Non-Coding RNA in Type 2 Diabetes Cardio–Renal Complications and SGLT2 Inhibitor Response
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs in T2DM
2.1. Identification of T2DM miRNA Biomarkers
2.2. Circulating miRNA as Biomarkers of T2DM
| ncRNA | Expression Level | Comparison Groups | Source | Identification Method | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-375, miR-30a, miR-34a, miR-7a, miR-486-5p miR-17-92 cluster, miR-130a-3p, miR-130b-3p, and miR-152-3p | Up | Mouse models of T2DM/healthy controls | Murine pancreatic beta-cells, pancreatic beta-cell lines | qRT-PCR | [33] |
| miR-6948-5p; miR-6964-3p; miR-677-5p; miR-670-3p; 12_4382 | Up | Mice on a high-fat diet/low-fat diet | Pancreatic islets | RNA-seq | [34] |
| miR-3572-5p; miR-216a-3p; miR-802-3p; miR-1188-5p | Down | ||||
| hsa-miR-4660; hsa-miR-451a; hsa-miR-3146 | Up | Patients with SIRD/healthy individuals | Blood serum | RNA-seq | [55] |
| hsa-miR-221-5p; hsa-miR-6852-5p; hsa-miR-224-5p; hsa-miR-199a-5p; hsa-miR-30e-3p; hsa-miR-1301-3p; hsa-miR-214-3p; hsa-miR-744-5p; hsa-miR-766-3p; hsa-miR-1307-3p; hsa-miR-432-5p | Down | ||||
| hsa-miR-3143; hsa-miR-942-3p; hsa-miR-20b-5p; hsa-miR-576-5p; hsa-miR-548ay-5p; hsa-miR-548d-5p; hsa-miR-454-5p; hsa-miR-324-3p; hsa-miR-1843 | Down | Patients with SIDD/healthy individuals | |||
| hsa-miR-548s | Up | Patients with MARD/healthy individuals | |||
| hsa-miR-3928-3p; hsa-miR-378c | Down | ||||
| hsa-miR-129-5p; hsa-miR-548bc; hsa-miR-3614-5p; hsa-miR-6866-5p; hsa-miR-6741-5p; hsa-miR-320a-3p; hsa-miR-5000-3p; hsa-miR-320e; hsa-miR-576-3p | Up | Patients with MOD/healthy individuals | |||
| hsa-miR-6837-3p; hsa-miR-6763-5p; hsa-miR-144-5p; hsa-miR-625-5p; hsa-miR-30e-3p; hsa-miR-628-3p; hsa-miR-152-3p; hsa-miR-570-3p; hsa-miR-584-5p; hsa-miR-26b-5p; hsa-miR-1197; hsa-miR-3177-3p; hsa-miR-659-5p; hsa-miR-1271-5p; hsa-miR-361-5p; hsa-miR-628-5p; hsa-miR-181a-5p; hsa-miR-191-5p | Up | Patients with MEOD/healthy individuals | |||
| hsa-miR-486-5p | Down | ||||
| miR-30a-5p | Up | Patients with T2DM/healthy individuals | Whole blood | qRT-PCR | [54] |
| miR-30d | Up | Patients with T2DM/healthy individuals | Blood serum | ||
| miR-34a; miR-146a | Up | Patients with T2DM/healthy individuals | PBMCs | ||
| miR-320a; miR-126; miR-21; miR-15a; miR-145 | Down | Patients with T2DM/healthy individuals | Blood plasma | ||
| miR-223 | Down | Patients with prediabetes/healthy individuals | Serum microvesicles | ||
| miR-150 | Up | Rats with T2DM/rats without T2DM | Cardiomyocytes | ||
| miR-103 | Down | Rats with T2DM/rats without T2DM | PBMCs | ||
| miR-126-3p; miR-223-3p; miR-21-5p; miR-15a-5p; miR-24-3p | Down | Patients with T2DM/healthy individuals | Blood plasma | qRT-PCR | [53] |
| miR-34a-5p; miR-148a-3p; miR-30d-5p | Up | ||||
| miR-199b-5p; miR-548o-3p | Up | Patients with T2DM/healthy individuals | Blood plasma | RNA-seq | [23] |
| miR-202-5p; miR-1255b-5p | Down | ||||
| ENST00000381108.3; ENST00000515544.1; ENST00000539543.1; ENST00000508174.1; ENST00000564527.1 | Up | Patients with T2DM/healthy individuals | PBMCs | Microarray | [42] |
| TCONS_00017539; ENST00000430816.1; ENST00000533203.1; ENST00000609522.1; ENST00000417079.1 | Down | ||||
| XR_108954.2 | Up | Patients with T2DM/healthy individuals | PBMCs | Microarray+ qRT-PCR | |
| RP4-605O3.4; AC074117.2 | Down | Patients with T2DM or prediabetes/healthy individuals | Blood serum | qRT-PCR | [51] |
| MALAT1; TUG1; MIAT; NEAT1 | Up | Patients with T2DM/healthy individuals | Blood serum | qRT-PCR | [52] |
| circRNA_008565 | Down | Rats with T2DM/rats without T2DM | Pancreatic β-cells | Microarray+ qRT-PCR | [33] |
| circRNA_0054633 | Up | Women with gestational diabetes mellitus/healthy women | Blood serum | qRT-PCR |
2.3. lncRNA and circRNA as Biomarkers of T2DM
3. Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs in Diabetic Cardiovascular Complications
3.1. Cardiovascular Complications in T2DM
3.2. miRNAs in Diabetic Cardiovascular Complications
3.3. lncRNA and circRNA in Cardiovascular Complications
4. Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs in Diabetic Nephropathy
4.1. Renal Complications in T2DM
4.2. miRNAs in Diabetic Nephropathy
4.3. lncRNA and circRNA in Diabetic Nephropathy
5. Inflammation and Innate Immune Cells in T2DM: The Role of Non-Coding RNAs
5.1. miRNAs in Monocytes in T2DM
5.2. lncRNAs and circRNAs in Monocytes in T2DM
6. Involvement of ncRNAs in the SGLT2-i Effect on Cardiac and Renal Complications of T2DM
6.1. SGLT2-i Effect on the Cardiovascular System State and Function
6.2. Effect of microRNA on the Cardiovascular System Condition and Functions Under the Treatment with SGLT2-i
6.2.1. miR-21 and miR-92 in the Effect of SGLT2-i
6.2.2. miR-30d in the Effect of SGLT2-i
6.2.3. miR-181a and Empagliflozin
6.2.4. miR-193b and Empagliflozin
6.2.5. miR-30e-5p and miR199a-3p in the Effect of Dapagliflozin
6.2.6. Potential Role of miR-141 in the Effect of SGLT2-i
6.3. SGLT2-is Effect on the Renal System
6.4. Effect of microRNA and lncRNA on the Renal System Condition and Functions Under SGLT2-is Treatment
6.4.1. miR-21 in the Effect of DN Therapy by Empagliflozin and Dapagliflozin in Different Models
6.4.2. Exosomal miR 27a-3p, 190a-5p and 196b-5p as Therapy Efficacy Markers
6.4.3. lncRNA, circRNA, and miRNA Identification and Study in DN Treatment with Dapagliflozin and Empagliflozin
6.5. Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Immune Cells in T2DM: Involvement of ncRNAs
| Specific Inhibitor/Kidney or Heart | ncRNA | Mouse/Rat Model, Patients’ Cohort | Effect of Specific Inhibitor | Major Effect in Cells or in Circulation | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empagliflozin/Heart | miR-21 | Rat model of STZ-induced hyperglycemia | Empagliflozin treatment leads to decreased TGF-β1 level/increased expression of the matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) in heart tissue | Empagliflozin administration for seven weeks decreases (compared to metformin) miR-21 levels in heart tissue | [213] |
| Empagliflozin/Heart/ HFpEF | miR-21 miR-92 | Age-related T2DM patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFPEF) | Empagliflozin improves endothelial function by reducing mitochondrial calcium overload and the generation of reactive oxygen species | Empagliflozin (not metformin) decreases biomarkers of HF: circulating miR-21 and miR-92 levels in T2DM patients with HFPEF | [191,215] |
| SGLT2 inhibitor (not specified)/Heart/DCM | miR-30d | Rat model of diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) on a high-fat diet and with (STZ)-induced diabetes | SGLT2 inhibitor (not specified) improved cardiac function due to enhancing autophagy by reducing the expression level of miR-30d | SGLT2-i improves DCM by affecting the miR-30d/KLF9/VEGFA pathway, which regulates the expression of autophagy factors protein light chain 3 (LC3-II) and p62/SQSTM1 (p62/sequestosome 1) | [219] |
| Empagliflozin/Heart/HFpEF | miR-193b | Rat model of combined precapillary and postcapillary pulmonary hypertension (CPCPH): obese ZSF-1 rats treated with SU5416 to stimulate resting pulmonary hypertension | Empagliflozin ameliorates metabolic syndrome and reduces mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation | Empagliflozin downregulates miR-193b, resulting in restoration of NFYA-SGCβ1-cgmp signaling in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells and improvement in EIPH symptoms | [223] |
| Dapagliflozin/Heart/TD2M, hypertension | miR-30e-5p miR-199a-3p | Patients with T2DM and hypertension (blood pressure >130/80 mm Hg) | Short-term treatment (4 weeks) by dapagliflozin improves endothelial function, systemic vascular function | Dapagliflozin increases circulating levels of antihypertrophic miR-30e-5p, decrease in circulating levels of prohypertrophic miR-199a-3p, which are involved in the pathophysiology of CV disease and heart failure | [225] |
| Dapagliflozin/Kidney/Renal vascular function | miR-27b miR-200b | Patients with T2DM and hypertension (blood pressure > 130/80 mm Hg) | Dapagliflozin demonstrates beneficial effect on the kidneys’ ability to dilate blood vessels | Dapagliflozin’s nephroprotective effect correlates with the pretreatment levels of circulating miR-27b and miR-200b | [225] |
| Empagliflozin/Kidney | miR-21 | High glucose (HG) treated human kidney proximal tubule cells (HK-2) | Empagliflozin treatment ameliorated HG-induced inflammation and inhibited epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and HK-2 cell migration | Empagliflozin ameliorates AGE–induced RECK expression suppression via oxidative stress/TRAF3IP2/NF-κb and p38 MAPK/miR-21 pathways in HK-2 cells | [237] |
| Dapagliflozin/Kidney | miR-21 miR-181a | Gentamicin-induced renal injury in Wistar rats | Dapagliflozin administration decreases markers of kidney injury, such as increased creatinine, blood urea, and urine protein | Dapagliflozin improves kidney function and structure in association with an increase in miR-21 and a decrease in miR-181a expression in kidney tissue | [242] |
| Empagliflozin/Kidney | miR-27a-3p, miR-190a-5p, miR-196b-5p | Murine model of early T2DM associated with obesity and insulin resistance on a high-fat diet | Empagliflozin treatment results in improved renal function parameters | Empagliflozin changes urinary exosomal miRNA profiles, including increased levels of miR-27a-3p, miR-190a-5p, miR-196b-5p | [243] |
| Dapagliflozin/Kidney | circRNA_012448 miR-29b-2-5p | HG-treated cultured human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2) | The target genes of dapagliflozin-related circRNAs primarily focused on gene expression, glucose metabolic process, extracellular exosome, epigenetics, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism, amino acid metabolism, and lysosome pathways | Dapagliflozin treatment of HG-treated HK-2 cells induced changes in multiple circRNAs expression, including the hsa_circRNA_012448-hsa-miR-29b-2-5p-GSK3β pathway | [246] |
| Dapagliflozin/Kidney/DN | lncRNA XR_382492.4, XR_873495.3, XR-388840.1, NR-015554.2, XR-382493.3, and XR-876705.2 | db/db mice model of T2DM nephropathy, RNA-seq study | Dapagliflozin improves glucose intolerance, high urinary albumin/creatinine ratio, and renal damage | Dapagliflozin treatment reversed the expression changes in XR_382492.4, XR_873495.3, XR-388840.1, NR-015554.2, XR-382493.3, and XR-876705.2 associated with DN in kidney tissue | [245] |
| Empagliflozin/Kidney/DN | miR-466i-3p, miR466f-3p, miR-709, miR-207, and miR-297b-3p | Murine streptozocin (STZ)–treated model of induced DN | The analysis of DEGs indicated that empagliflozin may inhibit the progression of diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting inflammation, apoptosis, and senescence | Empagliflozin treatment inhibits diabetic nephropathy according to the data of RNA-seq of kidney tissue from DN mice, empagliflozin-treated DN mice, and negative control | [239] |
7. Genetic Variants in Non-Coding RNA in T2DM
7.1. T2DM-Associated Variants in miRNAs
7.2. T2DM-Associated Variants in lncRNAs
| SNPs/Chromosome/Involvement in SGLT2-i Effect | SNP/Gene and Its Association with Diabetes Complications | Description of the Effect | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|
| rs2076380 G>A Chromosome: 20:38165127 (GRCh38) 20:36793529 (GRCh37) Location: 20:38165127 Cytogenetic region:20q11.23 SGLT2-i – | intron TGM2/ lncRNA TGM2 Mapped gene(s): TGM2 intron_variant lncRNA TGM2 is associated with T2DM No data on diabetic nephropathy and Cardiomyopathy | The AA genotype is associated with an increased risk of developing T2DM; risk allele A disrupts the secondary structure of this lncRNA, affecting its stability and the expression of TGM2 in pancreatic beta cells. Diminished LncTGM2 in human beta cells impairs glucose-stimulated insulin release. | [291] |
| rs7158663 A>G Chromosome: 14:100853087 (GRCh38) 14:101319424 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – | exon MEG3/lnc MEG3 lncRNA MEG3 is associated with diabetic nephropathy No data on diabetic cardiomyopathy | The GG genotype is associated with a protective effect against late-stage diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. | [292] |
| rs12427129 C>T, Chromosome: 12:53973906 (GRCh38) 12:54367690 (GRCh37) rs1899663 G>T Chromosome: 12:53967210 (GRCh38) 12:54360994 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – | intron HOTAIR/lnc HOTAIR Gene: HOXC11 HOTAIR lncRNA HOTAIR is associated with diabetic nephropathy and Diabetic Cardiomyopathy | The rs12427129-T allele is associated with an increased risk of diabetic retinopathy The rs1899663-TT genotype is associated with an increased risk of diabetic retinopathy | [293] |
| rs1333049 G>A,C Chromosome: 9:22125504 (GRCh38) 9:22125503 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – Metformin + | found at the intron of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B antisense RNA 1 (CDKN2B-AS1) lncRNA CDKN2B-AS1 is associated with diabetic nephropathy no data in diabetic cardiomyopathy | rs1333049 have shown significant association with poor metformin response rs1333049 is found to be significantly associated with HbA1c level in Mexican nonobese T2DM patients rs1333049 (SNP) in CDKN2B-AS1, located in the 9p21 region. is associated with advanced carotid artery atherosclerosis | [294,295,296] |
| rs2151280 G>A Chromosome: 9:22034720 (GRCh38) 9:22034719 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – | intron CDKN2B-AS1/ lnc CDKN2B-AS1 Gene: CDKN2B-AS1 lncRNA CDKN2B-AS1 is associated with diabetic nephropathy | The G allele is associated with an increased risk of proliferative diabetic retinopathy, decreased glomerular filtration rate, and high-density lipoprotein levels | [297] |
| rs2891168 A>G Chromosome: 9:22098620 (GRCh38) 9:22098619 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – | Gene: CDKN2B-AS1 lncRNA CDKN2B-AS1 is associated with diabetic nephropathy no data in diabetic cardiomyopathy | Susceptibility to coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus | [298] |
| rs55829688 Chromosome: 1:173868168 (GRCh38) 1:173837306 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – | Gene: GAS5 lncRNA GAS5 is associated with diabetic nephropathy and cardiomyopathy | Association of GAS5 gene polymorphisms with the progression of DKD. Carriers of at least one minor allele (C) of rs55829688 (TC and CC) more frequently suffer from advanced DKD than those homozygotes for the major allele (TT). | [299] |
| rs55829688 T>C Chromosome: 1:173868168 (GRCh38) 1:173837306 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – | intron GAS5/lnc GAS5 Gene: GAS5 lncRNA GAS5 is associated with diabetic nephropathy and cardiomyopathy | The C allele is associated with an increased risk of developing diabetic kidney disease, a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate | [299] |
