Involvement of a Novel Variant of FGFR1 Detected in an Adult Patient with Kallmann Syndrome in Regulation of Gonadal Steroidogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
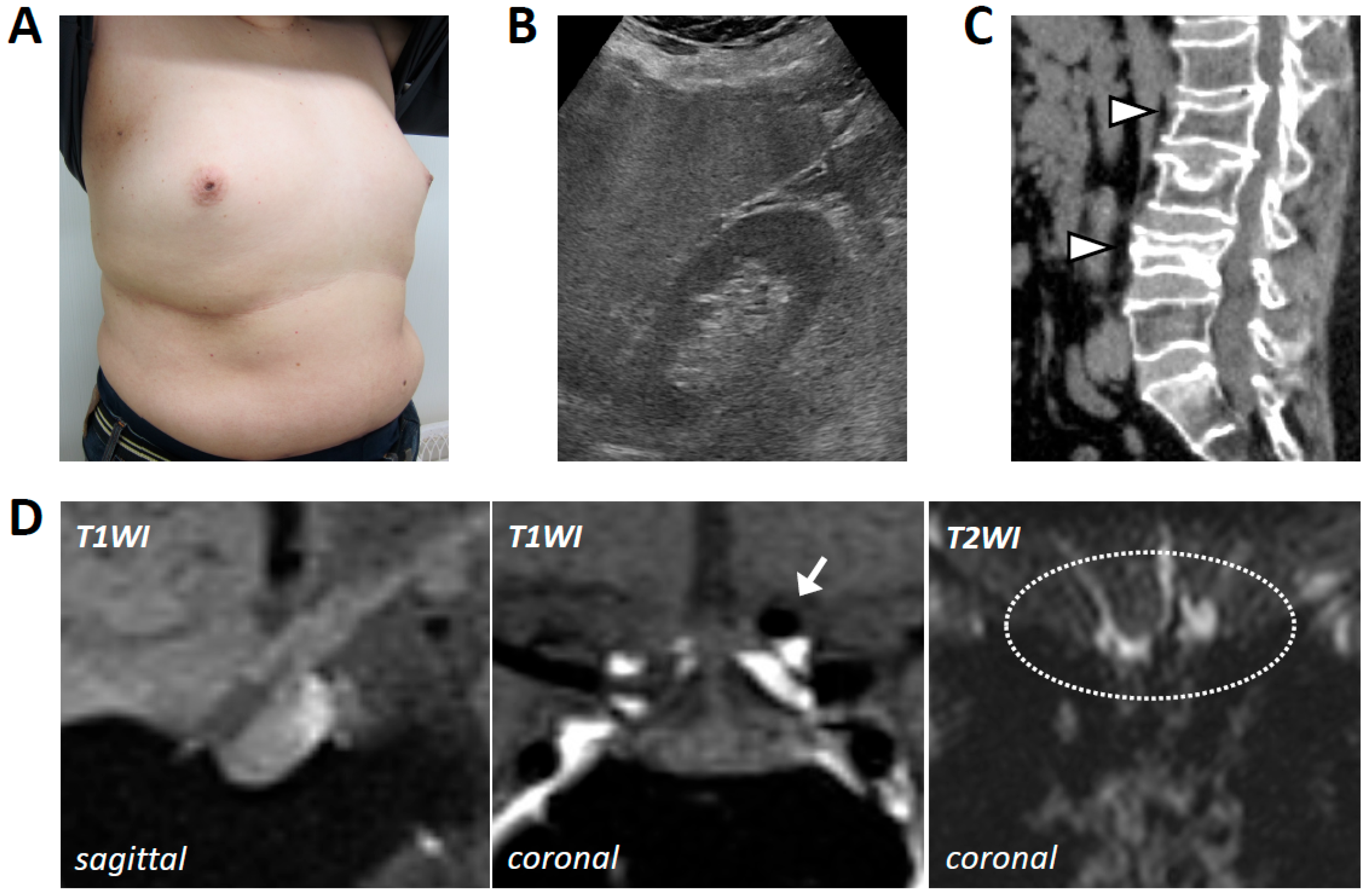
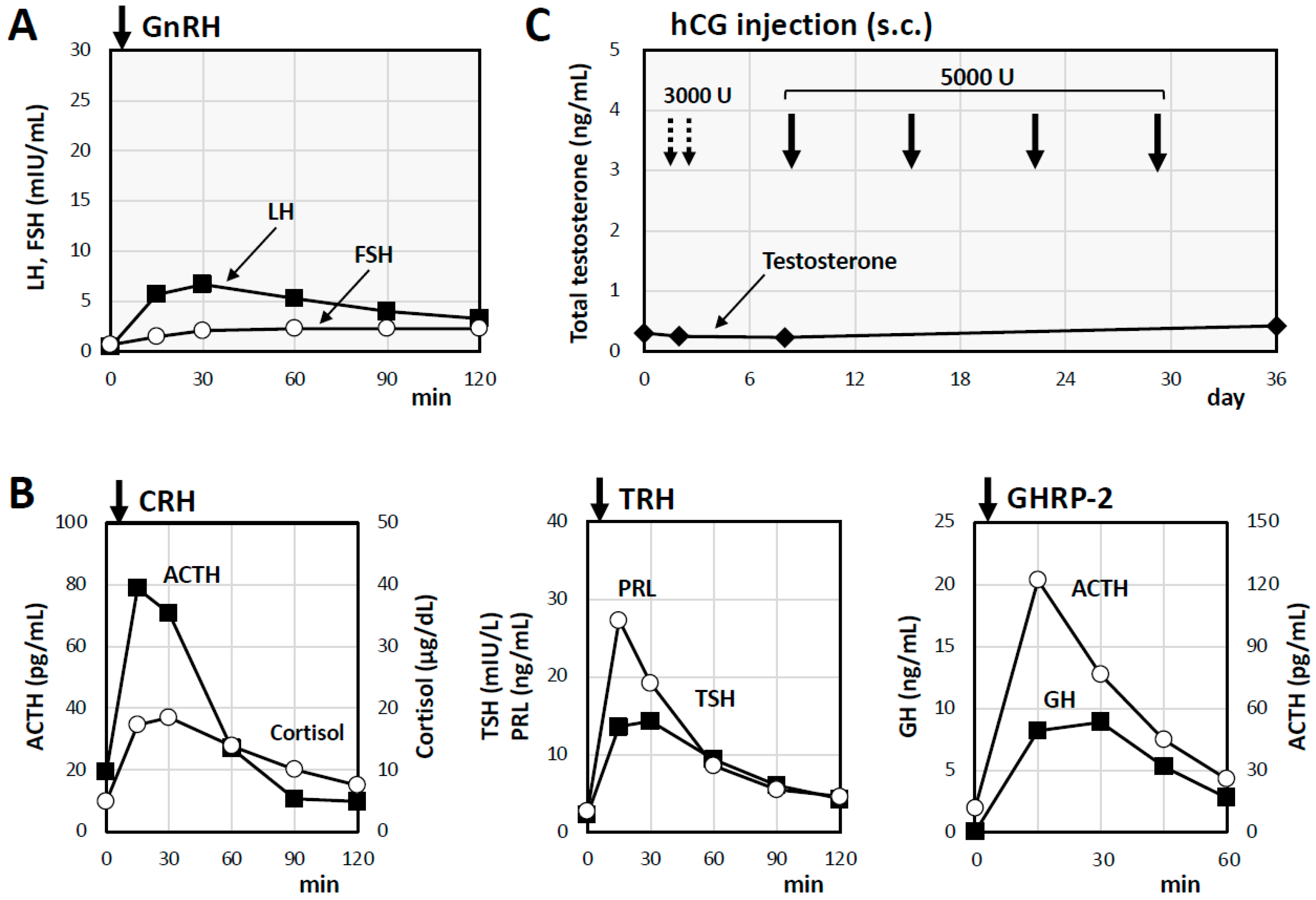
2. Case Presentation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Reagents
3.2. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
3.3. Transient Transfection of Plasmid Vectors
3.4. Statistics
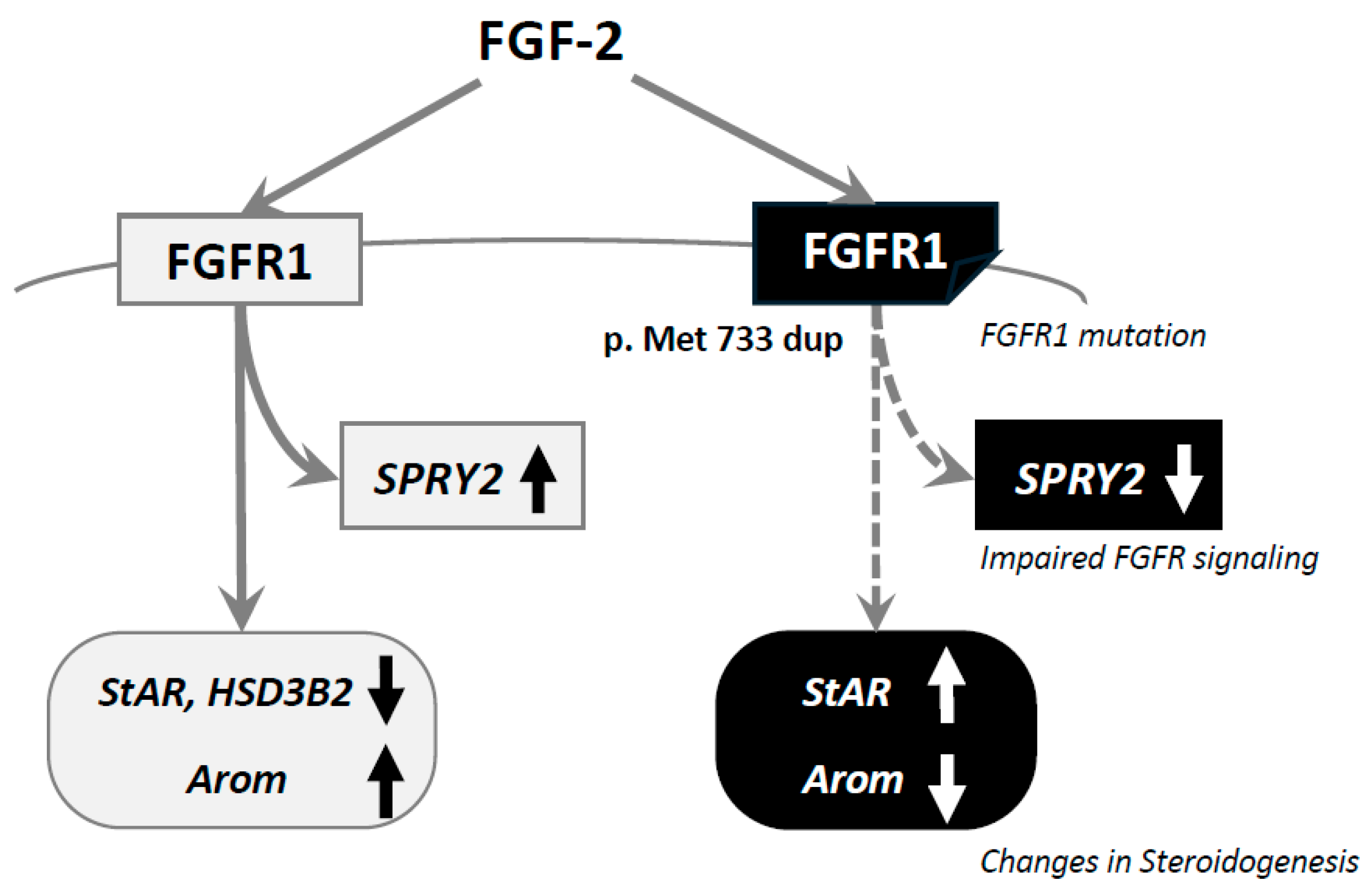
4. Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dodé, C.; Levilliers, J.; Dupont, J.M.; De Paepe, A.; Le Dû, N.; Soussi-Yanicostas, N.; Coimbra, R.S.; Delmaghani, S.; Compain-Nouaille, S.; Baverel, F.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations in FGFR1 cause autosomal dominant Kallmann syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, C.; de Roux, N. FGFR1 mutations in Kallmann syndrome. Front. Horm. Res. 2010, 39, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, N.; Katsumata, N.; Kagami, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Hori, N.; Kawakita, S.; Minowada, S.; Shimotsuka, A.; Shishiba, Y.; Yokozawa, M.; et al. Clinical assessment and mutation analysis of Kallmann syndrome 1 (KAL1) and fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1, or KAL2) in five families and 18 sporadic patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, U.; Bouloux, P.M.; Dattani, M.T.; de Roux, N.; Dodé, C.; Dunkel, L.; Dwyer, A.A.; Giacobini, P.; Hardelin, J.P.; Juul, A.; et al. Expert consensus document: European Consensus Statement on congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism–pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, S.; Brito, J.P.; Cunningham, G.R.; Hayes, F.J.; Hodis, H.N.; Matsumoto, A.M.; Snyder, P.J.; Swerdloff, R.S.; Wu, F.C.; Yialamas, M.A. Testosterone Therapy in Men with Hypogonadism: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1715–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, M.; Vezzoli, V.; Krausz, C.; Guizzardi, F.; Vezzani, S.; Simoni, M.; Bassi, I.; Duminuco, P.; Di Iorgi, N.; Giavoli, C.; et al. Characteristics of a nationwide cohort of patients presenting with isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH). Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamou, M.I.; Georgopoulos, N.A. Kallmann syndrome: Phenotype and genotype of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Metabolism 2018, 86, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maione, L.; Dwyer, A.A.; Francou, B.; Guiochon-Mantel, A.; Binart, N.; Bouligand, J.; Young, J. GENETICS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: Genetic counseling for congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and Kallmann syndrome: New challenges in the era of oligogenism and next-generation sequencing. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, R55–R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihara, K.; Shimatsu, A.; Hizuka, N.; Tanaka, T.; Seino, Y.; Katofor, Y. A simple diagnostic test using GH-releasing peptide-2 in adult GH deficiency. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 157, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Nakano, Y.; Iwata, N.; Soejima, Y.; Suyama, A.; Hasegawa, T.; Otsuka, F. Oxytocin enhances progesterone production with upregulation of BMP-15 activity by granulosa cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 646, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Nakano, Y.; Iwata, N.; Soejima, Y.; Suyama, A.; Hasegawa, T.; Otsuka, F. Stimulatory effects of vasopressin on progesterone production and BMP signaling by ovarian granulosa cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 667, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, Y.; Yanase, T.; Mu, Y.; Oba, K.; Ichino, I.; Saito, M.; Nomura, M.; Mukasa, C.; Okabe, T.; Goto, K.; et al. Establishment and characterization of a steroidogenic human granulosa-like tumor cell line, KGN, that expresses functional follicle-stimulating hormone receptor. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Chen, Y. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors (FGFRs): Structures and Small Molecule Inhibitors. Cells 2019, 8, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuss, B.; von Bohlen und Halbach, O. Fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in the central nervous system. Cell Tissue Res. 2003, 313, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Itoh, N. The Fibroblast Growth Factor signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2015, 4, 215–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, P.G.; Sirard, M.A. Transcriptomic analysis of gene cascades involved in protein kinase A and C signaling in the KGN line of human ovarian granulosa tumor cells. Biol. Reprod. 