STING Restricts EV-A71 Infection by Regulating T Cell Development and Enhancing Immune Cell Effector Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
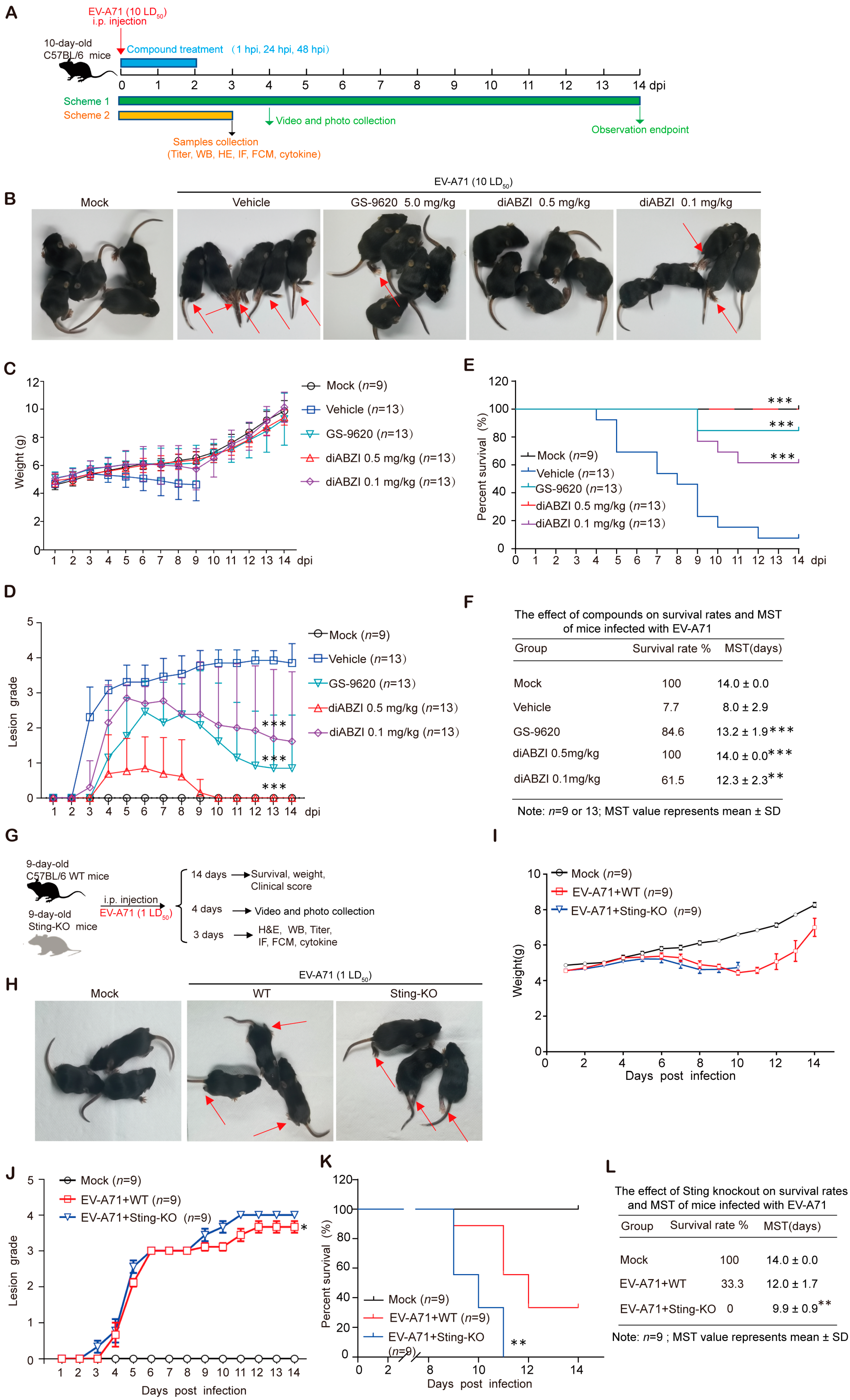
2.1. STING Activation Improves Survival Rates and Relieves Clinical Symptoms of EV-A71-Infected Mice
2.2. STING Knockout Significantly Enhances the Lethality and Exacerbates Severity of EV-A71 Infection in Mice
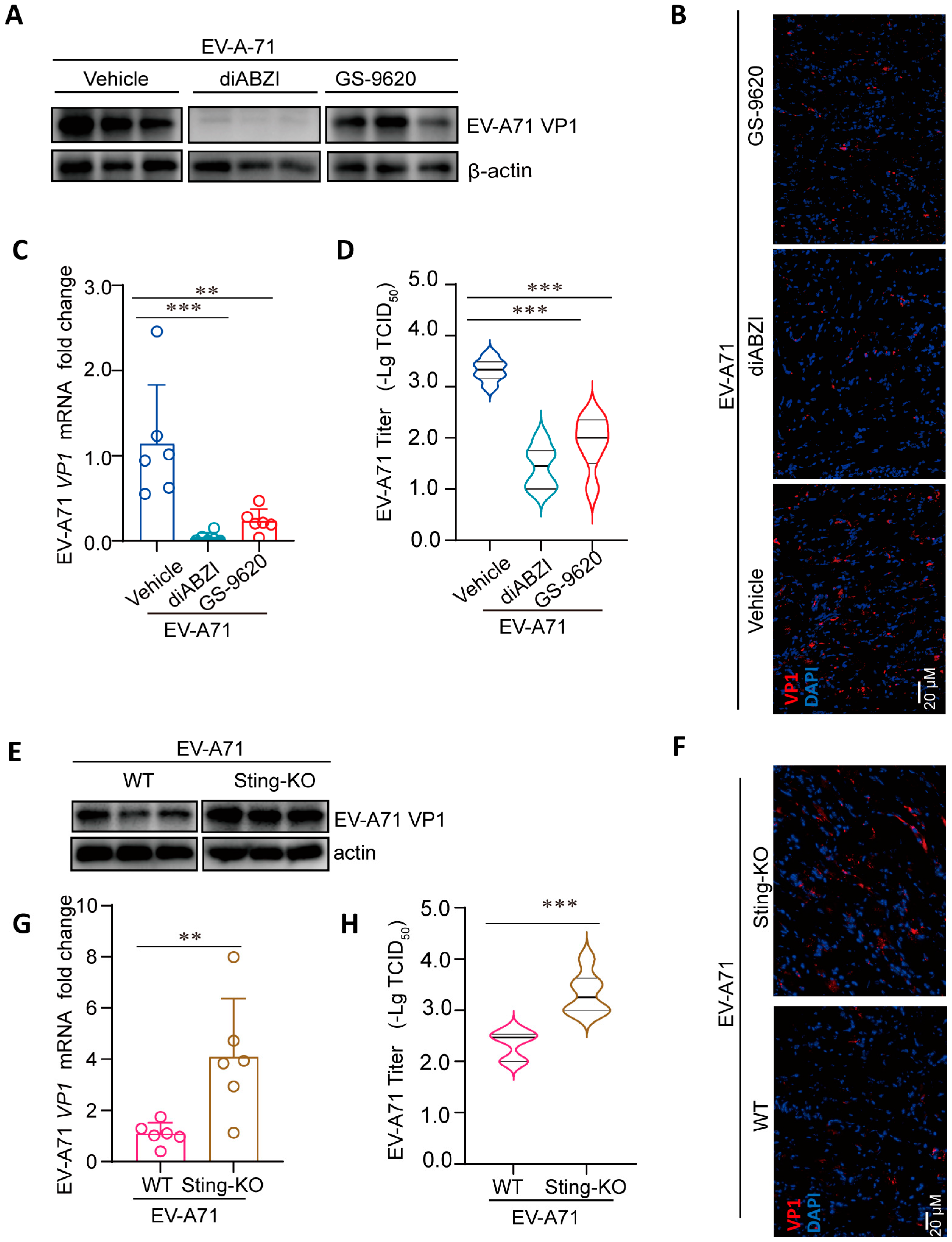
2.3. Regulation of STING Affects the Replication of EV-A71 in Mice
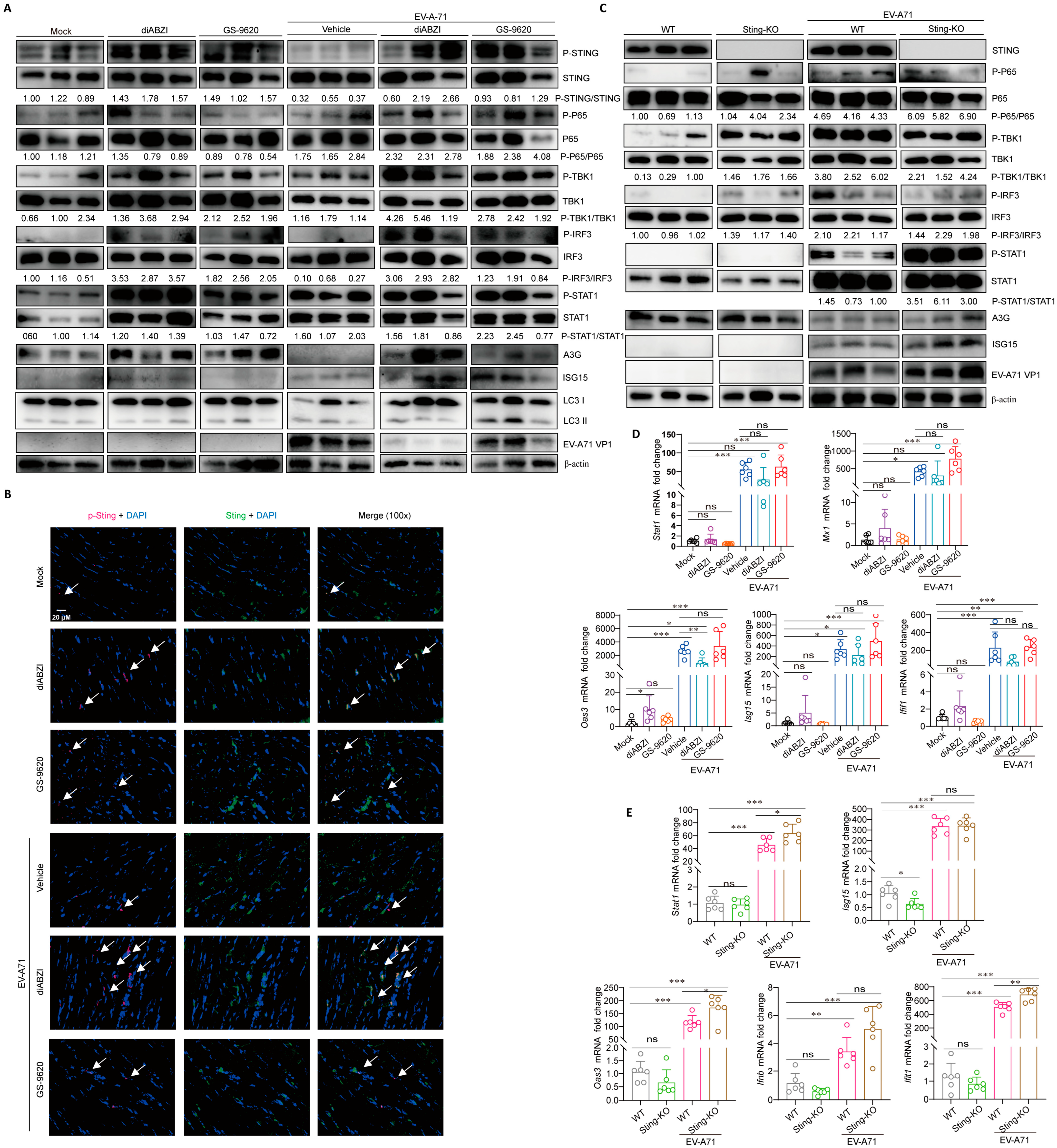
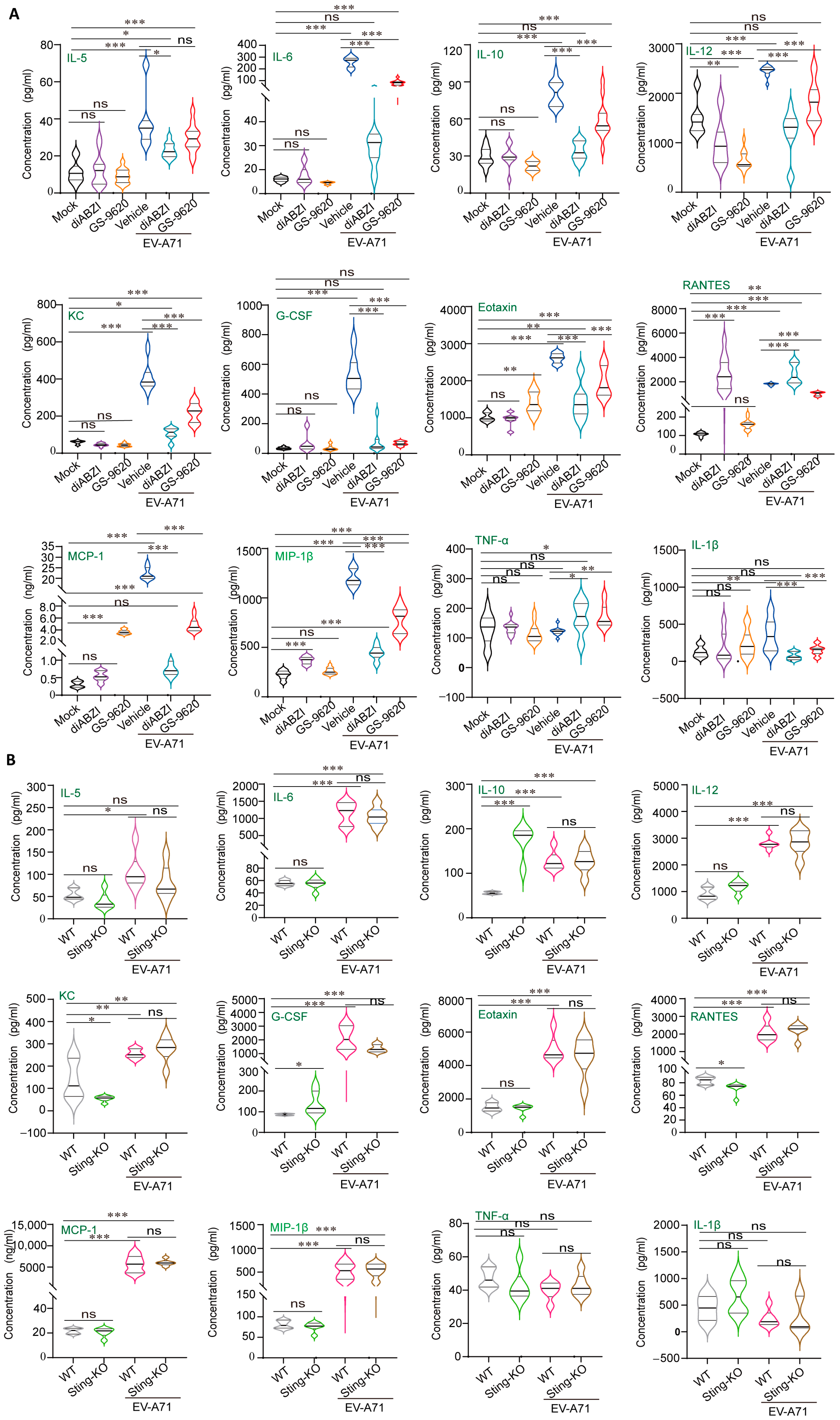
2.4. STING Affects Viral Replication Through the Regulation of Immunity and Inflammation
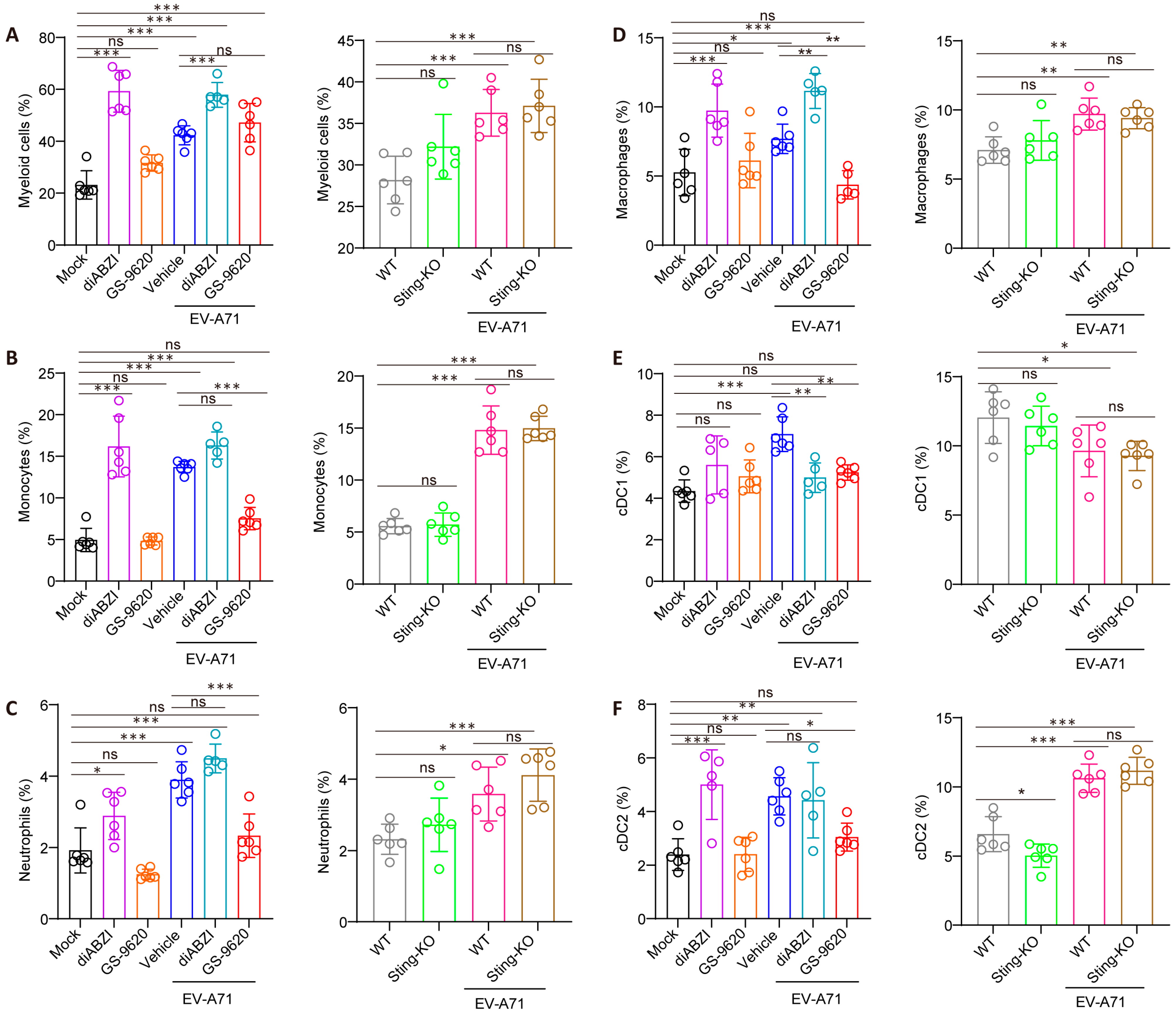
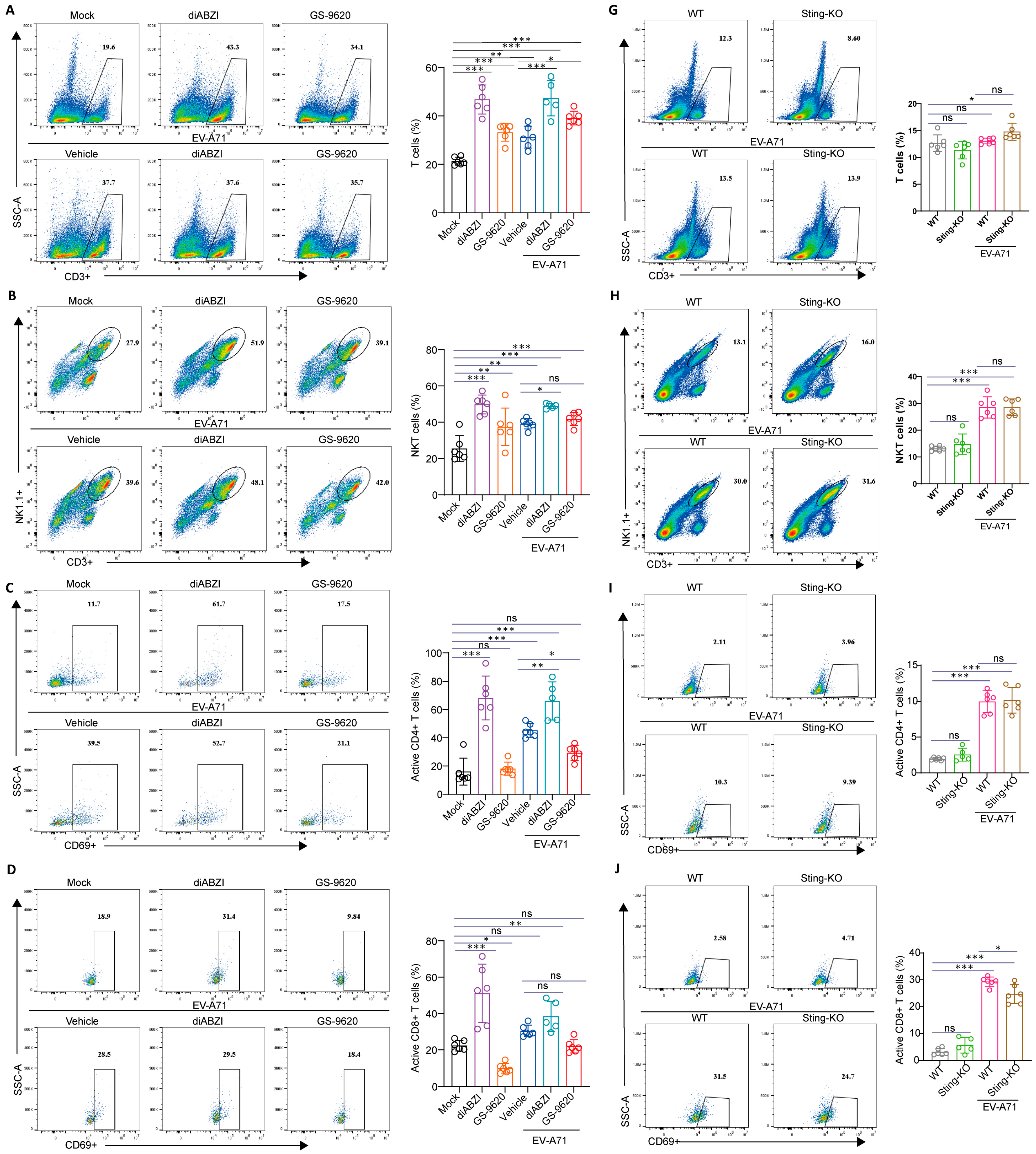
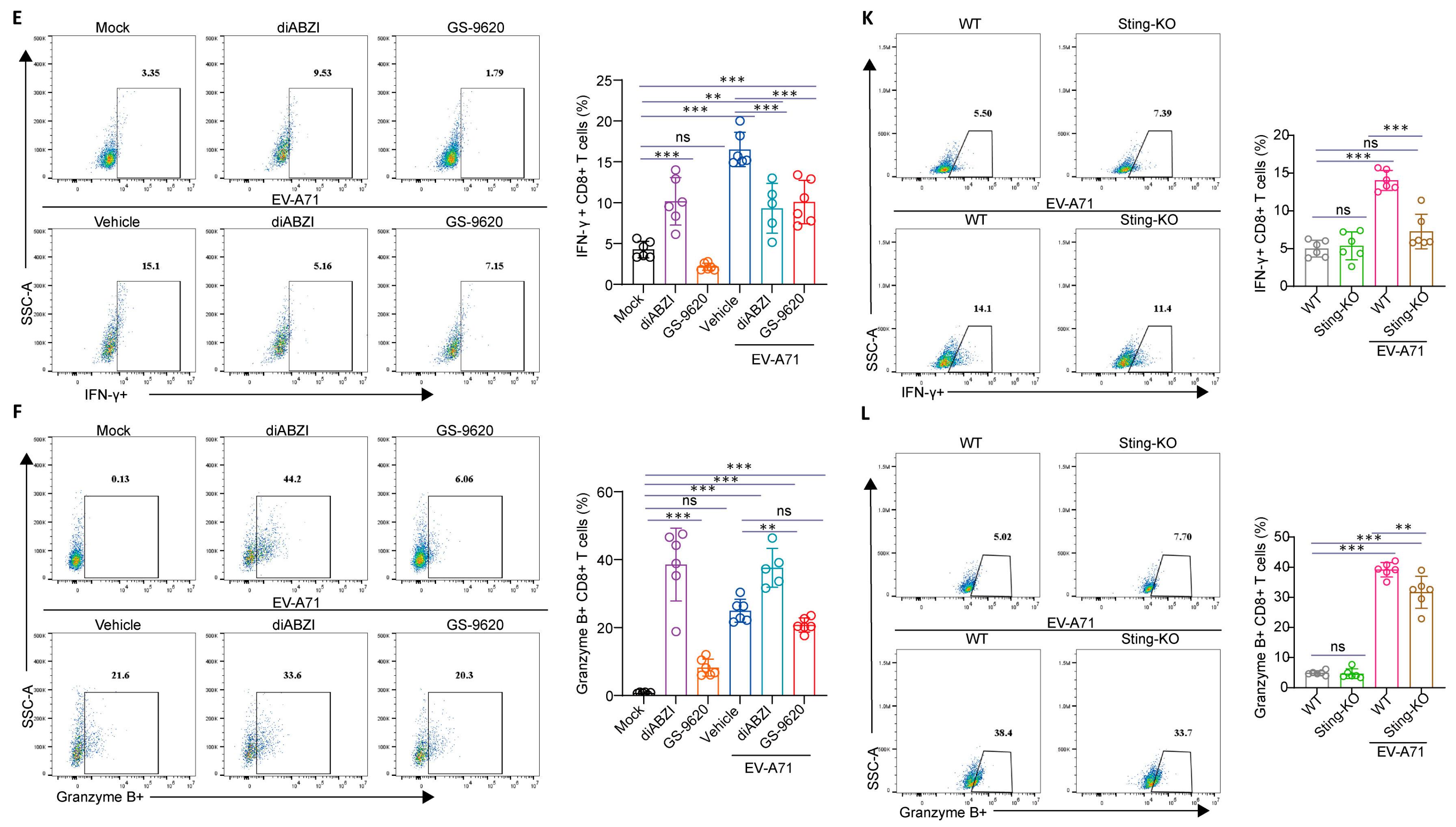
2.5. The Effect of STING on the Composition and Function of Immune Cells in the Spleen
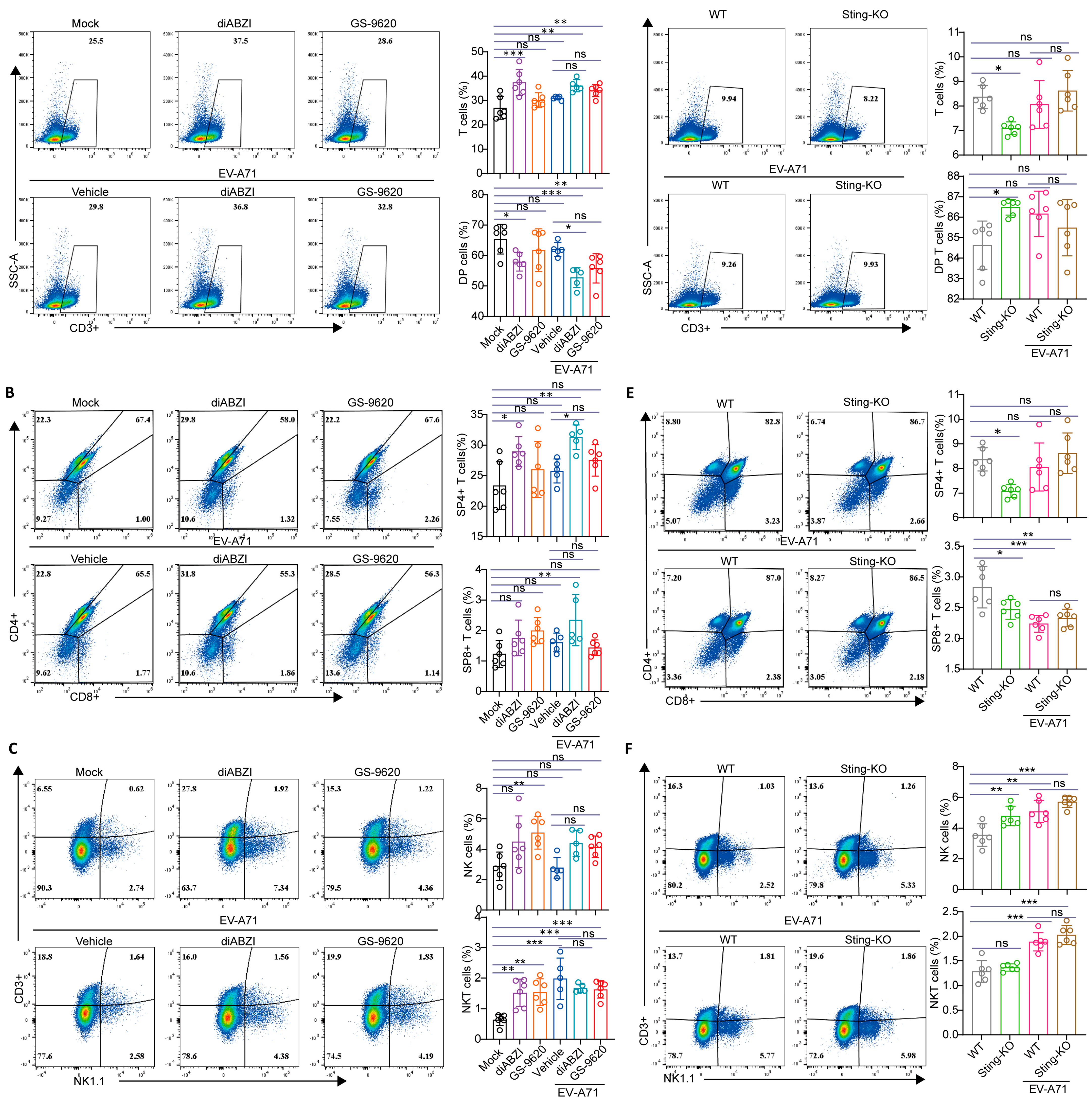
2.6. The Impact of STING on T-Cell Development in the Thymus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Viruses
4.2. Mice
4.3. Compounds
4.4. In Vivo Antiviral Study of diABZI and GS-9620
4.5. Effect of STING Knockout on EV-A71 Infection In Vivo
4.6. Quantitative Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Assay
4.7. Western Blot (WB) Assay
4.8. Virus Titer Determination in the Infected Mice
4.9. Immunofluorescent (IF) Staining
4.10. Multi-Cytokine/Chemokine Measurement by Luminex-Based Cytokine Bead Array
4.11. Flow Cytometry
4.12. Quantification and Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, B.S. Critical role of TLR activation in viral replication, persistence, and pathogenicity of Theiler’s virus. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1167972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isazadeh, A.; Heris, J.A.; Shahabi, P.; Mohammadinasab, R.; Shomali, N.; Nasiri, H.; Valedkarimi, Z.; Khosroshahi, A.J.; Hajazimian, S.; Akbari, M.; et al. Pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) in SARS-CoV-2. Life Sci. 2023, 329, 121940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, M.; Kato, H.; Fujita, T. Physiological functions of RIG-I-like receptors. Immunity 2024, 57, 731–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Shen, S.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; Cheng, L.; Cai, Y.; Wei, W.; Wang, Y.; Rui, Y.; Yu, X.-F. SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a inhibits cGAS-STING-mediated autophagy flux and antiviral function. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xue, Q.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Xue, Z.; Cao, W.; He, J.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Innate sensing of picornavirus infection involves cGAS-STING-mediated antiviral responses triggered by mitochondrial DNA release. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Li, Y.; Diao, F.; Lei, C.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Tien, P.; et al. The adaptor protein MITA links virus-sensing receptors to IRF3 transcription factor activation. Immunity 2008, 29, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, P.H.; Yuen, T.L.; Tang, T.T.; Leung, H.Y.; Lee, T.T.; Chan, P.; Cheng, Y.; Fung, S.-Y.; Ye, Z.-W.; Chan, C.-P. Age-Dependent Pathogenesis of Influenza A Virus H7N9 Mediated Through PB1-F2-Induced Mitochondrial DNA Release and Activation of cGAS-STING-NF-κB Signaling. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e70062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Chen, Z.J. STING specifies IRF3 phosphorylation by TBK1 in the cytosolic DNA signaling pathway. Sci. Signal 2012, 5, ra20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amurri, L.; Horvat, B.; Iampietro, M. Interplay between RNA viruses and cGAS/STING axis in innate immunity. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1172739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, T.; Little, M.A.; Brady, G. Targeting of the cGAS-STING system by DNA viruses. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 174, 113831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, S.; Maestre, A.M.; Pagni, S.; Patel, J.R.; Savage, T.; Gutman, D.; Maringer, K.; Bernal-Rubio, D.; Shabman, R.S.; Simon, V.; et al. DENV inhibits type I IFN production in infected cells by cleaving human STING. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gordesky-Gold, B.; Leney-Greene, M.; Weinbren, N.L.; Tudor, M.; Cherry, S. Inflammation-Induced, STING-Dependent Autophagy Restricts Zika Virus Infection in the Drosophila Brain. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 57–68.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Rui, Y.; Lou, M.; Yin, L.; Xiong, H.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, S.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, N.; et al. HIV-2/SIV Vpx targets a novel functional domain of STING to selectively inhibit cGAS-STING-mediated NF-κB signalling. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2552–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Cao, X.; Lu, J.; Huang, B.; Liu, Y.-J.; Kato, N.; Shu, H.-B.; Zhong, J. Hepatitis C virus NS4B blocks the interaction of STING and TBK1 to evade host innate immunity. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Zhou, Z.; Rui, Y.; Ye, R.; Xia, F.; Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Su, J.; Lou, M.; Yu, X.-F. TRAF3 activates STING-mediated suppression of EV-A71 and target of viral evasion. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Liu, C.C. Enterovirus 71, epidemiology, pathogenesis and management. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2009, 7, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, T.; Lewthwaite, P.; Perera, D.; Cardosa, M.J.; McMinn, P.; Ooi, M.H. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of enterovirus 71. Lancet Infect Dis. 2010, 10, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Gong, X.; Pang, L.L.; Gao, W.J.; Zhang, Y.T.; Li, X.