The Pathogenesis, Potential Biomarkers and Novel Therapeutic Strategies for Tubulointerstitial Nephritis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus—A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
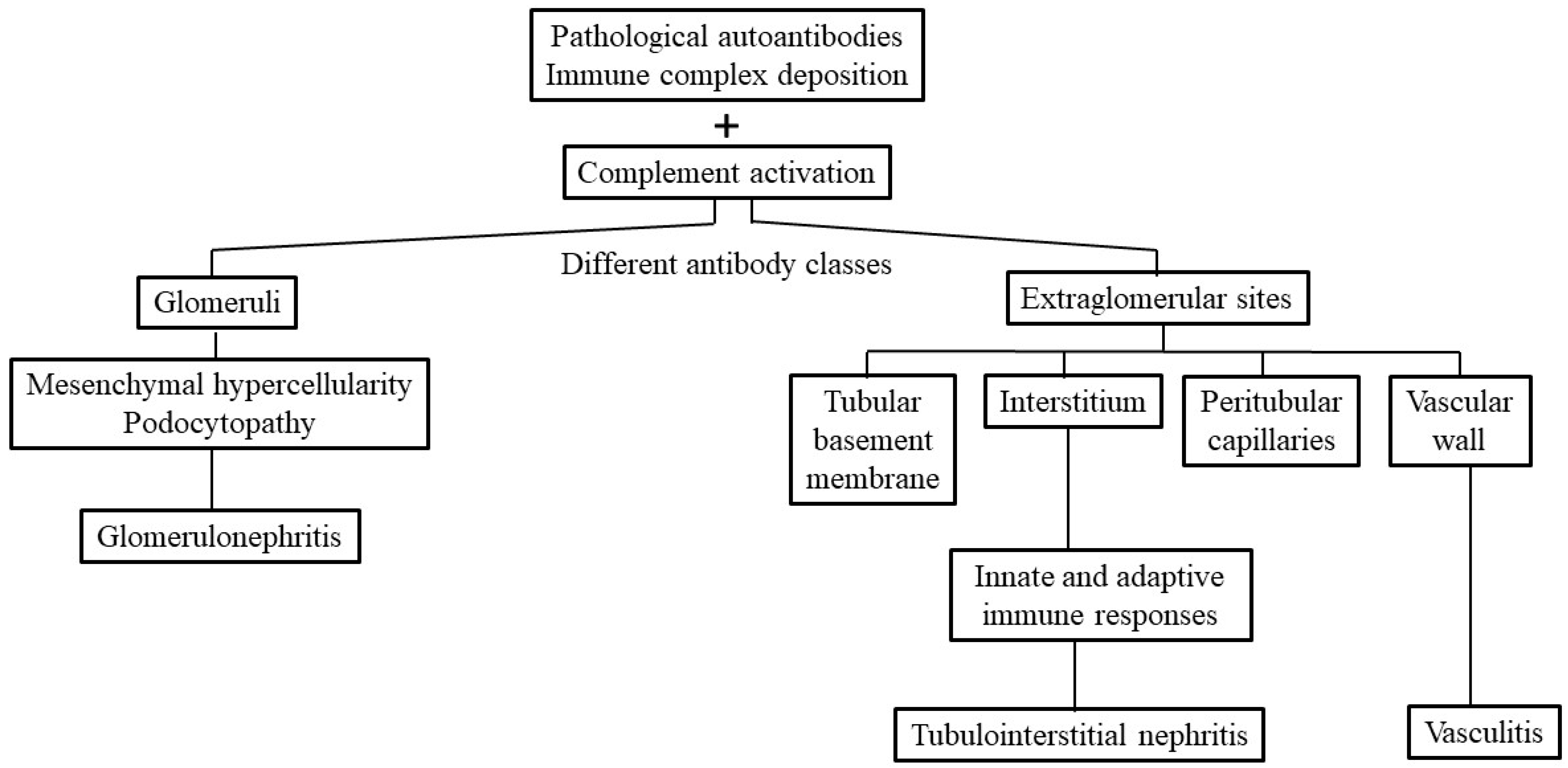
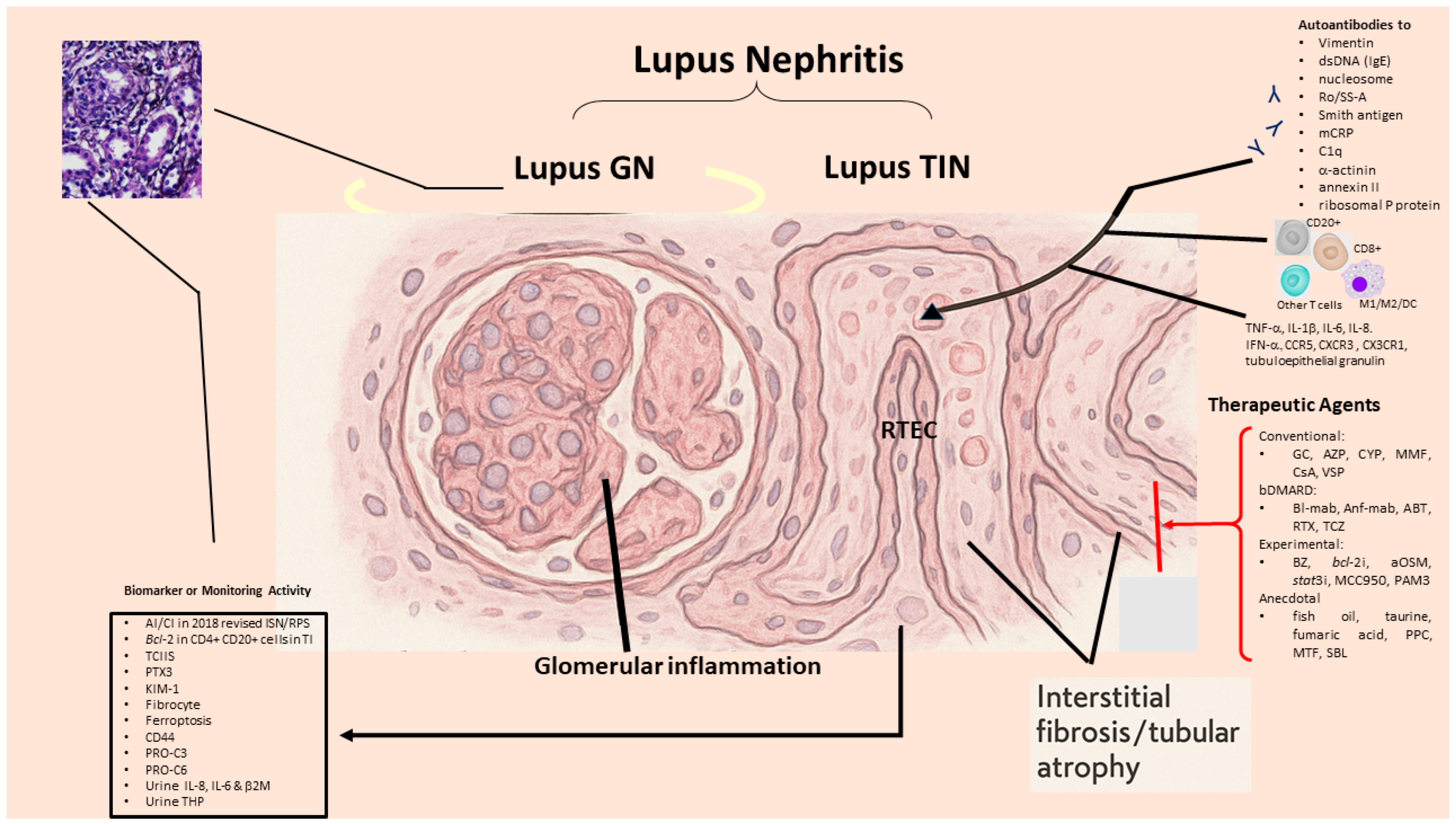
2. Pathologic Findings and Immunopathogenic Mechanisms in SLE-TIN
2.1. Immunopathological Findings in SLE-Tubulointerstitial Inflammation
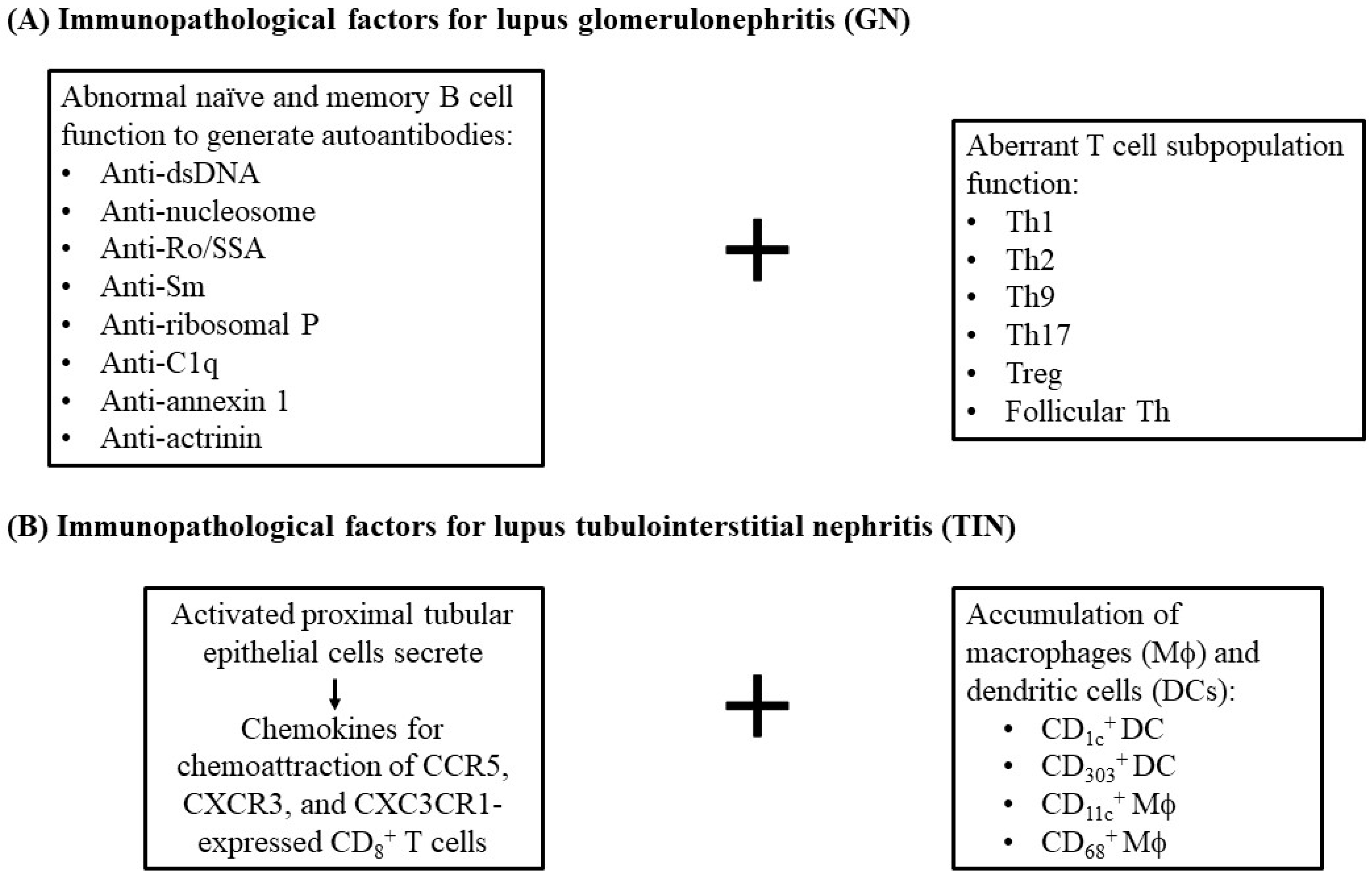
2.2. Immunopathogenic Basis for SLE-TIN