2017, 96, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhaus, R.; Proft, S.; Schuelke, M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schwarz, J.M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W446–W451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Hu, Y.; Cadman, S.; Bouloux, P. Diversity in fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 regulation: Learning from the investigation of Kallmann syndrome. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Schlessinger, J.; Hubbard, S.R. Structure of the FGF receptor tyrosine kinase domain reveals a novel autoinhibitory mechanism. Cell 1996, 86, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.S.; Taraska, S.; Faiman, C. The hormonal response to HCG stimulation in male children and adolescents. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1972, 34, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguni, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakano, Y.; Soejima, Y.; Suyama, A.; Takase, R.; Yasuda, M.; Hasegawa, K.; Otsuka, F. Trends of correlations between serum levels of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I in general practice. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1381083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, K.C.J.; Biller, B.M.K.; Radovick, S.; Carmichael, J.D.; Jasim, S.; Pantalone, K.M.; Hoffman, A.R. American association of clinical endocrinologists and American college of endocrinology guidelines for management of growth hormone deficiency in adults and patients transitioning from pediatric to adult care. Endocr. Pract. 2019, 25, 1191–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, F.A.; Trarbach, E.B.; Tusset, C.; Latronico, A.C.; Montenegro, L.R.; Carvalho, L.R.; Franca, M.M.; Otto, A.P.; Costalonga, E.F.; Brito, V.N.; et al. FGFR1 and PROKR2 rare variants found in patients with combined pituitary hormone deficiencies. Endocr. Connect. 