From Structure to Function: 2-Chloro-5-nitrobenzoic Acid Derivatives as Potential Next-Generation Antibacterials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis and Structural Characterization
2.2. Computational Study
2.3. Antibacterial Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis and Structural Characterization Data
4.1.1. Chemicals
4.1.2. Synthesis of Compound 1
4.1.3. Synthesis of Compound 2
4.1.4. Polarized Optical Microscopy (POM) with Linkam Hot Stage
4.1.5. Infrared Spectroscopy (IR)
4.1.6. Single Crystal X-Ray Diffraction (SCXRD)
4.1.7. Hirshfeld Surface Analysis
4.2. Assessment of Antibacterial Activity
4.2.1. Microbial Strains
4.2.2. Inhibition Zone Measurement
4.2.3. Bacterial Cell Viability Evaluation
4.2.4. Biofilm Inhibitory Activity Assessment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EWGs | Electron-withdrawing groups |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharides |
| 2Cl5NBH | 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| SCXRD | Single-crystal X-ray diffraction |
| MMEA | Methylethanolamine |
| ATCC | American type culture collection |
| Δψ | Electrochemical potential |
| ATR | Attenuated Total Reflectance |
| CCD | Charge coupled device |
| MoK | Molybdenum K-alpha |
| CIFs | Crystallographic information files |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| Gn | Gentamicin |
| Sxt | Sulfamethoxazole -trimethoprim |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TTC | 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride |
References
- Ahmed, S.K.; Hussein, S.; Qurbani, K.; Ibrahim, R.H.; Fareeq, A.; Mahmood, K.A.; Mohamed, M.G. Antimicrobial resistance: Impacts, challenges, and future prospects. J. Med. Surg. Public Health 2024, 2, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, M.P. Antimicrobial Resistance: The Impact from and on society according to one health approach. Societies 2024, 14, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Antunes, W.; Mota, S.; Madureira-Carvalho, Á.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Dias da Silva, D. An overview of the recent advances in antimicrobial resistance. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, M.; Frees, D.; Ingmer, H. Antibiotic resistance and the MRSA problem. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, E.J.A.; Wulandari, S.; Lovell, S.D.; Laabei, M. Novel antimicrobial strategies to treat multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 1456–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Mi, K.; Ma, W.; Zhang, L.; Huang, L. Salmonella antimicrobials inherited and the non-inherited resistance: Mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1176317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synowiec, A.; Żyła, K.; Gniewosz, M.; Kieliszek, M. An effect of positional isomerism of benzoic acid derivatives on anti-bacterial activity against Escherichia coli. Open Life Sci. 2021, 16, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, M.; Halip, L.; Bourosh, P.; Chicu, S.A.; Chumakov, Y. Synthesis, structure and toxicity evaluation of ethanolamine nitro/chloronitrobenzoates: A combined experimental and theoretical study. Chem. Cent. J. 2017, 11, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz Romero, M.C.; Murphy, T.; Morris, M.; Cummins, E.; Kerry, J.P. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan, organic acids and nano-sized solubilisates for potential use in smart antimicrobially-active packaging for potential food applications. Food Control 2013, 34, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, D.J.; Azlin-Hasim, S.; Cruz-Romero, M.; Cummins, E.; Kerry, J.P.; Morris, M.A. Antimicrobial effect of benzoic and sorbic acid salts and nano-solubilisates against Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas fluorescens and chicken microbiota biofilms. Food Control 2020, 107, 106786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, L.; Pan, Z.; Fang, B. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of the hybrid molecules between amoxicillin and derivatives of benzoic acid. Drug Dev. Res. 2021, 82, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, W.A.; Khalid, M.; Ashraf, A.; Shafiq, I.; Parvez, M.; Imran, M.; Irfan, A.; Hanif, M.; Khan, M.U.; Sher, F.; et al. Antibacterial metal complexes of o--sulfamoylbenzoic acid: Synthesis, characterization, and DFT study. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2022, 36, e6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faleye, O.S.; Boya, B.R.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, I.; Lee, J. Halogenated antimicrobial agents to combat drug-resistant pathogens. Pharmacol. Rev. 2023, 76, 90–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodi, D.; Ishihara, Y. “Magic Chloro”: Profound effects of the chlorine atom in drug discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 5305–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, S.; Huang, W.; Fan, H.; Zhou, Z. Novel drug-drug salts of enoxacin with enhanced antibacterial activity: Insights from solubility and lipid-water partition coefficient. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 385, 122443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croitor, L.; Vlase, G.; Vlase, T.; Bourosh, P.N.; Chumakov, Y.M.; Crisan, M. Relationship between crystal structure and thermal properties of polymorphic system methylethanolammonium 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 5437–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, M.; Vlase, G.; Szerb, E.I.; Vlase, T. Thermal and kinetics studies of primary, secondary and tertiary alkanolammonium salts of 4-nitrobenzoic acid. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 132, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, M.; Petric, M.; Vlase, G.; Vlase, T.; Siminel, A.V.; Bourosh, P.; Croitor, L. Organic salt versus salt cocrystal: Thermal behavior, structural and photoluminescence investigations. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicu, S.A.; Grozav, M.; Kurunczi, L.; Crisan, M. SAR for amine salts of carboxylic acids to Hydractinia echinata. Rev. Chim. 2008, 59, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Witt, S.N. Ethanolamine and phosphatidylethanolamine: Partners in health and disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4829180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Boros, E. Coordination complexes to combat bacterial infections: Recent developments, current directions and future opportunities. Chemistry 2021, 27, 7340–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilescu, O.; Bourosh, P.; Bulhac, I.; Shova, S.; Kravtsov, V.C.; Caraba, M.N.; Caraba, I.V.; Popescu, R.; Crisan, M.; Haidu, D.; et al. Laminated dihydrazone Zn(II) coordination polymer with prospects for sensory and multifunctional biomedical applications. Polyhedron 2024, 258, 117039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunadevi, A.; Porkodi, J.; Ramgeetha, L.; Raman, N. Biological evaluation, molecular docking and DNA interaction studies of coordination compounds gleaned from a pyrazolone incorporated ligand. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2019, 38, 656–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, S.K.; Singh, S.K. Metal-based drugs: Current use and future potential. Der. Pharm. Lett. 2009, 1, 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- Stautz, J.; Hellmich, Y.; Fuss, M.F.; Silberberg, J.M.; Devlin, J.R.; Stockbridge, R.B.; Hänelt, I. Molecular mechanisms for bacterial potassium homeostasis. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 166968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorobet, A.; Crisan, M.E.; Bourosh, P.; Siminel, A.V.; Croitor, L. Supramolecular architectures and photoluminescent properties of triethanolammonium 4-nitrobenzoate salt and its Ni(II) complexes. Polyhedron 2021, 193, 114893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorobet, A.; Crisan, M.E.; Bourosh, P.; Croitor, L. Structural investigation and Hirshfeld surface analysis of Cu(II) triethanolamine 4-nitrobenzoate. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2021, 66, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Gorobet, A.; Crisan, M.; Petric, M.; Bourosh, P.; Croitor, L. Structural study of Ca(II) coordination compound with triethanolamine and 4-nitrobenzoic acid. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2018, 63, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Pavia, D.L.; Lampman, G.M.; Kriz, G.S.; Vyvyan, J.R. Introduction to Spectroscopy, 5th ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, J. Organic Spectroscopy: Principles and Applications, 2nd ed.; Alpha Science International Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Abebe, A.A.; Birhanu, A.G. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Molecular mechanisms underlying drug resistance development and novel strategies to combat. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 7641–7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, W.F.D.; Fox, S.J.; Sun, D.; Maupin, C.M. bacterial membranes are more perturbed by the asymmetric versus symmetric loading of amphiphilic molecules. Membranes 2022, 12, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, S.E. Understanding substituent effects in noncovalent interactions involving aromatic rings. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akshay, S.D.; Deekshit, V.K.; Mohan Raj, J.; Maiti, B. Outer membrane proteins and efflux pumps mediated multi-drug resistance in Salmonella: Rising threat to antimicrobial therapy. ACS Infect. Dis. 2023, 9, 2072–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcour, A.H. Outer membrane permeability and antibiotic resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1794, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumawat, M.; Nabi, B.; Daswani, M.; Viquar, I.; Pal, N.; Sharma, P.; Tiwari, S.; Sarma, D.K.; Shubham, S.; Kumar, M. Role of bacterial efflux pump proteins in antibiotic resistance across microbial species. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 181, 106182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, C.; Newton-Foot, M.; Grobbelaar, M.; Whitelaw, A. Antibiotic-induced stress responses in Gram-negative bacteria and their role in antibiotic resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2025, 80, 1165–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, U.; Lee, C.R. Distinct roles of outer membrane porins in antibiotic resistance and membrane integrity in Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, D.S.; McIntosh, T.J. The lipopolysaccharide barrier: Correlation of antibiotic susceptibility with antibiotic permeability and fluorescent probe binding kinetics. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 11777–11787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahendran, K.R.; Kreir, M.; Weingart, H.; Fertig, N.; Winterhalter, M. Permeation of antibiotics through Escherichia coli OmpF and OmpC porins: Screening for influx on a single-molecule level. J. Biomol. Screen. 2010, 15, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CrysAlis RED, Version 1.171.34.76; Oxford Diffraction Ltd.: Abingdon, UK, 2003.
