Calmodulin Interaction Interface with Plasma Membrane Ca2+-ATPase Isoforms: An Integrative Bioinformatic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of PMCA Isoforms/Variants, CaMBDs, and Definition of Amino Acid Substitutions to Evaluate
2.2. Structural Analysis of PMCA CaMBD-CaM Complexes: Wild Type, Literature-Reported Mutations, and Tested Substitutions
2.3. Energetic Characterization of CaM-CaMBD Complexes
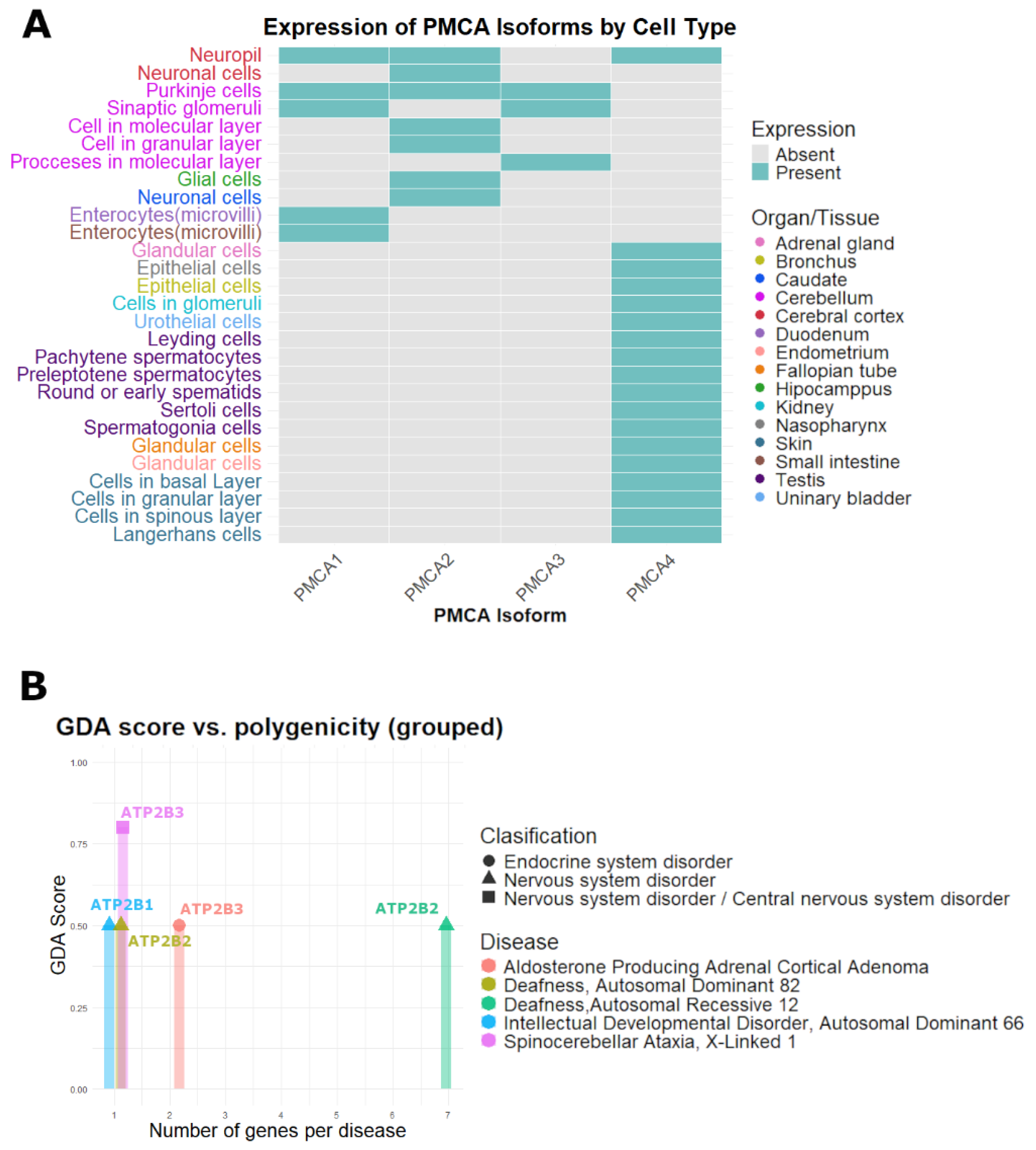
2.4. Potential Impact of Ca2+ Disruption Related to PMCA Genes in Pathological Phenotypes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
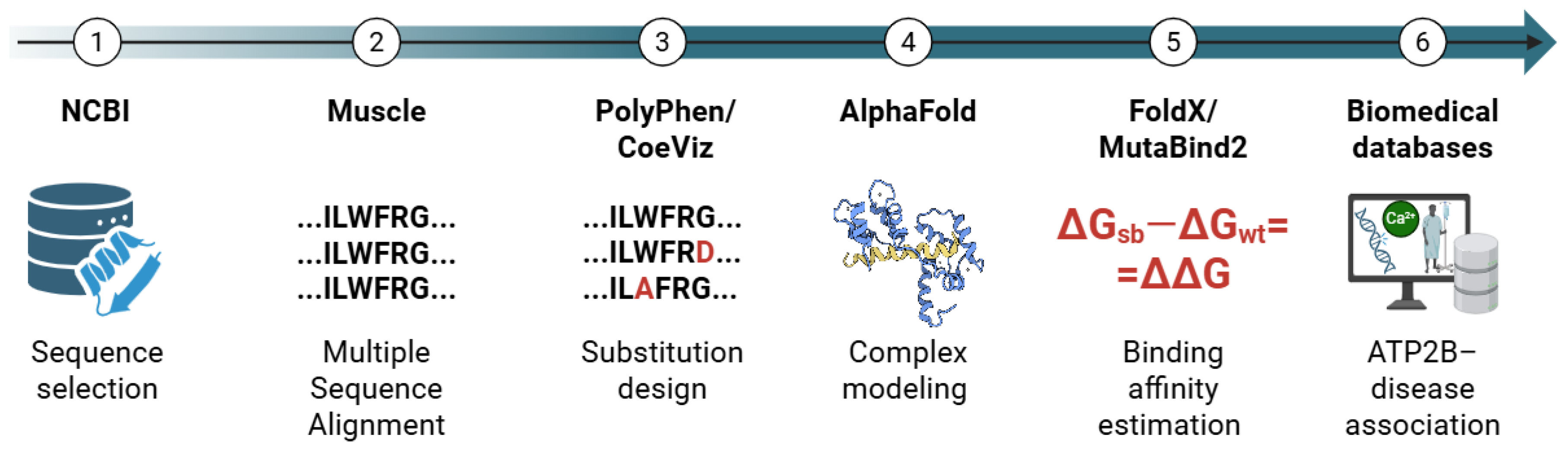
4.1. Design of the In Silico Approach
4.2. Retrieval of PMCA Isoform and Variant Sequences
4.3. CaMBD Delimitation
4.4. Definition and Rationale of Amino Acid Substitutions in the CaMBD of PMCA Isoforms
4.5. Prediction of Molecular Structures and Protein-Peptide Interactions
4.6. Determination of Energy Interaction and Variation of the Free Energy of Gibbs
4.7. Search for Potential Diseases Related to the ATP2B Gene Alteration
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PMCA | Plasma-membrane Ca2+-ATPase |
| CaMBD | Calmodulin Binding Domain |
| CaM | Calmodulin |
| ipTM | Inter-residue predicted TM-score |
| WT | Wild-type |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviation |
| pLDDT | Predicted local distance difference test |
| RefSeq | NCBI Reference Sequences |
| ΔG | Change in Gibbs Energy |
| GDA | Gene-disease associations |
| NgenesD | Total number of genes linked to that disease |
| DSI/DPI | Specificity/pleiotropy |
| HPO | Phenotypic annotations |
| OLS | Ontology Lookup Service |
| HPA | Human Protein Atlas |
| ACMG-AMP | American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics-Association for Molecular Pathology |
References
- Bootman, M.D.; Bultynck, G. Fundamentals of Cellular Calcium Signaling: A Primer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2020, 12, a038802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, D.E. Calcium Signaling. Cell 2007, 131, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisner, D.; Neher, E.; Taschenberger, H.; Smith, G. Physiology of Intracellular Calcium Buffering. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 2767–2845, Erratum in Physiol Rev. 2024, 104, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmgren, M.G.; Axelsen, K.B. Evolution of P-Type ATPases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Bioenerg. 1998, 1365, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmgren, M. P-Type ATPases: Many More Enigmas Left to Solve. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calì, T.; Brini, M.; Carafoli, E. Regulation of Cell Calcium and Role of Plasma Membrane Calcium ATPases. In International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 332, pp. 259–296. ISBN 978-0-12-812471-0. [Google Scholar]
- Hegedűs, L.; Zámbó, B.; Pászty, K.; Padányi, R.; Varga, K.; Penniston, J.T.; Enyedi, Á. Molecular Diversity of Plasma Membrane Ca2+ Transporting ATPases: Their Function Under Normal and Pathological Conditions. In Calcium Signaling; Islam, M.S., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1131, pp. 93–129. ISBN 978-3-030-12456-4. [Google Scholar]