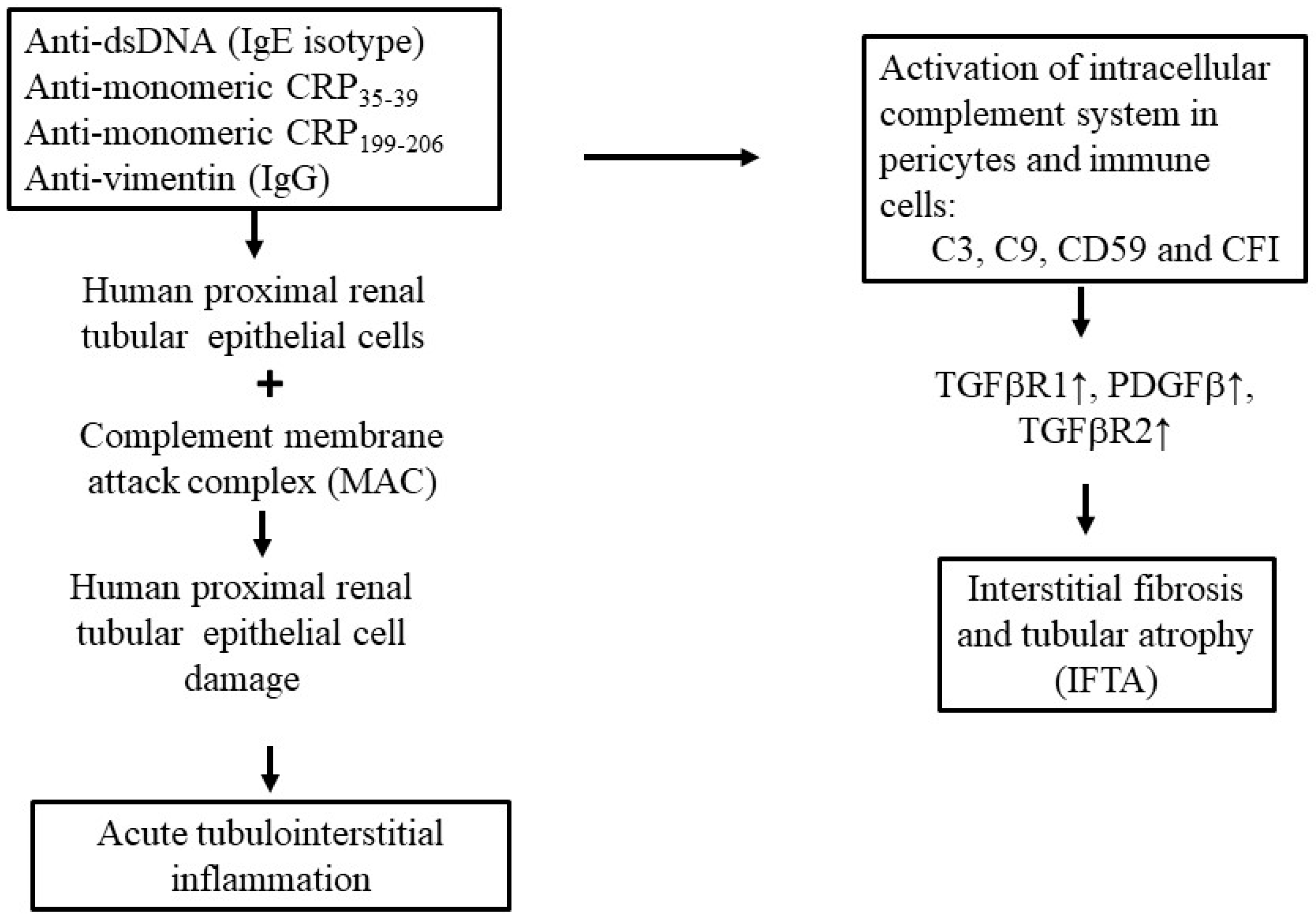
2.2.1. Role of Anti-dsDNA Antibodies
2.2.2. Role of Anti-Monomeric or Anti-Modified CRP (Anti-mCRP) Antibodies in SLE-Tubulointerstitial Inflammation
2.2.3. Other Autoantibodies That Induce Human Lupus TIN
2.2.4. Viral Infection as a Possible Etiology of Tubulointerstitial Nephritis in SLE
3. Factors Directly Associated with Interstitial Fibrosis/Tubular Atrophy (IFTA) in LN-Tubulointerstitial Inflammation
4. Specific or Nonspecific Biomarkers for SLE-TIN
4.1. Pentraxin 3 (PTX3) Is Closely Associated with TI Injury
