Specific Recognition of Glycoproteins: Design Strategies and Application Prospects of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Challenges in Glycoprotein Imprinting
- (a)
- Structural instability and conformational heterogeneity
- (b)
- Inefficient template removal and mass transfer limitations
- (c)
- Prominent non-specific binding and insufficient selectivity
3. Advanced Strategies for Glycoprotein-Imprinting
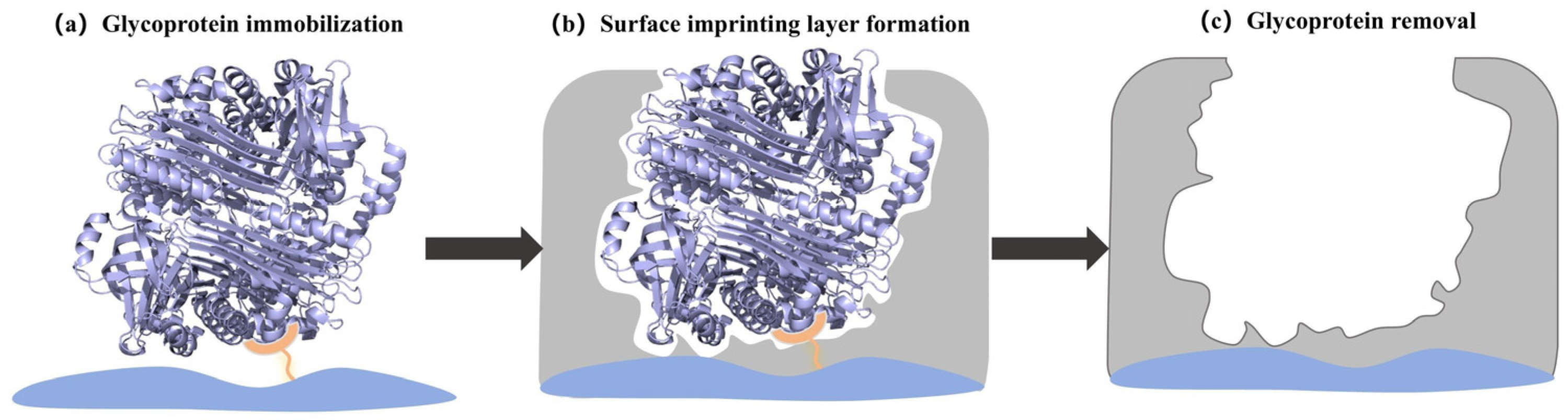
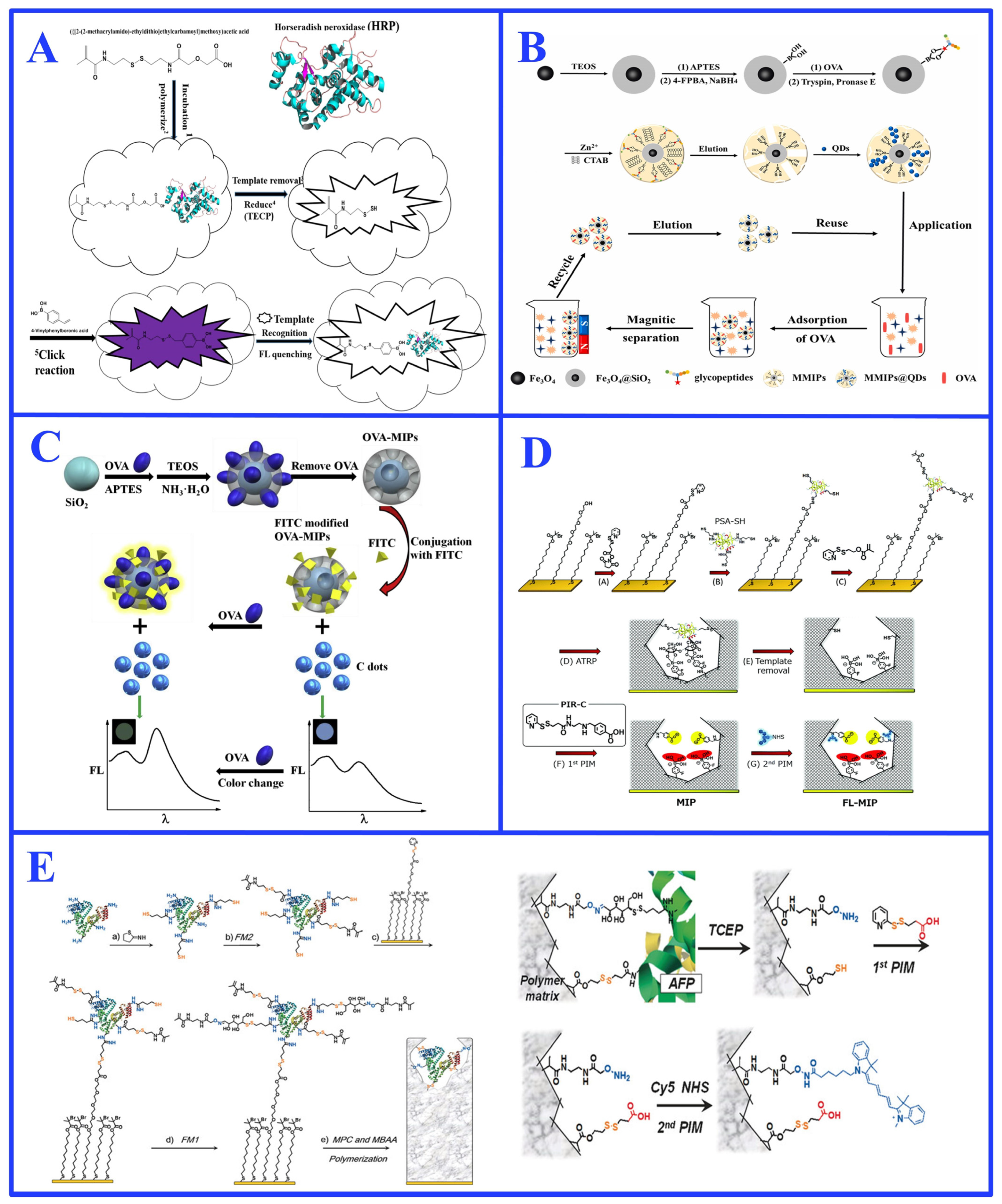
3.1. Oriented Surface Imprinting
3.1.1. Oriented Immobilization of the Template

3.1.2. Surface Imprinting Layer
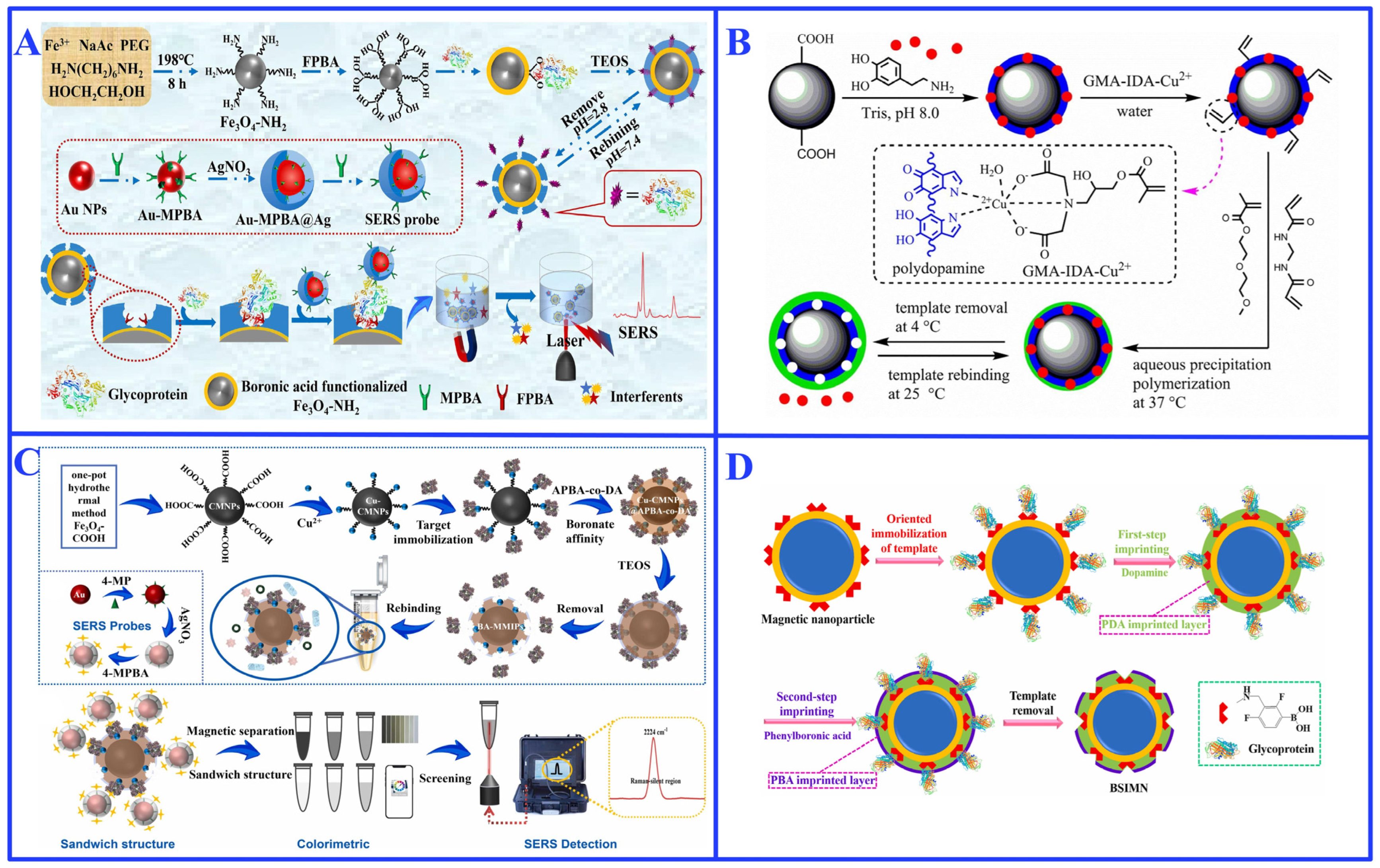
3.1.3. Functional Substrates
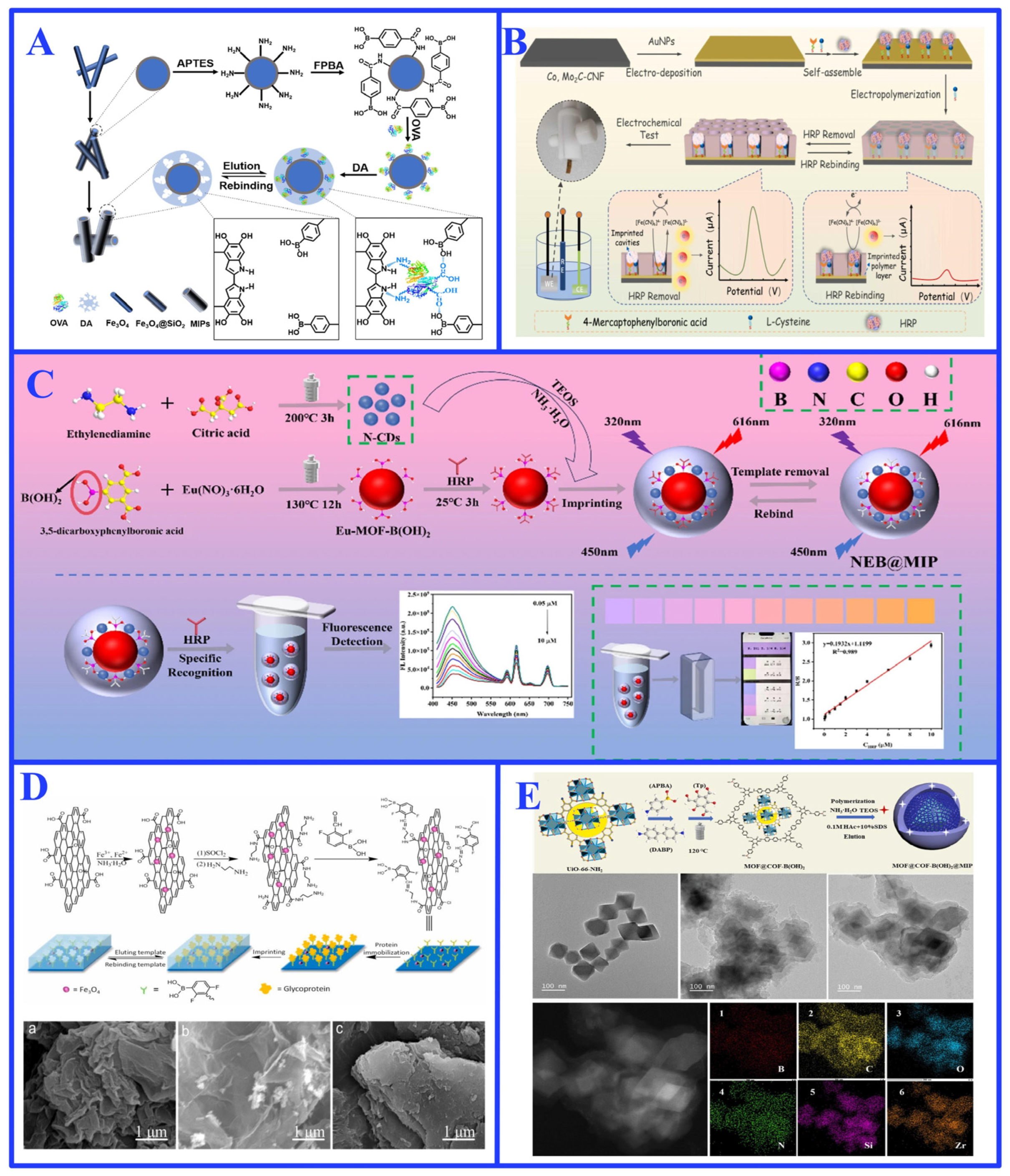
3.1.4. Challenges and Limitations
3.2. Epitope Imprinting
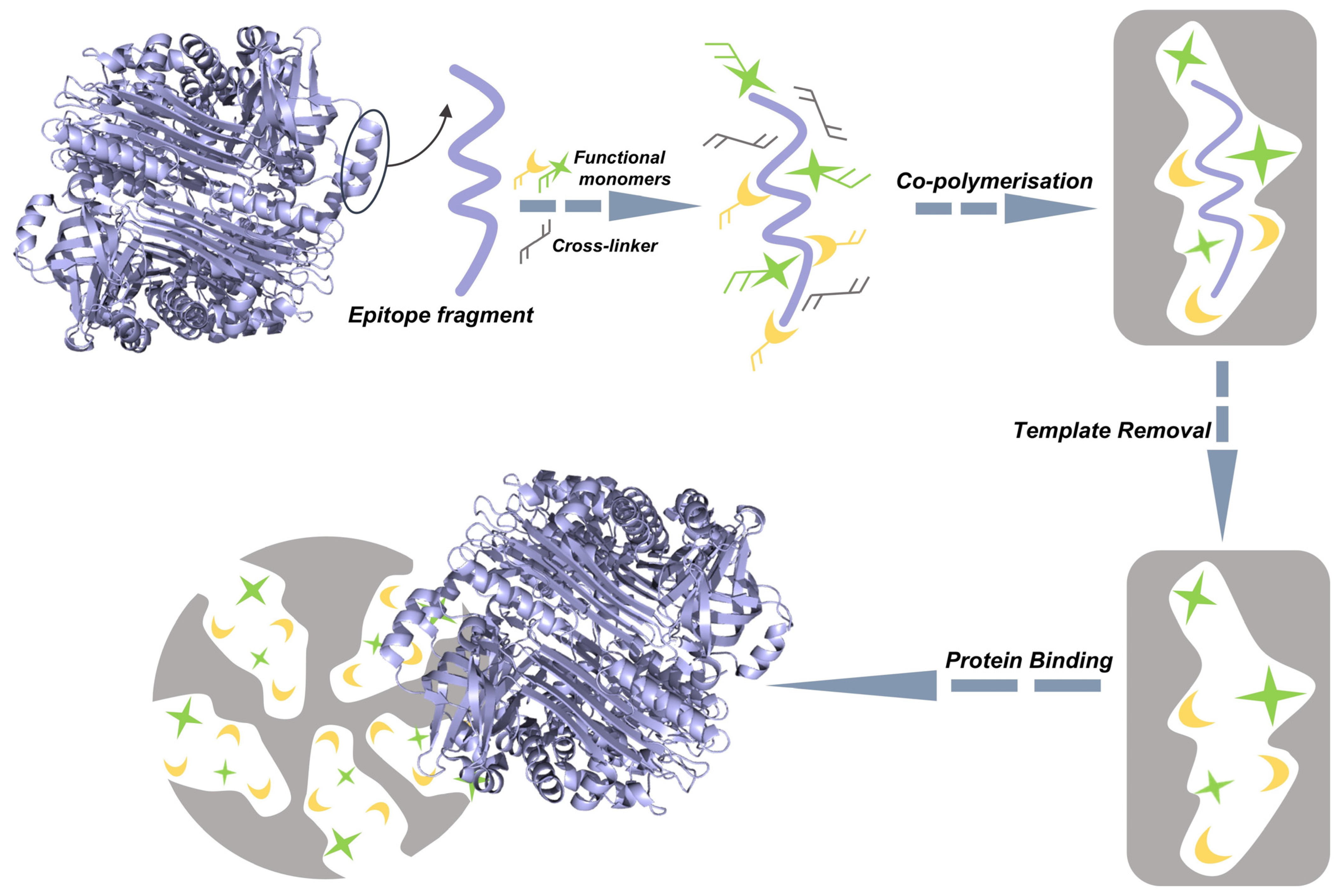
3.2.1. Single-Epitope Imprinting
3.2.2. Multi-Epitope Imprinting
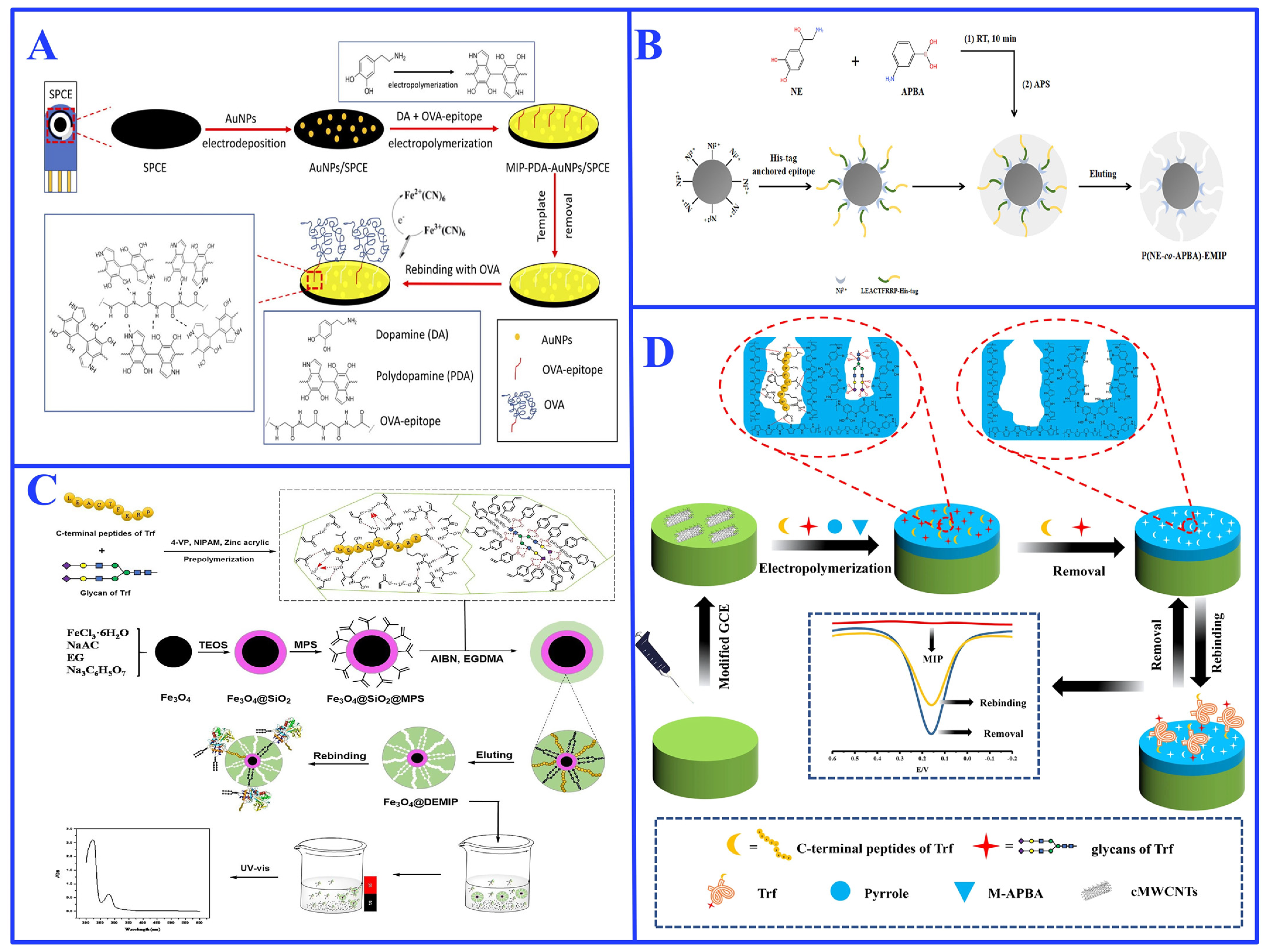
3.2.3. Challenges and Limitations
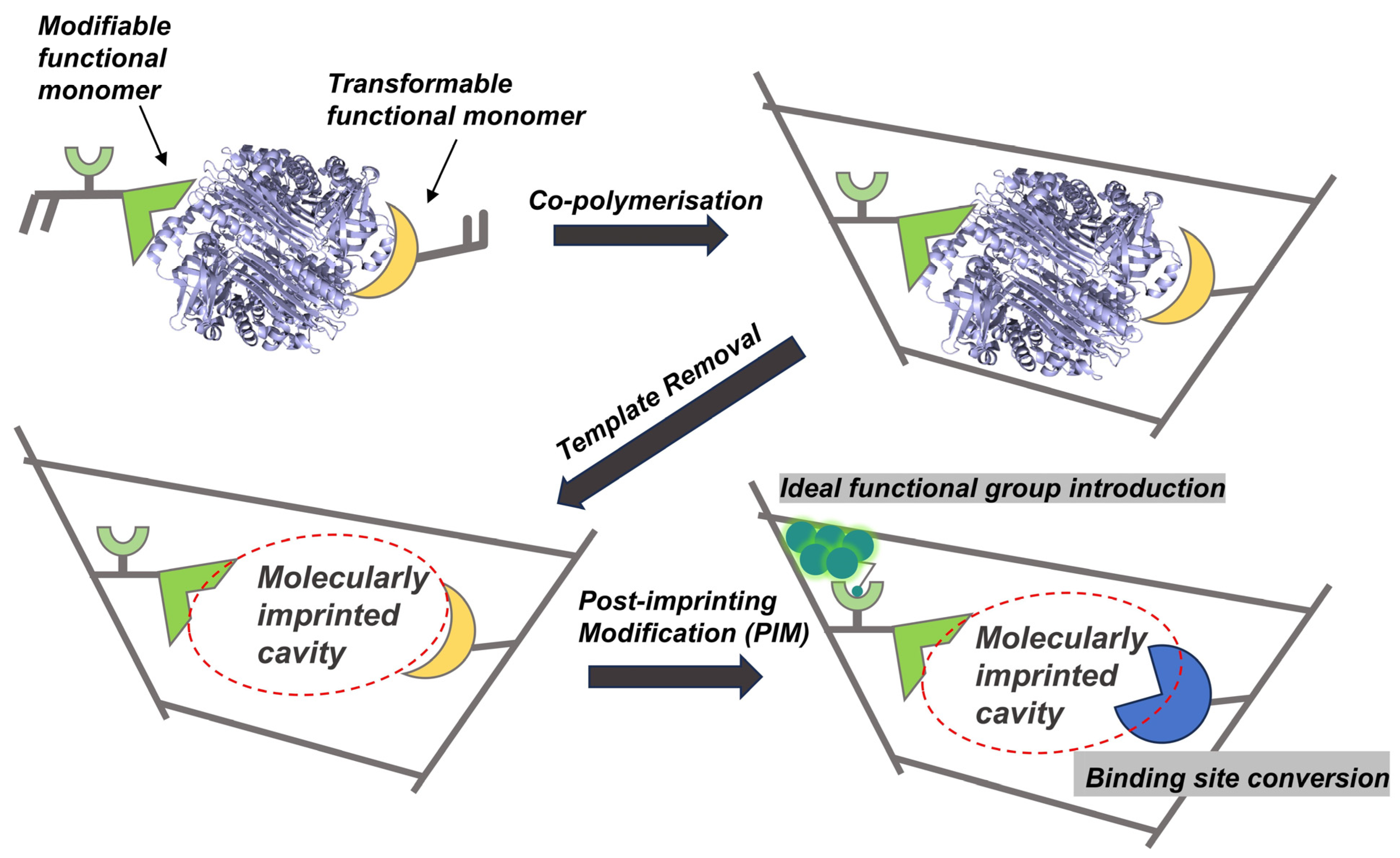
3.3. Post-Imprinting Modification
4. Comparative Analysis and Strategic Outlook
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Unione, L.; Ardá, A.; Jiménez-Barbero, J.; Millet, O. NMR of glycoproteins: Profiling, structure, conformation and interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2021, 68, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; P Chaudhary, B.; Zoetewey, D. Structural Insight into the Mechanism of N-Linked Glycosylation by Oligosaccharyltransferase. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, P. O-GlyThr: Prediction of human O-linked threonine glycosites using multi-feature fusion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, P.; Kang, H.; Lee, B. Glycosylation and behavioral symptoms in neurological disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, D.; Wang, W.; Jia, W.; Song, J.; Gong, L.; Zhong, L.; Yang, J. The effects of glycosylation modifications on monocyte recruitment and foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobral, D.; Francisco, R.; Duro, L.; Videira, P.A.; Grosso, A.R. Concerted Regulation of Glycosylation Factors Sustains Tissue Identity and Function. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vong, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Tanaka, K. Artificial Glycoproteins as a Scaffold for Targeted Drug Therapy. Small 2020, 16, 1906890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.A.H.; Bertozzi, C.R. The clinical impact of glycobiology: Targeting selectins, Siglecs and mammalian glycans. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 217–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomari, N.; Totonchy, J. Cytokine-Targeted Therapeutics for KSHV-Associated Disease. Viruses 2020, 12, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janecki, D.J.; Kao-Scharf, C.-Y.; Hoffmann, A. Discovery and Characterization of Unusual O-Linked Glycosylation of IgG4 Antibody Using LC-MS. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2025, 39, e9969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, V.; Daly, J.; Kim, J.; Piatnitca, L.; Yuen, K.A.; Kumar, B.; Taherzadeh Ghahfarrokhi, M.; Bui, T.Q.T.; Azadi, P.; Vu, L.P.; et al. The glycosyltransferase ST3GAL4 drives immune evasion in acute myeloid leukemia by synthesizing ligands for the glyco-immune checkpoint receptor Siglec-9. Leukemia 2025, 39, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aapro, M.S.; Chaplin, S.; Cornes, P.; Howe, S.; Link, H.; Koptelova, N.; Mehl, A.; Di Palma, M.; Schroader, B.K.; Terkola, R. Cost-effectiveness of granulocyte colony-stimulating factors (G-CSFs) for the prevention of febrile neutropenia (FN) in patients with cancer. Support. Care Cancer 2023, 31, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, M.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Park, M.; Li, C.H.; Lee, T.; Lee, J.-A.; Kim, Y.-M.; et al. Innate immune responses against mRNA vaccine promote cellular immunity through IFN-β at the injection site. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmermann, C. From chemotherapy to biotechnology: The transformation of the cancer research pipeline at Hoffmann-La Roche. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, D.; Chakraborty, D.; Sreenivasan, S.; Mishra, A.; Rathore, A.S. Higher concentration of trehalose dihydrate stabilizes recombinant IgG1 under forced stress conditions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2025, 114, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, S.; Wang, J.; Li, R.-J.; Hon, Y.Y.; Weis, S.L.; Wang, Y.-M.C.; Schuck, R.; Pacanowski, M. Clinical pharmacology considerations for first-in-human clinical trials for enzyme replacement therapy. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2024, 47, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero Roche, D.E.; Chandler, K.B. Clinical glycoprotein mass spectrometry: The future of disease detection and monitoring. J. Mass Spectrom. 2024, 59, e5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.-M.; Zhou, M.-T.; Li, S.-W.; Zhen, X.-C.; Yang, S. Glycoproteins as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases: A glycoproteomic approach. J. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 99, 1308–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zheng, H.