Synergistic Effect Evaluation and Mechanism Investigation of Vitamin B6 and B12 in Models of Neuroinflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Investigation of the Affinity Between the PLP-1 and the Vitamins
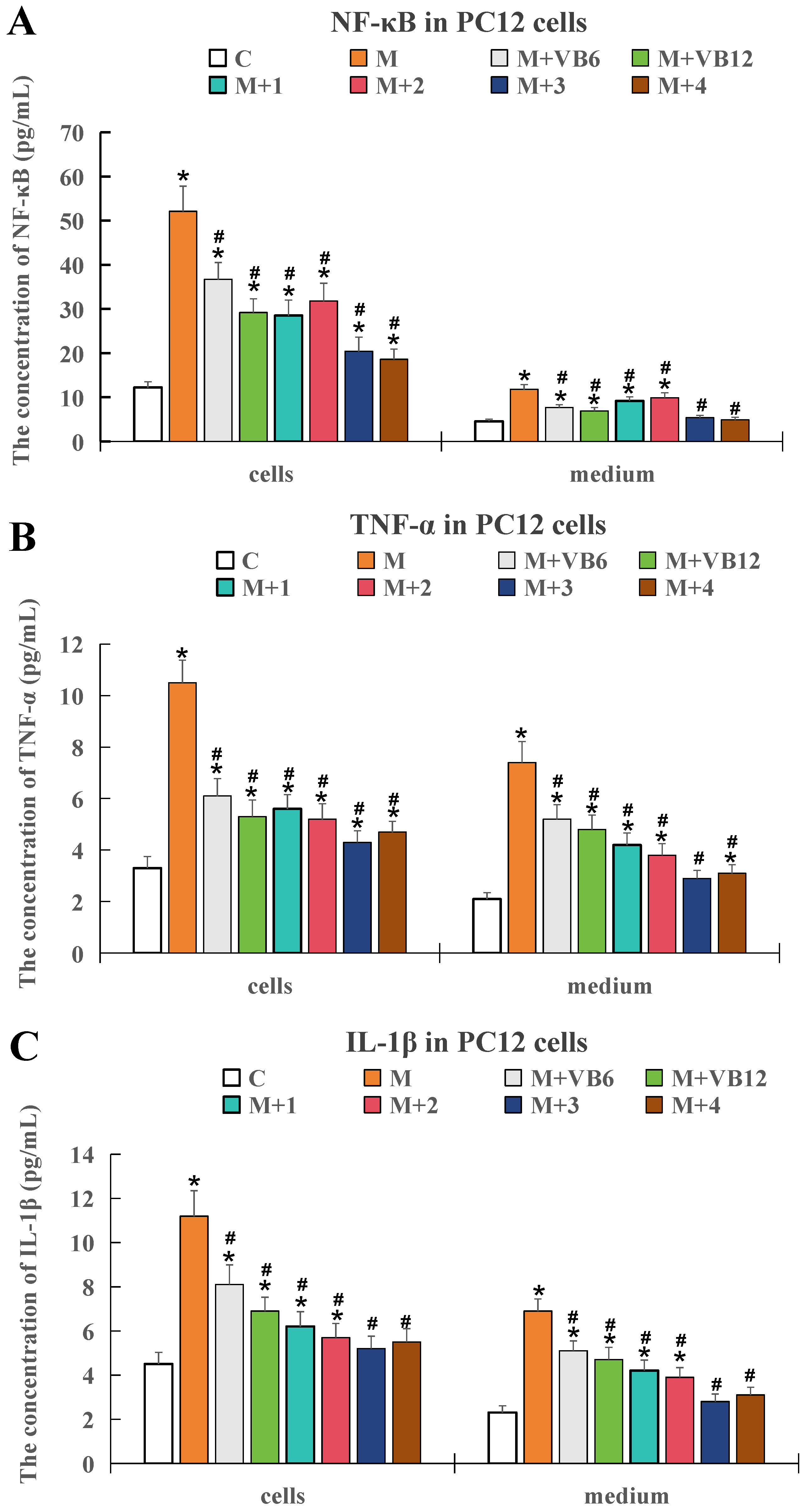
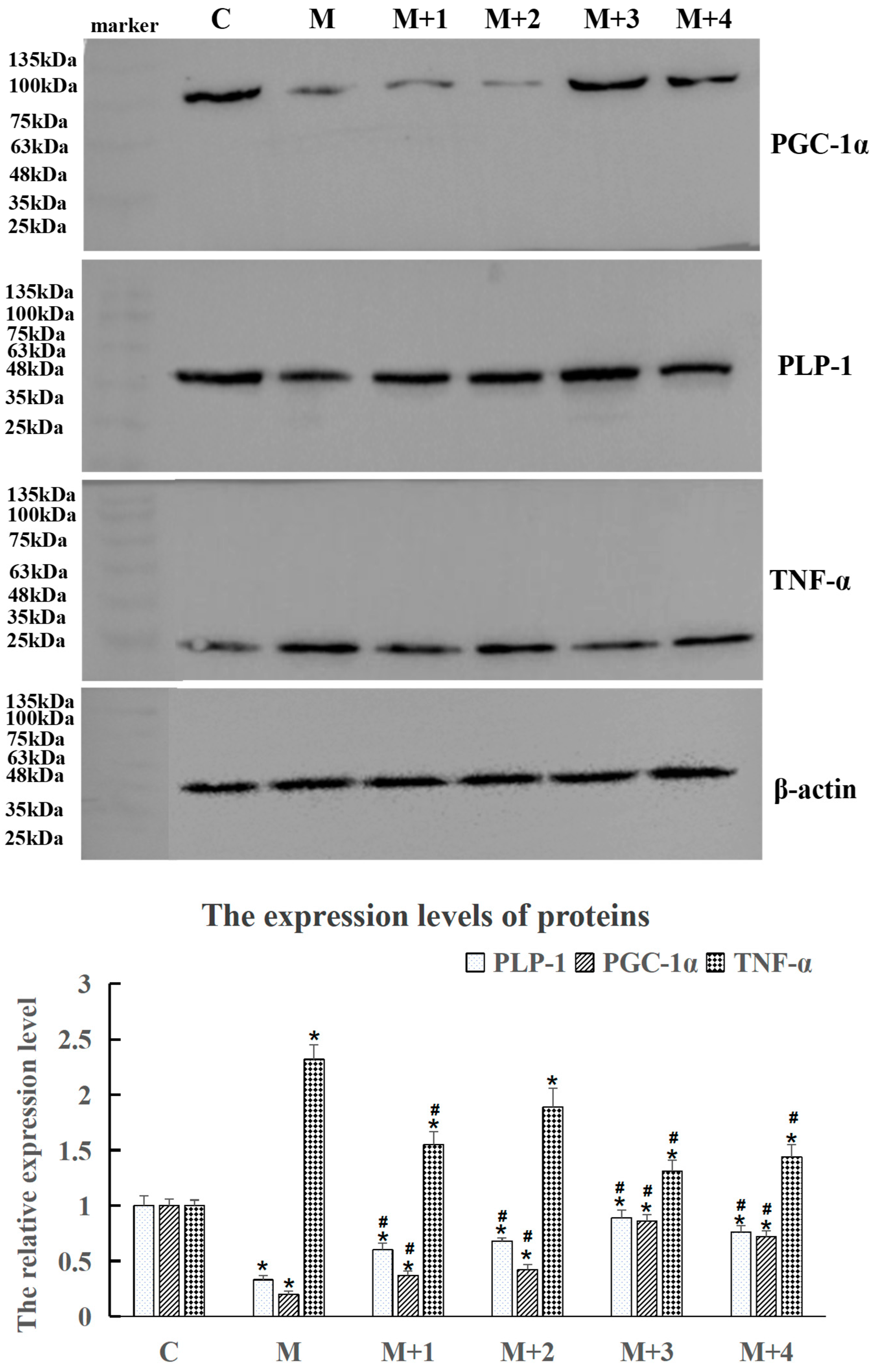
2.2. Determination of the Optimal VB6, VB12, and PLP-1 Combination Using Cell Experiments
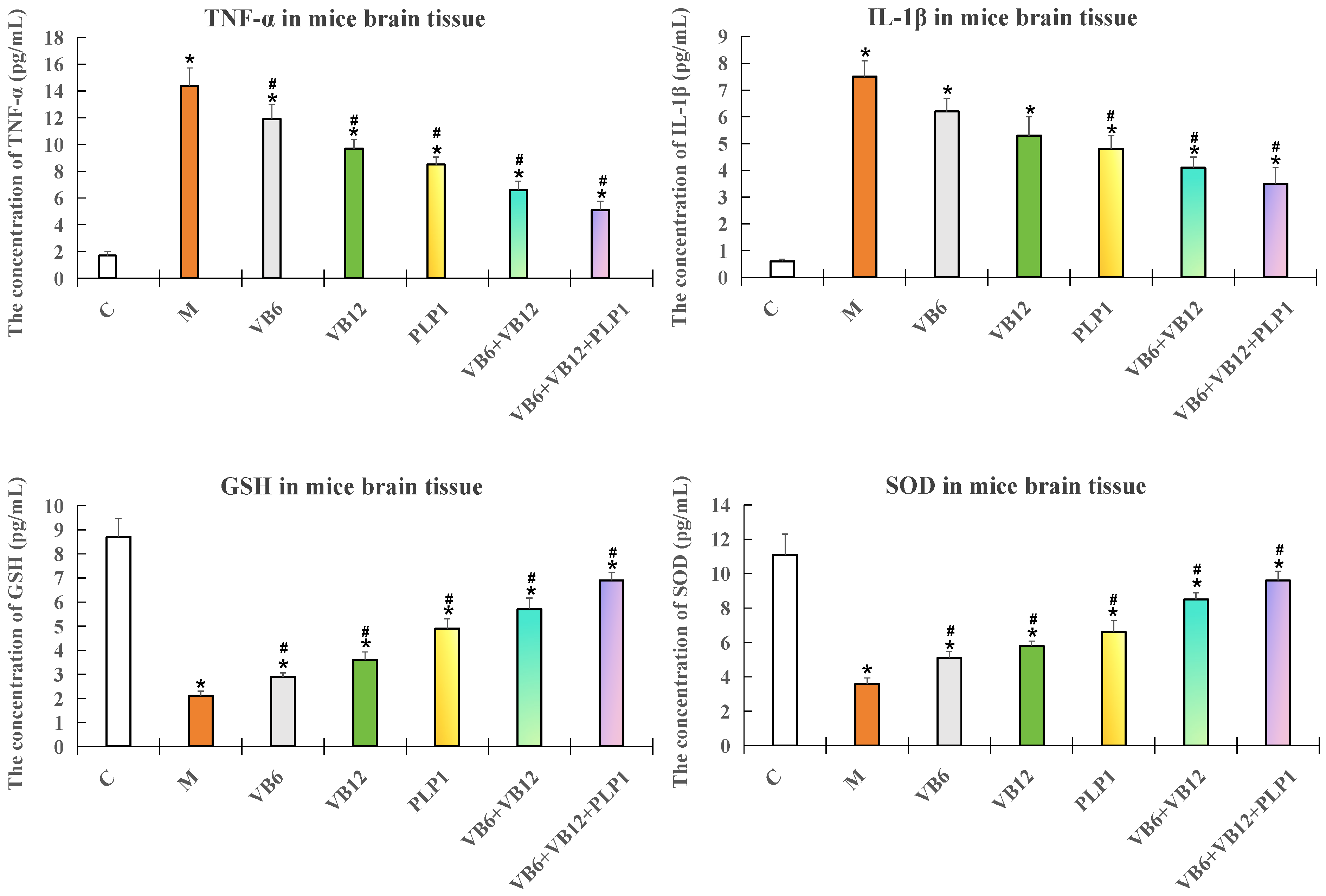
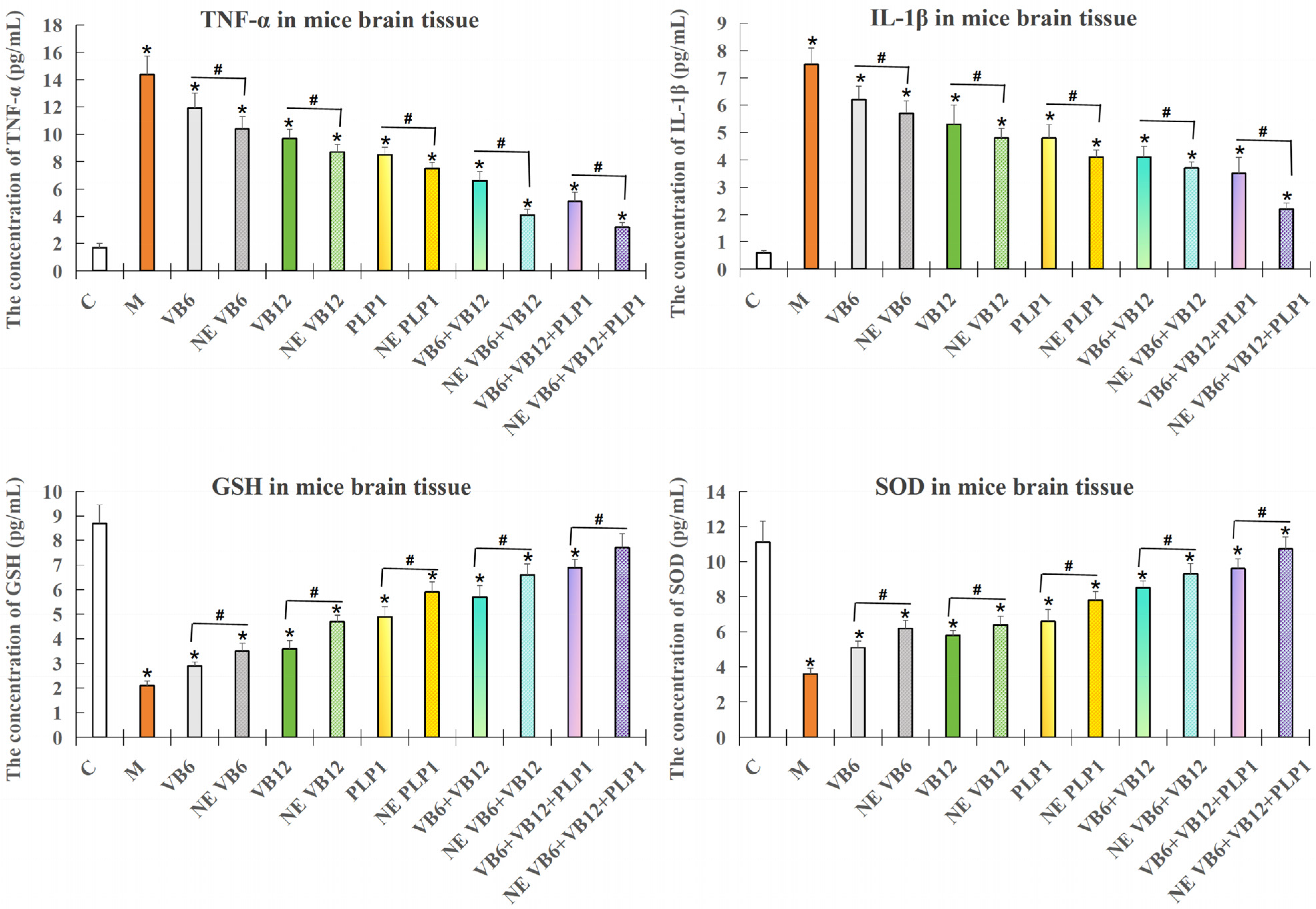
2.3. Validation of the Efficacy of the Intranasal Administration of Both the Free and Nano-Encapsulated Formulations
2.3.1. ELISA Detection of the Inflammatory Factors and Oxidative Damage Factors in Mouse Brain Tissue
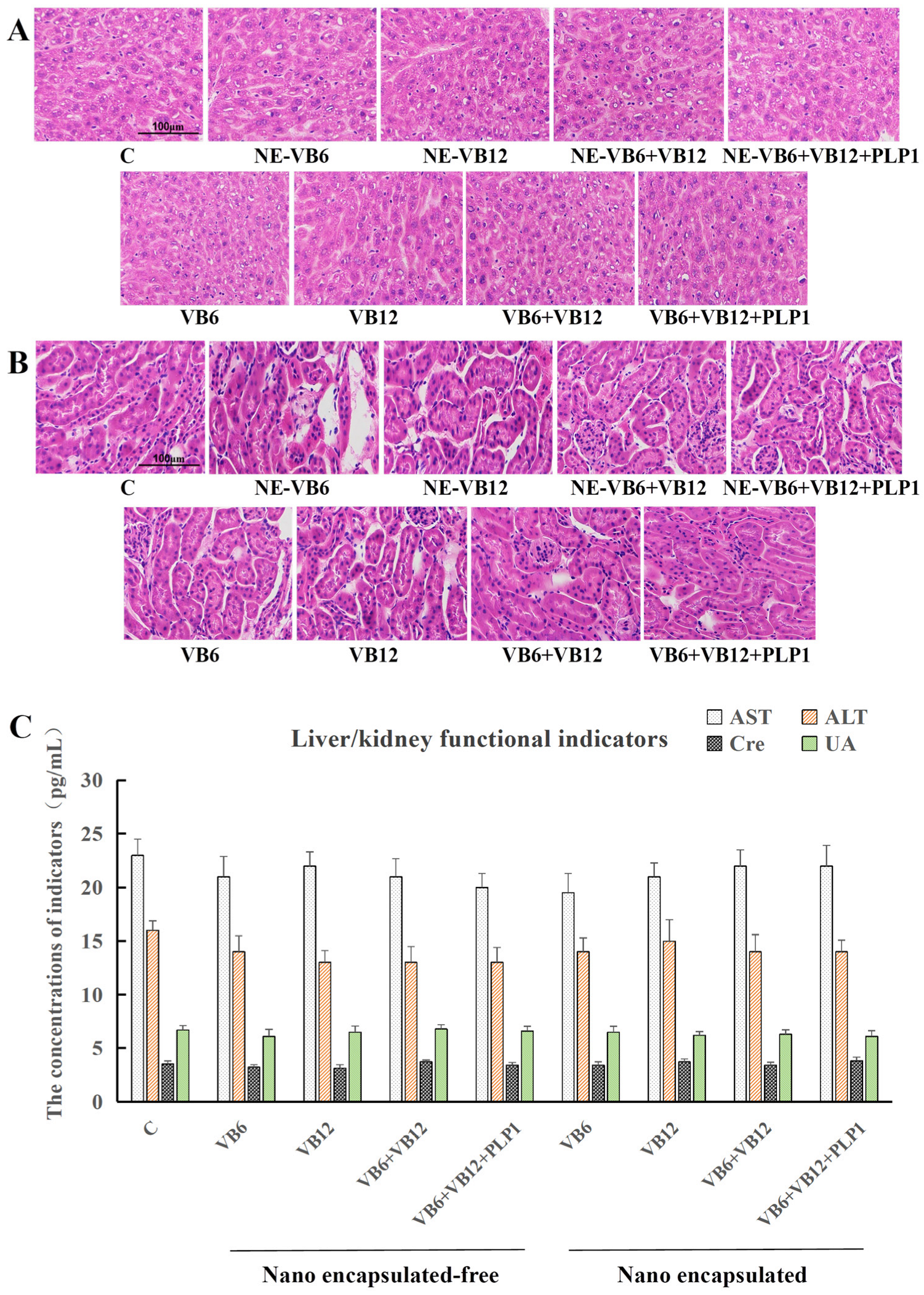
2.3.2. Absence of Systemic Toxicity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Determination of the Optimal Combination of VB6, VB12, and PLP-1 in the Drug Using Cell Experiments
4.1.1. Cell Culture
4.1.2. Construction of the Neurons Injury Model
4.1.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.2. Affinity Detection Between the PLP-1 Protein and Vitamins (B6/B12)
4.2.1. PLP-1 Protein
4.2.2. Molecular Docking Analysis of the PLP-1-Vitamin Interactions
- center_x = −5.6
- center_y = −11.3
- center_z = 9.1
- size_x = 15.8
- size_y = 18.4
- size_z = 15.2
- center_x = −7.9
- center_y = −22.8
- center_z = 11.3
- size_x = 26.7
- size_y = 30.8
- size_z = 22.6
4.3. In Vivo Efficacy Validation
4.3.1. Animal Grouping and Drug Administration
4.3.2. Vestibular Injury Model Establishment
4.3.3. Preparation of the Nanoparticles
4.3.4. Preparation of the Intranasal Formulations
4.4. Post-Treatment Analysis
4.4.1. Detection of the Vitamin Concentrations in the Mouse Blood
4.4.2. ELISA Detection of the Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Factors in the Mouse Brain Tissue
4.4.3. ELISA Detection of the Liver and Kidney Function Markers in the Mouse Serum
