Comparative Study on the Effects of Selenium-Enriched Yeasts with Different Selenomethionine Contents on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
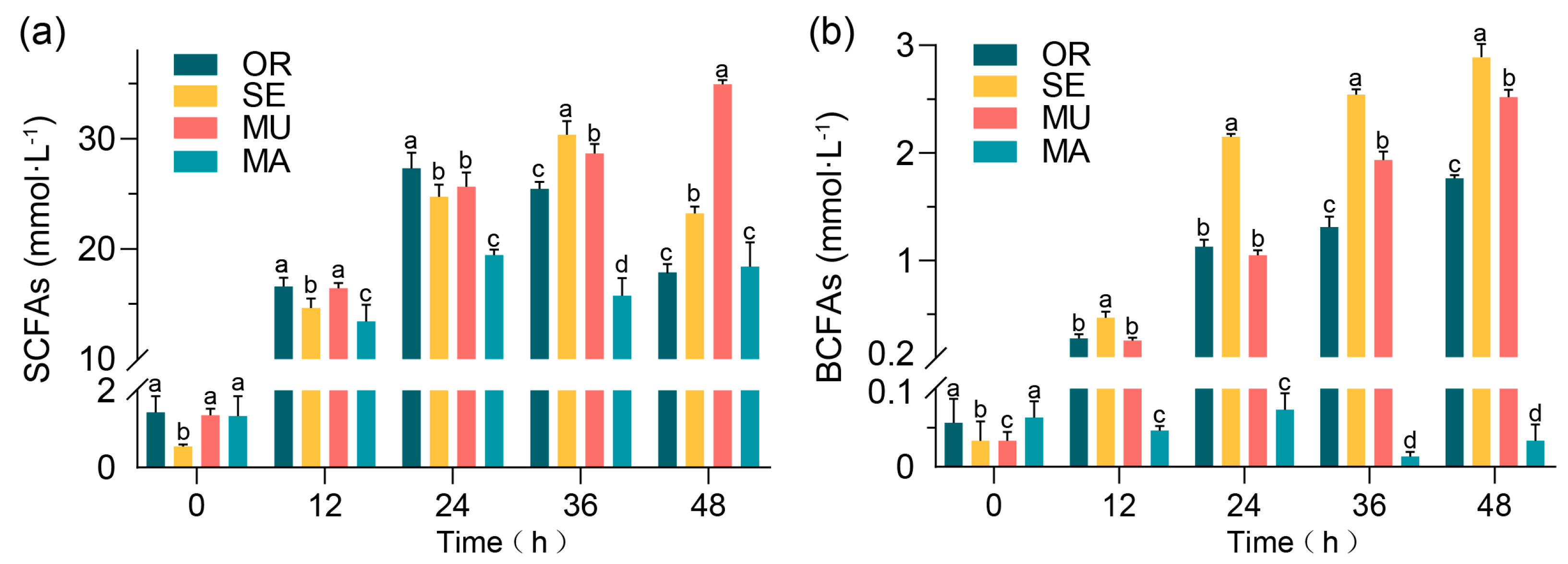
2.1. Effects of Selenium-Enriched Yeast with Various SeM Contents on SCFAs
2.2. Selenium-Enriched Yeast and Gut Flora
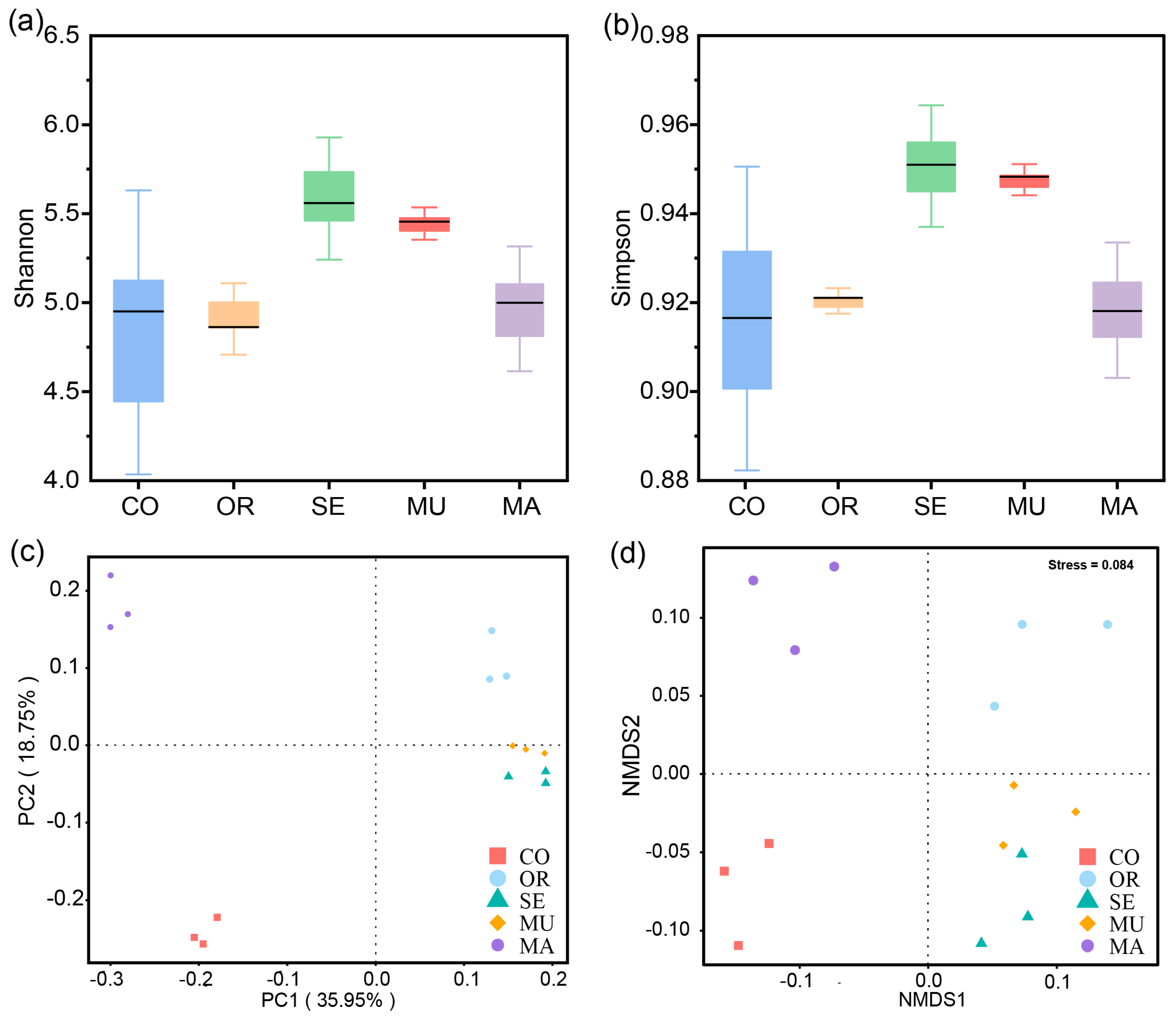
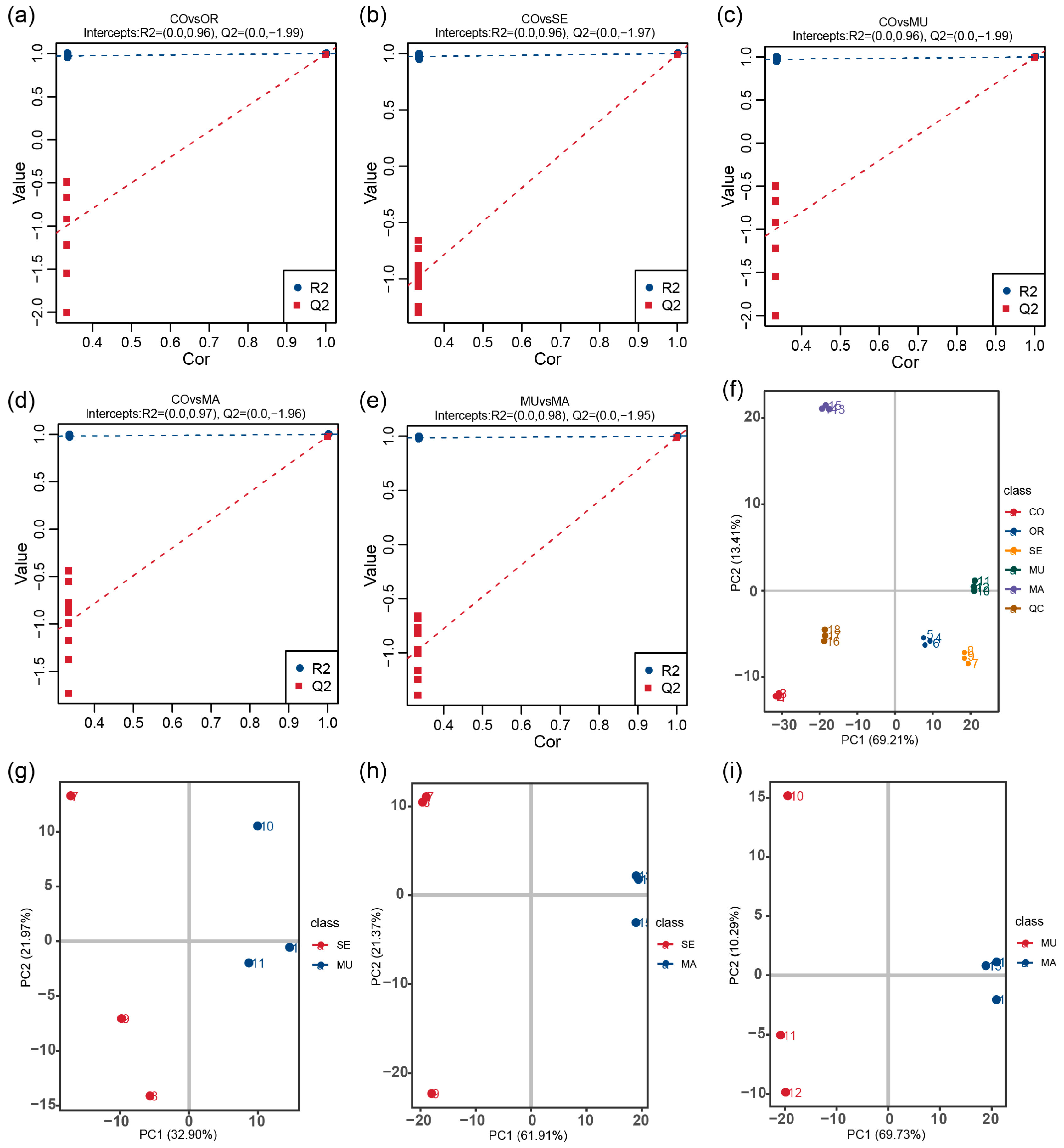
2.2.1. α- and β-Diversity of Gut Microbial Communities
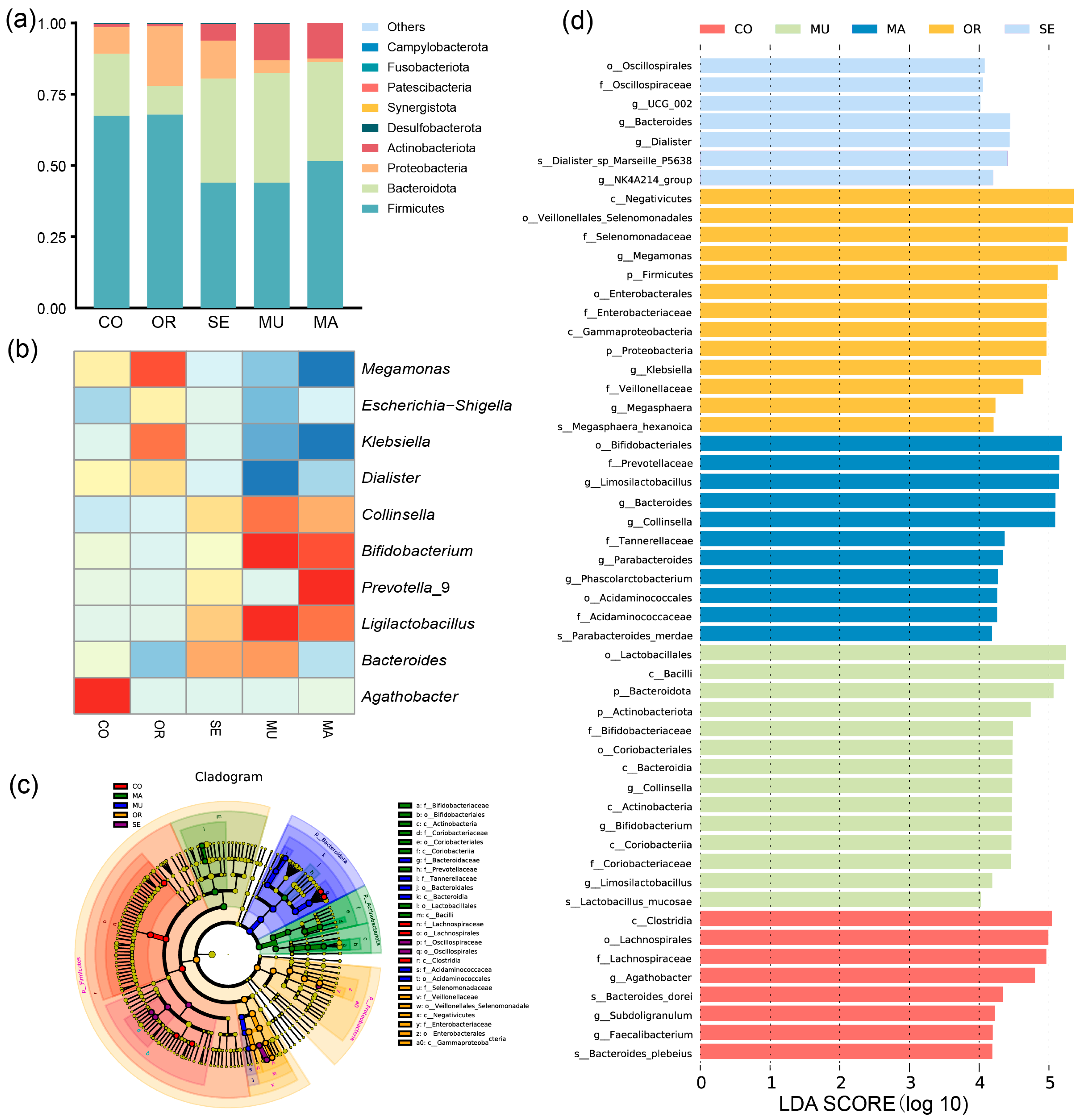
2.2.2. Effects of Selenium-Enriched Yeast with Various SeM Contents on Gut Flora
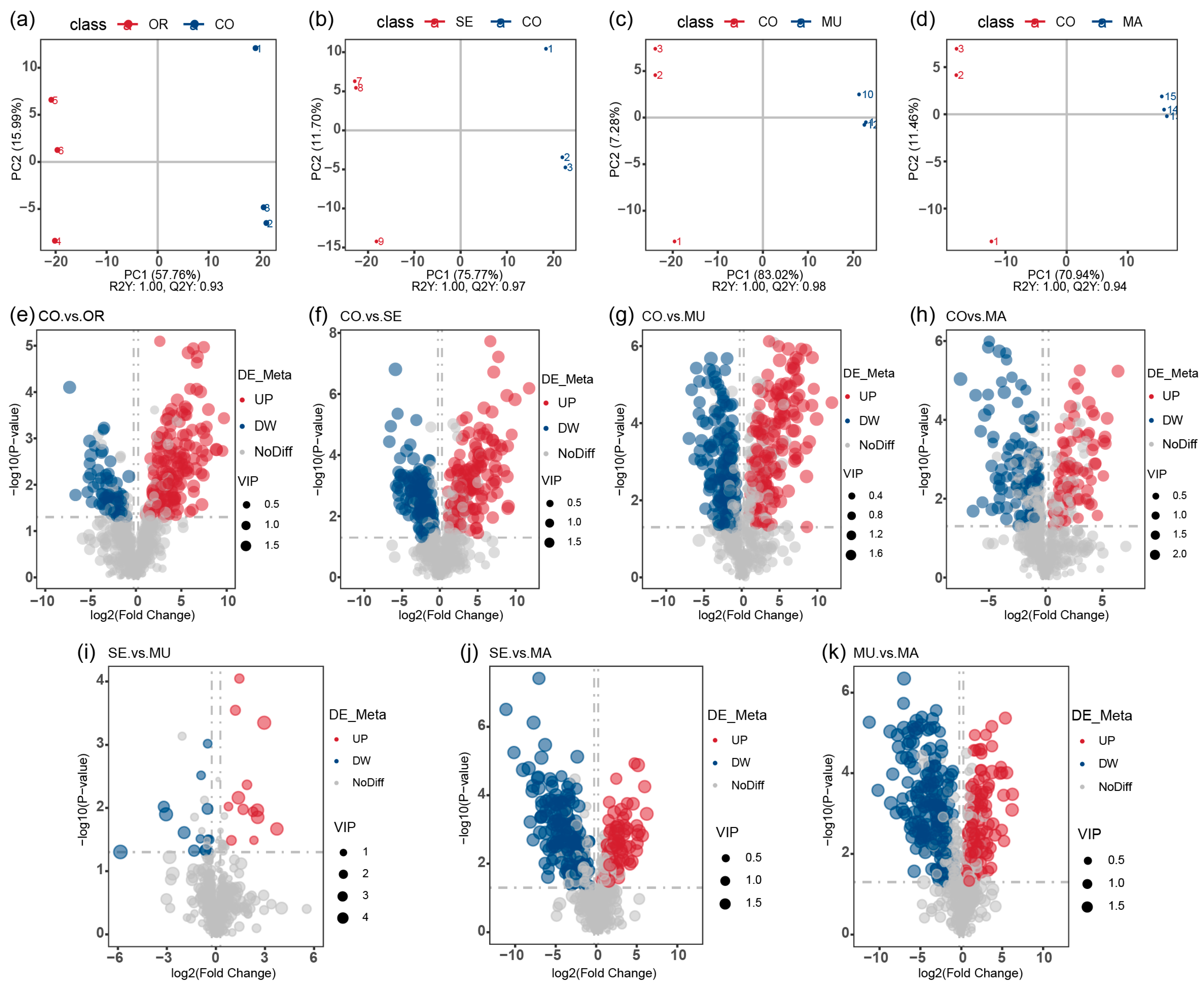
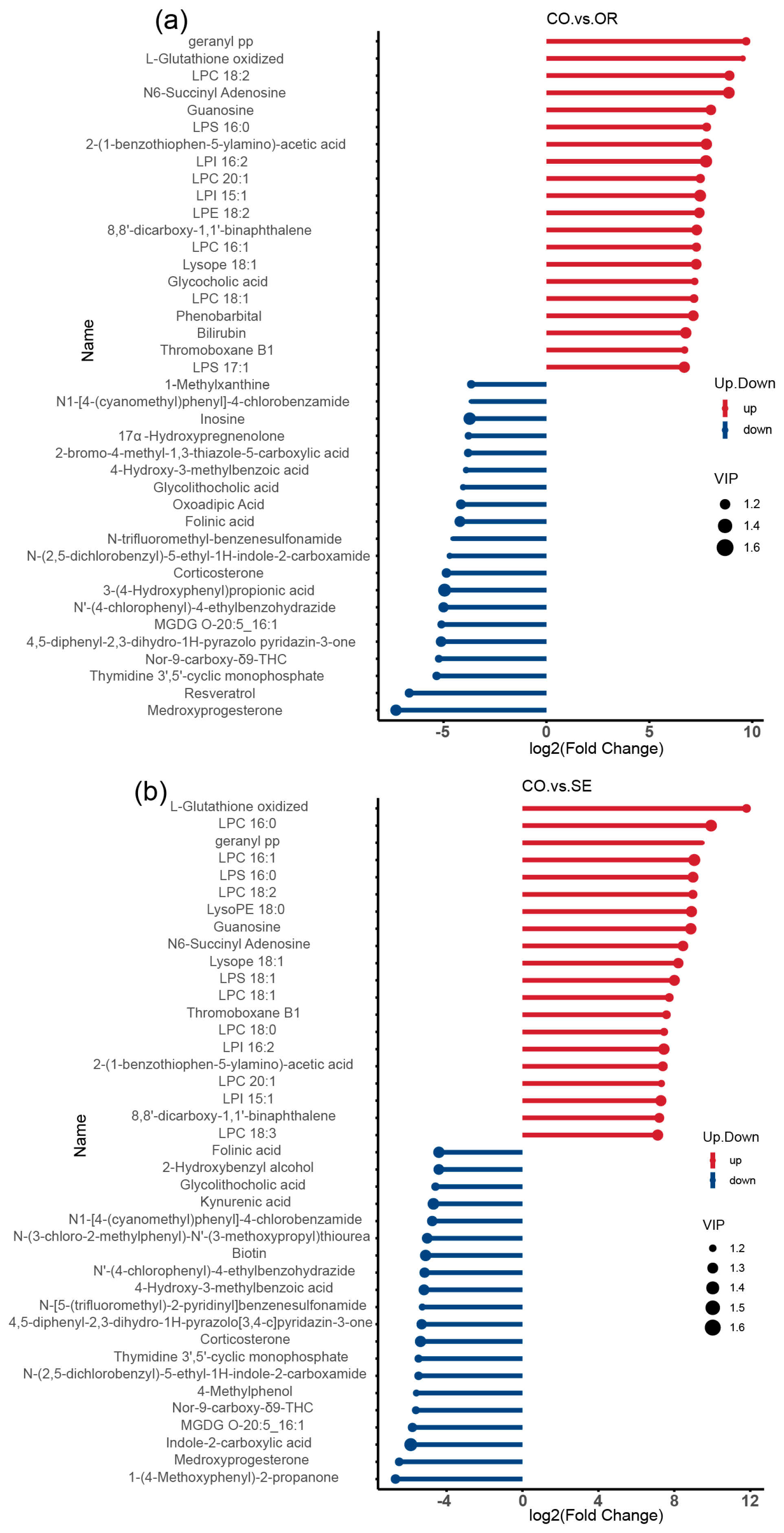
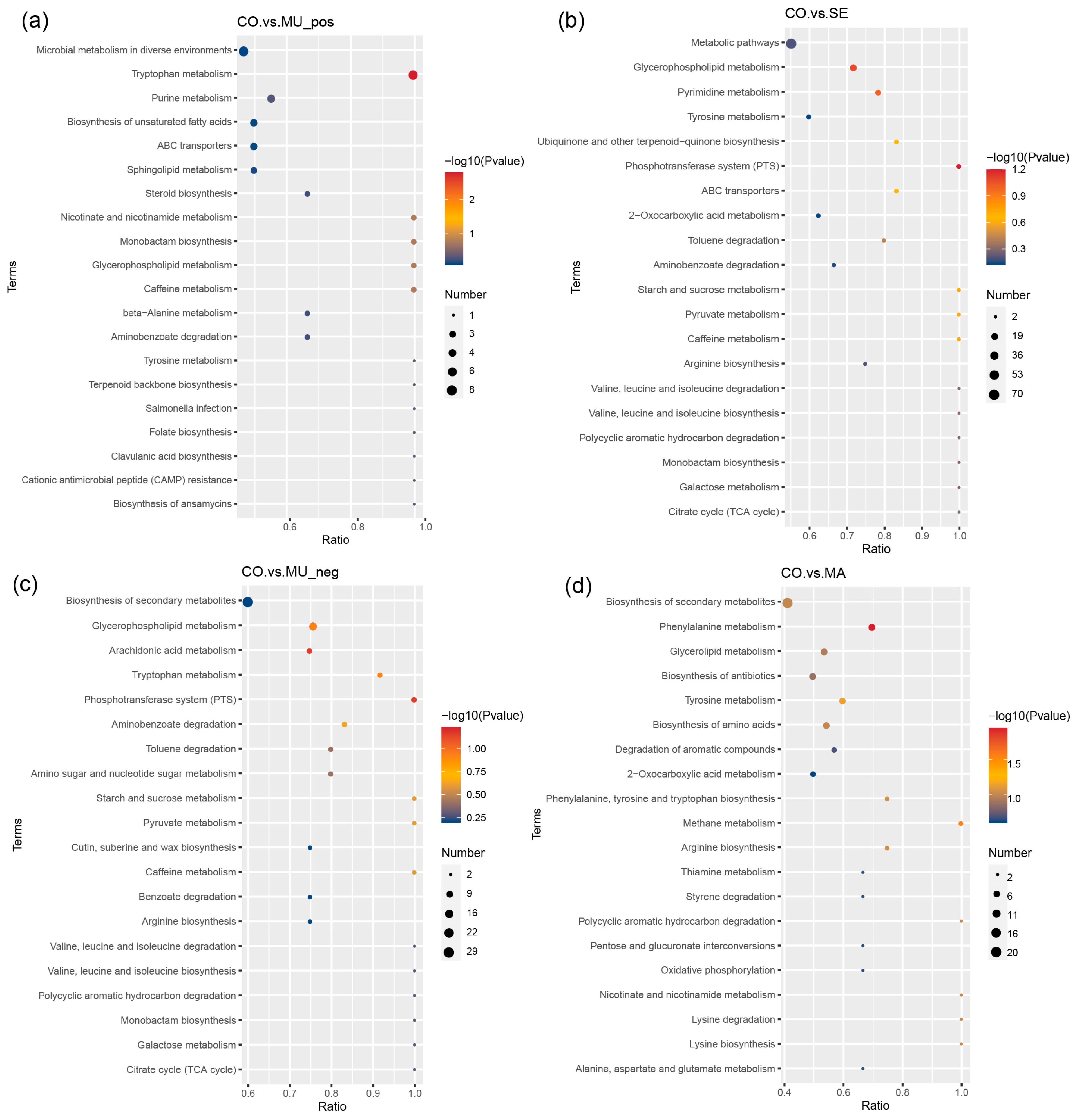
2.3. Effects of Selenium-Enriched Yeast with Various SeM Contents on Gut Metabolites
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation and Extraction of Selenium-Enriched Yeast Samples
4.3. Fecal Sources and Strain Preservation
4.4. In Vitro Dynamic Fecal Fermentation in BGR
4.5. Determination of SeM in Selenium-Enriched Yeasts
4.6. Determination of SCFAs
4.7. Extraction and Analysis of 16S rRNA Gene Sequence
4.8. Determination of Metabolites
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matos, R.P.; Lima, V.M.P.; Windmoller, C.C.; Nascentes, C.C. Correlation between the natural levels of selenium and soil physicochemical characteristics from the Jequitinhonha Valley (MG), Brazil. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 172, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.; Johnson, T.M.; Dhillon, K.S.; Mason, P.R. Fate of selenium in soils at a seleniferous site recorded by high precision Se isotope measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9690–9698. [Google Scholar]
- Rayman, M.P. Food-chain selenium and human health: Emphasis on intake. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weekley, C.M.; Harris, H.H. Which form is that? The importance of selenium speciation and metabolism in the prevention and treatment of disease. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8870–8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, H.; Liu, G.; Yousaf, B.; Ali, M.U.; Abbas, Q.; Munir, M.A.M.; Mian, M.M. Developmental selenium exposure and health risk in daily foodstuffs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 149, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P. Selenium and human health. Lancet 2012, 379, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defi, I.R.; Yamazaki, C.; Kameo, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Nakazawa, M.; Shinya, Y.; Sato, N.; Wada, N.; Shirakura, K.; Koyama, H. Acute phase response of selenium status and glutathione peroxidase activity in blood plasma before and after total knee arthroplasty surgery. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 144, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombo, S.; Schreck, E.; Dumat, C.; Laplanche, C.; Pierart, A.; Longchamp, M.; Besson, P.; Castrec-Rouelle, M. Bioaccessibility of selenium after human ingestion in relation to its chemical species and compartmentalization in maize. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R.; Hasan, M.M.; Khaleque, M.A. Efficient selenium(IV) detection and removal from water by tailor-made novel conjugate adsorbent. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, S.; Luguet, A.; Lorand, J.-P.; Wombacher, F.; Lissner, M. Selenium and tellurium systematics of the Earth’s mantle from high precision analyses of ultra-depleted orogenic peridotites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 86, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehlik-Tomas, V.; Zetic, V.G.; Stanzer, D.; Grba, S.; Vahcic, N. Zinc, copper and manganese enrichment in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisae. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 42, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Huang, K.; Qin, S.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, F. Antibacterial action of selenium-enriched probiotics against pathogenic Escherichia coli. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Abe, M.; Fukunaga, K.; Kikuchi, K. Bioavailability of selenium in the defatted dark muscle of tuna. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M.; Blazejak, S.; Gientka, I.; Bzducha-Wrobel, A. Accumulation and metabolism of selenium by yeast cells. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5373–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazard, M.; Blanquet, S.; Fisicaro, P.; Labarraque, G.; Plateau, P. Uptake of selenite by Saccharomyces cerevisiae involves the high and low affinity orthophosphate transporters. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 32029–32037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesti, G.M.; Combs, G.F., Jr. Studies on the enteric absorption of selenium in the chick using localized coccidial infections. Poult. Sci. 1976, 55, 2265–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Xu, J.; Yin, Z.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, Z.; Zhan, X. Fractionation, preliminary structural characterization and prebiotic activity of polysaccharide from the thin stillage of distilled alcoholic beverage. Process Biochem. 2022, 118, 52–64. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Marinelli, L.; Blottière, H.M.; Larraufie, P.; Lapaque, N. SCFA: Mechanisms and functional importance in the gut. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lührs, H.; Gerke, T.; Boxberger, F.; Backhaus, K.; Melcher, R.; Scheppach, W.; Menzel, T. Butyrate inhibits interleukin-1-mediated nuclear factor-kappa B activation in human epithelial cells. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2001, 46, 1968–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.A.; Petri, R.M.; Gruell, D.; Zebeli, Q.; Metzler-Zebeli, B.U. Transglycosylated starch modulates the gut microbiome and expression of genes related to lipid synthesis in liver and adipose tissue of pigs. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.S.; Chambers, E.S.; Morrison, D.J.; Frost, G. The role of short chain fatty acids in appetite regulation and energy homeostasis. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.H.; Macfarlane, G.T. The control and consequences of bacterial fermentation in the human colon. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1991, 70, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Besten, G.; van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomaeus, H.; Balogh, A.; Yakoub, M.; Homann, S.; Wilck, N. Short-chain fatty acid propionate protects from hypertensive cardiovascular damage. Circulation 2018, 139, 1407–1421. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, P.A.; van Zelm, M.C.; Muir, J.G.; Gibson, P.R. Review article: Short chain fatty acids as potential therapeutic agents in human gastrointestinal and inflammatory disorders. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, E.; Grootaert, C.; Verstraete, W.; Wiele, T.V.d. Propionate As a Health-Promoting Microbial Metabolite in the Human Gut. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Garcia, R.A.; McCubbin, T.; Navone, L.; Stowers, C.; Nielsen, L.K.; Marcellin, E. Microbial Propionic Acid Production. Fermentation 2017, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.C.-H.; Zhang, X.; Ji, F.; Lin, Y.; Liang, W.; Li, Q.; Chen, D.; Fong, W.; Kang, X.; Liu, W.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus suppresses non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular carcinoma through producing valeric acid. eBioMedicine 2024, 100, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamano, H.; Fukura, K.; Suzuki, M.; Sakamoto, K.; Yokogoshi, H.; Takeda, A. Advantageous effect of theanine intake on cognition. Nutr. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Lu, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, B.; Fan, D.; Li, C.; Wu, J.; He, L.; Zhu, X.; Du, Y. 5-hydroxytryptamine produced by enteric serotonergic neurons initiates colorectal cancer stem cell self-renewal and tumorigenesis. Neuron 2022, 110, 2268–2282.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeney, B.A.; Crowe, M.S.; Mahavadi, S.; Murthy, K.S.; Grider, J.R. Branched short-chain fatty acid isovaleric acid causes colonic smooth muscle relaxation via cAMP/PKA pathway. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology-Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Duan, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lyu, N.; Liu, F.; Liang, S.; Zhu, B. An examination of data from the American Gut Project reveals that the dominance of the genus Bifidobacterium is associated with the diversity and robustness of the gut microbiota. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wu, F.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, W.; Yue, J.; Xiao, B.; Luo, Z. Lactobacillus and intestinal diseases: Mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 260, 127019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiwaki, H.; Ueyama, J.; Kashihara, K.; Ito, M.; Hamaguchi, T.; Maeda, T.; Tsuboi, Y.; Katsuno, M.; Hirayama, M.; Ohno, K. Gut microbiota in dementia with Lewy bodies. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salonen, A.; Lahti, L.; Salojärvi, J.; Holtrop, G.; Korpela, K.; Duncan, S.H.; Date, P.; Farquharson, F.; Johnstone, A.M.; Lobley, G.E. Impact of diet and individual variation on intestinal microbiota composition and fermentation products in obese men. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2218–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morio, F.; Jean-Pierre, H.; Dubreuil, L.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Calvet, L.; Mercier, G.; Devine, R.; Marchandin, H. Antimicrobial susceptibilities and clinical sources of Dialister species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 4498–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lkhagva, E.; Chung, H.-J.; Ahn, J.-S.; Hong, S.-T. Host factors affect the gut microbiome more significantly than diet shift. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yachida, S.; Mizutani, S.; Shiroma, H.; Shiba, S.; Nakajima, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Watanabe, H.; Masuda, K.; Nishimoto, Y.; Kubo, M. Metagenomic and metabolomic analyses reveal distinct stage-specific phenotypes of the gut microbiota in colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, R.; Guo, M.; Zheng, H. Characteristics of gut microbiota in people with obesity. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255446. [Google Scholar]