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrae, C.F.; Edgington, P.R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Shields, G.P.; Taylor, R.; Towler, M.; van de Streek, J. Mercury: Visualization and analysis of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2006, 39, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, P.R.; Turner, M.J.; McKinnon, J.J.; Wolff, S.K.; Grimwood, D.J.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M.A. CrystalExplorer: A program for Hirshfeld surface analysis, visualization and quantitative analysis of molecular crystals. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2021, 54 Pt 3, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 27th ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Filimon, M.N.; Popescu, R.; Sinitean, A.; Maniu, P.; Dumitrescu, G.; Verdes, D.; Vlad, C.S. The Assessment of chitosan solutions effects on bacterial strains. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 1485–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlad, C.S.; Vlaia, L.; Vlaia, V.; Dumitraşcu, D.; Filimon, M.N.; Popescu, R.; Cimporescu, A.; Dehelean, C.; Onwubiko, C.E.; Daliborca, C.V. Chromatographic analysis and antibacterial potential of extracts of Gnetum africanum. Farmacia 2019, 67, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, R.; Filimon, M.N.; Vlad, D.C.; Verdes, D.; Moatar, A.; Moisei, G.; Gurani, K.; Caraba, I.V.; Petculescu Ciochina, L.; Pinzaru, I.; et al. Antiproliferative and antibacterial potential of tetrahexylammonium bromide-based ionic liquids. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berridge, M.V.; Herst, P.M.; Tan, A.S. Tetrazolium dyes as tools in cell biology: New insights into their cellular reduction. In Biotechnology Annual Review; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 11, pp. 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, P.; Petrovic, O. A colorimetric microtiter plate method for assessment of phage effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008, 74, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


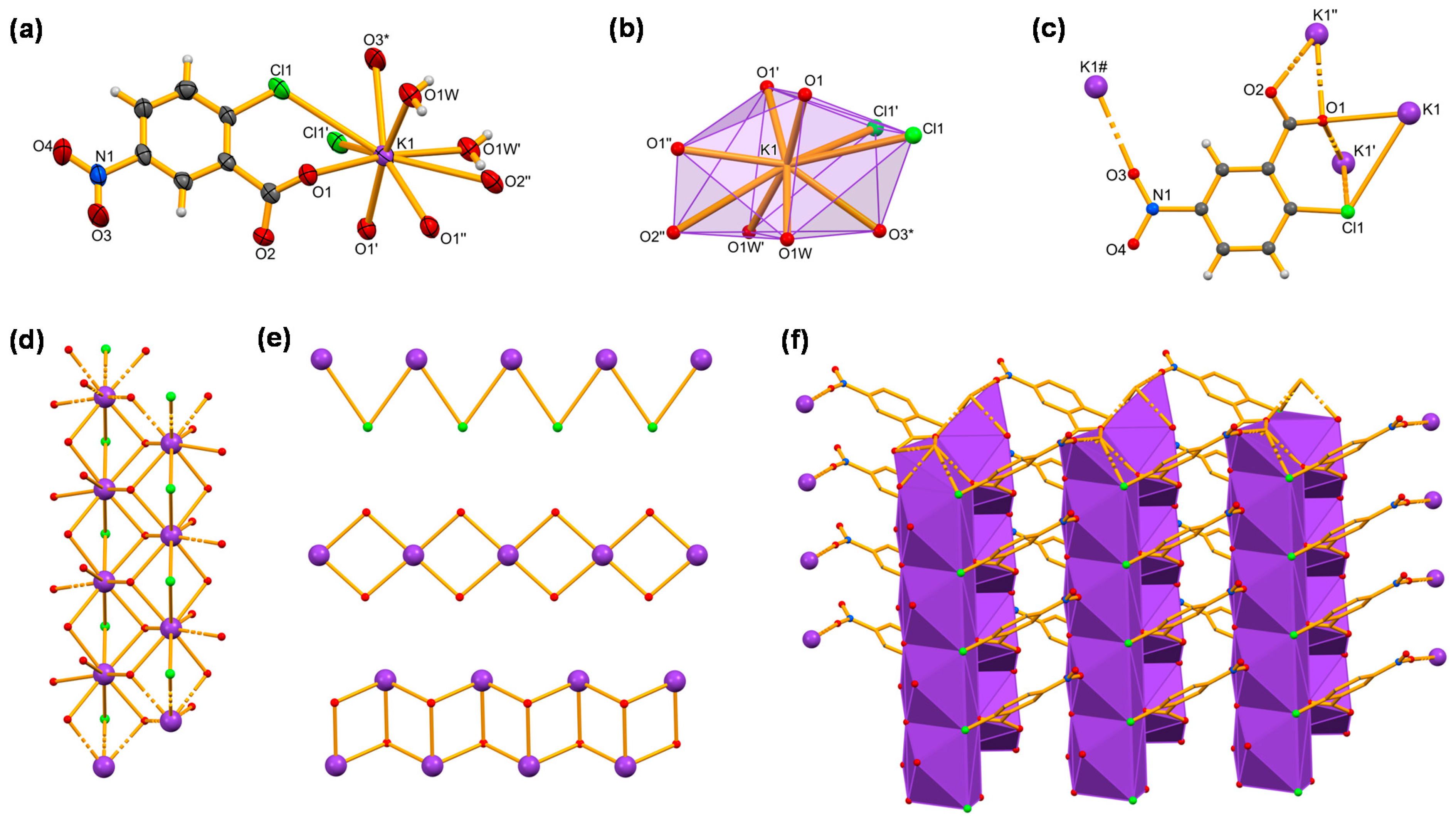
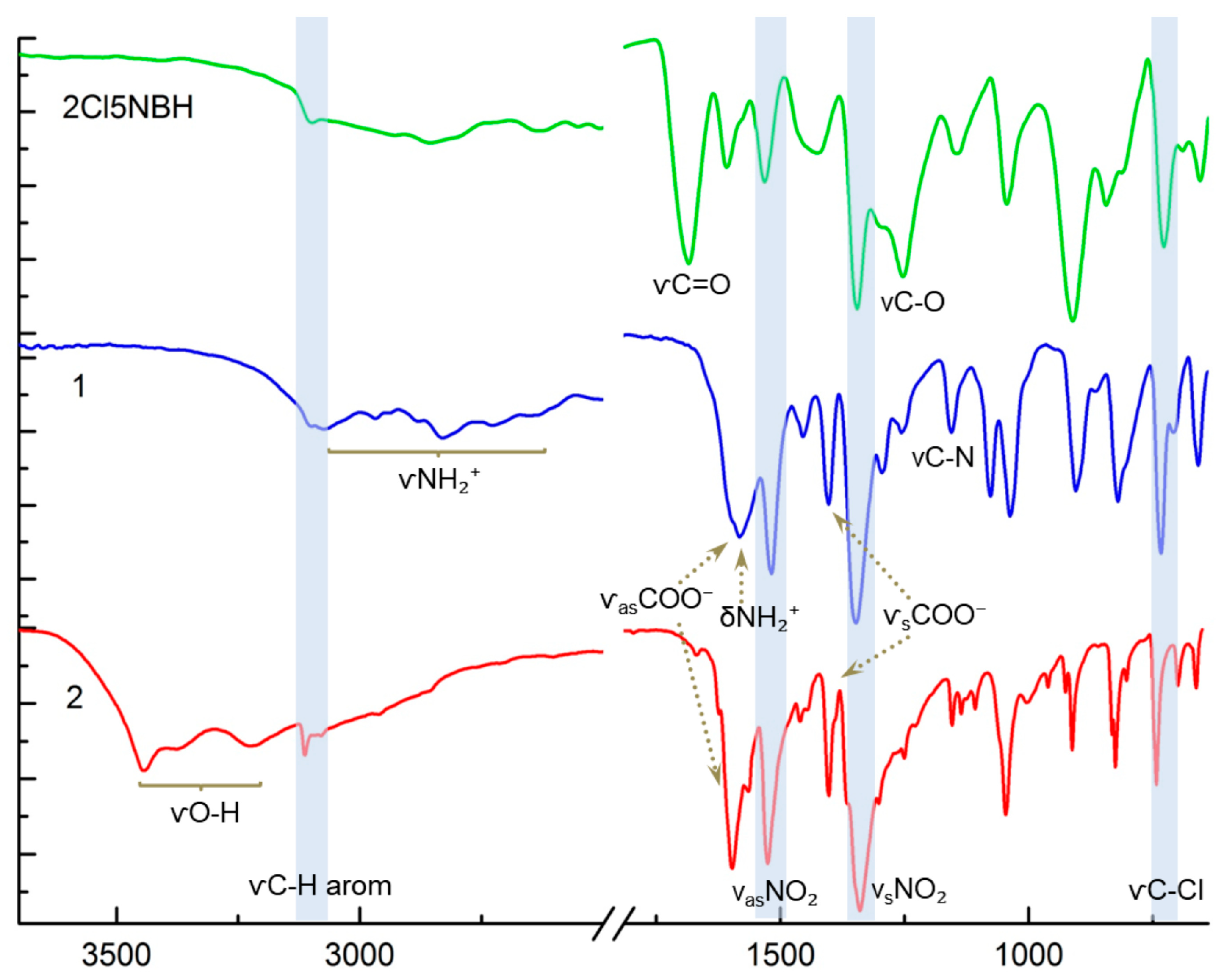
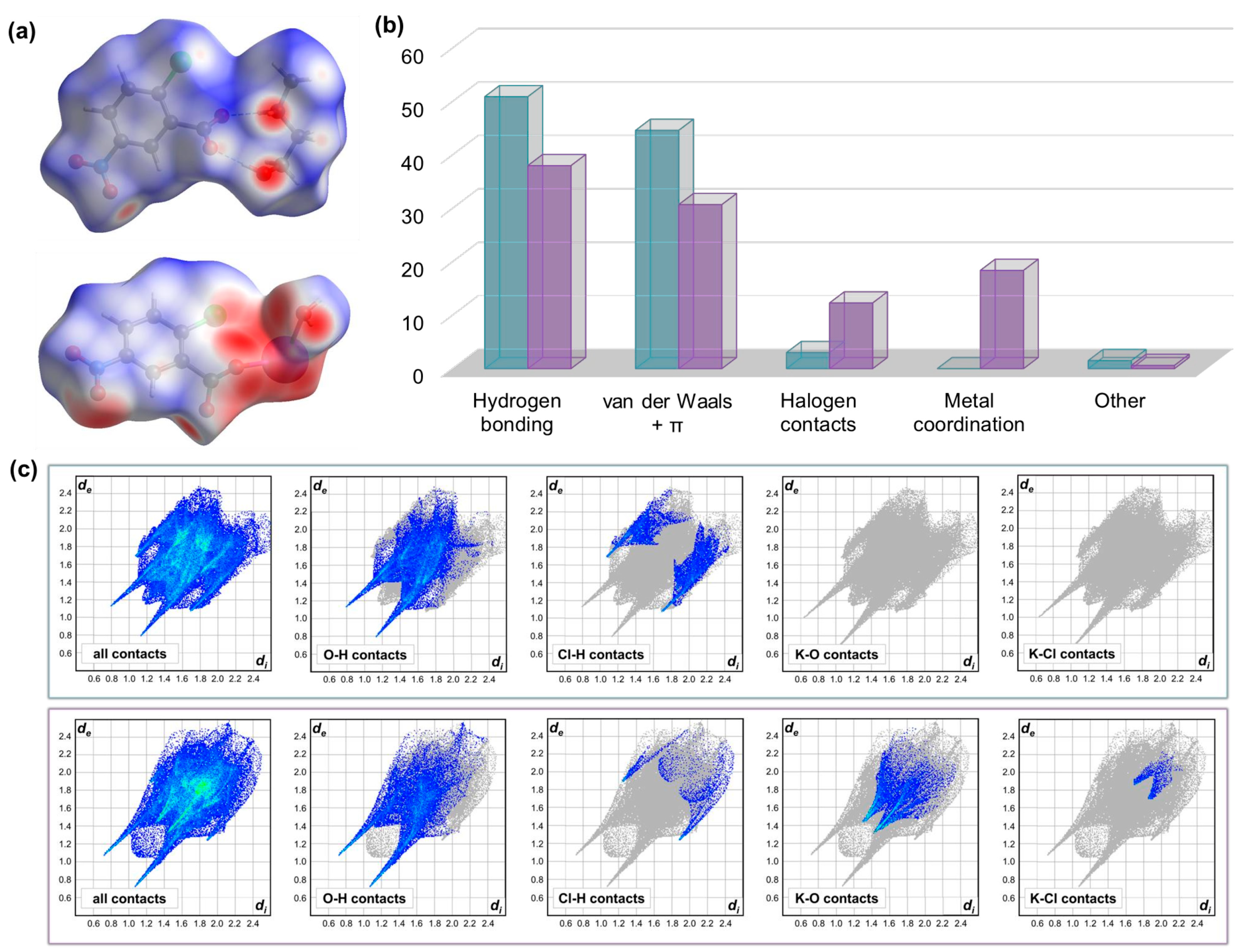