- Strehler, E.E. Plasma Membrane Calcium ATPases: From Generic Ca2+ Sump Pumps to Versatile Systems for Fine-Tuning Cellular Ca2+. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, J. The Plasma Membrane Calcium Pump (PMCA): Regulation of Cytosolic Ca2+, Genetic Diversities and Its Role in Sub-Plasma Membrane Microdomains. In Membrane Dynamics and Calcium Signaling; Krebs, J., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 981, pp. 3–21. ISBN 978-3-319-55857-8. [Google Scholar]
- Brini, M.; Carafoli, E. Calcium Pumps in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 1341–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobo, A.; Ishida, H.; Vogel, H.J.; Berchtold, M.W. Calmodulin as a Protein Linker and a Regulator of Adaptor/Scaffold Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-F.; Tsai, W.-C. Calmodulin: The Switch Button of Calcium Signaling. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2022, 34, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, V.S.; Richards, E.M.B.; Morris, R.; Dart, C.; Helassa, N. Structure–Function Diversity of Calcium-Binding Proteins (CaBPs): Key Roles in Cell Signalling and Disease. Cells 2025, 14, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoads, A.R.; Friedberg, F. Sequence Motifs for Calmodulin Recognition. FASEB J. 1997, 11, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamniuk, A.P.; Vogel, H.J. Calmodulin’s Flexibility Allows for Promiscuity in Its Interactions with Target Proteins and Peptides. Mol. Biotechnol. 2004, 27, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Vogel, H. Protein-Peptide Interaction Studies Demonstrate the Versatility of Calmodulin Target Protein Binding. Protein Pept. Lett. 2006, 13, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tidow, H.; Nissen, P. Structural Diversity of Calmodulin Binding to Its Target Sites. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 5551–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juranic, N.; Atanasova, E.; Filoteo, A.G.; Macura, S.; Prendergast, F.G.; Penniston, J.T.; Strehler, E.E. Calmodulin Wraps around Its Binding Domain in the Plasma Membrane Ca2+ Pump Anchored by a Novel 18-1 Motif. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4015–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyedi, A.; Vorherr, T.; James, P.; McCormick, D.J.; Filoteo, A.G.; Carafoli, E.; Penniston, J.T. The Calmodulin Binding Domain of the Plasma Membrane Ca2+ Pump Interacts Both with Calmodulin and with Another Part of the Pump. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 12313–12321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penheiter, A.R.; Filoteo, A.G.; Penniston, J.T.; Caride, A.J. Kinetic Analysis of the Calmodulin-Binding Region of the Plasma Membrane Calcium Pump Isoform 4b. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 2009–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmström, S.; Askerlund, P.; Palmgren, M.G. A Calmodulin-stimulated Ca2+-ATPase from Plant Vacuolar Membranes with a Putative Regulatory Domain at Its N-terminus. FEBS Lett. 1997, 400, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Vogel, H.J. The Solution Structure of a Plant Calmodulin and the CaM-Binding Domain of the Vacuolar Calcium-ATPase BCA1 Reveals a New Binding and Activation Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 38502–38510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Iglesias, J.R.; Pérez-Gordones, M.C.; Del Castillo, J.R.; Mijares, A.; Benaim, G.; Mendoza, M. Identification and Characterization of a Calmodulin Binding Domain in the Plasma Membrane Ca2+-ATPase from Trypanosoma equiperdum. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2018, 222, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, J. Structure, Function and Regulation of the Plasma Membrane Calcium Pump in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanni, G.; Calì, T.; Kalscheuer, V.M.; Ottolini, D.; Barresi, S.; Lebrun, N.; Montecchi-Palazzi, L.; Hu, H.; Chelly, J.; Bertini, E.; et al. Mutation of Plasma Membrane Ca2+ ATPase Isoform 3 in a Family with X-Linked Congenital Cerebellar Ataxia Impairs Ca2+ Homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14514–14519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicario, M.; Zanni, G.; Vallese, F.; Santorelli, F.; Grinzato, A.; Cieri, D.; Berto, P.; Frizzarin, M.; Lopreiato, R.; Zonta, F.; et al. A V1143F Mutation in the Neuronal-Enriched Isoform 2 of the PMCA Pump Is Linked with Ataxia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 115, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantilla, G.; Peréz-Gordones, M.C.; Cisneros-Montufar, S.; Benaim, G.; Navarro, J.-C.; Mendoza, M.; Ramírez-Iglesias, J.R. Structural Analysis and Diversity of Calmodulin-Binding Domains in Membrane and Intracellular Ca2+-ATPases. J. Membr. Biol. 2023, 256, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate Structure Prediction of Biomolecular Interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shi, S.; Fan, K.; Huang, Q.; Chen, J.; Bao, J.; Wei, T. Comprehensive Analysis of the EFNB1 Gene c.451G>A(p.Gly151Ser) Mutation: Structural, Functional, and Pathogenicity Insights through in Silico Analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 196, 110906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay Mele, B.; Bovenzi, J.; Andreotti, G.; Cubellis, M.V.; Monticelli, M. In Silico Analysis of Phosphomannomutase-2 Dimer Interface Stability and Heterodimerization with Phosphomannomutase-1. Molecules 2025, 30, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, P.; Ding, Y.; Wu, C.; Hu, L. Identification of Pathogenic Missense Mutations of NF1 Using Computational Approaches. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2024, 74, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeflich, K.P.; Ikura, M. Calmodulin in Action. Cell 2002, 108, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Wang, H.; Zheng, J.; Wei, Q.; Jia, Z. The Complex Structure of Calmodulin Bound to a Calcineurin Peptide. Proteins 2008, 73, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürvanger, Z.; Juhász, T.; Liliom, K.; Harmat, V. Structures of Calmodulin–Melittin Complexes Show Multiple Binding Modes Lacking Classical Anchoring Interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Rates of Conservative and Radical Nonsynonymous Nucleotide Substitutions in Mammalian Nuclear Genes. J. Mol. Evol. 2000, 50, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Enyedi, A.; Filoteo, A.G.; Strehler, E.E.; Penniston, J.T. Plasma Membrane Calcium Pump Isoform 4a Has a Longer Calmodulin-Binding Domain Than 4b. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 3714–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, S.W.; Leclerc, E. Novel Aspects of Calmodulin Target Recognition and Activation. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Nurden, P.; North, P.; Nurden, A.T.; Du, L.M.; Valentin, N.; Wilcox, D.A. C560Rβ3 Caused Platelet Integrin αIIbβ3 to Bind Fibrinogen Continuously, but Resulted in a Severe Bleeding Syndrome and Increased Murine Mortality. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggio, E.; Barazzuol, L.; Salmaso, A.; Milani, C.; Deligiannopoulou, A.; Cazorla, Á.G.; Jang, S.S.; Juliá-Palacios, N.; Keren, B.; Kopajtich, R.; et al. ATP2B2 de Novo Variants as a Cause of Variable Neurodevelopmental Disorders That Feature Dystonia, Ataxia, Intellectual Disability, Behavioral Symptoms, and Seizures. Genet. Med. 2023, 25, 100971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuschlein, F.; Boulkroun, S.; Osswald, A.; Wieland, T.; Nielsen, H.N.; Lichtenauer, U.D.; Penton, D.; Schack, V.R.; Amar, L.; Fischer, E.; et al. Somatic Mutations in ATP1A1 and ATP2B3 Lead to Aldosterone-Producing Adenomas and Secondary Hypertension. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naffa, R.; Hegedűs, L.; Hegedűs, T.; Tóth, S.; Papp, B.; Tordai, A.; Enyedi, Á. Plasma Membrane Ca2+ Pump Isoform 4 Function in Cell Migration and Cancer Metastasis. J. Physiol. 2024, 602, 1551–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.M.; Biesecker, L.G.; Rehm, H.L. Overview of Specifications to the ACMG/AMP Variant Interpretation Guidelines. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2019, 103, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsonis, P.; Wilhelm, K.; Williams, A.; Lichtarge, O. Genome Interpretation Using In Silico Predictors of Variant Impact. Hum. Genet. 2022, 141, 1549–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchetto, R.; Vorherr, T.; Brunner, J.; Carafoli, E. The Plasma Membrane Ca2+ Pump Contains a Site That Interacts with Its Calmodulin-Binding Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 2930–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penheiter, A.R.; Caride, A.J.; Enyedi, Á.; Penniston, J.T. Tryptophan 1093 Is Largely Responsible for the Slow Off Rate of Calmodulin from Plasma Membrane Ca2+ Pump 4b. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 17728–17732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, F.N.; Porollo, A. CoeViz: A Web-Based Tool for Coevolution Analysis of Protein Residues. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crick, F.H.C. Codon–Anticodon Pairing: The Wobble Hypothesis. J. Mol. Biol. 1966, 19, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerkvist, U. Two out of Three: An Alternative Method for Codon Reading. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 1759–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A Method and Server for Predicting Damaging Missense Mutations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.; Jordan, D.M.; Sunyaev, S.R. Predicting Functional Effect of Human Missense Mutations Using PolyPhen-2. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2013, 76, 7.20.1–7.20.41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymkowitz, J.W.H.; Rousseau, F.; Martins, I.C.; Ferkinghoff-Borg, J.; Stricher, F.; Serrano, L. Prediction of Water and Metal Binding Sites and Their Affinities by Using the Fold-X Force Field. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10147–10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, J.; Reche, R.; Cianferoni, D.; Orlando, G.; Van Der Kant, R.; Rousseau, F.; Schymkowitz, J.; Serrano, L. FoldX Force Field Revisited, an Improved Version. Bioinformatics 2025, 41, btaf064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhao, F.; Alvarez, R.V.; Goncearenco, A.; Panchenko, A.R.; Li, M. MutaBind2: Predicting the Impacts of Single and Multiple Mutations on Protein–Protein Interactions. iScience 2020, 23, 100939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thul, P.J.; Lindskog, C. The Human Protein Atlas: A Spatial Map of the Human Proteome. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Ramírez-Anguita, J.M.; Saüch-Pitarch, J.; Ronzano, F.; Centeno, E.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. The DisGeNET Knowledge Platform for Disease Genomics: 2019 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D845–D855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putman, T.E.; Schaper, K.; Matentzoglu, N.; Rubinetti, V.P.; Alquaddoomi, F.S.; Cox, C.; Caufield, J.H.; Elsarboukh, G.; Gehrke, S.; Hegde, H.; et al. The Monarch Initiative in 2024: An Analytic Platform Integrating Phenotypes, Genes and Diseases across Species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D938–D949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, J.; Lagrimas, J.; Iqbal, H.; Parkinson, H.; Harmse, H. OLS4: A New Ontology Lookup Service for a Growing Interdisciplinary Knowledge Ecosystem. Bioinformatics 2025, 41, btaf279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
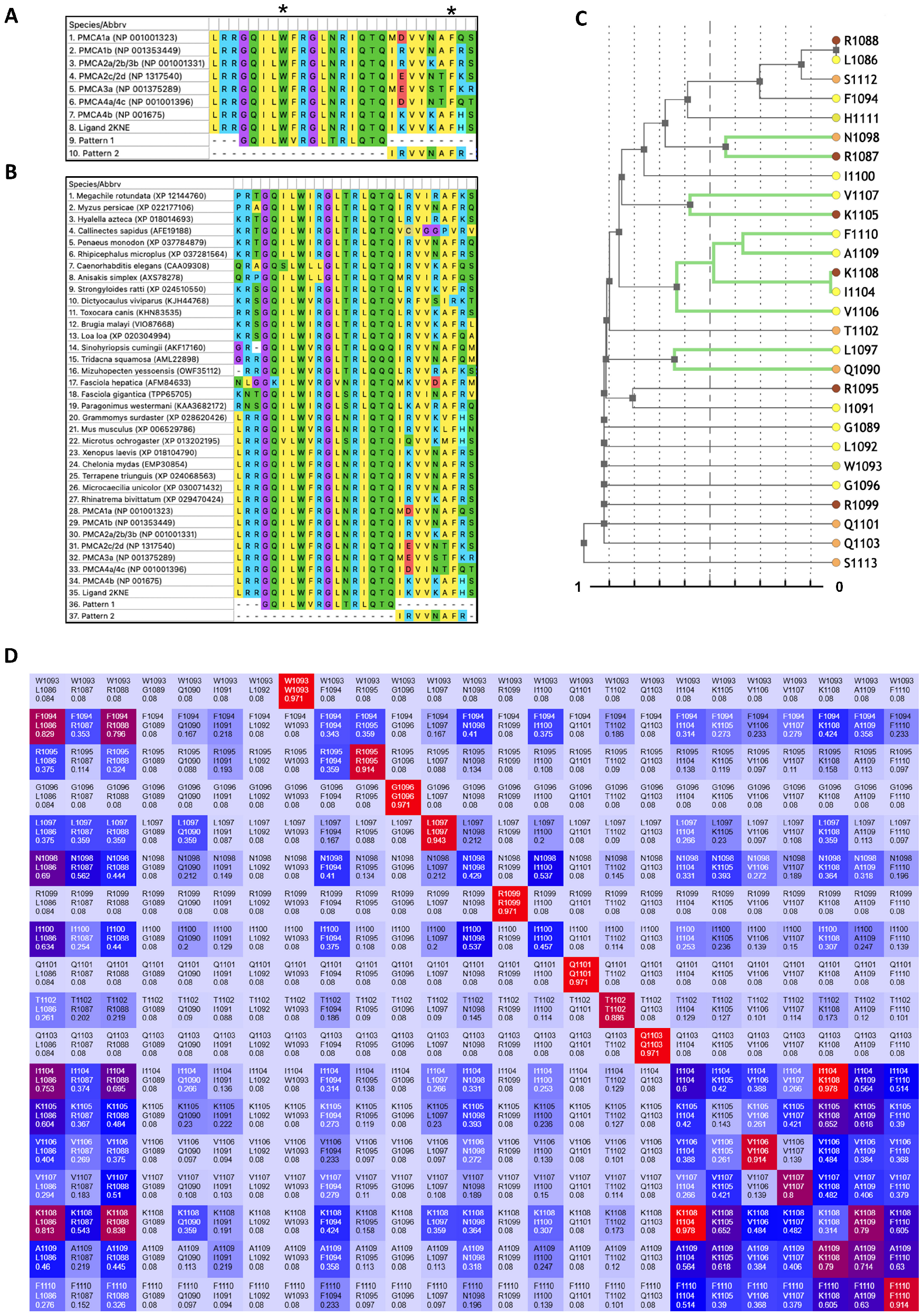
| Isoform/Triplets | T01 | T02 | T03 | T04 | T05 | T06 | T07 | T08 | T09 | T10 | T11 | T12 | T13 | T14 | T15 | T16 | T17 | T18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMCA1a [NP_001001323] | tgg (W) | ttt (F) | aga (R) | ggt (G) | ctg (L) | aac (N) | aga (R) | atc (I) | caa (Q) | aca (T) | cag (Q) | atg (M) | gat (D) | gta (V) | gtg (V) | aat (N) | gct (A) | ttc (F) |
| PMCA1b [NP_001353449.1] | tgg (W) | ttt (F) | aga (R) | ggt (G) | ctg (L) | aac (N) | aga (R) | atc (I) | caa (Q) | aca (T) | cag (Q) | att (I) | cga (R) | gtg (V) | gtg (V) | aat (N) | gca (A) | ttt (F) |
| PMCA4a [NP_001001396.1] | tgg (W) | ttc (F) | cgg (R) | ggc (G) | ctg (L) | aac (N) | cgt (R) | atc (I) | cag (Q) | act (T) | cag (Q) | atc (I) | gac (D) | gta (V) | att (I) | aac (N) | aca (T) | ttc (F) |
