A Conserved Planthopper MATH-BTB Protein Regulates Fecundity in Nilaparvata legens Stål
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of MATH Family Members in 31 Insect Species
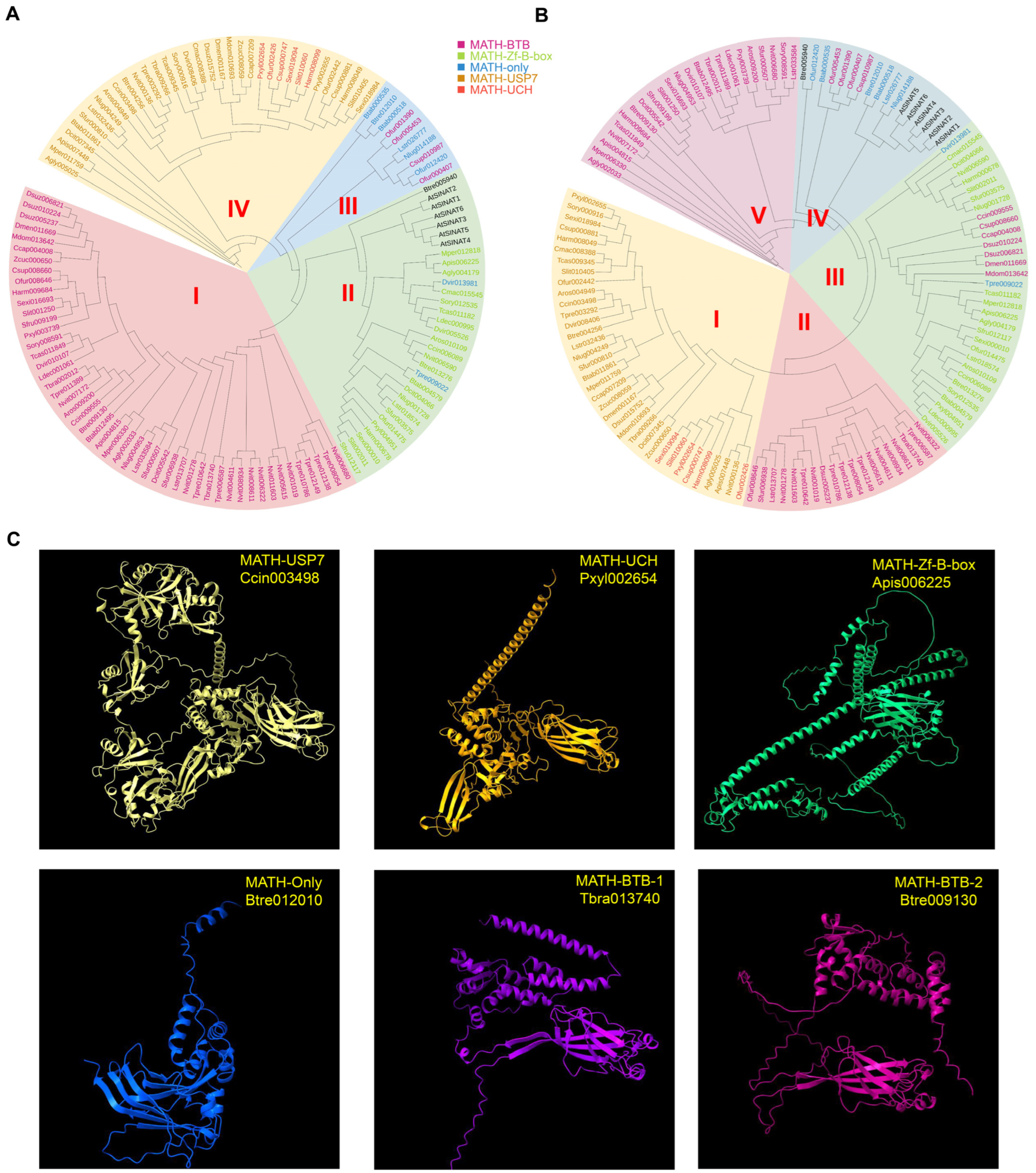
2.2. Phylogenetic Clustering of the 121 Identified MATH Family Members
2.3. Characterization and Evolutionary Analysis of Planthopper MATH Members
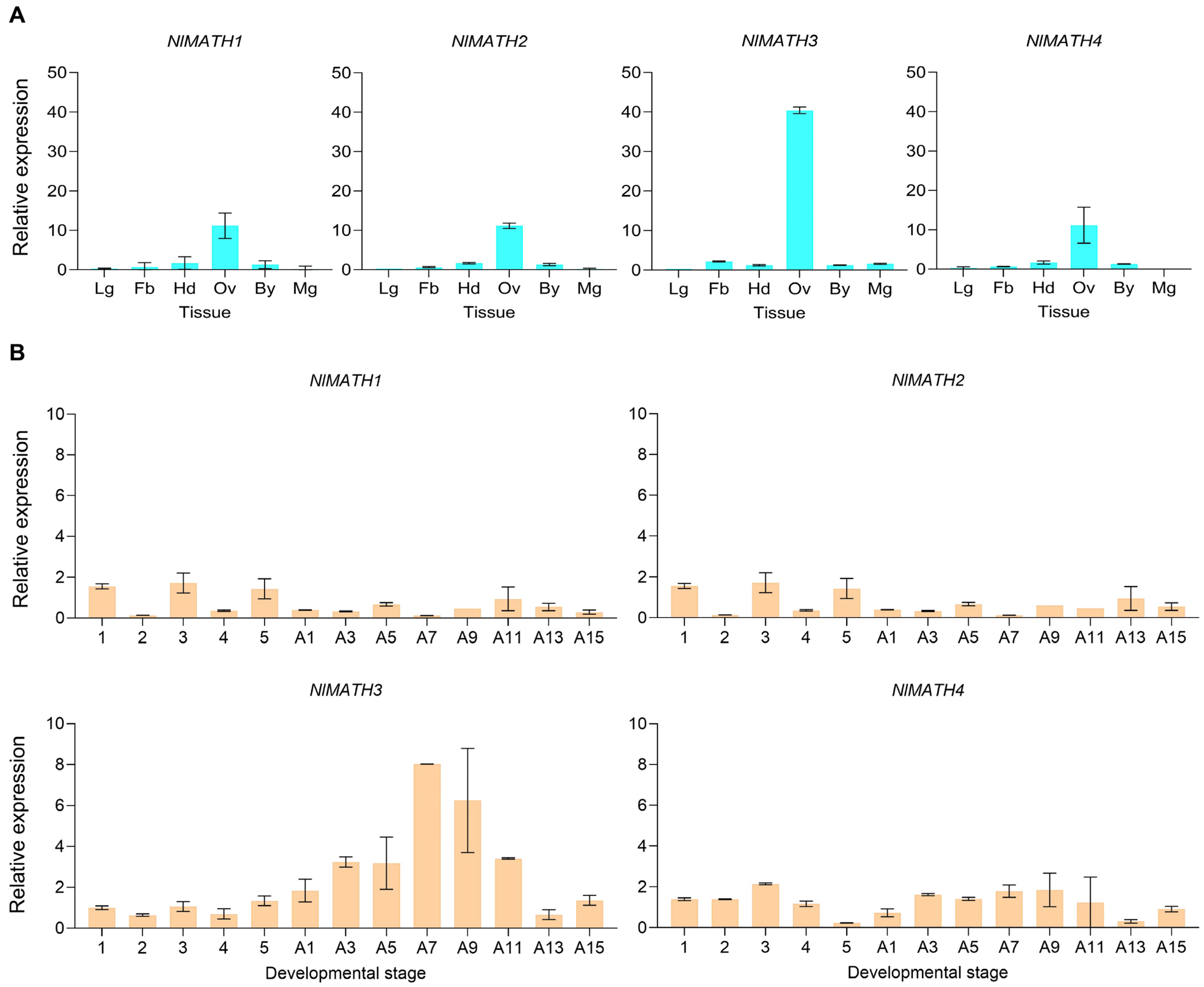
2.4. The Spatiotemporal Expression Patterns of the NlMATH Genes
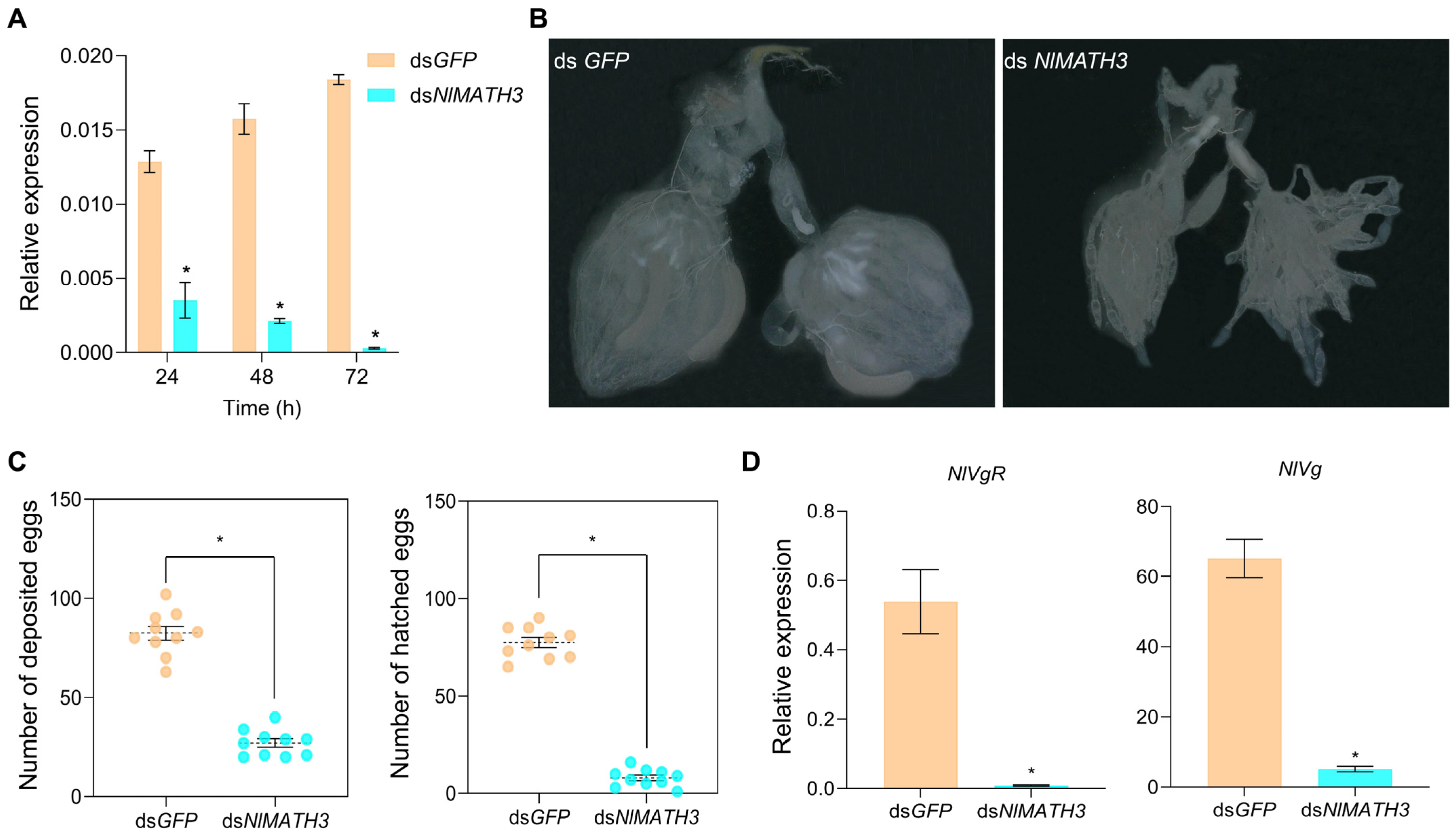
2.5. Fecundity Analysis of NlMATH3 Using RNAi
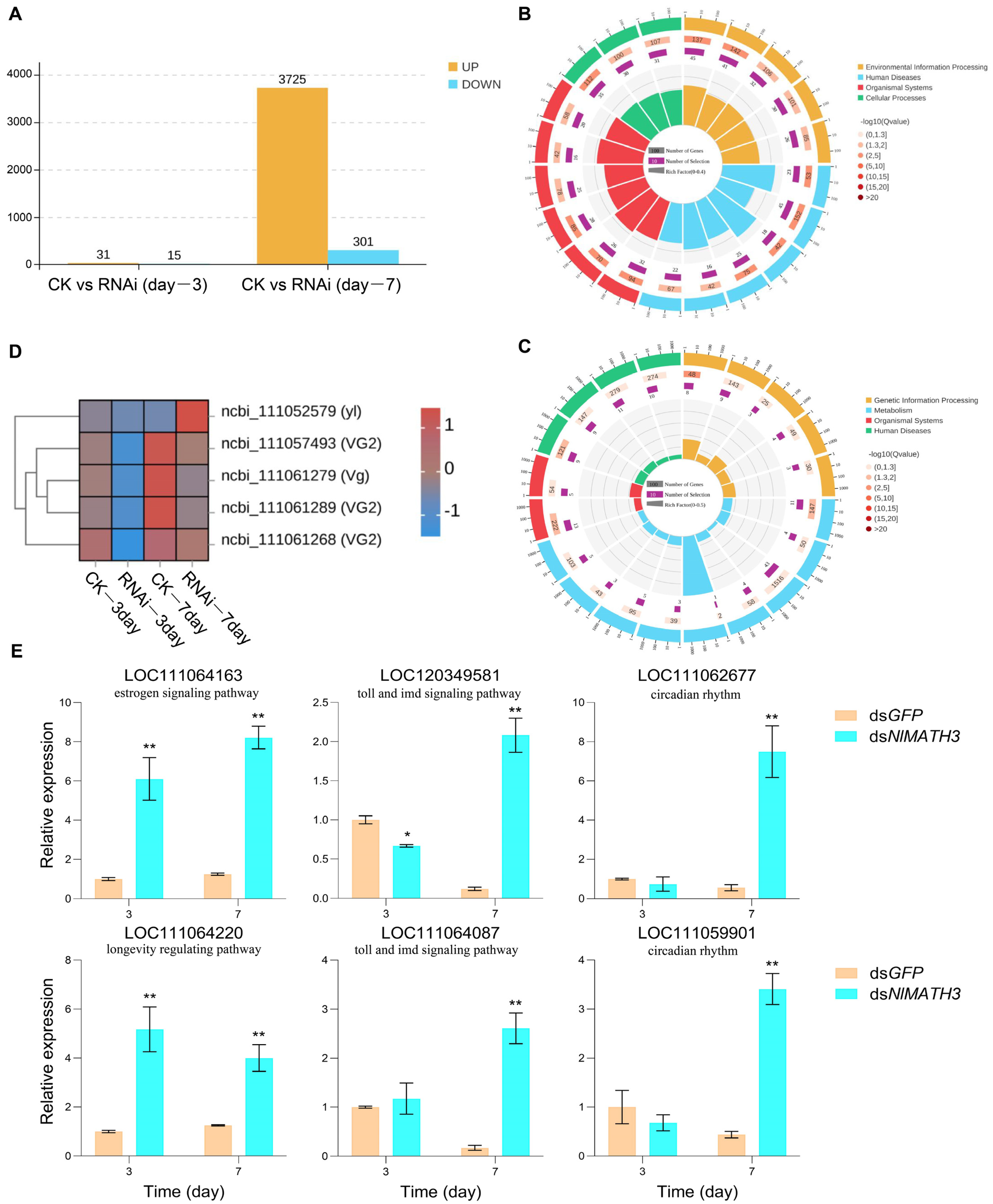
2.6. Transcriptomic Analysis of N. lugens Females After NlMATH3 Silencing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect Strains
4.2. Identification and Characterization of Insect MATH Members
4.3. Prediction of Protein 3D Structures and Phylogenetic Tree Construction
4.4. Duplication Events and Synteny Analysis
4.5. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) Analysis
4.6. RNAi and Bioassay of Fecundity in N. lugens Following dsRNA Injection
4.7. Transcriptomic Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rothe, M.; Wong, S.C.; Henzel, W.J.; Goeddel, D.V. A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell 1994, 78, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, J.M.; Pawlowski, K.; Haas, E.; Ware, C.F.; Godzik, A.; Reed, J.C. A diverse family of proteins containing tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 24242–24252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata, J.M.; Martínez-García, V.; Lefebvre, S. Phylogeny of the TRAF/MATH domain. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 597, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.C.; Burkitt, V.; Villa, A.R.; Tong, L.; Wu, H. Structural basis for self-association and receptor recognition of human TRAF2. Nature 1999, 398, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Xia, F.N.; Xiao, S.; Li, J. TRAF proteins as key regulators of plant development and stress responses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 431–448. [Google Scholar]