| rs10811661 T>C Chromosome: 9:22134095 (GRCh38) 9:22134094 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – | +13 kb from TSS ANRIL/lnc ANRIL lncRNA ANRIL is associated with diabetic nephropathy and cardiomyopathy | The T allele is associated with an increased risk of T2DM | [287,289,290,300,301] |
| The T allele is associated with decreased insulin secretion | [302,303,304] | ||
| The T allele is associated with increased expression of ANRIL in the islets of Langerhans | [305] | ||
| rs895819 A>G Chromosome: 19:13836478 (GRCh38) 19:13947292 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i + in Diabetic Nephropathy | miRNAs27a Gene: MIR23AHG MIR23A MIR24-2 MIR27A miR-27a-3p and miR-27b are associated with T2DM, coronary artery disease and diabetic nephropathy | miR-27a rs895819-GG genotype protects from coronary artery disease CAD risk subgroup analysis demonstrated that rs895819 C allele conveyed a significant protective effect against T2DM development in Caucasians | [278,279,306] |
| rs3746444 Chromosome: 20:34990448 (GRCh38) 20:33578251 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i -- | miR-499a Gene: MYH7B, MIR499A, MIR499B miR-499a is associated with T2DM and Diabetic cardiomyopathy | miR-499a rs3746444 A>G polymorphism is correlated with T2DM and diabetic polyneuropathy, with carriers of the GG genotype and the G allele being at an increased risk in the Romanian population | [283,307] |
| rs8089787 T>A,C,G Chromosome: 18:21826640 (GRCh38) 18:19406601 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – rs10877887 T>C Chromosome: 12:62603400 (GRCh38) 12:62997180 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – | miR-133a-1 Gene: MIB1 MIR133A1 MIR133A1HG miR-133a-1 is associated with myocardial fibrosis miRNA-let-7f Gene: LINC01465 MIRLET7I let-7f is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic disturbances in T2DM | miR-133a-1-rs8089787 and let-7f-rs10877887 were associated with impaired cardiac diastolic function in T2DM | [265] |
| rs10757278 A>G Chromosome: 9:22124478 (GRCh38) 9:22124477 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – | intron ANRIL/lncRNA ANRIL lncRNA ANRIL is associated with diabetic nephropathy and diabetic cardiomyopathy | The relative fast plasma glucose (FPG) and HbA1c levels were relatively lower in individuals with the AA genotype and higher in those with the GG genotype | [308] |
| rs1292037 T>C Chromosome: 17:59841547 (GRCh38) 17:57918908 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i + | miR-21 Gene: VMP1 MIR21 miR-21 is associated with susceptibility to coronary heart disease, diabetic cardiomyopathy and diabetic nephropathy | rs1292037C allele and C/C genotype in miR-21 were strongly associated with elevated susceptibility to coronary heart disease (CHD) in a Chinese Han population | [269] |
| rs1292037 T>C (see above) rs13137 A>G,T Chromosome: 17:59841670 (GRCh38) 17:57919031 (GRCh37) miR-21 SGLT2-i + rs78312845 A>C,G 17:7018112 (GRCh38) 17:6921431 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – | miR-21 Gene: VMP1 MIR21 miR-21 miR-21 is associated with susceptibility to diabetic cardiomyopathy and diabetic nephropathy miR-195 Gene: MIR195 miR-195 is associated with apoptosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy | the C allele of rs1292037 in miR-21 could increase the risk of T2DM the T allele of rs13137 in miR-21 could be a risk factor for T2DM rs78312845 in miR-195 contributed to the level of fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and HbA1C in nondiabetic group in the Han Chinese population | [309] |
| rs1076064 A>G Chromosome: 5:149732603 (GRCh38) 5:149112166 (GRCh37 SGLT2-i – rs13283671 C>A,T Chromosome: 9:21511741 (GRCh38) 9:21511740 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – | miR-378a Gene: MIR378A miR-378a-3p is associated with diabetic nephropathy miR-31 Gene: MIR31 MIR31HG C allele could increase the risk of developing T2DM miR-31-3p is associated with diabetic nephropathy | The results showed that miR-378a rs1076064 G allele could be a protective factor in T2DM, whereas the miR-31 rs13283671 C allele could increase the risk of T2DM | [270] |
| rs11614913 C>T Chromosome: 12:53991815 (GRCh38) 12:54385599 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i + | exon MIR196A2/stem-loop miR-196a-2 Gene: MIR196A2 miR 196b-5p is associated with diabetic nephropathy | The C allele is associated with an increased risk of T2DM | [271] |
| The T allele is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases in T2DM miR196a2 C>T (rs11614913) and miR499 A>G (rs3746444) were found to be strongly associated with increased risk for CAD | [272,310] | ||
| rs72563729 G>A Chromosome: 1:1167183 (GRCh38) 1:1102563 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i + | Gene: MIR200B miR 200b is associated with diabetic nephropathy miRNA-200c is associated with diabetic cardiomyopathy | allelic association of MIR200B variations with sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy | [311] |
| rs2910164 C>G Chromosome: 5:160485411 (GRCh38) 5:159912418 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – rs531564 G>C Chromosome: 8:9903189 (GRCh38) 8:9760699 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – | exon MIR146A/seed sequence miR-146a Gene: MIR146A MIR3142HG miRNA-146a is associated with inflammation in diabetic cardiomyopathy Gene: MIR124-1HG MIR124-1 miR-124a is a T2DM circulating marker | The G allele is associated with an increased risk of T2DM | [271] |
| miR-146a rs2910164 (G allele) and miR-124a rs531564 (C allele) might function as protective factors in T2DM in Asian population | [273] | ||
| rs4705342 T>C Chromosome: 5:149428408 (GRCh38) 5:148807971 (GRCh37) rs4705343 T>C Chromosome: 5:149428518 (GRCh38) 5:148808081 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – | promoter region of a gene cluster MIR143/145/miR143/145 Gene: MIR143 CARMN upstream_transcript_variant | The C-rs4705342 and C-rs4705343 alleles are associated with an increased and decreased risk of developing T2DM, respectively The CC genotype of rs4705342 might be a risk factor in T2DM by increasing the expression of miRNA-143 in the northern Chinese Han population | [260,261] |
| rs72631823 G>A Chromosome: 1:9151723 (GRCh38) 1:9211782 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – Metformin+ | exon MIR34A/terminal loop pre-miR-34a Gene: MIR34A MIR34AHG miR-34a is associated with diabetic kidney disease | Allele A promotes the formation of a relaxed form of the pre-miR-34a terminal loop, which facilitates its processing and leads to an increase in miR-34a expression in INS-1 and MIN6 cells. The effect of allograft inflammatory factor-1 on inflammation, oxidative stress, and autophagy via miR-34a/ATG4B pathway in diabetic kidney disease | [274,312,313] |
| rs60432575 G>A Chromosome: 20:57895403 (GRCh38) 20:56470459 (GRCh37) SGLT2-i – Sulfonylurea drug+ | MIR4532/hsa-miR-4532 urinary microRNA biomarkers in lupus nephritis and diabetic nephropathy | The G allele promotes efficient binding of miR-4532 to the 3′-untranslated region of KCNJ11 mRNA, resulting in decreased expression of KCNJ11 and Kir6.2 in HEK293 cells, as well as insulin secretion after stimulation of MIN6 cells with sulfonylurea drugs | [314,315,316] |
7.3. Future Perspectives in T2DM Pharmacogenetics
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, Regional and Country-Level Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2021 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119, Erratum in Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 204, 110945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Siddiqi, H.; Uribe, K.B.; Ostolaza, H.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Wakabayashi, M.; Bhalla, A.; Chopra, N.; Miyashita, H.; Mikami, T.; Ueyama, H.; Fujisaki, T.; Saigusa, Y.; Yamaji, T.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with SGLT-2 Inhibitors versus GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannino, G.C.; Andreozzi, F.; Sesti, G. Pharmacogenetics of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, the Route toward Tailored Medicine. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 35, e3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młynarska, E.; Czarnik, W.; Dzieża, N.; Jędraszak, W.; Majchrowicz, G.; Prusinowski, F.; Stabrawa, M.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: New Pathogenetic Mechanisms, Treatment and the Most Important Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Braunwald, E. Mechanisms of Cardiorenal Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 422–434, Erratum in J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2020.08.010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Wang, Z.; Okoth, K.; Toulis, K.A.; Denniston, A.K.; Singh, B.M.; Crowe, F.L.; Sainsbury, C.; Wang, J.; Nirantharakumar, K. Associations of Antidiabetic Drugs with Diabetic Retinopathy in People with Type 2 Diabetes: An Umbrella Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1303238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosz-Popek, J.; Eyileten, C.; Gager, G.M.; Nowak, A.; Szwed, P.; Wicik, Z.; Palatini, J.; von Lewinski, D.; Sourij, H.; Siller-Matula, J.M.; et al. The Interaction between Non-Coding RNAs and SGLT2: A Review. Int. J. Cardiol. 2024, 398, 131419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolski, F.; Mączewski, M. Cardiac Fibrosis: Mechanistic Discoveries Linked to SGLT2 Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, D.V.; Lam, C.S.P.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Yi, T.W.; Hocking, S.; Dawson, J.; Raichand, S.; Januszewski, A.S.; Jardine, M.J. Applications of SGLT2 Inhibitors beyond Glycaemic Control. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024, 20, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Jongs, N.; Chertow, G.M.; Langkilde, A.M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Rossing, P.; Sjöström, C.D.; Stefansson, B.V.; Toto, R.D.; et al. Effect of Dapagliflozin on the Rate of Decline in Kidney Function in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease with and without Type 2 Diabetes: A Prespecified Analysis from the DAPA-CKD Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 743–754, Erratum in Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00223-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bocchi, E.; Böhm, M.; Brunner–La Rocca, H.-P.; Choi, D.-J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure-Valenzuela, E.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Lin, W.; Tian, J. Roles of Non-Coding RNA in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S.; Amaral, P.P.; Carninci, P.; Carpenter, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Chen, R.; Dean, C.; Dinger, M.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNAs: Definitions, Functions, Challenges and Recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.-J.; Chen, L.-L.; Huarte, M. Gene Regulation by Long Non-Coding RNAs and Its Biological Functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 159. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-021-00330-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorkova, O.; Hsiao, J.; Wahlestedt, C. Basic Biology and Therapeutic Implications of LncRNA. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 87, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, G.K.; Khullar, N.; Sidhu, I.S.; Navik, U.S.; Reddy, A.P.; Reddy, P.H.; Bhatti, J.S. Emerging Role of Non-coding RNA in Health and Disease. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beňačka, R.; Szabóová, D.; Guľašová, Z.; Hertelyová, Z.; Radoňak, J. Non-Coding RNAs in Human Cancer and Other Diseases: Overview of the Diagnostic Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanian, F.; Azhir, Z.; Khalilian, S.; Grüning, B. Non-coding RNAs Underlying the Pathophysiological Links between Type 2 Diabetes and Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 405–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Z.; Lv, Y.; Shen, L.; Li, K.; Zheng, P.; Pan, P.; Feng, T.; Jin, L.; et al. High-Throughput Sequencing and Exploration of the LncRNA-circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8162524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudriashov, V.; Sufianov, A.; Mashkin, A.; Beilerli, A.; Ilyasova, T.; Liang, Y.; Lyulin, S.; Beylerli, O. The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Carbohydrate and Fat Metabolism in the Liver. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023, 8, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutikhin, A.G.; Sinitsky, M.Y.; Yuzhalin, A.E.; Velikanova, E.A. Whole-Transcriptome Sequencing: A Powerful Tool for Vascular Tissue Engineering and Endothelial Mechanobiology. High Throughput 2018, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Nie, L.; Wang, M.; Liao, W.; Huan, C.; Jia, Z.; Wei, D.; Liu, P.; Fan, K.; Mao, Z.; et al. Differential Expression of LncRNA-MiRNA-MRNA and Their Related Functional Networks in New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus among Chinese Rural Adults. Genes 2022, 13, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, I.; Varshney, S.; Karnati, S.; Naidu, S. The Multifaceted Roles of Circular RNAs in Cancer Hallmarks: From Mechanisms to Clinical Implications. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2024, 35, 102286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillone, K.; Caridà, G.; Luciano, F.; Cordua, A.; Di Martino, M.T.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P. A Systematic Review of Non-Coding RNA Therapeutics in Early Clinical Trials: A New Perspective against Cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiong, F.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Gao, G.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y. Oligonucleotide Therapies for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2024, 35, 102184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, F.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, D.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Q. Deciphering the Role of Non-Coding RNAs Involved in Sorafenib Resistance. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinetti, G.; Mutoli, M.; Greco, S.; Riccio, F.; Ben-Aicha, S.; Kenneweg, F.; Jusic, A.; de Gonzalo-Calvo, D.; Nossent, A.Y.; Novella, S.; et al. Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes: Role of Non-Coding RNAs in the Crosstalk between Immune and Cardiovascular Systems. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, C.; Lemos, N.E.; Corrêa, N.R.d.F.; Assmann, T.S.; Crispim, D. The Impact of LncRNAs in Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and In Silico Analyses. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 602597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubik, D.; Fitas, A.; Eyileten, C.; Jarosz-Popek, J.; Nowak, A.; Czajka, P.; Wicik, Z.; Sourij, H.; Siller-Matula, J.M.; De Rosa, S.; et al. MicroRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Pathophysiological Processes of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Emerging Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutics. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, D.; Jiang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, R.; Chen, M.; Lin, C.; Liu, D. Non-Coding RNAs in Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 961802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, M.; Eghtedarian, R.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Omrani, M.D. Non-Coding RNAs and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 129, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cheng, H. Emerging Roles of NcRNAs in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: From Mechanisms to Drug Discovery. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Gao, R.; Xie, Q.; Pan, X.; Tong, N. Whole Transcriptome Sequencing Analyses of Islets Reveal NcRNA Regulatory Networks Underlying Impaired Insulin Secretion and Increased β-Cell Mass in High Fat Diet-Induced Diabetes Mellitus. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0300965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kura, B.; Kindernay, L.; Singla, D.; Dulova, U.; Bartekova, M. Mechanistic Insight into the Role of Cardiac-Enriched MicroRNAs in Diabetic Heart Injury. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2025, 328, H865–H884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macvanin, M.T.; Gluvic, Z.; Bajic, V.; Isenovic, E.R. Novel Insights Regarding the Role of Noncoding RNAs in Diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 958–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Adnan, H.; Khawaja, M.A.; Butler, A.E. Novel Micro-Ribonucleic Acid Biomarkers for Early Detection of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Associated Complications—A Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, R.; Yao, Y.; Guan, H.; Tian, J. Discovering Diabetes Complications-Related MicroRNAs: Meta-Analyses and Pathway Modeling Approach. BMC Med. Genom. 2025, 18, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Han, Z.; Han, F.; Chang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xue, M.; Sun, B.; Chen, L. Triptolide Restores Autophagy to Alleviate Diabetic Renal Fibrosis through the MiR-141-3p/PTEN/Akt/MTOR Pathway. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 9, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, X.; Zhan, X.; Sun, L.; Gao, J.; Cao, Y.; Qiu, H. Construction of Competitive Endogenous RNA Network Reveals Regulatory Role of Long Non-coding RNAs in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3204–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Ma, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lv, L.; Zhang, G. Construction and Analysis of a LncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA Reveals Functional LncRNAs in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Su, Y.; Hou, Q.; Xu, Q.; Cai, R.; Wang, T.; Gong, X.; Yi, Q. Long Non-coding RNA Screening and Identification of Potential Biomarkers for Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Rao, X.; Jia, J.; Yan, T.; Li, D. Identification of Tubulointerstitial Genes and CeRNA Networks Involved in Diabetic Nephropathy via Integrated Bioinformatics Approaches. Hereditas 2022, 159, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielska, A.; Niemira, M.; Bauer, W.; Sidorkiewicz, I.; Szałkowska, A.; Skwarska, A.; Raczkowska, J.; Ostrowski, D.; Gugała, K.; Dobrzycki, S.; et al. Serum MiRNA Profile in Diabetic Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease as a Promising Non-Invasive Biomarker. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 888948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szydełko, J.; Czop, M.; Petniak, A.; Lenart-Lipińska, M.; Kocki, J.; Zapolski, T.; Matyjaszek-Matuszek, B. Identification of Plasma MiR-4505, MiR-4743-5p and MiR-4750-3p as Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers for Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Han, J.; Jin, J.; Su, F.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Xiao, F.; Pan, Q.; et al. Screening of Circular RNAs and Validation of CircANKRD36 Associated with Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, X.; Chenv, J.; Zhou, D.; Liu, K.; Chen, L.; Zhou, D.; Hu, Y. A Novel Identified Circular RNA, Circ_0000491, Aggravates the Extracellular Matrix of Diabetic Nephropathy Glomerular Mesangial Cells through Suppressing MiR-101b by Targeting TGFβRI. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3785–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Shi, Z.; Shan, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yan, B.; Zhao, C. Comparative Analysis of Differentially Expressed Circular RNAs in Polarized Macrophages. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 823517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halabi, N.; Thomas, B.; Chidiac, O.; Robay, A.; AbiNahed, J.; Jayyousi, A.; Al Suwaidi, J.; Bradic, M.; Abi Khalil, C. Dysregulation of Long Non-Coding RNA Gene Expression Pathways in Monocytes of Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xia, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, D.; Du, Y. Identification of Novel Target Genes in Exaggerated Cardiac Remodeling Following Myocardial Infarction in Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1536639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.S.; Kamel, M.M.; Agwa, S.H.A.; Hakeem, M.S.A.; El Meteini, M.S.; Matboli, M. Analysis of MRNA-MiRNA-LncRNA Differential Expression in Prediabetes/Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients as Potential Players in Insulin Resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1131171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Huang, H.; Lai, J.; Lin, S.; Huang, Y. Long Noncoding RNAs as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Diabetes Mellitus and Complications: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Diabetes 2024, 16, e13510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieco, G.E.; Besharat, Z.M.; Licata, G.; Fignani, D.; Brusco, N.; Nigi, L.; Formichi, C.; Po, A.; Sabato, C.; Dardano, A.; et al. Circulating MicroRNAs as Clinically Useful Biomarkers for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: MiRNomics from Bench to Bedside. Transl. Res. 2022, 247, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoob, G.; Ahmadi, Y.; Fatima rajani, H.; Khanbabaei, N.; Abolhasani, S. Circulating MicroRNAs as Predictive Biomarkers of Coronary Artery Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes Patients. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, F.; Khyriem, C.; Dsouza, S.; Abdul, F.; Alkhnbashi, O.; Faraji, H.; Farooqi, M.; Al Awadi, F.; Hassanein, M.; Ahmed, F.; et al. Characterizing Circulating MicroRNA Signatures of Type 2 Diabetes Subtypes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guo, S.; Li, W.; Yu, P. The Circular RNA Cdr1as, via MiR-7 and Its Targets, Regulates Insulin Transcription and Secretion in Islet Cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macvanin, M.T.; Gluvic, Z.; Radovanovic, J.; Essack, M.; Gao, X.; Isenovic, E.R. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: The Role of MicroRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1124613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillmann, W.H. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1160–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Mei, S.; Wuyun, Q.; Zhou, L.; Sun, D.; Yan, J. Epigenetics in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Clin. Epigenetics 2024, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manosroi, W.; Phimphilai, M.; Waisayanand, N.; Buranapin, S.; Deerochanawong, C.; Gunaparn, S.; Phrommintikul, A.; Wongcharoen, W. Glycated Hemoglobin Variability and the Risk of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Post-hoc Analysis of a Prospective and Multicenter Study. J. Diabetes Investig. 2023, 14, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yuan, D.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, L.; Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, R.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hui, R.; et al. The Association between Glycated Hemoglobin Levels and Long-Term Prognosis in Patients with Diabetes and Triple-Vessel Coronary Disease across Different Age Groups: A Cohort Study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 213, 111751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, L.; Akbar, N.; Braithwaite, A.T.; Krausgruber, T.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Bailey, J.; Corbin, A.L.; Khoyratty, T.E.; Chai, J.T.; Alkhalil, M.; et al. Hyperglycemia Induces Trained Immunity in Macrophages and Their Precursors and Promotes Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2021, 144, 961–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riksen, N.P.; Bekkering, S.; Mulder, W.J.M.; Netea, M.G. Trained Immunity in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Geng, K.; Wang, H.; Wan, S.; Ma, X.; Long, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Z. Hyperglycemia-Induced STING Signaling Activation Leads to Aortic Endothelial Injury in Diabetes. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinci, M.C.; Costantino, S.; Damiano, G.; Rurali, E.; Rinaldi, R.; Vigorelli, V.; Sforza, A.; Carulli, E.; Pirola, S.; Mastroiacovo, G.; et al. Persistent Epigenetic Signals Propel a Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype and Trained Innate Immunity in CD34+ Hematopoietic Stem Cells from Diabetic Patients. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendra, E.; Riabov, V.; Mossel, D.M.; Sevastyanova, T.; Harmsen, M.C.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Macrophage Activation and Function in Diabetes. Immunobiology 2019, 224, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatzadeh, M.; Payán-Gómez, C.; Kzhyshkowska, J.; Dik, W.A.; Leenen, P.J.M. Polarized Macrophages Show Diverse Pro-Angiogenic Characteristics Under Normo- and Hyperglycemic Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badillo-Garcia, L.E.; Liu, Q.; Ziebner, K.; Balduff, M.; Sevastyanova, T.; Schmuttermaier, C.; Klüter, H.; Harmsen, M.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Hyperglycemia Amplifies TLR-Mediated Inflammatory Response of M(IL4) Macrophages to Dyslipidemic Ligands. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2024, 116, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossel, D.M.; Moganti, K.; Riabov, V.; Weiss, C.; Kopf, S.; Cordero, J.; Dobreva, G.; Rots, M.G.; Klüter, H.; Harmsen, M.C.; et al. Epigenetic Regulation of S100A9 and S100A12 Expression in Monocyte-Macrophage System in Hyperglycemic Conditions. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, Y.J.; Dalan, R.; Cheung, C. The Interplay Between Immunity, Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seferović, P.M.; Paulus, W.J. Clinical Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: A Two-Faced Disease with Restrictive and Dilated Phenotypes. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.P.; Goodwin, J.E.; Tripathi, P.; Kanasaki, K.; Koya, D. Interactions among Long Non-Coding RNAs and MicroRNAs Influence Disease Phenotype in Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, F.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Y. MiR-208 Inhibits Myocardial Tissues Apoptosis in Mice with Acute Myocardial Infarction by Targeting Inhibition of PDCD4. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V. Cardiac-Specific MiRNA in Cardiogenesis, Heart Function, and Cardiac Pathology (with Focus on Myocardial Infarction). J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2016, 94, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ren, Y.; Shi, E.; Tan, Z.; Xiong, J.; Yan, L.; Jiang, X. Inhibition of the Let-7 Family MicroRNAs Induces Cardioprotection Against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Diabetic Rats. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 102, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Chen, S.; George, B.; Feng, Q.; Chakrabarti, S. MiR133a Regulates Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy in Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2010, 26, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. The Interregulatory Circuit between Non-Coding RNA and Apoptotic Signaling in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024, 9, 1080–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y. MiR-126 Overexpression Attenuates Oxygen-glucose Deprivation/Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response via the Activation of SIRT1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 23, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankauskas, S.S.; Gambardella, J.; Sardu, C.; Lombardi, A.; Santulli, G. Functional Role of MiR-155 in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Noncoding RNA 2021, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pofi, R.; Giannetta, E.; Galea, N.; Francone, M.; Campolo, F.; Barbagallo, F.; Gianfrilli, D.; Venneri, M.A.; Filardi, T.; Cristini, C.; et al. Diabetic Cardiomiopathy Progression Is Triggered by MiR122-5p and Involves Extracellular Matrix. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 14, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Sahil, A.; Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Dong, R.; Xue, H.; et al. Melatonin Alleviates Cardiac Fibrosis via Inhibiting LncRNA MALAT1/MiR-141-mediated NLRP3 Inflammasome and TGF-β1/Smads Signaling in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 5282–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, F.; Seyed Mohammadzad, M. Bioinformatics Analyses of Potential MicroRNAs and Their Target Genes in Myocardial Infarction Patients with Diabetes. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2025, 22, 14791641251335925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Pang, H.; Xie, Z.; Huang, G.; Zhou, Z. Circular RNAs in Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 885650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galis, P.; Bartosova, L.; Farkasova, V.; Bartekova, M.; Ferenczyova, K.; Rajtik, T. Update on Clinical and Experimental Management of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Addressing Current and Future Therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1451100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Lin, H.; Huang, X.; Weng, J.; Peng, F.; Wu, S. METTL14 Suppresses Pyroptosis and Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Downregulating TINCR LncRNA. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 38, Erratum in Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 416. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-025-07680-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Shan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cao, Q.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhao, X. RNA-Seq Analysis and Functional Characterization Revealed LncRNA NONRATT007560.2 Regulated Cardiomyocytes Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis Induced by High Glucose. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 18278–18287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, S.; Xiao, L.; Liang, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yao, R.; Liu, Y.; et al. LncRNA HOTAIR Functions as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Upregulate SIRT1 by Sponging MiR-34a in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 4944–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Lee, D. Interfering with Long Chain Noncoding RNA ANRIL Expression Reduces Heart Failure in Rats with Diabetes by Inhibiting Myocardial Oxidative Stress. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 18446–18456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Li, T.-T.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, X.-X.; Xue, G.-L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.-F.; et al. Ablation of Interleukin-17 Alleviated Cardiac Interstitial Fibrosis and Improved Cardiac Function via Inhibiting Long Non-Coding RNA-AK081284 in Diabetic Mice. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2018, 115, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Guan, J.; Xu, L.; Xiao, W.; Zhong, Q.; Ren, C.; Lu, J.; Liang, J.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA Crnde Attenuates Cardiac Fibrosis via Smad3-Crnde Negative Feedback in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Lv, J.; Sun, X.; Che, H.; Han, T.; Meng, S.; Bai, Y.; et al. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 Mediates Pyroptosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 1230–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.-F.; Ye, Y.-X.; Xu, J.-D.; He, Y.; Zhang, D.-W.; Xia, Z.-Y.; Wang, S. Long Non-Coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 Increases the Expression of PDCD4 by Targeting MiR-181a-5p, Contributing to Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Acta Diabetol. 2021, 58, 1251–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, Y.; Wang, M.-Z.; Xie, K.-L.; Cai, Y. Identification of Potentially Functional Circular RNA/Long Noncoding RNA-MicroRNA-MRNA Regulatory Networks Associated with Vascular Injury in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Integrated Microarray Analysis. J. Diabetes Res. 2023, 2023, 3720602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Duan, J.; Zhou, H. Perspectives of Circular RNAs in Diabetic Complications from Biological Markers to Potential Therapeutic Targets (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2023, 28, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Jian, D.; Li, W.; Tang, H.; Li, M. Hsa-CircRNA11783-2 in Peripheral Blood Is Correlated with Coronary Artery Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2017, 14, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, S.; Li, R.; Zhu, H.; Li, T.; Zheng, J.; Li, J.; et al. Circular RNAs in Human Diseases. MedComm 2024, 5, e699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-M.; Zhang, M.; Huang, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, J.-N.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Q.; Zheng, X.-L.; Yang, M.; et al. CircRNA_000203 Enhances the Expression of Fibrosis-Associated Genes by Derepressing Targets of MiR-26b-5p, Col1a2 and CTGF, in Cardiac Fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Yu, J.-W. A Novel Identified Circular RNA, CircRNA_010567, Promotes Myocardial Fibrosis via Suppressing MiR-141 by Targeting TGF-Β1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 487, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Xu, L.; Feng, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, X. Involvement of CircHIPK3 in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy in Mice. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Li, A.; Qin, Y.; Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Yue, E.; Ding, X.; et al. A Novel Circular RNA Mediates Pyroptosis of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Functioning as a Competing Endogenous RNA. Mol. Ther. Nucleic. Acids. 2019, 17, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Yang, F.; Yan, D.; Shen, M.; Jin, Z.; Zhan, L.; Liu, G.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.; et al. CircRNA DICAR as a Novel Endogenous Regulator for Diabetic Cardiomyopathy and Diabetic Pyroptosis of Cardiomyocytes. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzer, M.S.; Rohacs, T.; Susztak, K. How Many Cell Types Are in the Kidney and What Do They Do? Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2022, 84, 507–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xiong, Y.; Deng, X.; Wang, Y.; Gong, S.; Yang, S.; Yang, B.; Yang, Y.; Leng, Y.; Li, W.; et al. The Role of Intercellular Communication in Diabetic Nephropathy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1423784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joumaa, J.P.; Raffoul, A.; Sarkis, C.; Chatrieh, E.; Zaidan, S.; Attieh, P.; Harb, F.; Azar, S.; Ghadieh, H.E. Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Treatment Approaches for Diabetic Kidney Disease: Current Insights and Future Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, C. Recent Advances in the Management of Diabetic Kidney Disease: Slowing Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmaksoud, N.M.; AL-Noshokaty, T.M.; Abdelhamid, R.; Abdellatif, N.; Mansour, A.; Mohamed, R.; Mohamed, A.H.; Khalil, N.A.E.; Abdelhamid, S.S.; Mohsen, A.; et al. Deciphering the Role of MicroRNAs in Diabetic Nephropathy: Regulatory Mechanisms and Molecular Insights. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 256, 155237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Han, Z.; Li, C.; Yuan, X.; Guo, D. The Regulatory Role of MiRNA and LncRNA on Autophagy in Diabetic Nephropathy. Cell Signal 2024, 118, 111144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wu, Y.; Mai, Y.; Bu, S. Noncoding RNAs in Diabetic Nephropathy: Pathogenesis, Biomarkers, and Therapy. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 3960857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, J. Noncoding RNAs and Diabetic Kidney Disease. J. Diabetes Investig. 2025, 16, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Kaneko, S.; Yanai, K.; Aomatsu, A.; Hirai, K.; Ookawara, S.; Ishibashi, K.; Morishita, Y. MicroRNAs in Podocyte Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Liu, Y.; Guan, H. MicroRNA-145-5p Attenuates High Glucose-induced Apoptosis by Targeting the Notch Signaling Pathway in Podocytes. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, S.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, A.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, S.; Zhang, J. The MicroRNA in Ventricular Remodeling: The MiR-30 Family. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.-R.; Shao, J.-J.; Liang, B. MiR-135a Regulates Renal Fibrosis in Rats with Diabetic Kidney Disease through the Notch Pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, D.; Jiao, C.; Cui, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuen, P.S.T.; et al. MiR-150-Based RNA Interference Attenuates Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis through the SOCS1/JAK/STAT Pathway In Vivo and In Vitro. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-C.; Kuo, P.-L.; Hung, W.-W.; Wu, L.-Y.; Wu, P.-H.; Chang, W.-A.; Kuo, M.-C.; Hsu, Y.-L. Angpt2 Induces Mesangial Cell Apoptosis through the MicroRNA-33-5p-SOCS5 Loop in Diabetic Nephropathy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, W.; Zhao, X.; Wu, M.; Fu, X.; Jia, W.; Lu, M.; Li, H. MiR-214 Promotes Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy via Targeting SOCS1. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2021, 18, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, I.; Kavanagh, M.; Jimenez-Castilla, L.; Pardines, M.; Lazaro, I.; Herrero del Real, I.; Flores-Muñoz, M.; Egido, J.; Lopez-Franco, O.; Gomez-Guerrero, C. A Mutual Regulatory Loop between MiR-155 and SOCS1 Influences Renal Inflammation and Diabetic Kidney Disease. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2023, 34, 102041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Shi, H.-B. Potential Repressive Impact of MicroRNA-20a on Renal Tubular Damage in Diabetic Kidney Disease by Targeting C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 6. Arch. Med. Res. 2021, 52, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-H.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Ji, L.-L.; Chen, C. MiR-30c-5p Inhibits High Glucose-Induced EMT and Renal Fibrogenesis by down-Regulation of JAK1 in Diabetic Nephropathy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Ji, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, J. The Wnt Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Nephropathy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 9, 701547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wan, J.; Hou, X.; Geng, J.; Li, X.; Bai, X. MicroRNA-27a Promotes Podocyte Injury via PPARγ-Mediated β-Catenin Activation in Diabetic Nephropathy. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2658, Erratum in Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 652. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0637-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Tian, N.; Zou, D.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, N. Astragaloside IV Improves Renal Function and Fibrosis via Inhibition of MiR-21-Induced Podocyte Dedifferentiation and Mesangial Cell Activation in Diabetic Mice. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2018, 12, 2431–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Lou, Y.; Bao, J.; Yu, J. Hyperoside Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy Induced by STZ via Targeting the MiR-499–5p/APC Axis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 146, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Tian, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-27a Targets Sfrp1 to Induce Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy by Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Signalling. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20192794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Qiao, J.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Yu, Q.; Zhen, J.; Ma, Q.; Wang, Q.; Lv, Z.; et al. Podocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Mediate Renal Proximal Tubule Cells Dedifferentiation via MicroRNA-221 in Diabetic Nephropathy. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2020, 518, 111034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, A.; Das, F.; Ghosh-Choudhury, N.; Mariappan, M.M.; Kasinath, B.S.; Ghosh Choudhury, G. Reciprocal Regulation of MiR-214 and PTEN by High Glucose Regulates Renal Glomerular Mesangial and Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cell Hypertrophy and Matrix Expansion. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2017, 313, C430–C447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Said, Y.A.M.; Sallam, N.A.A.; Ain-Shoka, A.A.-M.; Abdel-Latif, H.A.-T. Geraniol Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy via Interference with MiRNA-21/PTEN/Akt/MTORC1 Pathway in Rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 2325–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khokhar, M.; Purohit, P.; Tomo, S.; Agarwal, R.G.; Gadwal, A.; Bajpai, N.K.; Bohra, G.K.; Shukla, R.K. PTEN, MMP2, and NF-ΚB and Regulating MicroRNA-181 Aggravate Insulin Resistance and Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy: A Case-Control Study. Kidney Dial. 2023, 3, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yan, R.; Liang, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Y.; Peng, W.; Xiao, Y.; et al. BMP-7 Inhibits Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy via MiR-21 Downregulation. Life Sci. 2019, 238, 116957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jung, E.-H.; Kim, G.-Y.; Kim, B.-C.; Lim, J.H.; Woo, C.-H. Itch E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Positively Regulates TGF-β Signaling to EMT via Smad7 Ubiquitination. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Jiang, M. MicroRNA-27a Adjusts Diabetic Nephropathy Patients and Inhibits TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. 2017, 10, 14266–14274. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.-L.; Liu, T.-T.; Lan, H.-Y. TGF-Beta as a Master Regulator of Diabetic Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tang, G.; Jia, J.; Zhu, N.; Yuan, W. Butyrate Alleviates Diabetic Kidney Disease by Mediating the MiR-7a-5p/P311/TGF-β1 Pathway. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 10462–10475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zha, D.; Wu, X. Inhibition of MiRNA-135a-5p Ameliorates TGF-β1-induced Human Renal Fibrosis by Targeting SIRT1 in Diabetic Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluitt, M.B.; Shivapurkar, N.; Kumari, M.; Singh, S.; Li, L.; Tiwari, S.; Ecelbarger, C.M. Systemic Inhibition of MiR-451 Increases Fibrotic Signaling and Diminishes Autophagic Response to Exacerbate Renal Damage in Tallyho/Jng Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2020, 319, F476–F486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijkerk, R.; Duijs, J.M.G.J.; Khairoun, M.; ter Horst, C.J.H.; van der Pol, P.; Mallat, M.J.; Rotmans, J.I.; de Vries, A.P.J.; de Koning, E.J.; de Fijter, J.W.; et al. Circulating MicroRNAs Associate With Diabetic Nephropathy and Systemic Microvascular Damage and Normalize After Simultaneous Pancreas–Kidney Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Chung, A.C.K.; Huang, X.R.; Meng, X.-M.; Hui, D.S.C.; Yu, C.-M.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-β/Smad3 Signaling Promotes Renal Fibrosis by Inhibiting MiR-29. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1462–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Wang, F.; Shao, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H. MicroRNA-126 Suppresses Inflammation in Endothelial Cells under Hyperglycemic Condition by Targeting HMGB1. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2017, 88, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Xuan, J.; Gao, X.; Ding, H.; Ma, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Roles of Physical Exercise-Induced MiR-126 in Cardiovascular Health of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zeng, M.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Fu, P.; Dong, Z. Exosomes in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Kidney Dis. 2023, 9, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Jiang, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, D.; Hu, Q. Mechanism of LncRNA-MiRNA in Renal Intrinsic Cells of Diabetic Kidney Disease and Potential Therapeutic Direction. DNA Cell Biol. 2025, 44, 304–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Wei, Q.; Wang, H.; Lv, Y.; Ye, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, L. Identification of Hub Genes and Potential CeRNA Networks of Diabetic Nephropathy by Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 767654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Jia, Y.-Y.; Wang, M.; Mu, L.; Li, H.-J. PTGER3 and MMP-2 Play Potential Roles in Diabetic Nephropathy via Competing Endogenous RNA Mechanisms. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Long, J.; Mise, K.; Galvan, D.L.; Overbeek, P.A.; Tan, L.; Kumar, S.V.; Chan, W.K.; Lorenzi, P.L.; Chang, B.H.; et al. PGC1α Is Required for the Renoprotective Effect of LncRNA Tug1 in Vivo and Links Tug1 with Urea Cycle Metabolites. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.F.; Tang, P.M.K.; Feng, M.; Xiao, J.; Huang, X.R.; Li, P.; Ma, R.C.W.; Lan, H.Y. Novel LncRNA Erbb4-IR Promotes Diabetic Kidney Injury in Db/Db Mice by Targeting MiR-29b. Diabetes 2018, 67, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, R.; Zhu, P.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 Affects Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis and Fibrosis through Regulating MiR-18b-5p/SORBS2 Axis and NF-ĸB Pathway in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Qiu, T.; Chen, H.; Tian, T.; Wang, D.; Lu, C. Silencing LncRNA SNHG14 Alleviates Renal Tubular Injury via the MiR-483-5p/HDAC4 Axis in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Hormones 2025, 24, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, G.; Ge, Z. LncRNA MALAT1 Promotes Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy by Targeting the MiR-2355-3p/IL6ST Axis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 647650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, J.; He, Y.; Deng, R.; Fan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X. The Role of MicroRNA-155 in Glomerular Endothelial Cell Injury Induced by High Glucose. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 2915–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Liu, X.; Ma, N. Triptolide Inhibits Oxidative Stress and Inflammation via the MicroRNA-155-5p/Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor to Reduce Podocyte Injury in Mice with Diabetic Nephropathy. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 12275–12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Dai, Y.; Jiang, L.; Gao, J. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Mechanisms of Diabetic Nephropathy via Novel Biomarkers and Competing Endogenous RNA Network. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 934022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, M.; Rui, T.; Yang, Z.; Shi, M. Depression of LncRNA DANCR Alleviates Tubular Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy by Regulating KLF5 through Sponge MiR-214-5p. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Li, H.; Yu, W. Xanthohumol Ameliorates Diabetic Kidney Disease through Suppression of Renal Fibrosis by Regulating SNHG10/MiR-378b. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1532517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Yang, J.-E. Stress-Related LncRNAs and Their Roles in Diabetes and Diabetic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, P.; Yang, C.; Wu, Y.; Wu, D.; Cao, Y.; Chu, Y.; Li, L. Circular RNAs: An Emerging Precise Weapon for Diabetic Nephropathy Diagnosis and Therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cang, Z.; Shen, L.; Peng, W.; Xi, L.; Jiang, X.; Ge, X.; Xu, B.; Huang, S. Circ_0037128/MiR-17-3p/AKT3 Axis Promotes the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy. Gene 2021, 765, 145076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Han, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L. Circular RNA CircRNA_15698 Aggravates the Extracellular Matrix of Diabetic Nephropathy Mesangial Cells via MiR-185/TGF-β1. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Zhao, M.; Li, K. Circ_0000491 Promotes Apoptosis, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Fibrosis in High Glucose-Induced Mesangial Cells by Regulating MiR-455-3p/Hmgb1 Axis. Nephron 2022, 146, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Fan, Q. CircACTR2: A Novel Mechanism Regulating High Glucose-Induced Fibrosis in Renal Tubular Cells Via Pyroptosis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Xia, L.; Ge, X.; Shen, L.; Cang, Z.; Peng, W.; Shao, K.; Huang, S. Circular RNA CircEIF4G2 Aggravates Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy by Sponging MiR-218. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 1799–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Zha, D.; Hu, C.; Wu, X. Circ_0000285 Promotes Podocyte Injury through Sponging MiR-654-3p and Activating MAPK6 in Diabetic Nephropathy. Gene 2020, 747, 144661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalamandris, S.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Oikonomou, E.; Papamikroulis, G.-A.; Vogiatzi, G.; Papaioannou, S.; Deftereos, S.; Tousoulis, D. The Role of Inflammation in Diabetes: Current Concepts and Future Perspectives. Eur. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 14, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, V.; La Grotta, R.; Carreras, F.; Giuliani, A.; Sabbatinelli, J.; Olivieri, F.; Berra, C.C.; Ceriello, A.; Prattichizzo, F. Inflammatory Trajectory of Type 2 Diabetes: Novel Opportunities for Early and Late Treatment. Cells 2024, 13, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanter, J.E.; Hsu, C.-C.; Bornfeldt, K.E. Monocytes and Macrophages as Protagonists in Vascular Complications of Diabetes. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, L.; Cao, S.; Li, W. Immune Inflammation and Metabolic Interactions in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Nephropathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1602594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q. Immune Cell Contribution to Vascular Complications in Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1549945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kzhyshkowska, J.; Neyen, C.; Gordon, S. Role of Macrophage Scavenger Receptors in Atherosclerosis. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kzhyshkowska, J.; Gratchev, A.; Brundiers, H.; Mamidi, S.; Krusell, L.; Goerdt, S. Phosphatidylinositide 3-Kinase Activity Is Required for Stabilin-1-Mediated Endosomal Transport of AcLDL. Immunobiology 2005, 210, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakova, E.; Iamshchikov, P.; Larionova, I.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Macrophage Scavenger Receptors: Tumor Support and Tumor Inhibition. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1096897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, J.; Kanter, J.E. Monocyte and Macrophage Foam Cells in Diabetes-Accelerated Atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1213177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Dai, H.; Zhou, Q.; Meng, X. The Immunology of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1542208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wen, Z.; Shi, P.; Ni, Q. The Role and Therapeutic Potential of Macrophages in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1393392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, Á.; Muñoz, K.; Nahuelpán, Y.; R. Saez, A.-P.; Mendoza, P.; Jara, C.; Cappelli, C.; Suarez, R.; Oyarzún, C.; Quezada, C.; et al. Intraglomerular Monocyte/Macrophage Infiltration and Macrophage–Myofibroblast Transition during Diabetic Nephropathy Is Regulated by the A2B Adenosine Receptor. Cells 2020, 9, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadane, A.; Veenstra, A.A.; Minns, M.S.; Tang, J.; Du, Y.; Abubakr Elghazali, F.; Lessieur, E.M.; Pearlman, E.; Kern, T.S. CCR2-Positive Monocytes Contribute to the Pathogenesis of Early Diabetic Retinopathy in Mice. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Castro, I.; Arroyo-Camarena, Ú.D.; Martínez-Reyes, C.P.; Gómez-Arauz, A.Y.; Duẽnas-Andrade, Y.; Hernández-Ruiz, J.; Béjar, Y.L.; Zaga-Clavellina, V.; Morales-Montor, J.; Terrazas, L.I.; et al. Corrigendum to ‘Human Monocytes and Macrophages Undergo M1-Type Inflammatory Polarization in Response to High Levels of Glucose’. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 192, 106, Erratum in Immunol. Lett. 2016, 176, 81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2016.06.001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moganti, K.; Li, F.; Schmuttermaier, C.; Riemann, S.; Klüter, H.; Gratchev, A.; Harmsen, M.C.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Hyperglycemia Induces Mixed M1/M2 Cytokine Profile in Primary Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, I.-K.; Hong, C.-W.; Jeon, J.-H. Impact of Hyperglycemia on Immune Cell Function: A Comprehensive Review. Diabetol. Int. 2024, 15, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Fang, Z. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals the Dysfunctional Characteristics of PBMCs in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Immunol. 2025, 15, 1501660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Dong, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Y. Expression of MiR-18a and MiR-34c in Circulating Monocytes Associated with Vulnerability to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Insulin Resistance. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3372–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassaifi, S.; Kaeffer, B.; Zarrouk, S. Cellular Phenotypic Transformation During Atherosclerosis: The Potential Role of MiRNAs as Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.W.; Dickson, A.M.; Clay, G.; McCaffrey, A.P.; Wilson, M.E. Identifying Functional MicroRNAs in Macrophages with Polarized Phenotypes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21816–21825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, M.; Suo, Q.; Lv, K. Expression Profiles of MiRNAs in Polarized Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Chen, H.; Wei, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, L.; Yuan, P.; Wang, F.; Yang, G.; Ma, J. Gold Nanoparticle-Based MiR155 Antagonist Macrophage Delivery Restores the Cardiac Function in Ovariectomized Diabetic Mouse Model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 4963–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Reddy, S.S.; Maurya, M.; Maurya, P.; Barthwal, M.K. MicroRNA-99a Mimics Inhibit M1 Macrophage Phenotype and Adipose Tissue Inflammation by Targeting TNFα. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, S.; Meng, F.; Li, X.; Gong, X. MiR-330-5p/Tim-3 Axis Regulates Macrophage M2 Polarization and Insulin Resistance in Diabetes Mice. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 95, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Tong, J.; Deng, B.; Zheng, J.; Lu, C. MiR-495 Regulates Macrophage M1/M2 Polarization and Insulin Resistance in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice via Targeting FTO. Pflugers Arch. 2019, 471, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szydełko, J.; Matyjaszek-Matuszek, B. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Coronary Artery Disease Related to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—From Pathogenesis to Potential Clinical Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuschnerus, K.; Straessler, E.T.; Müller, M.F.; Lüscher, T.F.; Landmesser, U.; Kränkel, N. Increased Expression of MiR-483-3p Impairs the Vascular Response to Injury in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2019, 68, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yan, D.; Yang, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhan, L.; Lu, L.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, C.; Long, P.; Chen, J.; et al. The Effect of MiR-471-3p on Macrophage Polarization in the Development of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Life Sci. 2021, 268, 118989, Erratum in Life Sci. 2023, 328, 121897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, S.; Randhawa, V.; Rizvi, S.H.M.; Sachan, M.; Wara, A.K.; Pérez-Cremades, D.; Weisbrod, R.M.; Hamburg, N.M.; Feinberg, M.W. MiR-369-3p Ameliorates Diabetes-Associated Atherosclerosis by Regulating Macrophage Succinate-GPR91 Signalling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 120, 1693–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mone, P.; Varzideh, F.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Pansini, A.; Lombardi, A.; Frullone, S.; Santulli, G. SGLT2 Inhibition via Empagliflozin Improves Endothelial Function and Reduces Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress: Insights From Frail Hypertensive and Diabetic Patients. Hypertension 2022, 79, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Ferrari, M.W.; Li, C.; Zhang, T.; Lyu, G.; Wang, Z. MiR-21-3p Inhibitor Exerts Myocardial Protective Effects by Altering Macrophage Polarization State and Reducing Excessive Mitophagy. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.A.; Amaram, V.; Das, S.; Tanwar, V.S.; Ganguly, R.; Wang, M.; Lanting, L.; Zhang, L.; Abdollahi, M.; Chen, Z.; et al. LncRNA DRAIR Is Downregulated in Diabetic Monocytes and Modulates Inflammatory Phenotype via Epigenetic Mechanisms. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e143289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Reddy, M.A.; Senapati, P.; Stapleton, K.; Lanting, L.; Wang, M.; Amaram, V.; Ganguly, R.; Zhang, L.; Devaraj, S.; et al. Diabetes Mellitus–Induced Long Noncoding RNA Dnm3os Regulates Macrophage Functions and Inflammation via Nuclear Mechanisms. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 1806–1820, Erratum in Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, e157. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATV.0000000000000082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, C.; Cimini, M.; Cheng, Z.; Benedict, C.; Wang, C.; Trungcao, M.; Mallaredy, V.; Rajan, S.; Garikipati, V.N.S.; Kishore, R. Role of Circular RNA Cdr1as in Modulation of Macrophage Phenotype. Life Sci 2022, 309, 121003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khayari, A.; Hakam, S.M.; Malka, G.; Rochette, L.; El Fatimy, R. New Insights into the Cardio-Renal Benefits of SGLT2 Inhibitors and the Coordinated Role of MiR-30 Family. Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, F.; Laborante, R.; Cappannoli, L.; Morciano, C.; Gugliandolo, S.; Pontecorvi, A.; Burzotta, F.; Donniacuo, M.; Cappetta, D.; Patti, G.; et al. The Effects of SGLT2i on Cardiac Metabolism in Patients with HFpEF: Fact or Fiction? Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2025, 24, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Verma, S.; Hassanabad, A.F.; Teng, G.; Belke, D.D.; Dundas, J.A.; Guzzardi, D.G.; Svystonyuk, D.A.; Pattar, S.S.; Park, D.S.J.; et al. Direct Effects of Empagliflozin on Extracellular Matrix Remodelling in Human Cardiac Myofibroblasts: Novel Translational Clues to Explain EMPA-REG OUTCOME Results. Can. J. Cardiol. 2020, 36, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Yang, N.; Luo, W.; Qian, J.; Zhu, W.; Ye, S.; Yuan, C.; Xu, D.; Liang, G.; Huang, W.; et al. Direct Cardio-Protection of Dapagliflozin against Obesity-Related Cardiomyopathy via NHE1/MAPK Signaling. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 2624–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Zhang, M.; Suo, M.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Pan, J.; Jin, T.; An, F. Dapagliflozin Alleviates Cardiac Fibrosis through Suppressing EndMT and Fibroblast Activation via AMPKα/TGF-β/Smad Signalling in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 7642–7659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Xu, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, F.; Tu, Z.; Qian, J.; Xu, S.; Xu, Y.; Hwa, J.; Li, J.; et al. Cardioprotective Mechanism of SGLT2 Inhibitor against Myocardial Infarction Is through Reduction of Autosis. Protein Cell 2022, 13, 336–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafey, M.; El-Agawy, M.S.E.; Eldosoky, M.; Ebrahim, H.A.; Elsherbini, D.M.A.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Asseri, S.M.; Elsherbiny, N.M. Role of Dapagliflozin and Liraglutide on Diabetes-Induced Cardiomyopathy in Rats: Implication of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 862394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhu, Q.-X.; Li, G.-Z.; Wang, T.; Zhou, H. Empagliflozin Ameliorates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Probably via Activating AMPK/PGC-1α and Inhibiting the RhoA/ROCK Pathway. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 1862–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhong, J.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, W. Canagliflozin Attenuates Lipotoxicity in Cardiomyocytes and Protects Diabetic Mouse Hearts by Inhibiting the MTOR/HIF-1α Pathway. iScience 2021, 24, 102521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Gallego, C.G.; Requena-Ibanez, J.A.; San Antonio, R.; Ishikawa, K.; Watanabe, S.; Picatoste, B.; Flores, E.; Garcia-Ropero, A.; Sanz, J.; Hajjar, R.J.; et al. Empagliflozin Ameliorates Adverse Left Ventricular Remodeling in Nondiabetic Heart Failure by Enhancing Myocardial Energetics. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1931–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zuo, Q.; Ma, S.; He, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y. Metabolomic Analysis of the Effects of Canagliflozin on HFpEF Rats and Its Underlying Mechanism. Endocr. Metab. Immune. Disord. Drug Targets. 2025, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hayali, M.A.; Sozer, V.; Durmus, S.; Erdenen, F.; Altunoglu, E.; Gelisgen, R.; Atukeren, P.; Atak, P.G.; Uzun, H. Clinical Value of Circulating Microribonucleic Acids MiR-1 and MiR-21 in Evaluating the Diagnosis of Acute Heart Failure in Asymptomatic Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marketou, M.; Kontaraki, J.; Zacharis, E.; Maragkoudakis, S.; Fragkiadakis, K.; Kampanieris, E.; Plevritaki, A.; Savva, E.; Malikides, O.; Chlouverakis, G.; et al. Peripheral Blood MicroRNA-21 as a Predictive Biomarker for Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction in Old Hypertensives. Am. J. Hypertens. 2024, 37, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolhasani, S.; Ahmadi, Y.; Fattahi, D.; Rostami, Y.; Chollou, K.M. microRNA-Mediated Regulation of Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2025, 39, e70017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Huang, X.; Xu, M.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, F.; Hua, F.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y. Value of Circulating MiRNA-21 in the Diagnosis of Subclinical Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2020, 518, 110944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, F.; Salerno, M.; Esposito, M.; Cocimano, G.; Pisanelli, D.; Malik, A.; Khan, A.A.; Pomara, C. New Insight into Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Diseases: An Integrative Analysis Approach to Identify TheranoMiRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh-Gavgani, E.; Oladghaffari, M.; Bahramian, S.; Majidazar, R.; Dolati, S. MicroRNA-21: A Critical Underestimated Molecule in Diabetic Retinopathy. Gene 2023, 859, 147212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridwan, M.; Dimiati, H.; Syukri, M.; Lesmana, R.; Zaini, L.M. Effects of SGLT2-Inhibitor on The Expression of MicroRNA-21, Transforming Growth Factor-Β1, and Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 in The Process of Cardiac Fibrosis in Hyperglycemic Model Rats. Indones. Biomed. J. 2024, 16, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Meng, C.; Han, F.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, X.; Zuo, M.; Xu, J.; Chang, B. Vildagliptin Attenuates Myocardial Dysfunction and Restores Autophagy via MiR-21/SPRY1/ERK in Diabetic Mice Heart. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 634365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mone, P.; Lombardi, A.; Kansakar, U.; Varzideh, F.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Pansini, A.; Marzocco, S.; De Gennaro, S.; Famiglietti, M.; Macina, G.; et al. Empagliflozin Improves the MicroRNA Signature of Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Diabetes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2023, 384, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, L.; Zhao, L.; Song, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Lau, C.W.; Yao, X.; Tian, X.Y.; et al. Inhibition of MiR-92a Suppresses Oxidative Stress and Improves Endothelial Function by Upregulating Heme Oxygenase-1 in Db/Db Mice. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardu, C.; D’Onofrio, N.; Trotta, M.C.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Nicoletti, G.F.; D’Amico, G.; Fumagalli, C.; Contaldi, C.; Pacileo, G.; Scisciola, L.; et al. Could Ghrelin Expression Regulate Diastolic Cardiac Function in Type 2 Diabetic Obese Patients? Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2025, 41, e70049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-P.; Chang, C.-C.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Huang, K.-J.; Sokal, E.M.; Chen, K.-H.; Hung, L.-M. Exosomal MicroRNAs MiR-30d-5p and MiR-126a-5p Are Associated with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction in STZ-Induced Type 1 Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-Y.; Wang, J.; Li, A.-Z. A Study of the Effects of SGLT-2 Inhibitors on Diabetic Cardiomyopathy through MiR-30d/KLF9/VEGFA Pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 6346–6359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Du, N.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Qin, W.; Shen, N.; Xu, C.; et al. MicroRNA-30d Regulates Cardiomyocyte Pyroptosis by Directly Targeting Foxo3a in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Huang, M.; Ye, Z.; Jing, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Xiang, Z.; Ding, M.; Li, T.; Ye, Q. Empagliflozin Attenuates Ventricular Fibrillation Postmyocardial Infarction Associated with Reduced Transforming Growth Factor- β 1/Smad3 Signaling and MiR-181a Expression. J. Int. Med. Res. 2025, 53, 03000605251353040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Fu, Y.; Yuan, W.; Luo, G.; Liu, F.; Luo, J. MALAT1 Regulates Hypertrophy of Cardiomyocytes by Modulating the MiR-181a/HMGB2 Pathway. Eur. J. Histochem. 2022, 66, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Wang, L.; Espinosa-Diez, C.; Wang, B.; Hahn, S.A.; Noda, K.; Rochon, E.R.; Dent, M.R.; Levine, A.R.; Baust, J.J.; et al. Metabolic Syndrome Mediates ROS-MiR-193b-NFYA–Dependent Downregulation of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase and Contributes to Exercise-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. Circulation 2021, 144, 615–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhao, M.; Li, Z.; Nie, H.; He, J.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; et al. Plasma MiR-193b-3p Is Elevated in Type 2 Diabetes and Could Impair Glucose Metabolism. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 814347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solini, A.; Seghieri, M.; Giannini, L.; Biancalana, E.; Parolini, F.; Rossi, C.; Dardano, A.; Taddei, S.; Ghiadoni, L.; Bruno, R.M. The Effects of Dapagliflozin on Systemic and Renal Vascular Function Display an Epigenetic Signature. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 4253–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, N.; Zhu, G.; Duan, X.; Ling, F. MiRNA-30e Mediated Cardioprotection of ACE2 in Rats with Doxorubicin-Induced Heart Failure through Inhibiting Cardiomyocytes Autophagy. Life Sci. 2017, 169, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wu, C.; Ren, L.; Bao, Y.; Han, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Y. MiR-30e-5p Is Sponged by Kcnq1ot1 and Represses Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertrophic Phenotypes in Cardiomyocytes by Targeting ADAM9. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 394, 112140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Liu, L.; Hou, N.; An, X.; Zhan, D.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, P.; Yu, L.; et al. MiR-199a Impairs Autophagy and Induces Cardiac Hypertrophy through MTOR Activation. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Azzouzi, H.; Leptidis, S.; Dirkx, E.; Hoeks, J.; van Bree, B.; Brand, K.; McClellan, E.A.; Poels, E.; Sluimer, J.C.; van den Hoogenhof, M.M.G.; et al. The Hypoxia-Inducible MicroRNA Cluster MiR-199a∼214 Targets Myocardial PPARδ and Impairs Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, C.; Fang, S. SGLT2 Promotes Cardiac Fibrosis Following Myocardial Infarction and Is Regulated by MiR-141. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rykova, E.Y.; Klimontov, V.V.; Shmakova, E.; Korbut, A.I.; Merkulova, T.I.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors: Focus on Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, B. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Diabetes-Induced Macrovascular and Microvascular Complications: The Role of Oxidative Stress. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castoldi, G.; Carletti, R.; Barzaghi, F.; Meani, M.; Zatti, G.; Perseghin, G.; Di Gioia, C.; Zerbini, G. Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors in Non-Diabetic Kidney Disease: Evidence in Experimental Models. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Dai, Y.; Lian, Y.; Song, H.; Dai, X.; Su, R.; Yin, J.; Gu, R. Dapagliflozin Inhibits Ferroptosis and Ameliorates Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic C57BL/6J Mice. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tai, S.; Zhang, N.; Fu, L.; Wang, Y. Dapagliflozin Prevents Oxidative Stress-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction via Sirtuin 1 Activation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchapakesan, U.; Pegg, K.; Gross, S.; Komala, M.G.; Mudaliar, H.; Forbes, J.; Pollock, C.; Mather, A. Effects of SGLT2 Inhibition in Human Kidney Proximal Tubular Cells—Renoprotection in Diabetic Nephropathy? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, N.A.; Carpenter, A.J.; Belenchia, A.; Aroor, A.R.; Noda, M.; Siebenlist, U.; Chandrasekar, B.; DeMarco, V.G. Empagliflozin Reduces High Glucose-Induced Oxidative Stress and MiR-21-Dependent TRAF3IP2 Induction and RECK Suppression, and Inhibits Human Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cell Migration and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Cell Signal 2020, 68, 109506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, N.; Yang, X.; Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Wang, T.; Xie, M.; Liu, H. Dapagliflozin Delays Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Kidney Disease by Inhibiting YAP/TAZ Activation. Life Sci. 2023, 322, 121671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, H.; Wu, X. RNA-Seq Analysis of CeRNA-Related Networks in the Regulatory Metabolic Pathway of Mice with Diabetic Nephropathy Subjected to Empagliflozin Intervention. Arch. Esp. Urol. 2023, 76, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroor, A.R.; Das, N.A.; Carpenter, A.J.; Habibi, J.; Jia, G.; Ramirez-Perez, F.I.; Martinez-Lemus, L.; Manrique-Acevedo, C.M.; Hayden, M.R.; Duta, C.; et al. Glycemic Control by the SGLT2 Inhibitor Empagliflozin Decreases Aortic Stiffness, Renal Resistivity Index and Kidney Injury. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tantawy, S.M.; Eraky, S.M.; Eissa, L.A. Promising Renoprotective Effect of Gold Nanoparticles and Dapagliflozin in Diabetic Nephropathy via Targeting MiR-192 and MiR-21. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 37, e23430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, D.I.; Khairy, E.; Saad, S.S.T.; Habib, E.K.; Hamouda, M.A. Potential Protective Effects of Dapagliflozin in Gentamicin Induced Nephrotoxicity Rat Model via Modulation of Apoptosis Associated MiRNAs. Gene 2019, 707, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, B.D.; Chau, J.; Kurtz, R.; Rosenberg, A.Z.; Sarder, P.; Border, S.P.; Ginley, B.; Rodriguez, O.; Albanese, C.; Knoer, G.; et al. Nascent Shifts in Renal Cellular Metabolism, Structure, and Function Due to Chronic Empagliflozin in Prediabetic Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2024, 326, C1272–C1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, F.; Li, W.; Zeng, C.; Xie, L.; Liu, Z. Increased Urinary MiR-196a Level Predicts the Progression of Renal Injury in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Xie, T.; Liu, T.; Chen, Z.; Yu, L.; Zhang, C.; Luo, J.; Chen, L.