Protective Role of p66Shc Deletion in Physiological Renal Aging: Effects on G Protein-Coupled Receptor 124 Expression and Associated Cellular Senescence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
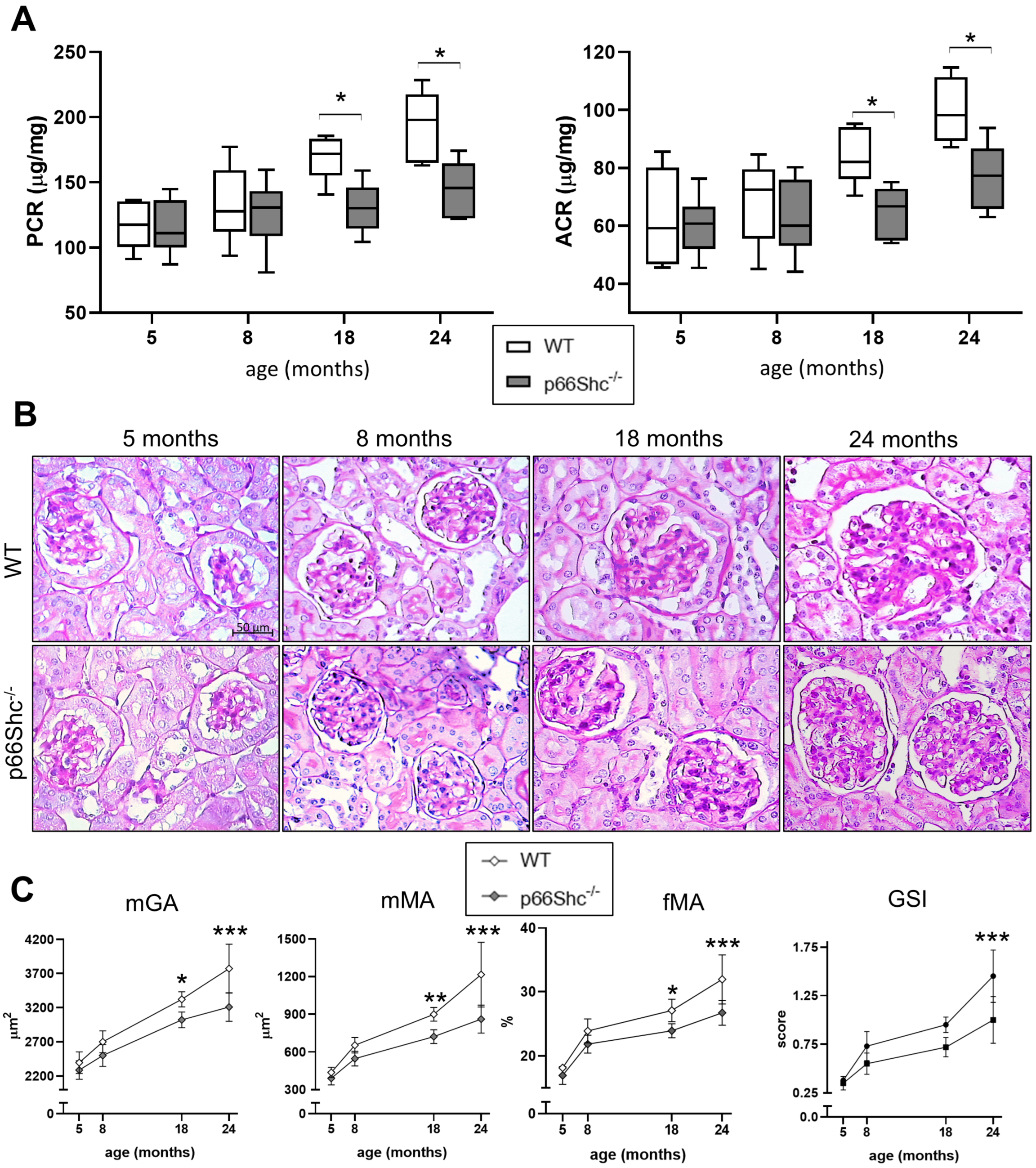
2.1. Renal Function and Structure
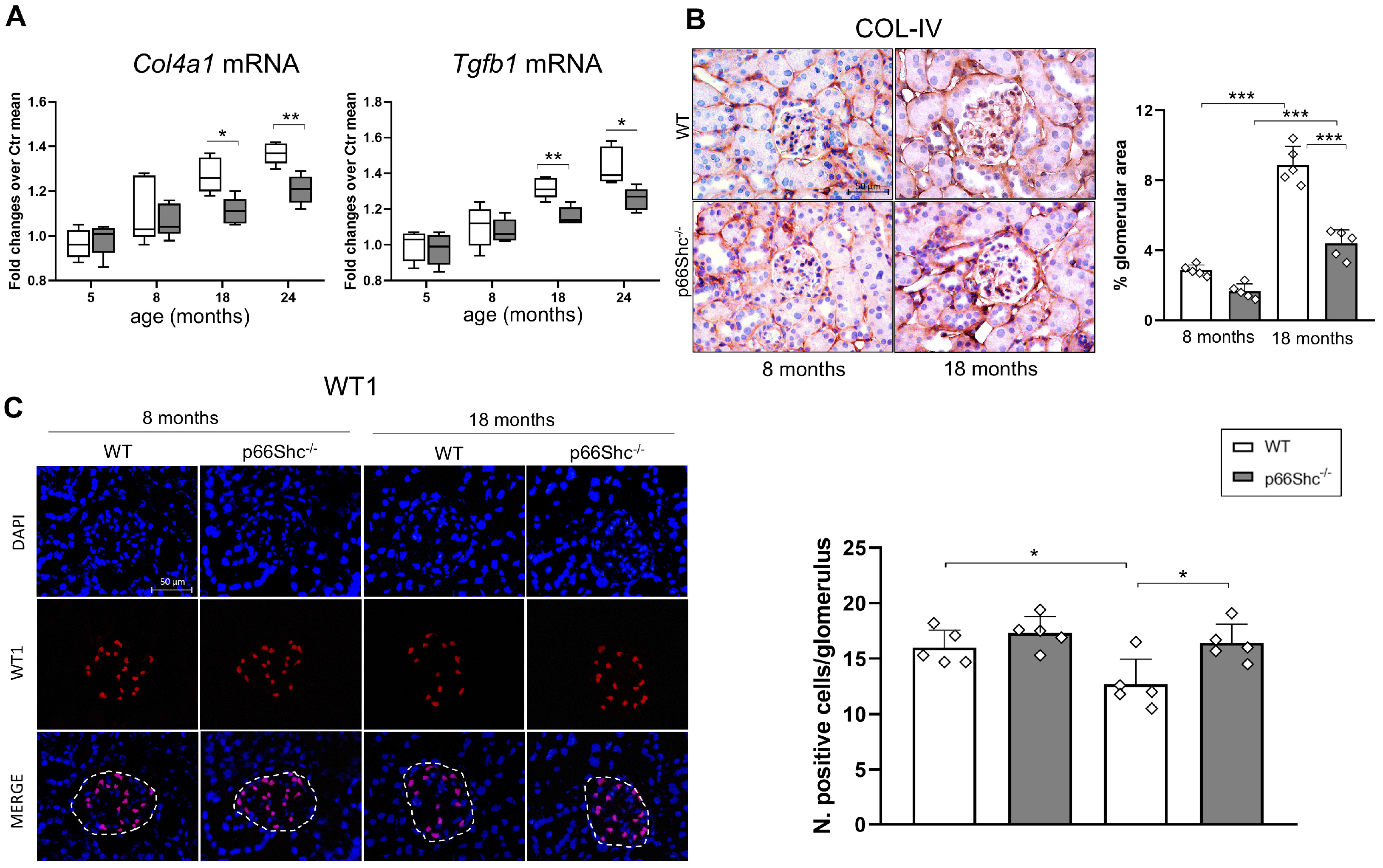
2.2. Renal Fibrosis, Podocyte Number, and Oxidative Stress Markers
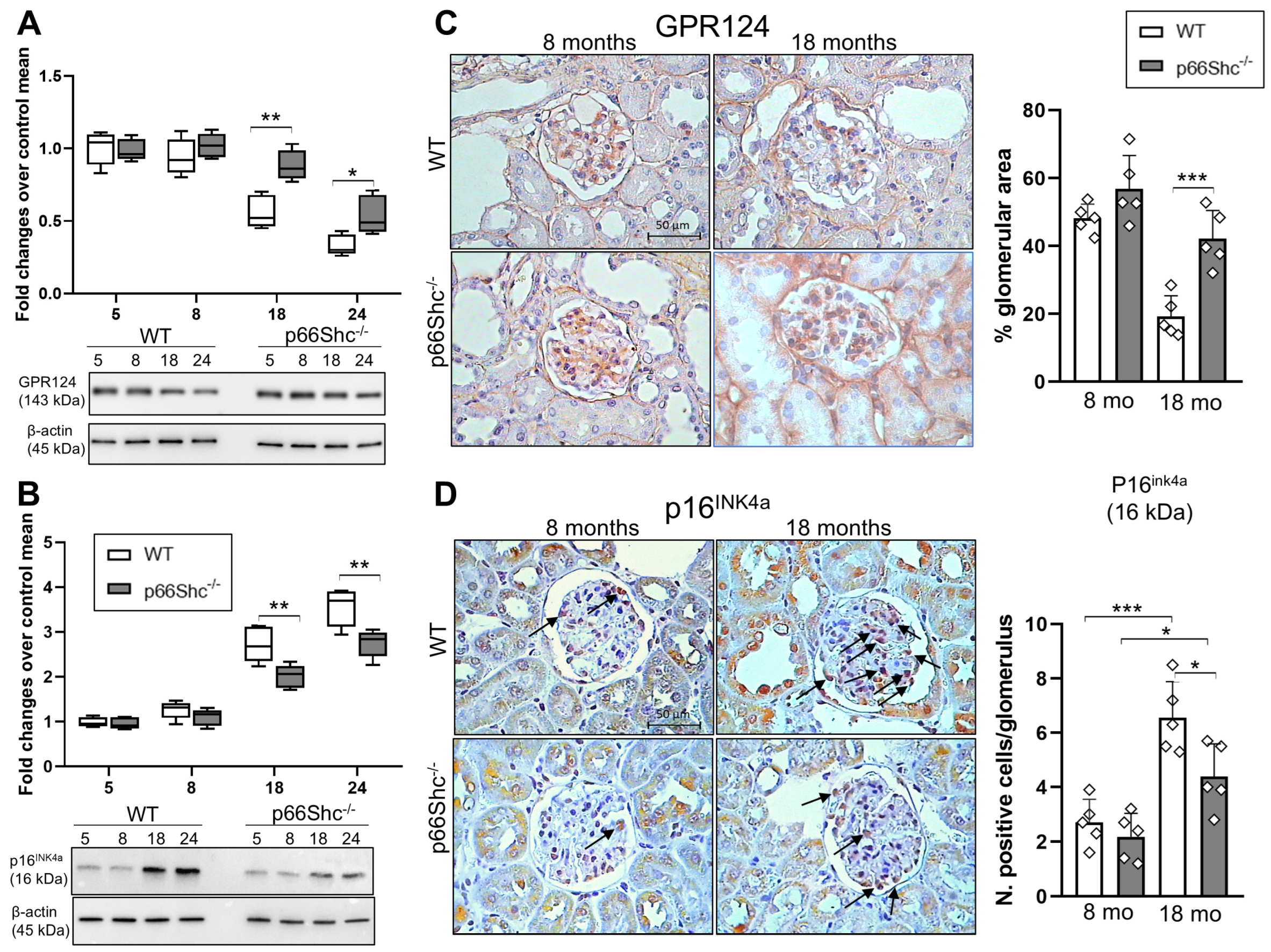
2.3. Renal Expression Levels of GPR124 and p16INK4a
2.4. Effect of p66Shc Silencing on the Expression Levels of GPR124 and Senescence-Related Markers in Cultured Podocytes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.1.1. In Vivo Study
4.1.2. In Vitro Study
4.2. Renal Function and Structure
4.3. Immunostaining
4.4. Western Blot
4.5. SA-β-Gal Staining
4.6. RT-PCR
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WT | Wild-type |
| AGEs | Advanced glycation endproducts |
| GPR124 | G protein-coupled receptor 124 |
| mGA | Mean glomerular area |
| mMa | Mean mesangial area |
| fMa | Fractional mesangial area |
| GSI | Glomerulosclerosis index |
| Col4a1 | Collagen IV α1-chain (gene) |
| Tgfb1 | Transforming growth factor-β1 |
| COL-IV | Collagen IV (protein) |
| p16INK4a | Protein16 inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 |
| ADR | Adriamycin |
| CDKN2A | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A |
| CDKN2D | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2D |
| CDKN1A | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A |
| SA-β-gal | Senescence-associated β-galactosidase |
References
- Giorgio, M.; Migliaccio, E.; Orsini, F.; Paolucci, D.; Moroni, M.; Contursi, C.; Pelliccia, G.; Luzi, L.; Minucci, S.; Marcaccio, M.; et al. Electron Transfer between Cytochrome c and P66Shc Generates Reactive Oxygen Species That Trigger Mitochondrial Apoptosis. Cell 2005, 122, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, C.; Martin-Padura, I.; De Nigris, F.; Giorgio, M.; Mansueto, G.; Somma, P.; Condorelli, M.; Sica, G.; De Rosa, G.; Pelicci, P.G. Deletion of the P66Shc Longevity Gene Reduces Systemic and Tissue Oxidative Stress, Vascular Cell Apoptosis, and Early Atherogenesis in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2112–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, R.S.; Orr, W.C. The Redox Stress Hypothesis of Aging. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francia, P.; Delli Gatti, C.; Bachschmid, M.; Martin-Padura, I.; Savoia, C.; Migliaccio, E.; Pelicci, P.G.; Schiavoni, M.; Lüscher, T.F.; Volpe, M.; et al. Deletion of P66shc Gene Protects against Age-Related Endothelial Dysfunction. Circulation 2004, 110, 2889–2895, Correction in Circulation. 2005, 111, 377–379. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000155488.34492.E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camici, G.G.; Schiavoni, M.; Francia, P.; Bachschmid, M.; Martin-Padura, I.; Hersberger, M.; Tanner, F.C.; Pelicci, P.G.; Volpe, M.; Anversa, P.; et al. Genetic Deletion of P66Shc Adaptor Protein Prevents Hyperglycemia-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5217–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliaccio, E.; Giogio, M.; Mele, S.; Pelicci, G.; Reboldi, P.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Lanfrancone, L.; Pelicci, P.G. The P66(Shc) Adaptor Protein Controls Oxidative Stress Response and Life Span in Mammals. Nature 1999, 402, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, J.J.; Tran, D.; Giorgio, M.; Griffey, S.M.; Koehne, A.; Laing, S.T.; Taylor, S.L.; Kim, K.; Cortopassi, G.A.; Lloyd, K.C.K.; et al. The Influence of Shc Proteins on Life Span in Mice. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia Castro, C.F.; Nardiello, C.; Hadzic, S.; Kojonazarov, B.; Kraut, S.; Gierhardt, M.; Schäffer, J.; Bednorz, M.; Quanz, K.; Heger, J.; et al. The Role of the Redox Enzyme P66Shc in Biological Aging of the Lung. Aging Dis. 2024, 15, 911–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.D.; Staruschenko, A.; Sorokin, A. Role of Adaptor Protein P66Shc in Renal Pathologies. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 314, F143–F153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.; Palygin, O.; Rufanova, V.A.; Chong, A.; Lazar, J.; Jacob, H.J.; Mattson, D.; Roman, R.J.; Williams, J.M.; Cowley, A.W.; et al. P66Shc Regulates Renal Vascular Tone in Hypertension-Induced Nephropathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2533–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashistha, H.; Marrero, L.; Reiss, K.; Cohen, A.J.; Malhotra, A.; Javed, T.; Bradley, A.; Abbruscato, F.; Giusti, S.; Jimenez, A.; et al. Aging Phenotype(s) in Kidneys of Diabetic Mice Are P66ShcA Dependent. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 315, F1833–F1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menini, S.; Amadio, L.; Oddi, G.; Ricci, C.; Pesce, C.; Pugliese, F.; Giorgio, M.; Migliaccio, E.; Pelicci, P.G.; Iacobini, C.; et al. Deletion of P66Shc Longevity Gene Protects against Experimental Diabetic Glomerulopathy by Preventing Diabetes-Induced Oxidative Stress. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1642–1650, Erratum in Diabetes. 2018, 67, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menini, S.; Iacobini, C.; Ricci, C.; Oddi, G.; Pesce, C.; Pugliese, F.; Block, K.; Abboud, H.E.; Giorgio, M.; Migliaccio, E.; et al. Ablation of the Gene Encoding P66Shc Protects Mice against AGE-Induced Glomerulopathy by Preventing Oxidant-Dependent Tissue Injury and Further AGE Accumulation. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, G.; Marrano, N.; Borrelli, A.; Rella, M.; D’Oria, R.; Genchi, V.A.; Caccioppoli, C.; Cignarelli, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; et al. The p66Shc Redox Protein and the Emerging Complications of Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Duan, Y.; Chu, Q.; Lv, H.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, M.; Tang, W.; Hu, H.; et al. G-Protein Coupled Receptor GPR124 Protects against Podocyte Senescence and Injury in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2025, 107, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wu, F.-r.; Wang, J.-n.; Gao, L.; Jiang, L.; Li, H.-D.; Ma, Q.; Liu, X.-q.; Wei, B.; Zhou, L.; et al. Nox4 in Renal Diseases: An Update. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 124, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.M.V.; Zeng, Y.; Maggiore, J.C.; Schweickart, R.A.; Eng, D.G.; Kaverina, N.; McKinzie, S.R.; Chang, A.; Loretz, C.J.; Thieme, K.; et al. Podocyte Injury at Young Age Causes Premature Senescence and Worsens Glomerular Aging. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2024, 326, F120–F134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashistha, H.; Singhal, P.C.; Malhotra, A.; Husain, M.; Mathieson, P.; Saleem, M.A.; Kuriakose, C.; Seshan, S.; Wilk, A.; DelValle, L.; et al. Null Mutations at the P66 and Bradykinin 2 Receptor Loci Induce Divergent Phenotypes in the Diabetic Kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2012, 303, F1629–F1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.; Imig, J.D.; Li, M.; Schupbach, P.; Woo, S.; Benbrook, D.M.; Sorokin, A. Prevention of Hypertension-Induced Renal Vascular Dysfunction through a P66Shc-Targeted Mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2025, 328, F693–F701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, A.; Cirulli, F. The P66Shc Gene Paves the Way for Healthspan: Evolutionary and Mechanistic Perspectives. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finetti, F.; Pellegrini, M.; Ulivieri, C.; Savino, M.T.; Paccagnini, E.; Ginanneschi, C.; Lanfrancone, L.; Pelicci, P.G.; Baldari, C.T. The Proapoptotic and Antimitogenic Protein P66SHC Acts as a Negative Regulator of Lymphocyte Activation and Autoimmunity. Blood 2008, 111, 5017–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomilov, A.A.; Bicocca, V.; Schoenfeld, R.A.; Giorgio, M.; Migliaccio, E.; Ramsey, J.J.; Hagopian, K.; Pelicci, P.G.; Cortopassi, G.A. Decreased Superoxide Production in Macrophages of Long-Lived P66Shc Knock-out Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunghi, B.; De Cunto, G.; Cavarra, E.; Fineschi, S.; Bartalesi, B.; Lungarella, G.; Lucattelli, M. Smoking P66Shc Knocked Out Mice Develop Respiratory Bronchiolitis with Fibrosis but Not Emphysema. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgio, M.; Berry, A.; Berniakovich, I.; Poletaeva, I.; Trinei, M.; Stendardo, M.; Hagopian, K.; Ramsey, J.J.; Cortopassi, G.; Migliaccio, E.; et al. The P66 Shc Knocked out Mice Are Short Lived under Natural Condition. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulivieri, C.; Fanigliulo, D.; Masi, G.; Savino, M.T.; Gamberucci, A.; Pelicci, P.G.; Baldari, C.T. P66Shc Is a Negative Regulator of FcεRI-Dependent Signaling in Mast Cells. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5095–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrussi, L.; Capitani, N.; Ulivieri, C.; Manganaro, N.; Granai, M.; Cattaneo, F.; Kabanova, A.; Mundo, L.; Gobessi, S.; Frezzato, F.; et al. P66Shc Deficiency in the Eμ-TCL1 Mouse Model of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Enhances Leukemogenesis by Altering the Chemokine Receptor Landscape. Haematologica 2019, 104, 2040–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenquist, R. P66Shc Deficiency Sets the Scene for Clinically Aggressive Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Haematologica 2019, 104, 1914–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciciliot, S.; Albiero, M.; Menegazzo, L.; Poncina, N.; Scattolini, V.; Danesi, A.; Pagnin, E.; Marabita, M.; Blaauw, B.; Giorgio, M.; et al. P66Shc Deletion or Deficiency Protects from Obesity but Not Metabolic Dysfunction in Mice and Humans. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y. Podocyte Aging and Diabetic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2025, 107, 596–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobini, C.; Menini, S.; Blasetti Fantauzzi, C.; Pesce, C.M.; Giaccari, A.; Salomone, E.; Lapolla, A.; Orioli, M.; Aldini, G.; Pugliese, G. FL-926-16, a Novel Bioavailable Carnosinase-Resistant Carnosine Derivative, Prevents Onset and Stops Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy in Db/Db Mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobini, C.; Oddi, G.; Menini, S.; Amadio, L.; Ricci, C.; Di Pippo, C.; Sorcini, M.; Pricci, F.; Pugliese, F.; Pugliese, G. Development of Age-Dependent Glomerular Lesions in Galectin-3/AGE-Receptor-3 Knockout Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2005, 