Left Ventricular Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction—Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Approach and Management During Cardiac Rehabilitation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Search Strategy
3. Pathophysiology of Post-AMI Left Ventricular Remodeling
3.1. Stages of Post-AMI LVR
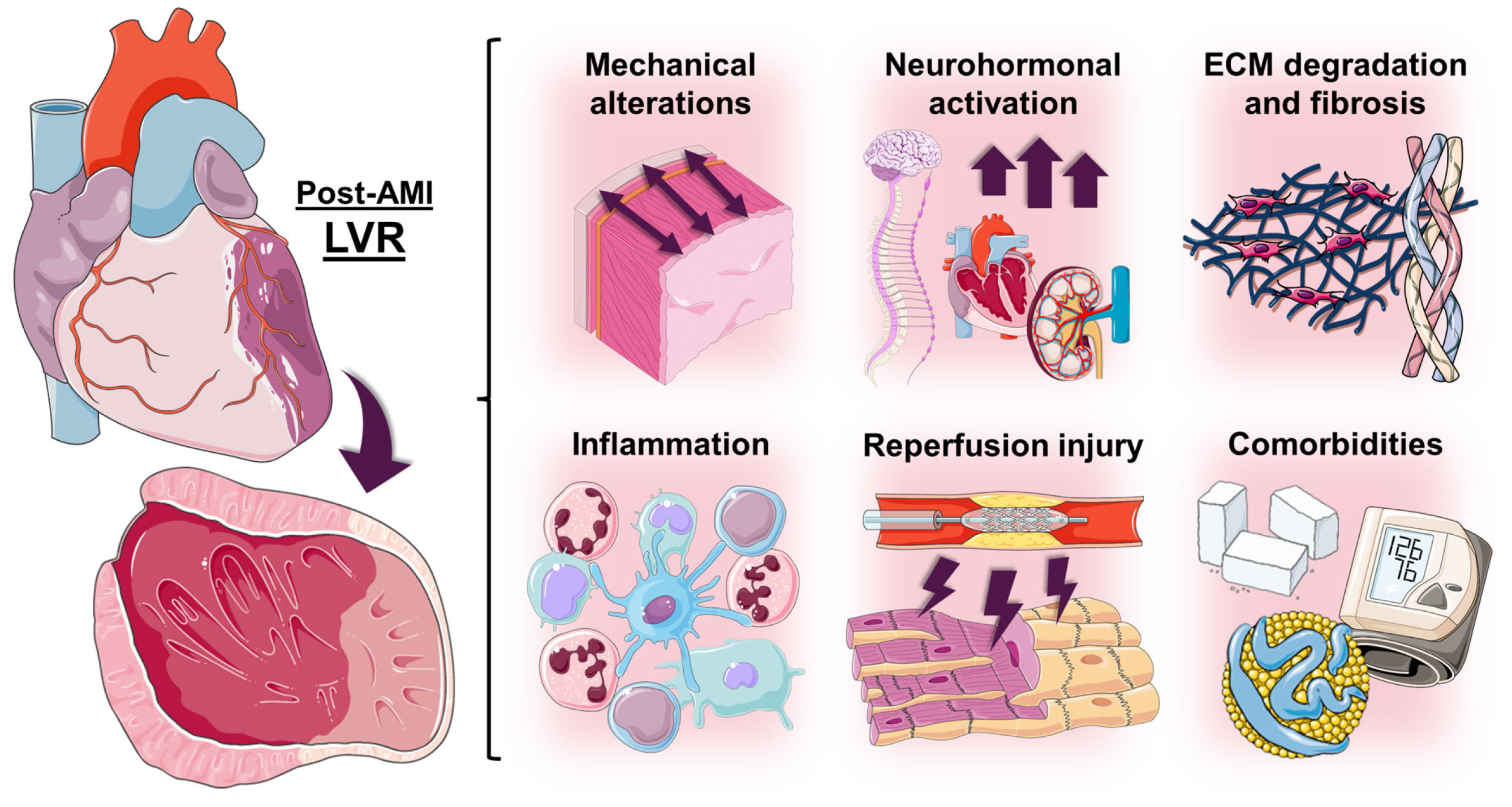
3.2. Factors Involved in the Pathophysiology of Post-AMI LVR
3.2.1. Mechanical Alterations
3.2.2. Neurohormonal Activation
3.2.3. Extracellular Matrix Degradation and Fibrosis
3.2.4. Inflammation
3.2.5. Reperfusion Injury
3.2.6. Comorbidities
4. Definition and Diagnosis of Post-AMI Left Ventricular Remodeling
4.1. Definition of Post-AMI LVR
| Study | Year | n | Imaging Modality | LVR Criteria | Follow-Up Timing | Endpoint | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆LVEDV | ∆LVESV | ∆LVEF | ||||||
| Bolognese et al. [17] | 2002 | 284 | TTE | >20% | - | - | 6 months | Cardiac death and aHF |
| Mannaerts et al. [73] | 2004 | 33 | TTE | >20% | - | - | 6 or 12 months | Prediction of LVR |
| van der Bijl et al. [67] | 2020 | 1995 | TTE | >20% | - | - | 3, 6, or 12 months | aHF |
| Silveira et al. [74] | 2021 | 50 | TTE | ≥15% | (and/or) ≥15% | - | 6 months | Prediction of LVR |
| Logeart et al. [75] | 2024 | 410 | TTE | >20% | - | - | 6 months | All-cause death or aHF |
| Bulluck et al. [76] | 2017 | 40 | CMR | ≥12% | (and) ≥12% | - | 5 months | Prediction of LVEF < 50% |
| Rodriguez-Palomares et al. [77] | 2019 | 374 | CMR | >15% | - | (and) ↓ > 3% | 6 months | CV death, aHF or VA |
| Alonso Tello et al. [78] | 2025 | 1067 | CMR | >15% | - | (and) ↓ > 3% | 6 months | CV death, aHF or VA |
| Reindl et al. [15] | 2019 | 224 | CMR | ≥10% | - | - | 4 months | All-cause death, AMI, stroke, or HF |
| Bulluck et al. [79] | 2020 | 285 | CMR | ≥12% | (and) ≥12% | - | 6 months | All-cause death or aHF |
| Shetelig et al. [80] | 2018 | 240 | CMR | ≥10 mL/m2 | - | - | 4 months | Association with interleukin-8 levels |
| Garg et al. [81] | 2017 | 50 | CMR | - | >15% | - | 3 months | Worsening of systolic function |
| Shetye et al. [82] | 2017 | 65 | CMR | ≥20% | (and/or) ≥15% | - | 4 months | Prediction of LVR |
| Sugano et al. [83] | 2017 | 71 | CMR | >5% | - | - | 6 months | Prediction of LVR |
| Fabregat-Andrés et al. [84] | 2015 | 31 | CMR | >10% | - | - | 6 months | Association with PGC-1α levels |
| Huttin et al. [85] | 2017 | 121 | CMR | >17.3 mL | - | (or) ↓ > 8.3% | 6 months | Association with vascular function |
| Eitel et al. [86] | 2011 | 154 | CMR | - | Any ↑ | Any ↓ | 6 months | Usefulness of intracoronary abciximab application |
4.2. Diagnosis of Post-AMI LVR
4.3. Sex-Related Differences and Specific Populations
5. Cardiac Rehabilitation and Left Ventricular Remodeling
5.1. Cardiac Rehabilitation After AMI
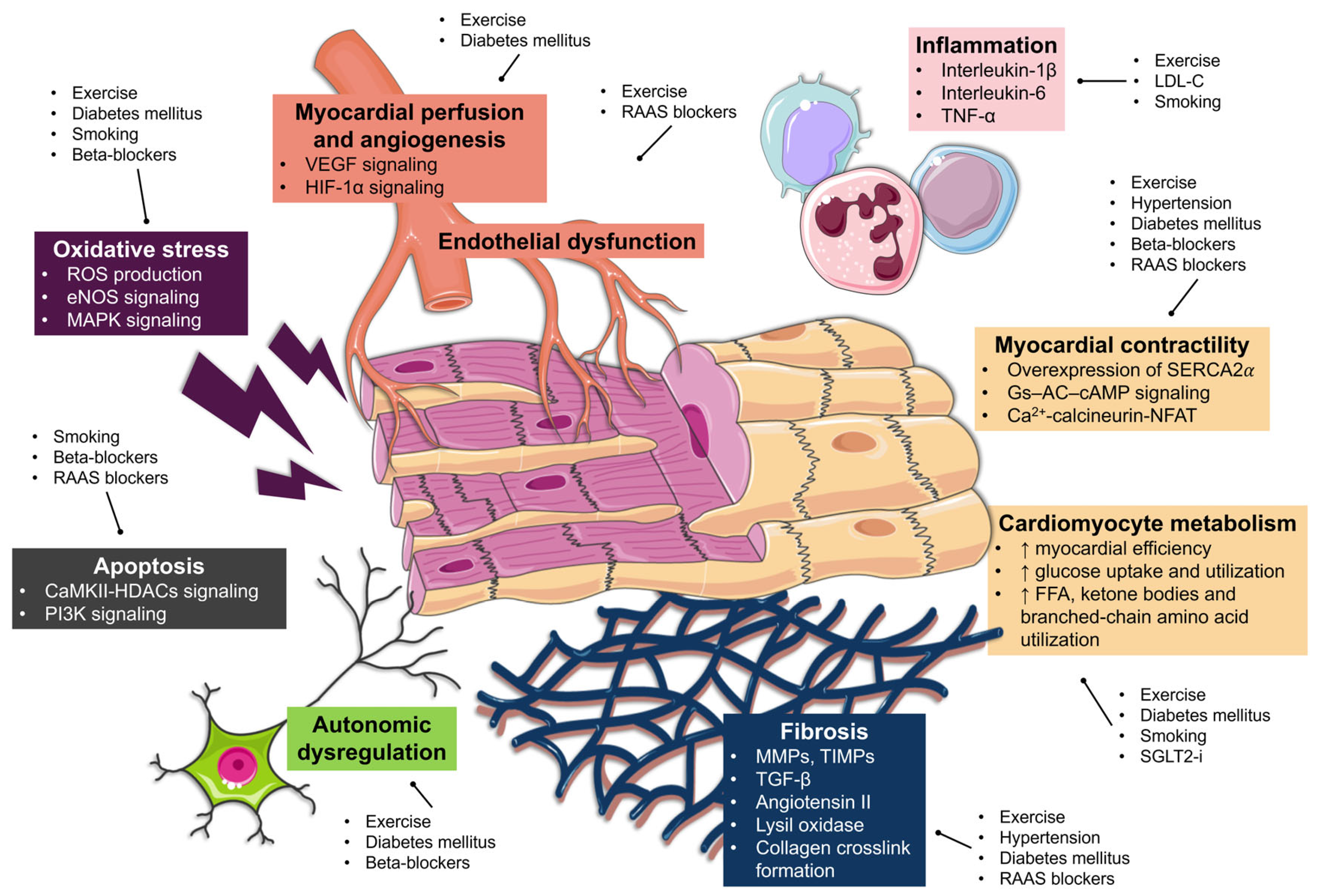
5.2. Exercise Training and LVR
5.3. CV Risk Factors Control and LVR
5.4. Smoking Habits and LVR
5.5. Pharmacological Therapy Optimization and LVR
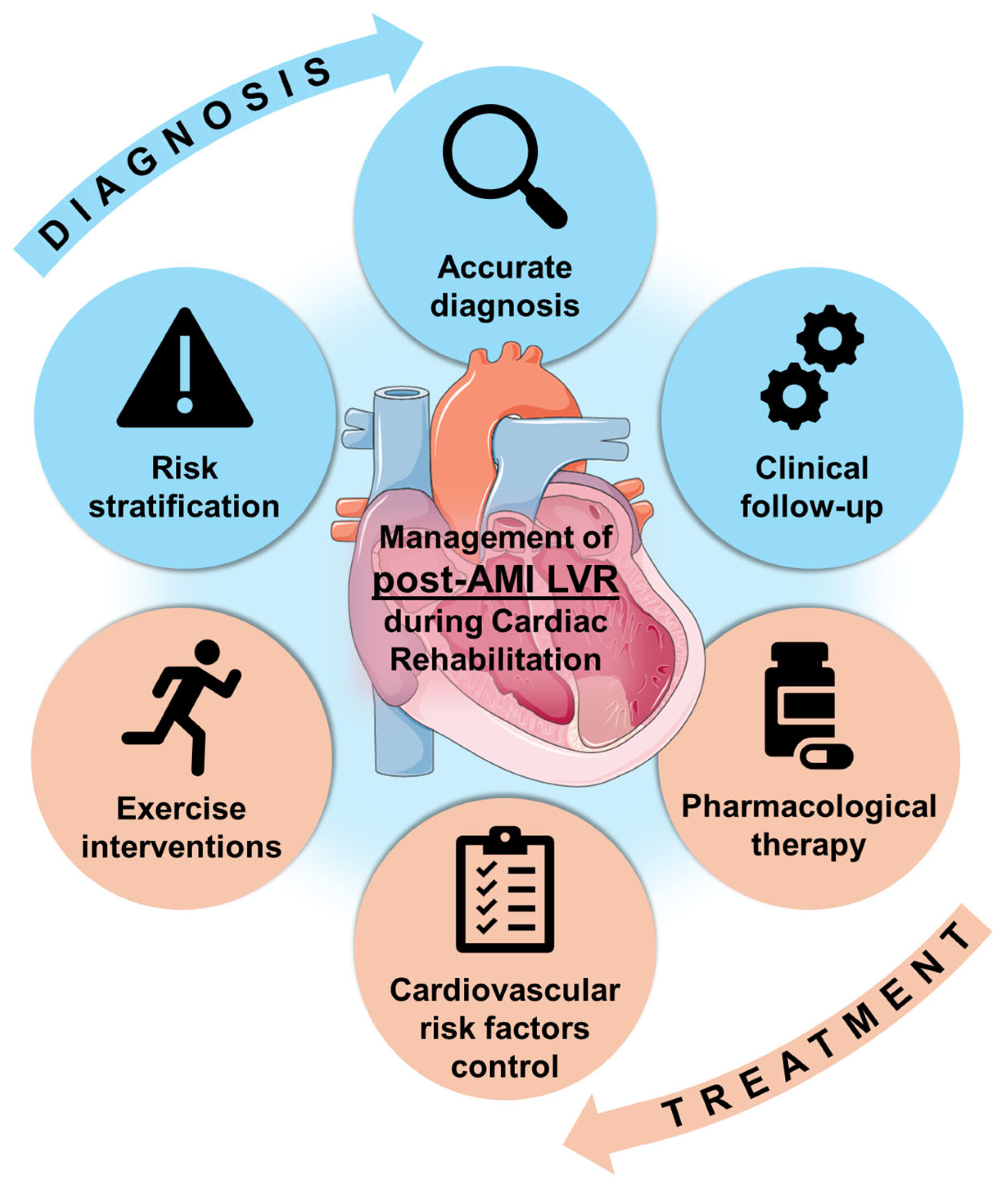
6. Current Clinical Management and Future Directions
6.1. Management of LVR During Cardiac Rehabilitation
| Categories | Risk Factor | Comments | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical factors | Age | Younger patients are more likely to experience adverse LVR, although elderly patients show a higher risk of incident HF across the full spectrum of LVEF ranges. | [11,100] |
| Gender | Women have an increased risk of adverse LVR, although this association appears to be mediated by comorbidities and CV risk factors. | [78] | |
| Hypertension | Uncontrolled hypertension increases the risk of adverse LVR. | [145,146] | |
| Diabetes mellitus | Poor glycemic control is associated with adverse LVR. | [149,150,151] | |
| Chronic kidney disease | AMI patients with chronic kidney disease show increased risk of adverse LVR. | [59,60] | |
| Infarct location | Anterior location is associated with increased area at risk, larger infarct size, and adverse LVR. | [192] | |
| ECG parameters | Parameters such as the number of leads with Q waves and residual ST-segment elevation >1 mm have been associated with reduced LVEF, higher LV volumes, and increased infarct size during follow-up. | [189] | |
| Imaging factors | LVEF | Although recovery from systolic dysfunction is possible, patients with initially lower LVEF have an increased risk of long-term reduced LVEF and higher LV volumes, which increases HF-related MACE. | [12,14] |
| Myocardial strain | CMR-derived longitudinal and circumferential global strain, as well as strain in remote myocardium, predict adverse LVR and MACE after AMI. | [69,193,194,195] | |
| LVEDV and LVESV | More dilated LV volumes after AMI are associated with an increased risk of adverse LVR during follow-up. | [75,196] | |
| Infarct size | Larger infarct size predicts long-term risk of adverse LVR. | [197] | |
| MVO | Early detection of CMR-derived MVO is associated with adverse LVR and MACE. Long-term persistence of MVO is also associated with adverse structural outcomes. | [197,198,199] | |
| Biomarkers | NT-proBNP | Higher NT-proBNP values are correlated with adverse LVR and can stratify the long-term risk of HF-related MACE. | [191,200] |
| High-sensitivity troponin | Higher high-sensitivity troponin levels during admission predict lower LVEF and more extensive infarct size at long-term follow-up. Elevated levels are also associated with incident HF after AMI. | [200,201] | |
| sST2 | Elevated sST2 levels after AMI are associated with more extensive infarctions, decreased LVEF, and higher LV volumes at follow-up. | [202] |
6.2. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGE | Advanced glycation end products |
| AMI | Acute myocardial infarction |
| ARB | Angiotensin receptor blocker |
| ACEI | Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor |
| ARNI | Angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CMR | Cardiac magnetic resonance |
| CR | Cardiac rehabilitation |
| CRP | Cardiac rehabilitation program |
| CV | Cardiovascular |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| FITT | Frequency, intensity, time, type |
| HF | Heart failure |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha |
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| LV | Left ventricle/Left ventricular |
| LVEF | Left ventricular ejection fraction |
| LVEDV | Left ventricular end-diastolic volume |
| LVESV | Left ventricular end-systolic volume |
| LVR | Left ventricular remodeling |
| MACE | Major adverse cardiac events |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| MRA | Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist |
| MVO | Microvascular obstruction |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| RAAS | Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system |
| RPE | Rating of perceived exertion |
| SERCA2α | Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase 2 alpha |
| SGLT2-i | Sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor |
| sST2 | Soluble suppression of tumorigenicity-2 |
| STEMI | ST-elevation myocardial infarction |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-beta |
| TIMP | Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
References
- Martin, S.S.; Aday, A.W.; Allen, N.B.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Bansal, N.; Beaton, A.Z.; et al. 2025 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of US and Global Data from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2025, 151, e41–e660, Correction in: 2025, 151. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Nabel, E.G.; Braunwald, E. A Tale of Coronary Artery Disease and Myocardial Infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 54–63, Correction in: N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaren, J.; De Alencar, J.N.; Aslanger, E.K.; Meyers, H.P.; Smith, S.W. From ST-Segment Elevation MI to Occlusion MI. JACC Adv. 2024, 3, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyland, S.J.; Eaton, R.E.; Max, M.E.; Egbert, S.B.; Wong, S.A.; Blais, D.M. Pharmacotherapy of Acute ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction and the Pharmacist’s Role, Part 1: Patient Presentation through Revascularization. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2025, 82, e578–e595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyland, S.J.; Max, M.E.; Eaton, R.E.; Wong, S.A.; Egbert, S.B.; Blais, D.M. Pharmacotherapy of Acute ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction and the Pharmacist’s Role, Part 2: Complications, Post-Revascularization Care, and Quality Improvement. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2025, 82, 775–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.V.; O’Donoghue, M.L.; Ruel, M.; Rab, T.; Tamis-Holland, J.E.; Alexander, J.H.; Baber, U.; Baker, H.; Cohen, M.G.; Cruz-Ruiz, M.; et al. 2025 ACC/AHA/ACEP/NAEMSP/SCAI Guideline for the Management of Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2025, 151, 13, Correction in: 2025, 151, e865. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001328. Correction in: 2025, 151, e1098. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001346. Correction in: 2025, 152, e402. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, R.A.; Rossello, X.; Coughlan, J.J.; Barbato, E.; Berry, C.; Chieffo, A.; Claeys, M.J.; Dan, G.-A.; Dweck, M.R.; Galbraith, M.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3720–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfern, J.; Gallagher, R.; O’Neil, A.; Grace, S.L.; Bauman, A.; Jennings, G.; Brieger, D.; Briffa, T. Historical Context of Cardiac Rehabilitation: Learning from the Past to Move to the Future. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 842567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahit, M.C.; Kochar, A.; Granger, C.B. Post-Myocardial Infarction Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2018, 6, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Garcés, V.; Merenciano-Gonzalez, H.; Gavara, J.; Gabaldon-Pérez, A.; Lopez-Lereu, M.P.; Monmeneu, J.V.; Nuñez, J.; Perez, N.; Rios-Navarro, C.; De Dios, E.; et al. MRI Investigation of the Differential Impact of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction after Myocardial Infarction in Elderly vs. Non-Elderly Patients to Predict Readmission for Heart Failure. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 58, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavara, J.; Marcos-Garces, V.; Lopez-Lereu, M.P.; Monmeneu, J.V.; Rios-Navarro, C.; de Dios, E.; Perez, N.; Merenciano, H.; Gabaldon, A.; Cànoves, J.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Assessment of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction at Any Time Post-Infarction for Prediction of Subsequent Events in a Large Multicenter STEMI Registry. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 56, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Garcés, V.; Perez, N.; Gavara, J.; Lopez-Lereu, M.P.; Monmeneu, J.V.; Rios-Navarro, C.; de Dios, E.; Merenciano-González, H.; Gabaldon-Pérez, A.; Cànoves, J.; et al. Risk Score for Early Risk Prediction by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance after Acute Myocardial Infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 349, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Garces, V.; Gavara, J.; Lopez-Lereu, M.P.; Monmeneu, J.V.; Rios-Navarro, C.; de Dios, E.; Perez, N.; Cànoves, J.; Gonzalez, J.; Minana, G.; et al. Ejection Fraction by Echocardiography for a Selective Use of Magnetic Resonance After Infarction. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, e011491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reindl, M.; Reinstadler, S.J.; Tiller, C.; Feistritzer, H.-J.; Kofler, M.; Brix, A.; Mayr, A.; Klug, G.; Metzler, B. Prognosis-Based Definition of Left Ventricular Remodeling after ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 2330–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, J.; Rong, J. Pharmacological Modulation of Cardiac Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8815349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognese, L.; Neskovic, A.N.; Parodi, G.; Cerisano, G.; Buonamici, P.; Santoro, G.M.; Antoniucci, D. Left Ventricular Remodeling After Primary Coronary Angioplasty: Patterns of Left Ventricular Dilation and Long-Term Prognostic Implications. Circulation 2002, 106, 2351–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frantz, S.; Hundertmark, M.J.; Schulz-Menger, J.; Bengel, F.M.; Bauersachs, J. Left Ventricular Remodelling Post-Myocardial Infarction: Pathophysiology, Imaging, and Novel Therapies. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2549–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, J.N.; Ferrari, R.; Sharpe, N. Cardiac Remodeling—Concepts and Clinical Implications: A Consensus Paper from an International Forum on Cardiac Remodeling. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 35, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curley, D.; Lavin Plaza, B.; Shah, A.M.; Botnar, R.M. Molecular Imaging of Cardiac Remodelling After Myocardial Infarction. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2018, 113, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Navarro, C.; Gavara, J.; De Dios, E.; Pérez-Solé, N.; Molina-García, T.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Ruiz-Saurí, A.; Bayés-Genís, A.; Carrión-Valero, F.; Chorro, F.J.; et al. Effect of Serum from Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction on Endothelial Cells. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. Engl. Ed. 2024, 77, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.; Molina-García, T.; Gavara, J.; De Dios, E.; Pérez-Solé, N.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Chorro, F.J.; Rios-Navarro, C.; Ruiz-Sauri, A.; Bodi, V. Novel Targets Regulating the Role of Endothelial Cells and Angiogenesis after Infarction: A RNA Sequencing Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Navarro, C.; Gavara, J.; Núñez, J.; Revuelta-López, E.; Monmeneu, J.V.; López-Lereu, M.P.; De Dios, E.; Pérez-Solé, N.; Vila, J.M.; Oltra, R.; et al. EpCAM and Microvascular Obstruction in Patients with STEMI: A Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Study. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. Engl. Ed. 2022, 75, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Dios, E.; Rios-Navarro, C.; Pérez-Solé, N.; Gavara, J.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Forteza, M.J.; Oltra, R.; Vila, J.M.; Chorro, F.J.; Bodi, V. Overexpression of Genes Involved in Lymphocyte Activation and Regulation Are Associated with Reduced CRM-Derived Cardiac Remodelling after STEMI. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 95, 107490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, N.G. The Inflammatory Response in Myocardial Injury, Repair and Remodelling. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2014, 11, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Dios, E.; Forteza, M.J.; Perez-Sole, N.; Molina-Garcia, T.; Gavara, J.; Marcos-Garces, V.; Jimenez-Navarro, M.; Ruiz-Sauri, A.; Rios-Navarro, C.; Bodi, V. Temporal and Spatial Dynamics in the Regulation of Myocardial Metabolism During the Ischemia-Reperfusion Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, Z.K.; Wang, D.-Z. How Cardiomyocytes Sense Pathophysiological Stresses for Cardiac Remodeling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 983–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blázquez-Bujeda, Á.; Ortega, M.; De Dios, E.; Gavara, J.; Perez-Solé, N.; Molina-Garcia, T.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Diaz, A.; Chorro, F.J.; Rios-Navarro, C.; et al. Changes in the Extracellular Matrix at Microvascular Obstruction Area after Reperfused Myocardial Infarction: A Morphometric Study. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 2023, 250, 152138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, M.; Ríos-Navarro, C.; Gavara, J.; De Dios, E.; Perez-Solé, N.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Ferrández-Izquierdo, A.; Bodí, V.; Ruiz-Saurí, A. Meta-Analysis of Extracellular Matrix Dynamics after Myocardial Infarction Using RNA-Sequencing Transcriptomic Database. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios-Navarro, C.; Ortega, M.; Marcos-Garces, V.; Gavara, J.; De Dios, E.; Perez-Sole, N.; Chorro, F.J.; Bodi, V.; Ruiz-Sauri, A. Interstitial Changes after Reperfused Myocardial Infarction in Swine: Morphometric and Genetic Analysis. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.; Fábrega-García, M.M.; Molina-García, T.; Gavara, J.; De Dios, E.; Pérez-Solé, N.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Padilla-Esquivel, J.J.; Diaz, A.; Martinez-Dolz, L.; et al. Novel Fibrillar and Non-Fibrillar Collagens Involved in Fibrotic Scar Formation after Myocardial Infarction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, N.G. The Extracellular Matrix in Myocardial Injury, Repair, and Remodeling. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1600–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross Stewart, K.M.; Walker, S.L.; Baker, A.H.; Riley, P.R.; Brittan, M. Hooked on Heart Regeneration: The Zebrafish Guide to Recovery. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 118, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos-Garcés, V.; Rios-Navarro, C.; Gómez-Torres, F.; Gavara, J.; de Dios, E.; Diaz, A.; Miñana, G.; Chorro, F.J.; Bodi, V.; Ruiz-Sauri, A. Fourier Analysis of Collagen Bundle Orientation in Myocardial Infarction Scars. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2022, 158, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, J.W.; Laksman, Z.; Gepstein, L. Making Better Scar: Emerging Approaches for Modifying Mechanical and Electrical Properties Following Infarction and Ablation. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2016, 120, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Reboll, M.R.; Korf-Klingebiel, M.; Wollert, K.C. Angiogenesis after Acute Myocardial Infarction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 1257–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Navarro, C.; Hueso, L.; Díaz, A.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Bonanad, C.; Ruiz-Sauri, A.; Vila, J.M.; Sanz, M.J.; Chorro, F.J.; Piqueras, L.; et al. Role of Antiangiogenic VEGF-A165b in Angiogenesis and Systolic Function after Reperfused Myocardial Infarction. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. Engl. Ed. 2021, 74, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.G.S.J.; Sharpe, N. Left Ventricular Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction: Pathophysiology and Therapy. Circulation 2000, 101, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leancă, S.A.; Crișu, D.; Petriș, A.O.; Afrăsânie, I.; Genes, A.; Costache, A.D.; Tesloianu, D.N.; Costache, I.I. Left Ventricular Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction: From Physiopathology to Treatment. Life 2022, 12, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Malagù, M.; Biscaglia, S.; Fucili, A.; Rizzo, P. Remodelling after an Infarct: Crosstalk between Life and Death. Cardiology 2016, 135, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalta, K.; Yilmaz, M.B.; Yalta, T.; Palabiyik, O.; Taylan, G.; Zorkun, C. Late Versus Early Myocardial Remodeling After Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Comparative Review on Mechanistic Insights and Clinical Implications. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 25, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, T. Clinical Assessment of Ventricular Wall Stress in Understanding Compensatory Hypertrophic Response and Maladaptive Ventricular Remodeling. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2021, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Su, Y.; Yeo, S.-Y.; Tan, R.-S.; Ghista, D.N.; Kassab, G. Left Ventricular Regional Wall Curvedness and Wall Stress in Patients with Ischemic Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 296, H573–H584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Heusch, G.; Libby, P.; Gersh, B.; Yellon, D.; Böhm, M.; Lopaschuk, G.; Opie, L. Cardiovascular Remodelling in Coronary Artery Disease and Heart Failure. Lancet 2014, 383, 1933–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, W.J.; Holmes, J.W. Why Is Infarct Expansion Such an Elusive Therapeutic Target? J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2015, 8, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, P.; Singh, M.; Singh, K. β-Adrenergic Receptor-Stimulated Cardiac Myocyte Apoptosis: Role of β 1 Integrins. J. Signal Transduct. 2011, 2011, 179057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoni, A.; Emdin, M.; Bramanti, F.; Iudice, G.; Francis, D.P.; Barsotti, A.; Piepoli, M.; Passino, C. Combined Increased Chemosensitivity to Hypoxia and Hypercapnia as a Prognosticator in Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haryono, A.; Ramadhiani, R.; Ryanto, G.R.T.; Emoto, N. Endothelin and the Cardiovascular System: The Long Journey and Where We Are Going. Biology 2022, 11, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, A.; Girerd, N.; Michel, J.; Ketelslegers, J.; Fay, R.; Vincent, J.; Bramlage, P.; Pitt, B.; Zannad, F.; Rossignol, P. Combined Baseline and One-Month Changes in Big Endothelin-1 and Brain Natriuretic Peptide Plasma Concentrations Predict Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction after Acute Myocardial Infarction: Insights from the Eplerenone Post-Acute Myocardial Infarction Heart Failure Efficacy and Survival Study (EPHESUS) Study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 241, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horio, T.; Nishikimi, T.; Yoshihara, F.; Matsuo, H.; Takishita, S.; Kangawa, K. Inhibitory Regulation of Hypertrophy by Endogenous Atrial Natriuretic Peptide in Cultured Cardiac Myocytes. Hypertension 2000, 35, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022, 145, 876–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726, Correction in: 2021, 42, 4901. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangogiannis, N.G.; Kovacic, J.C. Extracellular Matrix in Ischemic Heart Disease, Part 4/4. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2219–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W. Biomechanics of Infarcted Left Ventricle: A Review of Modelling. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2020, 10, 387–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nian, M.; Lee, P.; Khaper, N.; Liu, P. Inflammatory Cytokines and Postmyocardial Infarction Remodeling. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusch, G. Myocardial Ischaemia–Reperfusion Injury and Cardioprotection in Perspective. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 773–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xie, X.; Cao, F.; Wang, Y. Mitochondrial Metabolism in Myocardial Remodeling and Mechanical Unloading: Implications for Ischemic Heart Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 789267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenas, S. ROS and Redox Signaling in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Cardioprotection. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 117, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, K.; Anzai, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Anzai, A.; Kaneko, H.; Kohno, T.; Takahashi, T.; Kawamura, A.; Ogawa, S. Impact of Chronic Kidney Disease on Postinfarction Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Left Ventricular Remodeling. J. Card. Fail. 2008, 14, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-Y.; Huang, S.-C.; Chen, M.; Shih, J.-Y.; Hong, C.-S.; Wu, N.-C.; Ho, C.-H.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, Z.-C.; Chang, W.-T. Effects of Renal Impairment on Cardiac Remodeling and Clinical Outcomes after Myocardial Infarction. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 2842–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legallois, D.; Hodzic, A.; Alexandre, J.; Dolladille, C.; Saloux, E.; Manrique, A.; Roule, V.; Labombarda, F.; Milliez, P.; Beygui, F. Definition of Left Ventricular Remodelling Following ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Studies in the Past Decade. Heart Fail. Rev. 2022, 27, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothues, F.; Smith, G.C.; Moon, J.C.C.; Bellenger, N.G.; Collins, P.; Klein, H.U.; Pennell, D.J. Comparison of Interstudy Reproducibility of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance with Two-Dimensional Echocardiography in Normal Subjects and in Patients with Heart Failure or Left Ventricular Hypertrophy. Am. J. Cardiol. 2002, 90, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz-Menger, J.; Bluemke, D.A.; Bremerich, J.; Flamm, S.D.; Fogel, M.A.; Friedrich, M.G.; Kim, R.J.; Von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff, F.; Kramer, C.M.; Pennell, D.J.; et al. Standardized Image Interpretation and Post Processing in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance: Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR) Board of Trustees Task Force on Standardized Post Processing. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2013, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klug, G.; Metzler, B. Assessing Myocardial Recovery Following ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Short- and Long-Term Perspectives Using Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2013, 11, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.T.L.; Richardson, J.D.; Puri, R.; Nelson, A.J.; Bertaso, A.G.; Teo, K.S.L.; Worthley, M.I.; Worthley, S.G. The Role of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Following Acute Myocardial Infarction. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 1757–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, R.G.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Pasternak, R.C.; Markis, J.E.; Come, P.C.; Nakao, S.; Alderman, J.D.; Ferguson, J.J.; Safian, R.D.; Grossman, W. Left Ventricular Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction: A Corollary to Infarct Expansion. Circulation 1986, 74, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Bijl, P.; Abou, R.; Goedemans, L.; Gersh, B.J.; Holmes, D.R.; Ajmone Marsan, N.; Delgado, V.; Bax, J.J. Left Ventricular Post-Infarct Remodeling: Implications for Systolic Function Improvement and Outcomes in the Modern Era. JACC Heart Fail. 2020, 8, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardif, J.-C.; O’Meara, E.; Komajda, M.; Böhm, M.; Borer, J.S.; Ford, I.; Tavazzi, L.; Swedberg, K. Effects of Selective Heart Rate Reduction with Ivabradine on Left Ventricular Remodelling and Function: Results from the SHIFT Echocardiography Substudy. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 2507–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavara, J.; Rodriguez-Palomares, J.F.; Rios-Navarro, C.; Valente, F.; Monmeneu, J.V.; Lopez-Lereu, M.P.; Ferreira-Gonzalez, I.; Garcia Del Blanco, B.; Otaegui, I.; Canoves, J.; et al. Longitudinal Strain in Remote Non-Infarcted Myocardium by Tissue Tracking CMR: Characterization, Dynamics, Structural and Prognostic Implications. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 37, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bière, L.; Donal, E.; Jacquier, A.; Croisille, P.; Genée, O.; Christiaens, L.; Prunier, F.; Gueret, P.; Boyer, L.; Furber, A. A New Look at Left Ventricular Remodeling Definition by Cardiac Imaging. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 209, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canali, E.; Masci, P.; Bogaert, J.; Bucciarelli Ducci, C.; Francone, M.; McAlindon, E.; Carbone, I.; Lombardi, M.; Desmet, W.; Janssens, S.; et al. Impact of Gender Differences on Myocardial Salvage and Post-Ischaemic Left Ventricular Remodelling after Primary Coronary Angioplasty: New Insights from Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 13, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, A.N.; Fairbairn, T.A.; Artis, N.J.; Greenwood, J.P.; Plein, S. Timing of Cardiovascular MR Imaging after Acute Myocardial Infarction: Effect on Estimates of Infarct Characteristics and Prediction of Late Ventricular Remodeling. Radiology 2011, 261, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannaerts, H. Early Identification of Left Ventricular Remodelling after Myocardial Infarction, Assessed by Transthoracic 3D Echocardiography. Eur. Heart J. 2004, 25, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, C.F.D.S.M.P.D.; Malagutte, K.N.D.S.; Nogueira, B.F.; Reis, F.M.; Rodrigues, C.D.S.A.; Rossi, D.A.A.; Okoshi, K.; Bazan, R.; Martin, L.C.; Minicucci, M.F.; et al. Clinical and Echocardiographic Predictors of Left Ventricular Remodeling Following Anterior Acute Myocardial Infarction. Clinics 2021, 76, e2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logeart, D.; Taille, Y.; Derumeaux, G.; Gellen, B.; Sirol, M.; Galinier, M.; Roubille, F.; Georges, J.