The Mechanism of LTXN4C-Induced Ca2+ Influx Involves Latrophilin-Mediated Activation of Cav2.x Channels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
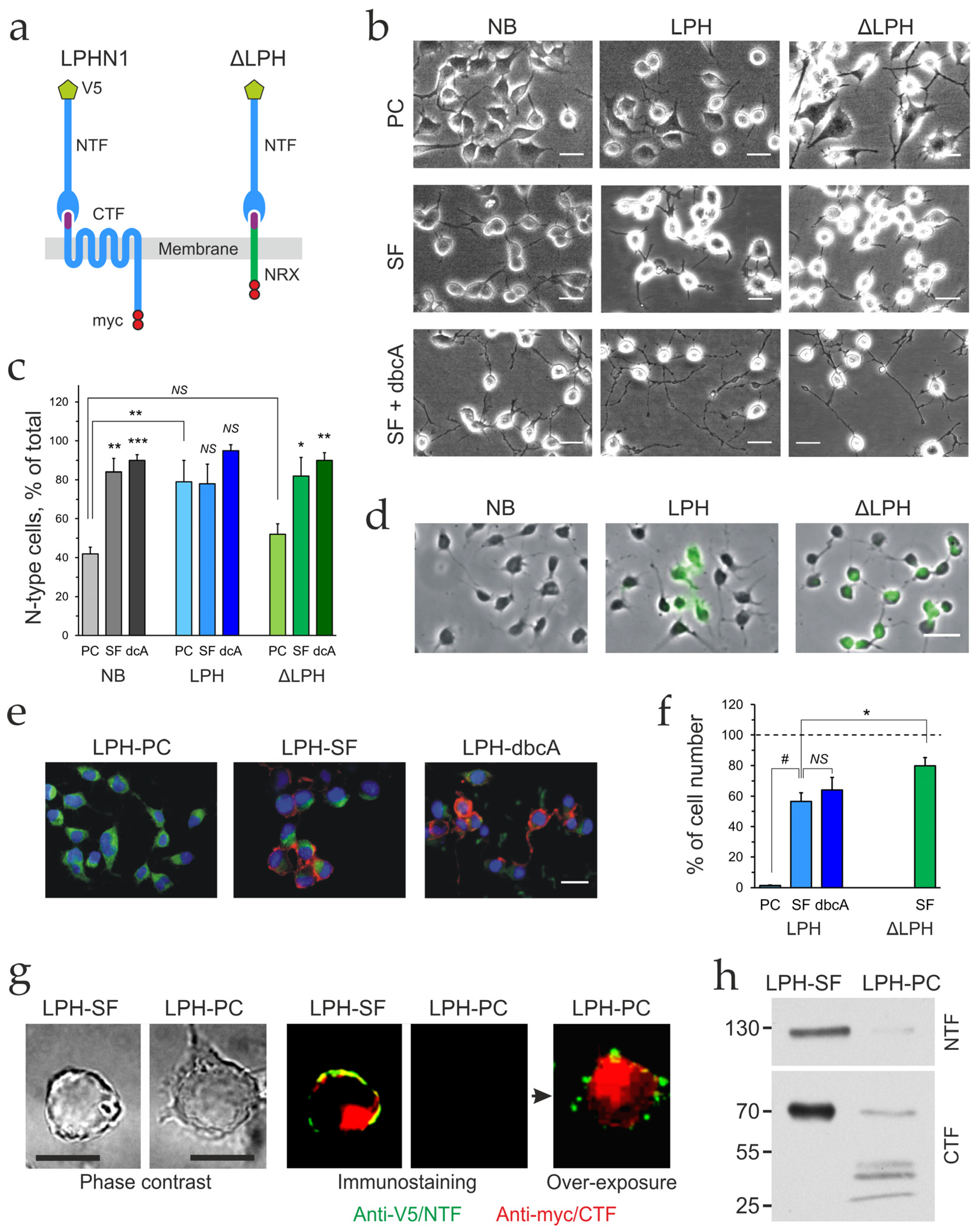
2.1. Differentiation Changes Cell Morphology and Receptor Expression
2.2. LPHN1 Activation by LTXN4C Elevates Ca2+cyt in the Presence of Ca2+e
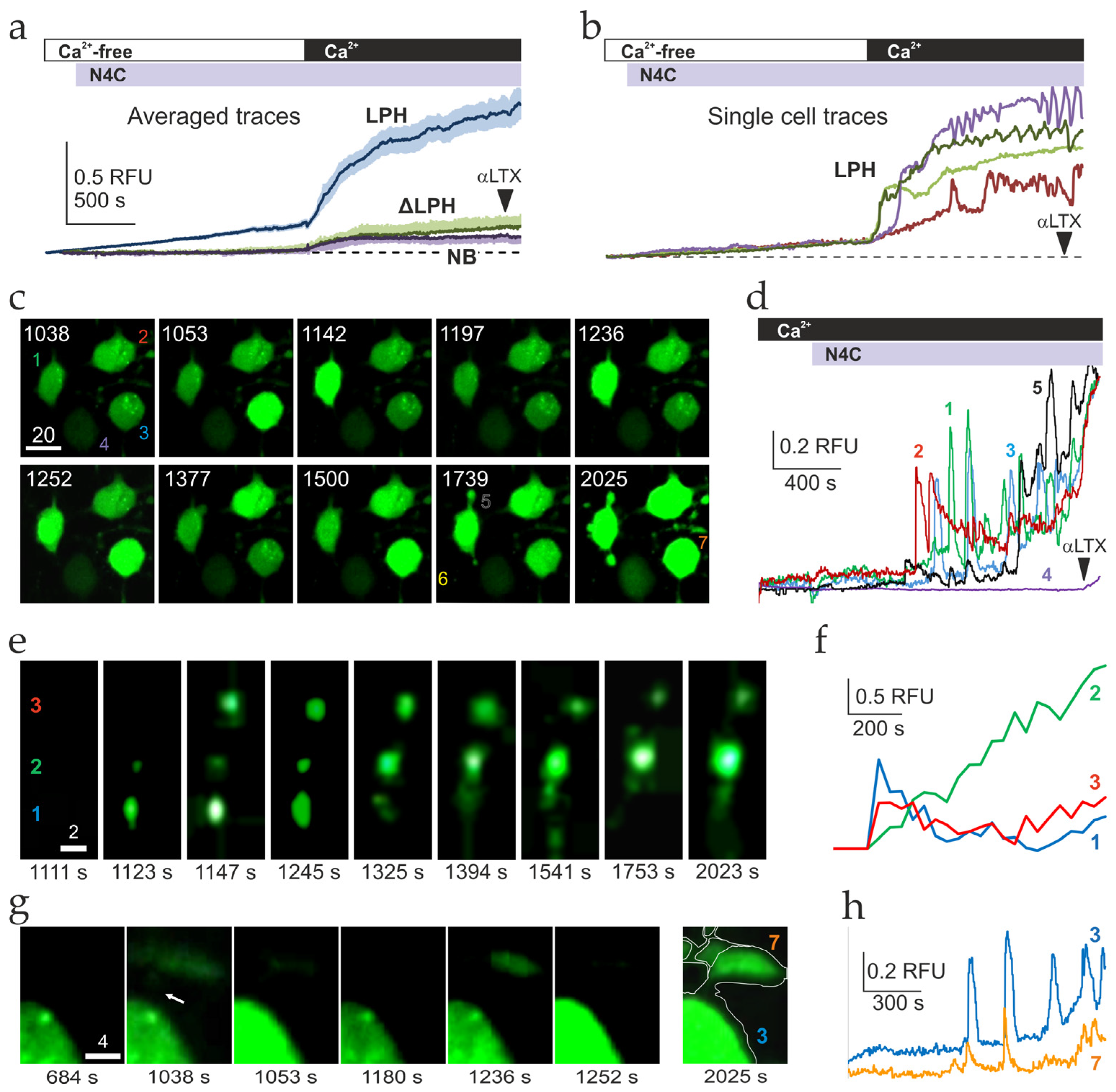
