.G.; supervision, K.L.M. and R.A.G.; project administration, K.L.M. and R.A.G.; funding acquisition, R.A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by Toronto Metropolitan University (TMU) specifically through the Dean’s Research Fund, the Dean’s Booster Fund and the ad hoc funding scheme. K.L.M. was the recipient of a Molecular Sciences Graduate Award funded through TMU.
Acknowledgments
Prof. Bryan D. Koivisto is thanked for allowing us to use his CV equipment during these research undertakings.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Pauson, P.L. Ferrocene—How it all began. J. Organomet. Chem. 2001, 637–639, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauson, P.L. Ferrocene and related compounds. Q. Rev. Chem. Soc. 1955, 9, 391–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, E.S. (Ed.) Ferrocenes: Compounds, Properties and Applications; Nova: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Togni, A.; Hayashi, T. (Eds.) Ferrocenes: Homogeneous Catalysis, Organic Synthesis, Materials Science; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Štěpnička, P. Forever young: The first seventy years of ferrocene. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 8085–8102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, M.; Gasser, G. The medicinal chemistry of ferrocene and its derivatives. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessières, A. Iron compounds as anticancer agents. In Metal-Based Anticancer Agents; Casini, A., Vessières, A., Meier-Menches, S.M., Eds.; RSC: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 62–90. [Google Scholar]
- Popova, L.V.; Babin, V.N.; Belousov, Y.A.; Nekrasov, Y.S.; Snegireva, A.E.; Borodina, N.P.; Shaposhnikova, G.M.; Bychenko, O.B.; Raevskii, P.M.; Morozova, N.B.; Ilyina, A.I.; Shitov, K.G. Antitumor effects of binuclear ferrocene derivatives. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1993, 7, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicher, T.; Hauptmann, S. The Chemistry of Heterocycles, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; pp. 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Keri, R.S.; Patil, M.R.; Patil, S.A.; Budagumpi, S. A comprehensive review in current developments of benzothiazole-based molecules in medicinal chemistry. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 207–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.K.; Rawal, R.K.; Bariwal, J. Recent advances in the chemistry and biology of benzothiazoles. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2015, 348, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, S. A comprehensive review on recent advances in the synthesis & pharmacotherapeutic potential of benzothiazoles. Anti-inflamm. Anti-Allergy Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 14, 98–112. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Sindhu, J.; Devi, M.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, R.; Hussain, K.; Kumar, P. Solid-supported materials-based synthesis of 2-substituted benzothiazoles: Recent developments and sanguine future. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 6388–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhilitskaya, L.V.; Shainyan, B.A.; Yarosh, N.O. Modern approaches to the synthesis and transformations of practically valuable benzothiazole derivatives. Molecules 2021, 26, 002190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, M.S.; Moraes, E.S.; da Luz, L.C.; da Silveira Santos, F.; Martin, A.; Benhida, R.; Duarte, L.G.T.A.; Rodembusch, F.S. Synthesis, photophysics, and theoretical calculations of styryl-based fluorophores harboring substituted benzothiazole acceptors. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 435, 114287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikashita, H.; Ishihara, M.; Takigawa, K.; Itoh, K. Synthetic application of benzothiazole ring system as an off-on type of leaving group. Synthesis of ketones and carboxylic acid derivatives from 2-(1-substituted 1-hydroxyalkyl)- and 2-(1-hydroxyalkyl)benzothiazoles. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1991, 64, 3256–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Frcic, A.; Clyburne, J.A.C.; Gossage, R.A.; Yu, H.-Z. Thin layer electrochemistry of 1,3-diferrocenyl-2-buten-1-one: Direct correlation between driving force and liquid/liquid interfacial electron transfer rates. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 5742–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; May, K.L.; Lough, A.J.; Gossage, R.A. The crystal and molecular structure of 1-ferrocenyl-3,3-bis(methylthio)prop-2-en-1-one. Z. Naturforsch. 2023, 78b, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.C.; Lough, A.J.; Gossage, R.A. Synthesis and structural studies of group 12 oxazoline-enolate coordination complexes of (Z)-1-R-2-(4′,4′-dimethyl-2′-oxazolin-2′-yl)-eth-1-en-1-ates: Part I: The zinc derivatives. Can. J. Chem. 2023, 101, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.C.; Lougth, A.J.; Gossage, R.A. Heteroatom Exchange Chemistry in (Z)-1-R-2-(4′,4′-dimethyl)-2′-oxazolin-2′yl)-eth-1-en-1-ols: Access to Chelate-stabilized Thioester Analogues of Dithiooxophosphoranes. Chem. Lett. 2022, 51, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, A.; Adjei, J.A.; Lough, A.J.; Wylie, R.S.; Gossage, R.A. Synthesis, Characterization, and Catalytic Exploration of Mononuclear Mo(VI) Dioxido Complexes of (Z)-1-R-2-(4′,4′-Dimethyl-2′-oxazolin-2′-yl)-eth-1-en-1-ates. Molecules 2022, 27, 001309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.C.; Chojnacka, M.W.; Quail, J.W.; Gardiner, M.G.; Decken, A.; Yates, B.F.; Gossage, R.A. Oxazoles revisited: On the nature of binding of benzoxazole and 2-methylbenzoxazole with the zinc and palladium halides. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 1594–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochida, T.; Shimizu, H.; Suzuki, S.; Akasaka, T. Synthesis and properties of azole-substituted ferrocenes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2006, 691, 4882–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snegur, L.V.; Simenel, A.A.; Nekrasov, Y.S.; Morozova, E.A.; Starikova, Z.A.; Peregudova, L.A.; Kuzmenko, Y.V.; Babin, V.N.; Ostrovskaya, L.A.; Bluchterova, N.V.; Fomina, M.M. Synthesis, structure and redox potentials of biologically active ferrocenylalkyl azoles. J. Organomet. Chem. 2004, 689, 2473–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Greñu, B.D.; Fernández-Aroca, D.M.; Organero, J.A.; Durá, G.; Jalón, F.A.; Sánchez-Prieto, R.; Ruiz-Hidalgo, M.J.; Rodríguez, A.M.; Santos, L.; Albasanz, J.L.; Manzano, B.R. Ferroazoles: Ferrocenyl derivatives of letrozole with dual effects as potent aromatase inhibitors and cytostatic agents. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 28, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, R.D. How to grow crystals for X-ray crystallography. Acta Cryst. 2024, C80, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, P. Practical suggestions for better crystal structures. Crystallogr. Rev. 2009, 15, 57–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etter, M.C.; Jahn, D.A.; Donahue, B.S.; Johnson, R.B.; Ojala, C. Growth and characterization of small organic crystals. J. Cryst. Growth 1986, 76, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lough, A.J.; (X-ray Crystallography Laboratory, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada). Personal communication, 2024.