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, Y. An Integrated RNA Sequencing and Network Pharmacology Approach Reveals the Molecular Mechanism of Dapagliflozin in the Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 967822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Guo, F.; Liu, Y.; Huang, F.; Fan, X.; Zhao, L.; Qin, G. Identification of Circular RNAs and Functional Competing Endogenous RNA Networks in Human Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells Treated with Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 3911–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Zhong, X.; Huang, X.R.; Meng, X.-M.; You, Y.; Chung, A.C.; Lan, H.Y. MicroRNA-29b Inhibits Diabetic Nephropathy in Db/Db Mice. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayekhi, M.; Safa, B.I.; Gonzalez, M.S.C.; Kim, S.F.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B. Systemic and Organ-Specific Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Ying, L.; Wu, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Qi, C.; Gu, L.; Mou, S.; Yan, Y.; Tian, M.; et al. Integrative ATAC-seq and RNA-seq Analysis Associated with Diabetic Nephropathy and Identification of Novel Targets for Treatment by Dapagliflozin. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2024, 42, e3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wei, C.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Guo, Z.; Qi, F. Apoptotic Bodies Extracted from Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Carry MicroRNA-21–5p to Induce M2 Polarization of Macrophages and Augment Skin Wound Healing by Targeting KLF6. Burns 2022, 48, 1893–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, M.; Cui, L.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Su, R.; Sun, K.; Hu, Y.; Yang, F.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Protect against Liver Fibrosis via Delivering MiR-148a to Target KLF6/STAT3 Pathway in Macrophages. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.-X.; Guan, C.; Li, C.-Y.; Xu, L.-Y.; Xin, Y.-L.; Song, Z.; Li, T.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Zhao, L.; Che, L.; et al. Formononetin Alleviates Ischemic Acute Kidney Injury by Regulating Macrophage Polarization through KLF6/STAT3 Pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2024, 52, 1487–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.-X.; Huang, L.-J.; Liu, H.-S.; Zhang, X.-X.; Li, M.; Cui, Y.-B.; Shao, C.; Hu, X.-L. Dapagliflozin Exerts Anti-Apoptotic Effects by Mitigating Macrophage Polarization via Modulation of the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B Signaling Pathway. World J. Diabetes 2025, 16, 97287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, E.; Keyhanfar, F.; Delbandi, A.-A.; Falak, R.; Hajimiresmaiel, S.J.; Shafiei, M. Dapagliflozin Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects via Inhibition of LPS-Induced TLR-4 Overexpression and NF-ΚB Activation in Human Endothelial Cells and Differentiated Macrophages. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 918, 174715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, K.; Lanting, L.L.; Jia, Y.; Yadav, S.; Reddy, M.A.; Magilnick, N.; Boldin, M.; Natarajan, R. Anti-Inflammatory Role of MicroRNA-146a in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Ma, A.; Xiao, Q.; Song, J.; Pan, X. MicroRNA-155 Promotes the Ox-LDL-Induced Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasomes via the ERK1/2 Pathway in THP-1 Macrophages and Aggravates Atherosclerosis in ApoE−/−Mice. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2019, 8, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.B.; Florez, J.C. Genetics of Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetes Complications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, M.; Maeda, S. Perspectives on Genetic Studies of Type 2 Diabetes from the Genome-wide Association Studies Era to Precision Medicine. J. Diabetes Investig. 2024, 15, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhichholiya, Y.; Suryan, A.K.; Suman, P.; Munshi, A.; Singh, S. SNPs in MiRNAs and Target Sequences: Role in Cancer and Diabetes. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 793523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahantigh, D.; Mirani Sargazi, F.; Sargazi, S.; Saravani, R.; Ghazaey Zidanloo, S.; Heidari Nia, M.; Piri, M. Relationship between Functional MiR-143/145 Cluster Variants and Susceptibility to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Preliminary Case-Control Study and Bioinformatics Analyses. Endocr. Res. 2021, 46, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Duan, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. A Functional Polymorphism of MicroRNA-143 Is Associated with the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in the Northern Chinese Han Population. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 994953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumensatt, M.; Wronkowitz, N.; Wiza, C.; Cramer, A.; Mueller, H.; Rabelink, M.J.; Hoeben, R.C.; Eckel, J.; Sell, H.; Ouwens, D.M. Adipocyte-Derived Factors Impair Insulin Signaling in Differentiated Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells via the Upregulation of MiR-143. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)–Mol. Basis Dis. 2014, 1842, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Ma, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, D.; Jin, Y.; Jin, Y. MiR-143 Inhibits Cell Proliferation by Targeting Autophagy-Related 2B in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer H1299 Cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wu, N.; Leong, M.C.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Z.; Li, R.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Yao, X.; et al. MiR-145 Improves Metabolic Inflammatory Disease through Multiple Pathways. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 12, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, R.; Zhu, F.; Shan, Z.; Ma, C.; Yang, J. Relation of Genetic Polymorphisms in MicroRNAs with Diastolic and Systolic Function in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 2877–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Li, T.; Hu, R.; Wu, L.; Li, M.; Meng, X. MicroRNA Let-7a and Let-7f as Novel Regulatory Factors of the Sika Deer (Cervus nippon) IGF-1R Gene. Growth Factors 2014, 32, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santovito, D.; De Nardis, V.; Marcantonio, P.; Mandolini, C.; Paganelli, C.; Vitale, E.; Buttitta, F.; Bucci, M.; Mezzetti, A.; Consoli, A.; et al. Plasma Exosome MicroRNA Profiling Unravels a New Potential Modulator of Adiponectin Pathway in Diabetes: Effect of Glycemic Control. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1681–E1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, H.; Karimi, J.; Khodadadi, I.; Tavilani, H. Correlation between MiR-103 and MiR-133a Expression and the Circulating ANGPTL8 in Type 2 Diabetic Patients and Healthy Control Subjects. Clin. Lab. 2019, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y. Association of Genetic Variants in LncRNA GAS5/MiR-21/MTOR Axis with Risk and Prognosis of Coronary Artery Disease among a Chinese Population. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, M.; Yang, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, F.; Jiao, M.; Tao, W.; Li, Y. Association of MiRNA Polymorphisms Involved in the PI3K/ATK/GSK3β Pathway with T2DM in a Chinese Population. Pharmgenomics. Pers. Med. 2025, 18, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Rahman, B.; Haq, T.U.; Jalil, F.; Khan, B.M.; Maodaa, S.N.; Al-Farraj, S.A.; El-Serehy, H.A.; Shah, A.A. Deciphering the Variants Located in the MIR196A2, MIR146A, and MIR423 with Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus in Pakistani Population. Genes 2021, 12, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buraczynska, M.; Zukowski, P.; Wacinski, P.; Ksiazek, K.; Zaluska, W. Polymorphism in MicroRNA-196a2 Contributes to the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Patients. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2014, 28, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Gao, W.; Luo, W.; Ai, L.; Hu, M. Significant Association between Microrna Gene Polymorphisms and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Susceptibility in Asian Population: A Meta-Analysis. Iran. J. Public Health 2020, 49, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, J.M.; Lango Allen, H.; Harries, L.W. A Rare SNP in Pre-MiR-34a Is Associated with Increased Levels of MiR-34a in Pancreatic Beta Cells. Acta Diabetol. 2014, 51, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mone, P.; de Donato, A.; Varzideh, F.; Kansakar, U.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Pansini, A.; Santulli, G. Functional Role of MiR-34a in Diabetes and Frailty. Front. Aging 2022, 3, 949924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mone, P.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Manzi, M.V.; Gambardella, J.; Coppola, A.; Kansakar, U.; Izzo, R.; Fiorentino, G.; Lombardi, A.; Varzideh, F.; et al. Endothelial Extracellular Vesicles Enriched in MicroRNA-34a Predict New-Onset Diabetes in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Patients: Novel Insights for Long COVID Metabolic Sequelae. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2024, 389, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, W.; Ning, M.; Zhou, X.; Wan, X.; Mi, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, B.; et al. A Functional SNP Rs895819 on Pre-MiR-27a Is Associated with Bipolar Disorder by Targeting NCAM1. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, B.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xin, S.; Xu, K. The Association of Two Common Polymorphisms in MiRNAs with Diabetes Mellitus. Medicine 2019, 98, e17414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, R.; Elfaki, I.; Javid, J.; Barnawi, J.; Altayar, M.A.; Albalawi, S.O.; Jalal, M.M.; Tayeb, F.J.; Yousif, A.; Ullah, M.F.; et al. Genetic Determinants of Cardiovascular Disease: The Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase 3 (ENOS3), Krüppel-Like Factor-14 (KLF-14), Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR), MiRNAs27a and Their Association with the Predisposition and Susceptibility to Coronary Artery Disease. Life 2022, 12, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, O.-K. Potential Roles of Adipocyte Extracellular Vesicle–Derived MiRNAs in Obesity-Mediated Insulin Resistance. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Jawad, A.M.; Ibrahim, I.H.; Zaki, M.E.; Elias, T.R.; Rasheed, W.I.; Amr, K.S. The Potential Role of MiR-27a and MiR-320a in Metabolic Syndrome in Obese Egyptian Females. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yu, J.; Li, G.; Sun, Z.; Wang, W.; Jiang, H.; Hong, Z. MiR-27a Promotes Insulin Resistance and Mediates Glucose Metabolism by Targeting PPAR-γ-Mediated PI3K/AKT Signaling. Aging 2019, 11, 7510–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burada, E.; Roșu, M.-M.; Sandu, R.E.; Burada, F.; Cucu, M.G.; Streață, I.; Petre-Mandache, B.; Popescu-Hobeanu, G.; Cara, M.-L.; Țucă, A.-M.; et al. MiR-499a Rs3746444 A>G Polymorphism Is Correlated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Polyneuropathy in a Romanian Cohort: A Preliminary Study. Genes 2023, 14, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, D.; Zhang, R.-R.; Yu, L.-W.; Zhao, J.-Y.; Yang, X.-Y.; Jiang, S.-S.; Ma, D.; Qiao, B.; Zhang, F.; et al. A TBX5 3′UTR Variant Increases the Risk of Congenital Heart Disease in the Han Chinese Population. Cell Discov. 2017, 3, 17026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipoor, B.; Ghaedi, H.; Meshkani, R.; Omrani, M.D.; Sharifi, Z.; Golmohammadi, T. The Rs2910164 Variant Is Associated with Reduced MiR-146a Expression but Not Cytokine Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2018, 41, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, M.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. The Variant at TGFBRAP 1 Is Significantly Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Affects Diabetes-related Mi RNA Expression. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.; Voight, B.F.; Lyssenko, V.; Burtt, N.P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Chen, H.; Roix, J.J.; Kathiresan, S.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Daly, M.J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analysis Identifies Loci for Type 2 Diabetes and Triglyceride Levels. Science (1979) 2007, 316, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, G.; Spurgeon, C.J.; Tabassum, R.; Bhaskar, S.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Mahajan, A.; Chavali, S.; Kumar, M.V.K.; Prakash, S.; Dwivedi, O.P.; et al. Impact of Common Variants of PPARG, KCNJ11, TCF7L2, SLC30A8, HHEX, CDKN2A, IGF2BP2, and CDKAL1 on the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in 5,164 Indians. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Goyal, Y.; Bhatt, D.; Beg, M.M.A.; Dev, K.; Alsahli, M.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Association Between CDKAL1, HHEX, CDKN2A/2B and IGF2BP2 Gene Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to Type 2 Diabetes in Uttarakhand, India. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadheel, H.K.; Kaftan, A.N.; Naser, F.H.; Hussain, M.K.; Algenabi, A.H.A.; Mohammad, H.J.; Al-Kashwan, T.A. Association of CDKN2A/B Gene Polymorphisms (Rs10811661 and Rs2383208) with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Sample of Iraqi Population. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2022, 23, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Moro, I.; Rojas-Márquez, H.; Sebastian-delaCruz, M.; Mentxaka-Salgado, J.; Olazagoitia-Garmendia, A.; Mendoza, L.M.; Lluch, A.; Fantuzzi, F.; Lambert, C.; Ares Blanco, J.; et al. A Long Non-Coding RNA That Harbors a SNP Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Regulates the Expression of TGM2 Gene in Pancreatic Beta Cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1101934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brondani, L.A.; Dandolini, I.; Girardi, E.; Canani, L.H.; Crispim, D.; Dieter, C. Association between the G/G Genotype of the LncRNA MEG3 Rs7158663 Polymorphism and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 68, e240024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.-C.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.-S.; Kornelius, E.; Tang, C.-H.; Lee, C.-Y.; Chien, H.-W.; Yang, S.