Antitumor Activity of Metformin in Combination with Binimetinib Against Melanoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Silico Analysis
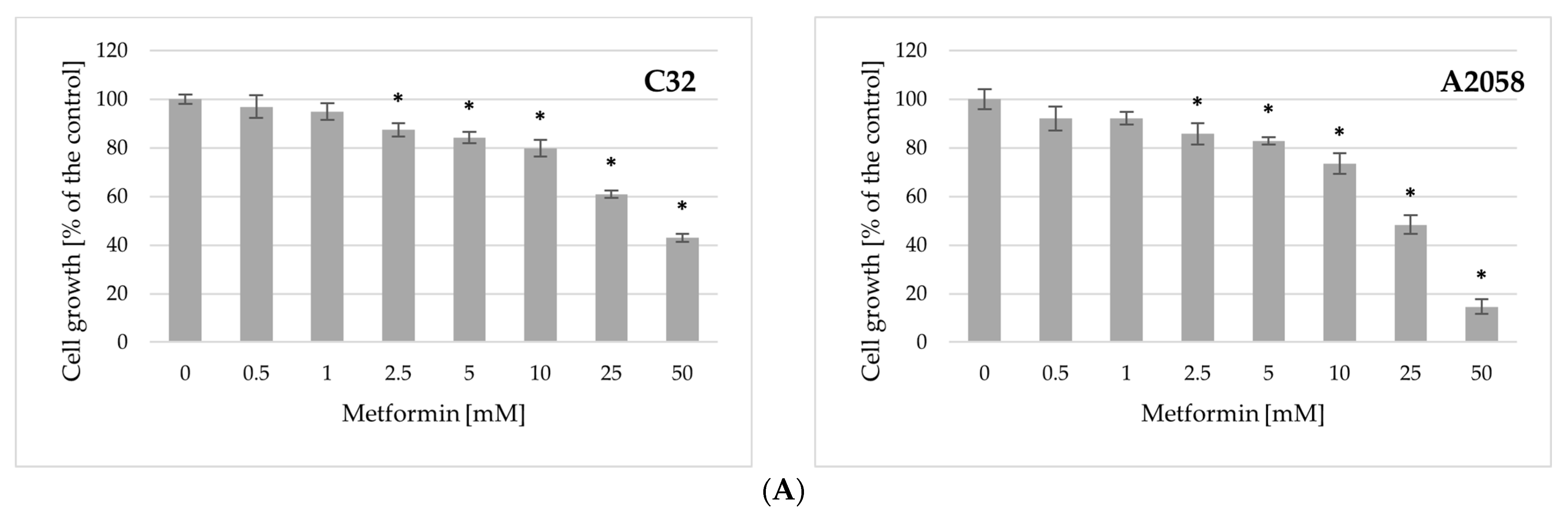
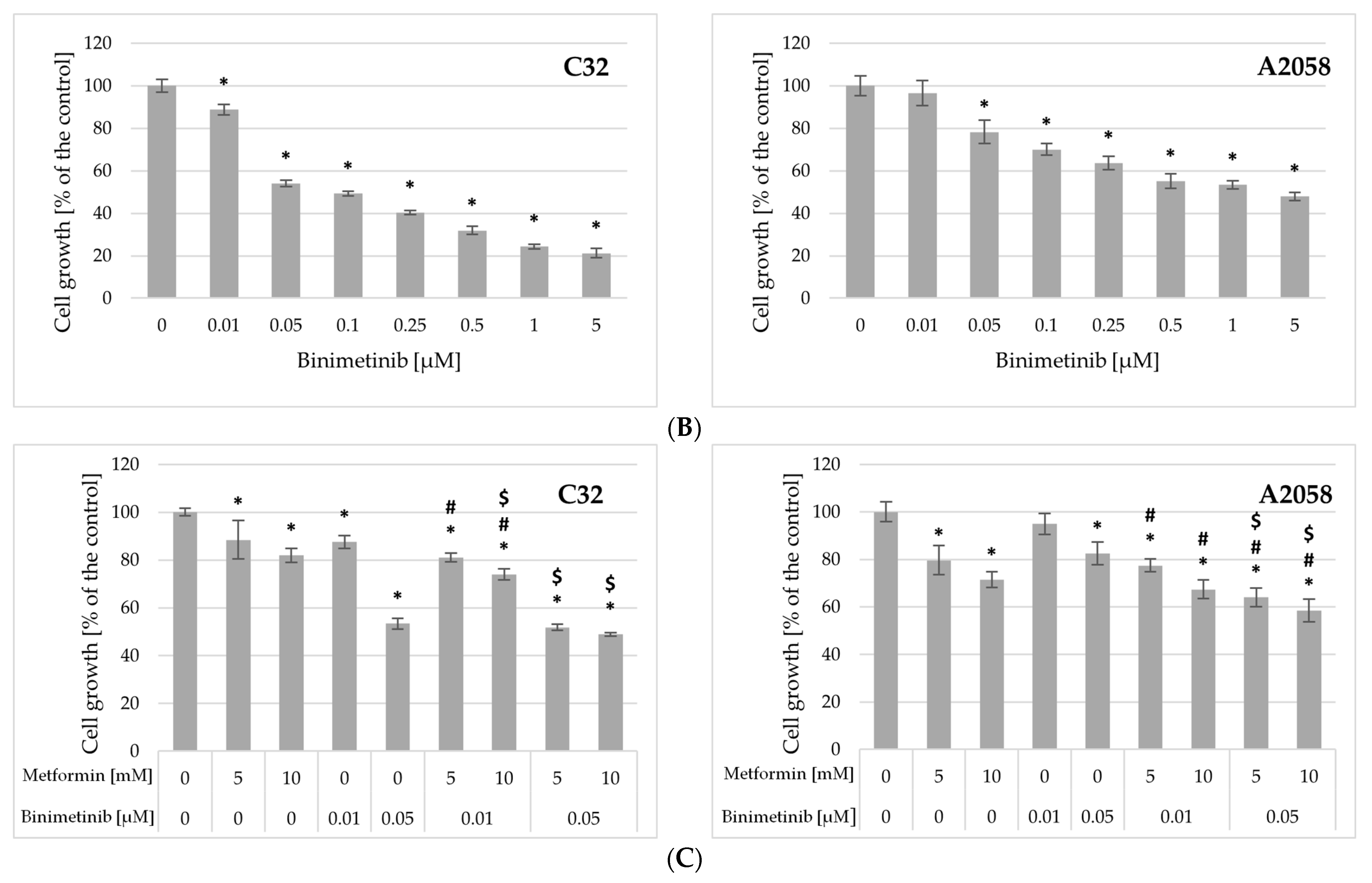
2.2. Impact of Metformin and Binimetinib on Cell Growth
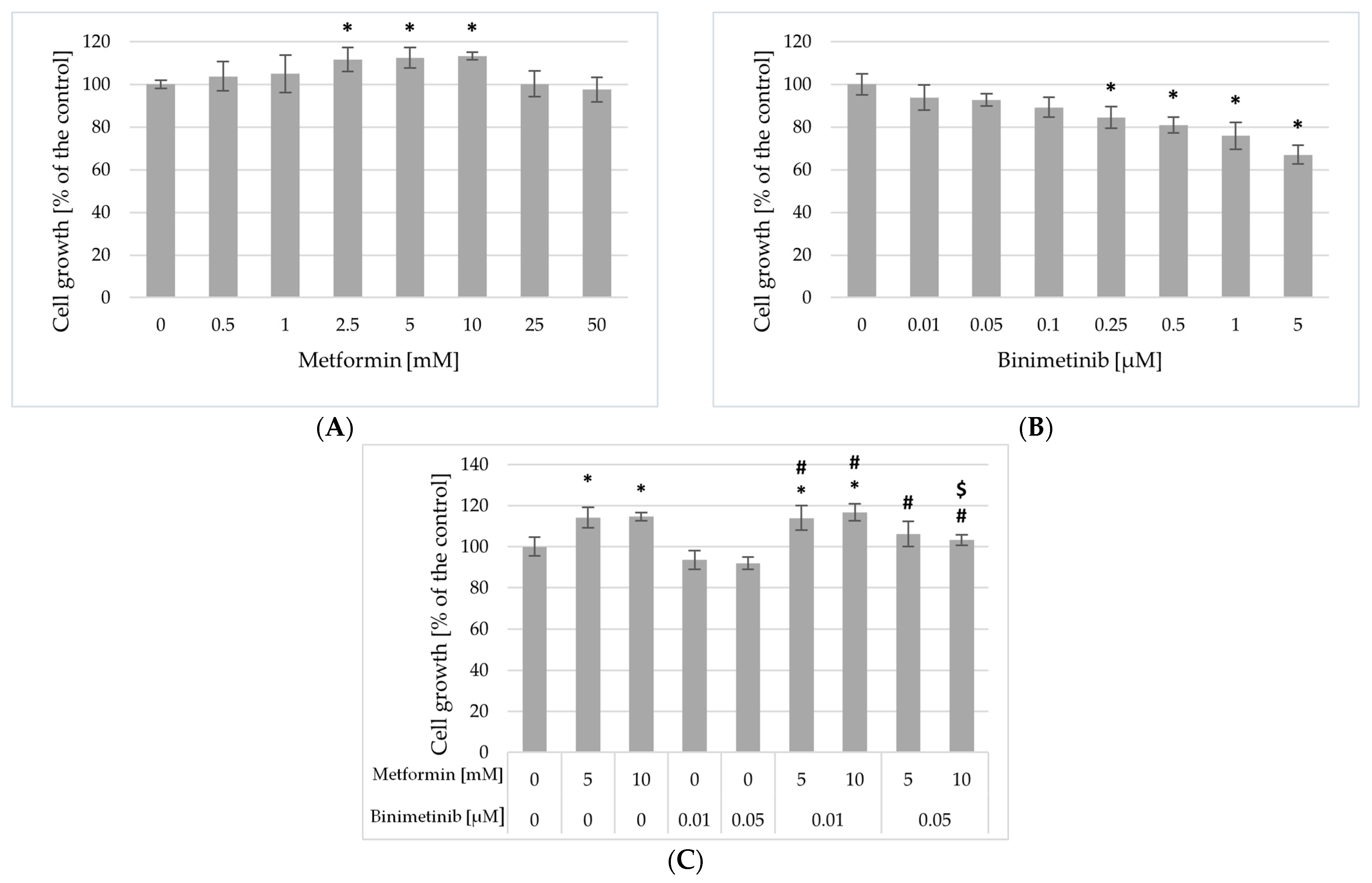
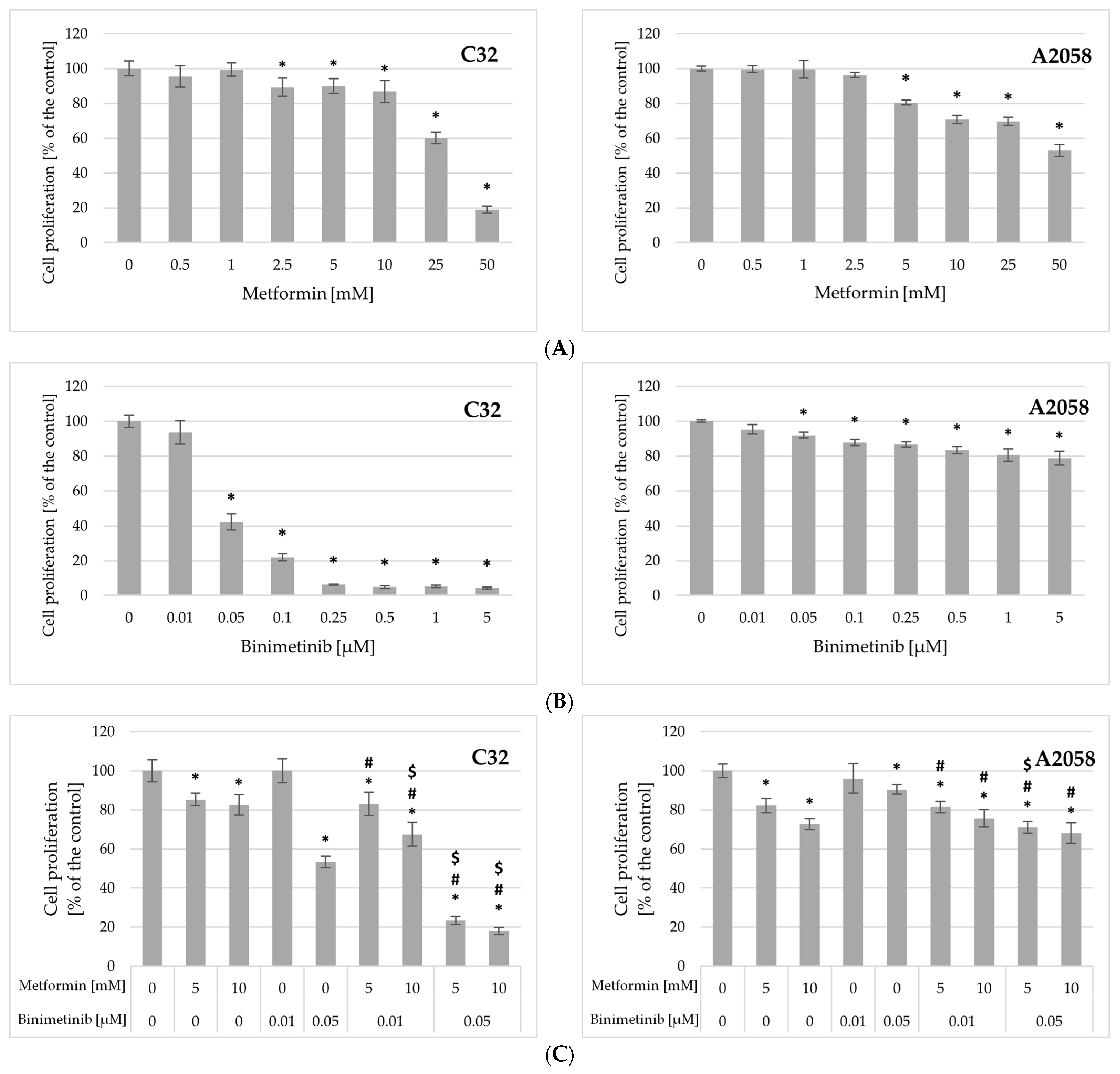
2.3. Impact of Metformin and Binimetinib on Cells Proliferation
2.4. The Influence of Metformin and Binimetinib on Melanoma Cell Cycle
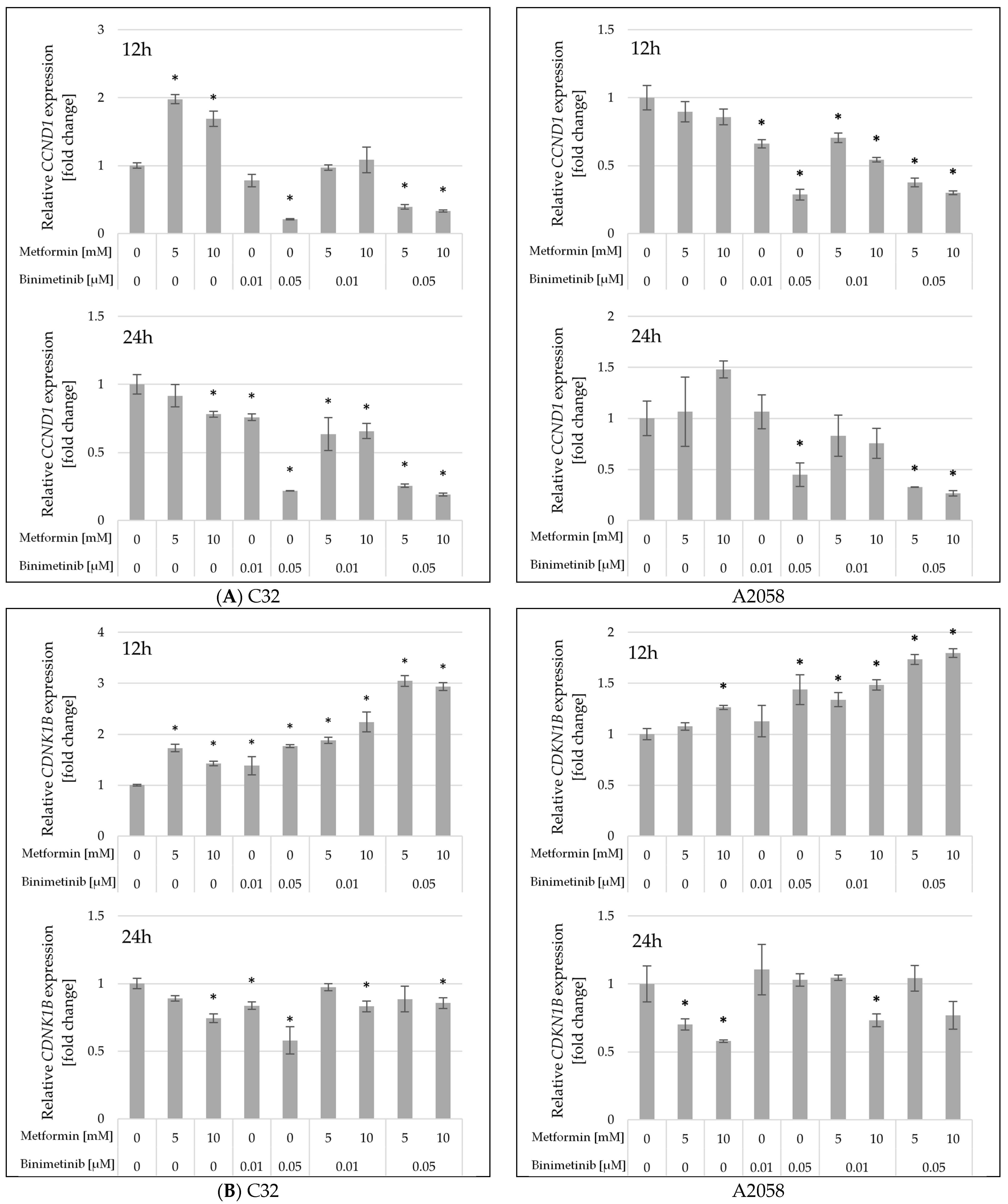
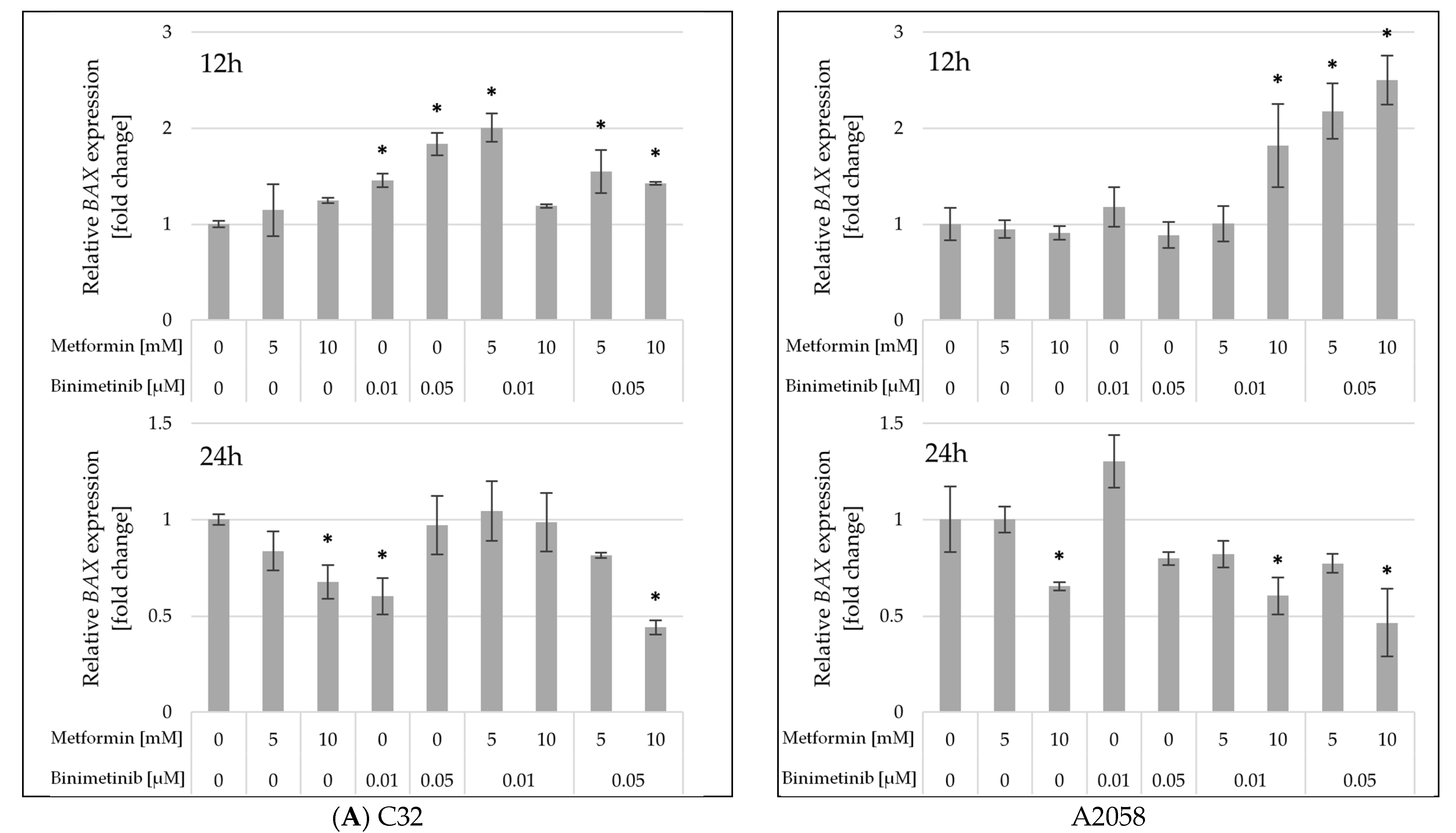
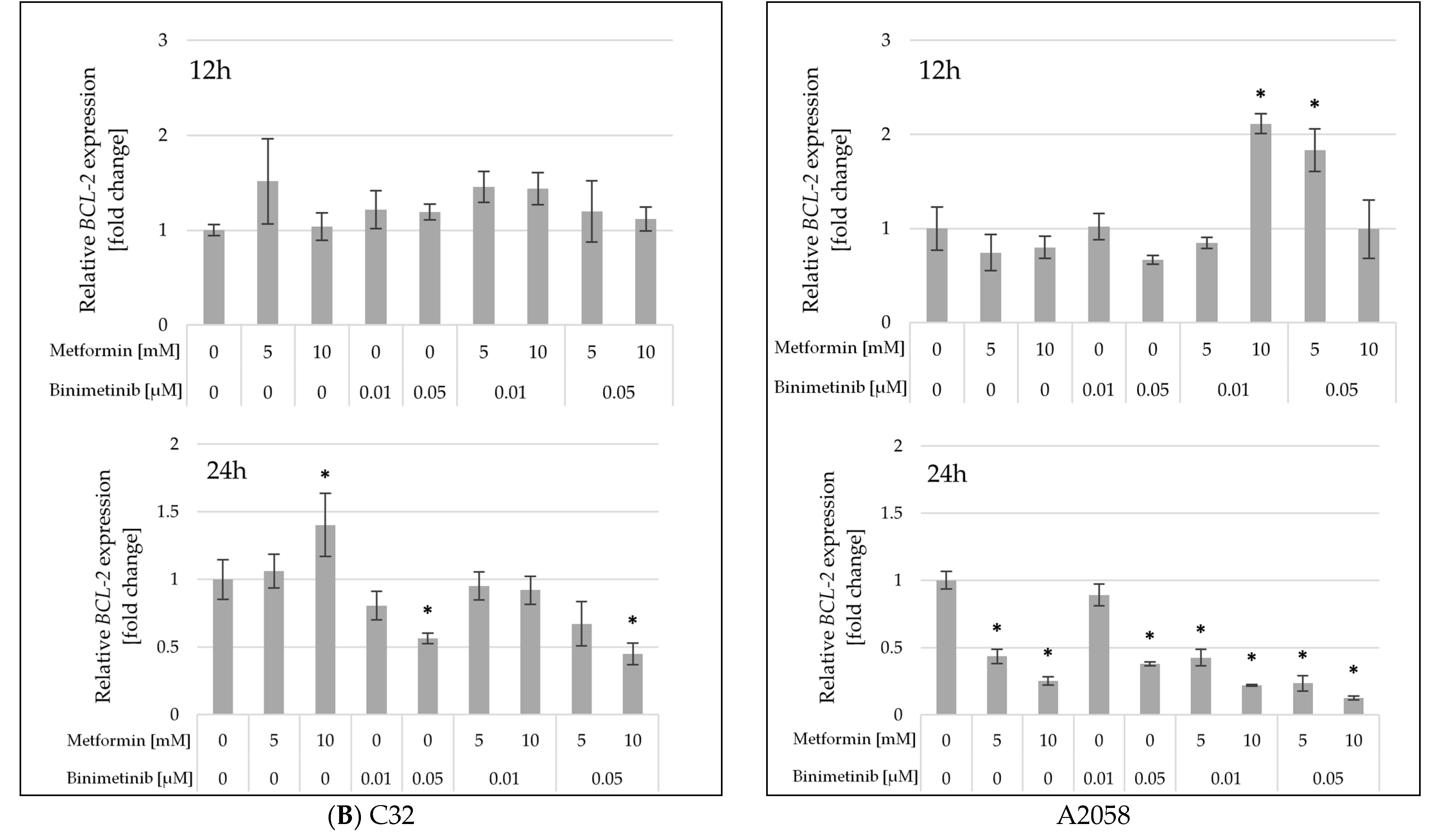
2.5. The Influence of Metformin and Binimetinib on the mRNA Expression of Genes Encoding Proteins Involved in Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis Processes
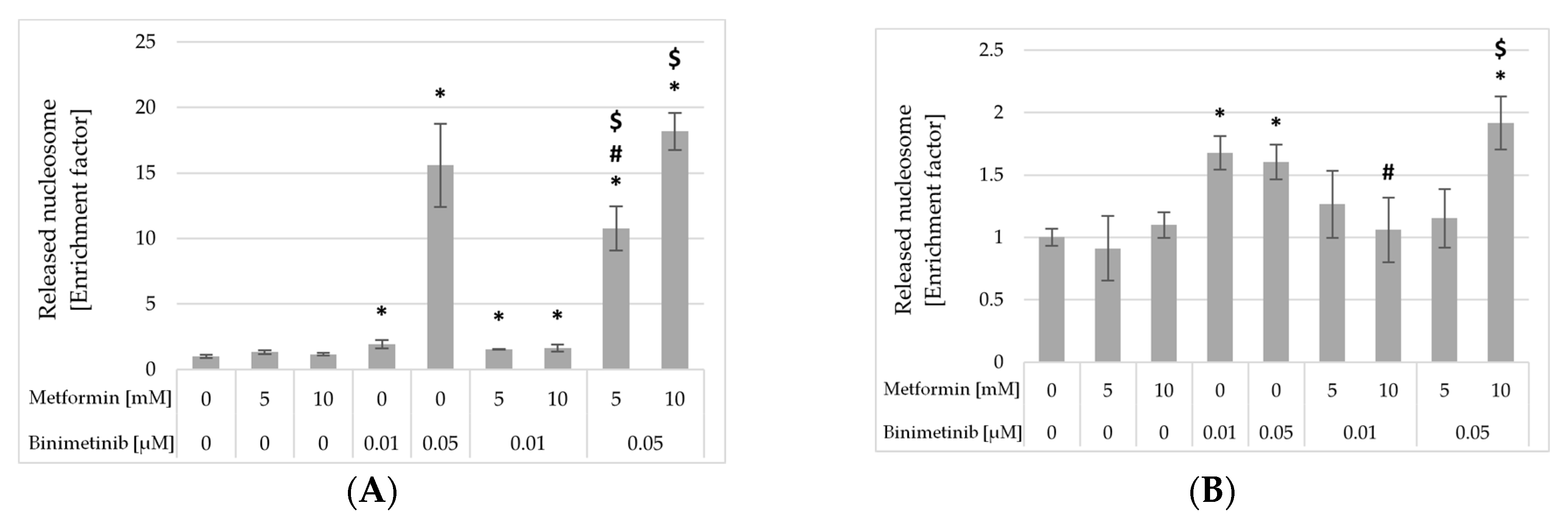
2.6. Impact of Metformin and Binimetinib on DNA Fragmentation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Silico Drugs Interaction Analysis
4.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.3. Preparation of Drug Solutions
4.4. Cell Growth Assay
4.5. Evaluation of the Cell Proliferation
4.6. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.7. Total RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Assessment
4.8. DNA Fragmentation Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| AMPK | 5′AMP-activated protein kinase |
| BAX | Gene encoding BAX protein |
| BCL-2 | Gene encoding BCL-2 protein |
| Bin | Binimetinib |
| BRAF | Protein kinase encoded by the BRAF oncogene, member of the MAPK signaling cascade |
| BRAF | B-raf proto-oncogene |
| BrdU | 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine |
| CCND1 | Gene encoding cyclin D1 protein |
| CDK4 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 |
| CDK6 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 |
| CDKN1B | Gene encoding p27 protein |
| CI | Combination Index |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ErbB | Family of receptor tyrosine kinases, structurally related to the epidermal growth factor receptor |
| IC50 | Inhibitory concentration |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| MEK | Protein kinase, member of the MAPK signaling cascade |
| Met | Metformin |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin kinase |
| NRAS | Neuroblastoma ras viral oncogene homolog |
| PD-1 | Programmed death receptor 1 |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| RT-qPCR | Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| SRB | Sulforhodamine B |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyba, T.; Randi, G.; Bray, F.; Martos, C.; Giusti, F.; Nicholson, N.; Gavin, A.; Flego, M.; Neamtiu, L.; Dimitrova, N.; et al. The European Cancer Burden in 2020: Incidence and Mortality Estimates for 40 Countries and 25 Major Cancers. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 157, 308–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochez, L.; Volkmer, B.; Hoorens, I.; Garbe, C.; Röcken, M.; Schüz, J.; Whiteman, D.C.; Autier, P.; Greinert, R.; Boonen, B. Skin Cancer in Europe Today and Challenges for Tomorrow. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2025, 39, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niekerk, C.C.; Groenewoud, H.M.M.; Verbeek, A.L.M. Trends and Projections in Cutaneous Melanoma Death in the Netherlands from 1950 to 2045. Medicine 2021, 100, e27784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, P.P.; Pavet, V.; Marais, R. The Journey from Melanocytes to Melanoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, J.F.; Weissfeld, J.L.; Ferris, L.K. Characteristics and Survival of Patients with Invasive Amelanotic Melanoma in the USA. Melanoma Res. 2013, 23, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasowska, D.; Kurzepa, J.; Błaszczak, E. Current State of Melanoma Treatment–from Conventional Therapies to Nanotechnology and Beyond. J. Pre Clin. Clin. Res. 2024, 18, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drugs Approved for Melanoma-NCI. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/melanoma (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- Amaral, T.; Ottaviano, M.; Arance, A.; Blank, C.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Donia, M.; Dummer, R.; Garbe, C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Gogas, H.; et al. Cutaneous Melanoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2025, 36, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, C.D.; Khushalani, N.I.; Angeles, C.; Petrella, T.M. Current State of Adjuvant Therapy for Melanoma: Less Is More, or More Is Better? Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2022, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.M.M.; Donnelly, L.A.; Emslie-Smith, A.M.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin and Reduced Risk of Cancer in Diabetic Patients. BMJ 2005, 330, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowker, S.L.; Majumdar, S.R.; Veugelers, P.; Johnson, J.A. Increased Cancer-Related Mortality for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Use Sulfonylureas or Insulin. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landman, G.W.D.; Kleefstra, N.; van Hateren, K.J.J.; Groenier, K.H.; Gans, R.O.B.; Bilo, H.J.G. Metformin Associated with Lower Cancer Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes: ZODIAC-16. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Benhawy, S.A.; El-Sheredy, H.G. Metformin and Survival in Diabetic Patients with Breast Cancer. J. Egypt. Public Health Assoc. 2014, 89, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiteerakij, R.; Petersen, G.M.; Bamlet, W.R.; Chaffee, K.G.; Zhen, D.B.; Burch, P.A.; Leof, E.R.; Roberts, L.R.; Oberg, A.L. Metformin Use and Survival of Patients With Pancreatic Cancer: A Cautionary Lesson. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, P.-T.; Chuang, T.-J.; Huang, S.-H.; Wu, T.-H.; Huang, W.-C.; Wang, J.