Methyl (2E)-3-[3-Benzyl-2-(3-methoxy-3-oxoprop-1-yn-1-yl)-2-(1-naphthyl)imidazolidin-1-yl]acrylate
Abstract
1. Introduction
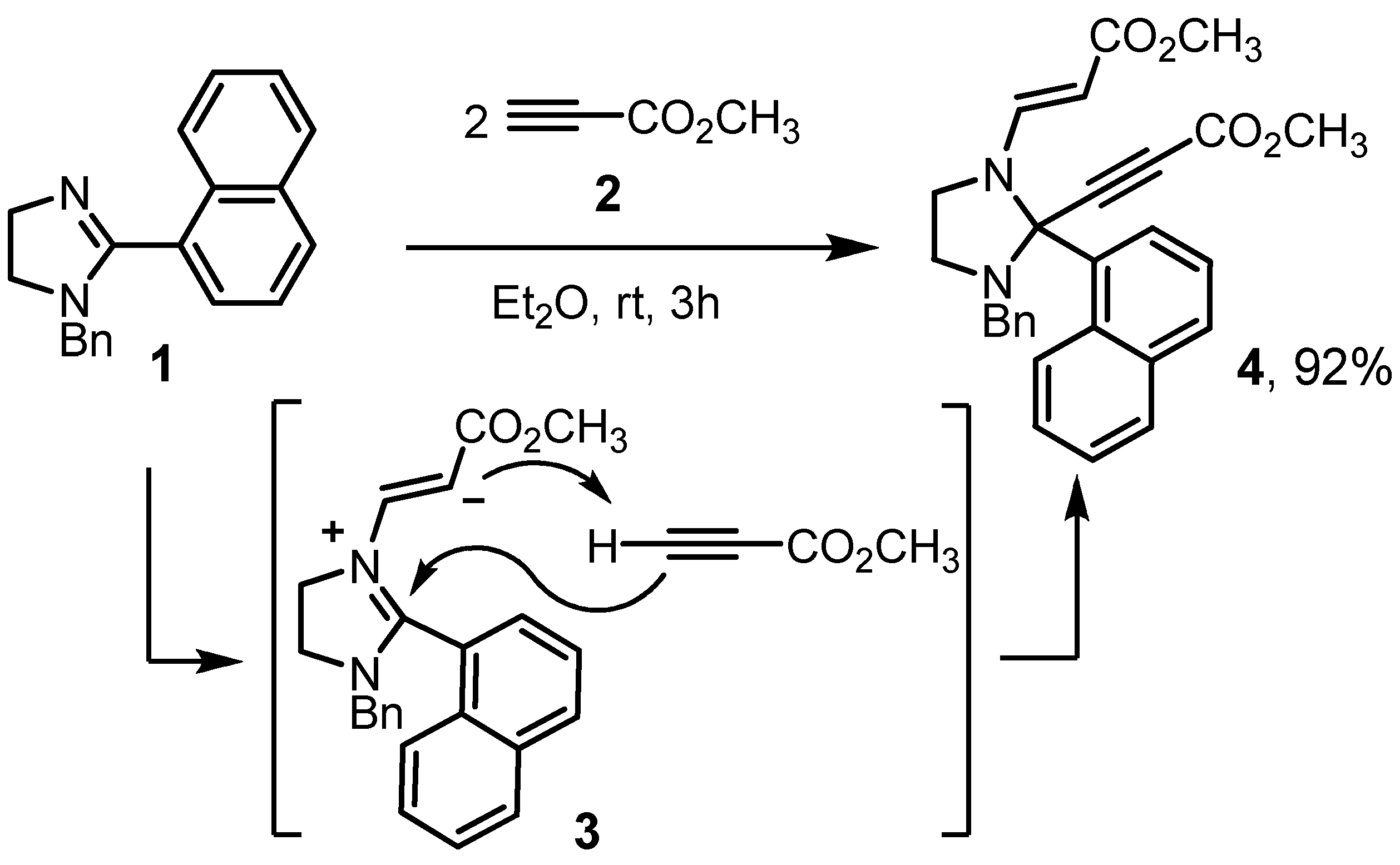
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Methyl (2E)-3-[3-Benzyl-2-(3-methoxy-3-oxoprop-1-yn-1-yl)-2-(1-naphthyl)imidazolidin-1-yl]acrylate
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lauder, K.; Toscani, A.; Scalacci, N.; Castagnolo, D. Synthesis and Reactivity of Propargylamines in Organic Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 14091–14200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, T. Gold-Catalyzed Transformations of Propargyl Alcohols and Propargyl Amines. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2018, 7, 1758–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Chen, K.; Shi, C.; Huang, D. Recent Advances in Reactions of Propargylamines. Synthesis 2020, 52, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossy, J.; Poitevin, C.; Sallé, L.; Gomez Pardo, D. The Thermal Rearrangement of N-Alkyl-N-Vinylpropargylamines into 2-Methylpyrroles. A New Synthesis of Annulated[b]Pyrroles. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 6709–6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnihan, E.C.; Colletti, S.L.; Toste, F.D.; Shen, H.C. Gold(I)-catalyzed regioselective cyclizations of silyl ketene amides and carbamates with alkynes. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 6287–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremner, W.S.; Organ, M.G. Formation of Substituted Pyrroles via an Imine Condensation/Aza-Claisen Rearrangement/Imine-Allene Cyclization Process by MAOS. J. Comb. Chem. 2008, 10, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacchi, S.; Fabrizi, G.; Filisti, E. N-Propargylic β-Enaminones: Common Intermediates for the Synthesis of Polysubstituted Pyrroles and Pyridines. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 2629–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, J.; Chen, Y.; Yue, B.; Xu, M.; Jin, H. Synthesis of Polysubstituted Pyrroles from Activated Alkynes and N-Propargylamines through Base-Catalyzed Cascade Reaction. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 3164–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Konishi, T.; Hanzawa, Y. Synthesis of Pyrroles by Gold(I)-Catalyzed Amino-Claisen Rearrangement of N-Propargyl Enaminone Derivatives. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 372–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Wan, B. Highly regioselective migration of the sulfonyl group: Easy access to functionalized pyrroles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1693–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, F.; Kan, X.