Abstract
Here we describe the preparation of 2-(4-((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)thio)-benzylidene)-hydrazine-1-carbothioamide in two steps. In the first step, 1,3-dihydro-2H-1,3-benzimidazole-2-thione was reacted with 4-fluorobenzaldehyde in DMSO to get 4-[(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]benzaldehyde in high yield. The reaction of the obtained aldehyde with thiosemicarbazide in ethanol at reflux temperature yielded 2-({4-[(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]phenyl}methylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide. The structure of the synthesized compounds was established by NMR spectroscopy (1H, 13C), mass spectrometry, and infrared spectroscopy.
1. Introduction
Benzimidazoles are one of the important heterocyclic templates for the intensive investigation in chemical sciences due to their well-known applications and interesting biological activity profile [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Thiosemicarbazone moiety is another privileged structure that is found in several molecules with a wide range of biological activities representing several important classes in drug discovery [7,8,9,10,11,12]. Thiosemicarbazones have been postulated as biologically active compounds and display different types of biological activity, such as anticancer [11,13], anti-HIV [14,15], anticonvulsant [16,17], antimalarial [18,19], anti-inflammatory [20], enzymatic inhibition [9,10,21], antiviral [22], antioxidant [23], antifungal [24], and antibacterial [24,25]. Additionally, the flexibility of thiosemicarbazones as nitrogen and sulfur donors consents them to bring on a great diversity of coordination modes [26].
In this communication, we describe an improved process for the preparation of 4-[(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]benzaldehyde [27]. We also report the preparation of 2-({4-[(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]phenyl}methylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide via the condensation of the synthesized aldehyde with thiosemicarbazide. The authors trust that this is the first report that discloses the synthesis and spectral analysis of 2-({4-[(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]phenyl}methylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide because the exact structure search in the SciFinder database for this compound did not provide any hit or reference. The reported compounds can be assessed.
2. Results and Discussion
Refluxing of 1,3-dihydro-2H-1,3-benzimidazole-2-thione with 4-fluorobenzaldehyde in DMSO/anhydrous K2CO3 mixture gave 4-((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)thio)benzaldehyde 3. The product was isolated in 92% yield. The preparation of 3 is also provided in the literature [27], wherein a mixture of 1,3-dihydro-2H-1,3-benzimidazole-2-thione, 4-iodobenzaldehyde, CuI, 1,10-phenanthroline, K2CO3, and DMF was heated to 140 °C for 18 h. Further, the final product was purified by column chromatography to provide 3 in 87% yield. The current process does not make use of many reagents/parameters of the reported method, such as CuI, 1,10-phenanthroline, DMF, temperature, reaction duration, and column chromatography. These features make the current process an economical, safe, and less time-consuming process. Condensation of the latter with thiosemicarbazide in refluxing EtOH containing a catalytic amount of AcOH gave thiosemicarbazone derivative 4 (Scheme 1). The molecular structures of compounds 3 and 4 were established by spectral data. The IR spectrum of compound 3 displayed the presence of the imino group at 3153 cm−1, carbonyl group at 1693 cm−1, and C=N at 1590 cm−1.(Figures S1 and S2) Additionally, compound 4 showed strong absorption bands at 3411, 3303, and 3158 cm−1 for the NH2/NH groups and 1594 cm−1 for C=N. The 1H NMR of 3 displayed the presence of singlet δH 12.52 for benzimidazole-NH and 9.95 for carboxaldehyde proton, and the aromatic protons (Ar-H) were found in the spectrum at δH 7.11–7.88. 13C NMR (DMSO-d6) showed signals at δC 192.4 assigned to the C=O group, 143.7 ppm assigned to C=N, 140.9 ppm assigned to C-N, in addition to 109.5 ppm assigned aromatic carbons at δC 134.7. The 1H NMR of 4 exhibited the presence of an amino group at δH 8.01, azomethine proton at δH 8.24, a singlet at δH 11.49 for NH-CS, and a singlet at 12.84 for imidazole-NH, in addition to the presence of Ar-Hs at 7.19–8.46 ppm. 13C NMR (DMSO-d6) showed signals at δC 178.0 assigned to the C=S group, δC 145.9 assigned to CH=N, δC 143.7 assigned to C=N, δC 141.1 to C-N, and Ar-C at δC 135.3–111.1 (Figure S3–S6).