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Q. Progress in Monolithic Column-based Separation and Enrichment of Glycoproteins. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 48, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Qing, G. Enrichment driven glycoproteomics: New materials, new methods, and beyond. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 168, 117290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kombe Kombe, A.J.; Xie, J.; Zahid, A.; Ma, H.; Xu, G.; Deng, Y.; Nsole Biteghe, F.A.; Mohammed, A.; Dan, Z.; Yang, Y.; et al. Detection of Circulating VZV-Glycoprotein E-Specific Antibodies by Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA) for Varicella–Zoster Diagnosis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmelter, C.; Brueck, A.; Perumal, N.; Qu, S.; Pfeiffer, N.; Grus, F.H. Lectin-Based Affinity Enrichment and Characterization of N-Glycoproteins from Human Tear Film by Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2023, 28, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, H.; Yue, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, L.; Nie, Y.; Ye, M. Highly Efficient Enrichment of O-GlcNAc Glycopeptides Based on Chemical Oxidation and Reversible Hydrazide Chemistry. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 16618–16627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamonti, M.; Zhai, Z.; Moreschini, M.; Wilson, J.W.; Zhou, M.; Schoenmakers, P.J.; Gargano, A.F.G. Influence of ion-pairing reagents on the separation of intact glycoproteins using hydrophilic-interaction liquid chromatography—High-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1688, 463721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delafield, D.G.; Li, L. Recent Advances in Analytical Approaches for Glycan and Glycopeptide Quantitation. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2021, 20, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, J.; Zhen, X.; Chen, L.; Yuan, W.; Feng, Q.; Liu, X. Rational construction of fluorescent molecular imprinted polymers for highly efficient glycoprotein detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1209, 339875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse Sum Bui, B.; Mier, A.; Haupt, K. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Synthetic Antibodies for Protein Recognition: The Next Generation. Small 2023, 19, 2206453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.J.; Yu, S.W.; Gao, S.J.; Guo, H.X. Research Progress of Molecular Imprinting Technology. In Advanced Engineering Materials III; PTS 1-3; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Wollerau, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 1678–1681. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrani, S.; Sadati Behbahani, E.; Ghaedi, M.; Amrollahi Miandeh, Y.; Asfaram, A. Molecular imprinted technology using in biosensing: A review. Microchem. J. 2024, 203, 110888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Ayela, C. Molecular Imprinting; Haupt, K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.J.; Yu, S.W.; Li, H.X. Synthesis of Novel Separation Materials Based on Molecular Imprinting Technology. In Advanced Engineering Materials II; PTS 1-3; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Wollerau, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 1441–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Polyakov, M.V. Adsorption properties and structure of silica gel. Zhur. Fiz. Khim. 1931, 2, 799–805. [Google Scholar]
- Wulff, G. The use of polymers with enzyme-analogous structures for the resolution of racemates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1972, 11, 341. [Google Scholar]
- Wulff, G.; Sarhan, A.; Zabrocki, K. Enzyme-analogue built polymers and their use for the resolution of racemates. Tetrahedron Lett. 1973, 14, 4329–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshady, R.; Mosbach, K. Synthesis of substrate-selective polymers by host-guest polymerization. Die Makromol. Chem. 1981, 182, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlatakis, G.; Andersson, L.I.; Müller, R.; Mosbach, K. Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting. Nature 1993, 361, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glad, M.; Norrlöw, O.; Sellergren, B.; Siegbahn, N.; Mosbach, K. Use of silane monomers for molecular imprinting and enzyme entrapment in polysiloxane-coated porous silica. J. Chromatogr. A 1985, 347, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X.; Wilson, G.; Zong, R.; Fu, Q. Antibody mimics for precise identification of proteins based on molecularly imprinted polymers: Developments and prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Du, M.; Wu, W.; Yang, J.; Chen, Q. Advances in the selection of functional monomers for molecularly imprinted polymers: A review. J. Sep. Sci. 2024, 47, 2400353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazys, E.; Ratautaite, V.; Mohsenzadeh, E.; Boguzaite, R.; Ramanaviciute, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Formation of molecularly imprinted polymers: Strategies applied for the removal of protein template (review). Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 337, 103386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Jiang, L.-Y.; Ma, J.-T.; Jia, Q. Application of Molecular Imprinting Technology in Post-translational Modified Protein Enrichment. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, M. Perspective towards nanomaterial-integrated molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)-based electrochemical sensors for protein biomarkers detection: A review. Microchem. J. 2025, 215, 114314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Zhu, S.; Amin, F.R.; Hussain, D.; Du, Z.; Hu, L. Molecular imprinting of glycoproteins: From preparation to cancer theranostics. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2406–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Lin, Z. Recent advances in protein-imprinted polymers: Synthesis, applications and challenges. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6571–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B. Anti-nonspecific adsorption segments-assisted self-driven surface imprinted fibers for efficient protein separation. AIChE J. 2022, 68, e17802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalecki, J.; Iskierko, Z.; Cieplak, M.; Sharma, P.S. Oriented Immobilization of Protein Templates: A New Trend in Surface Imprinting. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3710–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietl, S.; Sobek, H.; Mizaikoff, B. Epitope-imprinted polymers for biomacromolecules: Recent strategies, future challenges and selected applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Z. Post-imprinting modification of molecularly imprinted polymer for proteins detection: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Haupt, K.; Mosbach, K. The Use of Immobilized Templates—A New Approach in Molecular Imprinting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 2115–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Hong, L.; Xie, X.; Liu, K.; Yang, J.; Wang, S. Nanomaterials-Based Surface Protein Imprinted Polymers: Synthesis and Medical Applications. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2021, 222, 2000222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yao, J.; Zou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, Y.; et al. A general method to improve imprinting efficiency in surface protein imprinting by enhanced pre-assembly. Acta Biomater. 2025, 198, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, T.; Tang, F.; Li, W.; Zhang, J. In situ growth of boronic acid-decorated metal-organic frameworks on chitosan microspheres for highly selective enrichment of cis-diol molecules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 304, 140935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Zou, T.; Tang, F.; Zhang, J. Fabrication of boronic acid-functionalized covalent organic framework for the selective adsorption of cis-diol-containing compounds. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 644, 158698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.; Wang, S.; Bie, Z.; He, H.; Liu, Z. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers specific to glycoproteins, glycans and monosaccharides via boronate affinity controllable–oriented surface imprinting. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 964–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Pang, J.; Xu, S.; He, H.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z. A Glycoform-Resolved Dual-Modal Ratiometric Immunoassay Improves the Diagnostic Precision for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202113528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.-y.; Jiang, Z.-q.; Wang, X.-y.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.-q.; Liu, W.-w.; Ding, L.-x. Synthesis of hollow molecular imprinting nanoparticles based on polyethylenimine and boronate affinity for selective extraction of ovalbumin. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1705, 464181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lin, B.; Wang, Y.; Guo, M.; Cao, Y. Precise detection of prostate specific antigen in serum: A surface molecular imprinted sensor based on novel cooperated signal amplification strategy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 302, 126998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Han, T.; Cheng, M.; Dong, L. Wulff-type boronic acid-functionalized quantum dots for rapid and sensitive detection of Gram-negative bacteria. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 356, 131332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, H.; Liu, Z. Recent progress and application of boronate affinity materials in bioanalysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 140, 116271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-H.; Li, C.-H.; Zuo, J.-L. Dynamic polymeric materials based on reversible B–O bonds with dative boron–nitrogen coordination. SmartMat 2023, 4, e1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Yang, C.; Guo, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, N.; Wang, L.; Ngo, H.H.; Li, J. Preparation and application of teamed boronate affinity magnetic protein imprinted polymer: Pollutants removal, filter resistance improvement and synergistic glycoprotein recovery under physiological pH in sequencing batch reactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 518, 164868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Wu, X.