-H. The Impact of Metformin on Survival in Diabetes Patients with Operable Colorectal Cancer: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Int. Med. Res. 2023, 51, 03000605231168033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarhini, Z.; Manceur, K.; Magne, J.; Mathonnet, M.; Jost, J.; Christou, N. The Effect of Metformin on the Survival of Colorectal Cancer Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheaton, W.W.; Weinberg, S.E.; Hamanaka, R.B.; Soberanes, S.; Sullivan, L.B.; Anso, E.; Glasauer, A.; Dufour, E.; Mutlu, G.M.; Budigner, G.S.; et al. Metformin Inhibits Mitochondrial Complex I of Cancer Cells to Reduce Tumorigenesis. eLife 2014, 3, e02242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakikhani, M.; Dowling, R.; Fantus, I.G.; Sonenberg, N.; Pollak, M. Metformin Is an AMP Kinase-Dependent Growth Inhibitor for Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10269–10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.R. Meeting Metformin Again for the First Time. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadu7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashayeri Ahmadabad, H.; Mohammadi Panah, S.; Ghasemnejad-Berenji, H.; Ghojavand, S.; Ghasemnejad-Berenji, M.; Khezri, M.R. Metformin and the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway: Implications for Cancer, Cardiovascular, and Central Nervous System Diseases. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 1035–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Nie, J.; Ma, X.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting PI3K in Cancer: Mechanisms and Advances in Clinical Trials. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.; Lux, A.; O’Callaghan, F. The Journey of Metformin from Glycaemic Control to mTOR Inhibition and the Suppression of Tumour Growth. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zager, J.S.; Eroglu, Z. Encorafenib/Binimetinib for the Treatment of BRAF-Mutant Advanced, Unresectable, or Metastatic Melanoma: Design, Development, and Potential Place in Therapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 9081–9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahar, M.E.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.R. Targeting the RAS/RAF/MAPK Pathway for Cancer Therapy: From Mechanism to Clinical Studies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, E.; Downward, J. RAS Interaction with PI3K: More Than Just Another Effector Pathway. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Bergami, P.; Fitchman, B.; Ronai, Z. Understanding Signaling Cascades in Melanoma. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaviano, A.; Foo, A.S.C.; Lam, H.Y.; Yap, K.C.H.; Jacot, W.; Jones, R.H.; Eng, H.; Nair, M.G.; Makvandi, P.; Geoerger, B.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Transduction Pathway and Targeted Therapies in Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, O.; Barrón, F.; Padilla, M.