2.3. Ca2+ Signaling Induced by LPHN1 Activation in Individual Cells
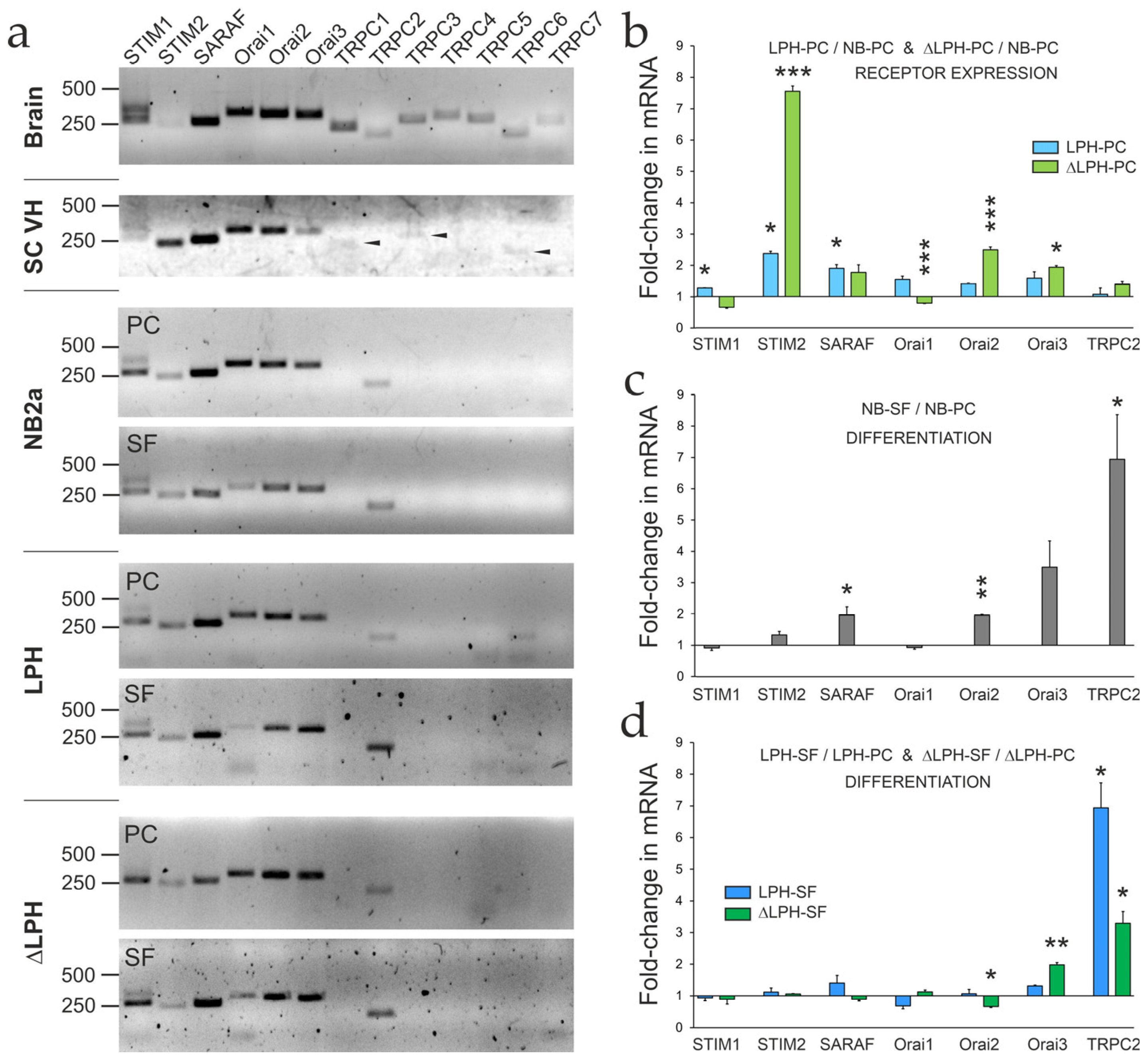
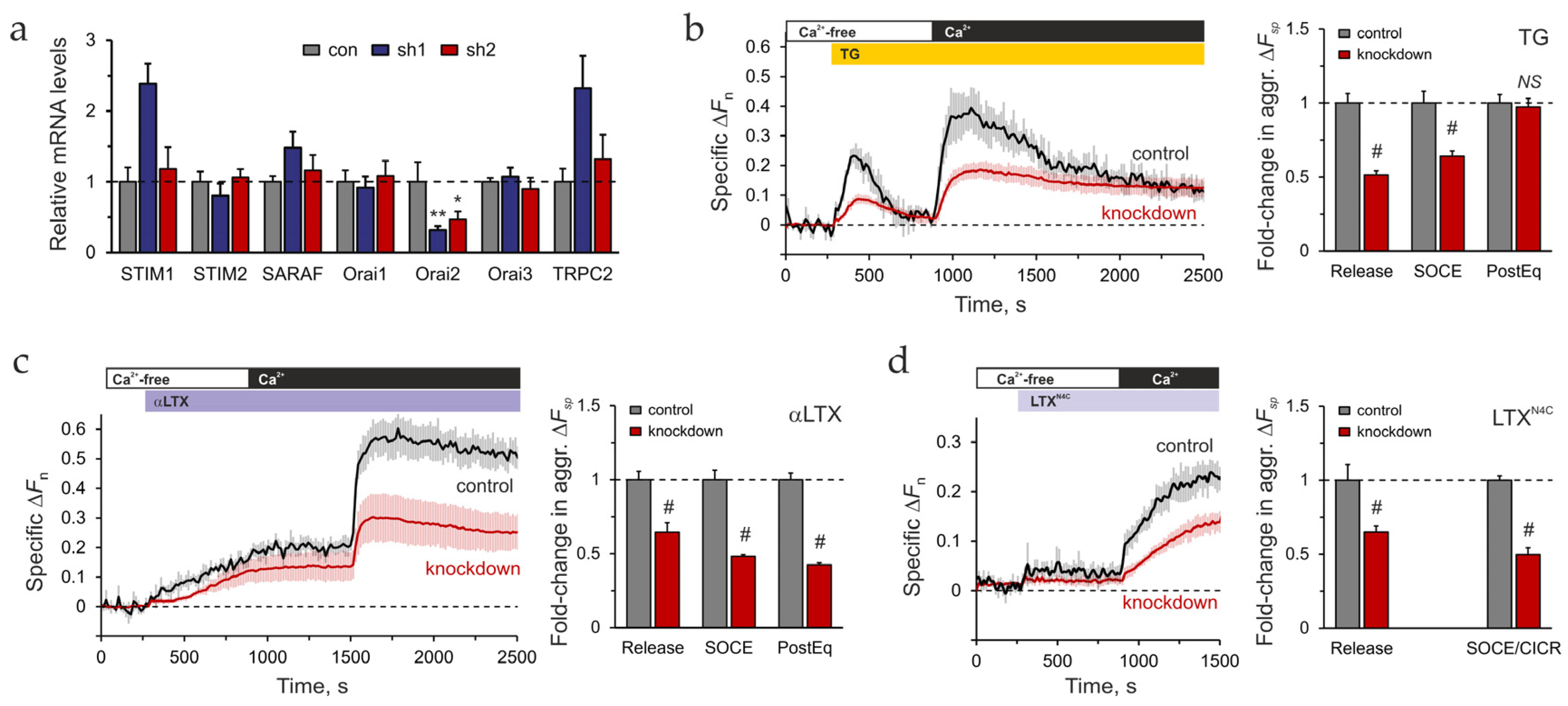
2.4. Expression of SOCE-Associated Proteins
2.5. The Role of Orai2 in LPHN1-Mediated LTXN4C Action
2.6. The Role of STIM2 in LPHN1-Mediated LTXN4C Action
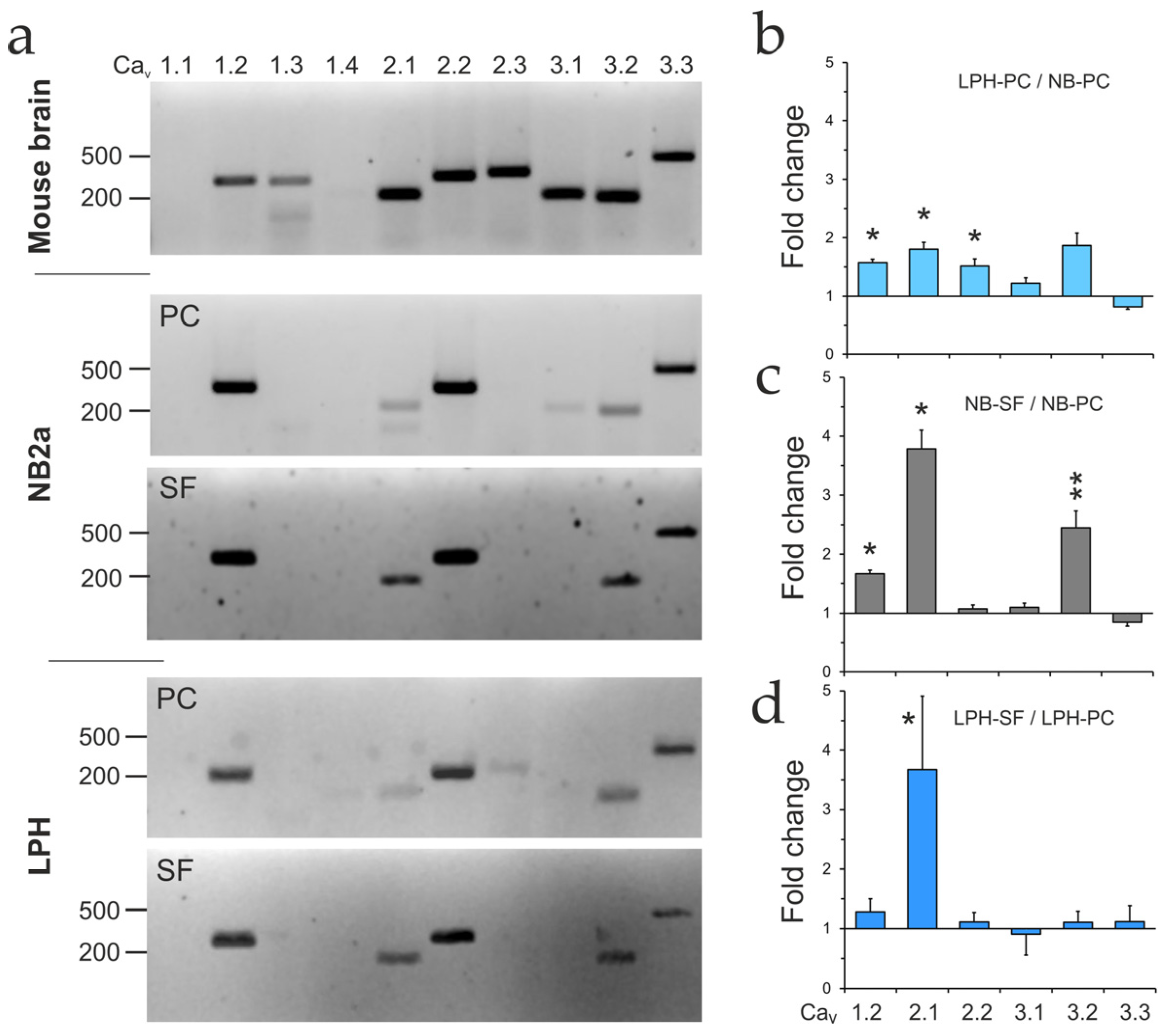