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Cai, C. Molecular imprinting resonant light scattering sensor based on teamed boronate affinity for highly specific detection of glycoprotein. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 112260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mışraklı, M.; Rizzo, S.A.; Bordano, V.; Bozza, A.; Ferraris, L.; Marini, E.; Muntoni, E.; Capucchio, M.T.; Scomparin, A.; Battaglia, L. Concanavalin a Grafted Nanoemulsions for Nasal Delivery: Preliminary Studies with Fluorescently Labelled Formulations. Materials 2024, 17, 4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, M.R.; Colaco, V.; Bandi, S.P.; Hebbar, S.; Datta, D.; Dhas, N.; Singh, S.; Madhystha, H.K. Demystifying multipronged approaches of wheat germ agglutinin-mediated drug delivery, targeting, and imaging: An explicative review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 102, 106307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Wang, F.; Sun, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chen, R.; Ma, X.; Liu, C. Selective extraction of bioactive glycoprotein in neutral environment through Concanavalin A mediated template immobilization and dopamine surface imprinting. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 86455–86463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, K.; Khazaipoul, S.; Wort, J.L.; Sobczak, A.I.S.; Mkami, H.E.; Stewart, A.J.; Bode, B.E. Investigating Native Metal Ion Binding Sites in Mammalian Histidine-Rich Glycoprotein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 8064–8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Gao, P.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Lv, J. Histidine-based coordinative polymers for efficient intracellular protein delivery via enhanced protein binding, cellular uptake, and endosomal escape. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 1765–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Bi, S.; Zhang, B.; Tong, Y.; Chen, X.; Tian, M. Synthesis of nanoparticles with a combination of metal chelation and molecular imprinting for efficient and selective extraction of glycoprotein. Microchem. J. 2021, 167, 106262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J. A comparative study of photoresponsive molecularly imprinted polymers with different shell thicknesses: Effects on 6-O-α-maltosyl-β-cyclodextrin separation. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 4060–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhu, H.; Ma, Y.; Liu, N.; Niu, X.; Wei, M.; Pan, J. Rational design and fabrication of surface molecularly imprinted polymers based on multi-boronic acid sites for selective capture glycoproteins. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 367, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Chen, B.; He, J. Boronate Affinity Molecular Imprinting Based Sugar and Ovalbumin Fiber Optic SPR Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 34387–34393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumsap, T.; Bamrungsap, S.; Thu, V.T.; Nguyen, L.T. Development of epitope-imprinted polydopamine magnetic nanoparticles for selective recognition of allergenic egg ovalbumin. Chem. Pap. 2022, 76, 6129–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Tong, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Bi, S.; Tian, M. Metal oxide–based macroporous ordered double affinity molecularly imprinted polymer for specific separation and enrichment of glycoprotein from food samples: A co-modification of DMSA and boronate affinity. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, S.M.; NA, A.; Abd-elFatah, N.N.; Morsi, M.M.; Shaker, N. Recognition and adsorption characteristics of tramadol hydrochloride molecules in molecular imprinted poly (MAA-co-EGDMA). Egypt. J. Chem. 2020, 63, 4565–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharif, H.F.; Turner, N.W.; Reddy, S.M.; Sullivan, M.V. Application of thymine-based nucleobase-modified acrylamide as a functional co-monomer in electropolymerised thin-film molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) for selective protein (haemoglobin) binding. Talanta 2022, 240, 123158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Álvarez, M.; Martín-Esteban, A.; Turiel, E. Evaluation of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate as comonomer in the preparation of water-compatible molecularly imprinted polymers for triazinic herbicides. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 2356–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoshima, Y.; Kawamura, A.; Takashima, Y.; Miyata, T. Design of molecularly imprinted hydrogels with thermoresponsive drug binding sites. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6644–6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agibayeva, L.; Melnikov, Y.; Kubiyeva, D.; Kondaurov, R. Impact of Crosslinking Agent on Sorption Properties of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Relation to Silver. Polymers 2025, 17, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Q. Surface molecularly imprinted thermo-sensitive polymers based on light-weight hollow magnetic microspheres for specific recognition of BSA. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 486, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Duan, A.; Xie, S.