The Gene Ail for the Attachment–Invasion Locus Protein of Yer-Sinia Enterocolitica Biotype 1A Strains Is Located on the Genomes of Novel Prophages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
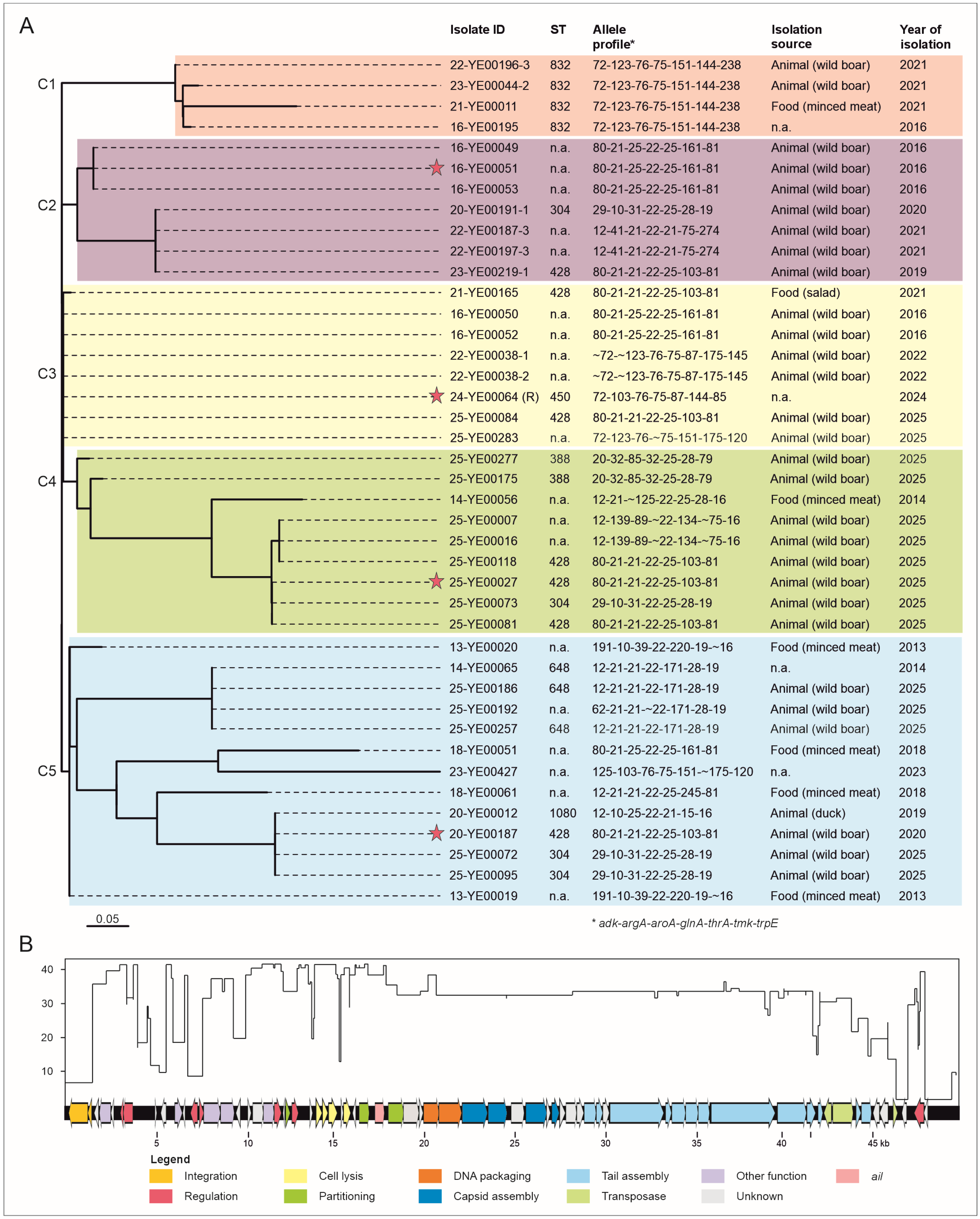
2.1. Out of 370 BT 1A Genomes, 41 Contain a Prophage-Associated Ail Gene
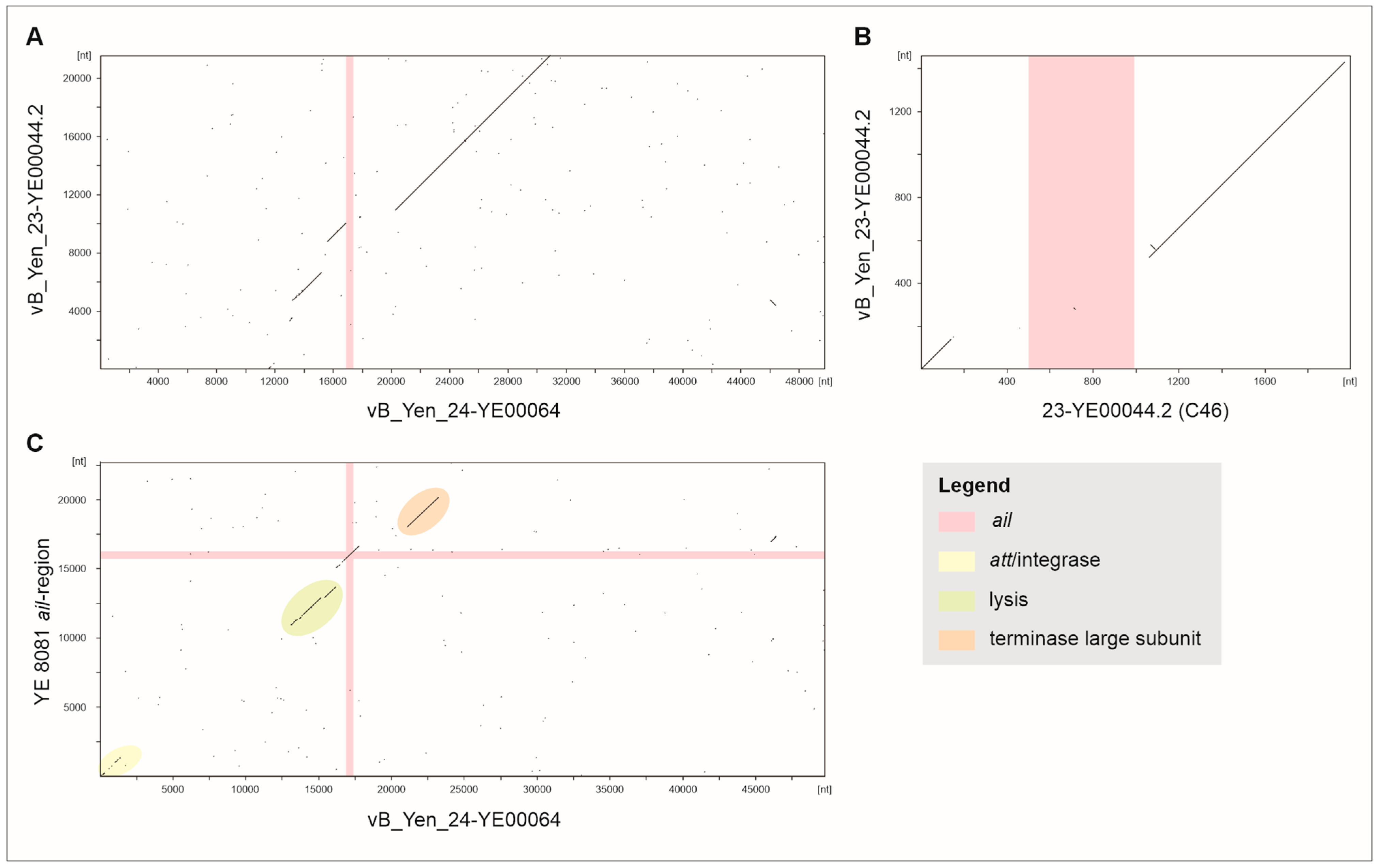
2.2. Comparison of the Prophages Indicates Relationships Between Them
2.3. Relocation of Ail in Cluster C1 and Analysis of 1B/O:8 Strains
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Source and Typing of Y. enterocolitica Strains
4.2. Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
4.3. Genome Accession Numbers
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carniel, E. The Yersinia high-pathogenicity island: An iron-uptake island. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Monitoring and identification of human enteropathogenic Yersinia spp. ESFA J. 2007, 595, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Boqvist, S.; Pettersson, H.; Svensson, A.; Andersson, Y. Sources of sporadic Yersinia enterocolitica infection in children in Sweden, 2004: A case-control study. Epidemiol. Infect. 2009, 137, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centorame, P.; Sulli, N.; De Fanis, C.; Colangelo, O.V.; De Massis, F.; Conte, A.; Persiani, T.; Marfoglia, C.; Scattolini, S.; Pomilio, F.; et al. Identification and characterization of Yersinia enterocolitica strains isolated from pig tonsils at slaughterhouse in Central Italy. Vet Ital. 2017, 53, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Korte, T.; Korkeala, H. Contamination of carcasses, offals, and the environment with yadA-positive Yersinia enterocolitica in a pig slaughterhouse. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Korte, T.; Korkeala, H. Transmission of Yersinia enterocolitica 4/O:3 to pets via contaminated pork. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 32, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Stolle, A.; Korkeala, H. Molecular epidemiology of Yersinia enterocolitica infections. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 47, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroff, S.M.; Kapperud, G.; Hutwagner, L.C.; Nesbakken, T.; Bean, N.H.; Lassen, J.; Tauxe, R.V. Sources of sporadic Yersinia enterocolitica infections in Norway: A prospective case-control study. Epidemiol. Infect. 1994, 112, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauxe, R.V.; Wauters, G.; Goossens, V.; Noyen, R.V.; Vandepitte, J.; Martin, S.M.; Mol, P.D.; Thiers, G. Yersinia enterocolitica infections and pork: The missing link. Lancet 1987, 329, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt-Samoraj, A.; Syczyło, K.; Szczerba-Turek, A.; Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Jabłoński, A.; Łabuć, S.; Pajdak, J.; Oshakbaeva, N.; Szweda, W. Presence of ail and ystB genes in Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 1A isolates from game animals in Poland. Veter- J. 2017, 221, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joutsen, S.; Johansson, P.; Laukkanen-Ninios, R.; Björkroth, J.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M. Two copies of the ail gene found in Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia kristensenii. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 247, 108798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guern, A.-S.; Martin, L.; Savin, C.; Carniel, E. Yersiniosis in France: Overview and potential sources of infection. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 46, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirjavainen, V.; Jarva, H.; Biedzka-Sarek, M.; Blom, A.M.; Skurnik, M.; Meri, S. Yersinia enterocolitica serum resistance proteins YadA and ail bind the complement regulator c4b-binding protein. PLOS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, J.J.; Plecha, S.C.; Krukonis, E.S. Ail provides multiple mechanisms of serum resistance to Yersinia pestis. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 111, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, V.L.; Beer, K.B.; Heusipp, G.; Young, B.M.; Wachtel, M.R. Identification of regions of Ail required for the invasion and serum resistance phenotypes. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraushaar, B.; Dieckmann, R.; Wittwer, M.; Knabner, D.; Konietzny, A.; Mäde, D.; Strauch, E. Characterization of a Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 1A strain harbouring an ail gene. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihvonen, L.M.; Jalkanen, K.; Huovinen, E.; Toivonen, S.; Corander, J.; Kuusi, M.; Skurnik, M.; Siitonen, A.; Haukka, K. Clinical isolates of Yersinia enterocolitica Biotype 1A represent two phylogenetic lineages with differing pathogenicity-related properties. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, E.; Greig, D.R.; Schaefer, U.; Wright, M.J.; Dallman, T.J.; McNally, A.; Jenkins, C. Identification and typing of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis isolated from human clinical specimens in England between 2004 and 2018. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, A.; Cheasty, T.; Fearnley, C.; Dalziel, R.; Paiba, G.; Manning, G.; Newell, D. Comparison of the biotypes of Yersinia enterocolitica isolated from pigs, cattle and sheep at slaughter and from humans with yersiniosis in Great Britain during 1999–2000. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 39, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNally, A.; Dalton, T.; La Ragione, R.M.; Stapleton, K.; Manning, G.; Newell, D.G. Yersinia enterocolitica isolates of differing biotypes from humans and animals are adherent, invasive and persist in macrophages, but differ in cytokine secretion profiles in vitro. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, L.; Horn, B.; Armstrong, B.; Wright, J.; Strydom, H.; Wang, J.; Paine, S.; Thom, K.; Orton, A.; Robson, B.; et al. A case-control study and molecular epidemiology of yersiniosis in Aotearoa New Zealand. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2024, 62, e0075424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, L.; Strydom, H.; Paine, S.; Wang, J.; Wright, J. Yersiniosis in New Zealand. Pathogens 2021, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, R.; Joutsen, S.; Hofer, E.; Sade, E.; Bjorkroth, J.; Ziegler, D.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M. Characteristics of Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 1A strains isolated from patients and asymptomatic carriers. