4-Amino-2-(p-tolyl)-7H-chromeno[5,6-d]oxazol-7-one
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
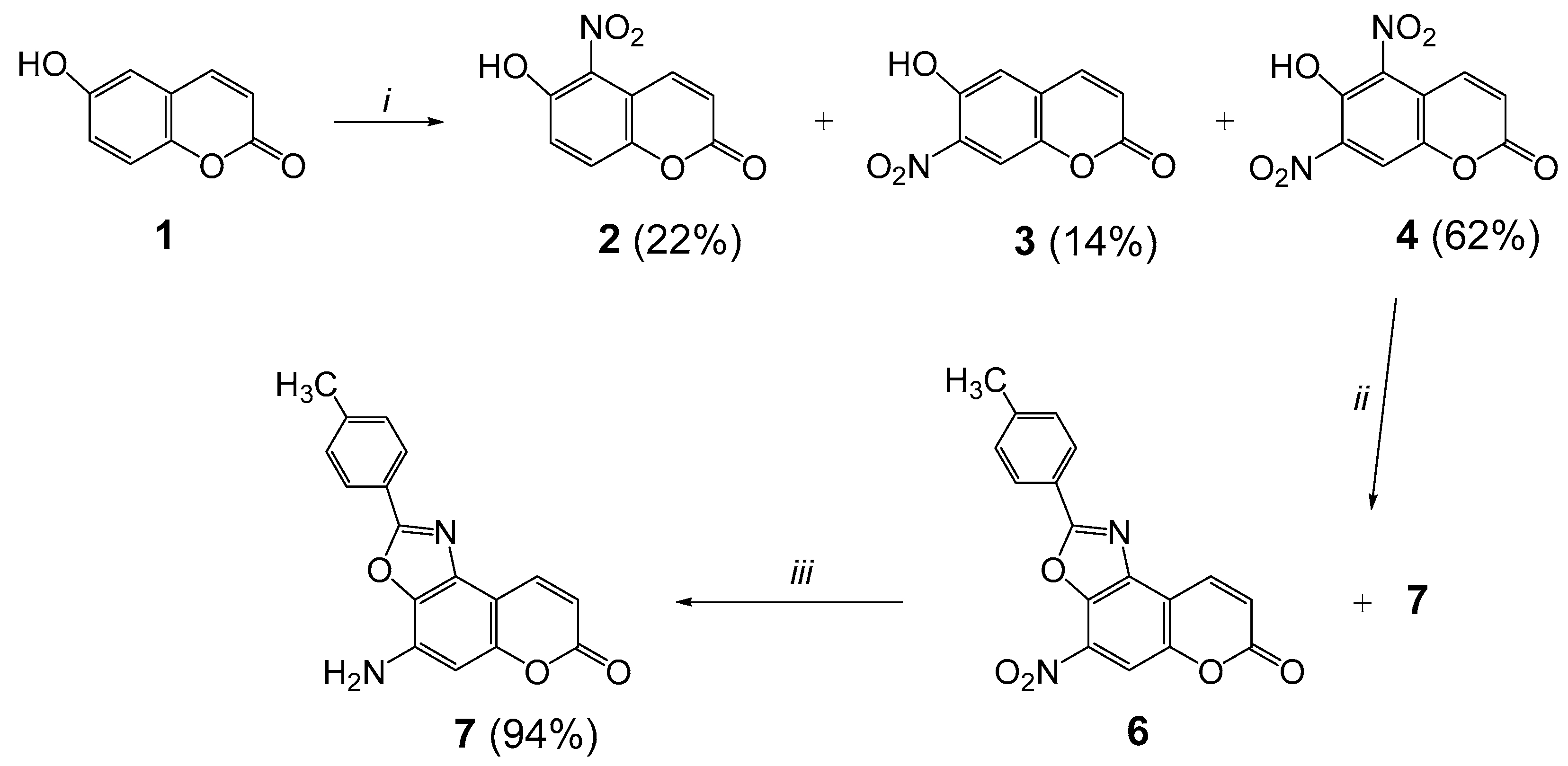
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Biology
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of 6-Hydroxy-5,7-dinitrocoumarin (4)
3.3. Synthesis of 4-Nitro-2-(p-tolyl)-7H-chromeno[5,6-d]oxazol-7-one (6)
3.4. Synthesis of 4-Amino-2-(p-tolyl)-7H-chromeno[5,6-d]oxazol-7-one (7)
3.5. Biological Experiments: In Vitro Assays
- Antilipid peroxidation: the AAPH protocol was followed [25].
- Lipoxygenase inhibition: according to our previous protocol [25].
- Antioxidant activity: interaction with the stable free radical DPPH (final concentration 0.05 mM) in ethanol absolute (final concentration of the tested compounds 0.1 mM) [25].