| 1 | 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| CCDC number | 2480318 | 2480317 |
| Formula | C10H13ClN2O5 | C7H5ClKNO5 |
| Formula weight | 276.67 | 257.67 |
| Crystal system | Triclinic | Orthorhombic |
| Space group | P-1 | P212121 |
| Z | 2 | 4 |
| a (Å) | 7.2496 (10) | 4.0939 (3) |
| b (Å) | 7.9607 (15) | 8.5779 (7) |
| c (Å) | 12.3583 (14) | 27.559 (2) |
| α (°) | 102.928 (12) | 90 |
| β (°) | 96.824 (10) | 90 |
| γ (°) | 113.819 (15) | 90 |
| V (Å3) | 618.19 (17) | 967.77 (13) |
| Dc (g/cm−3) | 1.486 | 1.768 |
| Μ (mm−1) | 0.324 | 0.824 |
| F (000) | 288 | 520 |
| Crystal size (mm3) | 0.80 × 0.30 × 0.18 | 0.60 × 0.04 × 0.03 |
| Reflections collected/unique | 3325/2167 [R(int) = 0.0198] | 2380/1673 [R(int) = 0.0268] |
| Completeness (%) | 99.5 | 99.5 |
| Reflections with [I > 2σ(I)] | 1581 | 1440 |
| Parameters | 165 | 143 |
| GOF on F2 | 0.999 | 1.007 |
| R1, wR2 [I > 2σ(I)] | 0.0469, 0.1218 | 0.0556, 0.1369 |