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q. Base-promoted intramolecular cyclization of: N-alkyl, N-propargylic β-enaminones for the synthesis of polysubstituted pyrroles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 68454–68459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Lv, W.; Yu, J.; Xiao, S.; Cheng, G. Base-promoted C-C bond cleavage for the synthesis of 2,3,4-trisubstituted pyrroles from: N-propargyl β-enaminones. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 3103–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikayuki, Y.; Miyashige, T.; Yonekawa, S.; Kirita, A.; Matsuo, N.; Teramoto, H.; Sasaki, S.; Higashiyama, K.; Yamauchi, T. Transition-Metal-Free Synthesis of Pyridine Derivatives by Thermal Cyclization of N-Propargyl Enamines. Synthesis 2020, 52, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matouš, P.; Kadaník, M.; Timoracký, M.; Kuneš, J.; Maříková, J.; Růžička, A.; Kočovský, P.; Pour, M. Nucleophile-assisted cyclization of β-propargylamino acrylic compounds catalyzed by gold(i): A rapid construction of multisubstituted tetrahydropyridines and their fused derivatives. Org. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 3356–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golantsov, N.E.; Golubenkova, A.S.; Festa, A.A.; Varlamov, A.V.; Voskressensky, L.G. A Domino Route toward Polysubstituted Pyrroles from 2-Imidazolines and Electron-Deficient Alkynes. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 4726–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujioka, H.; Murai, K.; Kubo, O.; Ohba, Y.; Kita, Y. One-pot synthesis of imidazolines from aldehydes: Detailed study about solvents and substrates. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubenkova, A.S.; Golantsov, N.E.; Festa, A.A.; Voskressensky, L.G. 1-Benzyl-2-(Thien-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole. MolBank 2020, 2020, M1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golubenkova, A.S.; Golantsov, N.E.; Voskressensky, L.G. Methyl (2E)-3-[3-Benzyl-2-(3-methoxy-3-oxoprop-1-yn-1-yl)-2-(1-naphthyl)imidazolidin-1-yl]acrylate. Molbank 2021, 2021, M1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1176
Golubenkova AS, Golantsov NE, Voskressensky LG. Methyl (2E)-3-[3-Benzyl-2-(3-methoxy-3-oxoprop-1-yn-1-yl)-2-(1-naphthyl)imidazolidin-1-yl]acrylate. Molbank. 2021; 2021(1):M1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1176
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolubenkova, Alexandra S., Nikita E. Golantsov, and Leonid G. Voskressensky. 2021. "Methyl (2E)-3-[3-Benzyl-2-(3-methoxy-3-oxoprop-1-yn-1-yl)-2-(1-naphthyl)imidazolidin-1-yl]acrylate" Molbank 2021, no. 1: M1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1176
APA StyleGolubenkova, A. S., Golantsov, N. E., & Voskressensky, L. G. (2021). Methyl (2E)-3-[3-Benzyl-2-(3-methoxy-3-oxoprop-1-yn-1-yl)-2-(1-naphthyl)imidazolidin-1-yl]acrylate. Molbank, 2021(1), M1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1176