| PMCA4c [NP_001352712.1] | tgg (W) | ttc (F) | cgg (R) | ggc (G) | ctg (L) | aac (N) | cgt (R) | atc (I) | cag (Q) | act (T) | cag (Q) | atc (I) | gac (D) | gta (V) | att (I) | aac (N) | aca (T) | ttc (F) |
| PMCA2c [NP_001317540.1] | tgg (W) | ttc (F) | cga (R) | ggc (G) | ctg (L) | aat (N) | cgg (R) | atc (I) | cag (Q) | aca (T) | cag (Q) | att (I) | gaa (E) | gtc (V) | gtc (V) | aat (N) | act (T) | ttc (F) |
| PMCA2d [NP_001350791.1] | tgg (W) | ttc (F) | cga (R) | ggc (G) | ctg (L) | aat (N) | cgg (R) | atc (I) | cag (Q) | aca (T) | cag (Q) | att (I) | gaa (E) | gta (V) | gtc (V) | aat (N) | act (T) | ttc (F) |
| PMCA3a [NP_001375289.1] | tgg (W) | ttc (F) | cgg (R) | ggc (G) | ctg (L) | aac (N) | cgg (R) | att (I) | cag (Q) | acg (T) | cag (Q) | atg (M) | gag (E) | gta (V) | gtg (V) | agt (S) | acc (T) | ttc (F) |
| PMCA4b [NP_001675.3] | tgg (W) | ttc (F) | cgg (R) | ggc (G) | ctg (L) | aac (N) | cgt (R) | atc (I) | cag (Q) | act (T) | cag (Q) | atc (I) | aaa (K) | gtg (V) | gtc (V) | aaa (K) | gcg (A) | ttc (F) |
| PMCA2a [NP_001001331.1] | tgg (W) | ttc (F) | cga (R) | ggc (G) | ctg (L) | aat (N) | cgg (R) | atc (I) | cag (Q) | aca (T) | cag (Q) | atc (I) | cgc (R) | gtc (V) | gtg (V) | aag (K) | gcg (A) | ttc (F) |
| PMCA2b [NP_001340493.1] | tgg (W) | ttc (F) | cga (R) | ggc (G) | ctg (L) | aat (N) | cgg (R) | atc (I) | cag (Q) | aca (T) | cag (Q) | atc (I) | cgc (R) | gtc (V) | gtg (V) | aag (K) | gcg (A) | ttc (F) |
| PMCA3b [NP_001001344.1] | tgg (W) | ttc (F) | cgg (R) | ggc (G) | ctg (L) | aac (N) | cgg (R) | att (I) | cag (Q) | acg (T) | cag (Q) | atc (I) | cgg (R) | gtg (V) | gtg (V) | aaa (K) | gcg (A) | ttc (F) |
| Nucleotide conservation | *** | ** | * | ** | *** | ** | * | ** | ** | ** | *** | ** | ** | * | * | * | ** | |
| Original Residue | L | N | I | V | F | |||||||||||||
| Potential changes in the second position of the triplet | cgg | atc/att | acc/act | gaa/gag/gac | tct/tcc | |||||||||||||
| Final residue after nucleotide changes | R | I | T | E/D | S |
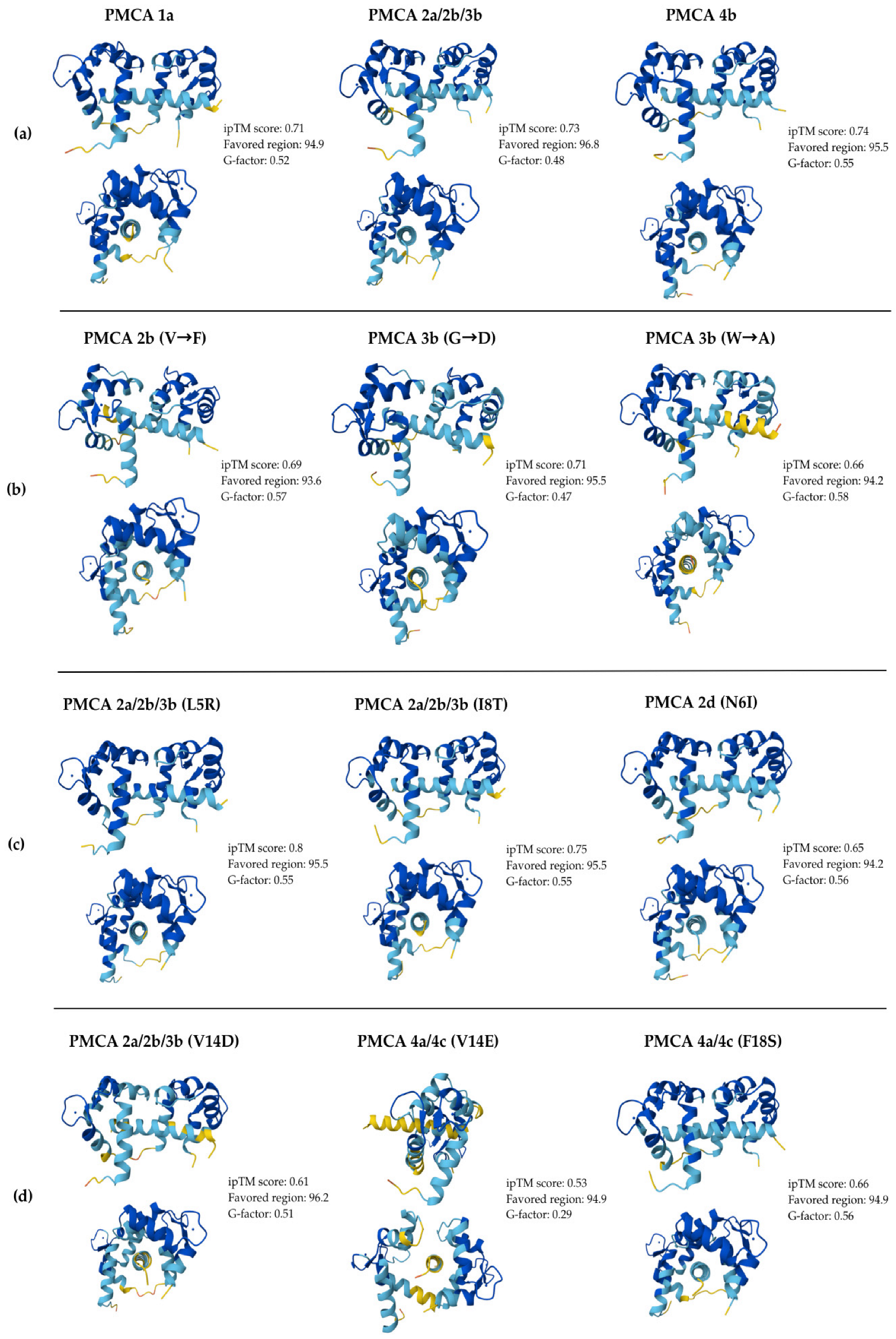
| Wild-Type Models | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isoform WT Group | ipTM | |||||
| Model 0 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | IC95 | |
| PMCA1a | 0.71 | 0.68 | 0.67 | 0.65 | 0.65 | [0.64–0.7] |
| PMCA1b | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.68 | 0.66 | 0.61 | [0.62–0.74] |
| PMCA2a/2b/3b | 0.73 | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.63 | 0.62 | [0.61–0.72] |
| PMCA2/c/2d | 0.59 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.53 | [0.52–0.58] |
| PMCA3a | 0.64 | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.55 | 0.55 | [0.54–0.64] |
| PMCA4a/4c | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.56 | [0.56–0.63] |
| PMCA4b | 0.74 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.62 | 0.59 | [0.58–0.72] |
| Literature-Reported Mutations | ||||||
| Model 0 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | IC95 | |
| PMCA2b V → F | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.60 | 0.62 | [0.6–0.73] |