4.5. Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE) Staining of Liver/Kidney Tissues
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALA | Alanine |
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| ASN | Asparagine |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| B6/VB6 | Vitamin B6 |
| B12/VB12 | Vitamin B12 |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| CHO | Chinese Hamster Ovary |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CoA | Coenzyme A |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| Cre | Creatinine |
| ECL | Enhanced Chemiluminescence |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| HRP | Horseradish Peroxidase |
| HS | Horse Serum |
| ICR | Institute of Cancer Research |
| IκBα | Inhibitor of Kappa B Alpha |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| iNOS | Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| ITC | Isothermal Titration Calorimetry |
| LC-MS | Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry |
| LEU | Leucine |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa-Light-Chain-Enhancer of Activated B cells |
| NLRP3 | NOD-Like Receptor Family Pyrin Domain Containing 3 |
| Nrf-2 | Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor 2 |
| P | Probability Value |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PC12 | Pheochromocytoma 12 |
| PEG | Polyethylene Glycol |
| PGC-1α | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Coactivator 1-alpha |
| PHE | Phenylalanine |
| PLP-1 | Proteolipid Protein 1 |
| p-JNK | Phospho-c-Jun N-terminal Kinase |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Fluoride |
| Raw 264.7 | Raw 264.7 Cell Line |
| RPMI 1640 | Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| SER | Serine |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| SPR | Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| TBST | Tris-Buffered Saline with Tween-20 |