2015, 4, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iorgi, N.; Morana, G.; Allegri, A.E.; Napoli, F.; Gastaldi, R.; Calcagno, A.; Patti, G.; Loche, S.; Maghnie, M. Classical and non-classical causes of GH deficiency in the paediatric age. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 30, 705–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, N.; Mizuno, Y.; Seno, S.; Koyama, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Shibata, H.; Narumi, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Ishii, T. A novel missense variant of FGFR1 in a Japanese girl with Kallmann syndrome and holoprosencephaly. Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2023, 32, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, C.; Bastos, M.; Pignatelli, D.; Borges, T.; Aragüés, J.M.; Fonseca, F.; Pereira, B.D.; Socorro, S.; Lemos, M.C. Novel FGFR1 mutations in Kallmann syndrome and normosmic idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: Evidence for the involvement of an alternatively spliced isoform. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 104, 1261–1267.e1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raivio, T.; Sidis, Y.; Plummer, L.; Chen, H.; Ma, J.; Mukherjee, A.; Jacobson-Dickman, E.; Quinton, R.; Van Vliet, G.; Lavoie, H.; et al. Impaired fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling as a cause of normosmic idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 4380–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koika, V.; Varnavas, P.; Valavani, H.; Sidis, Y.; Plummer, L.; Dwyer, A.; Quinton, R.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C.; Pitteloud, N.; Sertedaki, A.; et al. Comparative functional analysis of two fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) mutations affecting the same residue (R254W and R254Q) in isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH). Gene 2013, 516, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.A. Mechanisms of fibroblast growth factor signaling in the ovarian follicle. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 228, R31–R43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, R.K.; Spicer, L.J. Effects of basic fibroblast growth factor and heparin on follicle-stimulating hormone-induced steroidogenesis by bovine granulosa cells. J. Anim. Sci. 1994, 72, 