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.; Dabke, G.; Strakova, L.; Jenkins, C.; Saavedra-Campos, M.; McManus, O.; Paranthaman, K. Introduction of PCR testing reveals a previously unrecognized burden of yersiniosis in Hampshire, UK. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbran, C.; May, F.; Alexander, K.; Hunter, I.; Stafford, R.; Bell, R.; Cowdry, A.; Vosti, F.; Jurd, S.; Graham, T.; et al. Yersiniosis outbreaks in Gold Coast residential aged care facilities linked to nutritionally-supplemented milkshakes, January–April 2023. Commun. Dis. Intell. 2024, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, B.P.I.; Cressey, P.; Armstrong, B.; Lopez, L. Annual Report Concerning Foodborne Diseases in New Zealand 2022; New Zealand Food Safety Technical Paper No: 2023/17; Ministry for Primary Industries: Wellington, NZ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Platt-Samoraj, A. Toxigenic Properties of Yersinia enterocolitica Biotype 1A. Toxins 2022, 14, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, N.R.; Howard, S.; Wren, B.W.; Holden, M.T.; Crossman, L.; Challis, G.L.; Churcher, C.; Mungall, K.; Brooks, K.; Chillingworth, T.; et al. The complete genome sequence and comparative genome analysis of the high pathogenicity Yersinia enterocolitica strain 8081. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejek, A.M.; Hovde, C.J.; Minnich, S.A. Yersinia pestis Ail: Multiple roles of a single protein. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.J.; Horlbog, J.A.; Diethelm, A.; Stephan, R.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M. Characteristics and comparative genome analysis of Yersinia enterocolitica and related species associated with human infections in Switzerland 2019–2023. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2024, 123, 105652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sihvonen, L.M.; Hallanvuo, S.; Haukka, K.; Skurnik, M.; Siitonen, A. The ail gene is present in some Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 1A strains. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syczyło, K.; Platt-Samoraj, A.; Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Szczerba-Turek, A.; Pajdak-Czaus, J.; Łabuć, S.; Procajło, Z.; Socha, P.; Chuzhebayeva, G.; Szweda, W. The prevalence of Yersinia enterocolitica in game animals in Poland. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerl, J.A.; Barac, A.; Jackel, C.; Fuhrmann, J.; Gadicherla, A.; Hertwig, S. Phage vB_YenS_P400, a Novel Virulent Siphovirus of Yersinia enterocolitica Isolated from Deer. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popp, A.; Hertwig, S.; Lurz, R.; Appel, B. Comparative study of temperate bacteriophages isolated from Yersinia. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 23, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwig, S.; Popp, A.; Freytag, B.; Lurz, R.; Appel, B. Generalized transduction of small Yersinia enterocolitica plasmids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3862–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerl, J.A.; El-Mustapha, S.; Bölcke, M.; Trampert, H.; Barac, A.; Jäckel, C.; Gadicherla, A.K.; Hertwig, S. Host Range, Morphology and Sequence Analysis of Ten Temperate Phages Isolated from Pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica Strains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marggraf, M.; Barac, A.; Hammerl, J.A.; Hertwig, S. Improvement of the EN ISO 10273:2017 method for the cultural detection of Yersinia enterocolitica in meat. Food Microbiol. 