2.7. VGCC Expression
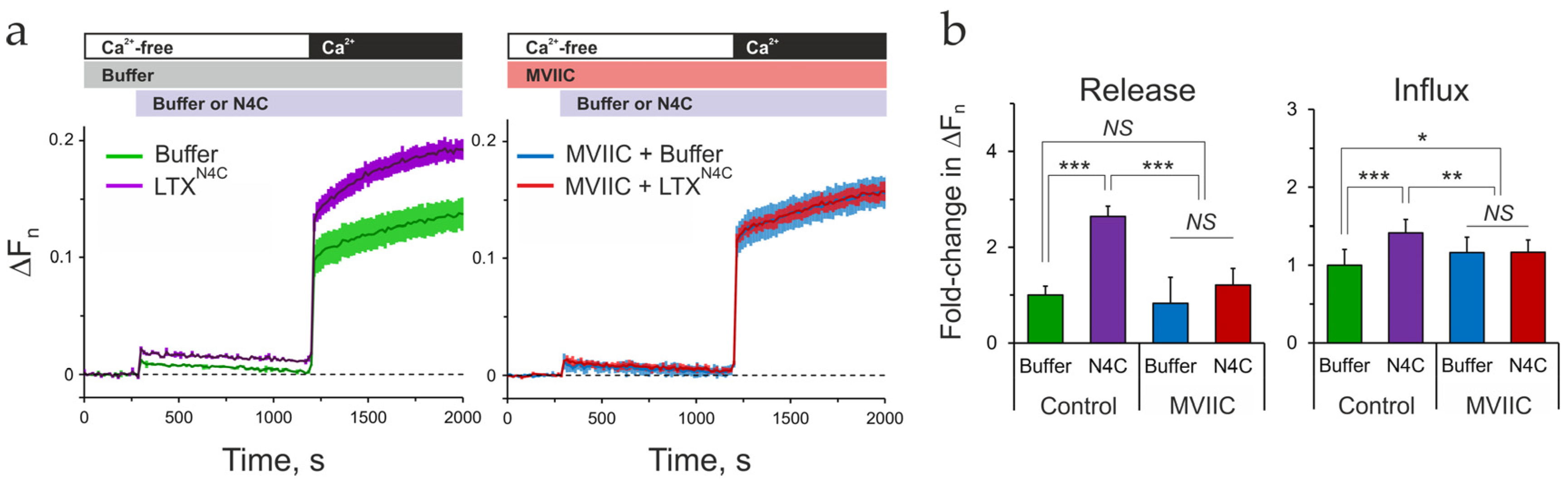
2.8. Cav2.1 Is Critical for LPHN1-Mediated LTXN4C Action
3. Discussion
3.1. NB Cells as a Neuronal Model
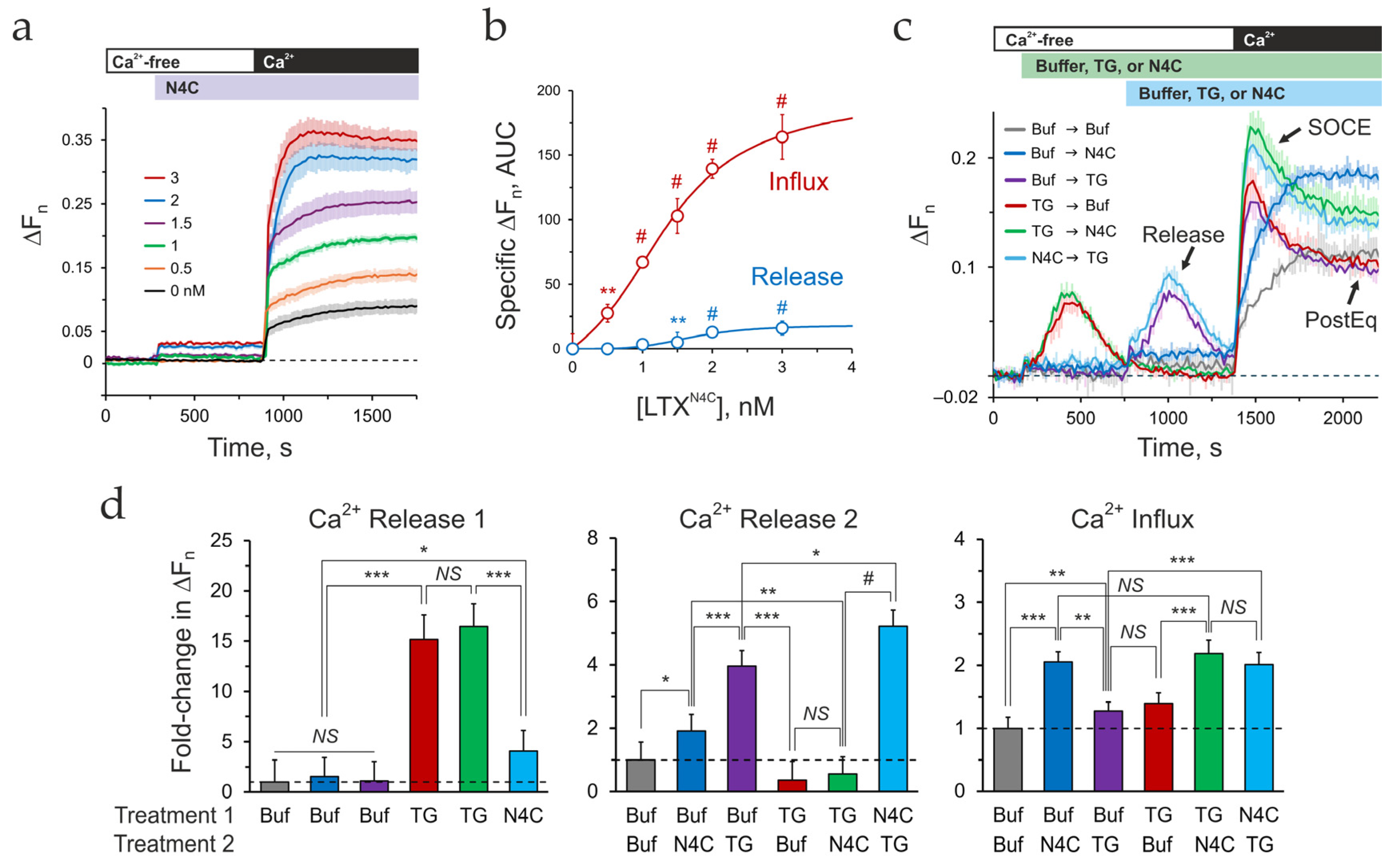
3.2. Deciphering the LTXN4C-Induced Calcium Signature
- Depletion of the LTXN4C-sensitive pools alone induces a gradual, non-inactivating influx, manifesting as combined asynchronous oscillations in individual cells.
- Depletion of the TG-sensitive ER alone produces a standard transient SOCE peak.
- When ER depletion follows LTXN4C-sensitive pools release, the subsequent SOCE is strongly augmented.
- Surprisingly, pre-depleting the ER, despite abolishing the LTXN4C-specific release, still produces an augmented SOCE.