-L.; Trochu, J.-N.; Launay, J.-M.; et al. Patterns of Left Ventricular Remodeling Post-Myocardial Infarction, Determinants, and Outcome. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2024, 113, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulluck, H.; Go, Y.Y.; Crimi, G.; Ludman, A.J.; Rosmini, S.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Bhuva, A.N.; Treibel, T.A.; Fontana, M.; Pica, S.; et al. Defining Left Ventricular Remodeling Following Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Using Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2016, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Palomares, J.F.; Gavara, J.; Ferreira-González, I.; Valente, F.; Rios, C.; Rodríguez-García, J.; Bonanad, C.; García Del Blanco, B.; Miñana, G.; Mutuberria, M.; et al. Prognostic Value of Initial Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients with Reperfused STEMI. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 2445–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso Tello, A.; Sambola, A.; Valente, F.; Sao, A.; Ródenas-Alesina, E.; Rello, P.; Maymi, M.; Barrabés, J.A.; Otaegui, I.; García Del Blanco, B.; et al. Sex-Based Differences in Adverse Left Ventricular Remodelling and Clinical Outcomes after ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2025, 26, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulluck, H.; Carberry, J.; Carrick, D.; McEntegart, M.; Petrie, M.C.; Eteiba, H.; Hood, S.; Watkins, S.; Lindsay, M.; Mahrous, A.; et al. Redefining Adverse and Reverse Left Ventricular Remodeling by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Following ST-Segment–Elevation Myocardial Infarction and Their Implications on Long-Term Prognosis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, e009937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetelig, C.; Limalanathan, S.; Hoffmann, P.; Seljeflot, I.; Gran, J.M.; Eritsland, J.; Andersen, G.Ø. Association of IL-8 with Infarct Size and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with STEMI. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Broadbent, D.A.; Swoboda, P.P.; Foley, J.R.J.; Fent, G.J.; Musa, T.A.; Ripley, D.P.; Erhayiem, B.; Dobson, L.E.; McDiarmid, A.K.; et al. Extra-Cellular Expansion in the Normal, Non-Infarcted Myocardium Is Associated with Worsening of Regional Myocardial Function after Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2016, 19, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetye, A.M.; Nazir, S.A.; Razvi, N.A.; Price, N.; Khan, J.N.; Lai, F.Y.; Squire, I.B.; McCann, G.P.; Arnold, J.R. Comparison of Global Myocardial Strain Assessed by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Tagging and Feature Tracking to Infarct Size at Predicting Remodelling Following STEMI. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2017, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, A.; Seo, Y.; Ishizu, T.; Watabe, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Machino-Ohtsuka, T.; Takaiwa, Y.; Kakefuda, Y.; Aihara, H.; Fumikura, Y.; et al. Value of 3-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Echocardiography in the Prediction of Microvascular Obstruction and Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients with ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Circ. J. 2017, 81, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fabregat-Andrés, Ó.; Ridocci-Soriano, F.; Estornell-Erill, J.; Corbí-Pascual, M.; Valle-Muñoz, A.; Berenguer-Jofresa, A.; Barrabés, J.A.; Mata, M.; Monsalve, M. Blood PGC-1α Concentration Predicts Myocardial Salvage and Ventricular Remodeling After ST-Segment Elevation Acute Myocardial Infarction. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. Engl. Ed. 2015, 68, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Huttin, O.; Mandry, D.; Eschalier, R.; Zhang, L.; Micard, E.; Odille, F.; Beaumont, M.; Fay, R.; Felblinger, J.; Camenzind, E.; et al. Cardiac Remodeling Following Reperfused Acute Myocardial Infarction Is Linked to the Concomitant Evolution of Vascular Function as Assessed by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2016, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eitel, I.; Friedenberger, J.; Fuernau, G.; Dumjahn, A.; Desch, S.; Schuler, G.; Thiele, H. Intracoronary versus Intravenous Bolus Abciximab Application in Patients with ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: 6-Month Effects on Infarct Size and Left Ventricular Function: The Randomised Leipzig Immediate PercutaneouS Coronary Intervention Abciximab i.v. versus i.c. in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Trial (LIPSIAbciximab-STEMI). Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2011, 100, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funaro, S.; La Torre, G.; Madonna, M.; Galiuto, L.; Scara, A.; Labbadia, A.; Canali, E.; Mattatelli, A.; Fedele, F.; Alessandrini, F.; et al. Incidence, Determinants, and Prognostic Value of Reverse Left Ventricular Remodelling after Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Results of the Acute Myocardial Infarction Contrast Imaging (AMICI) Multicenter Study. Eur. Heart J. 2009, 30, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubert, M.A.; White, J.A.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Velazquez, E.J.; Rao, S.V.; Crowley, A.L.; Zeymer, U.; Kasprzak, J.D.; Guetta, V.; Krucoff, M.W.; et al. Cardiac Remodeling after Large ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction in the Current Therapeutic Era. Am. Heart J. 2020, 223, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnat, T.; Veselka, J.; Honek, J. Left Ventricular Reverse Remodelling and Its Predictors in Non-ischaemic Cardiomyopathy. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 2070–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, N.; Smith, S.C.; Huo, Y.; Fonarow, G.C.; Ge, J.; Taubert, K.A.; Morgan, L.; et al. Sex Differences in In-Hospital Management and Outcomes of Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome: Findings from the CCC Project. Circulation 2019, 139, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Panichella, G.; Barison, A.; Maffei, S.; Cameli, M.; Coiro, S.; D’Ascenzi, F.; Di Mario, C.; Liga, R.; Marcucci, R.; et al. Sex-Related Differences in Ventricular Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 339, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huded, C.P.; Johnson, M.; Kravitz, K.; Menon, V.; Abdallah, M.; Gullett, T.C.; Hantz, S.; Ellis, S.G.; Podolsky, S.R.; Meldon, S.W.; et al. 4-Step Protocol for Disparities in STEMI Care and Outcomes in Women. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2122–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmidou, I.; Redfors, B.; Selker, H.P.; Thiele, H.; Patel, M.R.; Udelson, J.E.; Magnus Ohman, E.; Eitel, I.; Granger, C.B.; Maehara, A.; et al. Infarct Size, Left Ventricular Function, and Prognosis in Women Compared to Men after Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Results from an Individual Patient-Level Pooled Analysis of 10 Randomized Trials. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piro, M.; Della Bona, R.; Abbate, A.; Biasucci, L.M.; Crea, F. Sex-Related Differences in Myocardial Remodeling. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, L.; McAndrew, T.C.; Chung, E.S.; Stancak, B.; Svendsen, J.H.; Monteiro, J.; Fischer, T.M.; Kueffer, F.; Ryan, T.; Bax, J.; et al. Predictors of Left Ventricular Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction in Patients with a Patent Infarct Related Coronary Artery After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (from the Post-Myocardial Infarction Remodeling Prevention Therapy [PRomPT] Trial). Am. J. Cardiol. 2018, 121, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Bijl, P.; Abou, R.; Goedemans, L.; Gersh, B.J.; Holmes, D.R.; Ajmone Marsan, N.; Delgado, V.; Bax, J.J. Left Ventricular Remodelling after ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Sex Differences and Prognosis. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilio, F.; Musella, F.; Ceriello, L.; Ciliberti, G.; Pavan, D.; Manes, M.T.; Selimi, A.; Scicchitano, P.; Iannopollo, G.; Albani, S.; et al. Sex Differences in Patients Presenting with Acute Coronary Syndrome: A State-of-the-Art Review. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabaldón-Pérez, A.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Gavara, J.; López-Lereu, M.P.; Monmeneu, J.V.; Pérez, N.; Ríos-Navarro, C.; de Dios, E.; Merenciano-González, H.; Cànoves, J.; et al. Prognostic Value of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Early after ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction in Older Patients. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennezat, P.V.; Lamblin, N.; Mouquet, F.; Tricot, O.; Quandalle, P.; Aumegeat, V.; Equine, O.; Nugue, O.; Segrestin, B.; De Groote, P.; et al. The Effect of Ageing on Cardiac Remodelling and Hospitalization for Heart Failure after an Inaugural Anterior Myocardial Infarction. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 1992–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Wang, X.; Guo, Q.; Yan, Y.; Gong, W.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, G.; Wang, H.; Xu, L.; Nie, S. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Shows Increased Adverse Ventricular Remodeling in Younger Patients after ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 4637–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzwedel, A.; Jensen, K.; Rauch, B.; Doherty, P.; Metzendorf, M.