Targeting Ferroptosis to Restore Salivary Gland Homeostasis in an Obesity Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
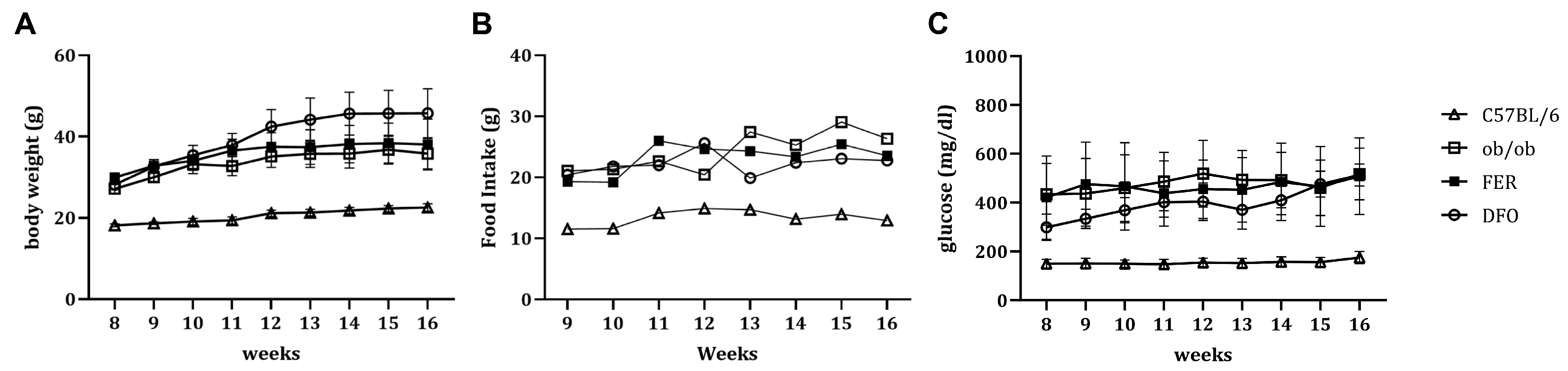
2.1. Obesity-Associated Changes in Weight, Nutrient Intake, and Glycemic Status
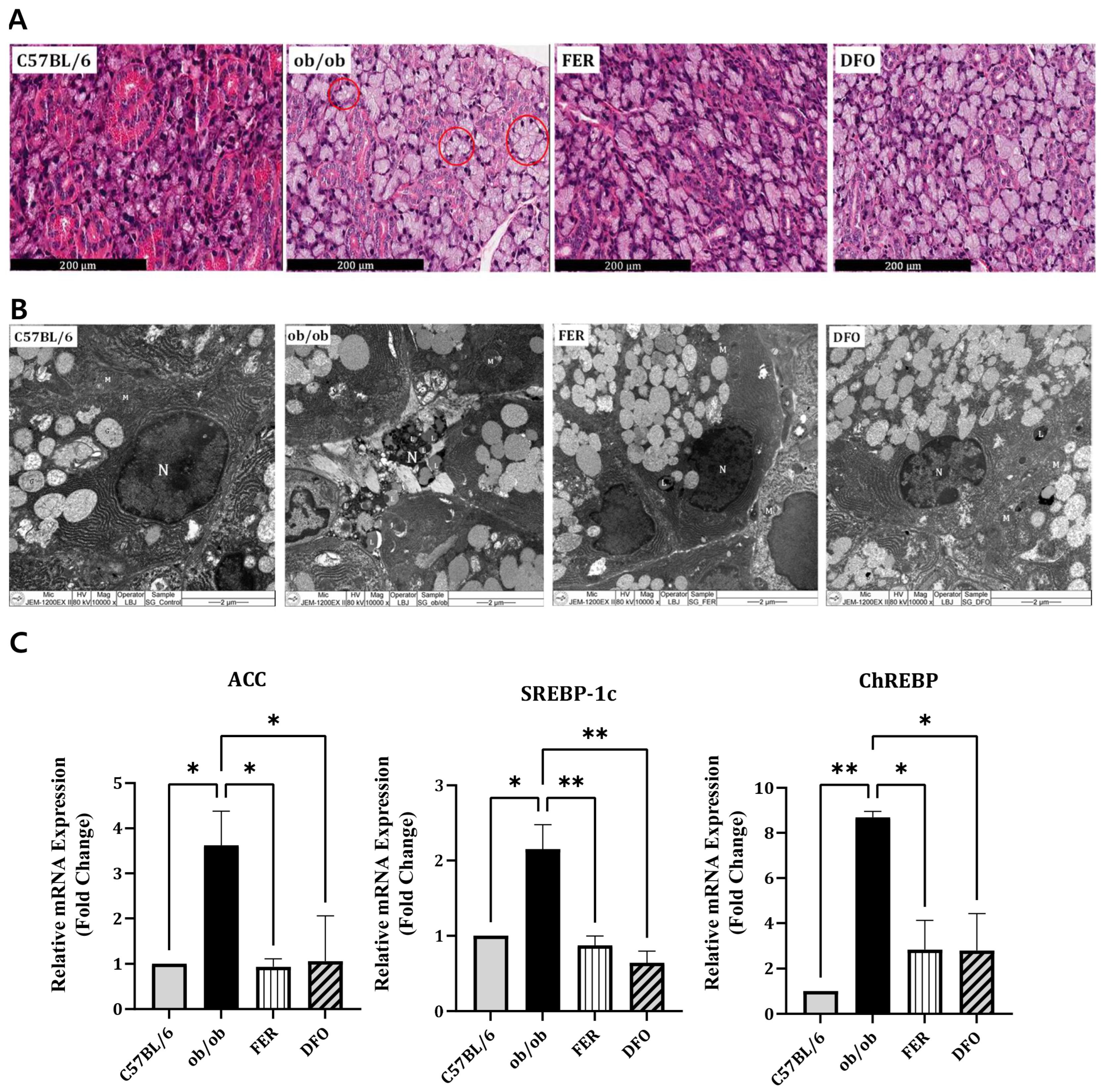
2.2. Enhanced Lipogenesis in the Salivary Glands of Obese Mice
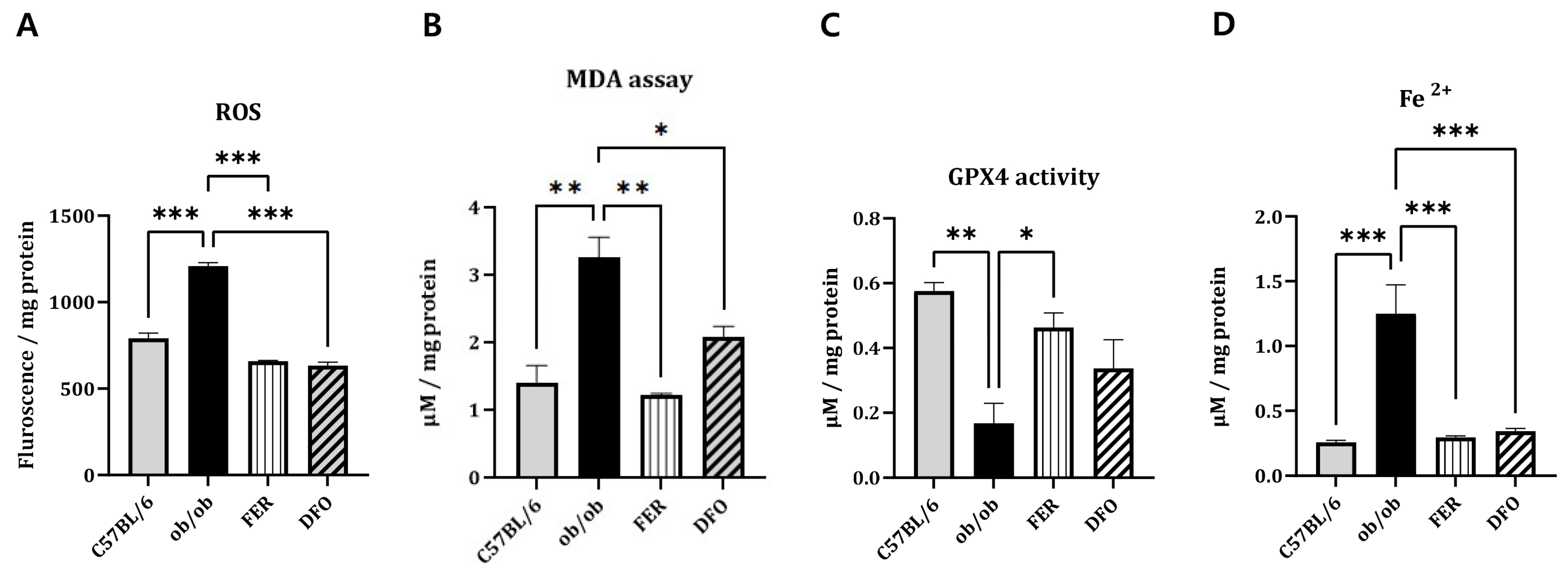
2.3. Ferroptosis-Associated Oxidative Stress and Iron Dysregulation
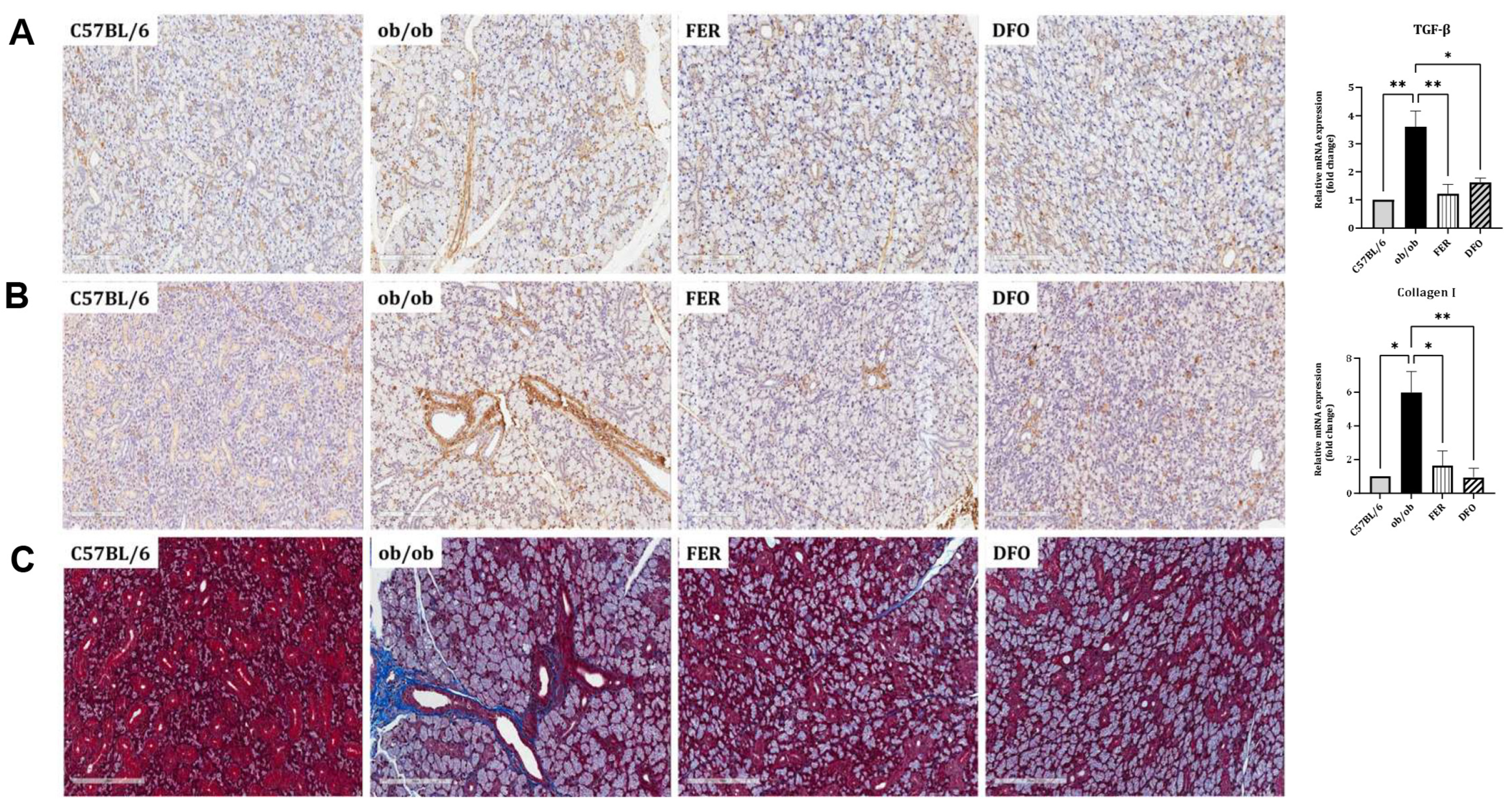
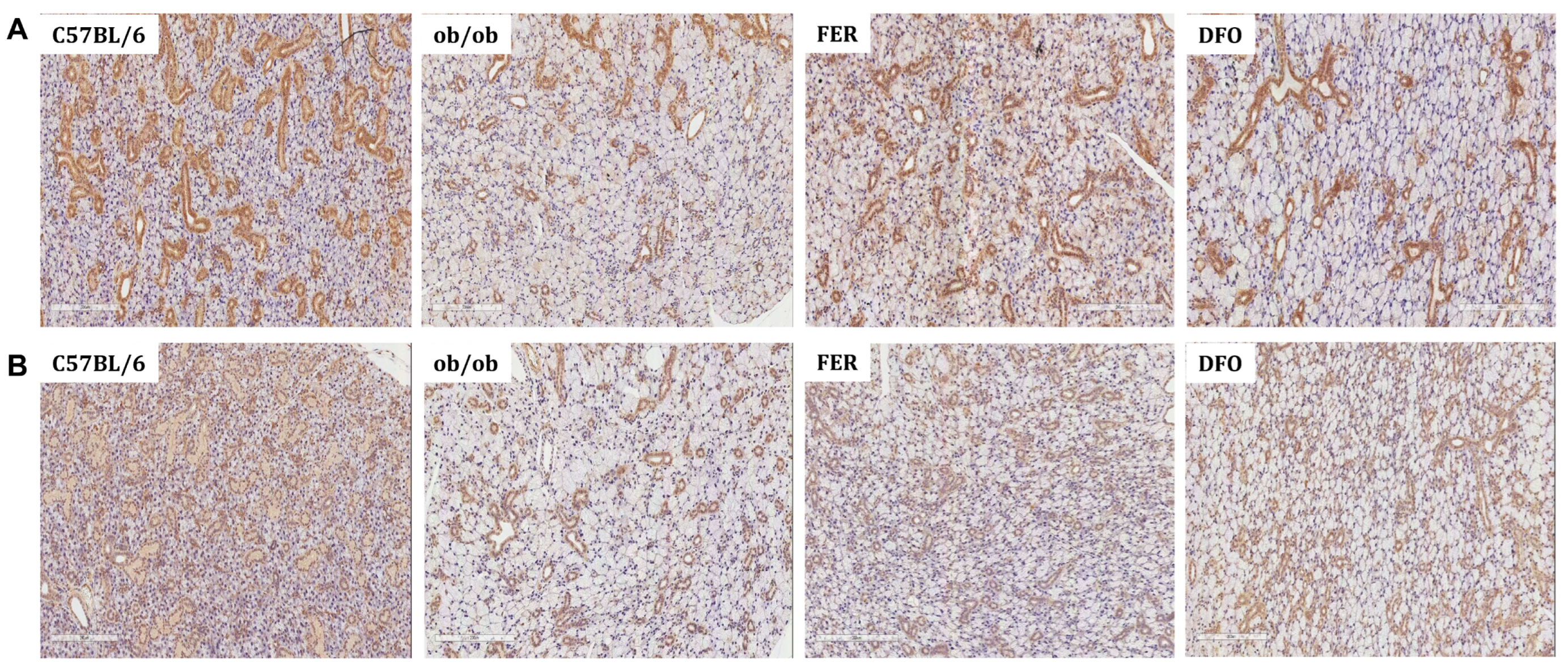
2.4. Obesity-Induced Fibrosis and Inflammation in the Salivary Glands
2.5. Functional Deterioration of the Salivary Glands and Its Reversal by Ferroptosis Inhibitors
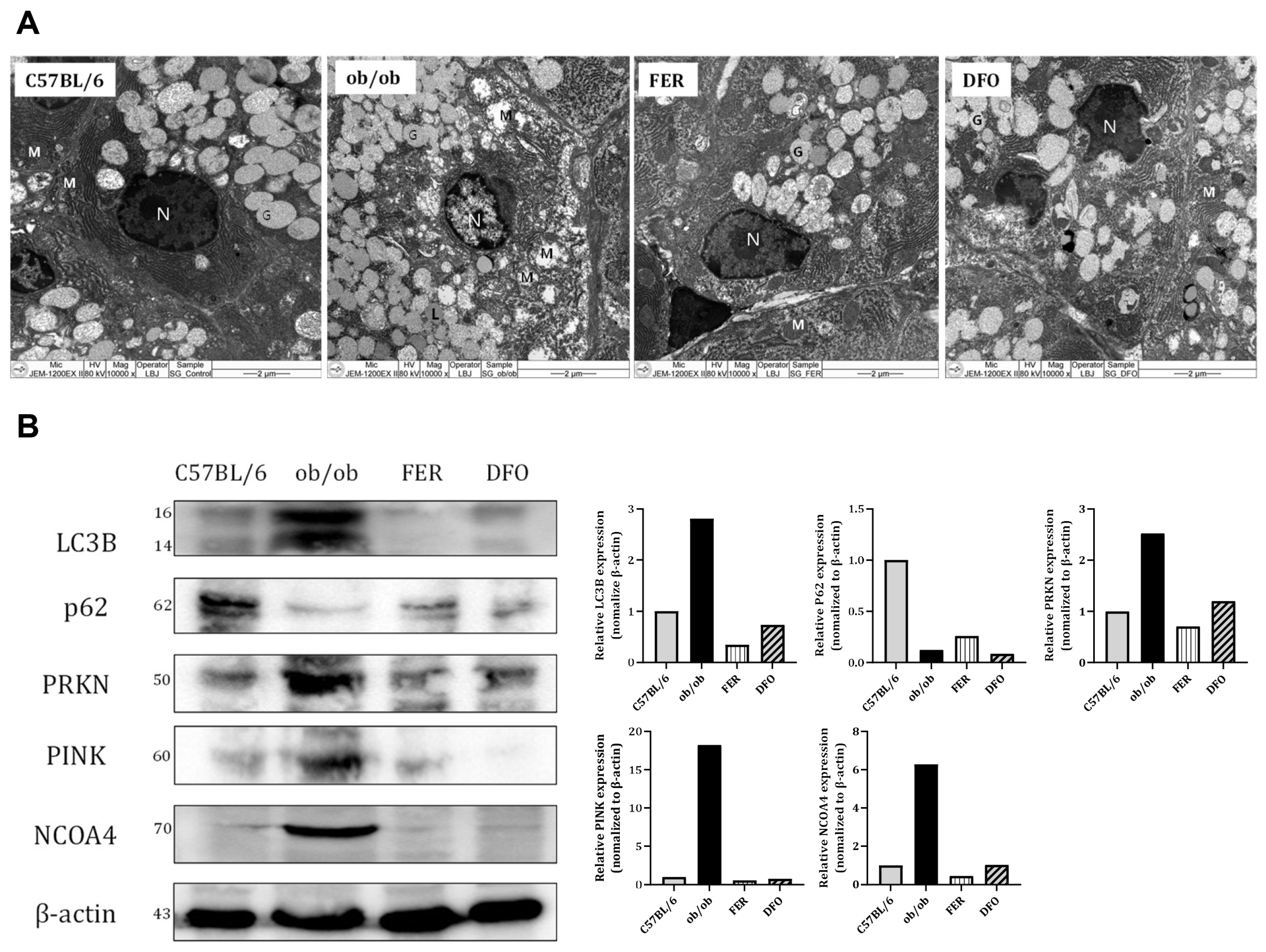
2.6. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Selective Autophagy Imbalance in the Obese Salivary Glands
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Models and Experimental Design
4.2. Measurement of Lipid Peroxidation
4.3. Cytosolic Iron Quantification
4.4. Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
4.5. GPX4 Activity Assay
4.6. Histological and Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.9. Western Blotting
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Haslam, D.W.; James, W.P. Obesity. Lancet 2005, 366, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, R.J. Obesity and obesity-induced inflammatory disease contribute to atherosclerosis: A review of the pathophysiology and treatment of obesity. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 11, 504–529. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Qiu, T.; Li, L.; Yu, R.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Proud, C.G.; Jiang, T. Pathophysiology of obesity and its associated diseases. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2403–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Munzberg, H.; Rezai-Zadeh, K.; Keenan, M.; Coulon, D.; Lu, H.; Berthoud, H.R.; Ye, J. Leptin deficient ob/ob mice and diet-induced obese mice responded differently to Roux-en-Y bypass surgery. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewska, A.; Ziembicka, D.; Zendzian-Piotrowska, M.; Maciejczyk, M. The Impact of High-Fat Diet on Mitochondrial Function, Free Radical Production, and Nitrosative Stress in the Salivary Glands of Wistar Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 2606120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.M.; Bolze, F.; Thorup, I.; Nowak, J.; Dalsgaard, C.M.; Skydsgaard, M.; Berthelsen, L.O.; Keane, K.A.; Soeborg, H.; Sjogren, I.; et al. The Effect of Diet-induced Obesity on Toxicological Parameters in the Polygenic Sprague-Dawley Rat Model. Toxicol. Pathol. 2018, 46, 777–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, F.; Yin, H.L.; Huang, Z.J.; Lin, Z.T.; Mao, N.; Sun, B.; Wang, G. Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockwell, B.R. Ferroptosis turns 10: Emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic applications. Cell 2022, 185, 2401–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Dong, L.