2696–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aharoni, D.; Meiri, I.; Atzmon, R.; Vlodavsky, I.; Amsterdam, A. Differential effect of components of the extracellular matrix on differentiation and apoptosis. Curr. Biol. 1997, 7, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, A.; Hsueh, A.J. Fibroblast growth factor as an intraovarian hormone: Differential regulation of steroidogenesis by an angiogenic factor. Regul. Pept. 1986, 16, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, T.; Otsuka, F.; Yamashita, M.; Inagaki, K.; Nakamura, E.; Tsukamoto, N.; Takeda, M.; Suzuki, J.; Makino, H. Functional relationship between fibroblast growth factor-8 and bone morphogenetic proteins in regulating steroidogenesis by rat granulosa cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 325, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, T.; Otsuka, F.; Nakamura, E.; Inagaki, K.; Ogura-Ochi, K.; Tsukamoto, N.; Takeda, M.; Makino, H. Regulatory role of kit ligand-c-kit interaction and oocyte factors in steroidogenesis by rat granulosa cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 358, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garor, R.; Abir, R.; Erman, A.; Felz, C.; Nitke, S.; Fisch, B. Effects of basic fibroblast growth factor on in vitro development of human ovarian primordial follicles. Fertil. Steril. 2009, 91, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analyte | Result | Unit | Reference Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complete blood count | |||
| White blood cells | 7980 | /μL | [3300–8600] |
| Red blood cells | 442 × 104 | /μL | [435 × 104–555 × 104] |
| Platelets | 336 × 103 | /μL | [158 × 103–348 × 103] |
| Biochemistry | |||
| Albumin | 3.7 | g/dL | [4.1–5.1] |
| Aspartate transaminase | 34 | U/L | [13–30] |
| Alanine transaminase | 57 | U/L | [10–42] |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 81 | U/L | [38–113] |
| γ-glutamyl transpeptidase | 38 | U/L | [13–64] |
| Lactate dehydrogenase | 180 | U/L | [124–222] |
| Sodium | 137 | mmol/L | [138–145] |
| Potassium | 4.1 | mmol/L | [3.6–4.8] |
| Chloride | 102 | mmol/L | [101–108] |
| Blood urea nitrogen | 10.4 | mg/dL | [8–20] |
| Creatinine | 0.57 | mg/dL | [0.65–1.07] |
| Triglyceride | 108 | mg/dL | [40–234] |
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol | 154 | mg/dL | [65–163] |