- Sunnerhagen, M.; Pursglove, S.; Fladvad, M. The new MATH: Homology suggests shared binding surfaces in meprin tetramers and TRAF trimers. FEBS Lett. 2002, 530, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Ma, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Gao, Y.; Zhai, C.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Evolution and Expression of the Meprin and TRAF Homology Domain-Containing Gene Family in Solanaceae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; He, X.; Shen, W.; Liu, C.; Ruan, Y. Phylogenetic Analysis of Brassica rapa MATH-Domain Proteins. Curr. Genom. 2004, 14, 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Arkee, T.; Bishop, G.A. TRAF family molecules in T cells: Multiple receptors and functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bishop, G.A. The multifaceted roles of TRAFs in the regulation of B-cell function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, B.; Aleithan, F.; Abdul-Sater, Z.; Abdul-Sater, A. The evolving role of TRAFs in mediating inflammatory responses. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häcker, H.; Tseng, P.H.; Karin, M. Expanding TRAF function: TRAF3 as a tri-faced immune regulator. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P. TRAF molecules in cell signaling and in human diseases. J. Mol. Signal 2013, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.E.; Harikumar, K.B.; Hait, N.C.; Allegood, J.; Strub, G.M.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate is a missing cofactor for the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF2. Nature 2010, 465, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, X.; Zhong, X.; Li, M.; Ao, K.; Li, X. Plant TRAF proteins regulate NLR immune receptor turnover. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Li, M.W.; Feke, A.; Liu, W.; Saffer, A.M.; Gendron, J.M. GIGANTEA recruits the UBP12 and UBP13 deubiquitylases to regulate accumulation of the ZTL photoreceptor complex. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Xia, F.N.; Xie, L.J.; Yu, L.J.; Chen, Q.F.; Xiao, S. TRAF family proteins regulate autophagy dynamics by modulating AUTOPHAGY PROTEIN6 stability in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 890–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottrell, D.G.; Schoenly, K.G. Resurrecting the ghost of green revolutions past: The brown planthopper as a recurring threat to high-yielding rice production in tropical Asia. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2012, 15, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heong, K.L.; Hardy, B. Planthoppers: New Threats to the Sustainability of Intensive Rice Production Systems in Asia; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Mao, Q.; Xie, L.; Wei, T. Infection route of rice grassy stunt virus, a tenuivirus, in the body of its brown planthopper vector, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) after ingestion of virus. Virus. Res. 2014, 188, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, W.; Kang, K.; Pang, R.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, W. FoxO directly regulates the expression of TOR/S6K and vitellogenin to modulate the fecundity of the brown planthopper. Sci. China Life Sci. 2021, 64, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.X. Recent advances in molecular biology research of a rice pest, the brown planthopper. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.E.; Rotenberg, D. Disruption of insect transmission of plant viruses. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 8, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Palli, S.R. Mechanisms, applications, and challenges of insect RNA interference. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, L.; He, Q.; Zhou, S.T. Regulatory mechanisms of vitellogenesis in insects. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 593613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.T.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, M.X.; Zhou, Q. Nutritional signaling regulates vitellogenin synthesis and egg development through juvenile hormone in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, J.; Kang, K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W. Activation of the TOR signalling pathway by glutamine regulates insect fecundity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, J.C.; Xue, J.; Lu, J.B.; Huang, H.J.; Xu, H.J.; Zhang, C.X. Effect of RNAi-mediated knockdown of NlTOR gene on fertility of male Nilaparvata lugens. J. Insect. Physiol. 