Predictive Analysis and Validation of Critical Missense SNPs of the ABH2 Gene Using Structural Bioinformatics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Functional Properties of ABH2
3. Impact of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) on ABH2 Activity
4. Prediction of SNP Consequences on Protein Function
5. Selection of the Most Significant SNP-Associated Amino Acid Substitutions
6. Functional Roles of the Identified Residues
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
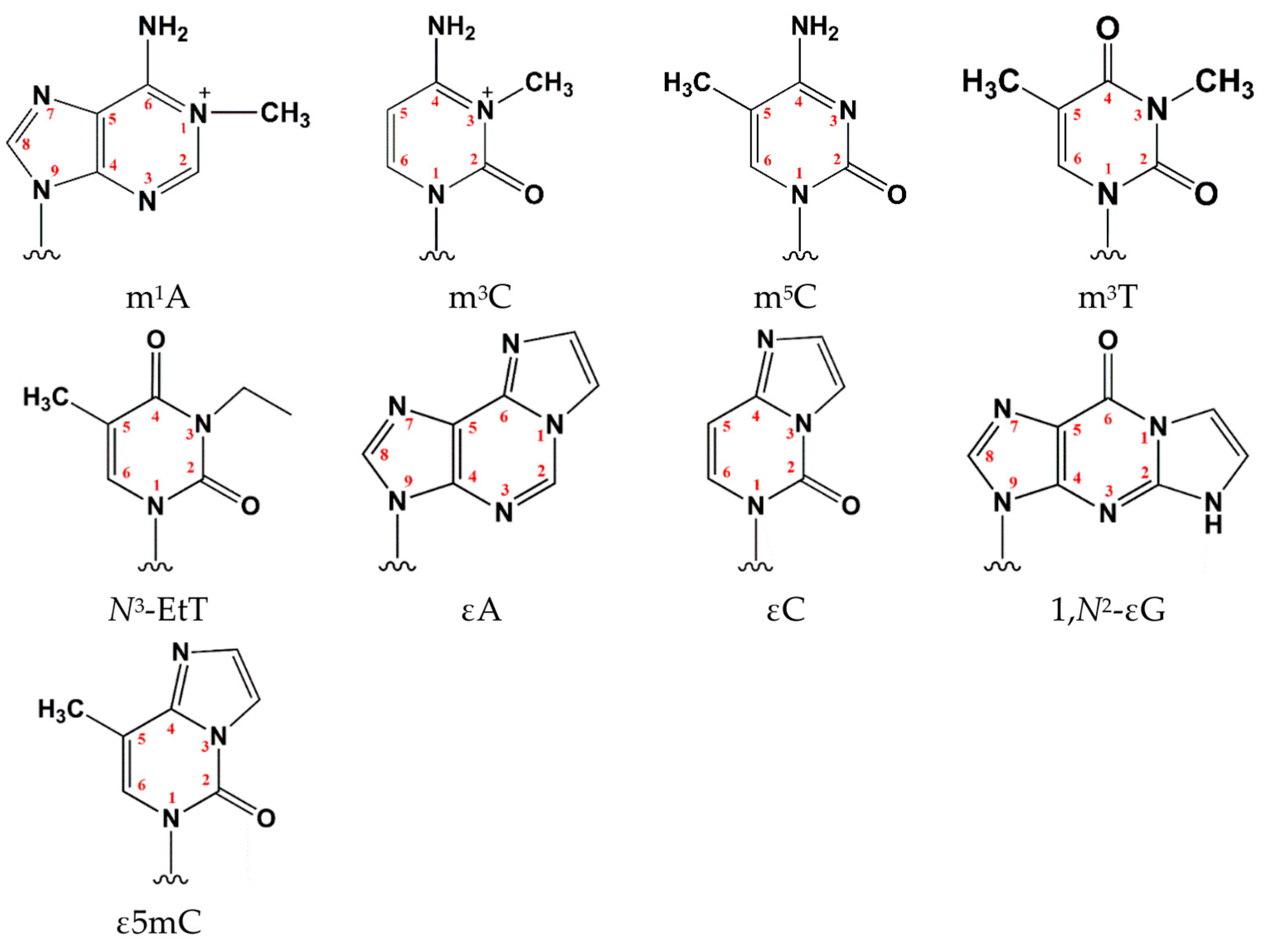
Abbreviations
| 1,N2-εG | 1,N2-ethenoguanosine |
| εA | 1,N6-ethenoadenosine |
| ε5mC | 3,N4-etheno-5-methylcytosine |
| εC | 3,N4-ethenocytidine |
| m5C | 5-methylcytosine |
| αKG | α-ketoglutarate |
| DSBH s | Double-stranded β-helix fold |
| N3-EtT | N3-ethylthymidine |
| m1A | N1-methyladenosine |
| m3C | N3-methylcytidine |
| m3T | N3-methylthymidine |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
References
- Schofield, C.J.; Zhang, Z. Structural and Mechanistic Studies on 2-Oxoglutarate-Dependent Oxygenases and Related Enzymes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1999, 9, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedgwick, B. Repairing DNA-Methylation Damage. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishina, Y.; Duguid, E.M.; He, C. Direct Reversal of DNA Alkylation Damage. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, S.S. DNA Adduct Formation from Tobacco-Specific N-Nitrosamines. Mutat. Res. 1999, 424, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeles, B.I.; Singh, V.; Delaney, J.C.; Li, D.; Essigmann, J.M. The AlkB Family of Fe(II)/α-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenases: Repairing Nucleic Acid Alkylation Damage and Beyond. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 20734–20742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsov, N.A.; Kanazhevskaya, L.Y.; Fedorova, O.S. DNA Demethylation in the Processes of Repair and Epigenetic Regulation Performed by 2-Ketoglutarate-Dependent DNA Dioxygenases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, T.; Sedgwick, B.; Sekiguchi, M.; Nakabeppu, Y. Regulation and Expression of the Adaptive Response to Alkylating Agents. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1988, 57, 133–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V. The DNA-Repair Protein AlkB, EGL-9, and Leprecan Define New Families of 2-Oxoglutarate- and Iron-Dependent Dioxygenases. Genome Biol. 2001, 2, research0007.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falnes, P.Ø.; Johansen, R.F.; Seeberg, E. AlkB-Mediated Oxidative Demethylation Reverses DNA Damage in Escherichia coli. Nature 2002, 419, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trewick, S.C.; Henshaw, T.F.; Hausinger, R.P.; Lindahl, T.; Sedgwick, B. Oxidative Demethylation by Escherichia coli AlkB Directly Reverts DNA Base Damage. Nature 2002, 419, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ougland, R.; Rognes, T.; Klungland, A.; Larsen, E. Non-Homologous Functions of the AlkB Homologs. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 7, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; He, C. DNA Repair by Reversal of DNA Damage. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a012575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, T.; Trewick, S.C.; Koivisto, P.; Bates, P.A.; Lindahl, T.; Sedgwick, B. Reversal of DNA Alkylation Damage by Two Human Dioxygenases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16660–16665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerken, T.; Girard, C.A.; Tung, Y.