Unlocking the Hidden Potential of Agave tequilana for the Green Synthesis of Antibacterial ZnO Nanomaterials: A Waste-to-Value Nanotechnology Approach
Abstract
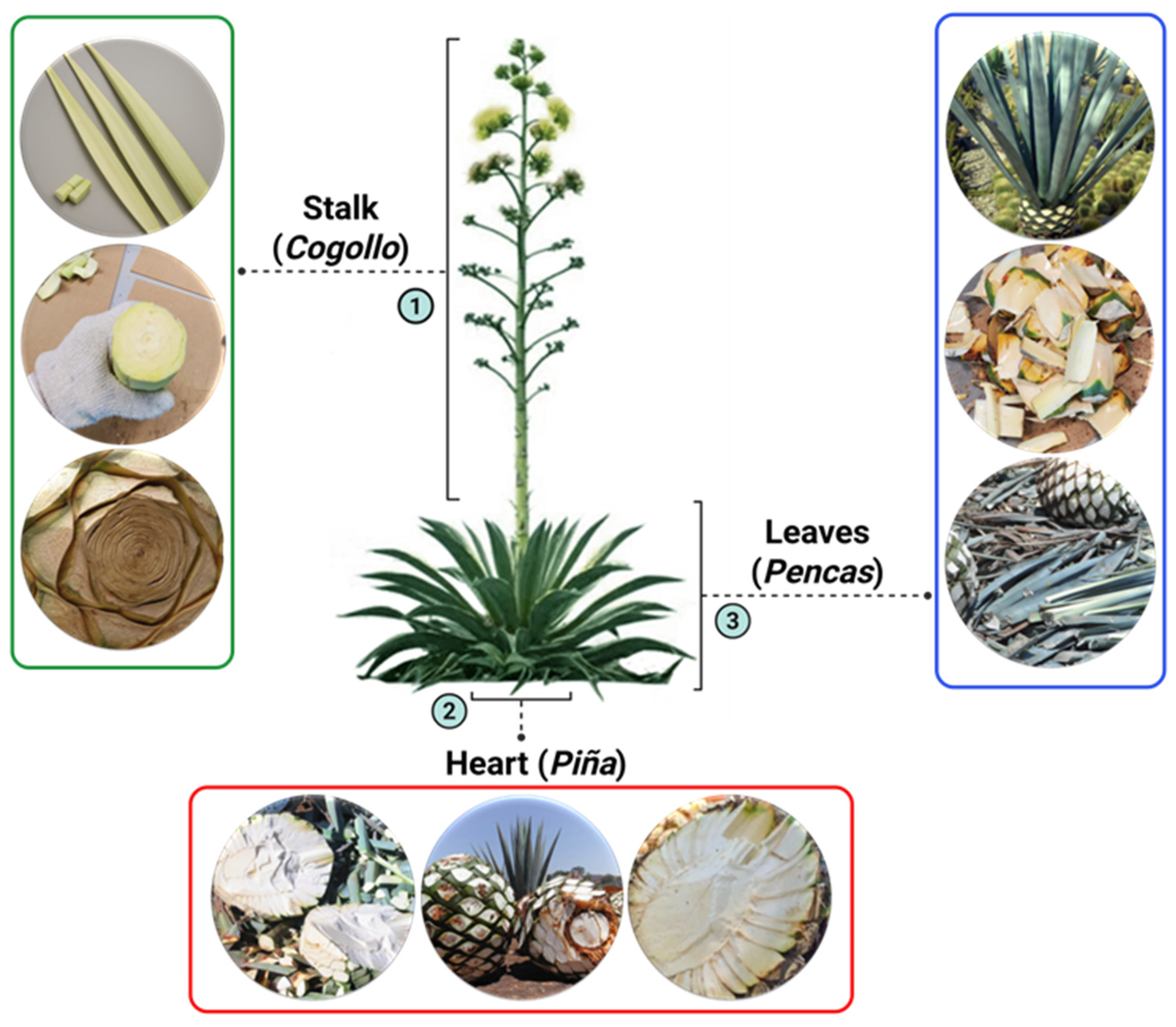
1. Introduction
2. Results
Antibacterial Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Collection of Plants (Agave tequilana)
4.3. Green Synthesis of ZnO-NPs Using Extracts of Different Parts of Agave tequilana
4.4. Materials Characterization
4.5. Antibacterial Activity Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Anti-Microbial Resistance |
| ZnO | Zinc Oxide |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| ZnO-NPs | Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles |
| MO | Metal Oxide |
| MO-NPs | Metal Oxide Nanoparticles |
| ZnO-S | Zinc Oxide Stalk |
| ZnO-H | Zinc Oxide Heart |
| ZnO-L | Zinc Oxide Leaves |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| XRD | X-Ray Diffraction |
| ATR | Attenuated Total Reflectance |
| FTIR | Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| FESEM | Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| EDS | Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| mL | Milliliter |
| g | Gram |
| mg | Milligram |
| µg | Microgram |
| Eg | Bandgap |
| eV | Electron Volt |
| NIR | Near-Infrared |
| nm | Nanometer |
| mm | Millimeter |
| cm | Centimeter |
| L | Liter |
| IZ | Inhibition Zones |
| FWHM | Full Width at Half Maximum |
| JCPDS | Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards |
References
- Tiwari, A.; Shaik, A.H.; Brianna, B.; Anwar, A.; Chandan, M.R. Anti-cancer and antimicrobial efficacy of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized via green route using Amaranthus dubius (Spleen Amaranth) leaves extract. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2025, 18, 2453532. [Google Scholar]
- Aldeen, T.S.; Mohamed, H.E.A.; Maaza, M. ZnO nanoparticles prepared via a green synthesis approach: Physical properties, photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2022, 160, 110313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, V.; Raizada, P.; Singh, P.; Cuong, H.N.; Saini, A.; Saini, R.V.; Van Le, Q.; Nadda, A.K.; Le, T.-T.; Nguyen, V.-H. Sustainable and green trends in using plant extracts for the synthesis of biogenic metal nanoparticles toward environmental and pharmaceutical advances: A review. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, S.; Jan, H.; Shah, S.A.; Shah, S.; Khan, A.; Akbar, M.T.; Rizwan, M.; Jan, F.; Wajidullah; Akhtar, N. Green synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using aqueous fruit extracts of Myristica fragrans: Their characterizations and biological and environmental applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9709–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshi, N.; Prashanthi, Y.; Rao, T.N.; Ahmed, F.; Kumar, S.; Oves, M. Biosynthesis of ZnO nanostructures using Azadirachta indica leaf extract and their effect on seed germination and seedling growth of tomato: An eco-friendly approach. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2020, 15, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sportelli, M.C.; Gaudiuso, C.; Volpe, A.; Izzi, M.; Picca, R.A.; Ancona, A.; Cioffi, N. Biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their application as bioactive agents: A critical overview. Reactions 2022, 3, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez-Salazar, M.I.; Niño-Castaño, V.E.; Dueñas-Cuellar, R.A.; Caldas-Arias, L.; Fernández, I.; Rodríguez-Páez, J.E. Chemical synthesis versus green synthesis to obtain ZnO powders: Evaluation of the antibacterial capacity of the nanoparticles obtained by the chemical method. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbaky, A.S.