Characterization of PRDM9 Multifunctionality in Yak Testes Through Protein Interaction Mapping
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
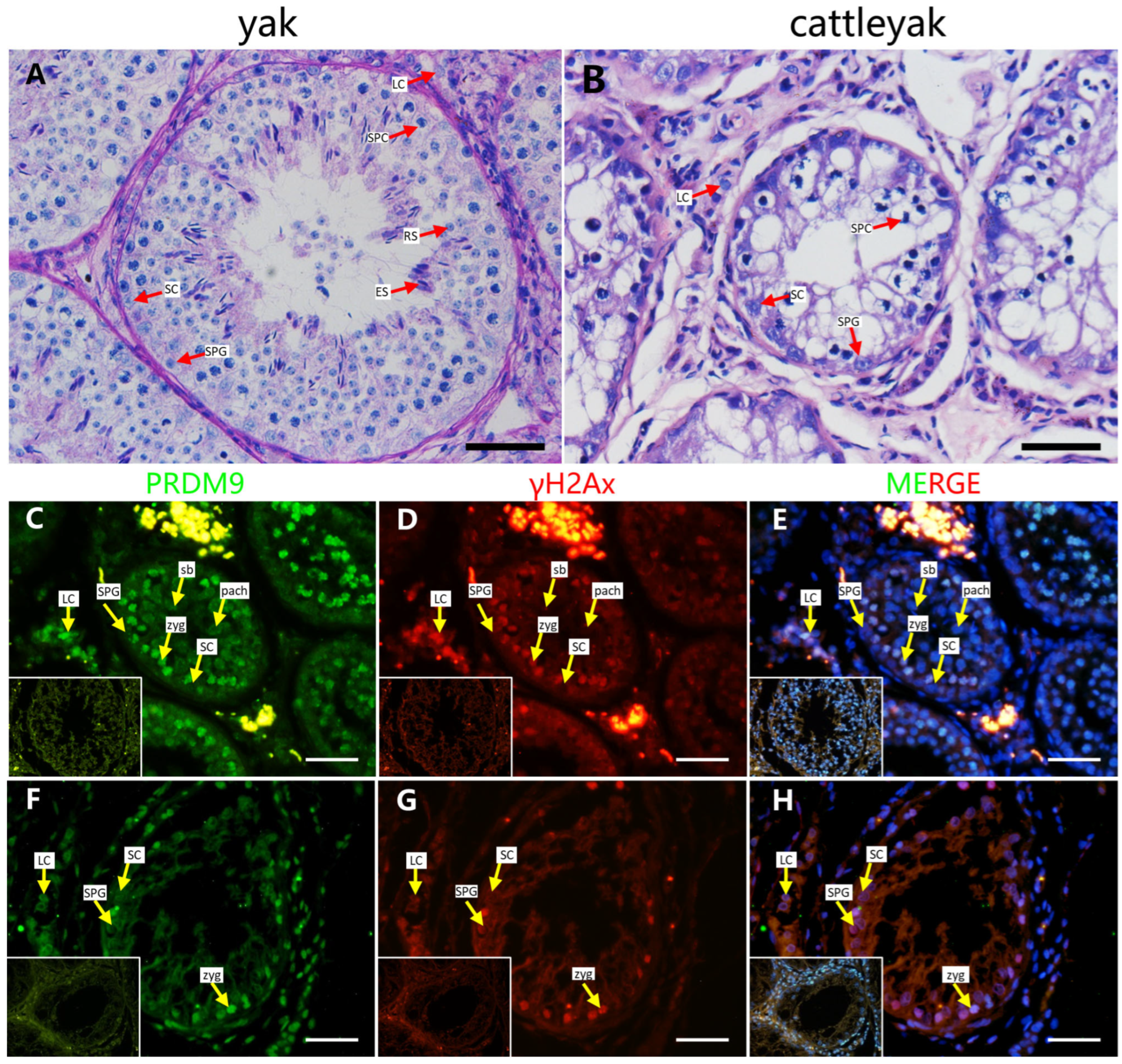
2.1. PRDM9 Expression Pattern in Yak and Cattleyak Spermatocytes
2.2. Self-Activation Test
2.3. A Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay Identifies Multiple PRDM9 Interactors in the Yak Testes
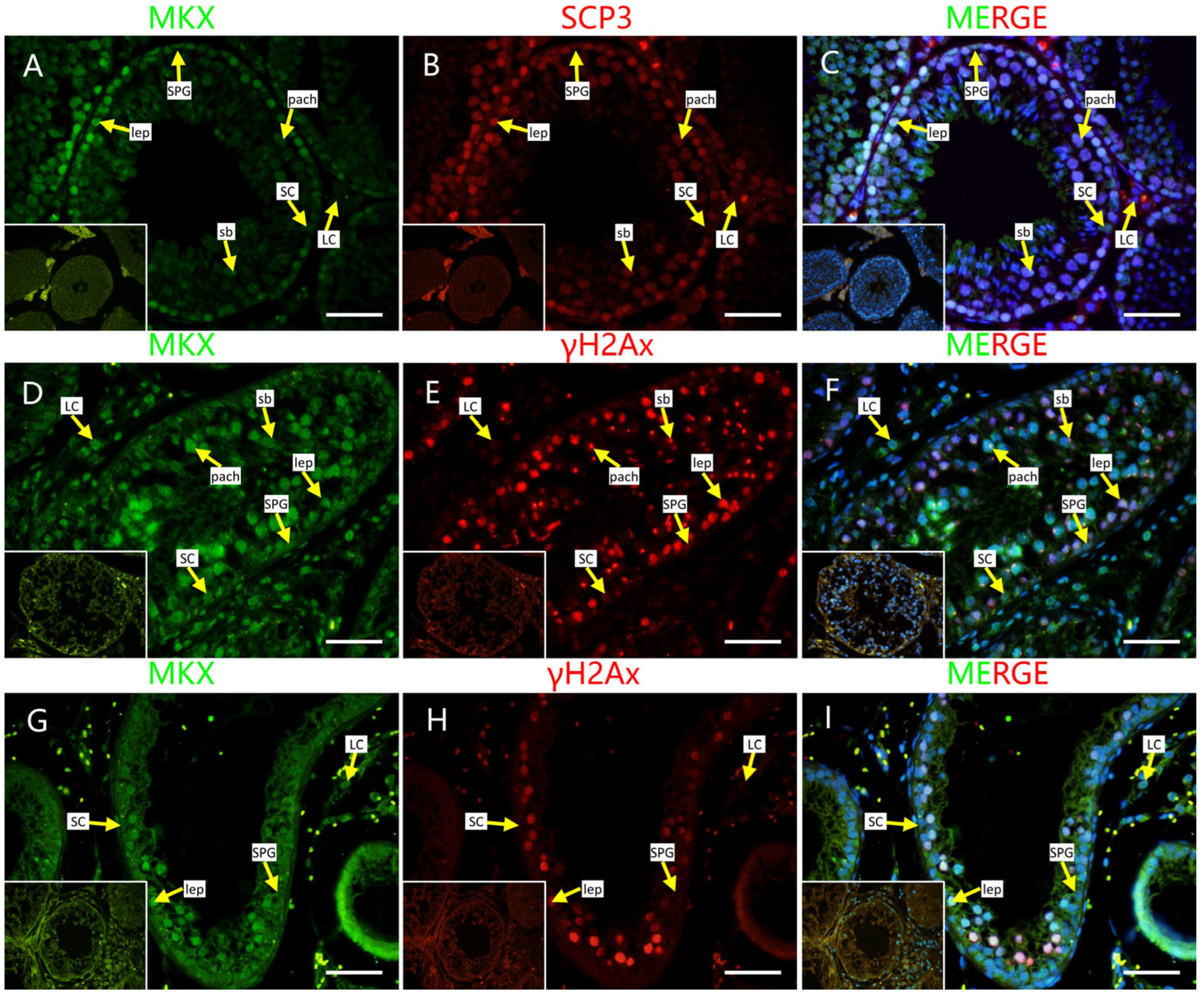
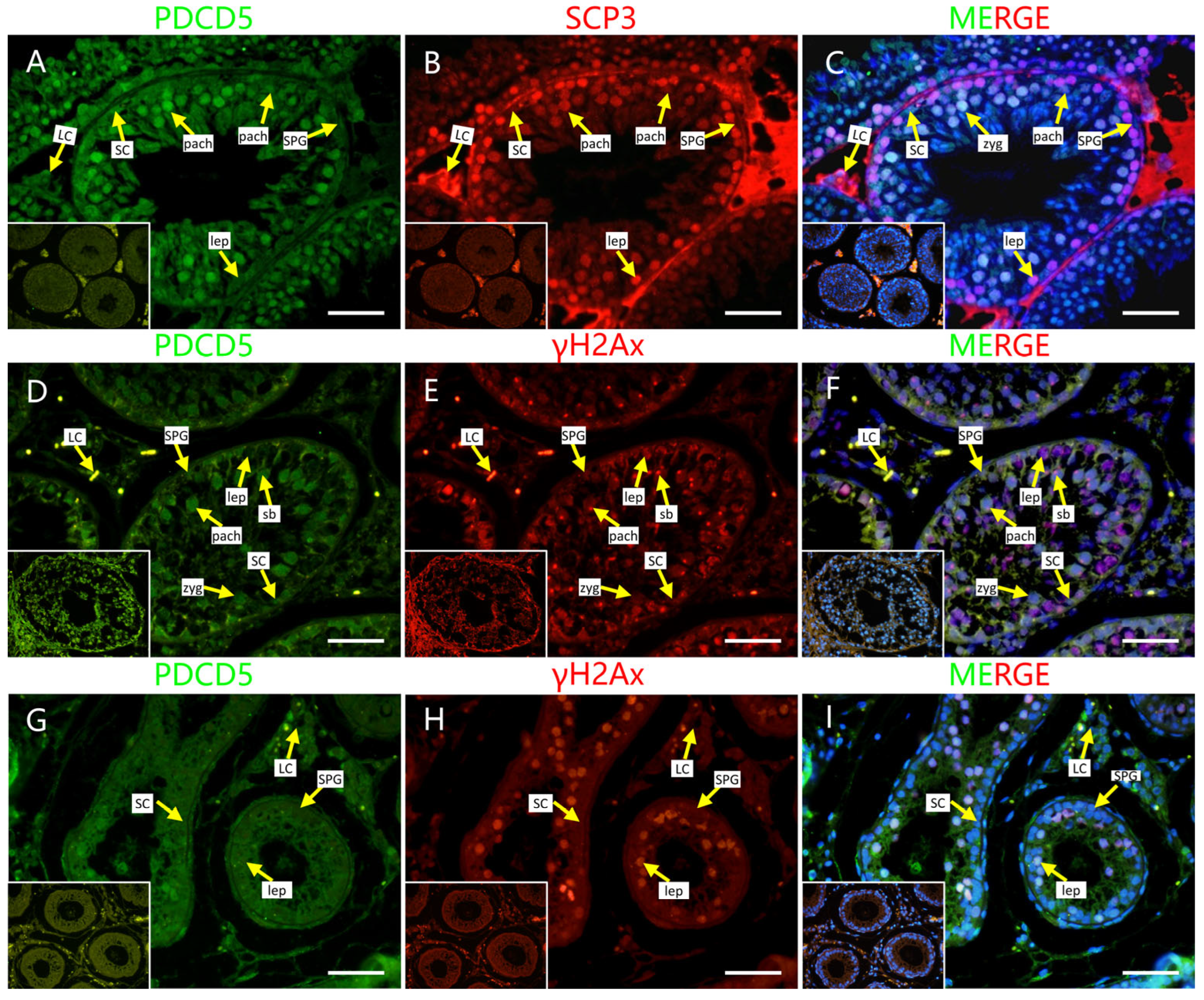
2.4. Localization of Screened PRDM9-Interacting Proteins in Testes of Mouse and Cattleyak
2.5. The Expression Profiles of PRDM9-Interacting Protein-Coding Genes in Cattleyak
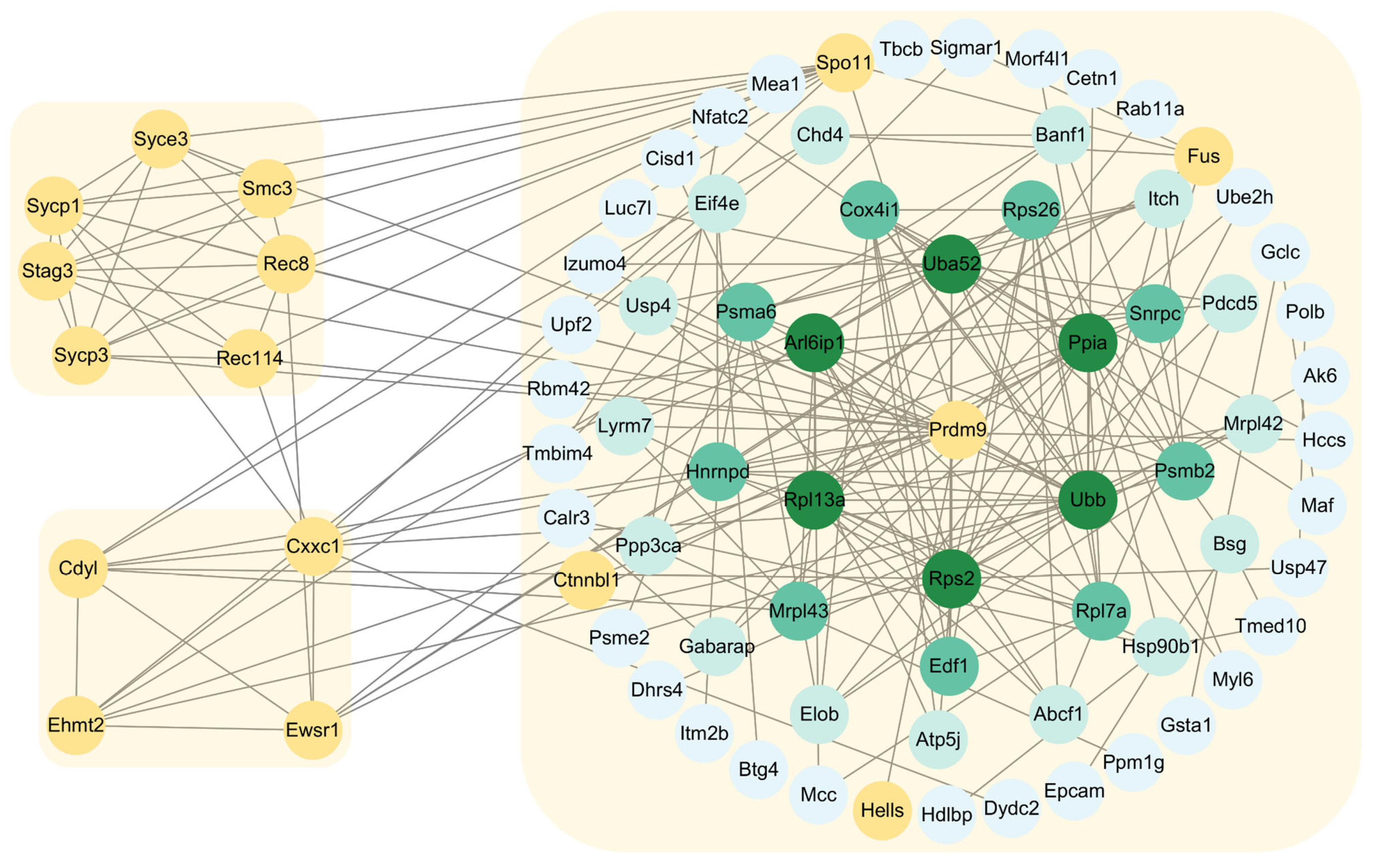
2.6. Construction of Protein–Protein Interaction Networks of PRDM9 in Yak Testes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Sample Preparation
4.2. Yeast Two-Hybrid (Y2H) and Y2H-seq Assay
4.3. Yeast Two-Hybrid Screen Validation and Prdm9 Domain Mapping
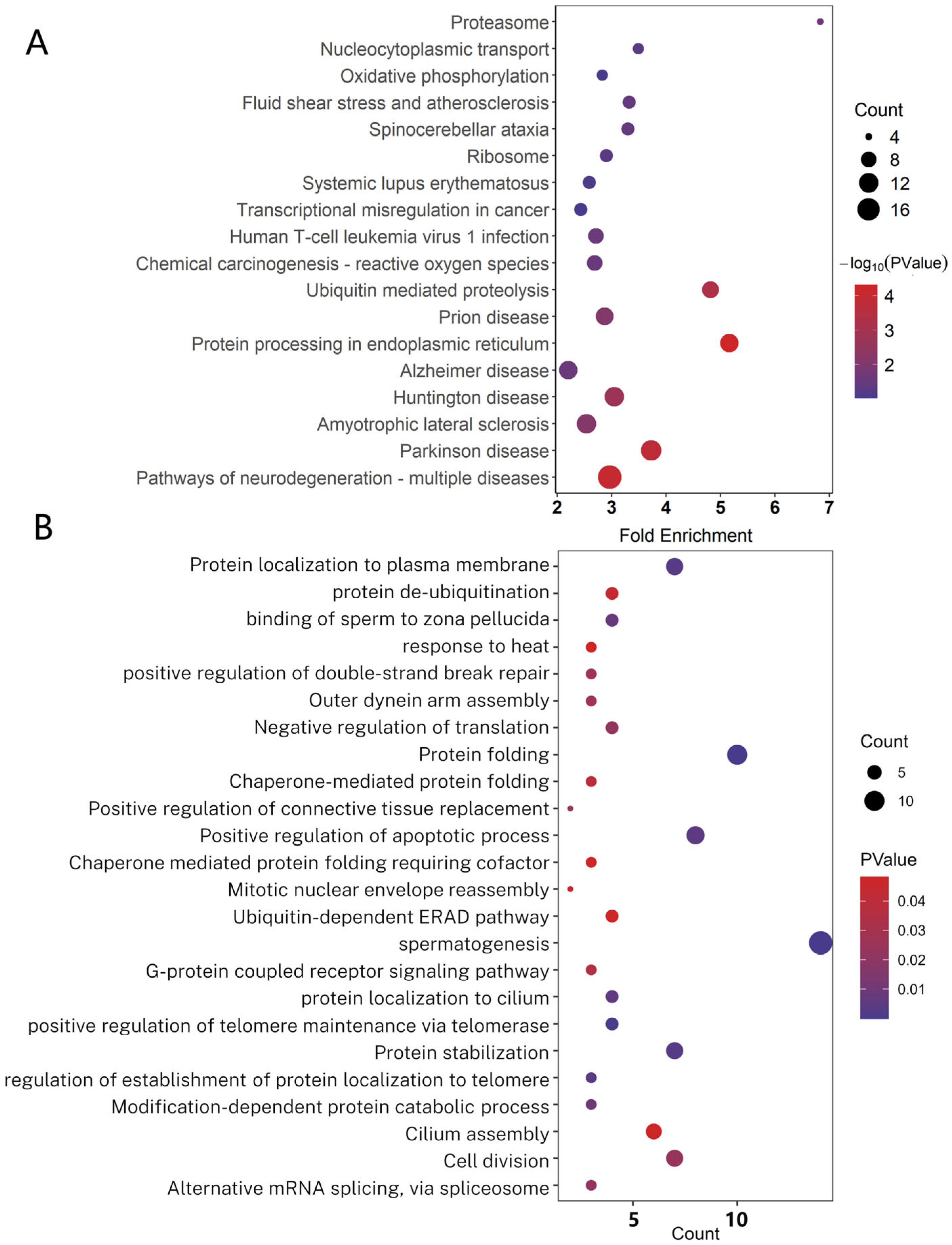
4.4. Gene Ontology (GO) and KEGG Analysis
4.5. Histomorphology and Immunofluorescence Staining [9]
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griswold, M.D. Spermatogenesis: The Commitment to Meiosis. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewiss, R.L.; Schleif, M.C.; Griswold, M.D. The role of retinoic acid in the commitment to meiosis. Asian J. Androl. 2021, 23, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, L.; An, G.; Yang, X.; Cui, M.; Song, X.; Lin, J.; Zhang, X.; Yao, Z.; Wan, C.; et al. Single-cell multi-omics sequencing of human spermatogenesis reveals a DNA demethylation event associated with male meiotic recombination. Nat. Cell Biol. 2023, 25, 