Changes in Gut Microbiota According to Disease Severity in a Lupus Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Grouping Based on Immunological Markers of Lupus
2.2. Progressive Changes in Fecal Gut Microbiota Composition and Diversity with Lupus Severity
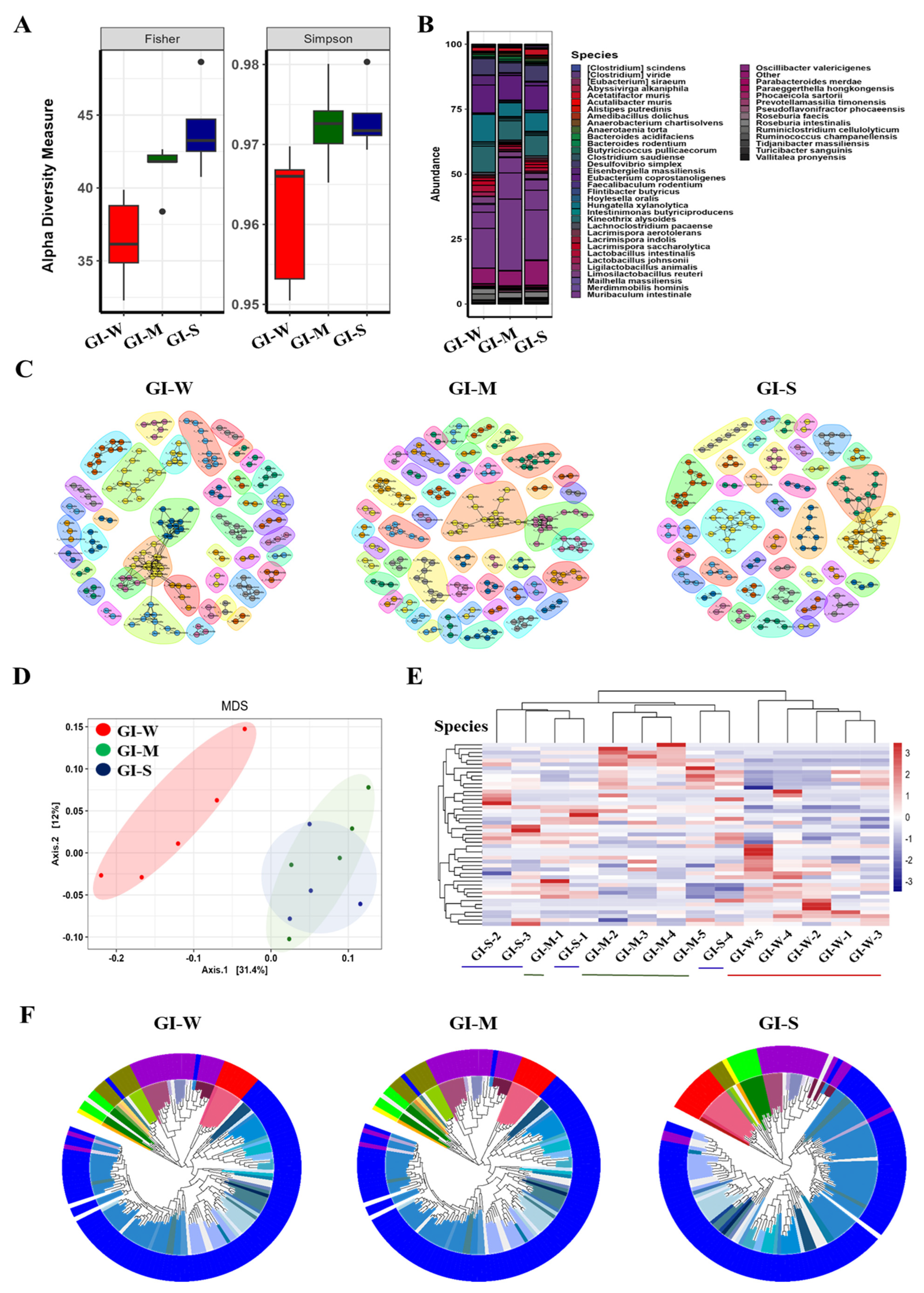
2.3. Progressive and Detailed Characterization of Gastrointestinal (GI) Microbiota Reveals Greater Microbial Shifts with Lupus Severity Compared to Fecal Analysis
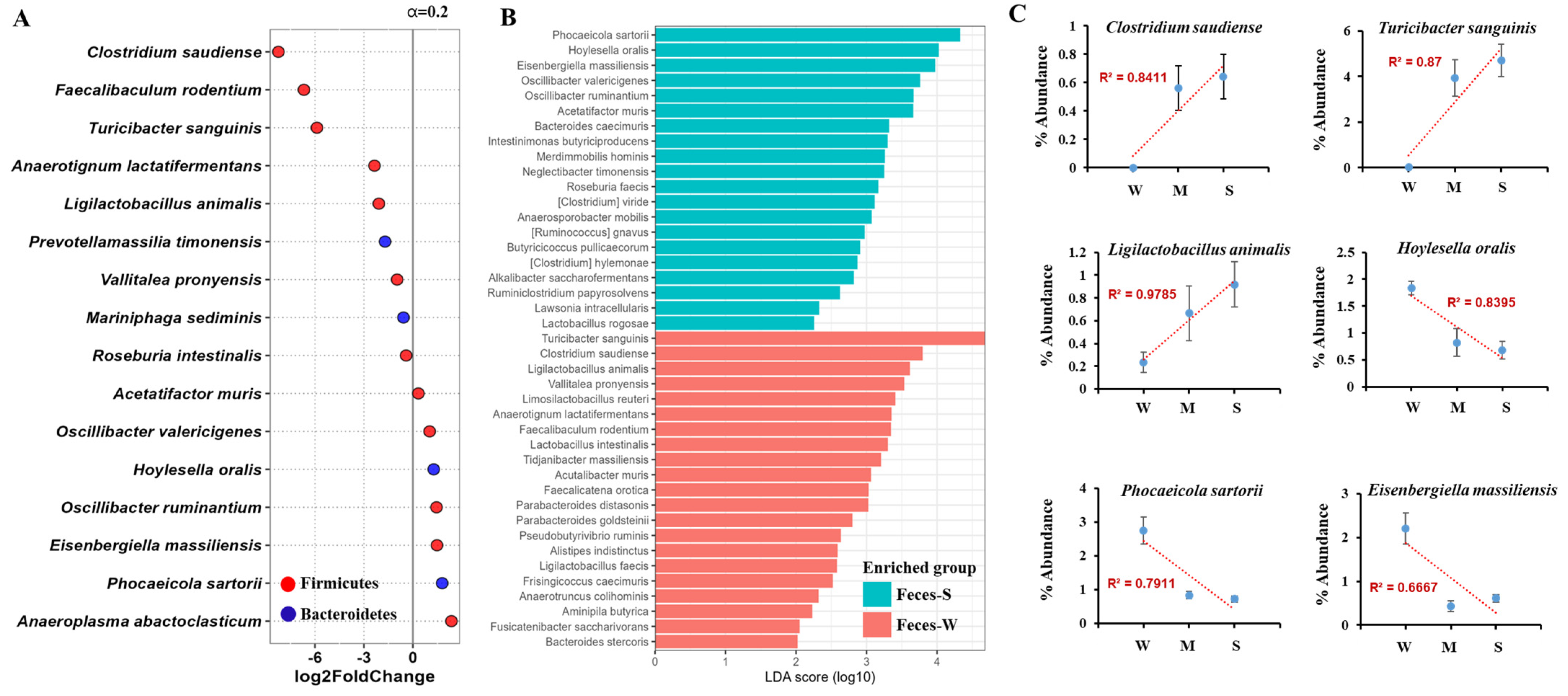
2.4. Fecal Microbiota Analysis Reveals Key Microbial Shifts Associated with Lupus Severity Through DESeq and LEfSe Approaches
2.5. Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiota Shows Stronger Association with Lupus Severity and Provides Greater Sensitivity and Accuracy Compared to Fecal Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal
4.2. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
4.3. Characterizing Microbiome Diversity and Abundance Through α-Diversity Analysis
4.4. Characterizing Microbial Differences with β-Diversity Analysis
4.5. Visualizing Microbial Relationships Through Heatmaps and Phylogenetic Trees
4.6. Co-Occurrence Network Mapping of Microbial Communities
4.7. Microbial Abundance Analysis
4.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.9. Urine Albumin and Creatinine Assays
4.10. Data and Statistical Analyses
4.11. Ethics Approval
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cojocaru, M.; Cojocaru, I.M.; Silosi, I.; Vrabie, C.D. Manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Maedica 2011, 6, 330. [Google Scholar]
- Mok, C.C.; Lau, C.S. Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Pathol. 2003, 56, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Liang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, W. Genetic Polymorphisms in Genes Involved in the Type I Interferon System (STAT4 and IRF5): Association with Asian SLE Patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 43, 2403–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, T. Gut microbiota: A newly identified environmental factor in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1202850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeltsch-David, H.; Muller, S. Neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus and cognitive dysfunction: The MRL-lpr mouse strain as a model. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulinello, M.; Putterman, C. The MRL/lpr mouse strain as a model for neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. BioMed Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 207504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizui, M.; Koga, T.; Lieberman, L.A.; Beltran, J.; Yoshida, N.; Johnson, M.C.; Tsokos, G.C. IL-2 protects lupus-prone mice from multiple end-organ damage by limiting CD4− CD8− IL-17–producing T cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2168–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wu, C.; Li, L.J.; Fan, Y.G.; Pan, H.F.; Tao, J.H.; Ye, D.Q. RNAi silencing of HIF-1α ameliorates lupus development in MRL/lpr mice. Inflammation 2018, 41, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, A.