| PMCA3b W → A | 0.66 | 0.63 | 0.59 | 0.61 | 0.55 | [0.56–0.66] |
| PMCA3b G → D | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.68 | [0.68–0.72] |
| Evaluated Substitutions | ||||||
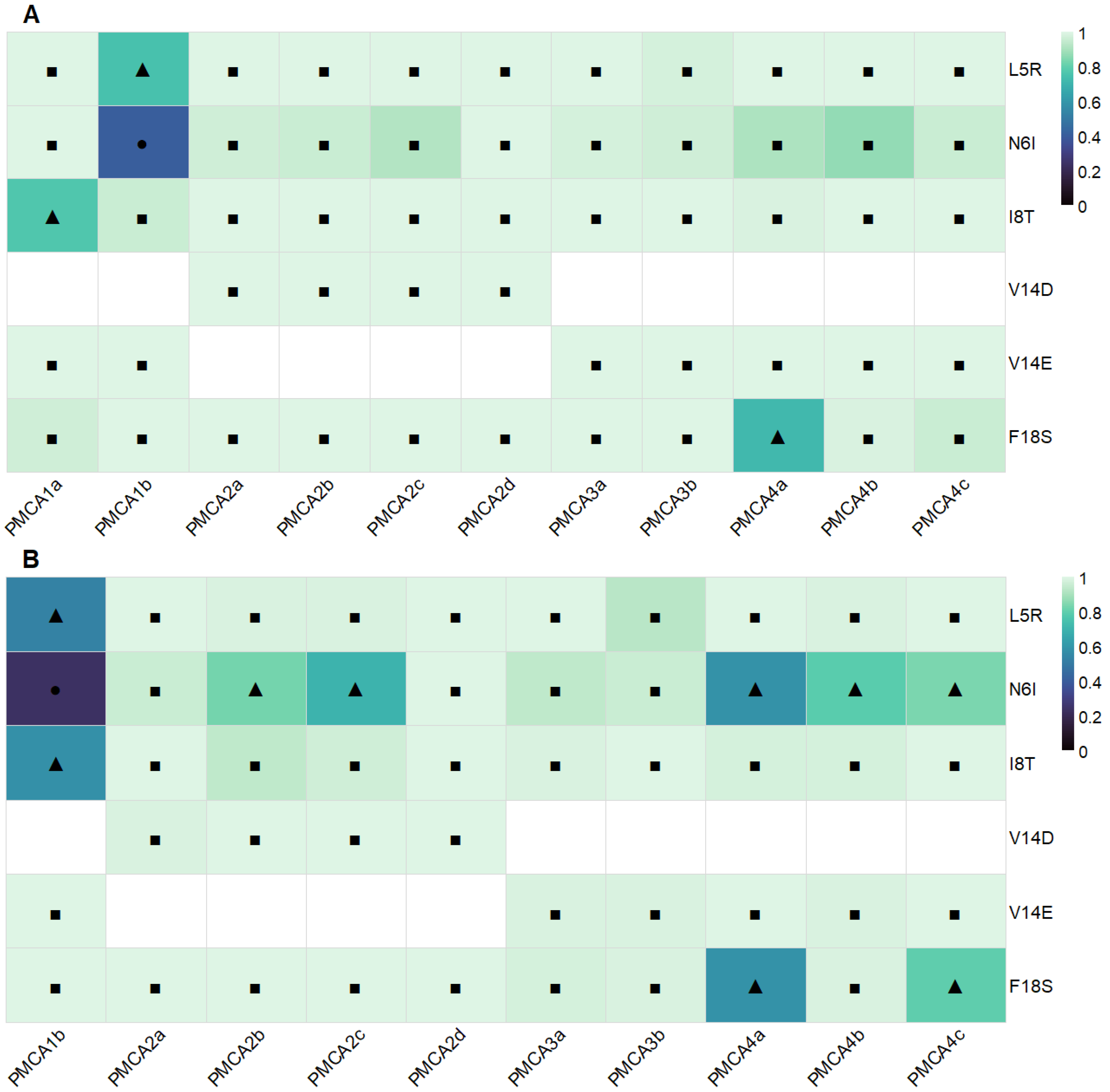
| L5R | Model 0 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | IC95 |
| PMCA1a | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.62 | [0.63–0.69] |
| PMCA1b | 0.73 | 0.66 | 0.68 | 0.66 | 0.61 | [0.61–0.72] |
| PMCA2a/2b/3b | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.68 | [0.64–0.77] |
| PMCA2/c/2d | 0.62 | 0.59 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 0.57 | [0.55–0.62] |
| PMCA3a | 0.68 | 0.55 | 0.61 | 0.56 | 0.58 | [0.53–0.66] |
| PMCA4a/4c | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.6 | 0.41 | [0.46–0.71] |
| PMCA4b | 0.67 | 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.64 | 0.62 | [0.62–0.67] |
| N6I | Model 0 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | IC95 |
| PMCA1a | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.6 | [0.59–0.72] |
| PMCA1b | 0.68 | 0.65 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.61 | [0.61–0.68] |
| PMCA2a/2b/3b | 0.68 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.57 | 0.58 | [0.56–0.67] |
| PMCA2/c/2d | 0.65 | 0.62 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.4 | [0.44–0.68] |
| PMCA3a | 0.65 | 0.6 | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.35 | [0.41–0.72] |
| PMCA4a/4c | 0.57 | 0.61 | 0.55 | 0.58 | 0.53 | [0.53–0.61] |
| PMCA4b | 0.7 | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.54 | [0.51–0.67] |
| I8T | Model 0 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | IC95 |
| PMCA1a | 0.82 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.68 | 0.62 | [0.62–0.81] |
| PMCA1b | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.7 | 0.74 | [0.69–0.78] |
| PMCA2a/2b/3b | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.43 | [0.5–0.83] |
| PMCA2/c/2d | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.58 | [0.59–0.65] |
| PMCA3a | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.64 | [0.64–0.67] |
| PMCA4a/4c | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.6 | [0.59–0.69] |
| PMCA4b | 0.7 | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.58 | 0.62 | [0.57–0.68] |
| V14E/D | Model 0 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | IC95 |
| PMCA1a | 0.6 | 0.59 | 0.6 | 0.58 | 0.54 | [0.55–0.61] |
| PMCA1b | 0.62 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.56 | 0.4 | [0.43–0.63] |
| PMCA2a/2b/3b | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.57 | 0.55 | 0.56 | [0.55–0.61] |
| PMCA2/c/2d | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.38 | [0.37–0.59] |
| PMCA3a | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.52 | [0.52–0.58] |
| PMCA4a/4c | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.37 | [0.33–0.55] |
| PMCA4b | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.41 | [0.43–0.56] |
| F18S | Model 0 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | IC95 |
| PMCA1a | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.64 | 0.62 | 0.59 | [0.59–0.7] |