1520–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelkowski, M.; Olson, M.A.; Wang, M.; Pawlowski, W. Diversity and Determinants of Meiotic Recombination Landscapes. Trends Genet. TIG 2019, 35, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagouraga, B.; Clément, J.A.J.; Duret, L.; Kadlec, J.; de Massy, B.; Baudat, F. PRDM9 Methyltransferase Activity Is Essential for Meiotic DNA Double-Strand Break Formation at Its Binding Sites. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 853–865.e856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Biot, M.; Clément, J.A.; Teragaki, M.; Urbach, S.; Robert, T.; Baudat, F.; Grey, C.; de Massy, B. PRDM9 activity depends on HELLS and promotes local 5-hydroxymethylcytosine enrichment. eLife 2020, 9, 57117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruce, C.; Dlamini, S.; Ananda, G.; Bronkema, N.; Tian, H.; Paigen, K.; Carter, G.W.; Baker, C.L. HELLS and PRDM9 form a pioneer complex to open chromatin at meiotic recombination hot spots. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, E.; Odenthal-Hesse, L. Orchestrating recombination initiation in mice and men. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2023, 151, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvanov, E.D.; Tian, H.; Billings, T.; Saxl, R.L.; Spruce, C.; Aithal, R.; Krejci, L.; Paigen, K.; Petkov, P.M. PRDM9 interactions with other proteins provide a link between recombination hotspots and the chromosomal axis in meiosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Billings, T.; Petkov, P.M. EWSR1 affects PRDM9-dependent histone 3 methylation and provides a link between recombination hotspots and the chromosome axis protein REC8. Mol. Biol. Cell 