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, L.; Cao, Q. The molecular imprinting of magnetic nanoparticles with boric acid affinity for the selective recognition and isolation of glycoproteins. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 25524–25529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Peng, F.; Mi, F.; Wang, Y.; Geng, P.; Pang, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Guan, M. SERS-based boronate affinity biosensor with biomimetic specificity and versatility: Surface-imprinted magnetic polymers as recognition elements to detect glycoproteins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1191, 339289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Han, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, J.; Ou, L.; Fu, G. Facile modification of protein-imprinted polydopamine coatings over nanoparticles with enhanced binding selectivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumsap, T.; Bamrungsap, S.; Thu, V.T.; Nguyen, L.T. Epitope-imprinted polydopamine electrochemical sensor for ovalbumin detection. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 140, 107805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Fu, M.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Q. Protein recognition by polydopamine-based molecularly imprinted hollow spheres. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Yao, J.; Dai, X.; Pan, J. Double affinity integrated MIPs nanoparticles for specific separation of glycoproteins: A combination of synergistic multiple bindings and imprinting effect. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Huang, S.; Xie, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, M.; Zhao, M. Construction of Specific and Reversible Nanoreceptors for Proteins via Sequential Surface-Imprinting Strategy. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10540–10547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, C.; Liu, F.; Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Guan, M. Intelligent portable SERS-colorimetric dual-mode method based on bilayer amphiphilic-controllable surface imprinting for synergistic detection of glycoprotein disease markers. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2025, 439, 137829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.-Y.; Bai, C.-C.; Yu, S.-S.; Chen, M.-Y.; Dong, L.-Y.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Wang, X.-H. Fabrication of self-healing magnetic nanoreceptors for glycoprotein via integrating boronate-affinity-oriented and sequential surface imprinting. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1221, 340108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Randell, E.; Zhang, M.; Jia, Q. A review: Development and application of surface molecularly imprinted polymers toward amino acids, peptides, and proteins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1234, 340319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Jin, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xiong, S.; Wang, M.; Xu, J.; Wei, C.; Li, J. Microfluidic synthesis of pH-responsive molecularly imprinted silica nanospheres for fluorescence sensing target glycoprotein. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, P.; Guan, M.; Wang, Y.; Mi, F.; Zhang, S.; Rao, X. A double boronic acid affinity “sandwich” SERS biosensor based on magnetic boronic acid controllable-oriented imprinting for high-affinity biomimetic specific recognition and rapid detection of target glycoproteins. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Du, B.; Pei, F.; Liang, M.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Mu, X.; Tong, Z. A facile fluorescence imprinted strategy based on boronic acid functionalized MOF and Mg/N-CDs for discrimination of transferrin: Expansion for boronic acid functionalized MOF application. Microchem. J. 2024, 197, 109759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, P.; Chen, Q.; Wu, Y.; Tan, K. Preparation of mesoporous silica nanoparticles molecularly imprinted polymer for efficient separation and enrichment of perfluorooctane sulfonate. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 4363–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tu, T.; Wu, X. Efficient preparation of template immobilization-based boronate affinity surface-imprinted silica nanoparticles using poly(4-aminobenzyl alcohol) as an imprinting coating for glycoprotein recognition. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4419–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamruddin, N.M.; Herman, H.; Rijai, L.; Hasanah, A.N. Factors Affecting the Analytical Performance of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Polymers 2022, 14, 3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Q.; Chen, W.; Yu, H.; Liu, Q.; Fu, M. Surface imprinted core–shell nanorod for selective extraction of glycoprotein. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 615, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-S.; Yu, S.-S.; Chen, M.-Y.; Zuo, D.; Luo, Y.; Qiang, T.; Ma, H.; Yang, X.-F.; Ma, Y.-B.; Wang, X.