- Cerniani, A.; Passerini, R. The near-ultra-violet absorption spectra of some heterocyclic compounds. Part II. Benzothiazoles. J. Chem. Soc. 1954, 2261–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.D.; Yang, R.F. Vapor absorption spectra of benzoxazole, benzimidazole, and benzothiazole near 2850 Å. Can. J. Chem. 1970, 48, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyazhanskii, M.I.; Gilyanovskii, P.V.; Osipov, O.A. Luminescence and photochemistry of azoles (review). Chem. Heterocyclic Cmpds. 1977, 13, 1160–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, T.L.P.; Kuznetsova, A.; Gomes, J.R.B.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Tedim, J.; Ferreira, M.G.S. A computational UV-Vis spectroscopic study of the chemical speciation of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole corrosion inhibitor in aqueous solution. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2016, 135, 000078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarik, A.; Mahmood, S.; Rasool, N.; Hashmi, M.A.; Ammar, M.; Mutahir, S.; Ali, K.G.; Bilal, M.; Akhtar, M.N.; Ashraf, G.A. Computational study of benzothiazole derivatives for conformational, thermodynamic and spectroscopic features and their potential to act as antibacterials. Crystals 2022, 12, 000912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, Y.S.; Hendrickson, D.N.; Gray, H.B. Electronic structure of metallocenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1971, 93, 3603–3612. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, L.; Lacey, A.R.; Cooper, M.K. Analysis of substituted ferrocenes by infrared spectroscopy. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1988, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, N.; Ganesan, A.; Chantler, C.T.; Wang, F. Differentiation of ferrocene D5d and D5h conformers by IR spectroscopy. J. Organomet. Chem. 2012, 713, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Rathore, D.S.; Garg, G.; Khatri, K.; Saxena, R.; Sahu, S.K. Synthesis and evaluation of some benzothiazole derivatives as antidiabetic agents. Int. J. Pharma. Pharma. Sci. 2017, 9, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjunan, V.; Sakiladevi, S.; Rani, T.; Mythili, C.V.; Mohan, S. FTIR, FT-Raman, FT-NMR, UV-visible and quantum mechanical investigations of 2-amino-4-methylbenzothiazole. Spectrochim. Acta A 2012, 88, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duff, E.J.; Hughes, M.N.; Rutt, K.J. Structure and infrared spectra of some nitrato-complexes of cobalt(II), nickel(II), copper(II) and zinc(II) with heterocyclic ligands. J. Chem. Soc. A 1969, 2126–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.N.; Rutt, R.J. The far infrared spectra of some complexes of palladium(II) with thiazoles. Spectrochim. Acta 1971, 27A, 924–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, I.S.; Singh, R.; Rai, C.P. 2-Methylbenzothiazole complexes with some uranyl salts. Current Sci. 1978, 47, 622–624. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Aly, A.A.M.; El-Shabasy, M. Magnetic and spectral properties of 2-methylbenzoxazole, benzothiazole, and 2-methylbenzothiazole complexes with copper(II) dichloroacetate. Croat. Chem. Acta 1986, 59, 509–512. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, U.; Panunzi, B.; Roviello, A.; Tingoli, M.; Tuzi, A. Two aminobenzothiazole derivatives for Pd(II) and Zn(II) coordination. Synthesis, characterization and solid state fluorescence. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2011, 14, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemenko, M.V.; Slyusarenko, K.F. Complex formation by copper(II) chloride with 2-(hydroxyalkyl)-benzothiazoles. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 1964, 9, 1376–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Artemenko, M.V.; Slyusarenko, K.F. Formation of complexes of copper salts with 2-(hydroxyalkyl)-benzothiazoles and 2-methylbenzothiazole. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 1965, 10, 620–624. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).