| THR | Threonine |
| TMB | 3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| TYR | Tyrosine |
| UA | Uric Acid |
| V | Volt |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
References
- Zhang, N.; Song, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Lyu, Y.; Liu, J.; Mu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, G.; et al. IL-1β promotes glutamate excitotoxicity: Indications for the link between inflammatory and synaptic vesicle cycle in Ménière’s disease. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Mahmoudi, N.; Marouane, E.; Rastoldo, G.; Pericat, D.; Watabe, I.; Lapotre, A.; Tonetto, A.; Chabbert, C.; Tighilet, B. Microglial dynamics modulate vestibular compensation in a rodent model of vestibulopathy and condition the expression of plasticity mechanisms in the deafferented vestibular nuclei. Cells 2022, 11, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatti, D.; De Angelis, S.; Paolocci, G.; Minnetti, A.; Manzari, L.; Verdecchia, D.H.; Indovina, I.; Tramontano, M. The role of vestibular physical therapy in managing persistent postural-perceptual dizziness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigal, J.; Herrón-Arango, A.F.; Bedoya, M.J.; Chen, J.C.; Castillo-Bustamante, M. Persistent challenges: A comprehensive review of persistent postural-perceptual dizziness, controversies, and clinical complexities. Cureus 2024, 16, e60911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustina, A.D.; Danielski, L.G.; Novochadlo, M.M.; Goldim, M.P.; Joaquim, L.; Metzker, K.L.; DE Carli, R.J.; Denicol, T.; Cidreira, T.; Vieira, T.; et al. Vitamin B6 reduces oxidative stress in lungs and liver in experimental sepsis. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2019, 91, e20190434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, P.; Strippoli, V.; Fang, B.; Cimmino, L. B vitamins and one-carbon metabolism: Implications in human health and disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, K.; Dargahi, N.; Fraser, S.; Apostolopoulos, V. High-dose vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) displays strong anti-inflammatory properties in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated monocytes. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Zhuang, H.; Huang, W.; Sun, J. Neuroinflammation and energy metabolism: A dual perspective on ischemic stroke. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Yang, C.; Zadeh, M.; Sprague, S.M.; Lin, Y.-D.; Jain, H.S.; Determann, B.F., 2nd; Roth, W.H.; Palavicini, J.P.; Larochelle, J.; et al. Functional regulation of microglia by vitamin B12 alleviates ischemic stroke-induced neuroinflammation in mice. iScience 2024, 27, 109480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiz, A.K.; Gumus, E.; Karabulut, S.; Tastemur, Y.; Taskiran, A.S. Protective effects of lamotrigine and vitamin B12 on pentylenetetrazole-induced epileptogenesis in rats. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 118, 107915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicita, F.; Aiello, C.; Vasco, G.; Valeriani, M.; Stregapede, F.; Sancesario, A.; Armando, M.; Bertini, E. Expanding the clinical and mutational spectrum of the PLP-1-related hypomyelination of early myelinated structures (HEMS). Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, A.A.F.; Pierson, C.R.; Woltjer, R.L.; Hobson, G.M.; Golden, J.A.; Kupsky, W.J.; Schauer, G.M.; Bird, T.D.; Skoff, R.P.; Garbern, J.Y. Neuronal loss in Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease differs in various mutations of the proteolipid protein 1. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groh, J.; Hörner, M.; Martini, R. Teriflunomide attenuates neuroinflammation-related neural damage in mice carrying human PLP-1 mutations. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. The blood–brain barrier: Structure, regulation and drug delivery. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adepu, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Controlled Drug Delivery Systems: Current Status and Future Directions. Molecules 2021, 26, 5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yuhong, J.; Xin, P.; Han, J.L.; Du, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, W.; et al. Advances in Nanotechnology for Enhancing the Solubility and Bioavailability of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2024, 18, 1469–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miatmoko, A.; Mianing, E.A.; Sari, R.; Hendradi, E. Nanoparticles use for delivering ursolic acid in cancer therapy: A scoping review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 787226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L.; Song, P.; Liu, B.; Chen, Q.; Deng, G. Ursolic acid nanoparticles for glioblastoma therapy. Nanomedicine 2023, 50, 102684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kinoshita, T.; Kushiyama, H.; Suidasari, S.; Hatakeyama, M.; Imura, H.; Kato, N.; Suda, T. Vitamin B6 prevents IL-1β protein production by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 24517–24527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanaka, N.; Koyama, T.-A.; Komatsu, S.-I.; Nakamura, E.; Kanda, M.; Kato, N. Vitamin B6 suppresses NF-κB activation in LPS-stimulated mouse macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 16, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbs, G.B.Y.; Wasek, B.; Bottiglieri, T.; Malysheva, O.; Caudill, M.A.; Jadavji, N.M. Dietary vitamin B12 deficiency impairs motor function and changes neuronal survival and choline metabolism after ischemic stroke in middle-aged male and female mice. Nutr. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, A.; Rahman, M.U.; Khan, M.; Zahid, M.; Shahab, M.; Jiao, H.; Zeb, A.; Shah, S.A.; Khan, H. Vitamin B6 via p-JNK/Nrf-2/NF-κB signaling ameliorates cadmium chloride-induced oxidative stress mediated memory deficits in mice hippocampus. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2024, 23, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.W.; Jeon, S.; Kwon, Y.H. Dietary vitamin B6 restriction aggravates neurodegeneration in mice fed a high-fat diet. Life Sci. 2022, 309, 121041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Shastri, D.H.; Shah, J.; Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. Nasal delivery to the brain: Harnessing nanoparticles for effective drug transport. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formica, M.L.; Real, D.A.; Picchio, M.L.; Catlin, E.; Donnelly, R.F.; Paredes, A.J. On a highway to the brain: A review on nose-to-brain drug delivery using nanoparticles. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 29, 101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tan, J.; Guan, J. Lipid-based nanoparticles via nose-to-brain delivery: A mini review. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1214450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drath, I.; Richter, F.; Feja, M. Nose-to-brain drug delivery: From bench to bedside. Transl. Neurodegener. 2025, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xiong, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, M.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, X.; et al. Brain-targeted ursolic acid nanoparticles for anti-ferroptosis therapy in subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdan, H.; Patyal, P.; Kockara, N.T.; Wight, P.A. The wmN1 enhancer region in intron 1 is required for expression of human PLP1. Glia 2018, 66, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patyal, P.; Kockara, N.T.; Wight, P.A. The wmN1 Enhancer Region of the Mouse Myelin Proteolipid Protein Gene (mPlp1) is Indispensable for Expression of an mPlp1-lacZ Transgene in Both the CNS and PNS. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patyal, P.; Fil, D.; Wight, P.A. Plp1 in the enteric nervous system is preferentially expressedduring early postnatal development in mouse as DM20, whose expression appears reliant on an intronic enhancer. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1175614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.; Korem, M.; Almog, R.; Galboiz, Y. Vitamin B12, demyelination, remyelination and repair in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2005, 233, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruskamo, S.; Raasakka, A.; Pedersen, J.S.; Martel, A.; Škubník, K.; Darwish, T.; Porcar, L.; Kursula, P. Human myelin proteolipid protein structure and lipid bilayer stacking. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group | Treatment Description | Formulation | Dosage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Control | - | No treatment |
| 2 | Model | - | Model establishment only |
| 3 | VB6 | Free drug | VB6 (2 μmol/kg body weight (b.w.)) |
| 4 | VB12 | Free drug | VB12 (0.2 μmol/kg b.w.) |
| 5 | VB6 + VB12 | Free drug | VB6 (2 μmol/kg b.w.) + VB12 (0.2 μmol/kg b.w.) |
| 6 | PLP-1 + VB6 + VB12 | Free drug | PLP-1 (1 μmol/kg b.w.) + VB6 (2 μmol/kg b.w.) + VB12 (0.2 μmol/kg b.w.) |
| 7 | Nano-VB6 | Nano-encapsulated | VB6 (2 μmol/kg b.w.) |
| 8 | Nano-VB12 | Nano-encapsulated | VB12 (0.2 μmol/kg b.w.) |
| 9 | Nano-VB6-VB12 | Nano-encapsulated | VB6 (2 μmol/kg b.w.) + VB12 (0.2 μmol/kg b.w.) |
| 10 | Nano-PLP-1-VB6-VB12 | Nano-encapsulated | PLP-1 (1 μmol/kg b.w.) + VB6 (2 μmol/kg b.w.) + VB12 (0.2 μmol/kg b.w.) |
| Parameter | Condition | |
|---|---|---|