-H.; et al. Functionalized pyrite nanozyme probe and imprinted polymer modified with hydrophilic layer for rapid colorimetric analysis of glycoprotein in serum. Talanta 2023, 261, 124665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhao, X.; Song, X.; Chen, L. Simultaneous magnetic purification and detection of transferrin in human serum using an imprinting-based fluorescence sensor by boronate affinity and secondary signal amplification assay. Analyst 2025, 150, 2410–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, H.; Khare, P.; Singh, S.; Singh, S.P. Carbon nanomaterials integrated molecularly imprinted polymers for biological sample analysis: A critical review. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 121966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lv, C.; Xing, Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Xie, X. Electrospinning carbon fibers based molecularly imprinted polymer self-supporting electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of glycoprotein. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 396, 134552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Guo, Z.; Chen, W.; Yu, H.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Q.; Fu, M. Biomass activated carbon–derived imprinted polymer with multi-boronic acid sites for selective capture of glycoprotein. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 596, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.A.; Abd-Elaziem, W.; Elsheikh, A.; Zayed, A.A. Advancements in nanomaterials for nanosensors: A comprehensive review. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 4015–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Li, S.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, F.; Chen, C.; Cai, C. Rapid, efficient and highly selective separation and enrichment of glycoprotein by surface-imprinted MOF nanoparticles loaded with high-density boric acid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Hu, W.; Luo, S.; Pei, F.; Lei, W.; Wang, J.; Tong, Z.; Liu, B.; Du, B.; Hao, Q.; et al. A novel smartphone-mediated ratiometric fluorescence imprinting sensor based on boric acid-functionalized Eu-MOF for the detection of horseradish peroxidase. Microchim. Acta 2025, 192, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Nica, V.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Song, W.; Zhang, Q. Fabrication of Raspberry-like Cytochrome C Surface-Imprinted Nanoparticles Based on MOF Composites for High-Performance Protein Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 31010–31020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.-J.; Luo, X.; Ning, G.-H.; Li, D. Covalent Metal–Organic Frameworks: Fusion of Covalent Organic Frameworks and Metal–Organic Frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res. 2025, 58, 746–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaixing, L.; Chao, L.; Qinqin, Z.; Chen, H.; Wenjing, Z.; Bingbing, X.; Xue, Q.; Guixia, L.; Zhifang, N. Magnetic nanocomposites as multifunctional carriers for enzymes immobilization: A review. Chem. Pap. 2024, 78, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Guo, Z.; Ding, Q.; Zhao, C.; Yu, H.; Zhu, X.; Fu, M.; Liu, Q. Magnetic-graphene oxide based molecular imprinted polymers for selective extraction of glycoprotein at physiological pH. Polymer 2021, 215, 123384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.-C.; Wang, D.; Liu, M.-X.; Ma, Y.-R.; Sun, Y.; Duan, R.; Dong, L.-Y.; Wang, X.-H. Ultrasensitive and specific detection of glycoprotein with boronic acid-modified / fluorescein isothiocyanate-loaded graphene oxide as signal amplification matrix. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Pei, F.; Du, B.; Wang, J.; Liang, M.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Mu, X.; Tong, Z. A fluorescence-electrochemistry dual-mode imprinted sensing platform constructed by boric acid-functionalized MOF@COF core-shell composite for sensitive detection of glycoprotein. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 407, 135494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Tian, J.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Peptide-cross-linked protein-imprinted polymers: Easy template removal and excellent imprinting effect. CCS Chem. 2019, 1, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachkov, A.; Minoura, N. Recognition of oxytocin and oxytocin-related peptides in aqueous media using a molecularly imprinted polymer synthesized by the epitope approach. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 889, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachkov, A.; Minoura, N. Towards molecularly imprinted polymers selective to peptides and proteins. The epitope approach. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 2001, 1544, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, H.; Huang, C.-S.; Shea, K.J. Selective Protein Capture by Epitope Imprinting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2392–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Q. Advances in epitope molecularly imprinted polymers for protein detection: A review. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 1660–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumsap, T.; Corpuz, A.; Nguyen, L.T. Epitope-imprinted polymers: Applications in protein recognition and separation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 11403–11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y.; Gao, J.; Ma, Y.; Pan, G. Epitope-imprinted biomaterials with tailor-made molecular targeting for biomedical applications. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 45, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Liu, Z. Specific recognition of proteins and peptides via controllable oriented surface imprinting of boronate affinity-anchored epitopes. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 1831–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.; Chai, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, R.; Hu, S. Recent progress in epitope-imprinted polymers for disease diagnosis and treatment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2025, 193, 118423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.P.B.; Reis, R.L.; Peppas, N.A.; Gomes, M.E.; Domingues, R.M.A. Epitope-imprinted polymers: Design principles of synthetic binding partners for natural biomacromolecules. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi9884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Xing, R.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Liu, Z. Orthogonal dual molecularly imprinted polymer-based plasmonic immunosandwich assay: A double characteristic recognition strategy for specific detection of glycoproteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 145, 111729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, W.; Pei, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Epitope Imprinting Technology: Progress, Applications, and Perspectives toward Artificial Antibodies. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquardini, L.; Bossi, A.M. Molecularly imprinted polymers by epitope imprinting: A journey from molecular interactions to the available bioinformatics resources to scout for epitope templates. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 6101–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xue, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, H.; Jia, Q. Preparation of dual-functional epitope imprinted polymers for the enrichment of transferrin. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1730, 465111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Jia, Q. Epitope molecularly imprinted polymers based on host-guest interaction: Specific recognition of CD59. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1755, 466056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, R.; Yu, Y.-C.; Lan, R. Progress in Application of Dual/Multi-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49, e21205–e21215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.-P.; Jia, C.; He, X.-W.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Thermosensitive Metal Chelation Dual-Template Epitope Imprinting Polymer Using Distillation–Precipitation Polymerization for Simultaneous Recognition of Human Serum Albumin and Transferrin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9060–9068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijałkowski, P.; Pryshchepa, O.; van Eldik, R.; Pomastowski, P. Ovotransferrin—Multifunctional protein: Structure, bioactivity, and industrial potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 317, 144810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-Y.; Li, Q.-Y.; Yang, L.-L.; Ma, R.-R.; Wang, C.-Z.; Zhou, L.-D.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Xia, Z.-N.; Yuan, C.-S. Synergistic recognition of transferrin by using performance dual epitope imprinted polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1186, 339117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.-Y.; Xu, H.-X.; Li, Q.; Zheng, Q.-Y.; Wang, C.-Z.; Zhou, L.-D.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Yuan, C.-S. Specific capture and determination of glycoprotein using a hybrid epitopes and monomers-mediated molecular-imprinted polymer enzyme-free electrochemical biosensor. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, O.M.T. Cancer glycan epitopes: Biosynthesis, structure and function. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 670–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Sunayama, H.; Takano, E.; Kitayama, Y. Post-imprinting and In-Cavity Functionalization. In Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Biotechnology; Mattiasson, B., Ye, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 95–106. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, T.; Sunayama, H. Beyond natural antibodies—A new generation of synthetic antibodies created by post-imprinting modification of molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 6243–6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.; Wen, Y.; He, H.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Z. Recent progress in the combination of molecularly imprinted polymer-based affinity extraction and mass spectrometry for targeted proteomic analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunayama, H.; Kitayama, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Regulation of protein-binding activities of molecularly imprinted polymers via post-imprinting modifications to exchange functional groups within the imprinted cavity. J. Mol. Recognit. 2018, 31, e2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.-Y.; Fu, J.-X.; Huang, J.-Y.; Wang, C.-H.; Zheng, Q.-Y.; Zhou, L.-D.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Yuan, C.-S. A dual-capture-system polymer based on imprinted cavities and post-imprinting modification sites with significantly improved affinity and specificity for sialic acid and sialylated glycoprotein. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Li, D.; Feng, X.; Fu, G. Synthesis of carbon dots-based surface protein-imprinted nanoparticles via sandwich-structured template pre-assemble and post-imprinting modification for enhanced fluorescence detection. Microchem. J. 2022, 180, 107611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Deng, Q.; Wang, S. One-step post-imprint modification achieve dual-function of glycoprotein fluorescent sensor by “Click Chemistry”. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Arabi, M.; Fu, L.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Fluorescent nanosensor designing via hybrid of carbon dots and post-imprinted polymers for the detection of ovalbumin. Talanta 2020, 211, 120727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, T.; Takano, E.; Sunayama, H.; Kamon, Y.; Horikawa, R.; Kitayama, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Signalling molecular recognition nanocavities with multiple functional groups prepared by molecular imprinting and sequential post-imprinting modifications for prostate cancer biomarker glycoprotein detection. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 7987–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, R.; Sunayama, H.; Kitayama, Y.; Takano, E.; Takeuchi, T. A Programmable Signaling Molecular Recognition Nanocavity Prepared by Molecular Imprinting and Post-Imprinting Modifications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13023–13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunayama, H.; Takamiya, K.; Takano, E.; Horikawa, R.; Kitayama, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Simultaneous Detection of Two Tumor Marker Proteins Using Dual-Colored Signaling Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Prepared via Multi-Step Post-Imprinting Modifications. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2021, 94, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunayama, H.; Takeuchi, T. Protein-imprinted polymer films prepared via cavity-selective multi-step post-imprinting modifications for highly selective protein recognition. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 6183–6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, L.E.; Robinson, J.; Cutsor, J.; Brase, G. Sustainable Development. In Solar Powered Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles: A Sustainable Development; Erickson, L.E., Robinson, J., Cutsor, J., Brase, G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 115–121. [Google Scholar]

| Evaluation Criterion | Oriented Surface Imprinting | Epitope Imprinting | Post-Imprinting Modification | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imprinting Factor | Moderate–High | Very High | Variable (can be enhanced) | Gold-standard metric for specificity |
| Adsorption Capacity | High | Low–Moderate | Dependent on the base MIP | Reflects practical loading potential |
| Binding Kinetics | Fast | Moderate | Kinetics of the base MIP | Critical for throughput and biomimetic sensing speed |
| Template Removal | Good (surface sites only) | Very High (due to small template) | Good (depends on base MIP) | Impacts MIP preparation ease and final purity |
| Generality | Low (needs specific handle) | Low–Moderate (needs effective epitope) | High (versatile chemistry) | Applicability to diverse, unmodified targets |
| Fabrication Complexity | Moderate | Low–Moderate | High | Multi-step synthesis/modification in PIM |
| Functional Versatility | Limited (by immobilization chemistry) | Limited (by epitope) | Very High (tailorable) | Ease of integrating diverse transduction mechanisms (optical, electrochemical) and stimuli-responsive release triggers |
| Optimal Application Scenario | High-capacity, high-throughput processing (e.g., preparative enrichment) | High-fidelity analysis in complex matrices (e.g., diagnostic detection) | Function-driven system design (e.g., signal transduction, controllable release) | Primary criterion for rational strategy selection |
| Key Strength | Capacity, speed, easy integration with functional supports | Specificity, reproducibility, gentle elution | Unmatched ability to engineer functionality post-synthesis | |
| Key Limitation | Target scope limited by required handles | Performance hinges on epitope choice | Complexity, reproducibility, risk of cavity distortion |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Xie, P.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Xie, C.-F.; Fan, J.-P. Specific Recognition of Glycoproteins: Design Strategies and Application Prospects of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010528
Xie P, Chen Z-Y, Xie C-F, Fan J-P. Specific Recognition of Glycoproteins: Design Strategies and Application Prospects of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010528
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Ping, Zi-Ying Chen, Chun-Fang Xie, and Jie-Ping Fan. 2026. "Specific Recognition of Glycoproteins: Design Strategies and Application Prospects of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010528
APA StyleXie, P., Chen, Z.-Y., Xie, C.-F., & Fan, J.-P. (2026). Specific Recognition of Glycoproteins: Design Strategies and Application Prospects of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010528