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Parodis, I. Advances in the pharmacological management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2024, 25, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ahmet, A.; Ward, L.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Mandelcorn, E.D.; Leigh, R.; Kim, H. A practical guide to the monitoring and management of the complications of systemic corticosteroid therapy. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.M.; Edwards, M.R.; Mu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Vieson, M.D.; Reilly, C.M.; Bankole, A.A. Gut microbiota in human systemic lupus erythematosus and a mouse model of lupus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02288-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parada Venegas, D.; De la Fuente, M.K.; Landskron, G.; González, M.J.; Quera, R.; Dijkstra, G.; Hermoso, M.A. Short chain fatty acids (SCFAs)-mediated gut epithelial and immune regulation and its relevance for inflammatory bowel diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 277. [Google Scholar]
- De Filippis, F.; Paparo, L.; Nocerino, R.; Della Gatta, G.; Carucci, L.; Russo, R.; Berni Canani, R. Specific gut microbiome signatures and the associated pro-inflammatory functions are linked to pediatric allergy and acquisition of immune tolerance. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Nagafuchi, Y.; Fujio, K. Clinical and immunological biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.L.; Waxman, F.J. Glomerular deposition of immune complexes made with IgG2a monoclonal antibodies. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubtsova, K.; Rubtsov, A.V.; Thurman, J.M.; Mennona, J.M.; Kappler, J.W.; Marrack, P. B cells expressing the transcription factor T-bet drive lupus-like autoimmunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balow, J.E. Clinical presentation and monitoring of lupus nephritis. Lupus 2005, 14, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeva-Andany, M.M.; Fernández-Fernández, C.; Funcasta-Calderón, R.; Ameneiros-Rodríguez, E.; Adeva-Contreras, L.; Castro-Quintela, E. Insulin resistance is associated with clinical manifestations of diabetic kidney disease (glomerular hyperfiltration, albuminuria, and kidney function decline). Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2022, 18, 64–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispín, J.C.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Terhorst, C.; Tsokos, G.C. Ongoing T cell-driven inflammation in lupus nephritis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2014, 36, 443–457. [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv, G.; Twig, G.; Shor, D.B.A.; Furer, A.; Sherer, Y.; Mozes, O.; Comaneshter, D.; Amital, H. A volcanic explosion of autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: A cross-sectional study of 1,000 patients. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 65, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, A.; Aranow, C. Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 365, 2110–2121. [Google Scholar]
