PD-L1-Targeting Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Preclinical Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Drug | Formulation | Disease | Phase | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNU166945 | Polymer conjugate of PTX prodrug | Solid Tumors | Phase I | [22] |
| EndoTAG-1 | PTX in neutral and cationic liposomes | Advanced Head and Neck Cancer and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer | Phase I/II | [17,20] |
| Ang1005 | PTX covalently linked to Angiopep-2 peptide | Recurrent CNS metastasis from breast cancer | Phase II | [42] |
| OncoGel | PTX in biodegradable Gel | Esophageal Cancer | Phase II | [43] |
| Genexol-PM | Polymeric micelle encapsulation of PTX | Metastatic Breast Cancer, NSCLC, Ovarian Cancer | Phase II | [11,14,15,16] |
| NK105 | Polymeric micelle encapsulation of PTX | Recurrent Breast Cancer | Phase III | [12] |
| CT-1203 | Macromolecule PTX conjugate with polyglutamic acid | NSCLC | Phase III | [44] |
| Abraxane | Albumin-bound PTX nanoparticle | NSCLC, Breast Cancer, advanced Pancreatic Cancer | Approved | [10,45,46] |
| Drug | Formulation | Disease | Phase | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LE-SN38 | Liposome-encapsulated SN-38 | Colorectal Cancer after progression on oxaliplatin | Preclinical Phase I | [18,19] |
| IMMU-130 | Antibody–drug conjugate of SN-38 and anti-CEACAM5 | Colorectal Cancer | Phase I/II | [24] |
| NK012 | Polymeric micelle encapsulated SN-38 | Colorectal Cancer | Phase II | [13] |
| IMMU-132 | Antibody–drug conjugate of SN-38 and anti-TROP2 | Recurrent and refractory Triple-Negative Breast Cancer | Approved | [9] |
| Onivyde | Irinotecan liposome | Colorectal Cancer, Pancreatic Cancer, Esophago-gastric Cancer | Approved | [21] |
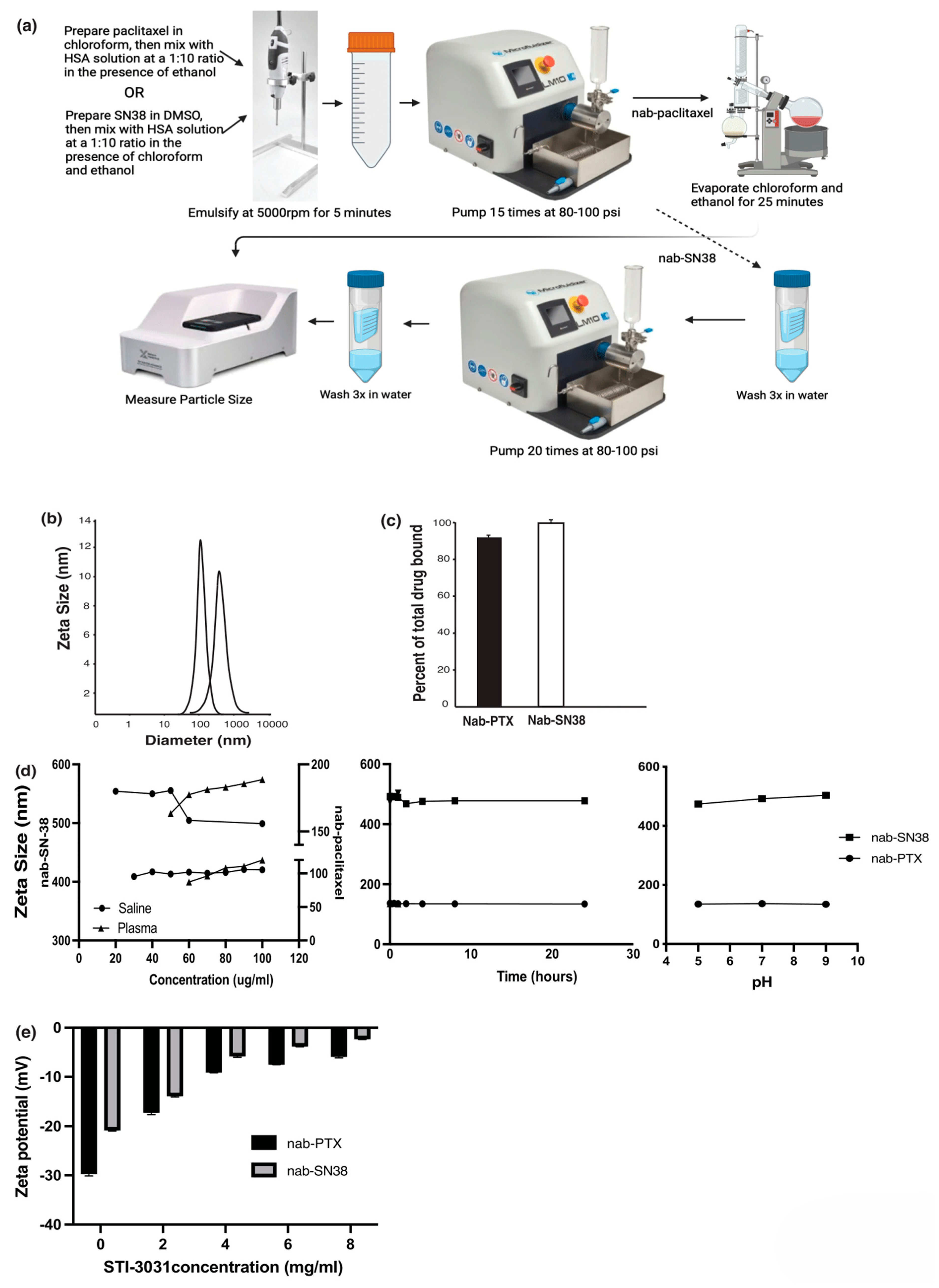
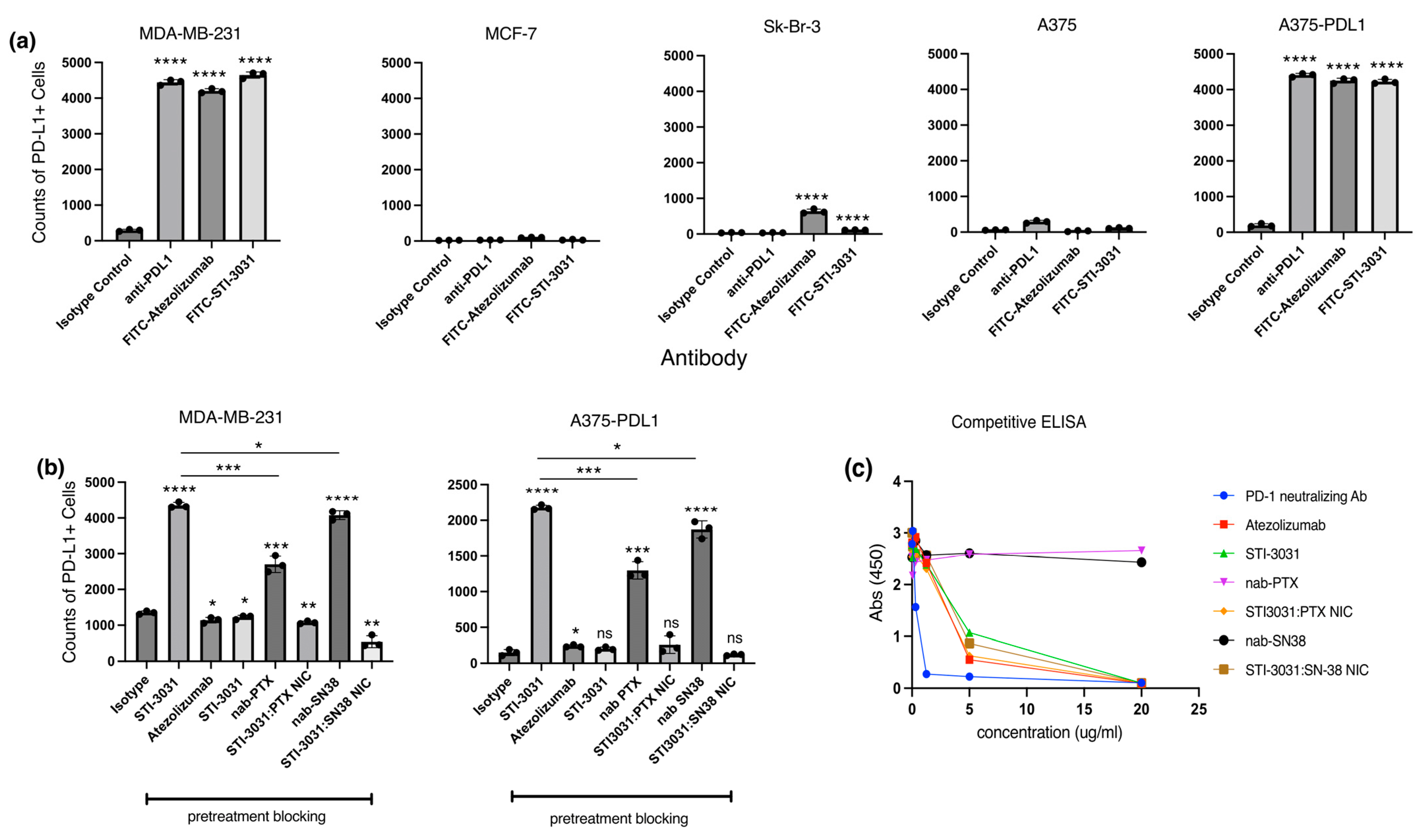
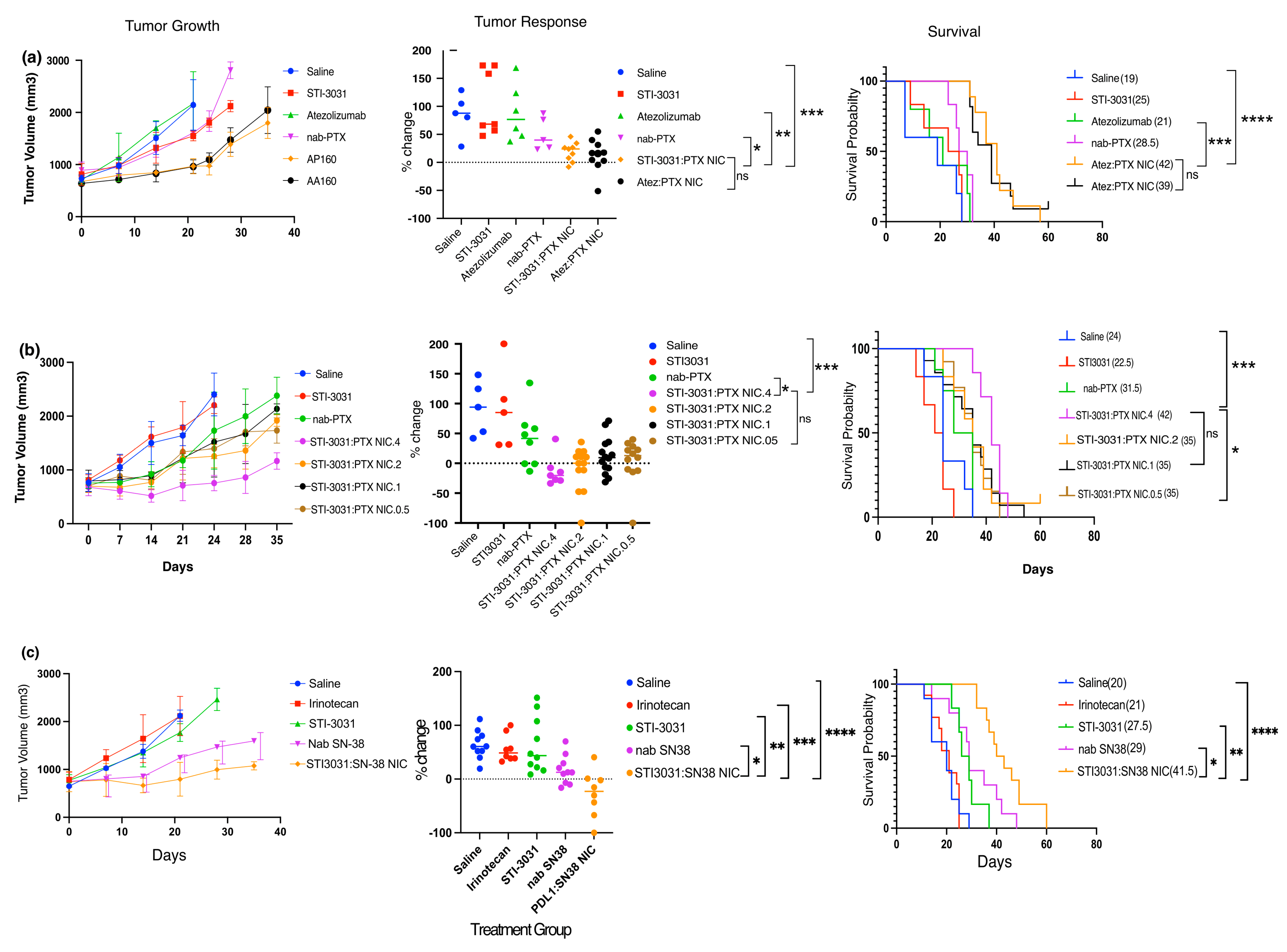
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Nab | Nanoparticles of Albumin |
| NIC | Nano-immune conjugate |
| PTX | paclitaxel |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 |
| TNBC | Triple-Negative Breast Cancer |
| SPR | Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunsorbant assay |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almansour, N.M. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Brief Review About Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Signaling Pathways, Treatment and Role of Artificial Intelligence. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 836417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, A.; Krasnoselskyi, M.; Starikov, V.; Kartashov, S.; Zhulkevych, I.; Vlasenko, V.; Oleshko, K.; Bilodid, O.; Sadchikova, M.; Vinnyk, Y. Triple-negative breast cancer: Current treatment strategies and factors of negative prognosis. J. Med. Life 2022, 15, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senkus, E.; Kyriakides, S.; Ohno, S.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Poortmans, P.; Rutgers, E.; Zackrisson, S.; Cardoso, F.; Committee, E.G. Primary breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26 (Suppl. S5), v8–v30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P. Biology and Management of Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2016, 21, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoti, A.E.; Omoti, C.E. Ocular toxicity of systemic anticancer chemotherapy. Pharm. Pract. 2006, 4, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ramadori, G.; Cameron, S. Effects of systemic chemotherapy on the liver. Ann. Hepatol. 2010, 9, 133–143. [Google Scholar]
- Shayne, M.; Culakova, E.; Poniewierski, M.S.; Wolff, D.; Dale, D.C.; Crawford, J.; Lyman, G.H. Dose intensity and hematologic toxicity in older cancer patients receiving systemic chemotherapy. Cancer 2007, 110, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardia, A.; Mayer, I.A.; Vahdat, L.T.; Tolaney, S.M.; Isakoff, S.J.; Diamond, J.R.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Moroose, R.L.; Santin, A.D.; Abramson, V.G.; et al. Sacituzumab Govitecan-hziy in Refractory Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socinski, M.A.; Bondarenko, I.; Karaseva, N.A.; Makhson, A.M.; Vynnychenko, I.; Okamoto, I.; Hon, J.K.; Hirsh, V.; Bhar, P.; Zhang, H.; et al. Weekly nab-paclitaxel in combination with carboplatin versus solvent-based paclitaxel plus carboplatin as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Final results of a phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.K.; Jung, M.; Sym, S.J.; Shin, D.B.; Kang, S.M.; Kyung, S.Y.; Park, J.W.; Jeong, S.H.; Cho, E.K. A phase II trial of Cremorphor EL-free paclitaxel (Genexol-PM) and gemcitabine in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 74, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Mukai, H.; Saeki, T.; Ro, J.; Lin, Y.C.; Nagai, S.E.; Lee, K.S.; Watanabe, J.; Ohtani, S.; Kim, S.B.; et al. A multi-national, randomised, open-label, parallel, phase III non-inferiority study comparing NK105 and paclitaxel in metastatic or recurrent breast cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, T.; Tsuji, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takeda, K.; Uetake, H.; Esaki, T.; Amagai, K.; Sakai, D.; Baba, H.; Kimura, M.; et al. A phase II study of NK012, a polymeric micelle formulation of SN-38, in unresectable, metastatic or recurrent colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 82, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, S.W.; Shin, S.W.; Kim, J.S.; Park, K.; Lee, M.Y.; Heo, D.S. Multicenter phase II trial of Genexol-PM, a novel Cremophor-free, polymeric micelle formulation of paclitaxel, with cisplatin in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 2009–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Chung, H.C.; Im, S.A.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, S.B.; Rha, S.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Ro, J. Multicenter phase II trial of Genexol-PM, a Cremophor-free, polymeric micelle formulation of paclitaxel, in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 108, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Kim, Y.M.; Cho, C.H.; Kim, Y.T.; Kim, S.M.; Hur, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, B.G.; Kim, S.C.; Ryu, H.S.; et al. An Open-Label, Randomized, Parallel, Phase II Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of a Cremophor-Free Polymeric Micelle Formulation of Paclitaxel as First-Line Treatment for Ovarian Cancer: A Korean Gynecologic Oncology Group Study (KGOG-3021). Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 50, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awada, A.; Bondarenko, I.N.; Bonneterre, J.; Nowara, E.; Ferrero, J.M.; Bakshi, A.V.; Wilke, C.; Piccart, M.; CT4002 study Group. A randomized controlled phase II trial of a novel composition of paclitaxel embedded into neutral and cationic lipids targeting tumor endothelial cells in advanced triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Chien, P.Y.; Sheikh, S.; Zhang, A.; Ali, S.; Ahmad, I. Enhanced therapeutic efficacy of a novel liposome-based formulation of SN-38 against human tumor models in SCID mice. Anticancer Drugs 2004, 15, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A. Preclinical Safety, Pharmacokinetics and antitumor efficacy profile of liposome-entrapped SN-38 Formulation. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 331–342. [Google Scholar]
- Strieth, S.; Dunau, C.; Michaelis, U.; Jager, L.; Gellrich, D.; Wollenberg, B.; Dellian, M. Phase I/II clinical study on safety and antivascular effects of paclitaxel encapsulated in cationic liposomes for targeted therapy in advanced head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2014, 36, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Onivyde for the therapy of multiple solid tumors. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 3001–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerum Terwogt, J.M.; ten Bokkel Huinink, W.W.; Schellens, J.H.; Schot, M.; Mandjes, I.A.; Zurlo, M.G.; Rocchetti, M.; Rosing, H.; Koopman, F.J.; Beijnen, J.H. Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of PNU166945, a novel water-soluble polymer-conjugated prodrug of paclitaxel. Anticancer Drugs 2001, 12, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.L.; Lai, P.S.; Lin, F.H.; Yueh-Hsiu Wu, S.; Shieh, M.J. Dual chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy in an HT-29 human colon cancer xenograft model using SN-38-loaded chlorin-core star block copolymer micelles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3614–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindan, S.V.; Cardillo, T.M.; Rossi, E.A.; Trisal, P.; McBride, W.J.; Sharkey, R.M.; Goldenberg, D.M. Improving the therapeutic index in cancer therapy by using antibody-drug conjugates designed with a moderately cytotoxic drug. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1836–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Mumper, R.J. Paclitaxel Nano-Delivery Systems: A Comprehensive Review. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 1000164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Zhao, X.; Gao, S.; Huang, D.; Sui, M. Advances in delivery of Irinotecan (CPT-11) active metabolite 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 568, 118499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Jia, L.; He, Z.; Wang, Y. Recent advances in SN-38 drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 637, 122886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, C.; Kim, T.W.; Bendell, J.; Argiles, G.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Falcone, A.; Fakih, M.; Kozloff, M.; Segal, N.H.; et al. Atezolizumab with or without cobimetinib versus regorafenib in previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (IMblaze370): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubens, M.A.; Sequist, L.V.; Stevenson, J.P.; Powell, S.F.; Villaruz, L.C.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Langer, C.J.; Patnaik, A.; Borghaei, H.; Jalal, S.I.; et al. Pembrolizumab in combination with ipilimumab as second-line or later therapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: KEYNOTE-021 cohorts D and H. Lung Cancer 2019, 130, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.J.; Ajani, J.A.; Kuzdzal, J.; Zander, T.; Van Cutsem, E.; Piessen, G.; Mendez, G.; Feliciano, J.; Motoyama, S.; Lievre, A.; et al. Adjuvant Nivolumab in Resected Esophageal or Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lee, M.; Xia, J.; Luo, T.; Liu, J.; Rodriguez, M.; Lin, W. Two-Stage SN38 Release from a Core-Shell Nanoparticle Enhances Tumor Deposition and Antitumor Efficacy for Synergistic Combination with Immune Checkpoint Blockade. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 21417–21430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, J.; Liao, Y.P.; Tang, I.; Zheng, E.; Qiu, W.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Ji, Y.; Mei, K.C.; et al. Combination Chemo-Immunotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer Using the Immunogenic Effects of an Irinotecan Silicasome Nanocarrier Plus Anti-PD-1. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, P.; Adams, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Iwata, H.; Dieras, V.; Hegg, R.; Im, S.A.; Shaw Wright, G.; et al. Atezolizumab and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Huang, D.; Zhao, L.; Li, T.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors plus nab-paclitaxel for patients with non-small cell lung cancer who have progressed after platinum-based chemotherapy. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920936882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, R.; Blasi, L.; Alu, M.; Gristina, V.; Cicero, G. Clinical efficacy of nab-paclitaxel in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miele, E.; Spinelli, G.P.; Miele, E.; Tomao, F.; Tomao, S. Albumin-bound formulation of paclitaxel (Abraxane ABI-007) in the treatment of breast cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2009, 4, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Zheng, X.; Lin, J.; Li, P.; Lin, L. Nab-paclitaxel (abraxane)-based chemotherapy to treat elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A single center, randomized and open-label clinical trial. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 27, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparreboom, A.; Scripture, C.D.; Trieu, V.; Williams, P.J.; De, T.; Yang, A.; Beals, B.; Figg, W.D.; Hawkins, M.; Desai, N. Comparative preclinical and clinical pharmacokinetics of a cremophor-free, nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel (ABI-007) and paclitaxel formulated in Cremophor (Taxol). Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 4136–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevala, W.K.; Buhrow, S.A.; Knauer, D.J.; Reid, J.M.; Atanasova, E.A.; Markovic, S.N. Antibody-Targeted Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3954–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevala, W.K.; Butterfield, J.T.; Sutor, S.L.; Knauer, D.J.; Markovic, S.N. Antibody-targeted paclitaxel loaded nanoparticles for the treatment of CD20(+) B-cell lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, M. A phase I trial of Nab-Paclitaxel/Bevacizumab (AB160) nano-immunoconjugate therapy for metastatic gynecological malignancies: MC1371. Gynecol. Oncol. 2023, 176, S189–S190. [Google Scholar]