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, S.; Gong, S.; Meng, L.; Xin, Y.; Jiang, X. Mechanism, Prevention, and Treatment of Radiation-Induced Salivary Gland Injury Related to Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.K.; Kim, J.M.; Shin, S.C.; Sung, E.S.; Kim, H.S.; Park, G.C.; Cheon, Y.I.; Lee, J.C.; Lee, B.J. The mechanism of submandibular gland dysfunction after menopause may be associated with the ferroptosis. Aging 2020, 12, 21376–21390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Shin, S.C.; Cheon, Y.I.; Kim, H.S.; Park, G.C.; Kim, H.K.; Han, J.; Seol, J.E.; Vasileva, E.A.; Mishchenko, N.P.; et al. Effect of Echinochrome A on Submandibular Gland Dysfunction in Ovariectomized Rats. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, Y.I.; Kim, J.M.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.C.; Park, G.C.; Sung, E.S.; Lee, M.; Lee, B.J. Effect of deferoxamine and ferrostatin-1 on salivary gland dysfunction in ovariectomized rats. Aging 2023, 15, 2418–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.C.; Bang, S.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Shin, S.C.; Cheon, Y.I.; Park, H.; Suh, S.; Cho, J.H.; Sung, E.S.; Lee, M.; et al. Ferrostatin-1 Prevents Salivary Gland Dysfunction in an Ovariectomized Rat Model by Suppressing Mitophagy-Driven Ferroptosis. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Park, G.C.; Lee, H.W.; Bang, S.