2021, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yuan, S.; Gao, L.; Li, M.; Yu, X.; Zhan, J.; Yin, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Lu, G.; et al. The histone modification reader ZCWPW1 links histone methylation to PRDM9-induced double-strand break repair. eLife 2020, 9, 53459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahgoub, M.; Paiano, J.; Bruno, M.; Wu, W.; Pathuri, S.; Zhang, X.; Ralls, S.; Cheng, X.; Nussenzweig, A.; Macfarlan, T.S. Dual histone methyl reader ZCWPW1 facilitates repair of meiotic double strand breaks in male mice. eLife 2020, 9, 53360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.; Hatton, E.; Altemose, N.; Hussin, J.G.; Pratto, F.; Zhang, G.; Hinch, A.G.; Moralli, D.; Biggs, D.; Diaz, R.; et al. Re-engineering the zinc fingers of PRDM9 reverses hybrid sterility in mice. Nature 2016, 530, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.D.; Gao, X.; Wang, G.W.; Wu, S.X.; Yang, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Yang, Q.E. Identification of Candidate Genes Related to Hybrid Sterility by Genomic Structural Variation and Transcriptome Analyses in Cattle-yak. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 108, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, P.; Jing, K.; Li, Y.; Yue, B.; Wu, Z.; Dong, W.; Zhong, J.; Cai, X. Overexpression of TAF4B Promoted the Proliferation of Undifferentiated Spermatogonia in Cattleyak In Vitro. Reprod. Domest. Anim. Zuchthyg. 2024, 59, e14738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandor, C.; Li, W.; Coppieters, W.; Druet, T.; Charlier, C.; Georges, M. Genetic variants in REC8, RNF212, and PRDM9 influence male recombination in cattle. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Wang, G.W.; Xu, S.R.; Zhang, X.N.; Yang, Q.E. The expression of histone methyltransferases and distribution of selected histone methylations in testes of yak and cattle-yak hybrid. Theriogenology 2020, 144, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, P.; Li, B.; Huang, S.Y. HDOCK: A web server for protein-protein and protein-DNA/RNA docking based on a hybrid strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W365–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, S.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, R.; Arora, R.; De, S. Zinc Finger Domain of the PRDM9 Gene on Chromosome 1 Exhibits High Diversity in Ruminants but Its Paralog PRDM7 Contains Multiple Disruptive Mutations. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, F.; Fujiwara, Y.; Reinholdt, L.G.; Hu, J.; Saxl, R.L.; Baker, C.L.; Petkov, P.M.; Paigen, K.; Handel, M.A. Nuclear localization of PRDM9 and its role in meiotic chromatin modifications and homologous synapsis. Chromosoma 2015, 124, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, Q.; Nie, Y.; Han, F.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.X.; Niu, S. Determination of conifer age biomarker DAL1 interactome using Y2H-seq. For. Res. 2021, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, T.; Zhang, F.; Hayakawa, N.; Ohtani, Y.; Shinmyozu, K.; Nakayama, J.; Andreassen, P.R. MRG15 binds directly to PALB2 and stimulates homology-directed repair of chromosomal breaks. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, D.U.; Kirsanov, O.; Geyer, C.B.; Magnuson, T. Mammalian SWI/SNF chromatin remodeler is essential for reductional meiosis in males. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamori, N.; Tominaga, K.; Sato, T.; Riehle, K.; Iwamori, T.; Ohkawa, Y.; Coarfa, C.; Ono, E.; Matzuk, M.M. MRG15 is required for pre-mRNA splicing and spermatogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States Am. 2016, 113, E5408–E5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Tao, H.; He, J.; Huang, S.Y. The HDOCK server for integrated protein-protein docking. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1829–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Dong, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. De novo protein design with a denoising diffusion network independent of pretrained structure prediction models. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; George, R.; Noyes, M.B.; Rowton, M.; Liu, W.; Jiang, R.; Wolfe, S.A.; Wilson-Rawls, J.; Rawls, A. Characterization of the DNA-binding properties of the Mohawk homeobox transcription factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 35351–35359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, C.A.; Acosta, S.A.; Anderson, D.M.; Rogers, G.E.; Wilson-Rawls, J.; Rawls, A. The Transcription Factor Mohawk Facilitates Skeletal Muscle Repair via Modulation of the Inflammatory Environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riascos-Bernal, D.F.; Sibinga, N.E.S.; Kitsis, R.N. PDCD5 says no to NO. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4535–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, X.; Luo, L.; Sun, J.; Guo, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Ni, B. The role of p53 in male infertility. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1457985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazaki, M.; Wittayarat, M.; Sambuu, R.; Sugita, A.; Kawaguchi, M.; Hirata, M.; Tanihara, F.; Takagi, M.; Taniguchi, M.; Otoi, T.; et al. Disruption of cell proliferation and apoptosis balance in the testes of crossbred cattle-yaks affects spermatogenic cell fate and sterility. Reprod. Domest. Anim. Zuchthyg. 