2017, 98, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q. Deficiency of Brummer impairs lipid mobilization and JH-mediated vitellogenesis in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Front. Physiol 2018, 9, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.; Qiu, J.; Li, T.; Yang, P.; Yue, L.; Zhang, W. The regulation of lipid metabolism by a hypothetical P-loop NTPase and its impact on fecundity of the brown planthopper. BBA Gen. Subj. 2017, 1864, 129492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, C.; Chen, M.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, Z. Characterization of MicroRNAs Associated with Reproduction in the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Zhu, X.H.; Wan, P.J.; He, J.C.; Wang, W.X.; Fu, Q. Knockdown of the chromatin remodeling ATPase gene Brahma impairs the reproductive potential of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 184, 105106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Yuan, X.B.; Chen, S.J.; Chen, H.H.; Xu, N.; Xu, H.J. The histone deacetylase NlHDAC1 regulates both female and male fertility in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Open. Biol. 2018, 8, 180158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Shu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. Molecular characterization and RNA interference analysis of vitellogenin receptor from Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). J. Insect. Physiol. 2015, 73, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kang, K.; Zhang, W. Discovery and functional identification of fecundity-related genes in the brown planthopper by large-scale RNA interference. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2016, 25, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, C. Vitellogenin and vitellogenin-like genes in the brown planthopper. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, F.; Zhang, D.; Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J. Role of nuclear protein Akirin in the modulation of female reproduction in Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1415746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Song, Q. Male selenoprotein F-like (SPF-L) influences female reproduction and population growth in Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.T.; Zhou, Q. TOR pathway-mediated juvenile hormone synthesis regulates nutrient-dependent female reproduction in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Zeng, R. Adipokinetic hormone receptor mediates trehalose homeostasis to promote vitellogenin uptake by oocytes in Nilaparvata lugens. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, G.; Zhang, W. Mutations in NlInR1 affect normal growth and lifespan in the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 124, 103426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, S.; Hao, Z.; Tang, T.; Liu, F. Involvement of TRAF6 in regulating immune defense and ovarian development in Musca domestica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 1262–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lin, Q.; Fei, H.; He, Z.; Xu, H.; Gao, C. Discovery of deaminase functions by structure-based protein clustering. Cell 2023, 186, 3182–3195.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, M.; DiMaio, F.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Baker, D. Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network. Science 2021, 373, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Hassabis, D. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandonia, J.M.; Guan, L.; Lin, S.; Yu, C.; Fox, N.K.; Brenner, S.E. SCOPe: Improvements to the structural classification of proteins—Extended database to facilitate variant interpretation and machine learning. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D553–D559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.L.; Wan, P.J.; Wang, W.X.; Lai, F.X.; Fu, Q. Ran involved in the development and reproduction is a potential target for RNA-interference-based pest management in Nilaparvata lugens. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.K.; Luo, Y.J.; Deng, Y.M.; Li, Y.; Pang, X.Q.; Tang, B. Insulin receptors regulate the fecundity of Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2020, 23, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Finn, R.D.; Eddy, S.R.; Bateman, A.; Punta, M. Challenges in homology search: HMMER3 and convergent evolution of coiled-coil regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Jing, D.; Tang, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Duanmu, H.; Cong, Y.; Chen, M.; Ye, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. InsectBase 2.0: A comprehensive gene resource for insects. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1040–D1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant. 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.; Yuan, L.Y.; Li, Y.F.; Xiao, H.X.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.J.; Zhang, Z.F. Salivary protein 7 of the brown planthopper functions as an effector for mediating tricin metabolism in rice plants. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Dai, Y.; Gong, G.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, C.; Li, Y.; Yuan, L.; Xiao, H.; Jin, F.; Pang, R.; et al. A Conserved Planthopper MATH-BTB Protein Regulates Fecundity in Nilaparvata legens Stål. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010219
Dai Y, Gong G, Wang S, Guo Y, Qiu C, Li Y, Yuan L, Xiao H, Jin F, Pang R, et al. A Conserved Planthopper MATH-BTB Protein Regulates Fecundity in Nilaparvata legens Stål. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010219
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Yangshuo, Gu Gong, Shiqi Wang, Yujing Guo, Caili Qiu, Yanfang Li, Longyu Yuan, Hanxiang Xiao, Fengliang Jin, Rui Pang, and et al. 2026. "A Conserved Planthopper MATH-BTB Protein Regulates Fecundity in Nilaparvata legens Stål" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010219
APA StyleDai, Y., Gong, G., Wang, S., Guo, Y., Qiu, C., Li, Y., Yuan, L., Xiao, H., Jin, F., Pang, R., & Zhang, Z. (2026). A Conserved Planthopper MATH-BTB Protein Regulates Fecundity in Nilaparvata legens Stål. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010219