| PMCA1b | 0.71 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.61 | [0.63–0.73] |
| PMCA2a/2b/3b | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.6 | 0.43 | 0.42 | [0.41–0.68] |
| PMCA2/c/2d | 0.68 | 0.6 | 0.59 | 0.63 | 0.6 | [0.57–0.67] |
| PMCA3a | 0.65 | 0.61 | 0.6 | 0.59 | 0.58 | [0.57–0.64] |
| PMCA4a/4c | 0.66 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.6 | 0.4 | [0.45–0.7] |
| PMCA4b | 0.58 | 0.6 | 0.57 | 0.47 | 0.45 | [0.45–0.62] |
| Evaluated Substitutions | Literature Reported Mutations | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FoldX | MutaBind2 | ||||||||||||
| Pattern 1 | Pattern 2 | Pattern 1 | Pattern 2 | ||||||||||
| L5R | N6I | I8T | V14E/D | F18S | L5R | N6I | I8T | V14E/D | F18S | ||||
| PMCA (Isoform)/Gibbs Function | ΔΔG | ΔΔG | ΔΔG | ΔΔG | ΔΔG | ΔΔG | ΔΔG | ΔΔG | ΔΔG | ΔΔG | PMCA (Isoform) | FoldX ΔΔG | MutaBind2 ΔΔG |
| PMCA1a | −3.92 | −0.72 | −4.14 | 3.42 | 1.17 | 1.98 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 2.95 | 5.04 | PMCA2b (V → F) | 1.98 | 4.24 |
| PMCA1b | −0.69 | −4.97 | 5.82 | 3.15 | 5.64 | 0.21 | 0.31 | 2.5 | 3.13 | 4.23 | PMCA3b (W → A) | 15.88 | 3.51 |
| PMCA2a_2b_3b | 8.01 | 2.91 | 7.09 | 7.29 | 6.59 | 1.9 | 0.85 | 2.53 | 3.67 | 4.2 | PMCA3b (G → D) | 9.29 | 2.39 |
| PMCA2c_2d | 0.22 | −8.28 | 2.21 | 9.19 | 4.99 | 1.72 | 0.72 | 2.57 | 3.77 | 4.33 | |||
| PMCA3a | 3.11 | 1.15 | 4.59 | 4.99 | 0.19 | 2.6 | 1.56 | 2.9 | 3.35 | 4.57 | |||
| PMCA4a_4c | −2.79 | 1.72 | 3.77 | 12.05 | 7.9 | 1.85 | 0.05 | 2.97 | 3.45 | 4.59 | |||
| PMCA4b | 2.6 | 8.06 | 5.43 | 16.12 | 3.73 | 1.92 | 0.22 | 2.77 | 2.91 | 4.61 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Fresneda, M.; Lizano, E.; Echeverría-Garcés, G.; Herrera-Yela, A.; Feijóo, D.; Vivas-Colmenares, G.V.; López-Zaplana, A.; Pedelini, L.; Mendoza, M.; Navarro, J.C.; et al. Calmodulin Interaction Interface with Plasma Membrane Ca2+-ATPase Isoforms: An Integrative Bioinformatic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311750
Martínez-Fresneda M, Lizano E, Echeverría-Garcés G, Herrera-Yela A, Feijóo D, Vivas-Colmenares GV, López-Zaplana A, Pedelini L, Mendoza M, Navarro JC, et al. Calmodulin Interaction Interface with Plasma Membrane Ca2+-ATPase Isoforms: An Integrative Bioinformatic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311750
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Fresneda, Miguel, Esteban Lizano, Gabriela Echeverría-Garcés, Andres Herrera-Yela, Danna Feijóo, Grecia Victoria Vivas-Colmenares, Alvaro López-Zaplana, Leda Pedelini, Marta Mendoza, Juan Carlos Navarro, and et al. 2025. "Calmodulin Interaction Interface with Plasma Membrane Ca2+-ATPase Isoforms: An Integrative Bioinformatic Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311750
APA StyleMartínez-Fresneda, M., Lizano, E., Echeverría-Garcés, G., Herrera-Yela, A., Feijóo, D., Vivas-Colmenares, G. V., López-Zaplana, A., Pedelini, L., Mendoza, M., Navarro, J. C., & Ramírez-Iglesias, J. R. (2025). Calmodulin Interaction Interface with Plasma Membrane Ca2+-ATPase Isoforms: An Integrative Bioinformatic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311750