-I.; Hackbusch, M.; Völler, H.; Schmid, J.-P.; Davos, C.H. Effectiveness of Comprehensive Cardiac Rehabilitation in Coronary Artery Disease Patients Treated According to Contemporary Evidence Based Medicine: Update of the Cardiac Rehabilitation Outcome Study (CROS-II). Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 1756–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibben, G.; Faulkner, J.; Oldridge, N.; Rees, K.; Thompson, D.R.; Zwisler, A.-D.; Taylor, R.S. Exercise-Based Cardiac Rehabilitation for Coronary Heart Disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021, CD001800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibben, G.O.; Faulkner, J.; Oldridge, N.; Rees, K.; Thompson, D.R.; Zwisler, A.-D.; Taylor, R.S. Exercise-Based Cardiac Rehabilitation for Coronary Heart Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 452–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosetti, M.; Abreu, A.; Corrà, U.; Davos, C.H.; Hansen, D.; Frederix, I.; Iliou, M.C.; Pedretti, R.F.E.; Schmid, J.-P.; Vigorito, C.; et al. Secondary Prevention through Comprehensive Cardiovascular Rehabilitation: From Knowledge to Implementation. 2020 Update. A Position Paper from the Secondary Prevention and Rehabilitation Section of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 460–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrenberg, M.; Falter, M.; Dendale, P. Cost-Effectiveness of Cardiac Telerehabilitation in Coronary Artery Disease and Heart Failure Patients: Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2020, 1, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrenberg, M.; Wilhelm, M.; Hansen, D.; Völler, H.; Cornelissen, V.; Frederix, I.; Kemps, H.; Dendale, P. The Future Is Now: A Call for Action for Cardiac Telerehabilitation in the COVID-19 Pandemic from the Secondary Prevention and Rehabilitation Section of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golbus, J.R.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Barac, A.; Cornwell, W.K.; Dunn, P.; Forman, D.E.; Martin, S.S.; Schorr, E.N.; Supervia, M. Digital Technologies in Cardiac Rehabilitation: A Science Advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 148, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkonde-Price, C.; Reynolds, K.; Najem, M.; Yang, S.-J.; Batiste, C.; Cotter, T.; Lahti, D.; Gin, N.; Funahashi, T. Comparison of Home-Based vs Center-Based Cardiac Rehabilitation in Hospitalization, Medication Adherence, and Risk Factor Control Among Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2228720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolín-Boronat, C.; Merenciano-González, H.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Martínez Mas, M.L.; Climent Alberola, J.I.; Civera, J.M.; Valls Reig, M.; Ruiz Hueso, M.; Castro Carmona, P.; Perez, N.; et al. Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Reduction and Therapeutic Adherence During Cardiac Rehabilitation After Myocardial Infarction. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolín-Boronat, C.; Merenciano-González, H.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Martínez-Mas, M.L.; Climent Alberola, J.I.; Pérez, N.; López-Bueno, L.; Esteban-Argente, M.C.; Valls Reig, M.; Arizón Benito, A.; et al. Dynamics of HDL-Cholesterol Following a Post-Myocardial Infarction Cardiac Rehabilitation Program. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 26, 25399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Garcés, V.; Merenciano-González, H.; Martínez Mas, M.L.; Palau, P.; Climent Alberola, J.I.; Perez, N.; López-Bueno, L.; Esteban Argente, M.C.; Valls Reig, M.; Muñoz Alcover, R.; et al. Short-Course High-Intensity Statin Treatment during Admission for Myocardial Infarction and LDL-Cholesterol Reduction—Impact on Tailored Lipid-Lowering Therapy at Discharge. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.M.; Pack, Q.R.; Aberegg, E.; Brewer, L.C.; Ford, Y.R.; Forman, D.E.; Gathright, E.C.; Khadanga, S.; Ozemek, C.; Thomas, R.J. Core Components of Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs: 2024 Update: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association and the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation. Circulation 2024, 150, e328–e347, Correction in: 2025, 151, e965–e966. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolín-Boronat, C.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Merenciano-González, H.; Martínez Mas, M.L.; Climent Alberola, J.I.; Perez, N.; López-Bueno, L.; Esteban Argente, M.C.; Valls Reig, M.; Arizón Benito, A.; et al. Depression, Anxiety, and Quality of Life in a Cardiac Rehabilitation Program Without Dedicated Mental Health Resources Post-Myocardial Infarction. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, M.; Evenson, K.R.; Aylward, A.; Cyr, J.M.; Kucharska-Newton, A. Psychosocial Services Provided by Licensed Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs. Front. Rehabil. Sci. 2023, 4, 1093086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, P.; Gorodeski, E.Z.; Marcum, Z.A.; Forman, D.E. Cardiac Rehabilitation to Optimize Medication Regimens in Heart Failure. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2019, 35, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, B.; Fonarow, G.C.; Goldberg, L.R.; Guglin, M.; Josephson, R.A.; Forman, D.E.; Lin, G.; Lindenfeld, J.; O’Connor, C.; Panjrath, G.; et al. Cardiac Rehabilitation for Patients with Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1454–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, B. Contemporary Pharmacological Treatment and Management of Heart Failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2024, 21, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunwald, E. Evolution of the Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction: A 20th Century Saga. Lancet 1998, 352, 1771–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannuzzi, P.; Tavazzi, L.; Temporelli, P.L.; Corrá, U.; Imparato, A.; Gattone, M.; Giordano, A.; Sala, L.; Schweiger, C.; Malinverni, C. Long-Term Physical Training and Left Ventricular Remodelling after Anterior Myocardial Infraction: Results of the Excercise in Anterior Myocardial Infraction (EAMI) Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1993, 22, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubach, P.; Myers, J.; Dziekan, G.; Goebbels, U.; Reinhart, W.; Vogt, P.; Ratti, R.; Muller, P.; Miettunen, R.; Buser, P. Effect of Exercise Training on Myocardial Remodeling in Patients with Reduced Left Ventricular Function After Myocardial Infarction: Application of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Circulation 1997, 95, 2060–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykowsky, M.; Scott, J.; Esch, B.; Schopflocher, D.; Myers, J.; Paterson, I.; Warburton, D.; Jones, L.; Clark, A.M. A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Exercise Training on Left Ventricular Remodeling Following Myocardial Infarction: Start Early and Go Longer for Greatest Exercise Benefits on Remodeling. Trials 2011, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrints, C.; Andreotti, F.; Koskinas, K.C.; Rossello, X.; Adamo, M.; Ainslie, J.; Banning, A.P.; Budaj, A.; Buechel, R.R.; Chiariello, G.A.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Coronary Syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3415–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virani, S.S.; Newby, L.K.; Arnold, S.V.; Bittner, V.; Brewer, L.C.; Demeter, S.H.; Dixon, D.L.; Fearon, W.F.; Hess, B.; Johnson, H.M.; et al. 2023 AHA/ACC/ACCP/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline for the Management of Patients with Chronic Coronary Disease: A Report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2023, 148, e9–e119, Correction in: 2023, 148, e148. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001183. Correction in: 2023, 148, e186. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Lu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yang, D.; Wu, H.-F.; Bian, Z.-P.; Xu, J.-D.; Gu, C.-R.; Wang, L.-S.; Chen, X.-J. The Effects of Different Initiation Time of Exercise Training on Left Ventricular Remodeling and Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction after Myocardial Infarction. Disabil. Rehabil. 2016, 38, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, G.; Stöhr, E.J.; Oxborough, D.; Kimani, P.; Shave, R. Effect of Exercise Training on Left Ventricular Mechanics after Acute Myocardial Infarction–an Exploratory Study. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 61, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Mi, Y.; Ding, M.; Gao, X. Effects of Exercise Training on Left Ventricular Systolic and Diastolic Function after Myocardial Infarction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 12, 1526326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, G.; Gaze, D.; Oxborough, D.; O’Driscoll, J.; Shave, R. Reverse Left Ventricular Remodeling: Effect of Cardiac Rehabilitation Exercise Training in Myocardial Infarction Patients with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 52, 370–378. [Google Scholar]