-Á.S.; Avilés-Salas, A.; Ramírez-Tirado, L.A.; Arguelles Jiménez, M.J.; Vergara, E.; Zatarain-Barrón, Z.L.; Hernández-Pedro, N.; Cardona, A.F.; et al. Effect of Metformin Plus Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Compared With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Alone in Patients With Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, e192553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutros, A.; Croce, E.; Ferrari, M.; Gili, R.; Massaro, G.; Marconcini, R.; Arecco, L.; Tanda, E.T.; Spagnolo, F. The Treatment of Advanced Melanoma: Current Approaches and New Challenges. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2024, 196, 104276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhullar, K.S.; Lagarón, N.O.; McGowan, E.M.; Parmar, I.; Jha, A.; Hubbard, B.P.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Kinase-Targeted Cancer Therapies: Progress, Challenges and Future Directions. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Approves Encorafenib and Binimetinib in Combination for Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma with BRAF Mutations. 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-encorafenib-and-binimetinib-combination-unresectable-or-metastatic-melanoma-braf (accessed on 22 October 2025).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Approves Encorafenib with Binimetinib for Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with a BRAF V600E Mutation. 2023. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-encorafenib-binimetinib-metastatic-non-small-cell-lung-cancer-braf-v600e-mutation (accessed on 22 October 2025).
- Kakadia, S.; Yarlagadda, N.; Awad, R.; Kundranda, M.; Niu, J.; Naraev, B.; Mina, L.; Dragovich, T.; Gimbel, M.; Mahmoud, F. Mechanisms of Resistance to BRAF and MEK Inhibitors and Clinical Update of US Food and Drug Administration-Approved Targeted Therapy in Advanced Melanoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 7095–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanda, M.; Cohen, M.S. Advances in the Discovery and Development of Melanoma Drug Therapies. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 1319–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryabaya, O.; Prokofieva, A.; Akasov, R.; Khochenkov, D.; Emelyanova, M.; Burov, S.; Markvicheva, E.; Inshakov, A.; Stepanova, E. Metformin Increases Antitumor Activity of MEK Inhibitor Binimetinib in 2D and 3D Models of Human Metastatic Melanoma Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 2548–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, J.; Park, D.; Lee, Y. Antitumor Effect of Metformin in Combination with Binimetinib on Melanoma Cells. Dev. Reprod. 2021, 25, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mert, I.; Chhina, J.; Allo, G.; Dai, J.; Seward, S.; Carey, M.S.; Llaurado, M.; Giri, S.; Rattan, R.; Munkarah, A.R. Synergistic Effect of MEK Inhibitor and Metformin Combination in Low Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 146, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, D.; Lee, Y. Metformin Synergistically Potentiates the Antitumor Effects of Imatinib in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Dev. Reprod. 