-C.L.; Webby, C.J.; Saudek, V.; Hewitson, K.S.; Yeo, G.S.H.; McDonough, M.A.; Cunliffe, S.; McNeill, L.A.; et al. The Obesity-Associated FTO Gene Encodes a 2-Oxoglutarate-Dependent Nucleic Acid Demethylase. Science 2007, 318, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurowski, M.A.; Bhagwat, A.S.; Papaj, G.; Bujnicki, J.M. Phylogenomic Identification of Five New Human Homologs of the DNA Repair Enzyme AlkB. BMC Genom. 2003, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.F.; Carter, K.C.; Wang, R.P.; Shell, B.K. Molecular Cloning and Functional Analysis of a Human cDNA Encoding an Escherichia coli AlkB Homolog, a Protein Involved in DNA Alkylation Damage Repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, Q. The Role of Demethylase AlkB Homologs in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1153463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.C.; He, C. M6 A RNA Methylation: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Potential. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e105977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Yan, H.; Hou, Y.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, E.; He, J.; Cai, Z. RNA Demethylase ALKBH5 in Cancer: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Potential. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Gu, Q.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q. The Biological Function of m6A Demethylase ALKBH5 and Its Role in Human Disease. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, K.; Lenz, S.A.P.; Tang, Q.; Chen, F.; Qi, R.; Jost, M.; Drennan, C.L.; Essigmann, J.M.; Wetmore, S.D.; Li, D. DNA Repair Enzymes ALKBH2, ALKBH3, and AlkB Oxidize 5-Methylcytosine to 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine, 5-Formylcytosine and 5-Carboxylcytosine In Vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 5522–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falnes, P. Repair of 3-Methylthymine and 1-Methylguanine Lesions by Bacterial and Human AlkB Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 6260–6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qi, R.; Harcourt, E.M.; Chen, Y.-T.; Barbosa, G.M.; Peng, Z.; Howarth, S.; Delaney, S.; Li, D. 3,N4-Etheno-5-Methylcytosine Blocks TET1-3 Oxidation but Is Repaired by ALKBH2, 3 and FTO. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, 12378–12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringvoll, J.; Moen, M.N.; Nordstrand, L.M.; Meira, L.B.; Pang, B.; Bekkelund, A.; Dedon, P.C.; Bjelland, S.; Samson, L.D.; Falnes, P.Ø.; et al. AlkB Homologue 2–Mediated Repair of Ethenoadenine Lesions in Mammalian DNA. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4142–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringvoll, J.; Nordstrand, L.M.; Vagbo, C.B.; Talstad, V.; Reite, K.; Aas, P.A.; Lauritzen, K.H.; Liabakk, N.B.; Bjork, A.; Doughty, R.W.; et al. Repair Deficient Mice Reveal mABH2 as the Primary Oxidative Demethylase for Repairing 1meA and 3meC Lesions in DNA. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Wang, P.; Nay, S.L.; Wang, J.; Dai, X.; O’Connor, T.R.; Wang, Y. Roles of Aag, Alkbh2, and Alkbh3 in the Repair of Carboxymethylated and Ethylated Thymidine Lesions. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Jin, S.G.; Cai, S.; Chen, Y.; Pfeifer, G.P.; O’Connor, T.R. Repair of Methylation Damage in DNA and RNA by Mammalian AlkB Homologues. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 39448–39459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.G.; Yi, C.; Duguid, E.M.; Sullivan, C.T.; Jian, X.; Rice, P.A.; He, C. Crystal Structures of DNA/RNA Repair Enzymes AlkB and ABH2 Bound to dsDNA. Nature 2008, 452, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Chen, B.; Qi, B.; Zhang, W.; Jia, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.J.; Dinner, A.R.; Yang, C.-G.; He, C. Duplex Interrogation by a Direct DNA Repair Protein in Search of Base Damage. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Fu, Y.; He, C. Nucleic Acid Oxidation in DNA Damage Repair and Epigenetics. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4602–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, I.J.; McDonough, M.A.; Ehrismann, D.; Kershaw, N.J.; Granatino, N.; Schofield, C.J. Structural Studies on 2-Oxoglutarate Oxygenases and Related Double-Stranded Beta-Helix Fold Proteins. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 644–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waheed, S.O.; Ramanan, R.; Chaturvedi, S.S.; Lehnert, N.; Schofield, C.J.; Christov, C.Z.; Karabencheva-Christova, T.G. Role of Structural Dynamics in Selectivity and Mechanism of Non-Heme Fe(II) and 2-Oxoglutarate-Dependent Oxygenases Involved in DNA Repair. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 795–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannessen, T.-C.A.; Prestegarden, L.; Grudic, A.; Hegi, M.E.; Tysnes, B.B.; Bjerkvig, R. The DNA Repair Protein ALKBH2 Mediates Temozolomide Resistance in Human Glioblastoma Cells. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 15, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaina, B.; Christmann, M. DNA Repair in Personalized Brain Cancer Therapy with Temozolomide and Nitrosoureas. DNA Repair 2019, 78, 128–141, Erratum in: DNA Repair 2019, 80, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Nakamura, M.; Anai, S.; De Velasco, M.; Tanaka, M.; Tsujikawa, K.; Ouji, Y.; Konishi, N. A Novel Human AlkB Homologue, ALKBH8, Contributes to Human Bladder Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3157–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, Y.; Ooshio, I.; Fusamae, Y.; Kitae, K.; Kawaguchi, M.; Jingushi, K.; Hase, H.; Harada, K.; Hirata, K.; Tsujikawa, K. AlkB Homolog 3-Mediated tRNA Demethylation Promotes Protein Synthesis in Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claussnitzer, M.; Dankel, S.N.; Kim, K.-H.; Quon, G.; Meuleman, W.; Haugen, C.; Glunk, V.; Sousa, I.S.; Beaudry, J.L.; Puviindran, V.; et al. FTO Obesity Variant Circuitry and Adipocyte Browning in Humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dina, C.; Meyre, D.; Gallina, S.; Durand, E.; Körner, A.; Jacobson, P.; Carlsson, L.M.S.; Kiess, W.; Vatin, V.; Lecoeur, C.; et al. Variation in FTO Contributes to Childhood Obesity and Severe Adult Obesity. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frayling, T.M.; Timpson, N.J.; Weedon, M.N.; Zeggini, E.; Freathy, R.M.; Lindgren, C.M.; Perry, J.R.B.; Elliott, K.S.; Lango, H.; Rayner, N.W.; et al. A Common Variant in the FTO Gene Is Associated with Body Mass Index and Predisposes to Childhood and Adult Obesity. Science 2007, 316, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smemo, S.; Tena, J.J.; Kim, K.-H.; Gamazon, E.R.; Sakabe, N.J.; Gómez-Marín, C.; Aneas, I.; Credidio, F.L.; Sobreira, D.R.; Wasserman, N.F.; et al. Obesity-Associated Variants within FTO form Long-Range Functional Connections with IRX3. Nature 2014, 507, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freathy, R.M.; Timpson, N.J.; Lawlor, D.A.; Pouta, A.