4.2. Renal Tubular Epithelial Granulin Is Implicated in TLR9/IFN-α-Mediated Tubulointerstitial Injury in LN
4.3. Urinary Excretion of β2-Microglubulin (β-2M) in SLE-Tubulointerstitial Inflammation
4.4. Tamm-Horsfall Protein (THP) in SLE-Tubulointerstitial Inflammation
4.5. Tissue and Cell Collagens: Biomarkers Associated with Kidney Fibrosis in SLE-Tubulointerstitial Inflammation
4.6. Fibrocyte
4.7. Ferroptosis
4.8. CD44 Molecule
4.9. Parvovirus B19
5. Controversies Regarding the Tubulointerstitial Inflammation, Tubular Atrophy and Fibrosis as Predictors for Renal Outcome in LN
6. Potential Therapeutic Strategy for SLE-Tubulointerstitial Inflammation
6.1. Novel Therapeutic Strategies in Murine SLE
6.2. Bcl-2 as a Therapeutic Target in Human Tubulointerstitial Inflammation
6.3. Anti-Oncostatin M Antibody (Anti-OSM) Inhibits TI Lesion in Murine LN-Tubulointerstitial Inflammation
6.4. STAT3 Inhibitors Ameliorate TI Lesion in Autoimmune Lupus Mice
6.5. Roles and Therapeutic Potential of NLRP3 Inflammasome in LN-Tubulointerstitial Inflammation
6.6. Macrophages as a Potential Therapeutic Target in LN-Tubulointerstitial Inflammation
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
- Investigation of more reliable urinary biomarkers in relation to SLE-tubulointerstitial inflammation histopathology.
- Identification of driving genes in SLE-tubulointerstitial inflammation based on bioinformatics and AI.
- Identification of novel therapeutic modalities to transform phenotypic M1 to M2 macrophages in SLE-tubulointerstitial inflammation by hampering oxidative stresses.