2017, 21, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Kim, T.; Choi, S.; Ko, H.; Park, D.; Lee, Y. Combination of BEZ235 and Metformin Has Synergistic Effect on Cell Viability in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Dev. Reprod. 2018, 22, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomic, T.; Botton, T.; Cerezo, M.; Robert, G.; Luciano, F.; Puissant, A.; Gounon, P.; Allegra, M.; Bertolotto, C.; Bereder, J.-M.; et al. Metformin Inhibits Melanoma Development through Autophagy and Apoptosis Mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.-W.; Li, S.-C.; Tsai, K.-W. Metformin Treatment Suppresses Melanoma Cell Growth and Motility Through Modulation of microRNA Expression. Cancers 2019, 11, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oscilowska, I.; Rolkowski, K.; Baszanowska, W.; Huynh, T.Y.L.; Lewoniewska, S.; Nizioł, M.; Sawicka, M.; Bielawska, K.; Szoka, P.; Miltyk, W.; et al. Proline Dehydrogenase/Proline Oxidase (PRODH/POX) Is Involved in the Mechanism of Metformin-Induced Apoptosis in C32 Melanoma Cell Line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczkowski, D.J.; Johannessen, C.M.; Abudayyeh, O.; Kim, J.W.; Cooper, Z.A.; Piris, A.; Frederick, D.T.; Barzily-Rokni, M.; Straussman, R.; Haq, R.; et al. A Melanoma Cell State Distinction Influences Sensitivity to MAPK Pathway Inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumar, J.; Shahbazian, D.; Aziz, S.A.; Jilaveanu, L.B.; Kluger, H.M. MEK Targeting in N-RAS Mutated Metastatic Melanoma. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Washio, J.; Sato, S.; Abiko, Y.; Shinohara, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Otani, H.; Sasaki, S.; Wang, X.; Takahashi, N. Rewired Cellular Metabolic Profiles in Response to Metformin under Different Oxygen and Nutrient Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; Ma, W.; Sun, Q. Metformin Inhibits Proliferation and Proinflammatory Cytokines of Human Keratinocytes in Vitro via mTOR-Signaling Pathway. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessner, H.; Sinnberg, T.; Kosnopfel, C.; Smalley, K.S.M.; Beck, D.; Praetorius, C.; Mai, M.; Beissert, S.; Kulms, D.; Schaller, M.; et al. BRAF Inhibitors Amplify the Proapoptotic Activity of MEK Inhibitors by Inducing ER Stress in NRAS-Mutant Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6203–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Heo, J.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, S.; Nam, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, M.K. Curcumin Enhances the Anticancer Effects of Binimetinib on Melanoma Cells by Inducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Cell Apoptosis with Necroptosis. Ann. Dermatol. 