- Sequeira, R.P.; McDonald, J.A.; Marchesi, J.R.; Clarke, T.B. Commensal Bacteroidetes protect against Klebsiella pneumoniae colonization and transmission through IL-36 signalling. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Chen, Z.; Chen, M.; Chen, G.; Huang, Q.; Yang, X.; Yin, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W.; Lin, H.; et al. Reduced stress-associated FKBP5 DNA methylation together with gut microbiota dysbiosis is linked with the progression of obese PCOS patients. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.P. Redox Potential of GSH/GSSG Couple: Assay and Biological Significance. In Methods in Enzymology; Sies, H., Packer, L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 348, pp. 93–112. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, J.S.; Steinauer, K.K.; Hornung, B.; Irish, J.M.; Lecane, P.; Birrell, G.W.; Peehl, D.M.; Knox, S.J. Role of glutathione depletion and reactive oxygen species generation in apoptotic signaling in a human B lymphoma cell line. Cell Death Differ. 2002, 9, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, J.J.; Land, S.C. Redox signaling-mediated regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory cytokine biosynthesis in alveolar epithelial cells. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2002, 4, 179–193. [Google Scholar]
- Zitka, O.; Skalickova, S.; Gumulec, J.; Masarik, M.; Adam, V.; Hubalek, J.; Trnkova, L.; Kruseova, J.; Eckschlager, T.; Kizek, R. Redox status expressed as GSH: GSSG ratio as a marker for oxidative stress in paediatric tumour patients. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 4, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, J.; Liu, W.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, X. Succinylation modification: A potential therapeutic target in stroke. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapskog, A.B.; Aksnes, M.; Edwin, T.H.; Ueland, P.M.; Ulvik, A.; Fang, E.F.; Eldholm, R.S.; Halaas, N.B.; Saltvedt, I.; Giil, L.M.; et al. Higher concentrations of kynurenic acid in CSF are associated with the slower clinical progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 5573–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, A.E.; Lee, N.; Matthew-Onabanjo, A.N.; Spears, M.E.; Park, S.J.; Youkana, D.; Doshi, M.B.; Peppers, A.; Li, R.; Joseph, A.B. Selenium detoxification is required for cancer-cell survival. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 603–611. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, D.J.; Duarte-Salles, T.; Hybsier, S.; Trichopoulou, A.; Stepien, M.; Aleksandrova, K.; Overvad, K.; Tjonneland, A.; Olsen, A.; Affret, A.; et al. Prediagnostic selenium status and hepatobiliary cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition cohort. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Mu, C.-l.; Farzi, A.; Zhu, W.-Y. Tryptophan metabolism: A link between the gut microbiota and brain. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 709–723. [Google Scholar]
- Calder, P.C. Marine Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes: Effects, Mechanisms and Clinical Relevance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2015, 1851, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran-Ressler, R.R.; Bae, S.; Lawrence, P.; Wang, D.H.; Brenna, J.T. Branched-chain Fatty Acid Content of Foods and Estimated Intake in the USA. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Mao, B.; Tang, X.; Huang, J.; Guo, R.; Zhao, J.; Cui, S.; Chen, W. Comparison of Selenium-Enriched Lactobacillusparacasei, Selenium-Enriched Yeast, and Selenite for the Alleviation of DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhan, X. Efficient precious metal Rh(III) adsorption by waste P. pastoris and P. pastoris surface display from high-density culture. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 427, 128140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Zhan, X.; Xia, W. Synthesis, characterization, and biological evaluation of novel selenium-containing chitosan derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 284, 119185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, M.; Eck, A.; Koenen, M.E.; Savelkoul, P.H.; Budding, A.E.; Venema, K. Evaluation of an optimal preparation of human standardized fecal inocula for in vitro fermentation studies. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 117, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.J.; Poudel, R.; Van Haute, M.J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; Singh, M.; Liu, S. Pulse processing affects gas production by gut bacteria during in vitro fecal fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; Van Haute, M.J.; Rose, D.J. Processing has differential effects on microbiota-accessible carbohydrates in whole grains during in vitro fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01705-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Keshavarzian, A.; Rose, D.J. Impact of dietary fiber fermentation from cereal grains on metabolite production by the fecal microbiota from normal weight and obese individuals. J. Med. Food 2013, 16, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Míguez, B.; Vila, C.; Venema, K.; Parajó, J.C.; Alonso, J.L. Prebiotic effects of pectooligosaccharides obtained from lemon peel on the microbiota from elderly donors using an in vitro continuous colon model (TIM-2). Food Funct. 2020, 11, 9984–9999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Yang, J.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Yin, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhan, X. Structural characterization and in vitro evaluation of the prebiotic potential of an exopolysaccharide produced by Bacillus thuringiensis during fermentation. Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 2022, 163, 113532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Yu, D.; Yin, Z.; Zhan, X. Comparative Study on the Effects of Selenium-Enriched Yeasts with Different Selenomethionine Contents on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073315
Zhang Z, Zhu L, Zhang H, Yu D, Yin Z, Zhan X. Comparative Study on the Effects of Selenium-Enriched Yeasts with Different Selenomethionine Contents on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073315
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zijian, Li Zhu, Hongtao Zhang, Dan Yu, Zhongwei Yin, and Xiaobei Zhan. 2025. "Comparative Study on the Effects of Selenium-Enriched Yeasts with Different Selenomethionine Contents on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073315
APA StyleZhang, Z., Zhu, L., Zhang, H., Yu, D., Yin, Z., & Zhan, X. (2025). Comparative Study on the Effects of Selenium-Enriched Yeasts with Different Selenomethionine Contents on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073315