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Ruokonen, A.; Ebrahim, S.; Shields, B.; Zeggini, E.; Weedon, M.N.; et al. Common Variation in the FTO Gene Alters Diabetes-Related Metabolic Traits to the Extent Expected given Its Effect on BMI. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuteri, A.; Sanna, S.; Chen, W.-M.; Uda, M.; Albai, G.; Strait, J.; Najjar, S.; Nagaraja, R.; Orrú, M.; Usala, G.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Scan Shows Genetic Variants in the FTO Gene Are Associated with Obesity-Related Traits. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, L.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.-X.; Winblad, B.; Fratiglioni, L.; Graff, C. The Obesity Related Gene, FTO, Interacts with APOE, and Is Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease Risk: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 23, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, C.; Tosto, G.; Mayeux, R.; Luchsinger, J.A.; NIA-LOAD/NCRAD Family Study Group; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Genetic Variants in the Fat and Obesity Associated (FTO) Gene and Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, A.; Zhou, J.; Sinha, R.A.; Singh, B.K.; Ghosh, S.; Lim, K.-H.; Chow, P.K.-H.; Woon, E.C.Y.; Yen, P.M. Hepatic FTO Expression Is Increased in NASH and Its Silencing Attenuates Palmitic Acid-Induced Lipotoxicity. Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun. 2016, 479, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, D.; Wang, F.; Xu, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, H. Expression of Demethylase Genes, FTO and ALKBH1, Is Associated with Prognosis of Gastric Cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Wu, T.P.; Gimple, R.C.; Li, Z.; Prager, B.C.; Wu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Gorkin, D.U.; et al. N6-Methyladenine DNA Modification in Glioblastoma. Cell 2018, 175, 1228–1243.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, J.A.; Meira, L.B.; Lee, C.-Y.I.; Moroski-Erkul, C.A.; Abolhassani, N.; Taghizadeh, K.; Eichinger, L.W.; Muthupalani, S.; Nordstrand, L.M.; Klungland, A.; et al. DNA Repair Is Indispensable for Survival after Acute Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2680–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aas, P.A.; Otterlei, M.; Falnes, P.; Vågbø, C.B.; Skorpen, F.; Akbari, M.; Sundheim, O.; Bjørås, M.; Slupphaug, G.; Seeberg, E.; et al. Human and Bacterial Oxidative Demethylases Repair Alkylation Damage in Both RNA and DNA. Nature 2003, 421, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Tian, R.; Zuo, Y. Multi-Substrate Selectivity Based on Key Loops and Non-Homologous Domains: New Insight into ALKBH Family. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.; Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, J. Down-Regulation of ALKBH2 Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity in H1299 Lung Cancer Cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetica, V.; Genitori, L.; Giunti, L.; Sanzo, M.; Bernini, G.; Massimino, M.; Sardi, I. Pediatric Brain Tumors: Mutations of Two Dioxygenases (hABH2 and hABH3) That Directly Repair Alkylation Damage. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 94, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Shimada, K.; Anai, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Konishi, N. ALKBH2, a Novel AlkB Homologue, Contributes to Human Bladder Cancer Progression by Regulating MUC1 Expression. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Li, L.; Xu, P.; Fang, J.; Xiao, S.; Chen, S. Frequent Down-Regulation of hABH2 in Gastric Cancer and Its Involvement in Growth of Cancer Cells. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, B.; Ye, K.; Cheng, S. ALKBH2 Inhibition Alleviates Malignancy in Colorectal Cancer by Regulating BMI1-Mediated Activation of NF-κB Pathway. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, F.S.; Brooks, L.D.; Chakravarti, A. A DNA Polymorphism Discovery Resource for Research on Human Genetic Variation. Genome Res. 1998, 8, 1229–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Samson, L.D.; Hübscher, U.; van Loon, B. The Interaction between ALKBH2 DNA Repair Enzyme and PCNA Is Direct, Mediated by the Hydrophobic Pocket of PCNA and Perturbed in Naturally-Occurring ALKBH2 Variants. DNA Repair 2015, 35, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Shiraishi, K.; Sunami, K.; Momozawa, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Matsuda, K.; Saito, M.; Goto, A.; Honda, T.; et al. Genomic Profiles of Pathogenic and Moderate-Penetrance Germline Variants Associated with Risk of Early-Onset Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2025, 20, 1626–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, P.C.; Henikoff, S. Accounting for Human Polymorphisms Predicted to Affect Protein Function. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.C.; Henikoff, S. Predicting Deleterious Amino Acid Substitutions. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A Method and Server for Predicting Damaging Missense Mutations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircher, M.; Witten, D.M.; Jain, P.; O’Roak, B.J.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J. A General Framework for Estimating the Relative Pathogenicity of Human Genetic Variants. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, N.M.; Rothstein, J.H.; Pejaver, V.; Middha, S.; McDonnell, S.K.; Baheti, S.; Musolf, A.; Li, Q.; Holzinger, E.; Karyadi, D.; et al. REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Wei, P.; Jian, X.; Gibbs, R.; Boerwinkle, E.; Wang, K.; Liu, X. Comparison and Integration of Deleteriousness Prediction Methods for Nonsynonymous SNVs in Whole Exome Sequencing Studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 2125–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Novati, G.; Pan, J.; Bycroft, C.; Žemgulytė, A.; Applebaum, T.; Pritzel, A.; Wong, L.H.; Zielinski, M.; Sargeant, T.; et al. Accurate Proteome-Wide Missense Variant Effect Prediction with AlphaMissense. Science 2023, 381, eadg7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Chan, A.P. PROVEAN Web Server: A Tool to Predict the Functional Effect of Amino Acid Substitutions and Indels. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2745–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriotti, E.; Calabrese, R.; Fariselli, P.; Martelli, P.L.; Altman, R.B.; Casadio, R. WS-SNPs&GO: A Web Server for Predicting the Deleterious Effect of Human Protein Variants Using Functional Annotation. BMC Genom. 2013, 14 (Suppl. S3), S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER-PSEP: Predicting Disease-Causing Genetic Variants Using Position-Specific Evolutionary Preservation. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2230–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendl, J.; Stourac, J.; Salanda, O.; Pavelka, A.; Wieben, E.D.; Zendulka, J.; Brezovsky, J.; Damborsky, J. PredictSNP: Robust and Accurate Consensus Classifier for Prediction of Disease-Related Mutations. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capriotti, E.; Calabrese, R.; Casadio, R. Predicting the Insurgence of Human Genetic Diseases Associated to Single Point Protein Mutations with Support Vector Machines and Evolutionary Information. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2729–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, F.A.d.O.; Andrade, E.S.d.; Palmero, E.I. Insights on Variant Analysis in Silico Tools for Pathogenicity Prediction. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1010327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottaz, A.; David, F.P.A.; Veuthey, A.-L.; Yip, Y.L. Easy Retrieval of Single Amino-Acid Polymorphisms and Phenotype Information Using SwissVar. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 851–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suybeng, V.; Koeppel, F.; Harlé, A.; Rouleau, E. Comparison of Pathogenicity Prediction Tools on Somatic Variants. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, C.; Li, C.; Boerwinkle, E. dbNSFP v3.0: A One-Stop Database of Functional Predictions and Annotations for Human Non-Synonymous and Splice Site SNVs. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendl, J.; Musil, M.; Štourač, J.; Zendulka, J.; Damborský, J.; Brezovský, J. PredictSNP2: A Unified Platform for Accurately Evaluating SNP Effects by Exploiting the Different Characteristics of Variants in Distinct Genomic Regions. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.C.; Henikoff, S. SIFT: Predicting Amino Acid Changes That Affect Protein Function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3812–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, E. A Comparison on Predicting Functional Impact of Genomic Variants. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2022, 4, lqab122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Mohammad, T.; Anjum, F.; Shafie, A.; Singh, I.K.; Abdullaev, B.; Pasupuleti, V.R.; Adnan, M.; Yadav, D.K.; Hassan, M.I. Comparative Analysis of Web-Based Programs for Single Amino Acid Substitutions in Proteins. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskar, R.; Ali, S. Mutational Analysis and Assessment of Its Impact on Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Genomes from India. Gene 2021, 778, 145470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Huang, X.; Muruganujan, A.; Tang, H.; Mills, C.; Kang, D.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER Version 11: Expanded Annotation Data from Gene Ontology and Reactome Pathways, and Data Analysis Tool Enhancements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D183–D189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnager, R.; Dang, A.S. Comprehensive In-Silico Prediction of Damage Associated SNPs in Human Prolidase Gene. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriotti, E.; Fariselli, P. PhD-SNPg: Updating a Webserver and Lightweight Tool for Scoring Nucleotide Variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W451–W458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingerdissen, H.M.; Torcivia-Rodriguez, J.; Hu, Y.; Chang, T.