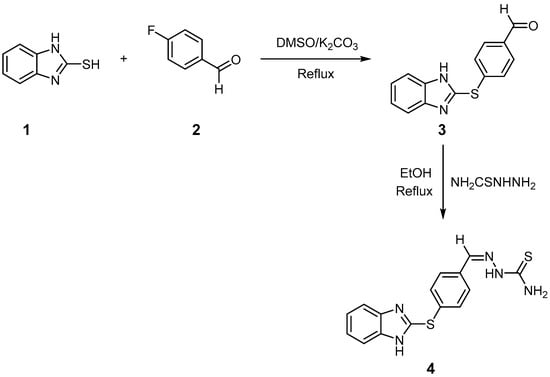
Scheme 1.
Preparation of 4-[(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]benzaldehyde and 2-({4-[(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]phenyl}methylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
The uncorrected melting points were determined by a Stuart melting point apparatus. IR (KBr) was obtained from a Shimadzu 440 spectrometer (ν, cm−1). NMR spectra were recorded by a JEOL ECA-500 spectrometer. The chemical shifts (δ in ppm) were recorded relative to tetramethylsilane (TMS). The elemental analyses were performed at the Microanalytical Center, Cairo University, Cairo (Egypt).
3.2. 4-[(1H-Benzimidazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]benzaldehyde (3)
A mixture of 1,3-dihydro-2H-1,3-benzimidazole-2-thione 1 (10 mmol, 1.5 g) and 4-fluorobenzaldehyde 2 (10 mmol, 1.24 g) in dimethyl sulfoxide (25 mL) was refluxed along with anhydrous potassium carbonate (2 g) for 1 h, cooled, and transferred into crushed ice. The obtained product was collected and recrystallized to afford 3 as colorless solid. Yield: 2.34 g (92%); m.p.: 164–166 °C (acetic acid/water, 7:3); IR (KBr, cm–1): 3153 (NH), 3069 (arom.-CH), 1693 (C=O), 1590 cm−1 (C=N); 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 7.10 (m, 1H, ArH), 7.20 (d, 2H, ArH, J = 5.0 Hz), 7.50 (dd, 3H, ArH, J = 5.0 Hz), 7.86 (d, 2H, ArH, J = 10.0 Hz), 9.95 (s, 1H, CHO), 12.52 (hump, 1H, benzimidazole-NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 109.5, 110.5, 119.4, 122.6, 124.3, 128.1, 128.9, 129.8, 130.2, 130.3, 130.8, 132.2, 134.7 (Ar’C), 140.9 (C-N), 143.7, 147.1 (C=N), 192.2 (C=O). Anal. calcd for C14H10N2OS: C, 66.12; H, 3.96; N, 11.02; found: C, 65.94; H, 3.81; N, 10.87.