2022, 57, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Li, Y.; Yin, L.; Yuan, S.; Wang, F. The Intricate Functional Networks of Pre-mRNA Alternative Splicing in Mammalian Spermatogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, J.M.D.; Chan, A.L.; La, H.M.; Rossello, F.J.; Änkö, M.L.; Fuller-Pace, F.V.; Hobbs, R.M. DDX5 plays essential transcriptional and post-transcriptional roles in the maintenance and function of spermatogonia. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamer, G.; Roepers-Gajadien, H.L.; van Duyn-Goedhart, A.; Gademan, I.S.; Kal, H.B.; van Buul, P.P.; Ashley, T.; de Rooij, D.G. Function of DNA-protein kinase catalytic subunit during the early meiotic prophase without Ku70 and Ku86. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 68, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.A.; Sfeir, A.; Takai, H.; Scherthan, H. Ku70 and non-homologous end joining protect testicular cells from DNA damage. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 3095–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Name | Annotation | Reads Counts |
|---|---|---|
| PSMA6 | Proteasome subunit | 67,149 |
| MKX | Homeobox KN domain | 52,051 |
| COPS9 | Myeloma-overexpressed-like | 45,554 |
| SPA17 | IQ calmodulin-binding motif | 30,014 |
| C3H1orf50 | Protein of unknown function (DUF2452) | 23,775 |
| TMED10 | emp24/gp25L/p24 family/GOLD | 23,746 |
| CISD1 | Iron-binding zinc finger CDGSH type | 23,164 |
| BSG | Immunoglobulin domain | 21,796 |
| LOC100297779 | GAGE protein | 21,367 |
