Immune-Based Biomarkers as Predictors of Mortality in ECMO Therapy for Severe COVID-19 ARDS: Insights from a Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics at Baseline
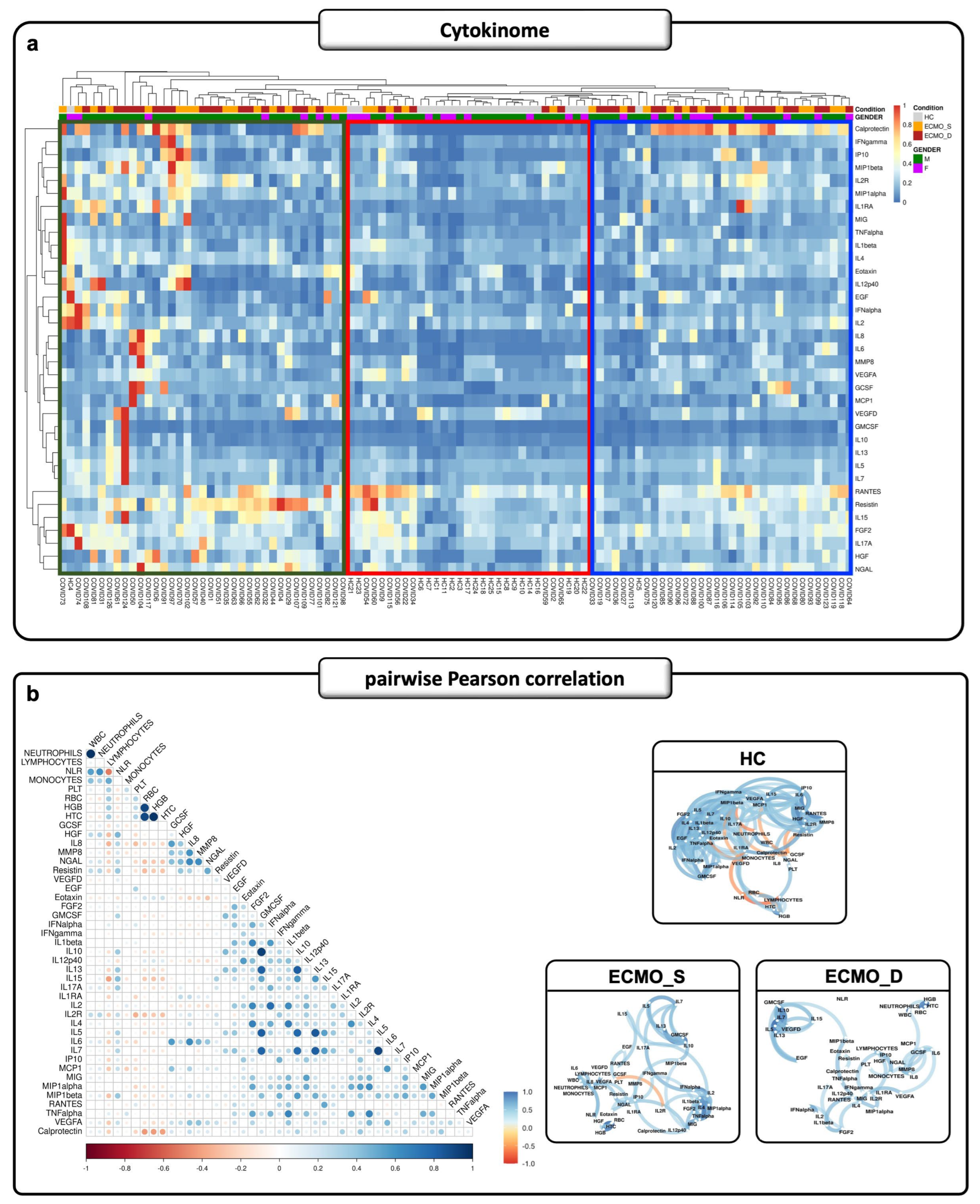
2.2. Cytokinome Profile Evaluation in Critical COVID-19 ICU Patients
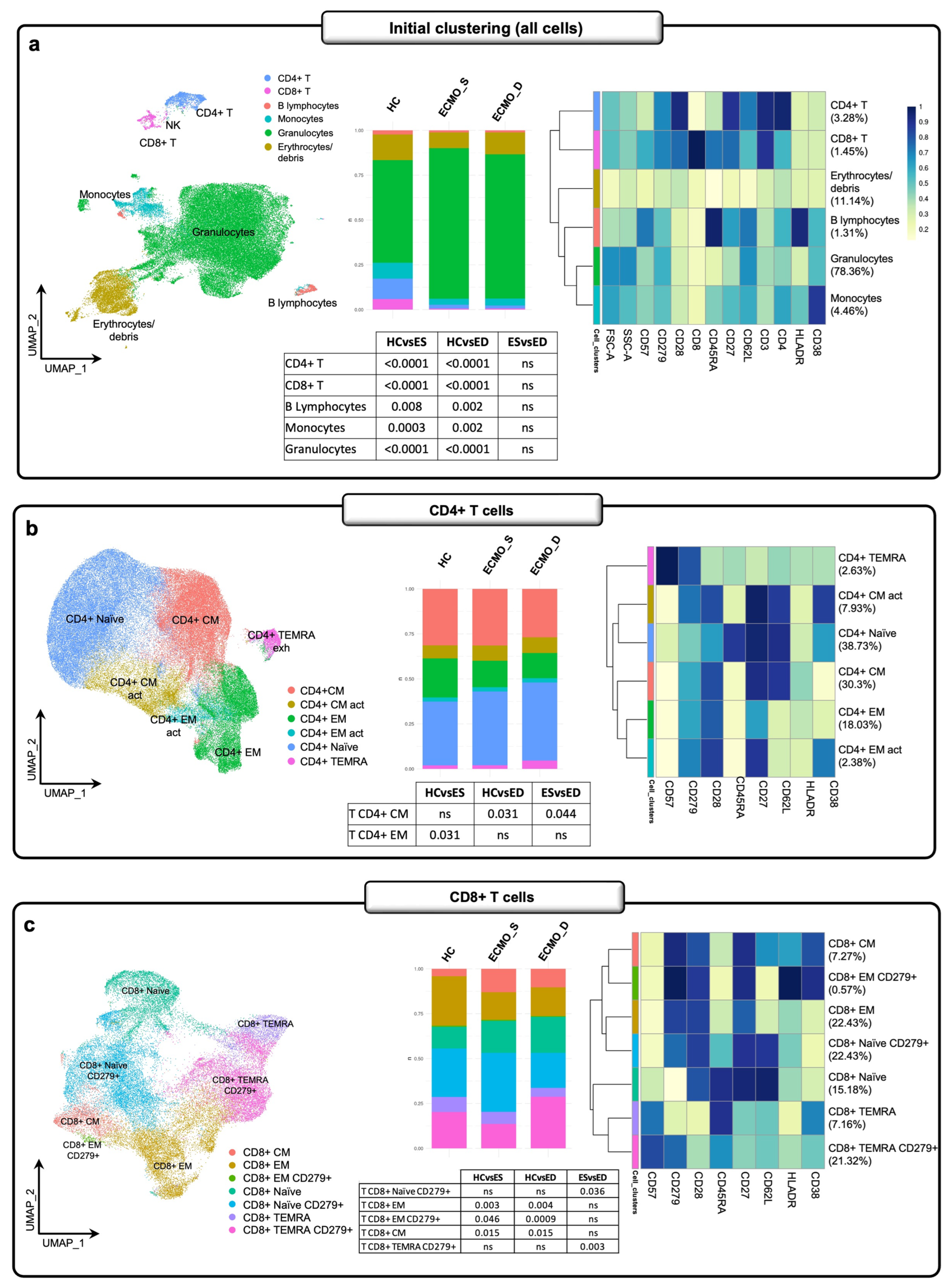
2.3. Cytokine Production in ECMO Patients Also Depends on Inflamed Peripheral Blood Cells
2.4. Exhausted T Cell Immune Signature in ECMO-Supported Patients
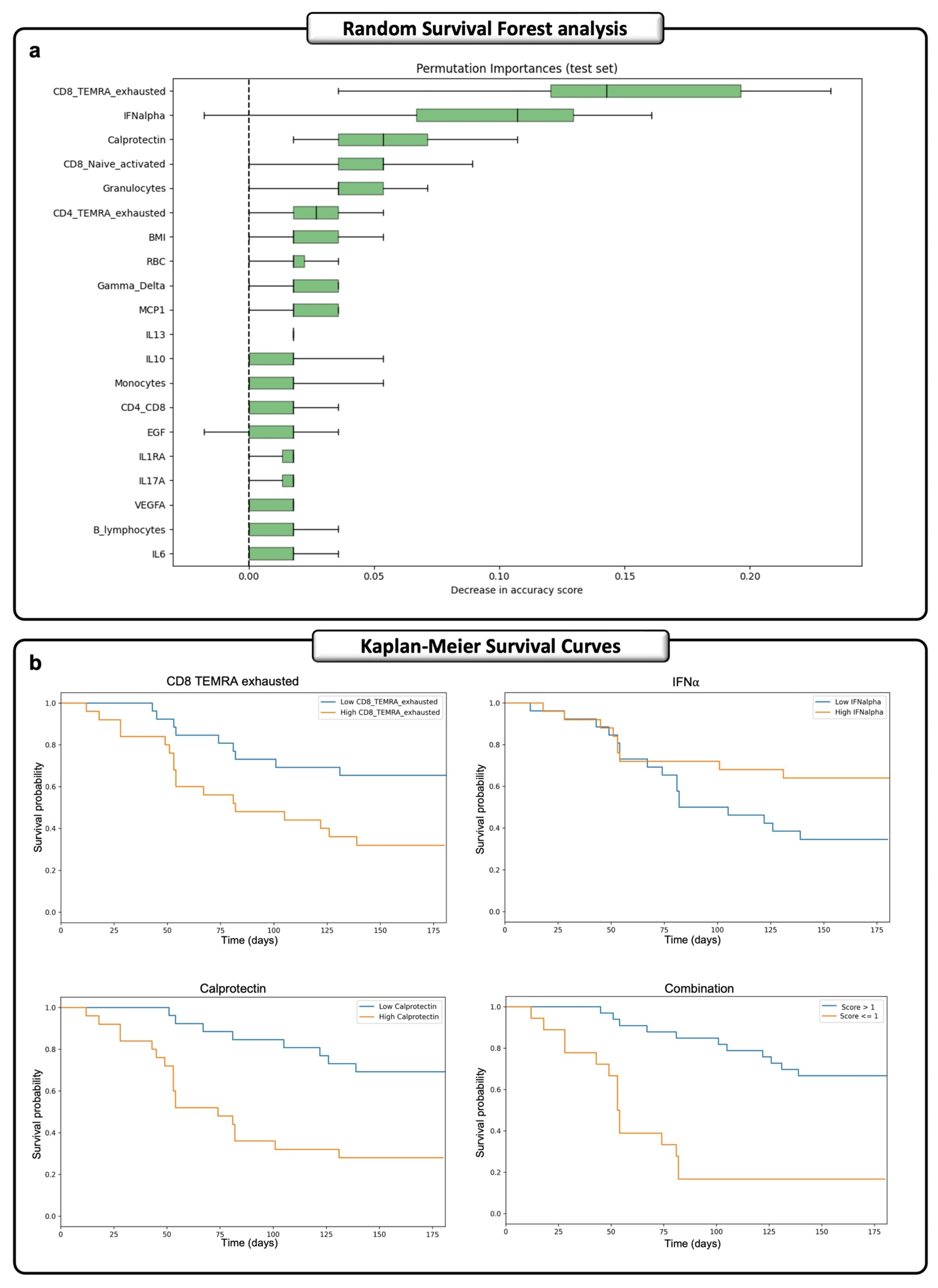
2.5. A Machine-Learning Time-Dependent Approach Identified a Predictive Signature of Death for ECMO Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Cohorts and Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
4.2. Laboratory Analyses
4.3. Cytokinome Profile
4.4. Whole Blood Total RNA-Seq
4.5. CIBERSORTx Analysis
4.6. Flow Cytometry
4.7. Random Survival Forest (RSF) Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shih, E.; DiMaio, J.M.; Squiers, J.J.; Banwait, J.K.; Meyer, D.M.; George, T.J.; Schwartz, G.S. the Baylor Scott & White ECMO for COVID Group. Venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for patients with refractory coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Multicenter experience of referral hospitals in a large health care system. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2022, 163, 1071–1079.e3. [Google Scholar]
- Mallick, T.; Barakat, M.; Baptiste, T.R.; Hasan, M.; Engdahl, R. Successful Use of Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in a Patient with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia. Cureus 2020, 12, e11938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, G.; Arcadipane, A.; Tuzzolino, F.; Occhipinti, G.; Panarello, G.; Carcione, C.; Bonicolini, E.; Vitiello, C.; Lorusso, R.; Conaldi, P.G.; et al. Identification of a Circulating miRNA Signature to Stratify Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noah, M.A.; Peek, G.J.; Finney, S.J.; Griffiths, M.J.; Harrison, D.A.; Grieve, R.; Sadique, M.Z.; Sekhon, J.S.; McAuley, D.F.; Firmin, R.K.; et al. Referral to an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation center and mortality among patients with severe 2009 influenza A(H1N1). JAMA 2011, 306, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar]