289, F611–F621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobini, C.; Vitale, M.; Sentinelli, F.; Haxhi, J.; Pugliese, G.; Menini, S. Renal Expression and Localization of the Receptor for (Pro)Renin and Its Ligands in Rodent Models of Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome, and Age-Dependent Focal and Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casagrande, V.; Iuliani, G.; Menini, S.; Pugliese, G.; Federici, M.; Menghini, R. Restoration of Renal TIMP3 Levels via Genetics and Pharmacological Approach Prevents Experimental Diabetic Nephropathy. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iacobini, C.; Vitale, M.; Sentinelli, F.; Lucarelli, A.; Haxhi, J.; Sergio, I.; Pugliese, G.; Menini, S. Protective Role of p66Shc Deletion in Physiological Renal Aging: Effects on G Protein-Coupled Receptor 124 Expression and Associated Cellular Senescence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211096
Iacobini C, Vitale M, Sentinelli F, Lucarelli A, Haxhi J, Sergio I, Pugliese G, Menini S. Protective Role of p66Shc Deletion in Physiological Renal Aging: Effects on G Protein-Coupled Receptor 124 Expression and Associated Cellular Senescence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):11096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211096
Chicago/Turabian StyleIacobini, Carla, Martina Vitale, Federica Sentinelli, Antonietta Lucarelli, Jonida Haxhi, Ilaria Sergio, Giuseppe Pugliese, and Stefano Menini. 2025. "Protective Role of p66Shc Deletion in Physiological Renal Aging: Effects on G Protein-Coupled Receptor 124 Expression and Associated Cellular Senescence" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 11096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211096
APA StyleIacobini, C., Vitale, M., Sentinelli, F., Lucarelli, A., Haxhi, J., Sergio, I., Pugliese, G., & Menini, S. (2025). Protective Role of p66Shc Deletion in Physiological Renal Aging: Effects on G Protein-Coupled Receptor 124 Expression and Associated Cellular Senescence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 11096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211096