2023, 35, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niessner, H.; Hüsch, A.; Kosnopfel, C.; Meinhardt, M.; Westphal, D.; Meier, F.; Schilling, B.; Sinnberg, T. Exploring the In Vitro and In Vivo Therapeutic Potential of BRAF and MEK Inhibitor Combination in NRAS-Mutated Melanoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryabaya, O.O.; Abramov, I.S.; Khochenkov, D.A.; Akasov, R.; Sholina, N.V.; Prokofieva, A.A. Rapamycin Synergizes the Cytotoxic Effects of MEK Inhibitor Binimetinib and Overcomes Acquired Resistance to Therapy in Melanoma Cell Lines in Vitro. Invest. New Drugs 2021, 39, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Park, D. Effect of Metformin in Combination With Trametinib and Paclitaxel on Cell Survival and Metastasis in Melanoma Cells. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgillo, F.; Sasso, F.C.; Della Corte, C.M.; Vitagliano, D.; D’Aiuto, E.; Troiani, T.; Martinelli, E.; De Vita, F.; Orditura, M.; De Palma, R.; et al. Synergistic Effects of Metformin Treatment in Combination with Gefitinib, a Selective EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in LKB1 Wild-Type NSCLC Cell Lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3508–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, M.-S.; Chuang, M.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-P.; Yang, T.-M.; Chen, P.-C.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.-H. Metformin Prolongs Survival in Type 2 Diabetes Lung Cancer Patients With EGFR-TKIs. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1534735419869491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.-J.; Wu, G.; Zhou, X.; Sun, J.; Bai, J.; Ren, B.; et al. Combination of Metformin and Gefitinib as First-Line Therapy for Nondiabetic Advanced NSCLC Patients with EGFR Mutations: A Randomized, Double-Blind Phase II Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6967–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, C.-W.; Wang, C.-C.; Wang, S.-S.; Lin, P. ChemDIS-Mixture: An Online Tool for Analyzing Potential Interaction Effects of Chemical Mixtures. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-C. Drug Combination Studies and Their Synergy Quantification Using the Chou-Talalay Method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pathway Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Description | Adj.P Met | Adj.P Bin | Adj.P Joint |
| hsa04910 | Insulin signaling pathway | 6.53 × 10−16 | 1.05 × 10−3 | 6.83 × 10−19 |
| hsa05200 | Pathways in cancer | 4.48 × 10−13 | 2.15 × 10−4 | 9.65 × 10−17 |
| hsa04010 | MAPK signaling pathway | 1.67 × 10−7 | 6.30 × 10−4 | 1.05 × 10−10 |
| R-HSA-5675221 | Negative regulation of MAPK pathway | 8.62 × 10−6 | 2.33 × 10−5 | 2.01 × 10−10 |
| hsa04012 | ErbB signaling pathway | 7.53 × 10−6 | 4.04 × 10−4 | 3.04 × 10−9 |
| hsa04370 | VEGF signaling pathway | 1.86 × 10−5 | 3.18 × 10−4 | 5.92 × 10−9 |
| R-HSA-2428933 | SHC-related events triggered by IGF1R | 1.13 × 10−2 | 9.28 × 10−7 | 1.05 × 10−8 |