- Matter, M.A.; Paneni, F.; Libby, P.; Frantz, S.; Stähli, B.E.; Templin, C.; Mengozzi, A.; Wang, Y.-J.; Kündig, T.M.; Räber, L.; et al. Inflammation in Acute Myocardial Infarction: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frodermann, V.; Rohde, D.; Courties, G.; Severe, N.; Schloss, M.J.; Amatullah, H.; McAlpine, C.S.; Cremer, S.; Hoyer, F.F.; Ji, F.; et al. Exercise Reduces Inflammatory Cell Production and Cardiovascular Inflammation via Instruction of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Bo, W.; Liang, Q.; Zhu, W.; Cai, M.; Tian, Z. Exercise Training Alleviates Cardiac Fibrosis through Increasing Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and Regulating TGF-Β1-Smad2/3-MMP2/9 Signaling in Mice with Myocardial Infarction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wan, W.; Powers, A.S.; Li, J.; Ji, L.L.; Lao, S.; Wilson, B.; Erikson, J.M.; Zhang, J.Q. Effects of Exercise Training on Cardiac Function and Myocardial Remodeling in Post Myocardial Infarction Rats. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2008, 44, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giallauria, F.; Acampa, W.; Ricci, F.; Vitelli, A.; Torella, G.; Lucci, R.; Del Prete, G.; Zampella, E.; Assante, R.; Rengo, G.; et al. Exercise Training Early after Acute Myocardial Infarction Reduces Stress-Induced Hypoperfusion and Improves Left Ventricular Function. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giallauria, F.; Acampa, W.; Ricci, F.; Vitelli, A.; Maresca, L.; Mancini, M.; Grieco, A.; Gallicchio, R.; Xhoxhi, E.; Spinelli, L.; et al. Effects of Exercise Training Started within 2 Weeks after Acute Myocardial Infarction on Myocardial Perfusion and Left Ventricular Function: A Gated SPECT Imaging Study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2012, 19, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leosco, D.; Rengo, G.; Iaccarino, G.; Golino, L.; Marchese, M.; Fortunato, F.; Zincarelli, C.; Sanzari, E.; Ciccarelli, M.; Galasso, G.; et al. Exercise Promotes Angiogenesis and Improves β-Adrenergic Receptor Signalling in the Post-Ischaemic Failing Rat Heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 78, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Liang, Q.; Cai, M.; Tian, Z. HIF-1α-induced Up-regulation of microRNA-126 Contributes to the Effectiveness of Exercise Training on Myocardial Angiogenesis in Myocardial Infarction Rats. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 12970–12979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Deel, E.D.; Octavia, Y.; De Waard, M.C.; De Boer, M.; Duncker, D.J. Exercise Training Has Contrasting Effects in Myocardial Infarction and Pressure Overload Due to Divergent Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Meng, X.; Li, G.; Gokulnath, P.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J. Exercise Training after Myocardial Infarction Attenuates Dysfunctional Ventricular Remodeling and Promotes Cardiac Recovery. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, B.; Lira, F.S.; Consolim-Colombo, F.M.; Rocha, J.A.; Caperuto, E.C.; De Angelis, K.; Irigoyen, M.-C. Role of Exercise Training on Autonomic Changes and Inflammatory Profile Induced by Myocardial Infarction. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 702473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, N.; Sanghvi, M.M.; Piechnik, S.K.; Neubauer, S.; Munroe, P.B.; Petersen, S.E. The Effect of Blood Lipids on the Left Ventricle. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, K.; Packwood, W.; Varlamov, O.; Muller, M.; Xie, A.; Wu, M.D.; Abraham-Fan, R.-J.; López, J.A.; Lindner, J.R. Elevated LDL Cholesterol Increases Microvascular Endothelial VWF and Thromboinflammation After Myocardial Infarction. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2023, 43, 1041–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Chang, G.; Liu, J.; Sun, G.; Liu, L.; Qin, S.; Zhang, D. Simvastatin Ameliorates Ventricular Remodeling via the TGF-Β1 Signaling Pathway in Rats Following Myocardial Infarction. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 5093–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Luo, R.; Sun, X.; Shen, F.; Hong, B.; Wang, Z. Effects of High-Dose Rosuvastatin on Ventricular Remodelling and Cardiac Function in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buono, F.; Spinelli, L.; Giallauria, F.; Assante Di Panzillo, E.; Di Marino, S.; Ferrara, F.; Vigorito, C.; Trimarco, B.; Morisco, C. Usefulness of Satisfactory Control of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol to Predict Left Ventricular Remodeling After a First ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Successfully Reperfused. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 107, 1772–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomek, J.; Bub, G. Hypertension-induced Remodelling: On the Interactions of Cardiac Risk Factors. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 4027–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenchaiah, S.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Sutton, M.S.J.; Plappert, T.; Rouleau, J.-L.; Lamas, G.A.; Sasson, Z.; Parker, J.O.; Geltman, E.M.; Solomon, S.D. Effect of Antecedent Systemic Hypertension on Subsequent Left Ventricular Dilation after Acute Myocardial Infarction (from the Survival and Ventricular Enlargement Trial). Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 94, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, A.M.; Nicholls, M.G.; Troughton, R.W.; Lainchbury, J.G.; Elliott, J.; Frampton, C.; Espiner, E.A.; Crozier, I.G.; Yandle, T.G.; Turner, J. Antecedent Hypertension and Heart Failure after Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizza, V.; Tondi, L.; Patti, A.M.; Cecchi, D.; Lombardi, M.; Perone, F.; Ambrosetti, M.; Rizzo, M.; Cianflone, D.; Maranta, F. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Pathophysiology, Imaging Assessment and Therapeutical Strategies. Int. J. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Risk Prev. 2024, 23, 200338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, C.; Braunwald, E.; Zelniker, T.A. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Revisited. The Interplay between Diabetes and Heart Failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2025, 438, 133554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, Q.; Guo, R.; Yan, Y.; Gong, W.; Zheng, W.; Wang, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Nie, S. Glycemic Status and Myocardial Strain by Cardiac MRI in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 59, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanajima, Y.; Iwahashi, N.; Kirigaya, J.; Horii, M.; Minamimoto, Y.; Gohbara, M.; Abe, T.; Okada, K.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Kosuge, M.; et al. Prognostic Importance of Glycemic Variability on Left Ventricular Reverse Remodeling after the First Episode of ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.D.; Shen, Y.; Lu, L.; Ding, F.H.; Yang, Z.K.; Zhang, R.Y.; Shen, W.F.; Jin, W.; Wang, X.Q. Insulin Resistance and Dysglycemia Are Associated with Left Ventricular Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction in Non-Diabetic Patients. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Pu, H.; He, W.; Zhou, X.; Tong, N.; Peng, L. Cardiac Remodeling and Subclinical Left Ventricular Dysfunction in Adults with Uncomplicated Obesity: A Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Study. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 2035–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, M.A.; Karthikeyan, K.; Abdullah, O.; Ghadban, R. Obesity and Cardiac Remodeling in Adults: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 61, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Jeinsen, B.; Vasan, R.S.; McManus, D.D.; Mitchell, G.F.; Cheng, S.; Xanthakis, V. Joint Influences of Obesity, Diabetes, and Hypertension on Indices of Ventricular Remodeling: Findings from the Community-Based Framingham Heart Study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorimachi, H.; Obokata, M.; Omote, K.; Reddy, Y.N.V.; Takahashi, N.; Koepp, K.E.; Ng, A.C.T.; Rider, O.J.; Borlaug, B.A. Long-Term Changes in Cardiac Structure and Function Following Bariatric Surgery. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouton, A.J.; Flynn, E.R.; Moak, S.P.; Li, X.; Da Silva, A.A.; Wang, Z.; Do Carmo, J.M.; Hall, M.E.; Hall, J.E. Interaction of Obesity and Hypertension on Cardiac Metabolic Remodeling and Survival Following Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e018212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavara, J.; Merenciano-Gonzalez, H.; Llopis-Lorente, J.; Molina-Garcia, T.; Perez-Solé, N.; De Dios, E.; Marcos-Garces, V.; Monmeneu, J.V.; Lopez-Lereu, M.P.; Canoves, J.; et al. Impact of Epicardial Adipose Tissue on Infarct Size and Left Ventricular Systolic Function in Patients with Anterior ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, N.W.S.; Kong, G.; Venisha, S.; Chin, Y.H.; Ng, C.H.; Muthiah, M.; Khoo, C.M.; Chai, P.; Kong, W.; Poh, K.-K.; et al. Long-Term Prognosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction Associated with Metabolic Health and Obesity Status. Endocr. Pract. 2022, 28, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moholdt, T.; Lavie, C.J.; Nauman, J. Sustained Physical Activity, Not Weight Loss, Associated with Improved Survival in Coronary Heart Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres Valgas Da Silva, C.; Shettigar, V.K.; Baer, L.A.; Abay, E.; Pinckard, K.M.; Vinales, J.; Sturgill, S.L.; Vidal, P.; Ziolo, M.T.; Stanford, K.I. Exercise Training after Myocardial Infarction Increases Survival but Does Not Prevent Adverse Left Ventricle Remodeling and Dysfunction in High-Fat Diet Fed Mice. Life Sci. 2022, 311, 121181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.; Abidi, E.; Ghali, R.; Booz, G.W.; Kobeissy, F.; Zouein, F.A. Functional, Cellular, and Molecular Remodeling of the Heart under Influence of Oxidative Cigarette Tobacco Smoke. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 3759186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, D.; Yimer, W.K.; Mentz, R.J.; Shah, A.M.; White, W.B.; Blaha, M.J.; Oshunbade, A.; Hamid, A.; Suzuki, T.; Clark, D.R.; et al. Cigarette Smoking, Smoking Cessation, and Heart Failure Subtypes: Insights from the Jackson Heart Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e032921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savko, C.; Esquer, C.; Molinaro, C.; Rokaw, S.; Shain, A.G.; Jaafar, F.; Wright, M.K.; Phillips, J.A.; Hopkins, T.; Mikhail, S.; et al. Myocardial Infarction Injury Is Exacerbated by Nicotine in Vape Aerosol Exposure. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2025, 14, e038012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, N.D.; Oakes, J.M.; Whitehead, A.K.; Lazartigues, E.; Yue, X.; Gardner, J.D. Nicotine and Novel Tobacco Products Drive Adverse Cardiac Remodeling and Dysfunction in Preclinical Studies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 993617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symons, R.; Masci, P.G.; Francone, M.; Claus, P.; Barison, A.; Carbone, I.; Agati, L.; Galea, N.; Janssens, S.; Bogaert, J. Impact of Active Smoking on Myocardial Infarction Severity in Reperfused ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients: The Smoker’s Paradox Revisited. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2756–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.D.; Lindson, N.; Hartmann-Boyce, J.; Wahedi, A.; Hajizadeh, A.; Theodoulou, A.; Thomas, E.T.; Lee, C.; Aveyard, P. Smoking Cessation for Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, CD014936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aid, J.; Tanjeko, A.T.; Serré, J.; Eggelbusch, M.; Noort, W.; De Wit, G.M.J.; Van Weeghel, M.; Puurand, M.; Tepp, K.; Gayan-Ramirez, G.; et al. Smoking Cessation Only Partially Reverses Cardiac Metabolic and Structural Remodeling in Mice. Acta Physiol. 2024, 240, e14145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, R.S.; Rigotti, N.A.; Benowitz, N.L.; Cummings, K.M.; Jazayeri, M.-A.; Morris, P.B.; Ratchford, E.V.; Sarna, L.; Stecker, E.C.; Wiggins, B.S. 2018 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on Tobacco Cessation Treatment. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 3332–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, A.; Shetty Ujjar, S.; Seddiki, M.O.; Jheinga, M.; Fan, L. Smoking Cessation Strategies After Acute Coronary Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, Z.; Cheng, Y. A Pathway and Network Review on Beta-Adrenoceptor Signaling and Beta Blockers in Cardiac Remodeling. Heart Fail. Rev. 2014, 19, 799–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo Miranda, P.; Gasevic, D.; Trin, C.; Stub, D.; Zoungas, S.; Kaye, D.M.; Orman, Z.; Eliakundu, A.L.; Talic, S. Beta-Blocker Therapy After Myocardial Infarction. JACC Adv. 2025, 4, 101582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, B.; Remme, W.; Zannad, F.; Neaton, J.; Martinez, F.; Roniker, B.; Bittman, R.; Hurley, S.; Kleiman, J.; Gatlin, M. Eplerenone, a Selective Aldosterone Blocker, in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction after Myocardial Infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1309–1321, Correction in: N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, K.; Kasama, S.; Toyama, T.; Kasahara, M.; Kurabayashi, M. Effects of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist Eplerenone on Cardiac Sympathetic Nerve Activity and Left Ventricular Remodeling after Reperfusion Therapy in Patients with First ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 2325–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Packer, M.; Desai, A.S.; Gong, J.; Lefkowitz, M.P.; Rizkala, A.R.; Rouleau, J.L.; Shi, V.C.; Solomon, S.D.; Swedberg, K.; et al. Angiotensin–Neprilysin Inhibition versus Enalapril in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Lu, C.; Chen, Q.; Xu, T.; Li, D. Effects of the Angiotensin-Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor on Cardiac Reverse Remodeling: Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrado, J.; Cain, C.; Mauro, A.G.; Romeo, F.; Ockaili, R.; Chau, V.Q.; Nestler, J.A.; Devarakonda, T.; Ghosh, S.; Das, A.; et al. Sacubitril/Valsartan Averts Adverse Post-Infarction Ventricular Remodeling and Preserves Systolic Function in Rabbits. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2342–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfau, D.; Thorn, S.L.; Zhang, J.; Mikush, N.; Renaud, J.M.; Klein, R.; deKemp, R.A.; Wu, X.; Hu, X.; Sinusas, A.J.; et al. Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor Attenuates Myocardial Remodeling and Improves Infarct Perfusion in Experimental Heart Failure. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Claggett, B.; Lewis, E.F.; Granger, C.B.; Køber, L.; Maggioni, A.P.; Mann, D.L.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Rouleau, J.-L.; Solomon, S.D.; et al. Angiotensin Receptor–Neprilysin Inhibition in Acute Myocardial Infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1845–1855, Correction in: N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.M.; Claggett, B.; Prasad, N.; Li, G.; Volquez, M.; Jering, K.; Cikes, M.; Kovacs, A.; Mullens, W.; Nicolau, J.C.; et al. Impact of Sacubitril/Valsartan Compared with Ramipril on Cardiac Structure and Function After Acute Myocardial Infarction: The PARADISE-MI Echocardiographic Substudy. Circulation 2022, 146, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellis, A.; Mauro, C.; Barbato, E.; Trimarco, B.; Morisco, C. The PARADISE-MI Trial: A New Opportunity to Improve the Left Ventricular Remodelling in Reperfused STEMI. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 3698–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Kumar, B.; Ashique, S.; Yasmin, S.; Venkatesan, K.; Islam, A.; Ghosh, S.; Sahu, A.; Bhui, U.; Ansari, M.Y. A Critical Review on SGLT2 Inhibitors for Diabetes Mellitus, Renal Health, and Cardiovascular Conditions. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2025, 221, 112050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.M.Y.; Brooksbank, K.J.M.; Wetherall, K.; Mangion, K.; Roditi, G.; Campbell, R.T.; Berry, C.; Chong, V.; Coyle, L.; Docherty, K.F.; et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Left Ventricular Volumes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, or Prediabetes, and Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (SUGAR-DM-HF). Circulation 2021, 143, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acquaro, M.; Scelsi, L.; Mascolo, C.; Pelosi, C.; Greco, A.; Turco, A.; Schirinzi, S.; Lattanzio, M.; Resasco, T.; Mercurio, V.; et al. Dapagliflozin Effects on Left Ventricular Remodeling and Filling Pressures in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2025, 38, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Gallego, C.G.; Requena-Ibanez, J.A.; San Antonio, R.; Ishikawa, K.; Watanabe, S.; Picatoste, B.; Flores, E.; Garcia-Ropero, A.; Sanz, J.; Hajjar, R.J.; et al. Empagliflozin Ameliorates Adverse Left Ventricular Remodeling in Nondiabetic Heart Failure by Enhancing Myocardial Energetics. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1931–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Lewinski, D.; Kolesnik, E.; Tripolt, N.J.; Pferschy, P.N.; Benedikt, M.; Wallner, M.; Alber, H.; Berger, R.; Lichtenauer, M.; Saely, C.H.; et al. Empagliflozin in Acute Myocardial Infarction: The EMMY Trial. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 4421–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.; Jones, W.S.; Udell, J.A.; Anker, S.D.; Petrie, M.C.; Harrington, J.; Mattheus, M.; Zwiener, I.; Amir, O.; Bahit, M.C.; et al. Empagliflozin after Acute Myocardial Infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1455–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.; Erlinge, D.; Storey, R.F.; McGuire, D.K.; De Belder, M.; Eriksson, N.; Andersen, K.; Austin, D.; Arefalk, G.; Carrick, D.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Myocardial Infarction without Diabetes or Heart Failure. NEJM Evid. 2024, 3, EVIDoa2300286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolin-Boronat, C.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Merenciano-González, H.; Perez, N.; Pérez Del Villar, C.; Gavara, J.; Lopez-Lereu, M.P.; Monmeneu, J.V.; Herrera Flores, C.; Domenech-Ximenos, B.; et al. Prediction of Left Ventricular Thrombus after Myocardial Infarction: A Cardiac Magnetic Resonance-Based Prospective Registry. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2025, 131, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merenciano-González, H.; Marcos-Garcés, V.; Gavara, J.; Pedro-Tudela, A.; Lopez-Lereu, M.P.; Monmeneu, J.V.; Perez, N.; Rios-Navarro, C.; de Dios, E.; Gabaldón-Pérez, A.; et al. Residual ST-Segment Elevation to Predict Long-Term Clinical and CMR-Derived Outcomes in STEMI. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Garcés, V.; Perez, N.; Gavara, J.; Lopez-Lereu, M.P.; Monmeneu, J.V.; Rios-Navarro, C.; de Dios, E.; Merenciano-González, H.; Gabaldon-Pérez, A.; Ferrero-De-Loma-Osorio, Á.; et al. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Outperforms Echocardiography to Predict Subsequent Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Therapies in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 991307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Solé, N.; De Dios, E.; Gavara, J.; Ríos-Navarro, C.; Marcos-Garces, V.; Merenciano, H.; Climent, J.I.; López-Bueno, L.; Payá, A.; De La Espriella, R.; et al. NT-proBNP to Guide Risk Stratification after Cardiac Rehabilitation in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2025, 137, S0953620525001670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, W.; You, Z.; Yang, N.; Lin, L.; Li, Y. Risk Factors for Left Ventricular Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction: A Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2024, 103, e40496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavara, J.; Rodriguez-Palomares, J.F.; Valente, F.; Monmeneu, J.V.; Lopez-Lereu, M.P.; Bonanad, C.; Ferreira-Gonzalez, I.; Garcia del Blanco, B.; Rodriguez-Garcia, J.; Mutuberria, M.; et al. Prognostic Value of Strain by Tissue Tracking Cardiac Magnetic Resonance After ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, A.A.; Romero, J.; Levsky, J.M.; Haramati, L.B.; Phuong, N.; Rezai-Gharai, L.; Cohen, S.; Restrepo, L.; Ruiz-Guerrero, L.; Fisher, J.D.; et al. Circumferential Strain Acquired by CMR Early after Acute Myocardial Infarction Adds Incremental Predictive Value to Late Gadolinium Enhancement Imaging to Predict Late Myocardial Remodeling and Subsequent Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2017, 50, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reindl, M.; Tiller, C.; Holzknecht, M.; Lechner, I.; Eisner, D.; Riepl, L.; Pamminger, M.; Henninger, B.; Mayr, A.; Schwaiger, J.P.; et al. Global Longitudinal Strain by Feature Tracking for Optimized Prediction of Adverse Remodeling after ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 110, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, L.; Zhu, T.; Qu, X.; Buayiximu, K.; Feng, S.; Zhu, Z.; Ni, J.; Du, R.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Predictive Value of Early Left Ventricular End-Diastolic Volume Changes for Late Left Ventricular Remodeling after ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Cardiol. J. 2024, 31, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodi, V.; Monmeneu, J.V.; Ortiz-Perez, J.T.; Lopez-Lereu, M.P.; Bonanad, C.; Husser, O.; Minana, G.; Gomez, C.; Nunez, J.; Forteza, M.J.; et al. Prediction of Reverse Remodeling at Cardiac MR Imaging Soon after First ST-Segment–Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Results of a Large Prospective Registry. Radiology 2016, 278, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troger, F.; Pamminger, M.; Poskaite, P.; Reindl, M.; Holzknecht, M.; Lechner, I.; Tiller, C.; Von Der Emde, S.; Kaser, A.; Oberhollenzer, F.; et al. Clinical Impact of Persistent Microvascular Obstruction in CMR After Reperfused STEMI. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2025, 18, e017645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodi, V.; Sanchis, J.; Nunez, J.; Mainar, L.; Lopez-Lereu, M.P.; Monmeneu, J.V.; Rumiz, E.; Chaustre, F.; Trapero, I.; Husser, O.; et al. Prognostic Value of a Comprehensive Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Assessment Soon after a First ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2009, 2, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezin, A.E.; Berezin, A.A. Adverse Cardiac Remodelling after Acute Myocardial Infarction: Old and New Biomarkers. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 1215802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinstadler, S.J.; Feistritzer, H.-J.; Klug, G.; Mair, J.; Tu, A.M.-D.; Kofler, M.; Henninger, B.; Franz, W.-M.; Metzler, B. High-Sensitivity Troponin T for Prediction of Left Ventricular Function and Infarct Size One Year Following ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 202, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, R.A.P.; Miller, A.M.; Murphy, G.E.J.; Clements, S.; Steedman, T.; Connell, J.M.C.; McInnes, I.B.; Dargie, H.J.; McMurray, J.J.V. Serum Soluble ST2. A Potential Novel Mediator in Left Ventricular and Infarct Remodeling After Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Huang, X.; Ma, J.; Huang, J.; Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, H.; Huang, W. Value of Three-Dimensional Strain Parameters for Predicting Left Ventricular Remodeling after ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 33, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varasteh, Z.; Weber, W.A.; Rischpler, C. Nuclear Molecular Imaging of Cardiac Remodeling after Myocardial Infarction. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gissler, M.C.; Antiochos, P.; Ge, Y.; Heydari, B.; Gräni, C.; Kwong, R.Y. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Evaluation of LV Remodeling Post-Myocardial Infarction. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2024, 17, 1366–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzknecht, M.; Reindl, M.; Tiller, C.; Lechner, I.; Perez Cabrera, R.; Mayr, A.; Brenner, C.; Klug, G.; Bauer, A.; Metzler, B.; et al. Clinical Risk Score to Predict Early Left Ventricular Thrombus After ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 14, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, F.A.H.; França, C.N.; Fonseca, H.A.R.; Serra, A.J.; Izar, M.C. Key Inflammatory Players for Infarcted Mass and Cardiac Remodeling after Acute Myocardial Infarction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 12, 1609705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matta, A.; Ohlmann, P.; Nader, V.; Moussallem, N.; Carrié, D.; Roncalli, J. A Review of Therapeutic Approaches for Post-Infarction Left Ventricular Remodeling. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauersachs, J.; Solomon, S.D.; Anker, S.D.; Antorrena-Miranda, I.; Batkai, S.; Viereck, J.; Rump, S.; Filippatos, G.; Granzer, U.; Ponikowski, P.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of CDR132L in Patients with Reduced Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction after Myocardial Infarction: Rationale and Design of the HF-REVERT Trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2024, 26, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itzhar, A.; Yosef, G.; Eilon-Ashkenazy, M.; Shmidov, Y.; Gil, H.; Lacham-Hartman, S.; Elyagon, S.; Etzion, S.; Bitton, R.; Cohen, S.; et al. Potent Inhibition of MMP-9 by a Novel Sustained-Release Platform Attenuates Left Ventricular Remodeling Following Myocardial Infarction. J. Control. Release 2023, 364, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Phase 1 CRP-Admission for AMI | |
| Diagnosis | Early risk stratification. Evaluate CV risk factors. Assessment of structural repercussions of AMI (LVEF, LVEDV, LVESV) *. |
| Treatment | Therapeutic planning for CV risk factors control. Initiation of low-intensity physical activity. Initiation of targeted therapy if LV dysfunction is present or there is risk of adverse LVR. |
| Phase 2 CRP-First months after discharge | |
| Diagnosis | Individualized clinical follow-up according to patient risk. Reassessment of structural repercussions of AMI (LVEF, LVEDV, LVESV) in the chronic phase *. |
| Treatment | Aim for achievement of CV risk factors goals. Exercise testing and exercise interventions (in-hospital and/or ambulatory) at moderate- to high-intensity levels. Optimization and up-titration of targeted therapies for LV dysfunction or LVR. |
| Phase 3 CRP-Long-term follow-up | |
| Diagnosis | Reassess achievement of CV risk factors goals. Follow-up (clinical, biomarkers, imaging *) for LVR monitoring. |
| Treatment | Maintenance of regular exercise training. Ensure therapeutic adherence (including lifestyle habits and pharmacological therapy). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marcos-Garcés, V.; Bertolín-Boronat, C.; Merenciano-González, H.; Martínez Mas, M.L.; Climent Alberola, J.I.; López-Bueno, L.; Payá Rubio, A.; Pérez-Solé, N.; Ríos-Navarro, C.; de Dios, E.; et al. Left Ventricular Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction—Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Approach and Management During Cardiac Rehabilitation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210964
Marcos-Garcés V, Bertolín-Boronat C, Merenciano-González H, Martínez Mas ML, Climent Alberola JI, López-Bueno L, Payá Rubio A, Pérez-Solé N, Ríos-Navarro C, de Dios E, et al. Left Ventricular Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction—Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Approach and Management During Cardiac Rehabilitation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):10964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210964
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarcos-Garcés, Víctor, Carlos Bertolín-Boronat, Héctor Merenciano-González, María Luz Martínez Mas, Josefa Inés Climent Alberola, Laura López-Bueno, Alfonso Payá Rubio, Nerea Pérez-Solé, César Ríos-Navarro, Elena de Dios, and et al. 2025. "Left Ventricular Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction—Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Approach and Management During Cardiac Rehabilitation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 10964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210964
APA StyleMarcos-Garcés, V., Bertolín-Boronat, C., Merenciano-González, H., Martínez Mas, M. L., Climent Alberola, J. I., López-Bueno, L., Payá Rubio, A., Pérez-Solé, N., Ríos-Navarro, C., de Dios, E., Gavara, J., Moratal, D., Rodriguez-Palomares, J. F., Ortiz-Pérez, J. T., Sanchis, J., & Bodi, V. (2025). Left Ventricular Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction—Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Approach and Management During Cardiac Rehabilitation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 10964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210964