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Babalghith, A.O.; Selim, S.; Mohamed, A.M.J.A. Green synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles using Pelargonium odoratissimum (L.) aqueous leaf extract and their antioxidant, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activities. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusefi, M.; Shameli, K.; Ali, R.R.; Pang, S.-W.; Teow, S.-Y. Evaluating anticancer activity of plant-mediated synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles using Punica granatum fruit peel extract. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1204, 127539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad Khan, M.; Lone, S.A.; Shahid, M.; Zeyad, M.T.; Syed, A.; Ehtram, A.; Elgorban, A.M.; Verma, M.; Danish, M. Phytogenically synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) potentially inhibit the bacterial pathogens: In vitro studies. Toxics 2023, 11, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Morshedi, M. Cutting-edge nanotechnology: Unveiling the role of zinc oxide nanoparticles in combating deadly gastrointestinal tumors. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2025, 13, 1547757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aigbe, U.O.; Osibote, O.A. Green synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles, and their various applications. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 13, 100401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, R.; Obeid, R.Z.; Abu-Huwaij, R. Plant mediated-green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: An insight into biomedical applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2023, 12, 20230112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, M.; Kalegowda, N.; Gowtham, H.G.; Ansari, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Alghamdi, S.; Shilpa, N.; Singh, S.B.; Thriveni, M.; Aiyaz, M. Plant-mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles: Advances in the new millennium towards understanding their therapeutic role in biomedical applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channa, G.M.; Iturbe-Ek, J.; Sustaita, A.O.; Melo-Maximo, D.V.; Bhatti, A.; Esparza-Sanchez, J.; Navarro-Lopez, D.E.; Lopez-Mena, E.R.; Sanchez-Lopez, A.L.; Lozano, L.M. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles from Natural Agave, Chiku, and Soursop Extracts: A Sustainable Approach to Antibacterial Applications. Crystals 2025, 15, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhujaily, M.; Albukhaty, S.; Yusuf, M.; Mohammed, M.K.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Al-Karagoly, H.; Alyamani, A.A.; Albaqami, J.; AlMalki, F.A. Recent advances in plant-mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles with their significant biomedical properties. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwa, H.U.R.; Khan, M.K.; Abbas, Z.; Riaz, R.; Abbas, R.Z.; Aleem, M.T.; Abbas, A.; Almutairi, M.M.; Alshammari, F.A.; Alraey, Y.J.L. Nanoparticles: Synthesis and their role as potential drug candidates for the treatment of parasitic diseases. Life 2022, 12, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geioushy, R.A.; El-Sherbiny, S.; Mohamed, E.T.; Fouad, O.A.; Samir, M. Mechanical characteristics and antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus of sustainable cellulosic paper coated with Ag and Cu modified ZnO nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, G.H.; Shaly, A.A.; Ragu, R.; Evangelin, G.; Mani, J.; Martin, A.; Linet, J.M. ZnO nanoparticles with altered structural and optical traits by Cu and Li doping for elevated photocatalytic activity toward organic pollutants. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2024, 46, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Moosavi, F.; Neri, G. Effect of Pb doping on the structural, optical and electrical properties of sol–gel ZnO nanoparticles. Discov. Mater. 