- Furusawa, Y.; Obata, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Endo, T.A.; Nakato, G.; Takahashi, D.; Nakanishi, Y.; Uetake, C.; Kato, K.; Kato, T.; et al. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature 2013, 504, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.M.; Howitt, M.R.; Panikov, N.; Michaud, M.; Gallini, C.A.; Bohlooly, Y.M.; Glickman, J.N.; Garrett, W.S. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science 2013, 341, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, N.; Campbell, C.; Fan, X.; Dikiy, S.; van der Veeken, J.; deRoos, P.; Liu, H.; Cross, J.R.; Pfeffer, K.; Coffer, P.J.; et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013, 504, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; McKenzie, C.; Potamitis, M.; Thorburn, A.N.; Mackay, C.R.; Macia, L. The role of short-chain fatty acids in health and disease. Adv. Immunol. 2014, 121, 91–119. [Google Scholar]
- Atarashi, K.; Tanoue, T.; Oshima, K.; Suda, W.; Nagano, Y.; Nishikawa, H.; Fukuda, S.; Saito, T.; Narushima, S.; Hase, K.; et al. Treg induction by a rationally selected mixture of Clostridia strains from the human microbiota. Nature 2013, 500, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.G.; Sefik, E.; Geva-Zatorsky, N.; Kua, L.; Naskar, D.; Teng, F.; Chang, Y.; Koohsari, H.; Horwitz, B.H.; Benoist, C.; et al. Identifying species of symbiont bacteria that modulate Th17 cell differentiation in the intestine. Science 2016, 351, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Pindjakova, J.; Sartini, C.; Lo Re, O.; Rappa, F.; Coupe, B.; Lelouvier, B.; Vinciguerra, M. Gut Dysbiosis and Adaptive Immune Response in Diet-Induced Obesity vs. Systemic Inflammation. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Hirota, K. The Pathogenicity of Th17 Cells in Autoimmune Diseases. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarilyo, G.; Lourenço, E.V.; Shi, F.D.; La Cava, A. IL-17 Promotes Murine Lupus. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.T.; Cresci, G.A. The Immunomodulatory Functions of Butyrate. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 6025–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qing, P.; Yang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y. Gut Microbiome and Metabolites in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Link, Mechanisms and Intervention. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 686501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, F.P.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, C.M.; Wang, X.X.; Bu, Y.J.; Cen, X.; Chen, J.W. Gut Microbiota Regulation of T Lymphocyte Subsets during Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. BMC Immunol. 