| GSTA1 | Glutathione S-transferase, C-terminal domain | 21,140 |
| C1H21orf2 | Leucine-rich repeat | 18,953 |
| ATP5PF | Mitochondrial ATP synthase coupling factor 6 | 18,702 |
| LOC616478 | Proline-rich | 18,353 |
| LOC505033 | Unknown protein | 16,516 |
| PDCD5 | Double-stranded DNA-binding domain | 14,782 |
| RAB11A | 50S ribosome-binding GTPase | 14,435 |
| NAGS | NAT, N-acetyltransferase | 12,480 |
| LOC100271685 | Unknown protein | 12,351 |
| TDRD1 | Domain of unknown function (DUF4537) | 10,740 |
| MORN5 | MORN repeat | 10,696 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Shu, S.; Fu, C.; Huang, R.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Peng, W. Characterization of PRDM9 Multifunctionality in Yak Testes Through Protein Interaction Mapping. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041420
Wang G, Shu S, Fu C, Huang R, Xu S, Zhang J, Peng W. Characterization of PRDM9 Multifunctionality in Yak Testes Through Protein Interaction Mapping. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(4):1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041420
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Guowen, Shi Shu, Changqi Fu, Rong Huang, Shangrong Xu, Jun Zhang, and Wei Peng. 2025. "Characterization of PRDM9 Multifunctionality in Yak Testes Through Protein Interaction Mapping" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 4: 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041420
APA StyleWang, G., Shu, S., Fu, C., Huang, R., Xu, S., Zhang, J., & Peng, W. (2025). Characterization of PRDM9 Multifunctionality in Yak Testes Through Protein Interaction Mapping. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(4), 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041420