3.3. Probing the Roles of Orai2 and STIM2
3.4. Identifying the Primary Ionic Effector: VGCCs
3.5. A Model for LPHN1-Mediated Activation of Neuronal VGCCs
3.6. Uniform Priming and Asynchronous Ca2+ Spiking
3.7. Limitations and Future Directions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. RNA Extraction
4.4. RT-PCR
4.5. Quantification of mRNA Expression
4.6. Immunocytochemistry
4.7. Fluorescent Ca2+cyt Recordings
4.7.1. Loading Cells with Fluo-4 AM
4.7.2. Population-Level Ca2+cyt Fluorescence Recording with Fluo-4
4.7.3. Ca2+cyt Fluorescence Recording in Single Cells by Confocal Microscopy with Fluo-4
4.7.4. Ca2+cyt Recording with GCaMP
4.8. Plasmid-Mediated Knockdown
4.9. Plasmid Transfection
4.10. Knocdown by Lentiviral Vector Transduction
4.11. Western Blotting
4.12. Image Analysis
4.13. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Explanation |
| [Ca2+] | Ca2+ concentration |
| ADGRL1 | Adhesion G-protein-coupled receptor L-type 1 |
| AFU | Arbitrary fluorescence units |
| AGPCR | Adhesion GPCR |
| AM | Acetoxymethyl ester |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| Ca2+cyt | Cytosolic Ca2+ |
| Ca2+e | Extracellular Ca2+ |
| Cav | α-Subunit of a VGCC |
| CICR | Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release |
| CTF | C-terminal fragment |
| DAG | Diacylglycerol |
| dbcAMP | Dibutyryl cAMP |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| FDA | Functional data analysis |
| GPCR | G-protein-coupled receptor |
| IP3 | Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate |
| KD | Knockdown |
| LPH-dbcA | NB cells stably expressing LPHN1 and differentiated by dbcAMP |
| LPHN1 | Latrophilin 1 |
| LPH-PC | Proliferating NB cells stably transfected with LPHN1 |
| LPH-SF | NB cells stably expressing LPHN1 and differentiated by serum deprivation |
| MOI | Multiplicity of infection |
| NB | Neuroblastoma 2a |
| NRX | Neurexin I |
| NTF | N-terminal fragment |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PIP2 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| PLC | Phospholipase C |
| PostEq | Post-SOCE Ca2+cyt equilibrium |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative RT-PCR |
| RB | Recording buffer |
| RFP | (Turbo) Red fluorescent protein |
| RFU | Relative fluorescence units |
| ROCC | Receptor-operated Ca2+ channel |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| RT-PCR | Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| RyR | Ryanodine receptor, Ca2+ release channel |
| SARAF | SOCE-associated regulatory factor |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SERCA | Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (Ca2+ pump) |
| SF | Serum-free |
| shRNA | Small hairpin RNA |
| SOCC | Store-operated Ca2+ channel |
| SOCE | Store-operated Ca2+ entry |
| STIM | Stromal interaction molecules |
| TG | Thapsigargin |
| TRPC | Transient receptor potential canonical |
| VGCC | Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel |
| αLTX | α-Latrotoxin |
| ΔLPH-dbcA | NB cells stably expressing ΔLPHN and differentiated by dbcAMP |
| ΔLPH-PC | Proliferating NB cells stably transfected with ΔLPHN |
| ΔLPH-SF | NB cells stably expressing ΔLPHN and differentiated by serum deprivation |
References
- Katz, B.; Miledi, R. The Timing of Calcium Action during Neuromuscular Transmission. J. Physiol. 1967, 189, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llinás, R.; Steinberg, I.Z.; Walton, K. Relationship between Presynaptic Calcium Current and Postsynaptic Potential in Squid Giant Synapse. Biophys. J. 1981, 33, 323–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, E.F. The Calcium Channel and the Organization of the Presynaptic Transmitter Release Face. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neher, E.; Sakaba, T. Multiple Roles of Calcium Ions in the Regulation of Neurotransmitter Release. Neuron 2008, 59, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emptage, N.J.; Reid, C.A.; Fine, A. Calcium Stores in Hippocampal Synaptic Boutons Ca2+ Entry, and Spontaneous Transmitter Release. Neuron 2001, 29, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llano, I.; González, J.; Caputo, C.; Lai, F.A.; Blayney, L.M.; Tan, Y.P.; Marty, A. Presynaptic Calcium Stores Underlie Large-Amplitude Miniature IPSCs and Spontaneous Calcium Transients. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 1256–1265, Erratum in Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, K.; Akita, T.; Osanai, M.; Shirasaki, T.; Kijima, H.; Kuba, K. A Ca2+-Induced Ca2+ Release Mechanism Involved in Asynchronous Exocytosis at Frog Motor Nerve Terminals. J. Gen. Physiol. 1998, 112, 593–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkus, C.R.L.; Stricker, C. The Contribution of Intracellular Calcium Stores to MEPSCs Recorded in Layer II Neurones of Rat Barrel Cortex. J. Physiol. 2002, 545, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; Nohmi, M.; Kuba, K. Characteristics of Ca2+ Release Induced by Ca2+ Influx in Cultured Bullfrog Sympathetic Neurones. J. Physiol. 1993, 464, 245–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.B.; Cunnane, T.C. Ryanodine-Sensitive Calcium Stores Involved in Neurotransmitter Release from Sympathetic Nerve Terminals of the Guinea-Pig. J. Physiol. 1996, 497, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, N.; Kijima, H. Ca2+-Dependent and -Independent Components of Transmitter Release at The Frog Neuromuscular Junction. J. Physiol. 1992, 455, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, W.M.; Zucker, R.S. Time Course of Transmitter Release Calculated from Simulations of a Calcium Diffusion Model. Biophys. J. 1992, 61, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, T.; Marty, A.; Llano, I. Presynaptic Calcium Stores and Synaptic Transmission. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2005, 15, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szikra, T.; Cusato, K.; Thoreson, W.B.; Barabas, P.; Bartoletti, T.M.; Krizaj, D. Depletion of Calcium Stores Regulates Calcium Influx and Signal Transmission in Rod Photoreceptors. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 4859–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, L.; Kuznicki, J. SOCE in Neurons: Signaling or Just Refilling? Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1853, 1940–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Alvarez, G.; Lu, B.; Yap, K.A.F.; Wong, L.C.; Thevathasan, J.V.; Lim, L.; Ji, F.; Tan, K.W.; Mancuso, J.J.; Tang, W.; et al. STIM2 Regulates PKA-Dependent Phosphorylation and Trafficking of AMPARs. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 1141–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakriya, M.; Lewis, R.S. Store-Operated Calcium Channels. Physiol Rev. 2015, 95, 1383–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhikara, A.; Maciąg, F.; Sorush, N.; Heine, M. Activity-Dependent Localization and Heterogeneous Dynamics of STIM1 and STIM2 at ER-PM Contacts in Hippocampal Neurons. bioRxiv 2024, 116290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanaday, N.L.; Nosyreva, E.; Shin, O.H.; Zhang, H.; Aklan, I.; Atasoy, D.; Bezprozvanny, I.; Kavalali, E.T. Presynaptic Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry Drives Excitatory Spontaneous Neurotransmission and Augments Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Neuron 2021, 109, 1314–1332.