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, W.T.; Shin, S.C.; Cheon, Y.I.; Lee, B.J. Amifostine and melatonin attenuate radiation-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrotic remodeling in the vocal folds and subglottic glands of rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 192, 118658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.C.; Bang, S.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Shin, S.C.; Cheon, Y.I.; Kim, K.M.; Park, H.; Sung, E.S.; Lee, M.; Lee, J.C.; et al. Inhibiting Ferroptosis Prevents the Progression of Steatotic Liver Disease in Obese Mice. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbowska, M.; Lukaszuk, B.; Miklosz, A.; Wroblewski, I.; Kurek, K.; Ostrowska, L.; Chabowski, A.; Zendzian-Piotrowska, M.; Zalewska, A. Sphingolipids metabolism in the salivary glands of rats with obesity and streptozotocin induced diabetes. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 2766–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Morozumi, T.; Takahashi, T.; Saruta, J.; Sakaguchi, W.; To, M.; Kubota, N.; Shimizu, T.; Kamata, Y.; Kawata, A.; et al. Effect of High Fat and Fructo-Oligosaccharide Consumption on Immunoglobulin A in Saliva and Salivary Glands in Rats. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Luo, P.; Guo, Z.; Yang, L.; Pu, J.; Han, F.; Cai, F.; Tang, J.; Wang, X. Lipid Metabolism: An Emerging Player in Sjogren’s Syndrome. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2025, 68, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G. Ferroptosis: Molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, X.; Xie, F.; Zhang, L.; Yan, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L. Ferroptosis in cancer and cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, Y.; Min, J.; Wang, F. Iron homeostasis and ferroptosis in human diseases: Mechanisms and therapeutic prospects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Wang, B.; Huang, R.; Zhang, C.; Fu, P.; Ma, L. Ferroptosis in organ fibrosis: From mechanisms to therapeutic medicines. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2024, 12, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zong, L.; Lin, J.; Liu, X.; Ning, S. Emerging roles of ferroptosis in pulmonary fibrosis: Current perspectives, opportunities and challenges. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, G.; Liao, H.; Li, R. Ferroptosis and renal fibrosis: Mechanistic insights and emerging therapeutic targets. Ren. Fail. 2025, 47, 2498629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Luo, Y.; Xia, Q.; He, K. Ferroptosis and Liver Fibrosis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 3361–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann Angeli, J.P.; Schneider, M.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Tyurin, V.A.; Hammond, V.J.; Herbach, N.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; Eggenhofer, E.; et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, G. Mitochondria regulation in ferroptosis. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 99, 151058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Kon, N.; Li, T.; Wang, S.J.; Su, T.; Hibshoosh, H.; Baer, R.; Gu, W. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature 2015, 520, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Luo, X.; Liu, W.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Q.; Cui, Y.; et al. Dynamic O-GlcNAcylation coordinates ferritinophagy and mitophagy to activate ferroptosis. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q.; Huang, J.; Huang, J. A Mitophagy-Related Gene Signature for Subtype Identification and Prognosis Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpellini, C.; Klejborowska, G.; Lanthier, C.; Hassannia, B.; Vanden Berghe, T.; Augustyns, K. Beyond ferrostatin-1: A comprehensive review of ferroptosis inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 44, 902–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbakhsh Ravari, F.; Ghasemi Gorji, M.; Rafiei, A. From iron-driven cell death to clot formation: The emerging role of ferroptosis in thrombogenesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 189, 118328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Miao, R.; Zhong, J. Targeting Iron Metabolism and Ferroptosis as Novel Therapeutic Approaches in Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| GENE | Sequence (5′3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | |
| GAPDH | AGCCCAAGATGCCCTTCAGT | CCGTGTTCCTACCCCCAATG |
| SREBP-1c | ACGGAGCCATGGATTGCACA | AAGGGTGCAGGTGTCACCTT |
| ChREBP | CTGGGGACCTAAACAGGAGC | GAAGCCACCCTATAGCTCCC |
| ACC | ATGGGCGGAATGGTCTCTTTC | TGGGGACCTTGTCTTCATCAT |
| TGF-β1 | GTGTGGAGCAACATGTGGAACTCTA | TTGGTTCAGCCACTGCCGTA |
| Collagen I | CCTCAGGGTATTGCTGGACAAC | CAGAAGGACCTTGTTTGCCAGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Park, G.C.; Park, H.; Bang, S.-Y.; Kim, J.M.; Shin, S.-C.; Cheon, Y.-i.; Kwon, H.-N.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, B.-J. Targeting Ferroptosis to Restore Salivary Gland Homeostasis in an Obesity Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010514
Park GC, Park H, Bang S-Y, Kim JM, Shin S-C, Cheon Y-i, Kwon H-N, Cho JH, Lee B-J. Targeting Ferroptosis to Restore Salivary Gland Homeostasis in an Obesity Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010514
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Gi Cheol, Hanaro Park, Soo-Young Bang, Ji Min Kim, Sung-Chan Shin, Yong-il Cheon, Ha-Nee Kwon, Jung Hwan Cho, and Byung-Joo Lee. 2026. "Targeting Ferroptosis to Restore Salivary Gland Homeostasis in an Obesity Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010514
APA StylePark, G. C., Park, H., Bang, S.-Y., Kim, J. M., Shin, S.-C., Cheon, Y.-i., Kwon, H.-N., Cho, J. H., & Lee, B.-J. (2026). Targeting Ferroptosis to Restore Salivary Gland Homeostasis in an Obesity Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010514