-L.; Liu, N.; Li, D.-D.; Jin, Y.; Duan, Z.-J. Cytokine responses and correlations thereof with clinical profiles in children with enterovirus 71 infections. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Lei, H.Y.; Liu, C.C. Cytokine immunopathogenesis of enterovirus 71 brain stem encephalitis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 876241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.P.; Feng, X.; Yan, H.P. Multiplex serum cytokine levels in patients with severe HFMD determined by Luminex suspension array. Beijing Yi Xue 2012, 34, 185–188. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liou, A.T.; Liao, C.C.; Chou, S.F.; Chang, Y.S.; Chang, C.S.; Shih, C. Hypoxia and therapeutic treatment of EV-A71 with an immune modulator TLR7 agonist in a new immunocompetent mouse model. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, B.; Chen, X.; Song, N.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Yu, P.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.; Qin, C. GS-9620 inhibits enterovirus 71 replication mainly through the NF-κB and PI3K-AKT signaling pathways. Antivir. Res. 2018, 153, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cui, B.; Yan, H.; Wu, S.; Wang, K.; Yang, G.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y. Targeting 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase against EV-A71 replication by upregulating interferon response. Antivir. Res. 2023, 209, 105497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, S.; Liu, Y. Anti-Enterovirus 71 Agents of Natural Products. Molecules 2015, 20, 16320–16333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Q.; Jiang, J.D.; Li, Y.H. Establishment of EV-A71 animal models with 2- week-old BALB/c mice. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2013, 48, 343–346. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, M.