3.3. 2-({4-[(1H-Benzimidazol-2-yl)sulfanyl]phenyl}methylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide (4)
A solution of aldehyde 3 (10 mmol, 2.54 g) and thiosemicarbazide (10 mmol, 0.91 g) was refluxed in EtOH (30 mL) containing acetic acid (5 mL) for 3 h. The obtained solid was collected and recrystallized to give 4. Yellow crystals: yield: 2.45 g (75%); m.p., 268–270 °C (dioxane); IR (KBr, cm–1): 3411, 3303, 3158 (NH2/NH), 3014 (arom.-CH), 1594 (C=N); 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ/ppm): 7.15 (dd, 2H, ArH, J = 5.0 Hz), 7.41 (d, 1H, ArH, J = 5.0 Hz), 7.44 (d, 1H, ArH, J = 10.0 Hz), 7.57 (d, 1H, ArH, J = 5.0 Hz), 7.81 (d, 2H, ArH, J = 10.0 Hz), 8.01 (d, 2H, NH2, J = 10.0 Hz), 8.24 (s, 1H, CH=N), 11.49 (s, 1H, NH-CS), 12.84 (s, 1H, benzimidazole-H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 111.1, 118.4, 121.7, 122.8, 128.2, 130.7, 133.1, 133.9, 135.3 (Ar’C), 141.1 (C-N), 143.7 (C=N), 145.9 (CH=N), 178.0 (C=S). Anal. calcd for C15H13N5S2: C, 55.02; H, 4.00; N, 21.39; found: C, 54.86; H, 3.84; N, 21.23.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online in Figures S1–S6 (FTIR, 1H NMR, and 13C NMR spectra of compounds 3 and 4).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.T.U., H.K.T. and M.Y.A.S.; methodology, M.T.U., H.K.T. and M.Y.A.S.; formal analysis, M.T.U., H.K.T. and M.Y.A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.T.U., H.K.T. and M.Y.A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was carried out with the financial support of Northern Border University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in the framework of the scientific project 2017-1-8-F-7413.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their deep gratitude to Northern Border University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, for providing financial support for this research (project 2017-1-8-F-7535).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wubulikasimu, R.; Yang, Y.; Xue, F.; Luo, X.; Shao, D.; Li, Y.; Ye, W. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Benzimidazole Derivatives Bearing a Heterocyclic Ring at 4/5 Position. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, 34, 2297–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xiang, P.; Zhou, T.; Wang, L.; Sun, C.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, L. Novel benzothiazole, benzimidazole and benzoxazole derivatives as potential antitumor agents: Synthesis and preliminary in vitro biological evaluation. Molecules 2012, 17, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Tandon, V. Synthesis and biological activity of novel inhibitors of topoisomerase I: 2-Arylsubstituted 2-bis-1H-benzimidazoles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoci, V.; Cucu, D.; Zbancioc, G.; Moldoveanu, C.; Mangalagiu, V.; Amariucai-Mantu, D.; Aricu, A.; Mangalagiu, I. Bis-(imidazole/benzimidazole)-pyridine derivatives: Synthesis, structure and antimycobacterial activity. Future Med. Chem. 2020, 12, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobis, K.; Foks, H.; Serocki, M.; Augustynowicz-kope, E.; Ave, G. Synthesis and evaluation of in vitro antimycobacterial activity of novel 1H-benzo[d]imidazole derivatives and analogues Agnieszka Napi o. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, D.; Kumar, K.; Knudson, S.; Slayden, R.; Ojima, I. SAR studies on trisubstituted benzimidazoles as inhibitors of Mtb FtsZ for the development of novel antitubercular agents. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9756–9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Lin, T.; Cory, J.; Cory, A.; Sartorelli, A. Synthesis and biological activity of 3- and 5-amino derivatives of pyridine-2-carboxaldehyde thiosemicarbazone. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 2586–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarasconi, P.; Capacchi, S.; Pelosi, G.; Cornia, M.; Albertini, R.; Bonati, A.; Dall’Aglio, P.; Lunghi, P.; Pinelli, S. Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization and biological properties of new natural aldehydes thiosemicarbazones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2000, 8, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.K.; Chavarria, G.E.; Charlton-Sevcik, A.K.; Arispe, W.M.; MacDonough, M.T.; Strecker, T.E.; Chen, S.E.; Siim, B.G.; Chaplin, D.J.; Trawick, M.L. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of potent thiosemicarbazone based cathepsin L inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, N.; Mallari, J.P.; Hansell, E.J.; Mackey, Z.; Doyle, P.; Zhou, Y.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; McKerrow, J.H.; Guy, R.K. Discovery of potent thiosemicarbazone inhibitors of rhodesain and cruzain. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.X.; Zhou, W.; Xia, C.N.; Wen, X. Synthesis and anticancer activity of Thiosemicarbazone. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 2213–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, M.S.; Zakaria, A.S.; Ignasius, P.P.; Al-Wabli, R.I.; Joe, I.H.; Attia, M.I. Synthesis, spectroscopic investigations, DFT studies, molecular docking and antimicrobial potential of certain new indole-isatin molecular hybrids: Experimental and theoretical approaches. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1153, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakherad, Z.; Safavi, M.; Fassihi, A.; Sadeghi-Aliabadi, H.; Bakherad, M.; Rastegar, H.; Ghasemi, J.B.; Sepehri, S.; Saghaie, L.; Mahdavi, M. Anti-cancer, anti-oxidant and molecular docking studies of thiosemicarbazone indole-based derivatives. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 2827–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, M.; Taslimi, P.; Shafiq, Z.; Khan, S.; Salmas, R.E.; Zangeneh, M.M.; Saeed, A.; Zangeneh, A.; Sadeghian, N.; Asari, A.; et al. Synthesis, bioactivity and binding energy calculations of novel 3-ethoxysalicylaldehyde based thiosemicarbazone derivatives. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 100, 103924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Ghaffari, R.; Sardari, S.; Farahani, Y.F.; Mohebbi, S. Discovery of novel isatin-based thiosemicarbazones: Synthesis, antibacterial, antifungal, and antimycobacterial screening. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 15, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kshirsagar, A.; Toraskar, M.P.; Kulkarni, V.M.; Dhanashire, S.; Kadam, V. Microwave assisted synthesis of potential anti-infective and anticonvulsant thiosemicarbazones. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 2009, 1, 696–701. [Google Scholar]
- Matsa, R.; Makam, P.; Kaushik, M.; Hoti, S.L.; Kannan, T. Thiosemicarbazone derivatives: Design, synthesis and in vitro antimalarial activity studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 137, 104986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.B.; Souza-Fagundes, E.M.; Soares, R.P.; Andrade, A.A.; Krettli, A.U.; Zani, C.L. Synthesis and antimalarial activity of semicarbazone and thiosemicarbazone derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Nonato, F.; Zafred, R.; Leite, N.; Ruiz, A.; Carvalho, J.; Silva, A.; Moura, R.; Lim, M. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory effect of derivative (E)-N-(4-bromophenyl)-2-(thiophen- 2-ylmethylene)-thiosemicarbazone. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 80, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hałdys, K.; Latajka, R. Thiosemicarbazones with tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Med. Chem. Commun. 2019, 10, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacruz, M.; Fabiani, M.; Castro, E.; Cavallaro, L.; Finkielsztein, L. Synthesis, antiviral evaluation and molecular docking studies of N4-aryl substituted/unsubstituted thiosemicarbazones derived from 1-indanones as potent anti-bovine viral diarrhea virus agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 4055–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Le, T.; Bui, T. Antioxidant activities of thiosemicarbazones from substituted benzaldehydes and N-(tetra-O-acetyl-β-D-galactopyranosyl)thiosemicarbazide. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 60, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoli, J.; Montalbano, S.; Spadola, G.; Rogolino, D.; Pelosi, G.; Bisceglie, F.; Restivo, F.; Degola, F.; Serra, O.; Buschini, A.; et al. Antiaflatoxigenic Thiosemicarbazones as Crop-Protective Agents: A Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10947–10953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sens, L.; Souza, A.; Pacheco, L.; Menegatti, A.; Mori, M.; Mascarello, A.; Nunes, R.; Terenzi, H. Synthetic thiosemicarbazones as a new class of Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein tyrosine phosphatase A inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 5742–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrido, R.; Gonzalez-Noya, A.M.; Romero, M.J.; Martinez-Calvo, M.; Lopez, M.V.; Gomez-Forneas, E.; Zaragoza, G.; Bermejo, M.R. Pentadentate thiosemicarbazones as versatile chelating systems. A comparative structural study of their metallic complexes. Dalton Trans. 2008, 47, 6776–6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Kovacevic, Z.; Siafakas, A.R.; Jansson, P.J.; Stefani, C.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Sharpe, P.C.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Richardson, D.R. Thiosemicarbazones from the old to new: Iron chelators that are more than just ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5271–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, A.N.; Stefan, E.; Caballero, F. Myc Modulators and Uses Thereof. U.S. Patent US10017520B2, 10 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).