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Sánchez, P.; del Arco, A.; Esteban, J.A.; Satrústegui, J. Store-Operated Calcium Entry Is Required for MGluR-Dependent Long Term Depression in Cortical Neurons. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobbersmed, J.R.L.; Grasskamp, A.T.; Jusyte, M.; Böhme, M.A.; Ditlevsen, S.; Sørensen, J.B.; Walter, A.M. Rapid Regulation of Vesicle Priming Explains Synaptic Facilitation despite Heterogeneous Vesicle:Ca2+ Channel Distances. eLife 2020, 9, e51032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putney, J.W. Capacitative Calcium Entry: From Concept to Molecules. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 231, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.; Yasui, T.; Fujisawa, S.; Yamada, R.X.; Yamada, M.K.; Nishiyama, N.; Matsuki, N.; Ikegaya, Y. Activity-Evoked Capacitative Ca2+ Entry: Implications in Synaptic Plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7737–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazbeck, P.; Tauseef, M.; Kruse, K.; Amin, M.R.; Sheikh, R.; Feske, S.; Komarova, Y.; Mehta, D. STIM1 Phosphorylation at Y361 Recruits Orai1 to STIM1 Puncta and Induces Ca 2+ Entry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itagaki, K.; Kannan, K.B.; Hauser, C.J. Lysophosphatidic Acid Triggers Calcium Entry through a Non-Store-Operated Pathway in Human Neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 77, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, N.; Yamada, S.; Yanagida, S.; Ono, A.; Yasuhiko, Y.; Nishida, M.; Kanda, Y. Lysophosphatidic Acid Promotes the Expansion of Cancer Stem Cells via TRPC3 Channels in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, R.G.; Sikorska, M.; Sandhu, J.K.; Lanthier, P.; Ribecco-Lutkiewicz, M.; Bani-Yaghoub, M. Differentiation of Mouse Neuro 2A Cells into Dopamine Neurons. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 186, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizawa, S.; Yamamuro, Y. Possible Involvement of DNA Methylation in Hippocampal Synaptophysin Gene Expression during Postnatal Development of Mice: DNA Methylation Regulates Syp Expression. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 132, 104587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehmelt, L.; Smart, F.M.; Ozer, R.S.; Halpain, S. The Role of Microtubule-Associated Protein 2c in the Reorganization of Microtubules and Lamellipodia during Neurite Initiation. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 9479–9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmoto, M.; Shibuya, Y.; Taniguchi, S.; Nakade, T.; Nomura, M.; Ikeda-Matsuo, Y.; Daikoku, T. Protective Effects of Butein on Corticosterone-Induced Cytotoxicity in Neuro2A Cells. IBRO Rep. 2020, 8, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigont, V.; Kolobkova, Y.; Skopin, A.; Zimina, O.; Zenin, V.; Glushankova, L.; Kaznacheyeva, E. Both Orai1 and TRPC1 Are Involved in Excessive Store-Operated Calcium Entry in Striatal Neurons Expressing Mutant Huntingtin Exon 1. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, C.I.; Feng, B.; Wang, J.B.; Golovina, V.A. Histidine Triad Nucleotide-Binding Protein 1 (HINT1) Regulates Ca2+ Signaling in Mouse Fibroblasts and Neuronal Cells via Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry Pathway. Am. J. Physiol.—Cell Physiol. 2013, 304, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Nayak, S.; Guin, S.; Mishra, A. Impact of Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation on Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase 2b Downregulation and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2025, 8, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, K.; Uldrijan, S.; Telkamp, M.; Röthlein, N.; Neyses, L. The Plasmamembrane Calmodulin-Dependent Calcium Pump: A Major Regulator of Nitric Oxide Synthase I. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volynski, K.E.; Silva, J.-P.P.; Lelianova, V.G.; Rahman, M.A.; Hopkins, C.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. Latrophilin Fragments Behave as Independent Proteins That Associate and Signal on Binding of LTXN4C. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4423–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davletov, B.A.; Shamotienko, O.G.; Lelianova, V.G.; Grishin, E.V.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. Isolation and Biochemical Characterization of a Ca2+-Independent α-Latrotoxin-Binding Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 23239–23245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushkaryov, Y.A.; Rohou, A.; Sugita, S. α-Latrotoxin and Its Receptors. In Pharmacology of Neurotransmitter Release; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 171–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.-P.J.-P.P.; Lelianova, V.G.; Ermolyuk, Y.S.; Vysokov, N.V.; Hitchen, P.G.; Berninghausen, O.; Rahman, M.A.; Zangrandi, A.; Fidalgo, S.; Tonevitsky, A.G.; et al. Latrophilin 1 and Its Endogenous Ligand Lasso/Teneurin-2 Form a High-Affinity Transsynaptic Receptor Pair with Signaling Capabilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12113–12118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.C.; Nazarko, O.V.; Sando III, R.; Salzman, G.S.; Li, N.S.; Sudhof, T.C.; Arac, D. Structural Basis of Latrophilin-FLRT-UNC5 Interaction in Cell Adhesion. Structure 2015, 23, 1678–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Cai, Z. Ginsenoside Rh3-Induced Neurotoxicity Involving the IP3R-Ca2+/NOX2/NF-κB Signaling Pathways. J. Nat. Med. 2025, 79, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Chang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, L. MicroRNA Analysis in Mouse Neuro-2a Cells after Pseudorabies Virus Infection. J. Neurovirol. 2017, 23, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma’ayan, A.; Jenkins, S.L.; Barash, A.; Iyengar, R. Neuro2A Differentiation by Gαi/o Pathway. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, cm1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hossain, M.S.; Mineno, K.; Katafuchi, T. Neuronal Orphan G-Protein Coupled Receptor Proteins Mediate Plasmalogens-Induced Activation of ERK and Akt Signaling. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Checco, J.W. Evaluating Functional Ligand-GPCR Interactions in Cell-Based Assays. Methods Cell Biol. 2021, 166, 15–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, J.K.; Islam, Q.S.; Benlaouer, O.; Tonevitskaya, S.A.; Petitto, E.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. α-Latrotoxin Actions in the Absence of Extracellular Ca2+ Require Release of Stored Ca2+. Toxins 2025, 17, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichtchenko, K.; Khvotchev, M.; Kiyatkin, N.; Simpson, L.; Sugita, S.; Südhof, T.C. α-Latrotoxin Action Probed with Recombinant Toxin: Receptors Recruit α-Latrotoxin but Do Not Transduce an Exocytotic Signal. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 6188–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.A.; Biedler, J.L.; Spengler, B.A. A Role for Distinct Cell Types in Determining Malignancy in Human Neuroblastoma Cell Lines and Tumors. Cancer Lett. 2003, 197, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.T.; Prasad, K.N. Differentiation of Mouse Neuroblastoma Cells in Vitro and in Vivo Induced by Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate (CAMP). J. Pediatr. Surg. 1976, 11, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.M.; Riddoch, F.C.; Robson, A.; Redfern, C.P.F.; Cheek, T.R. Mechanistic and Functional Changes in Ca2+ Entry after Retinoic Acid-Induced Differentiation of Neuroblastoma Cells. Biochem. J. 2005, 388, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitto, E.; Blackburn, J.K.; Rahman, M.A.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. The Dissociation of Latrophilin Fragments by Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) Inhibits LTXN4C-Induced Neurotransmitter Release. Toxins 2025, 17, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craney, A.; Rape, M. Dynamic Regulation of Ubiquitin-Dependent Cell Cycle Control. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 25, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, A.E.H.; Boardman, A.P.; Wang, D.C.; Huttlin, E.L.; Everley, R.A.; Dephoure, N.; Zhou, C.; Koren, I.; Gygi, S.P.; Elledge, S.J. Quantitative Proteomic Atlas of Ubiquitination and Acetylation in the DNA Damage Response. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foot, N.; Henshall, T.; Kumar, S. Ubiquitination and the Regulation of Membrane Proteins. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 253–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilberto, S.; Peter, M. Dynamic Ubiquitin Signaling in Cell Cycle Regulation. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, A.C.; Volynski, K.E.; Lelianova, V.G.; Orlova, E.V.; Van Renterghem, C.; Canepari, M.; Seagar, M.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. α-Latrotoxin, Acting via Two Ca2+-Dependent Pathways, Triggers Exocytosis of Two Pools of Synaptic Vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 44695–44703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capogna, M.; Volynski, K.E.; Emptage, N.J.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. The α-Latrotoxin Mutant LTXN4C Enhances Spontaneous and Evoked Transmitter Release in CA3 Pyramidal Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 4044–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wan, Q.; Lin, X.; Zhu, H.; Volynski, K.; Ushkaryov, Y.; Xu, T. α-Latrotoxin Modulates the Secretory Machinery via Receptor-Mediated Activation of Protein Kinase C. Traffic 2005, 6, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajus, S.; Vacher, P.; Huber, D.; Dubois, M.; Benassy, M.-N.N.; Ushkaryov, Y.; Lang, J. α-Latrotoxin Induces Exocytosis by Inhibition of Voltage-Dependent K+ Channels and by Stimulation of L-Type Ca2+ Channels via Latrophilin in Beta-Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 5522–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelyanova, V.G.; Thomson, D.; Ribchester, R.R.; Tonevitsky, E.A.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. Activation of α-Latrotoxin Receptors in Neuromuscular Synapses Leads to a Prolonged Splash Acetylcholine Release. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009, 147, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Déak, F.; Liu, X.; Khvotchev, M.; Li, G.; Kavalali, E.T.; Sugita, S.; Sudhof, T.C. α-Latrotoxin Stimulates a Novel Pathway of Ca2+-Dependent Synaptic Exocytosis Independent of the Classical Synaptic Fusion Machinery. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 8639–8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.; Volynski, K.; Brenner, T.; Ushkaryov, Y.; Walker, M.; Semyanov, A. Different Transporter Systems Regulate Extracellular GABA from Vesicular and Non-Vesicular Sources. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volynski, K.E.; Capogna, M.; Ashton, A.C.; Thomson, D.; Orlova, E.V.; Manser, C.F.; Ribchester, R.R.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. Mutant α-Latrotoxin (LTXN4C) Does Not Form Pores and Causes Secretion by Receptor Stimulation. This Action Does Not Require Neurexins. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 31058–31066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, J.O.; Silverman, B.W. Functional Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootman, M.D.; Rietdorf, K.; Collins, T.; Walker, S.; Sanderson, M. Ca2+-Sensitive Fluorescent Dyes and Intracellular Ca2+ Imaging. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2013, 8, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, R.; Lach, B.; Gregor, A.; Al-Mazidi, H.; Proulx, P. Retinoic Acid- and Staurosporine-Induced Bidirectional Differentiation of Human Neuroblastoma Cell Lines. Exp. Cell Res. 1992, 202, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palty, R.; Raveh, A.; Kaminsky, I.; Meller, R.; Reuveny, E. SARAF Inactivates the Store Operated Calcium Entry Machinery to Prevent Excess Calcium Refilling. Cell 2012, 149, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.; Ahuja, M.; Maléth, J.; Moreno Claudia, C.; Yuan Joseph, J.; Kim, M.S.; Muallem, S. The STIM1 CTID Domain Determines Access of SARAF to SOAR to Regulate Orai1 Channel Function. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 202, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serwach, K.; Gruszczynska-Biegala, J. Target Molecules of STIM Proteins in the Central Nervous System. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 617422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.T.; Ong, H.L.; Liu, X.; Ambudkar, I.S. Contribution and Regulation of TRPC Channels in Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry. Curr. Top Membr. 2013, 71, 149–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambudkar, I.S.; Ong, H.L.; Liu, X.; Bandyopadhyay, B.; Cheng, K.T. TRPC1: The Link between Functionally Distinct Store-Operated Calcium Channels. Cell Calcium 2007, 42, 213–223, Erratum in Cell Calcium 2008, 44, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, S.A.; Wissenbach, U.; Philipp, S.E.; Freichel, M.; Cavalié, A.; Flockerzi, V. Murine ORAI2 Splice Variants Form Functional Ca2+ Release-Activated Ca2+ (CRAC) Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 19375–19384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, T.; Goltstein, P.M.; Portugues, R.; Griesbeck, O. Putting a Finishing Touch on GECIs. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, A.B. Store-Operated CRAC Channels: Function in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegierski, T.; Kuznicki, J. Neuronal Calcium Signaling via Store-Operated Channels in Health and Disease. Cell Calcium 2018, 74, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootman, M.D.; Collins, T.J.; Peppiatt, C.M.; Prothero, L.S.; MacKenzie, L.; De Smet, P.; Travers, M.; Tovey, S.C.; Seo, J.T.; Berridge, M.J.; et al. Calcium Signalling—An Overview. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 12, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bers, D.M. Cardiac Excitation–Contraction Coupling. Nature 2002, 415, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamponi, G.W.; Striessnig, J.; Koschak, A.; Dolphin, A.C. The Physiology, Pathology, and Pharmacology of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels and Their Future Therapeutic Potential. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 821–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipscombe, D.; Helton, T.D.; Xu, W. L-Type Calcium Channels: The Low Down. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 92, 2633–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillyard, D.R.; Monje, V.D.; Mintz, I.M.; Bean, B.P.; Nadasdi, L.; Ramachandran, J.; Miljanich, G.; Azimi-Zoonooz, A.; McIntosh, J.M.; Cruz, L.J.; et al. A New Conus Peptide Ligand for Mammalian Presynaptic Ca2+ Channels. Neuron 1992, 9, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, A.; Tsien, R.W. Pharmacological Dissection of Multiple Types of Ca2+ Channel Currents in Rat Cerebellar Granule Neurons. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 2995–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, P.G.; Lewis, R.S.; Rao, A. Molecular Basis of Calcium Signaling in Lymphocytes: STIM and ORAI. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 28, 491–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soboloff, J.; Rothberg, B.S.; Madesh, M.; Gill, D.L. STIM Proteins: Dynamic Calcium Signal Transducers. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandman, O.; Liou, J.; Park, W.S.; Meyer, T. STIM2 Is a Feedback Regulator That Stabilizes Basal Cytosolic and Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Levels. Cell 2007, 131, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Manser, C.; Benlaouer, O.; Suckling, J.; Blackburn, J.K.; Silva, J.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. C-terminal Phosphorylation of Latrophilin-1/ADGRL1 Affects the Interaction between Its Fragments. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1456, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J.; Lipp, P.; Bootman, M.D. The Versatility and Universality of Calcium Signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitobello, A.; Mazel, B.; Lelianova, V.G.; Zangrandi, A.; Petitto, E.; Suckling, J.; Salpietro, V.; Meyer, R.; Elbracht, M.; Kurth, I.; et al. ADGRL1 Haploinsufficiency Causes a Variable Spectrum of Neurodevelopmental Disorders in Humans and Alters Synaptic Activity and Behavior in a Mouse Model. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 1436–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.-P.P.; Lelianova, V.; Hopkins, C.; Volynski, K.E.; Ushkaryov, Y. Functional Cross-Interaction of the Fragments Produced by the Cleavage of Distinct Adhesion G-Protein-Coupled Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6495–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruijter, J.M.; Ramakers, C.; Hoogaars, W.M.H.; Karlen, Y.; Bakker, O.; van den Hoff, M.J.B.; Moorman, A.F.M. Amplification Efficiency: Linking Baseline and Bias in the Analysis of Quantitative PCR Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grynkiewicz, G.; Poenie, M.; Tsien, R.Y. A New Generation of Ca2+ Indicators with Greatly Improved Fluorescence Properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maravall, M.; Mainen, Z.F.; Sabatini, B.L.; Svoboda, K. Estimating Intracellular Calcium Concentrations and Buffering without Wavelength Ratioing. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 2655–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volynski, K.E.; Meunier, F.A.; Lelianova, V.G.; Dudina, E.E.; Volkova, T.M.; Rahman, M.A.; Manser, C.; Grishin, E.V.; Dolly, J.O.; Ashley, R.H.; et al. Latrophilin, Neurexin, and Their Signaling-Deficient Mutants Facilitate α-Latrotoxin Insertion into Membranes but Are Not Involved in Pore Formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 41175–41183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristova, K.; Wimley, W.C. Determining the Statistical Significance of the Difference between Arbitrary Curves: A Spreadsheet Method. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Target | Primer Sequence | Size (bp) | Annealing T *, °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Forward/Reverse) | Optimal | Used | ||
| STIM1 | CCGCCCTAACCCCGCCCACT/CCCCCTCAATCAGCCGATGGC | 296 | 62.1 | 60 |
| STIM2 | TCAGCCGGCAATGATAGCAAG/TGGAAAGCCCCAGTGGAGTTA | 256 | 54.6 | 55 |
| SARAF | GCGCCTCCTCCGGGCTTTAA/TCCCTGCGCCTCCACCCA | 280 | 61.4 | 60 |
| Orai1 | CGGGACGCTGCTTTTCCTA/CGGTGTTAGAGAATGGTCCCC | 335 | 61.2 | 60 |
| Orai2 | CCTGTGGCCCCCAGATGTTGA/AGTACTGGCCCCCACGCAAGC | 327 | 59.9 | 60 |
| Orai3 | ACAGACCGCCACAAGCAGGAG/GCAGGCGGGCCTCTTTCC | 318 | 59.4 | 55 |
| TRPC1 | GAATCGCGTAACCAGCTCAGC/CTGCAGTGGGCCCAAAATAGA | 225 | 55.2 | 55 |
| TRPC2 | AAGGCCGCAGCCAGAGTGTCT/AGGAGGCGCAGTGCAAAGGAT | 181 | 58.3 | 60 |
| TRPC3 | GGAGGGGCCCCGGGAGTACAT/TCCGGGAGAAGCTGAGCACCA | 284 | 59.8 | 60 |
| TRPC4 | TTTGTTGGGGCCACCATGTTT/CGCCCAATTGTCCCGAAGC | 299 | 55.5 | 55 |
| TRPC5 | AAAACAAATGAGGGGCTAACA/CTTGGGCGCCACTAGCTCTTG | 280 | 54.4 | 55 |
| TRPC6 | CTCAAGGCCCCAAAGAATACT/GTCCCCCAGTGTGACTTTTGT | 179 | 51.8 | 55 |
| TRPC7 | GGCCGCGGGAGTACGTGCTA/CAACCGCAATGGCGTACAGCC | 261 | 60.3 | 60 |
| β-actin | TTCGCGGGCGACGATGC/GGGGCCACACGCAGCTCATT | 233 | 60.2 | 60 |
| Cycl. ** | TAAGCATGATCGGGAGGGTT/CGTCCAGATGAGGAGTCGGAA | 101 | 52.9 | 55 |
| Target | Primer Sequence | Size (bp) | Annealing T *, °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Forward/Reverse) | Optimal | Used | ||
| Cav1.1 | ACGCCAATGCCAATGTT/ACGTGCTCCTCAAAGTTCC | 334 | 56.4 | 56 |
| Cav1.2 | CAGACCCCTACGGCCCATCCCTACCCTA/TGTCTGCGGCGTTCTCCATCTCCTCTATTG | 353 | 64.0 | 63 |
| Cav1.3 | CGCGCTGCCCTGCCCCTG/CACTCCTCTGCTTGTCGCTGTTCTTGTTC | 337 | 62.0 | 61 |
| Cav1.4 | ACCATGTGCCACGCCGACG/GCCGCCAAGTTTGCCAAGGTATCC | 260 | 61.1 | 61 |
| Cav2.1 | CAAAGCCCGGCGACTGGATGACTACTC/GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGTGGCCGATGCTTCC | 253 | 63.4 | 63 |
| Cav2.2 | GACCCCACGCCCCAGCATCACCTACAAGA/CCATTGGGTACACGGCGGAGA | 354 | 61.7 | 61 |
| Cav2.3 | GCCACCAAAGCCTCGTCCCCTCCTCTCC/CCTCCGCCGCCGATAGTGCCCGTTAG | 376 | 65.2 | 63 |
| Cav3.1 | GGCGCCATCCCTAAACTACC/CAGGCGGATGTGCTTGGAGACTTT | 246 | 60.5 | 61 |
| Cav3.2 | CCCGGCCGATGAGGAGGTC/GGCCATCCCCATTATCCAGTTCC | 230 | 61.5 | 61 |
| Cav3.3 | GGGGGCCATTCCATTCAACC/GCCCGCAGCCCACGCAGACTA | 471 | 62.4 | 63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blackburn, J.K.; Silva, J.-P.; Petitto, E.; Cholewa, D.; Fasler-Kan, E.; Volynski, K.E.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. The Mechanism of LTXN4C-Induced Ca2+ Influx Involves Latrophilin-Mediated Activation of Cav2.x Channels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211200
Blackburn JK, Silva J-P, Petitto E, Cholewa D, Fasler-Kan E, Volynski KE, Ushkaryov YA. The Mechanism of LTXN4C-Induced Ca2+ Influx Involves Latrophilin-Mediated Activation of Cav2.x Channels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):11200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211200
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlackburn, Jennifer K., John-Paul Silva, Evelina Petitto, Dietmar Cholewa, Elizaveta Fasler-Kan, Kirill E. Volynski, and Yuri A. Ushkaryov. 2025. "The Mechanism of LTXN4C-Induced Ca2+ Influx Involves Latrophilin-Mediated Activation of Cav2.x Channels" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 11200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211200
APA StyleBlackburn, J. K., Silva, J.-P., Petitto, E., Cholewa, D., Fasler-Kan, E., Volynski, K. E., & Ushkaryov, Y. A. (2025). The Mechanism of LTXN4C-Induced Ca2+ Influx Involves Latrophilin-Mediated Activation of Cav2.x Channels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 11200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211200