2023, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Xiao, Z.; Luo, Y. Sustainable Nanotechnology for Food Preservation: Synthesis, Mechanisms, and Applications of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 19, 101743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiouani, K.; Hegazy, S.; Alsaeedi, H.; Bechelany, M.; Barhoum, A. Green Synthesis of Hexagonal-like ZnO nanoparticles modified with phytochemicals of clove (Syzygium aromaticum) and Thymus capitatus extracts: Enhanced antibacterial, antifungal, and antioxidant activities. Materials 2024, 17, 4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilavenil, K.; Senthilkumar, V.; Kasthuri, A. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles from three medicinal plants: A review of environmental and health applications. Discov. Catal. 2025, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Ramos, D.I.; Ortiz-Basurto, R.I.; García-Barradas, O.; Chacón-López, M.A.; Montalvo-González, E.; Pascual-Pineda, L.A.; Valenzuela-Vázquez, U.; Jiménez-Fernández, M. Lauroylated, Acetylated, and Succinylated Agave tequilana Fructans Fractions: Structural Characterization, Prebiotic, Antibacterial Activity and Their Effect on Lactobacillus paracasei under Gastrointestinal Conditions. Polymers 2023, 15, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, A.V.; Simpson, J.; Clench, M.R.; Gomez-Vargas, A.D.; Ordaz-Ortiz, J.J. Localization and Composition of Fructans in Stem and Rhizome of Agave tequilana Weber var. azul. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 608850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riwayati, I.; Winardi, S.; Madhania, S.; Shimada, M. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Cosmos caudatus: Effects of calcination temperature and precursor type on photocatalytic and antimicrobial activities. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Khan, M.A. Plant-derived metal nanoparticles (PDMNPs): Synthesis, characterization, and oxidative stress-mediated therapeutic actions. Future Pharmacol. 2023, 3, 252–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, M.; Mishra, D.; Sahoo, G. A review on green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, P.; Paul, D.R.; Sharma, A.; Choudhary, P.; Meena, P.; Nehra, S. Biogenic mediated Ag/ZnO nanocomposites for photocatalytic and antibacterial activities towards disinfection of water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 563, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, P.; Paul, D.R.; Sharma, A.; Hooda, D.; Yadav, R.; Meena, P.; Nehra, S.P. Phytoextract mediated ZnO/MgO nanocomposites for photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 385, 112049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, F.; Mascitti, A.; Rastelli, G.; d’Alessandro, N.; Tonucci, L. Sustainable Photocatalytic Reduction of Maleic Acid: Enhancing CuxO/ZnO Stability with Polydopamine. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golzarnezhad, F.; Allahdou, M.; Mehravaran, L.; Naderi, S. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles from the extract of Cymbopogon olivieri and investigation of their antimicrobial and anticancer effects. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Somaiah, S. Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Thryallis glauca (Cav.) Kuntze and their role as antioxidant and antibacterial. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2022, 85, 2835–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanimozhi, S.; Durga, R.; Sabithasree, M.; Kumar, A.V.; Sofiavizhimalar, A.; Kadam, A.A.; Rajagopal, R.; Sathya, R.; Azelee, N.I.W. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticle using Cissus quadrangularis extract and its invitro study. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2022, 34, 101930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, M.; Aslam, U.; Khalid, B.; Chen, B. Green route to synthesize Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Cassia fistula and Melia azadarach and their antibacterial potential. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Abdallah, Y.; Ali, M.A.; Masum, M.M.I.; Li, B.; Sun, G.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; An, Q. Lemon-fruit-based green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and titanium dioxide nanoparticles against soft rot bacterial pathogen Dickeya dadantii. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, S.S.; Sani, A.M.; Mohseni, S. Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles from leaf extract of Mentha pulegium (L.). Microb. Pathog. 2019, 131, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manojkumar, U.; Kaliannan, D.; Srinivasan, V.; Balasubramanian, B.; Kamyab, H.; Mussa, Z.H.; Palaniyappan, J.; Mesbah, M.; Chelliapan, S.; Palaninaicker, S. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Brassica oleracea var. botrytis leaf extract: Photocatalytic, antimicrobial and larvicidal activity. Chemosphere 2023, 323, 138263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, H.; Venugopal, K.; Rajagopal, K.; De Britto, S.; Nandini, B.; Pushpalatha, H.G.; Konappa, N.; Udayashankar, A.C.; Geetha, N.; Jogaiah, S. Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Eucalyptus globules and their fungicidal ability against pathogenic fungi of apple orchards. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, A.; Khatami, M.; Ebrahimy, O.; Sarani, M. Cytotoxic and antifungal studies of biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using extract of Prosopis farcta fruit. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2020, 13, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavithaa, K.; Paulpandi, M.; Ponraj, T.; Murugan, K.; Sumathi, S. Induction of intrinsic apoptotic pathway in human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells through facile biosynthesized zinc oxide nanorods. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2016, 2, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamah, S.A.; Albukhaty, S.; Falih, I.Q.; Dewir, Y.H.; Mahood, H.B. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Capparis spinosa L. fruit extract: Characterization, biocompatibility, and antioxidant activity. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efati, Z.; Shahangian, S.S.; Darroudi, M.; Amiri, H.; Hashemy, S.I.; Aghamaali, M.R. Green chemistry synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles in Lepidium sativum L. seed extract and evaluation of their anticancer activity in human colorectal cancer cells. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 32568–32576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, T.; Lokhande, R.; Khadke-Lokhande, L.; Chandorkar, J. Green synthesis, characterization, application and study of antimicrobial properties of zinc oxide nano particles using Cyathocline purpurea phytoextract. Pharma. Innov. 2023, 12, 2627–2633. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.H.; Andia, J.D.; Manjunatha, S.; Murali, M.; Amruthesh, K.; Jagannath, S. Antimitotic and DNA-binding potential of biosynthesized ZnO-NPs from leaf extract of Justicia wynaadensis (Nees) Heyne-A medicinal herb. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 101024. [Google Scholar]