2024, 25, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, O.; Goodrich, J.K.; Cullender, T.C.; Spor, A.; Laitinen, K.; Kling Backhed, H.; Everard, A.; Ley, R.E.; Hacin, B.; Clément, K. Host Remodeling of the Gut Microbiome and Metabolic Changes during Pregnancy. Cell 2012, 150, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An Obesity-Associated Gut Microbiome with Increased Capacity for Energy Harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, H.B.; Chung, H.J.; Hong, S.T. Identification of the intestinal microbes associated with locomotion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.S.; Koo, B.C.; Choi, Y.J.; Jung, W.W.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, S.J.; Chung, H.J. Identification of muscle strength-related gut microbes through human fecal microbiome transplantation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lkhagva, E.; Chung, H.J.; Hong, J.; Tang, W.H.W.; Lee, S.I.; Hong, S.T.; Lee, S. The regional diversity of gut microbiome along the GI tract of male C57BL/6 mice. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.S.; Lkhagva, E.; Jung, S.; Kim, H.J.; Chung, H.J.; Hong, S.T. Fecal microbiome does not represent whole gut microbiome. Cell. Microbiol. 2023, 2023, 6868417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group | IgG2a (μg/mL) | IgG (μg/mL) | Urine ACR (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lupus-weak | 1013.70 ± 30.26 | 210.55 ± 44.92 | 44.51 ± 12.14 |
| Lupus-medium | 1691.75 ± 9.54 | 2069.26 ± 879.29 | 102.34 ± 20.25 |
| Lupus-strong | 1736.46 ± 21.34 | 3133.95 ± 649.04 | 461.16 ± 188.68 |
| Sample | Strain | Relative Abundance (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lupus-Weak | Lupus-Medium | Lupus-Strong | ||
| Fecal | Clostridium saudiense | 0.00 | 0.56 | 0.64 |
| Turicibacter sanguinis | 0.01 | 3.93 | 4.71 | |
| Ligilactobacillus animalis | 0.23 | 0.66 | 0.91 | |
| Hoylesella oralis | 1.83 | 0.82 | 0.67 | |
| Phocaeicola sartorii | 2.74 | 0.83 | 0.72 | |
| Eisenbergiella massiliensis | 2.20 | 0.60 | 0.43 | |
| GI | Clostridium saudiense | 0.00 | 0.45 | 0.56 |
| Pseudoflavonifractor phocaeensis | 0.20 | 0.96 | 1.38 | |
| Intestinimonas butyriciproducens | 0.18 | 0.41 | 0.73 | |
| Ruminiclostridium cellulolyticum | 2.71 | 0.33 | 0.20 | |
| Lactobacillus johnsonii | 1.81 | 0.63 | 0.46 | |
| Kineothrix alysoides | 12.21 | 10.07 | 9.71 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, E.-J.; Ahn, J.-S.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, D.-H.; Chung, H.-J. Changes in Gut Microbiota According to Disease Severity in a Lupus Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031006
Han E-J, Ahn J-S, Choi Y-J, Kim D-H, Chung H-J. Changes in Gut Microbiota According to Disease Severity in a Lupus Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031006
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Eui-Jeong, Ji-Seon Ahn, Yu-Jin Choi, Da-Hye Kim, and Hea-Jong Chung. 2025. "Changes in Gut Microbiota According to Disease Severity in a Lupus Mouse Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031006
APA StyleHan, E.-J., Ahn, J.-S., Choi, Y.-J., Kim, D.-H., & Chung, H.-J. (2025). Changes in Gut Microbiota According to Disease Severity in a Lupus Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031006