- Piacente, C.; Martucci, G.; Miceli, V.; Pavone, G.; Papeo, A.; Occhipinti, G.; Panarello, G.; Lorusso, R.; Tanaka, K.; Arcadipane, A. A narrative review of antithrombin use during veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in adults: Rationale, current use, effects on anticoagulation, and outcomes. Perfusion 2020, 35, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.; Fernando, S.M.; Rochwerg, B.; Barbaro, R.P.; Hodgson, C.L.; Munshi, L.; MacLaren, G.; Ramanathan, K.; Hough, C.L.; Brochard, L.J.; et al. Prognostic factors associated with mortality among patients receiving venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oude Lansink-Hartgring, A.; Miranda, D.D.R.; Mandigers, L.; Delnoij, T.; Lorusso, R.; Maas, J.J.; Elzo Kraemer, C.V.; Vlaar, A.P.J.; Raasveld, S.J.; Donker, D.W.; et al. Health-related quality of life, one-year costs and economic evaluation in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in critically ill adults. J. Crit. Care 2023, 73, 154215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peek, G.J.; Mugford, M.; Tiruvoipati, R.; Wilson, A.; Allen, E.; Thalanany, M.M.; Hibbert, C.L.; Truesdale, A.; Clemens, F.; Cooper, N.; et al. Efficacy and economic assessment of conventional ventilatory support versus extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe adult respiratory failure (CESAR): A multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009, 374, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Gattinoni, L.; Combes, A.; Schmidt, M.; Peek, G.; Brodie, D.; Muller, T.; Morelli, A.; Ranieri, V.M.; Pesenti, A.; et al. Venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for acute respiratory failure: A clinical review from an international group of experts. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Bailey, M.; Sheldrake, J.; Hodgson, C.; Aubron, C.; Rycus, P.T.; Scheinkestel, C.; Cooper, D.J.; Brodie, D.; Pellegrino, V.; et al. Predicting survival after extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory failure. The Respiratory Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Survival Prediction (RESP) score. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, W.D.; Trindade, A.J.; Stokes, J.W.; Casey, J.D.; Benson, C.; Patel, Y.J.; Pugh, M.E.; Semler, M.W.; Bacchetta, M.; Rice, T.W. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Selection by Multidisciplinary Consensus: The ECMO Council. ASAIO J. 2023, 69, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortezaee, K.; Majidpoor, J. CD8+ T Cells in SARS-CoV-2 Induced Disease and Cancer-Clinical Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 864298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulakcsai, Z.; Szabo, L.; Szabo, Z.; Karaszi, E.; Szabo, T.; Fazekas, L.; Vereb, A.; Kovacs, N.F.; Nemeth, D.; Kovacs, E.; et al. T cell immune response predicts survival in severely ill COVID-19 patients requiring venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1179620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahi, H.; Talepoor, A.G.; Saleh, Z.; Eshkevar Vakili, M.; Heydarinezhad, P.; Karami, N.; Noroozi, M.; Meri, S.; Kalantar, K. Immune responses in mildly versus critically ill COVID-19 patients. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1077236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soma, P.; Bester, J. Pathophysiological Changes in Erythrocytes Contributing to Complications of Inflammation and Coagulation in COVID-19. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 899629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Multi-omics Blood ATlas (COMBAT) Consortium. A blood atlas of COVID-19 defines hallmarks of disease severity and specificity. Cell 2022, 185, 916–938.e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meizlish, M.L.; Pine, A.B.; Bishai, J.D.; Goshua, G.; Nadelmann, E.R.; Simonov, M.; Chang, C.H.; Zhang, H.; Shallow, M.; Bahel, P.; et al. A neutrophil activation signature predicts critical illness and mortality in COVID-19. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 1164–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abers, M.S.; Delmonte, O.M.; Ricotta, E.E.; Fintzi, J.; Fink, D.L.; de Jesus, A.A.A.; Zarember, K.A.; Alehashemi, S.; Oikonomou, V.; Desai, J.V.; et al. An immune-based biomarker signature is associated with mortality in COVID-19 patients. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e144455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrivee, B.; Pollet, I.; Karsan, A. Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 in bone marrow leads to accumulation of myeloid cells: Role of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 3015–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, C.R.P.; Borba-Junior, I.T.; De Lima, F.; Silva, J.R.A.; Bombassaro, B.; Palma, A.C.; Mansour, E.; Velloso, L.A.; Orsi, F.A.; Costa, F.T.M.; et al. Association of Ang/Tie2 pathway mediators with endothelial barrier integrity and disease severity in COVID-19. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1113968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Melo, D.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Liu, W.C.; Uhl, S.; Hoagland, D.; Moller, R.; Jordan, T.X.; Oishi, K.; Panis, M.; Sachs, D.; et al. Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19. Cell 2020, 181, 1036–1045.