- Kavya, J.; Murali, M.; Manjula, S.; Basavaraj, G.; Prathibha, M.; Jayaramu, S.; Amruthesh, K. Genotoxic and antibacterial nature of biofabricated zinc oxide nanoparticles from Sida rhombifolia Linn. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 101982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunchegowda, U.A.; Shivaram, A.B.; Mahadevamurthy, M.; Ramachndrappa, L.T.; Lalitha, S.G.; Krishnappa, H.K.N.; Anandan, S.; Sudarshana, B.S.; Chanappa, E.G.; Ramachandrappa, N.S. Biosynthesis of Zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Passiflora subpeltata: Characterization and antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli isolated from poultry faeces. J. Clust. Sci. 2021, 32, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melk, M.M.; El-Hawary, S.S.; Melek, F.R.; Saleh, D.O.; Ali, O.M.; El Raey, M.A.; Selim, N.M. Nano zinc oxide green-synthesized from Plumbago auriculata lam. alcoholic extract. Plants 2021, 10, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Awadh, A.A.; Shet, A.R.; Patil, L.R.; Shaikh, I.A.; Alshahrani, M.M.; Nadaf, R.; Mahnashi, M.H.; Desai, S.V.; Muddapur, U.M.; Achappa, S. Sustainable synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Raphanus sativus extract and its biomedical applications. Crystals 2022, 12, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Gunasangkaran, G.; Arumugam, V.A.; Muthukrishnan, S. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles of solanum nigrum and its anticancer activity via the induction of apoptosis in cervical cancer. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2022, 200, 2684–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, S.; Vaseeharan, B.; Malaikozhundan, B.; Shobiya, M. Laurus nobilis leaf extract mediated green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: Characterization and biomedical applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, M.; Varma, R.S.; Zafarnia, N.; Yaghoobi, H.; Sarani, M.; Kumar, V.G. Applications of green synthesized Ag, ZnO and Ag/ZnO nanoparticles for making clinical antimicrobial wound-healing bandages. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2018, 10, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, K.; Nazli, Z.-i.-H.; Munir, H.; Aslam, M.; Khalofah, A. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera leaf extract, probing antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 20413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, N.; Saha, S.; Chakraborty, M.; Maiti, M.; Das, S.; Basu, R.; Nandy, P. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Hibiscus subdariffa leaf extract: Effect of temperature on synthesis, anti-bacterial activity and anti-diabetic activity. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 4993–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregoso-Zamorano, B.E.; Mancilla-Villa, O.R.; Guevara-Gutiérrez, R.D.; Moreno-Hernández, A.; Figueroa-Bautista, P.; Can-Chulim, Á.; Hernández-Vargas, O.; Cruz-Crespo, E.; Ortega-Escobar, H.M.; Khalil Gardezi, A.J.T.L. Caracterización edafológica con cultivo de agave azul (Agave tequilana Weber) en Tonaya y Tuxcacuesco, Jalisco, México. Terra Latinoam. 2023, 41, e1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetreault, D.; McCulligh, C.; Lucio, C. Distilling agro-extractivism: Agave and tequila production in Mexico. J. Agrar. Chang. 2021, 21, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Villalba, W.G.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Ochoa-Martínez, L.A.; Rutiaga-Quiñones, O.M.; Gallegos-Infante, J.A.; González-Herrera, S.M. Agave fructans: A review of their technological functionality and extraction processes. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Chávez, J.; Villamiel, M.; Santos-Zea, L.; Ramírez-Jiménez, A.K. Agave by-products: An overview of their nutraceutical value, current applications, and processing methods. Polysaccharides 2021, 2, 720–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Sohnius, E.