2024, 117, 104384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauters, G.; Kandolo, K.; Janssens, M. Revised biogrouping scheme of Yersinia enterocolitica. Contrib. Microbiol. Immunol. 1987, 9, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hammerl, J.A.; Klein, I.; Lanka, E.; Appel, B.; Hertwig, S. Genetic and functional properties of the self-transmissible Yersinia enterocolitica plasmid pYE854, which mobilizes the virulence plasmid pYV. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 991–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerl, J.A.; Rivas, L.; Cornelius, A.; Manta, D.; Hertwig, S. The β-glucosidase gene for esculin hydrolysis of Yersinia enterocolitica is a suitable target for the detection of biotype 1A strains by polymerase chain reaction. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2025, 136, lxaf142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräuer, J.A.; Hammerl, J.A.; El-Mustapha, S.; Fuhrmann, J.; Barac, A.; Hertwig, S. The Novel Yersinia enterocolitica Telomere Phage vB_YenS_P840 Is Closely Related to PY54, but Reveals Some Striking Differences. Viruses 2023, 15, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerl, J.A.; Barac, A.; Erben, P.; Fuhrmann, J.; Gadicherla, A.; Kumsteller, F.; Lauckner, A.; Müller, F.; Hertwig, S. Properties of Two Broad Host Range Phages of Yersinia enterocolitica Isolated from Wild Animals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deneke, C.; Brendebach, H.; Uelze, L.; Borowiak, M.; Malorny, B.; Tausch, S.H. Species-Specific Quality Control, Assembly and Contamination Detection in Microbial Isolate Sequences with AQUAMIS. Genes 2021, 12, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaas, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Solving the problem of comparing whole bacterial genomes across different sequencing platforms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hammerl, J.A.; Hertwig, S. The Gene Ail for the Attachment–Invasion Locus Protein of Yer-Sinia Enterocolitica Biotype 1A Strains Is Located on the Genomes of Novel Prophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211166
Hammerl JA, Hertwig S. The Gene Ail for the Attachment–Invasion Locus Protein of Yer-Sinia Enterocolitica Biotype 1A Strains Is Located on the Genomes of Novel Prophages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):11166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211166
Chicago/Turabian StyleHammerl, Jens Andre, and Stefan Hertwig. 2025. "The Gene Ail for the Attachment–Invasion Locus Protein of Yer-Sinia Enterocolitica Biotype 1A Strains Is Located on the Genomes of Novel Prophages" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 11166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211166
APA StyleHammerl, J. A., & Hertwig, S. (2025). The Gene Ail for the Attachment–Invasion Locus Protein of Yer-Sinia Enterocolitica Biotype 1A Strains Is Located on the Genomes of Novel Prophages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 11166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211166