| Column | Agilent ZORBAX SB-C18 (4.6 × 150 mm, 5 μm) (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) | |
| Mobile phase | A: 0.2% formic acid in water B: Acetonitrile | |
| Flow rate | 0.2 mL/min | |
| Gradient elution | Time (min) | %B |
| 0–0.5 | 30 | |
| 0.5–2 | 30 → 80 | |
| 2–3 | 80 → 98 | |
| 3–5 | 98 | |
| 5–7 | 98 → 30 | |
| 7–9 | 30 | |
| Run time | 9 min | |
| Injection volume | 2 μL | |
| Column Temperature | 35 °C | |
| Detection Wavelength | 330 nm |
| Component | Concentration | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin B6 (VB6) | 25 µM | Molar ratio of VB6:VB12 = 10:1 |
| Vitamin B12 (VB12) | 2.5 µM | |
| PLP-1 protein | 5 µM | Molar ratio of VB6:PLP-1 = 5:1 |
| Vehicle | Physiological saline | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dou, X.; Cai, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Gao, D. Synergistic Effect Evaluation and Mechanism Investigation of Vitamin B6 and B12 in Models of Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210956
Dou X, Cai S, Liu Y, Wang J, Li H, Gao D. Synergistic Effect Evaluation and Mechanism Investigation of Vitamin B6 and B12 in Models of Neuroinflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):10956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210956
Chicago/Turabian StyleDou, Xixi, Shiru Cai, Yingbo Liu, Junyan Wang, Huiying Li, and Duo Gao. 2025. "Synergistic Effect Evaluation and Mechanism Investigation of Vitamin B6 and B12 in Models of Neuroinflammation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 10956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210956
APA StyleDou, X., Cai, S., Liu, Y., Wang, J., Li, H., & Gao, D. (2025). Synergistic Effect Evaluation and Mechanism Investigation of Vitamin B6 and B12 in Models of Neuroinflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 10956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210956