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, D.; Suzuki, M.; Xie, L.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Lee, K.-H. Recent progress in the development of coumarin derivatives as potent anti-HIV agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2003, 23, 322–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fylaktakidou, K.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Litinas, K.; Nicolaides, D. Natural and Synthetic Coumarin Derivatives with Anti-Inflammatory/Antioxidant Activities. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 3813–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, A. Studies on Coumarins and Coumarin-Related Compounds to Determine their Therapeutic Role in the Treatment of Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 3797–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, F.G.; Marrero, J.G.; Macías-Alonso, M.; González, M.C.; Córdova-Guerrero, I.; García, A.G.T.; Osegueda-Robles, S. Coumarin heterocyclic derivatives: Chemical synthesis and biological activity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 1472–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubrak, T.; Podgórski, R.; Stompor, M. Natural and Synthetic Coumarins and their Pharmacological Activity. Eur. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 15, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, Y.; Li, L. Coumarins as potential antidiabetic agents. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 69, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehian, F.; Nadri, H.; Jalili-Baleh, L.; Youseftabar-Miri, L.; Bukhari, S.N.A.; Foroumadi, A.; Küçükkilinç, T.T.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Khoobi, M. A review: Biologically active 3,4-heterocycle-fused coumarins. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 212, 113034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balalas, T.D.; Stratidis, G.; Papatheodorou, D.; Vlachou, E.-E.; Gabriel, C.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.J.; Litinas, K.E. One-pot Synthesis of 2-Substituted 4H-Chromeno[3,4-d]oxazol-4-ones from 4-Hydroxy-3-nitrocoumarin and Acids in the Presence of Triphenylphosphine and Phosphorus Pentoxide under Microwave Irradiation. SynOpen 2018, 2, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, B.; Sandeep, A.; Revathi, T. Green approach to synthesis of novel substituted 8H-pyrano[2,3-e]benzoxazole-8-ones. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 3, 404–411. [Google Scholar]
- Kontogiorgis, C.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Biological Evaluation of Several Coumarin Derivatives Designed as Possible Anti-inflammatory/Antioxidant Agents. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2003, 18, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, M.; Fellman, J.; Kaufman, K. The Effect of Structural Alterations on the Erythemal Activity of Furocoumarins: Psoralens ** From the Departments of Dermatology and Biochemistry, University of Oregon Medical School, Portland, Oregon and the Department of Chemistry, Kalamazoo College, Kalamazoo, Michigan. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1960, 35, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.M.S.; Hungerford, G.; Gonçalves, M.S.T.; Costa, S.P.G. Light triggering of 5-aminolevulinic acid from fused coumarin ester cages. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 2997–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.S.; Shukla, S.; Nandy, S.; Sahoo, H. Synthesis of novel coumarin derivatives and its biological evaluations. Eur. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 2, 899–908. [Google Scholar]
- Colotta, V.; Catarzi, D.; Varano, F.; Cecchi, L.; Filacchioni, G.; Martini, C.; Giusti, L.; Lucacchini, A. Tricyclic heteroaromatic systems. Synthesis and benzodiazepine receptor affinity of 2-substituted-1-benzopyrano[3,4-d]oxazol-4-ones,-thiazol-4-ones, and -imidazol-4-ones. Il Farm. 1998, 53, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofal, Z.M.; El-Zahar, M.I.; El-Karim, S.S.A. Novel Coumarin Derivatives with Expected Biological Activity. Molecules 2000, 5, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallacker, F.; Kratzer, P.; Lipp, M. Derivate des 2.4-Pyronons und 4-Hydroxy-cumarins. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1961, 643, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammon, D.W.; Hunter, R.; Wilson, S.A. An efficient synthesis of 7-hydroxy-2,6-dimethylchromeno[3,4-d]oxazol-4-one—A protected fragment of novenamine. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 10683–10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikachi, H.; Ichikawa, M. Studies on Synthesis of Coumarin Derivatives. XV. On the Preparation of Ethyl Pyranobenzoxazole-carboxylates. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1966, 14, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantegrel, B.; Nadi, A.I.; Gelin, S. Synthesis of [1]benzopyrano[3,4-d]isoxazol-4-ones from 2-substituted chromone-3-carboxylic esters. A reinvestigation of the reaction of 3-acyl-4-hydroxycoumarins with hydroxylamine. Synthesis of 4-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)isoxazol-5-ones. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 4419–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, K.D.; McBride, D.W.; Eaton, D.C. Synthetic Furocoumarins. VII. Oxazolocoumarins from 6-Hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin. J. Org. Chem. 1965, 30, 4344–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachou, E.-E.N.; Armatas, G.S.; Litinas, K.E. Synthesis of Fused Oxazolocoumarins from o -Hydroxynitrocoumarins and Benzyl Alcohol Under Gold Nanoparticles or FeCl3 Catalysis. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2017, 54, 2447–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saghier, A.M.M.; Naili, M.B.; Rammash, B.K.; Saleh, N.A.; Kreddan, K.M. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of some new fused chromenes. Arkivoc 2007, 2007, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.A.; Kulkarni, M.V.; Gopal, M.; Shahabuddin, M.; Sun, C.-M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel angularly fused polycyclic coumarins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 3584–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levrier, C.; Balastrier, M.; Beattie, K.D.; Carroll, A.; Martin, F.; Choomuenwai, V.; Davis, R.A. Pyridocoumarin, aristolactam and aporphine alkaloids from the Australian rainforest plant Goniothalamus australis. Phytochemistry 2013, 86, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symeonidis, T.S.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.J.; Litinas, K.E. Synthesis Through Three-Component Reactions Catalyzed by FeCl3of Fused Pyridocoumarins as Inhibitors of Lipid Peroxidation. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2013, 51, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markey, M.D.; Fu, Y.; Kelly, T.R. Synthesis of Santiagonamine. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 3255–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudale, A.A.; Kendall, J.; Miller, D.O.; Collins, J.L.; Bodwell, G.J. Povarov Reactions Involving 3-Aminocoumarins: Synthesis of 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydropyrido[2,3-c]coumarins and Pyrido[2,3-c]coumarins. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 8437–8447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heber, D.; Berghaus, T. Synthesis of 5H-[1]benzopyrano[4,3-b]pyridin-5-ones containing an azacannabinoidal structure. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1994, 31, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heber, D.; Ivanov, I.C.; Karagiosov, S.K. The vilsmeier reaction in the synthesis of 3-substituted [1]benzopyrano[4,3-b]pyridin-5-ones. An unusual pyridine ring closure. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1995, 32, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.T.; Das, D.K.; Islam, K.; Das, P. A simple and expedient synthesis of functionalized pyrido[2,3-c] coumarin derivatives using molecular iodine catalyzed three-component reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 6418–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, K.; Ponra, S.; Ghosh, D.; Taher, A. Efficient One-Pot Synthesis of Substituted 4,7-Phenanthroline, Pyrano-[3,2-f]quinoline and Pyrano[3,2-g]quinoline Derivatives by Aza-Diels-Alder Reaction. Synlett 2010, 2011, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.T.; Ahn, S.; Yoon, J.A. Total Synthesis of the Natural Pyridocoumarins Goniothaline A and B. Synthesis 2018, 51, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symeonidis, T.S.; Kallitsakis, M.; Litinas, K.E. Synthesis of [5,6]-fused pyridocoumarins through aza-Claisen rearrangement of 6-propargylaminocoumarins. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 5452–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symeonidis, T.S.; Lykakis, I.N.; Litinas, K.E. Synthesis of quinolines and fused pyridocoumarins from N-propargylanilines or propargylaminocoumarins by catalysis with gold nanoparticles supported on TiO2. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 4612–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, N.C.; Datta, M.; De, P.; Chakravarty, R. Studies on Regioselectivity of Nitration of Coumarins with Cerium(IV) Ammonium Nitrate: Solid-State Nitration of 6-Hydroxy-Coumarins on Montmorillonite K-10 Clay Support Under Microwave Irradiation. Synth. Commun. 2003, 33, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Yang, D.; Liu, Z.; Wu, L. Mono-nitration of Coumarins by Nitric Oxide. Synth. Commun. 2004, 34, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, R.S.A.; Guerra, F.Q.S.; Lima, E.D.O.; De Simone, C.A.; Tavares, J.F.; Scotti, L.; Scotti, M.T.; De Aquino, T.M.; De Moura, R.O.; Mendonça, F.J.B.; et al. Synthesis, Structure-Activity Relationships (SAR) and in Silico Studies of Coumarin Derivatives with Antifungal Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1293–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoulaki, S.; Daikopoulou, V.; Gkizis, P.L.; Tamiolakis, I.; Armatas, G.S.; Lykakis, I.N. Mechanistic Studies of the Reduction of Nitroarenes by NaBH4 or Hydrosilanes Catalyzed by Supported Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3504–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P. Direct Amination of Phenols under Metal-Free Conditions. Synlett 2013, 24, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vlachou, E.-E.N.; Balalas, T.D.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.J.; Litinas, K.E. 4-Amino-2-(p-tolyl)-7H-chromeno[5,6-d]oxazol-7-one. Molbank 2021, 2021, M1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1237
Vlachou E-EN, Balalas TD, Hadjipavlou-Litina DJ, Litinas KE. 4-Amino-2-(p-tolyl)-7H-chromeno[5,6-d]oxazol-7-one. Molbank. 2021; 2021(2):M1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1237
Chicago/Turabian StyleVlachou, Evangelia-Eirini N., Thomas D. Balalas, Dimitra J. Hadjipavlou-Litina, and Konstantinos E. Litinas. 2021. "4-Amino-2-(p-tolyl)-7H-chromeno[5,6-d]oxazol-7-one" Molbank 2021, no. 2: M1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1237
APA StyleVlachou, E.-E. N., Balalas, T. D., Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. J., & Litinas, K. E. (2021). 4-Amino-2-(p-tolyl)-7H-chromeno[5,6-d]oxazol-7-one. Molbank, 2021(2), M1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1237