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Wu, S.; Guo, T.; Cen, S.; Jiang, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. APOBEC3G is a restriction factor of EV71 and mediator of IMB-Z antiviral activity. Antivir. Res. 2019, 165, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Qian, S.; Fang, L.; Han, Y.; Zheng, C. Association study of inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression in hand foot and mouth disease. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 79425–79432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Feng, Z.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.; Meng, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yao, X.; Feng, Q.; et al. Global cytokine/chemokine profile identifies potential progression prediction indicators in hand-foot-and-mouth disease patients with Enterovirus A71 infections. Cytokine 2019, 123, 154765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.M.; Williams, A.; Eisenbarth, S.C. Structure and function of the immune system in the spleen. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaau6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Pei, J.; Luo, Q.; Zeng, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, Z.; Quan, J. Identification of α-Mangostin as an Agonist of Human STING. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 2057–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.C.; Araya, R.E.; Huang, A.; Chen, Q.; Di Modica, M.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Lopès, A.; Johnson, S.B.; Schwarz, B.; Bohrnsen, E.; et al. Microbiota triggers STING-type I IFN-dependent monocyte reprogramming of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2021, 184, 5338–5356.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, E.N.; Yu, C.; Vartabedian, V.F.; Jia, Y.; Kumar, M.; Gamo, A.M.; Vernier, W.; Ali, S.H.; Kissai, M.; Lazar, D.C.; et al. Antitumor activity of a systemic STING-activating non-nucleotide cGAMP mimetic. Science 2020, 369, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdrojewicz, Z.; Pachura, E.; Pachura, P. The Thymus: A Forgotten, But Very Important Organ. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 25, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.V.; Connors, T.J.; Farber, D.L. Human T Cell Development, Localization, and Function throughout Life. Immunity 2018, 48, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Law, C.S.; Kurra, S.; Simchoni, N.; Shum, A.K. Activated STING in the thymus alters T cell development and selection leading to autoimmunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 135, e180252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skopelja-Gardner, S.; An, J.; Elkon, K.B. Role of the cGAS-STING pathway in systemic and organ-specific diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, W.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; Zeng, Z.; Du, S. Gut microbiota modulate radiotherapy-associated antitumor immune responses against hepatocellular carcinoma Via STING signaling. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2119055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebina, I.; Fogg, L.G.; James, K.R.; Soon, M.S.F.; Akter, J.; Thomas, B.S.; Hill, G.; Engwerda, C.; Haque, A. IL-6 promotes CD4+ T-cell and B-cell activation during Plasmodium infection. Parasite Immunol. 2017, 39, e12455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi, B.; Chan, L.; Knapp, J.P.; Karimi, N.; Alizadeh, K.; Mehrani, Y.; Bridle, B.W.; Karimi, K. Cytokine Storm Syndrome in SARS-CoV-2 Infections: A Functional Role of Mast Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Misra, D.P.; Sharma, A.; Wakhlu, A.; Agarwal, V.; Negi, V.S. Vasculitis and vasculitis-like manifestations in monogenic autoinflammatory syndromes. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Shu, Z.; Sun, F.; Ma, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, W.; Mao, H.; Lei, X. Discovery and Total Synthesis of Anhydrotuberosin as a STING Antagonist for Treating Autoimmune Diseases. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2025, 64, e202407641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, K.; Tu, M.; Liu, W.; Ju, J. Therapeutic landscape in systemic lupus erythematosus: mtDNA activation of the cGAS-STING pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 133, 112114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Luo, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, H.; Song, Y.; et al. Targeting STING in dendritic cells alleviates psoriatic inflammation by suppressing IL-17A production. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2024, 21, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knox, K.; Jeltema, D.; Dobbs, N.; Yang, K.; Xing, C.; Song, K.; Tang, Z.; Torres-Ramirez, G.; Wang, J.; Gao, S. Dynamic STING repression orchestrates immune cell development and function. Sci. Immunol. 2025, 10, eado9933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Liu, J.; Leng, J.; Cai, L. The cGAS-STING pathway: More than fighting against viruses and cancer. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zuo, H.; Huang, H.D.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; He, C.; Hu, Y. STING as an emerging therapeutic target for drug discovery: Perspectives from the global patent landscape. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 44, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cui, B.; Yan, H.; Wu, S.; Wang, K.; Yang, G.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y. Metformin inhibits EV-A71 and CVA16 infections by regulating TRIB3-SCARB2 axis and activating AMPK. Antivir. Res. 2025, 235, 106081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, F.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Deng, H.; Dong, J.; Pang, J.; Song, D.; et al. Evaluation and mechanism study of Pien Tze Huang against EV-A71 infection. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1251731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, K.; Cui, B.; Yan, H.; Wu, S.; Wang, K.; Yang, G.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y. Tribbles pseudokinase 3 promotes enterovirus A71 infection via dual mechanisms. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2307514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Guo, J.H.; Feng, C.L.; Ding, Y.W.; Dong, B.; Han, Y.X.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, L.L.; Jiang, J.D. Berberine inhibits carcinogenesis through antagonizing the ATX-LPA-LPAR2-p38-leptin axis in a mouse hepatoma model. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2022, 26, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Qiao, L.; Sheng, W.; Yan, H.; Wang, K.; Yang, G.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y. STING Restricts EV-A71 Infection by Regulating T Cell Development and Enhancing Immune Cell Effector Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311441
Wang H, Wang Y, Wu S, Qiao L, Sheng W, Yan H, Wang K, Yang G, Jiang J, Li Y. STING Restricts EV-A71 Infection by Regulating T Cell Development and Enhancing Immune Cell Effector Function. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311441
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huiqiang, Ya Wang, Shuo Wu, Lijun Qiao, Wen Sheng, Haiyan Yan, Kun Wang, Ge Yang, Jiandong Jiang, and Yuhuan Li. 2025. "STING Restricts EV-A71 Infection by Regulating T Cell Development and Enhancing Immune Cell Effector Function" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311441
APA StyleWang, H., Wang, Y., Wu, S., Qiao, L., Sheng, W., Yan, H., Wang, K., Yang, G., Jiang, J., & Li, Y. (2025). STING Restricts EV-A71 Infection by Regulating T Cell Development and Enhancing Immune Cell Effector Function. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311441