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, J.; Yatim, N.; Barnabei, L.; Corneau, A.; Boussier, J.; Smith, N.; Pere, H.; Charbit, B.; Bondet, V.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; et al. Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Science 2020, 369, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, C.; Maia, C.; Garces, J.J.; Termini, R.; Perez, C.; Manrique, I.; Burgos, L.; Zabaleta, A.; Alignani, D.; Sarvide, S.; et al. FlowCT for the analysis of large immunophenotypic data sets and biomarker discovery in cancer immunology. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamariz-Amador, L.E.; Battaglia, A.M.; Maia, C.; Zherniakova, A.; Guerrero, C.; Zabaleta, A.; Burgos, L.; Botta, C.; Fortuno, M.A.; Grande, C.; et al. Immune biomarkers to predict SARS-CoV-2 vaccine effectiveness in patients with hematological malignancies. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Nicoll, M.; Ingham, R.J. AP-1 family transcription factors: A diverse family of proteins that regulate varied cellular activities in classical hodgkin lymphoma and ALK+ ALCL. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulati, M.; Caruso, C.; Colonna-Romano, G. From lymphopoiesis to plasma cells differentiation, the age-related modifications of B cell compartment are influenced by “inflamm-ageing”. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 36, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodruff, M.C.; Ramonell, R.P.; Nguyen, D.C.; Cashman, K.S.; Saini, A.S.; Haddad, N.S.; Ley, A.M.; Kyu, S.; Howell, J.C.; Ozturk, T.; et al. Extrafollicular B cell responses correlate with neutralizing antibodies and morbidity in COVID-19. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1506–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaluddin, M.S.; Weakley, S.M.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Resistin: Functional roles and therapeutic considerations for cardiovascular disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manz, M.G.; Boettcher, S. Emergency granulopoiesis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; John Wherry, E. T cell responses in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouan, Y.; Guillon, A.; Gonzalez, L.; Perez, Y.; Boisseau, C.; Ehrmann, S.; Ferreira, M.; Daix, T.; Jeannet, R.; Francois, B.; et al. Phenotypical and functional alteration of unconventional T cells in severe COVID-19 patients. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20200872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcanjo, A.; Guimaraes Pinto, K.; Logullo, J.; Leite, P.E.C.; Menezes, C.C.B.; Freire-de-Lima, L.; Diniz-Lima, I.; Decote-Ricardo, D.; Nunes Rodrigues-da-Silva, R.; Geraldo Freire-de-Lima, C.; et al. Critically Ill Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients Exhibit Hyperactive Cytokine Responses Associated With Effector Exhausted Senescent T Cells in Acute Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 1672–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.; Faridi, R.M.; Sligl, W.; Shabani-Rad, M.T.; Dharmani-Khan, P.; Parker, A.; Kalra, A.; Tripathi, M.B.; Storek, J.; Cohen Tervaert, J.W.; et al. Impaired natural killer cell counts and cytolytic activity in patients with severe COVID-19. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5035–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damoiseaux, J. The IL-2–IL-2 receptor pathway in health and disease: The role of the soluble IL-2 receptor. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 218, 108515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minutolo, A.; Petrone, V.; Fanelli, M.; Maracchioni, C.; Giudice, M.; Teti, E.; Coppola, L.; Sorace, C.; Iannetta, M.; Tony Miele, M.; et al. Thymosin alpha 1 restores the immune homeostasis in lymphocytes during Post-Acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 118, 110055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phua, S.X.; Lim, K.P.; Goh, W.W. Perspectives for better batch effect correction in mass-spectrometry-based proteomics. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 4369–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.M.; Steen, C.B.; Liu, C.L.; Gentles, A.J.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Scherer, F.; Khodadoust, M.S.; Esfahani, M.S.; Luca, B.A.; Steiner, D.; et al. Determining cell type abundance and expression from bulk tissues with digital cytometry. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhu, C.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Huo, Y.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomic landscape of human blood cells. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsunsky, I.; Millard, N.; Fan, J.; Slowikowski, K.; Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Baglaenko, Y.; Brenner, M.; Loh, P.R.; Raychaudhuri, S. Fast, sensitive and accurate integration of single-cell data with Harmony. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, T.; Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Hafemeister, C.; Papalexi, E.; Mauck, W.M., 3rd; Hao, Y.; Stoeckius, M.; Smibert, P.; Satija, R. Comprehensive Integration of Single-Cell Data. Cell 2019, 177, 1888–1902.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.M. Random Survival Forests. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2011, 6, 1974–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotberg, J.C.; Reynolds, D.; Kraft, B.D. Management of severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: A primer. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| ECMO Patients | |