| R-HSA-112412 | SOS-mediated signalling | 3.98 × 10−2 | 6.09 × 10−7 | 2.43 × 10−8 |
| hsa04722 | Neurotrophin signaling pathway | 3.65 × 10−5 | 9.85 × 10−4 | 3.60 × 10−8 |
| R-HSA-5673001 | RAF/MAP kinase cascade | 4.61 × 10−2 | 1.39 × 10−6 | 6.41 × 10−8 |
| R-HSA-1433557 | Signaling by SCF-KIT | 3.95 × 10−3 | 2.33 × 10−5 | 9.21 × 10−8 |
| hsa04664 | Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | 3.75 × 10−4 | 3.20 × 10−4 | 1.20 × 10−7 |
| hsa04510 | Focal adhesion | 1.50 × 10−5 | 3.74 × 10−2 | 5.59 × 10−7 |
| R-HSA-5668599 | RHO GTPases Activate NADPH Oxidases | 7.54 × 10−5 | 2.10 × 10−2 | 1.58 × 10−6 |
| hsa04916 | Melanogenesis | 3.57 × 10−3 | 5.71 × 10−4 | 2.04 × 10−6 |
| hsa04660 | T cell receptor signaling pathway | 1.37 × 10−2 | 6.38 × 10−4 | 8.76 × 10−6 |
| hsa04062 | Chemokine signaling pathway | 3.20 × 10−2 | 3.02 × 10−4 | 9.65 × 10−6 |
| hsa04650 | Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | 1.74 × 10−2 | 1.04 × 10−3 | 1.81 × 10−5 |
| hsa04912 | GnRH signaling pathway | 3.66 × 10−2 | 5.71 × 10−4 | 2.09 × 10−5 |
| SMP00358 | Fc Epsilon Receptor I Signaling in Mast Cells | 3.39 × 10−2 | 6.20 × 10−4 | 2.10 × 10−5 |
| R-HSA-109704 | PI3K Cascade | 9.88 × 10−3 | 4.79 × 10−2 | 4.73 × 10−4 |
| Go Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Description | Adj.P Met | Gene Ratio Met | Adj.P Bin | Gene Ratio Bin | Adj.P Joint |
| GO:0045944 | positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter | 1.25 × 10−16 | 94/615 | 2.71 × 10−2 | 4/18 | 3.39 × 10−18 |
| GO:0045893 | positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | 6.82 × 10−13 | 58/615 | 1.20 × 10−2 | 4/18 | 8.17 × 10−15 |
| GO:0000165 | MAPK cascade | 3.13 × 10−5 | 26/615 | 1.69 × 10−8 | 8/18 | 5.31 × 10−13 |
| GO:0008284 | positive regulation of cell proliferation | 1.17 × 10−8 | 46/615 | 2.53 × 10−2 | 3/18 | 2.97 × 10−10 |
| GO:0001934 | positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | 2.20 × 10−8 | 22/615 | 2.44 × 10−2 | 2/18 | 5.37 × 10−10 |
| GO:0001077 | transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding | 5.56 × 10−8 | 30/615 | 3.45 × 10−2 | 2/17 | 1.92 × 10−9 |
| GO:0005829 | cytosol | 1.19 × 10−7 | 168/613 | 1.93 × 10−2 | 8/18 | 2.30 × 10−9 |
| GO:0043524 | negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process | 1.27 × 10−5 | 18/615 | 2.00 × 10−4 | 4/18 | 2.55 × 10−9 |
| GO:0000978 | RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding | 1.19 × 10−6 | 35/615 | 4.97 × 10−2 | 2/17 | 5.93 × 10−8 |
| GO:0051721 | protein phosphatase 2A binding | 2.83 × 10−6 | 9/615 | 3.71 × 10−2 | 1/17 | 1.05 × 10−7 |
| GO:0006468 | protein phosphorylation | 5.79 × 10−6 | 39/615 | 2.53 × 10−2 | 3/18 | 1.47 × 10−7 |
| GO:0042149 | cellular response to glucose starvation | 7.77 × 10−6 | 9/615 | 3.70 × 10−2 | 1/18 | 2.88 × 10−7 |
| GO:0030335 | positive regulation of cell migration | 2.20 × 10−4 | 19/615 | 8.15 × 10−3 | 3/18 | 1.79 × 10−6 |
| GO:0032403 | protein complex binding | 1.50 × 10−4 | 21/615 | 1.87 × 10−2 | 3/17 | 2.81 × 10−6 |