- Development of molecules to target non-coding RNAs involved in LN and SLE-tubulointerstitial inflammation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, C.H.; Sammaritano, L.R. Systemic lupus erythematosus: A review. JAMA 2024, 331, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, L.; Seshan, S.V. Lupus nephritis—The significant contribution of electron microscopy. Glomerular Dis. 2021, 1, 180–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoskar, A.A.; Brodsky, S.V.; Nadasdy, G.; Bott, C.; Rovin, B.; Hebert, L.; Nadasdy, T. Discrepancies in glomerular and tubulointerstitial/vascular immune complex IgG subclasses in lupus nephritis. Lupus 2011, 20, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Henderson, S.G.; Brandt, D.; Liu, N.; Guttikonda, R.; Hsieh, C.; Kaverina, N.; Ulset, T.O.; Meehan, S.M.; Quigg, R.J.; et al. In situ B cell-mediated immune responses and tubulointerstitial inflammation in human lupus nephritis. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1849–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Ren, Y.L.; Cheng, M.; Guo, Z.L.; Zhang, J.C.; Cheng, H.; Xing, G.L.; Wang, S.X.; et al. Tubular basement membrane immune complex deposition is associated with activity and progression of lupus nephritis: A large multicenter Chinese study. Lupus 2018, 27, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, V.; Brainer, J.; Henriksen, K.J.; Cenacchi, G.; Chang, A. Extraglomerular immune complex deposition in lupus nephritis. Lupus 2022, 31, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.H.; D’Agati, V.; Appel, G.B.; Pirani, C.L. Tubulointerstitial disease in lupus nephritis—Relationship to immune deposits, interstitial inflammation, glomerular changes, renal function, and prognosis. Nephron 1986, 44, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Kishimoto, N.; Yamahara, H.; Kijima, Y.; Nose, A.; Uchiyama-Tanaka, Y.; Fukui, M.; Kitamura, T.; Tokoro, T.; Masaki, H.; et al. Predominant tubulointerstitial nephritis in a patient with systemic lupus nephritis. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2005, 9, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, S.; Nakabayashi, K.; Karube, M.; Arimura, Y.; Soejima, A.; Yamada, A.; Fujioka, Y. Tubulointerstitial immune complex nephritis in a patient with system lupus erythematosus—Role of peritubular capillaritis with immune complex deposits in the pathogenesis of the tubulointerstitial nephritis. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2006, 10, 146–151, Correction in Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2011, 15, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leatherwood, C.; Speyer, C.B.; Feldman, C.H.; D’Silva, K.; Gómez-Puerta, J.A.; Hoover, P.J.; Waikar, S.S.; McMahon, G.M.; Rennke, H.G.; Costenbader, K.H. Clinical characteristics and renal prognosis associated with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IFTA) and vascular injury in lupus nephritis biopsies. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perico, L.; Conti, S.; Benigni, A.; Remuzzi, G. Podocyte-actin dynamics in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 692–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Abdi, R.; Tsokos, G.C. The role of podocytes in lupus pathology. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2025, 27, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.S.; Schwartz, M.M.; Lewis, E.J. Association of glomerular podocytopathy and nephrotic proteinuria in mesangial lupus nephritis. Lupus 2006, 15, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, T.; Ichinose, K.; Tsokos, G.C. Tissue resident cell processes determine organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 234, 108919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brentjens, J.R.; Sepulveda, M.; Baliah, T.; Bentzel, C.; Erlanger, B.F.; Elwood, C.; Montes, M.; Hsu, K.C.; Andres, G.A. Interstitial immune complex nephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Kidney Int. 1975, 7, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, S.; Chang, T.M. Autoantibodies and resident renal cells in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis—Getting to know the unknown. Clin. Develop. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 139365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, D.Y.H.; Lai, K.N. Pathogenesis of renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus—The role of autoantibodies and lymphocytes subset abnormalities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7917–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockwell, P.; Calderwood, J.W.; Brooks, C.J.; Chakravorty, S.J.; Savage, C.O.S. Chemoattraction of T cells expressing CCR5, CXCR3 and CX3CR1 by proximal tubular epithelial cell chemokines. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002, 17, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassianos, A.J.; Wang, X.; Sampangi, S.; Afrin, S.; Wilkinson, R.; Healy, H. Fractalkine-CX3CR1-depedent recruitment and retention of human CD1c+ myeloid dendritic cells by in vitro-activated proximal tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Gu, X.; Herrera, G.A. Dendritic cells in renal biopsies of patients with acute tubulointerstitial nephritis. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 54, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Healy, H.; Kassianos, A.J. The emerging role of renal tubular epithelial cells in the immunological pathophysiology of lupus nephritis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 578952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, J.H.; Jung, J.; Jeon, H.; Lee, S.; Lim, J.S.; Go, H.; Oh, J.S.; Kim, Y.-G.; Lee, C.-K.; et al. Immunological characteristics and possible pathogenic role of urinary CD11c+ macrophages in lupus nephritis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cui, L.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, W. Clinicopathological significance of tubulointerstitial CD68 macrophages in proliferative lupus nephritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandersfeld, M.; Büttner-Herold, M.; Ferrazzi, F.; Amann, K.; Benz, K.; Daniel, C. Macrophage subpopulations in pediatric patients with lupus nephritis and other inflammatory diseases affecting the kidney. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Feng, X.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Z. Association between tubulointerstitial CD8+ T cells and renal prognosis in lupus nephritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 107877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoicӑi, T.; Avӑdӑnei, E.-R.; Giusca, S.-E.; Onofriescu, M.; Covic, A.C.; Dascalu, C.G.; Cӑruntu, I.-D. Dynamics of CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrates in lupus nephritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, S.; Tsang, R.C.W.; Sun, Y.; Leung, J.K.H.; Chan, T.M. Effect of human anti-DNA antibodies on proximal renal tubular epithelial cell cytokine expression—Implications on tubulointerstitial inflammation in lupus nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3281–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, S.; Ng, C.Y.C.; Au, K.Y.; Cheung, K.F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Yap, D.Y.H.; Chau, M.K.M.; Chan, T.M. Binding of anti-dsDNA antibodies to proximal tubular epithelial cells contributes to renal tubulointerstitial inflammation. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.-K.; Tsokos, G.C. New insights into the role of renal resident cell in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. Korean. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yuan, M.; Tan, Y.; Zhao, M. Serum IgE anti-dsDNA autoantibodies in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis are associated with tubulointerstitial inflammation. Ren. Fail. 2023, 45, 2273981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabs, W.J.; Lögering, B.A.; Gerke, P.; Kreft, B.; Wolber, E.-M.; Klinger, M.H.F.; Fricke, L.; Steinhoff, J. The kidney as a second site of human C-reactive protein formation in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasojima, K.; Schwab, C.; McGeer, E.G.; McGeer, P.L. Human neurons generate C-reactive protein and amyloid P—Upregulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 2000, 887, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuta, A.E.; Baum, L.L. C-reactive protein is produced by a small number of normal human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1986, 164, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Wright, J.R. Expression of C-reactive protein by alveolar macrophages. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 4815–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potempa, L.A.; Zeller, J.M.; Fiedel, B.A.; Kinoshita, C.M.; Gewurz, H. Stimulation of human neutrophils, monocytes, and platelets by modified C-reactive protein (CRP) expressing a neoantigenic specificity. Inflammation 1988, 12, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potempa, L.A.; Maldonado, B.A.; Laurent, P.; Zemel, E.S.; Gewurz, H. Antigenic, electrophoretic and binding alterations of human C-reactive protein modified selectively in the absence of calcium. Mol. Immunol. 1983, 20, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Yu, F.; Yang, H.; Chem, M.; Fang, Q.; Zhao, M.-H. Autoantibodies against monomeric C-reactive protein in sera from patients with lupus nephritis are associated with disease activity and renal tubulointerstitial lesions. Hum. Immunol. 2008, 69, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.-W.; Tan, Y.; Yu, F.; Zhao, M.-H. Interference of antimodified C-reactive protein autoantibodies from lupus nephritis in the biofunctions of modified C-reactive protein. Hum. Immunol. 2012, 73, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Tan, Y.; Zhao, M.-H. The role of anti-mCRP autoantibodies in lupus nephritis. Kidney Dis. 2023, 9, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Zhao, M.