|---|---|
| Patients, n | 80 |
| Mean age ± SD, years | 50.2 ± 8.8 |
| Male (n; %) | 61 (76.2%) |
| Hypertension (HTN) (n; %) | 38 (46.2%) |
| Chronic Cardiac Disease (n; %) | 3 (3.7%) |
| Diabetes (n; %) | 19 (22.5%) |
| Obesity (n; %) | 45 (56.2%) |
| Chronic Pulmonary disease (n; %) | 9 (10%) |
| Chronic Kidney Disease (n; %) | 3 (3.7%) |
| Transplantation (n; %) | 1 (1.2%) |
| Other comorbidities (n; %) | 25 (31.2%) |
| SOFA score (mean value ± SD) | 7.9 ± 2.6 |
| APACHE II score (mean value ± SD) | 16.3 ± 6 |
| SAPS II score (mean value ± SD) | 44 ± 13 |
| ICU-LOS, days (mean value ± SD) | 71.8 ± 56 |
| Death (n; %) | 44 (55%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Busà, R.; Panarello, G.; Gallo, A.; Miceli, V.; Castelbuono, S.; Sorrentino, M.C.; Amico, G.; Carcione, C.; Russelli, G.; Cuscino, N.; et al. Immune-Based Biomarkers as Predictors of Mortality in ECMO Therapy for Severe COVID-19 ARDS: Insights from a Retrospective Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010390
Busà R, Panarello G, Gallo A, Miceli V, Castelbuono S, Sorrentino MC, Amico G, Carcione C, Russelli G, Cuscino N, et al. Immune-Based Biomarkers as Predictors of Mortality in ECMO Therapy for Severe COVID-19 ARDS: Insights from a Retrospective Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010390
Chicago/Turabian StyleBusà, Rosalia, Giovanna Panarello, Alessia Gallo, Vitale Miceli, Salvatore Castelbuono, Maria Concetta Sorrentino, Giandomenico Amico, Claudia Carcione, Giovanna Russelli, Nicola Cuscino, and et al. 2026. "Immune-Based Biomarkers as Predictors of Mortality in ECMO Therapy for Severe COVID-19 ARDS: Insights from a Retrospective Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010390
APA StyleBusà, R., Panarello, G., Gallo, A., Miceli, V., Castelbuono, S., Sorrentino, M. C., Amico, G., Carcione, C., Russelli, G., Cuscino, N., Miele, M., Timoneri, F., Di Bella, M., Zito, G., Barbera, F., Badami, E., Corsale, A. M., Shekarkar Azgomi, M., Conaldi, P. G., ... Bulati, M. (2026). Immune-Based Biomarkers as Predictors of Mortality in ECMO Therapy for Severe COVID-19 ARDS: Insights from a Retrospective Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010390