| Fasting plasma glucose | 119 | mg/dL | [73–109] |
| Hemoglobin A1c | 6.2 | % | [4.9–6.0] |
| Endocrine data | |||
| Cortisol | 6.9 | μg/dL | [7.1–19.6] |
| Adrenocorticotropin | 20.8 | pg/mL | [7.2–63.3] |
| Free thyroxine | 1.47 | ng/dL | [0.97–1.69] |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone | 1.81 | mIU/L | [0.61–4.23] |
| Prolactin | 3.5 | ng/mL | [4.3–13.7] |
| Growth hormone | 0.04 | ng/mL | [0–2.47] |
| Insulin-like growth factor -I | 57.8 | ng/mL | [89–248] |
| Follicle-stimulating hormone | 0.7 | mIU/mL | [1.8–12] |
| Luteinizing hormone | 0.4 | mIU/mL | [2.2–8.4] |
| Testosterone | 0.29 | ng/mL | [1.87–9.02] |
| Free testosterone | 1.4 | pg/mL | [4.7–21.6] |
| Vasopressin | 0.9 | pg/mL | [0–2.8] |
| Osmolality | 281 | mOsm/kg | [276–292] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soejima, Y.; Otsuka, Y.; Kawaguchi, M.; Oguni, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakano, Y.; Yasuda, M.; Tokumasu, K.; Ueda, K.; Hasegawa, K.; et al. Involvement of a Novel Variant of FGFR1 Detected in an Adult Patient with Kallmann Syndrome in Regulation of Gonadal Steroidogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062713
Soejima Y, Otsuka Y, Kawaguchi M, Oguni K, Yamamoto K, Nakano Y, Yasuda M, Tokumasu K, Ueda K, Hasegawa K, et al. Involvement of a Novel Variant of FGFR1 Detected in an Adult Patient with Kallmann Syndrome in Regulation of Gonadal Steroidogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062713
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoejima, Yoshiaki, Yuki Otsuka, Marina Kawaguchi, Kohei Oguni, Koichiro Yamamoto, Yasuhiro Nakano, Miho Yasuda, Kazuki Tokumasu, Keigo Ueda, Kosei Hasegawa, and et al. 2025. "Involvement of a Novel Variant of FGFR1 Detected in an Adult Patient with Kallmann Syndrome in Regulation of Gonadal Steroidogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062713
APA StyleSoejima, Y., Otsuka, Y., Kawaguchi, M., Oguni, K., Yamamoto, K., Nakano, Y., Yasuda, M., Tokumasu, K., Ueda, K., Hasegawa, K., Iwata, N., & Otsuka, F. (2025). Involvement of a Novel Variant of FGFR1 Detected in an Adult Patient with Kallmann Syndrome in Regulation of Gonadal Steroidogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062713