| R1, wR2 (all data) | 0.0698, 0.1384 | 0.0649, 0.1446 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Croitor, L.; Gorobet, A.; Caraba, M.N.; Bourosh, P.; Caraba, I.V.; Haidu, D.; Crisan, M. From Structure to Function: 2-Chloro-5-nitrobenzoic Acid Derivatives as Potential Next-Generation Antibacterials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311607
Croitor L, Gorobet A, Caraba MN, Bourosh P, Caraba IV, Haidu D, Crisan M. From Structure to Function: 2-Chloro-5-nitrobenzoic Acid Derivatives as Potential Next-Generation Antibacterials. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311607
Chicago/Turabian StyleCroitor, Lilia, Anastasia Gorobet, Marioara Nicoleta Caraba, Pavlina Bourosh, Ion Valeriu Caraba, Daniela Haidu, and Manuela Crisan. 2025. "From Structure to Function: 2-Chloro-5-nitrobenzoic Acid Derivatives as Potential Next-Generation Antibacterials" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311607
APA StyleCroitor, L., Gorobet, A., Caraba, M. N., Bourosh, P., Caraba, I. V., Haidu, D., & Crisan, M. (2025). From Structure to Function: 2-Chloro-5-nitrobenzoic Acid Derivatives as Potential Next-Generation Antibacterials. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311607