-F. Association of Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR Polymorphism and the Clinical Manifestations of Diabetic Retinopathy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letonja, J.; Petrovič, D.; Petrovič, D. CDKN2B-AS1 Polymorphism Rs1333049 Is Associated with Advanced Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in a Slovenian Population. Biomol. Biomed. 2025, 25, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Osorio, A.S.; Musalem-Younes, C.; Cárdenas-Hernández, H.; Solares-Tlapechco, J.; Costa-Urrutia, P.; Medina-Contreras, O.; Granados, J.; López-Saucedo, C.; Estrada-Garcia, T.; Rodríguez-Arellano, M.E. Common Polymorphisms Linked to Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease in Europeans and Asians Are Associated with Type 2 Diabetes in Mexican Mestizos. Medicina 2019, 55, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Pacheco, E.; Nevado, J.B.; Cutiongco-de la Paz, E.M.C.; Jasul, G.V.; Aman, A.Y.C.L.; Ribaya, E.L.A.; Francisco, M.D.G.; Guanzon, M.L.V.V.; Uyking-Naranjo, M.L.; Añonuevo-Cruz, M.C.S.; et al. Variants of SLC2A10 May Be Linked to Poor Response to Metformin. J. Endocr. Soc. 2022, 6, bvac092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.-P.; Chien, H.-W.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.-S.; Su, S.-C.; Chang, L.-C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Yang, S.-F. Genetic Association of Diabetic Retinopathy with Long Noncoding RNA CDKN2B-AS1 Gene Polymorphism. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2025, 35, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yari, A.; Karam, Z.M.; Meybodi, S.M.E.; Sargazi, M.L.; Saeidi, K. CDKN2B-AS (Rs2891168), SOD2 (Rs4880), and PON1 (Rs662) Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to Coronary Artery Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Iranian Patients: A Case-control Study. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.-J.; Ting, K.-H.; Tsai, P.-Y.; Su, S.-C.; Yang, S.-F. Association of Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 Gene Polymorphism with Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 21, 2201–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matboli, M.; Kamel, M.M.; Essawy, N.; Bekhit, M.M.; Abdulrahman, B.; Mohamed, G.F.; Eissa, S. Identification of Novel Insulin Resistance Related CeRNA Network in T2DM and Its Potential Editing by CRISPR/Cas9. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, L.J.; Mohlke, K.L.; Bonnycastle, L.L.; Willer, C.J.; Li, Y.; Duren, W.L.; Erdos, M.R.; Stringham, H.M.; Chines, P.S.; Jackson, A.U.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study of Type 2 Diabetes in Finns Detects Multiple Susceptibility Variants. Science 2007, 316, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, J.P.; Morris, A.P. Multi-Ethnic Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Novel Locus for Type 2 Diabetes Susceptibility. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 24, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grarup, N.; Rose, C.S.; Andersson, E.A.; Andersen, G.; Nielsen, A.L.; Albrechtsen, A.; Clausen, J.O.; Rasmussen, S.S.; Jørgensen, T.; Sandbæk, A.; et al. Studies of Association of Variants Near the HHEX, CDKN2A/B, and IGF2BP2 Genes with Type 2 Diabetes and Impaired Insulin Release in 10,705 Danish Subjects. Diabetes 2007, 56, 3105–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hribal, M.L.; Presta, I.; Procopio, T.; Marini, M.A.; Stančáková, A.; Kuusisto, J.; Andreozzi, F.; Hammarstedt, A.; Jansson, P.-A.; Grarup, N.; et al. Glucose Tolerance, Insulin Sensitivity and Insulin Release in European Non-Diabetic Carriers of a Polymorphism Upstream of CDKN2A and CDKN2B. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Sharma, R.B.; Ly, S.; Stamateris, R.E.; Jesdale, W.M.; Alonso, L.C. CDKN2A/B T2D Genome-Wide Association Study Risk SNPs Impact Locus Gene Expression and Proliferation in Human Islets. Diabetes 2018, 67, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ‘t Hart, L.M.; Simonis-Bik, A.M.; Nijpels, G.; van Haeften, T.W.; Schäfer, S.A.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J.; Boomsma, D.I.; Groenewoud, M.J.; Reiling, E.; van Hove, E.C.; et al. Combined Risk Allele Score of Eight Type 2 Diabetes Genes Is Associated With Reduced First-Phase Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion During Hyperglycemic Clamps. Diabetes 2010, 59, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, T.U.; Zahoor, A.; Ali, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jalil, F.; Shah, A.A. Genetic Variants of MIR27A, MIR196A2 May Impact the Risk for the Onset of Coronary Artery Disease in the Pakistani Population. Genes 2022, 13, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, A.; Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, H.; Xu, S. Genetic Association of Long Non-Coding RNA ANRIL Polymorphism with the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in the Chinese Han Population. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2025, 17, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinelli-Arzubiaga, D.; Suasnabar Campos, C.E.; Laso-Salazar, M.C.; Abarca-Barriga, H. Polymorphic Variants and Risk of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2025, 25, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Tao, W.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Lu, T.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Yao, Y. The Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (Rs1292037 and Rs13137) in MiR-21 Were Associated with T2DM in a Chinese Population. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agiannitopoulos, K.; Samara, P.; Papadopoulou, M.; Efthymiadou, A.; Papadopoulou, E.; Tsaousis, G.N.; Mertzanos, G.; Babalis, D.; Lamnissou, K. MiRNA Polymorphisms and Risk of Premature Coronary Artery Disease. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2021, 62, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zal, N.; Safi, S.; Ahmadieh, H.; Fekri, S.; Najafi, S.; Forouhari, A.; Moghaddasi, A.; Hejazi, M.; Kheiri, B.; Eslami, M.; et al. Assessment of MIR200B Polymorphisms Association with Sight-Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2023, 35, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Liu, X.; Tang, J.; Chang, X.; Jin, H.; Zhu, B.; Hao, L.; Zhang, L. The Effect of Allograft Inflammatory Factor-1 on Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Autophagy via MiR-34a/ATG4B Pathway in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 1668000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-R.; He, F.-Z.; Liu, M.-Z.; Hu, J.-L.; Xu, H.; Zhou, H.-H.; Zhang, W. MIR4532 Gene Variant Rs60432575 Influences the Expression of KCNJ11 and the Sulfonylureas-Stimulated Insulin Secretion. Endocrine 2019, 63, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Sun, Z.; Du, H.; Zhou, T.; Zou, J.; Fu, W. Metformin Inhibits High Glucose-induced Apoptosis of Renal Podocyte through Regulating MiR-34a/SIRT1 Axis. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2024, 12, e1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas-Gonzalez, M.; Srivastava, A.; Pavkovic, M.; Bijol, V.; Rennke, H.G.; Stillman, I.E.; Zhang, X.; Parikh, S.; Rovin, B.H.; Afkarian, M.; et al. Identification, Confirmation, and Replication of Novel Urinary MicroRNA Biomarkers in Lupus Nephritis and Diabetic Nephropathy. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 1515–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechamethakun, S.; Muramatsu, M. Long Noncoding RNA Variations in Cardiometabolic Diseases. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 62, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, K.L.; Li, S.; Muñoz-Cabello, A.M.; Raguz, S.; Zeng, L.; Mujtaba, S.; Gil, J.; Walsh, M.J.; Zhou, M.-M. Molecular Interplay of the Noncoding RNA ANRIL and Methylated Histone H3 Lysine 27 by Polycomb CBX7 in Transcriptional Silencing of INK4a. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florez, J.C.; Pearson, E.R. A Roadmap to Achieve Pharmacological Precision Medicine in Diabetes. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.E.; Haffner, S.M.; Heise, M.A.; Herman, W.H.; Holman, R.R.; Jones, N.P.; Kravitz, B.G.; Lachin, J.M.; O’Neill, M.C.; Zinman, B.; et al. Glycemic Durability of Rosiglitazone, Metformin, or Glyburide Monotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2427–2443, Erratum in N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1387–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirmohamed, M. Pharmacogenomics: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreienkamp, R.J.; Voight, B.F.; Gloyn, A.L.; Udler, M.S. Genetics of Type 2 Diabetes. In Diabetes in America [Internet]; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Yee, S.W.; Seiser, E.L.; van Leeuwen, N.; Tavendale, R.; Bennett, A.J.; Groves, C.J.; Coleman, R.L.; van der Heijden, A.A.; Beulens, J.W.; et al. Variation in the Glucose Transporter Gene SLC2A2 Is Associated with Glycemic Response to Metformin. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1055–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.H.; Perry, J.A.; Jablonski, K.A.; Srinivasan, S.; Chen, L.; Todd, J.N.; Harden, M.; Mercader, J.M.; Pan, Q.; Dawed, A.Y.; et al. Identification of Genetic Variation Influencing Metformin Response in a Multiancestry Genome-Wide Association Study in the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP). Diabetes 2023, 72, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Cao, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Guo, Y. Association of SLC22A1, SLC22A2, SLC47A1, and SLC47A2 Polymorphisms with Metformin Efficacy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawed, A.Y.; Yee, S.W.; Zhou, K.; van Leeuwen, N.; Zhang, Y.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Etheridge, A.; Innocenti, F.; Xu, F.; Li, J.H.; et al. Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis Identifies Genetic Variants Associated With Glycemic Response to Sulfonylureas. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umapathysivam, M.M.; Araldi, E.; Hastoy, B.; Dawed, A.Y.; Vatandaslar, H.; Sengupta, S.; Kaufmann, A.; Thomsen, S.; Hartmann, B.; Jonsson, A.E.; et al. Type 2 Diabetes Risk Alleles in Peptidyl-Glycine Alpha-Amidating Monooxygenase Influence GLP-1 Levels and Response to GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Preprint 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Z.; Li, Q.; Huang, R.; Wang, J.; Weng, J.; Zhou, K.; Liang, H.; Wang, Y. KCNQ1 Variant Rs163184 Is a Potential Biomarker of Glycemic Response to Exenatide. Pharmacogenomics 2022, 23, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.; Cao, R. GLP1R Variant Is Associated with Response to Exenatide in Overweight Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Pharmacogenomics 2019, 20, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Yin, Z. Effect of Rs67085638 in Long Non-coding RNA (CCAT1) on Colon Cancer Chemoresistance to Paclitaxel through Modulating the MicroRNA-24-3p and FSCN1. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 3744–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.-W.; Chen, C.-J.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Yu, H.; Zeng, Z.; Jin, T.; Wang, T.-H.; Qin, W.; Huang, H.; Wu, X.-D.; et al. Associations Between MicroRNA-Related Genetic Polymorphisms and Clinical Response to Methotrexate in Chinese Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 3167–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykova, E.; Ershov, N.; Damarov, I.; Merkulova, T. SNPs in 3′UTR MiRNA Target Sequences Associated with Individual Drug Susceptibility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klen, J.; Dolžan, V. SGLT2 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: More than Just Glucose Regulation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mai, Z.; Yu, S.; Wang, B.; Lai, W.; Chen, G.; Zhou, C.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. Exploring the Pleiotropic Genes and Therapeutic Targets Associated with Heart Failure and Chronic Kidney Disease by Integrating MetaCCA and SGLT2 Inhibitors’ Target Prediction. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 4229194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degtyareva, A.O.; Antontseva, E.V.; Merkulova, T.I. Regulatory SNPs: Altered Transcription Factor Binding Sites Implicated in Complex Traits and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguet, F.; Anand, S.; Ardlie, K.G.; Gabriel, S.; Getz, G.A.; Graubert, A.; Hadley, K.; Handsaker, R.E.; Huang, K.H.; Kashin, S.; et al. The GTEx Consortium Atlas of Genetic Regulatory Effects across Human Tissues. Science (1979) 2020, 369, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.T.; Moyerbrailean, G.A.; Davis, G.O.; Wen, X.; Luca, F.; Pique-Regi, R. QuASAR: Quantitative Allele-Specific Analysis of Reads. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyerbrailean, G.A.; Richards, A.L.; Kurtz, D.; Kalita, C.A.; Davis, G.O.; Harvey, C.T.; Alazizi, A.; Watza, D.; Sorokin, Y.; Hauff, N.; et al. High-Throughput Allele-Specific Expression across 250 Environmental Conditions. Genome. Res. 2016, 26, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Arcelus, M.; Baglaenko, Y.; Arora, J.; Hannes, S.; Luo, Y.; Amariuta, T.; Teslovich, N.; Rao, D.A.; Ermann, J.; Jonsson, A.H.; et al. Allele-Specific Expression Changes Dynamically during T Cell Activation in HLA and Other Autoimmune Loci. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.-H.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Z. MRNA Therapeutics: New Vaccination and Beyond. Fundam. Res. 2023, 3, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
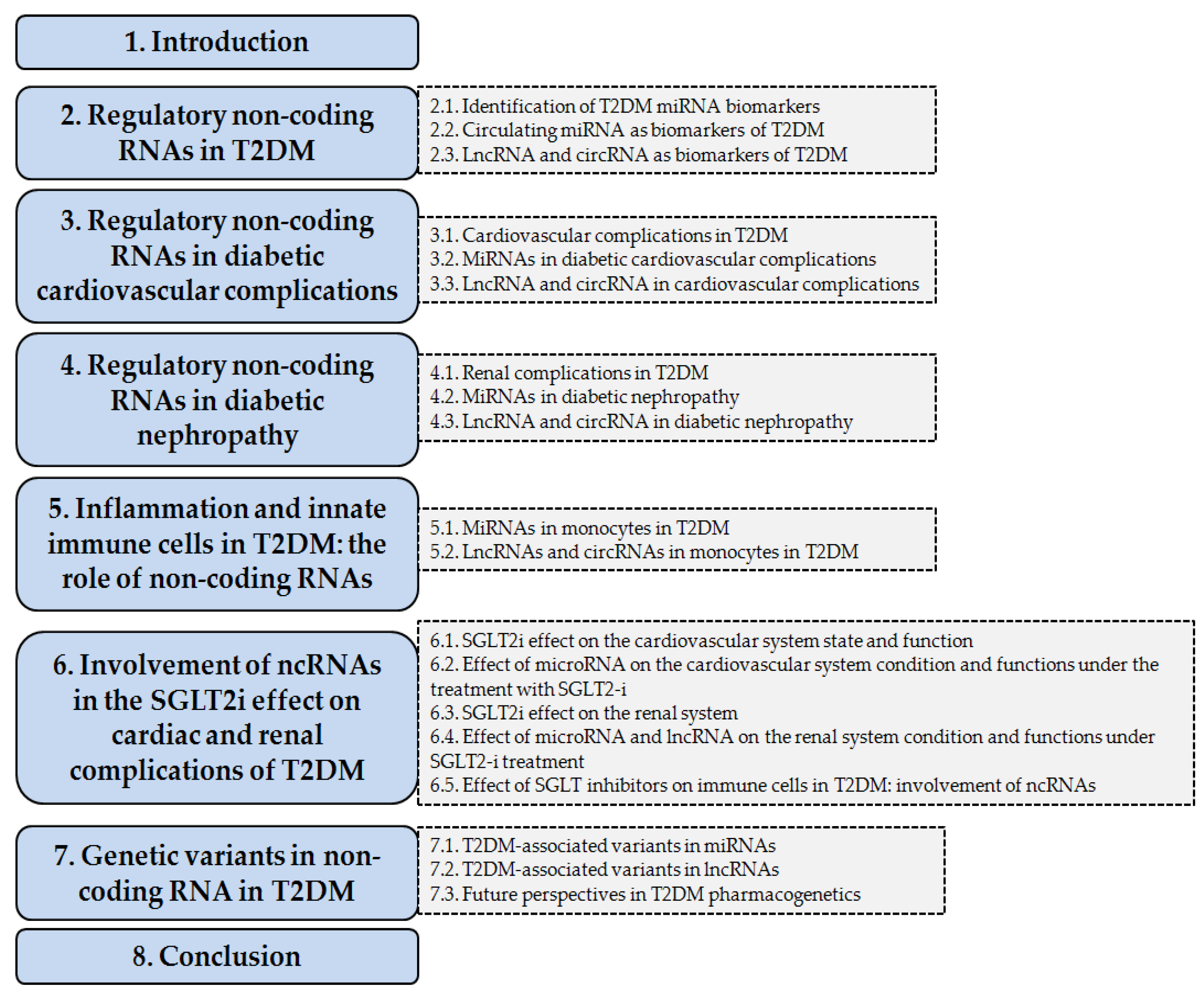

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rykova, E.; Shmakova, E.; Damarov, I.; Merkulova, T.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Non-Coding RNA in Type 2 Diabetes Cardio–Renal Complications and SGLT2 Inhibitor Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211198
Rykova E, Shmakova E, Damarov I, Merkulova T, Kzhyshkowska J. Non-Coding RNA in Type 2 Diabetes Cardio–Renal Complications and SGLT2 Inhibitor Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):11198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211198
Chicago/Turabian StyleRykova, Elena, Elena Shmakova, Igor Damarov, Tatiana Merkulova, and Julia Kzhyshkowska. 2025. "Non-Coding RNA in Type 2 Diabetes Cardio–Renal Complications and SGLT2 Inhibitor Response" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 11198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211198
APA StyleRykova, E., Shmakova, E., Damarov, I., Merkulova, T., & Kzhyshkowska, J. (2025). Non-Coding RNA in Type 2 Diabetes Cardio–Renal Complications and SGLT2 Inhibitor Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 11198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211198