-C.; Mazumder, R.; Kahsay, R. BioMuta and BioXpress: Mutation and Expression Knowledgebases for Cancer Biomarker Discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1128–D1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Karagiannis, K.; Zhang, H.; Dingerdissen, H.; Shamsaddini, A.; Wan, Q.; Simonyan, V.; Mazumder, R. Human Germline and Pan-Cancer Variomes and Their Distinct Functional Profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 11570–11588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.-J.; Shamsaddini, A.; Pan, Y.; Smith, K.; Crichton, D.J.; Simonyan, V.; Mazumder, R. A Framework for Organizing Cancer-Related Variations from Existing Databases, Publications and NGS Data Using a High-Performance Integrated Virtual Environment (HIVE). Database 2014, 2014, bau022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Sun, X.; Yang, C.-G. Mechanistic Insight into the Recognition of Single-Stranded and Double-Stranded DNA Substrates by ABH2 and ABH3. Mol. Biosyst. 2010, 6, 2143–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davletgildeeva, A.T.; Tyugashev, T.E.; Zhao, M.; Ishchenko, A.A.; Saparbaev, M.; Kuznetsov, N.A. Role of Individual Amino Acid Residues Directly Involved in Damage Recognition in Active Demethylation by ABH2 Dioxygenase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Edstrom, W.C.; Benach, J.; Hamuro, Y.; Weber, P.C.; Gibney, B.R.; Hunt, J.F. Crystal Structures of Catalytic Complexes of the Oxidative DNA/RNA Repair Enzyme AlkB. Nature 2006, 439, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davletgildeeva, A.T.; Tyugashev, T.E.; Zhao, M.; Kuznetsov, N.A.; Ishchenko, A.A.; Saparbaev, M.; Kuznetsova, A.A. Individual Contributions of Amido Acid Residues Tyr122, Ile168, and Asp173 to the Activity and Substrate Specificity of Human DNA Dioxygenase ABH2. Cells 2023, 12, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
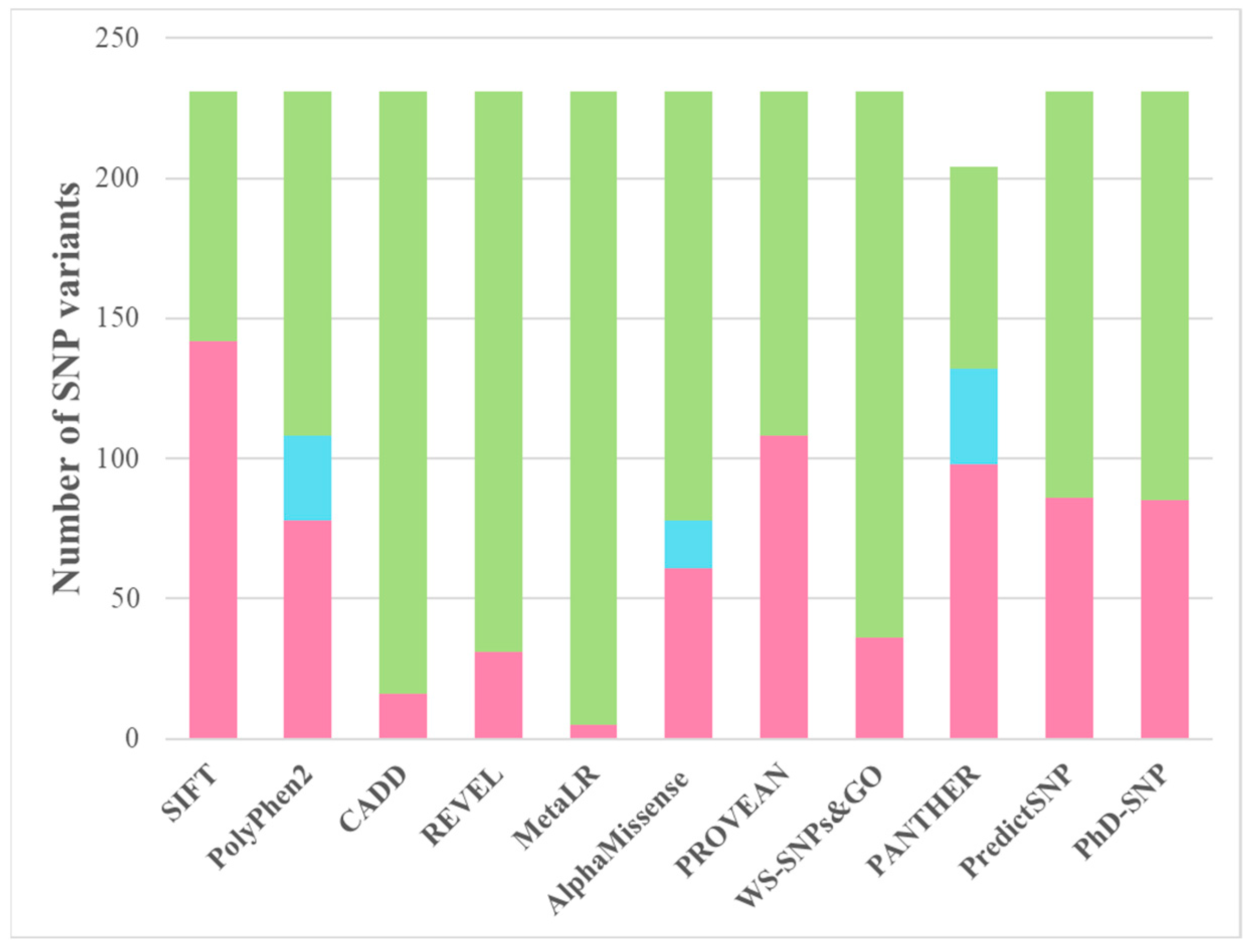
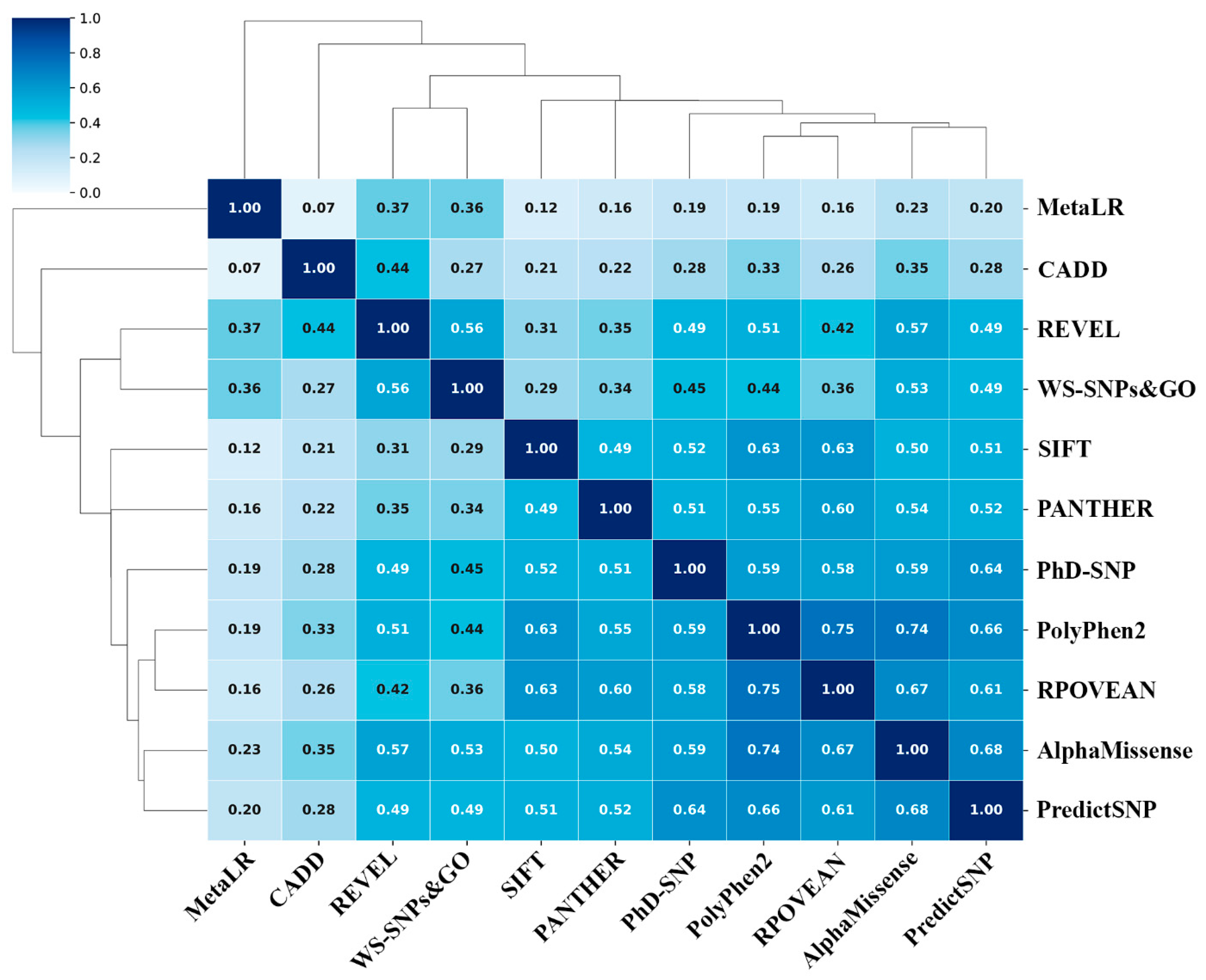
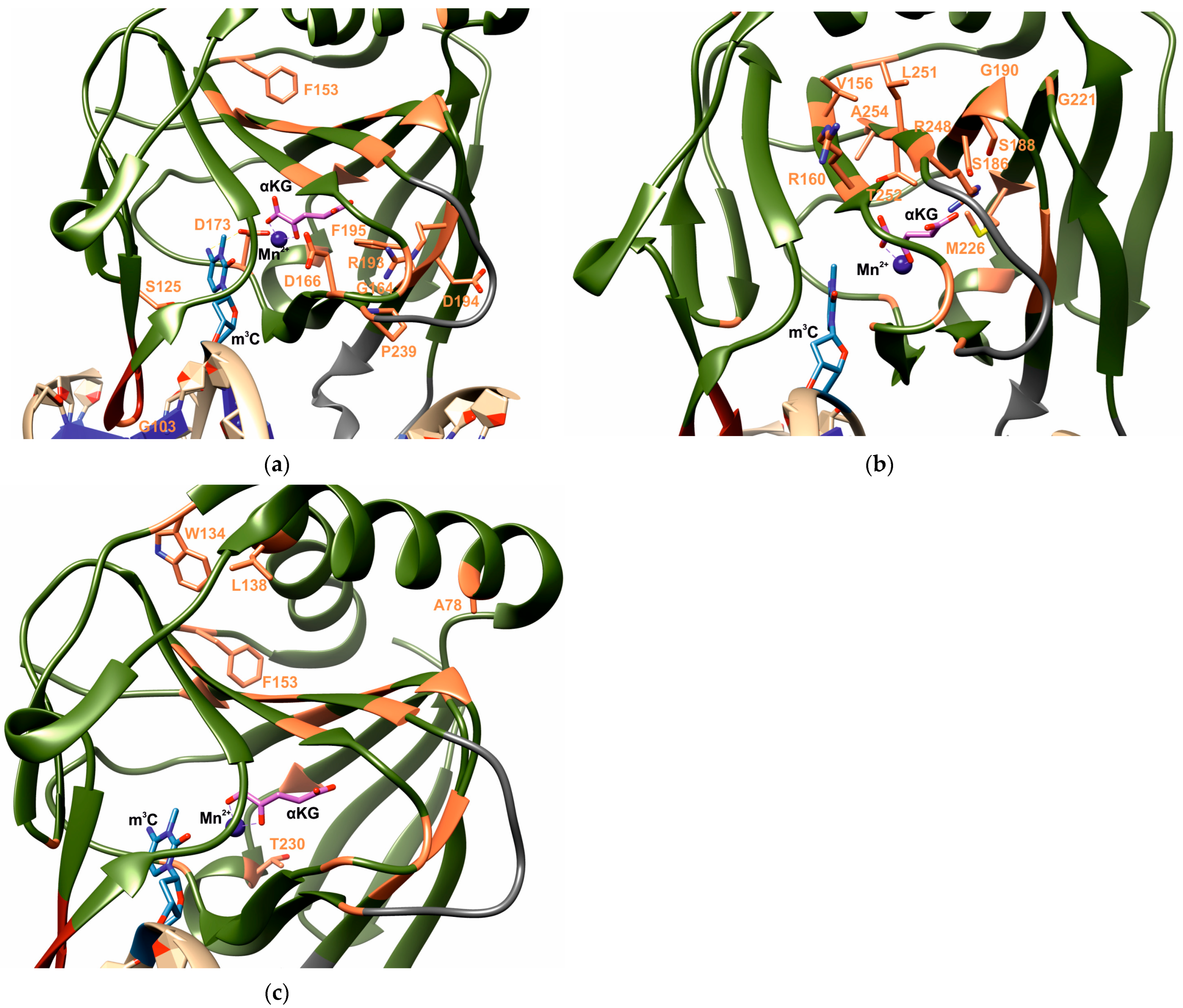
| Aa substitutions | SIFT | PolyPhen2 | CAAD | REVEL | MetaLR | Alpha Missense | PROVEAN | WS-SNPs&GO | PANTHER | PredictSNP | PhD-SNP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A78T | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. b. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| G103R | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| S125L | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. d. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | N. | Pr. ben. | Del. | Del. |
| W134C | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. d. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| W134R | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| L138P | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. d. | L. b. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| F153L | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | N. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| V156G | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| R160G | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. d. | L. b. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | N. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| G164D | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. b. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| D166G | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| D173N | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Dam. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| S186C | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. d. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | N. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| S186F | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. d. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | N. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| S188F | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. d. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| G190S | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. d. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| G190R | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. d. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| G190D | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| R193T | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. d. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| R193S | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. b. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| R193K | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| D194Y | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. d. | L. b. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| F195S | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. d. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| G221R | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| M226T | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| T230I | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | N. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| P239S | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | N. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| R248Q | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Dam. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| R248W | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Dam. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| L251P | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| T252I | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Tol. | l. p. | Dam. | N. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| R254C | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Dam. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
| R254H | Del. | Pr. dam. | L. b. | L. d. c. | Dam. | l. p. | Dam. | Dis. | Pr. dam. | Del. | Del. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davletgildeeva, A.T.; Tyugashev, T.E.; Sagalakova, V.V.; Zhao, M.; Kuznetsov, N.A. Predictive Analysis and Validation of Critical Missense SNPs of the ABH2 Gene Using Structural Bioinformatics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11593. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311593
Davletgildeeva AT, Tyugashev TE, Sagalakova VV, Zhao M, Kuznetsov NA. Predictive Analysis and Validation of Critical Missense SNPs of the ABH2 Gene Using Structural Bioinformatics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11593. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311593
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavletgildeeva, Anastasiia T., Timofey E. Tyugashev, Viktoriia V. Sagalakova, Mingxing Zhao, and Nikita A. Kuznetsov. 2025. "Predictive Analysis and Validation of Critical Missense SNPs of the ABH2 Gene Using Structural Bioinformatics" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11593. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311593
APA StyleDavletgildeeva, A. T., Tyugashev, T. E., Sagalakova, V. V., Zhao, M., & Kuznetsov, N. A. (2025). Predictive Analysis and Validation of Critical Missense SNPs of the ABH2 Gene Using Structural Bioinformatics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11593. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311593