-M.; Attig, R.; López, M.G. Quantification of selected volatile constituents and anions in Mexican Agave spirits (Tequila, Mezcal, Sotol, Bacanora). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3911–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhrani, M.A.; Tahira, A.; Bhatti, M.A.; Shah, A.A.; Shaikh, N.M.; Mari, R.H.; Vigolo, B.; Emo, M.; Albaqami, M.D.; Nafady, A. A green approach for the preparation of ZnO@C nanocomposite using agave americana plant extract with enhanced photodegradation. Nanotechnology 2022, 33, 505202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Hernández, J.M.; Escalante, A.; Murillo-Vázquez, R.N.; Delgado, E.; González, F.J.; Toríz, G. Use of Agave tequilana-lignin and zinc oxide nanoparticles for skin photoprotection. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 163, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, R.; Tinel, L.; Gonzalez, L.; Ciuraru, R.; Bernard, F.; George, C.; Volkamer, R. UV photochemistry of carboxylic acids at the air-sea boundary: A relevant source of glyoxal and other oxygenated VOC in the marine atmosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulet, J.C.; Ducasse, M.A.; Cheynier, V. Ultraviolet spectroscopy study of phenolic substances and other major compounds in red wines: Relationship between astringency and the concentration of phenolic substances. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2017, 23, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; LaRocca, C.A.; Bernat, J.D.; Lindsey, J.S. Digital database of absorption spectra of diverse flavonoids enables structural comparisons and quantitative evaluations. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 1087–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsipur, M.; Roushani, M.; Pourmortazavi, S.M. Electrochemical synthesis and characterization of zinc oxalate nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, S.A.; Wissa, D.; Hassan, H.; Ebnalwaled, A.; Khairy, S. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using low-cost plant extracts. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Gu, H. Ultraviolet detectors based on wide bandgap semiconductor nanowire: A review. Sensors 2018, 18, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, H.; Waheed, A.; Sharif, M.S.; Saleem, M.; Afreen, A.; Tariq, M.; Kamal, A.; Al-Onazi, W.A.; Al Farraj, D.A.; Ahmad, S. Green synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles from green algae and their assessment in various biological applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoohinkong, W.; Foophow, T.; Pecharapa, W. Synthesis and characterization of copper zinc oxide nanoparticles obtained via metathesis process. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 035003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Sharma, A.; Anand, K.; Panday, A.; Tagotra, S.; Kakran, S.; Singh, A.K.; Alam, M.W.; Kumar, S.; Bouzid, G. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using E. cardamomum and zinc nitrate precursor: A dual-functional material for water purification and antibacterial applications. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 16742–16765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.B.; Iftikhar, T.; Majeed, H. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles for the industrial biofortification of (Pleurotus pulmonarius) mushrooms. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaba, M.H.; El-Sherbiny, G.M.; Ewais, E.A.; Darwesh, O.M.; Moghannem, S.A. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) by Streptomyces baarnensis and its active metabolite (Ka): A promising combination against multidrug-resistant ESKAPE pathogens and cytotoxicity. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, K.; Asif, M.; Farooq, U.; Gilani, S.J.; Bin Jumah, M.N.; Ahmed, M.M. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory applications of Aerva persica aqueous-root extract-mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 15882–15892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.; Saied, E.; Eid, A.M.; Kouadri, F.; Alemam, A.M.; Hamza, M.F.; Alharbi, M.; Elkelish, A.; Hassan, S.E.-D. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using an aqueous extract of Punica granatum for antimicrobial and catalytic activity. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, M.; Kumar, S.; Gaur, J.; Kaushal, S.; Dalal, J.; Singh, G.; Misra, M.; Ahlawat, D.S. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Justicia adhatoda for photocatalytic degradation of malachite green and reduction of 4-nitrophenol. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 2958–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Ramírez, S.d.C.; Valle, E.-d.; Raymundo, J.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, G.; Ruíz-Luna, J.; Velasco-Velasco, V.A. Growth of Agave angustifolia Haw. In relation to its nutritional condition. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agríc. 2021, 12, 865–873. [Google Scholar]
- Babayevska, N.; Przysiecka, Ł.; Iatsunskyi, I.; Nowaczyk, G.; Jarek, M.; Janiszewska, E.; Jurga, S. ZnO size and shape effect on antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity profile. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Habib, I.; Maatouk, H.; Lemarchand, A.; Dine, S.; Roynette, A.; Mielcarek, C.; Traoré, M.; Azouani, R. Antibacterial size effect of ZnO nanoparticles and their role as additives in emulsion waterborne paint. J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irede, E.L.; Awoyemi, R.F.; Owolabi, B.; Aworinde, O.R.; Kajola, R.O.; Hazeez, A.; Raji, A.A.; Ganiyu, L.O.; Onukwuli, C.O.; Onivefu, A.P. Cutting-edge developments in zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis and applications for enhanced antimicrobial and UV protection in healthcare solutions. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 20992–21034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, J.; Chu, Y.; Guo, R.; Chen, P. Research on the antibacterial properties of nanoscale zinc oxide particles comprehensive review. Front. Mater. 2024, 11, 1449614. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Natural Resources; Species Survival Commission. IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]









| Plant Source | Part Used | Shape of NPs | Size (nm) | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lemongrass (Cymbopogon olivieri) | Leaves | Spherical | 28 | Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activity | [32] |
| Rain of Gold (Thryallis glauca) | Leaves | Hexagonal Wurtzite | 50 | Antioxidants and Antibacterial Activity | [33] |
| Veldt Grape (Cissus quadrangularis) | Stem | Spherical | 75–90 | Antibacterial and Anticancer Activity | [34] |
| Golden Shower Tree (Cassia fistula) | Leaves | Spherical | 68 | Antibacterial Activity | [35] |
| Lemon (Citrus limon) | Fruit | Cuboid, Hexagonal Prism, Thin Rods | 60.8 | Antibacterial and Antihemolytic Activity | [36] |
| Pennyroyal (Mentha pulegium) | Leaves | Semi Spherical | 40 | Antimicrobial Activity | [37] |
| Cauliflower (Brassica Var. botrytis) | Leaves | Flower Like | 52 | Antimicrobial Larvicidal Activity | [38] |
| Tasmanian Blue Gum (Eucalyptus globules) | Leaves | Spherical | 52–70 | Antifungal Activity | [39] |
| Syrian Mesquite (Prosopis farcta) | Aerial | Hexagonal | 40–80 | Antifungal and Breast Cancer (MCF-7) Activity | [40] |
| Sandalwood (Santalum album) | Leaves | Nanorods | 100 | Brest Cancer (MCF-7) Activity | [41] |
| Caper Bush (C. spinosa L.) | Fruit | Spherical | 37.49 | Antioxidant Activity | [42] |