| GO:0045740 | positive regulation of DNA replication | 6.00 × 10−4 | 8/615 | 8.15 × 10−3 | 2/18 | 4.89 × 10−6 |
| DO Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Description | Adj.P Met | Adj. P Bin | Adj. P Joint |
| DOID:3119 | gastrointestinal system cancer | 1.09 × 10−20 | 9.61 × 10−3 | 1.04 × 10−22 |
| DOID:684 | hepatocellular carcinoma | 8.74 × 10−21 | 2.75 × 10−2 | 2.40 × 10−22 |
| DOID:686 | liver carcinoma | 8.74 × 10−21 | 2.75 × 10−2 | 2.40 × 10−22 |
| DOID:3571 | liver cancer | 2.24 × 10−20 | 2.78 × 10−2 | 6.23 × 10−22 |
| DOID:10155 | intestinal cancer | 9.78 × 10−17 | 1.37 × 10−3 | 1.34 × 10−19 |
| DOID:3856 | male reproductive organ cancer | 1.22 × 10−17 | 1.23 × 10−2 | 1.50 × 10−19 |
| DOID:2531 | hematologic cancer | 2.32 × 10−17 | 8.48 × 10−3 | 1.97 × 10−19 |
| DOID:0060083 | immune system cancer | 2.67 × 10−17 | 8.75 × 10−3 | 2.33 × 10−19 |
| DOID:9256 | colorectal cancer | 2.05 × 10−16 | 1.37 × 10−3 | 2.80 × 10−19 |
| DOID:5672 | large intestine cancer | 2.37 × 10−16 | 1.37 × 10−3 | 3.24 × 10−19 |
| DOID:219 | colon cancer | 3.64 × 10−16 | 1.37 × 10−3 | 4.97 × 10−19 |
| DOID:10283 | prostate cancer | 1.21 × 10−17 | 4.18 × 10−2 | 5.04 × 10−19 |
| DOID:1324 | lung cancer | 8.31 × 10−17 | 7.16 × 10−3 | 5.95 × 10−19 |
| DOID:1240 | leukemia | 1.95 × 10−16 | 4.48 × 10−3 | 8.72 × 10−19 |
| DOID:0050615 | respiratory system cancer | 2.30 × 10−16 | 7.44 × 10−3 | 1.71 × 10−18 |
| DOID:0050686 | organ system cancer | 5.63 × 10−16 | 1.09 × 10−2 | 6.16 × 10−18 |
| DOID:3908 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | 1.19 × 10−14 | 2.64 × 10−3 | 3.15 × 10−17 |
| DOID:3905 | lung carcinoma | 2.40 × 10−14 | 4.21 × 10−3 | 1.01 × 10−16 |
| DOID:1749 | squamous cell carcinoma | 1.02 × 10−13 | 1.37 × 10−3 | 1.39 × 10−16 |
| DOID:1909 | melanoma | 1.41 × 10−11 | 1.37 × 10−3 | 1.92 × 10−14 |
| Gene | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| CCND1 | GCCTCTAAGATGAAGGAGAC | CCATTTGCAGCAGCTC |
| CDKN1B | AAAATGTTTCAGACGGTTCC | ATTCGAGCTGTTTACGTTTG |
| BAX | TCTGAGCAGATCATGAAGAC | TCCATGTTACTGTCCAGTTC |
| BCL-2 | GATTGTGGCCTTCTTTGAG | GTTCCACAAAGGCATCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wolan, R.; Wawszczyk, J.; Orchel, A.; Kapral, M. Antitumor Activity of Metformin in Combination with Binimetinib Against Melanoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311403
Wolan R, Wawszczyk J, Orchel A, Kapral M. Antitumor Activity of Metformin in Combination with Binimetinib Against Melanoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311403
Chicago/Turabian StyleWolan, Radosław, Joanna Wawszczyk, Arkadiusz Orchel, and Małgorzata Kapral. 2025. "Antitumor Activity of Metformin in Combination with Binimetinib Against Melanoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311403
APA StyleWolan, R., Wawszczyk, J., Orchel, A., & Kapral, M. (2025). Antitumor Activity of Metformin in Combination with Binimetinib Against Melanoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311403