- Kumthekar, P.; Tang, S.C.; Brenner, A.J.; Kesari, S.; Piccioni, D.E.; Anders, C.; Carrillo, J.; Chalasani, P.; Kabos, P.; Puhalla, S.; et al. ANG1005, a Brain-Penetrating Peptide-Drug Conjugate, Shows Activity in Patients with Breast Cancer with Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis and Recurrent Brain Metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2789–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuVall, G.A.; Tarabar, D.; Seidel, R.H.; Elstad, N.L.; Fowers, K.D. Phase 2: A dose-escalation study of OncoGel (ReGel/paclitaxel), a controlled-release formulation of paclitaxel, as adjunctive local therapy to external-beam radiation in patients with inoperable esophageal cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2009, 20, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, C.J.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Socinski, M.A.; Mikhailov, S.M.; Lesniewski-Kmak, K.; Smakal, M.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Orlov, S.V.; Dediu, M.; Heigener, D.; et al. Phase III trial comparing paclitaxel poliglumex (CT-2103, PPX) in combination with carboplatin versus standard paclitaxel and carboplatin in the treatment of PS 2 patients with chemotherapy-naive advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradishar, W.J.; Tjulandin, S.; Davidson, N.; Shaw, H.; Desai, N.; Bhar, P.; Hawkins, M.; O’Shaughnessy, J. Phase III trial of nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel compared with polyethylated castor oil-based paclitaxel in women with breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7794–7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, P.A.; Lacy, J.; Portales, F.; Sobrero, A.; Pazo-Cid, R.; Manzano Mozo, J.L.; Kim, E.J.; Dowden, S.; Zakari, A.; Borg, C.; et al. Nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer (LAPACT): A multicentre, open-label phase 2 study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.; Gatti-Mays, M.E.; Kalinsky, K.; Korde, L.A.; Sharon, E.; Amiri-Kordestani, L.; Bear, H.; McArthur, H.L.; Frank, E.; Perlmutter, J.; et al. Current Landscape of Immunotherapy in Breast Cancer: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.; Gray, R.J.; Demaria, S.; Goldstein, L.; Perez, E.A.; Shulman, L.N.; Martino, S.; Wang, M.; Jones, V.E.; Saphner, T.J.; et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancers from two phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trials: ECOG 2197 and ECOG 1199. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2959–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanowska, O.; Kuczkiewicz-Siemion, O.; Debowska, M.; Olszewski, W.P.; Jagiello-Gruszfeld, A.; Tysarowski, A.; Prochorec-Sobieszek, M. PD-L1-Positive High-Grade Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Respond Better to Standard Neoadjuvant Treatment-A Retrospective Study of PD-L1 Expression in Relation to Different Clinicopathological Parameters. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Teng, F.; Kong, L.; Yu, J. PD-L1 expression in human cancers and its association with clinical outcomes. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 5023–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Strome, S.E.; Salomao, D.R.; Tamura, H.; Hirano, F.; Flies, D.B.; Roche, P.C.; Lu, J.; Zhu, G.; Tamada, K.; et al. Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons Johnson, R.M.; Dong, H. Functional Expression of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (B7-H1) by Immune Cells and Tumor Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, R.; Li, C.; Song, Y.; Liu, G.; Huang, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhu, D.; Lu, C.; Lu, A.; et al. Nab-paclitaxel promotes the cancer-immunity cycle as a potential immunomodulator. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 3445–3460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M.; Chen, Y.H.; Ou, D.L.; Hsu, C.L.; Liu, J.H.; Ko, J.Y.; Hu, M.C.; Tan, C.T. SN-38, an active metabolite of irinotecan, enhances anti-PD-1 treatment efficacy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2023, 259, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Teicher, B.A.; Hassan, R. Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e254–e262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, J.Z.; Modi, S.; Chandarlapaty, S. Unlocking the potential of antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nevala, W.K.; Geng, L.; Xie, H.; Stueven, N.A.; Markovic, S.N. PD-L1-Targeting Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Preclinical Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073295
Nevala WK, Geng L, Xie H, Stueven NA, Markovic SN. PD-L1-Targeting Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Preclinical Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073295
Chicago/Turabian StyleNevala, Wendy K., Liyi Geng, Hui Xie, Noah A. Stueven, and Svetomir N. Markovic. 2025. "PD-L1-Targeting Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Preclinical Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073295
APA StyleNevala, W. K., Geng, L., Xie, H., Stueven, N. A., & Markovic, S. N. (2025). PD-L1-Targeting Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Preclinical Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073295