| Garden Cress (Lepidium sativum) | Seeds | Spherical | 37–45 | Anticancer Activity | [43] |
| Gangotra (Cyathocline purpurea) | Leaves | Spherical | 80–120 | Antimicrobial Activity | [44] |
| Maddu Toppu (Justicia wynaadensis) | Leaves | Hexagonal Wurtzite | 39 | Antimitotic and DNA-Binding | [45] |
| Arrowleaf Sida (Sida rhombifolia Linn) | Leaves | Spherical | 30.23 | Genotoxic and Antibacterial Activity | [46] |
| White Passionflower (Passiflora subpeltata) | Leaves | Hexagonal | 45–50 | Antibacterial Activity | [47] |
| Cape Leadwort (Plumbago auriculata) | Aerial | Hexagonal | 38.3 | Antiviral Activity | [48] |
| Radish (Raphanus sativus) | Leaves | Spherical/Hexagonal | 66.47 | Breast Cancer Cells Antibacterial Activity | [49] |
| Black Nightshade (Solanum nigrum) | Leaves | Quasi-Spherical | 30 | Anticancer Activity | [50] |
| Bay Laurel (Laurus nobilis) | Leaves | Flower | 47.27 | Antibacterial Activity | [51] |
| Sweet Leaf (Stevia) | Leaves | Rectangular | 50 | Antimicrobial Wound-healing Bandages | [52] |
| Horseradish Tree (Moringa oleifera) | Leaves | Spherical | 52.24 | Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activity | [53] |
| Roselle (Hibiscus subdariffa) | Leaves | Dumbbell | 190 | Antibacterial and Antidiabetic Activity | [54] |
| Nanomaterials Concentrations (μg/mL) | Zone of Inhibition (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO-S | ZnO-H | ZnO-L | ||||
| S. aureus | E. coli | S. aureus | E. coli | S. aureus | E. coli | |
| 5 | 14.52 ± 0.06 | 13.27 ± 0.30 | 10.93 ± 0.64 | 9.37 ± 0.23 | 9.48 ± 0.31 | 8.76 ± 0.78 |
| 10 | 15.48 ± 0.13 | 14.55 ± 0.73 | 11.70 ± 0.68 | 10.48 ± 0.47 | 10.88 ± 0.21 | 9.69 ± 0.32 |
| 20 | 16.05 ± 0.27 | 15.21 ± 0.44 | 12.44 ± 0.43 | 12.21 ± 0.59 | 11.44 ± 0.30 | 10.92 ± 0.50 |
| 30 | 17.37 ± 0.17 | 17.45 ± 0.48 | 13.57 ± 0.45 | 13.62 ± 0.53 | 11.83 ± 0.35 | 12.69 ± 0.82 |
| 40 | 18.34 ± 0.18 | 18.55 ± 0.46 | 14.41 ± 0.26 | 15.03 ± 0.61 | 12.27 ± 0.39 | 14.50 ± 0.27 |
| 50 | 21.49 ± 0.52 | 20.18 ± 0.76 | 18.02 ± 0.55 | 17.96 ± 0.53 | 14.24 ± 0.68 | 15.92 ± 0.19 |
| Control (Kanamycin) | 23.14 ± 0.38 | 22.53 ± 0.30 | 23.40 ± 0.56 | 19.19 ± 0.72 | 22.78 ± 0.69 | 17.87 ± 0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Channa, G.M.; Bhatti, A.; Sotelo, J.G.; Obregón, S.; Sánchez-Arreola, E.; Mejía-Méndez, J.L.; Navarro-López, D.E.; López-Mena, E.R.; Sánchez-López, A.L.; Lozano, L.M. Unlocking the Hidden Potential of Agave tequilana for the Green Synthesis of Antibacterial ZnO Nanomaterials: A Waste-to-Value Nanotechnology Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311545
Channa GM, Bhatti A, Sotelo JG, Obregón S, Sánchez-Arreola E, Mejía-Méndez JL, Navarro-López DE, López-Mena ER, Sánchez-López AL, Lozano LM. Unlocking the Hidden Potential of Agave tequilana for the Green Synthesis of Antibacterial ZnO Nanomaterials: A Waste-to-Value Nanotechnology Approach. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311545
Chicago/Turabian StyleChanna, Ghulam Mustafa, Atiya Bhatti, Juan G. Sotelo, Sergio Obregón, Eugenio Sánchez-Arreola, Jorge L. Mejía-Méndez, Diego E. Navarro-López, Edgar R. López-Mena, Angélica Lizeth Sánchez-López, and Luis Marcelo Lozano. 2025. "Unlocking the Hidden Potential of Agave tequilana for the Green Synthesis of Antibacterial ZnO Nanomaterials: A Waste-to-Value Nanotechnology Approach" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311545
APA StyleChanna, G. M., Bhatti, A., Sotelo, J. G., Obregón, S., Sánchez-Arreola, E., Mejía-Méndez, J. L., Navarro-López, D. E., López-Mena, E. R., Sánchez-López, A. L., & Lozano, L. M. (2025). Unlocking the Hidden Potential of Agave tequilana for the Green Synthesis of Antibacterial ZnO Nanomaterials: A Waste-to-Value Nanotechnology Approach. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311545