-H.; Tan, Y. The anti-mCRP199–206 antibodies aggravate tubulointerstitial lesions in lupus nephritis. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 268, 110353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Liu, X.-L.; Tan, Y.; Yu, F.; Zhao, M.-H. Urinary modified C-reactive protein is closely associated with tubulointerstitial lesions in lupus nephritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 6107911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.; Chang, A.; Brandt, D.; Guttikonda, R.; Utset, T.O.; Clark, M.R. Predicting outcomes of lupus nephritis with tubulointerstitial inflammation and scarring. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Wu, L.-H.; Tan, Y.; Li, L.-H.; Wang, C.-L.; Wang, W.-K.; Qu, Z.; Chen, M.-H.; Gao, J.-J.; Li, Z.-Y.; et al. Tubulointerstitial lesions of patients with lupus nephritis classified by the 2003 International Society of Nephrology and Renal Pathology Society system. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, A.J.; Chang, A.; Ko, K.; Dunand, C.J.H.; Henderson, S.; Maienschein-Cline, M.; Kaverina, N.; Rovin, B.H.; Ferrer, M.S.; Wolfgeher, D.; et al. Vimentin is a dominant target of in situ humoral immunity in human lupus tubulointerstitial nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 3359–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, A.J.; Cascino, M.D.; Dai, J.; Bermea, R.S.; Ko, K.; Vesselits, M.; Dragone, L.L.; Vaknin, N.M.; Legendre, M.; Markovitz, D.M.; et al. Anti-vimentin antibodies: A unique antibody class associated with therapy-resistant lupus nephritis. Lupus 2020, 29, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, A.J.; Asano, Y.; Mohsin, A.; Henry, C.; Abraham, R.; Chang, A.; Labno, C.; Wilson, P.C.; Clark, M.R. Machine learning to quantify in situ humoral selection in human lupus tubulointerstitial inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 593177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, M.; Kopp, J.B. Parvovirus B19 and the kidney. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2 (Suppl. S1), S47–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quanjine, A.; Fendri, F.; Kerdraon, R.; Dekeyser, M. Parvovirus B19-induced membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis in an immunocompetent adult patient: A case report. Cureus 2025, 17, e87038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Wada, Y.; Yamazaki, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Abe, T.; Naito, S.; Aoyama, T.; Sano, T.; Moriya, R.; Oda, T.; et al. Parvovirus B19-related membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis presenting with positive glomerular staining for nephritis-associated plasmin receptor: A case report and review of the literature. CEN Case Rep. 2025, 14, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, F.; Collazos, J.; Mendoza, F.; De la Viuda, J.M.; Cazallas, J.; Urkijo, J.C.; Flores, M. Systemic lupus erythematosus associated with acute parvovirus B19 infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2002, 8, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, S.; Hirata, M.; Ito, K.; Mizushima, I.; Fujii, H.; Yamada, K.; Nagata, M.; Kawano, M. Post-infectious acute glomerulonephritis with podocytopathy induced by parvovirus B19 infection. Pathol. Int. 2018, 68, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyam, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Ishimura, M.; Tetsuhara, K.; Imai, T.; Kanemasa, H.; Ueki, K.; Motomura, Y.; Kaku, N.; Sakai, Y.; et al. Parvovirus B19-infected tubulointerstitial nephritis in hereditary spherocytosis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wu, H.; Chiriboga, L.; Zeck, B.; Goilav, B.; Wang, S.; Londono-Jimenez, A.; Putterman, C.; Schwartz, D.; Pullman, J.; et al. Membrane attack complex (MAC) deposition in renal tubules is associated with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy: A pilot study. Lupus Sci. Med. 2022, 9, e000576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, D.; Xavier, S. Role of intracellular complement activation in kidney fibrosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 2880–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, S.; Sahu, R.K.; Landes, S.G.; Yu, J.; Taylor, R.P.; Ayyadevara, S.; Megyesi, J.; Stallcup, W.B.; Duffield, J.S.; Reis, E.S.; et al. Pericytes and immune cells contribute to complement activation in tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2017, 312, F516–F532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, S.; Sahu, R.K.; Bontha, S.V.; Mas, V.; Taylor, R.P.; Megyesi, J.; Thielens, N.M.; Portilla, D. Complement C1r serine protease contributes to kidney fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2019, 317, F1293–F1304, Correction in Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2020, 318, F283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Broder, A.; Shao, D.; Kesarwani, V.; Boderman, B.; Aguilan, J.; Sidoli, S.; Suzuki, M.; Greally, J.M.; Saenger, Y.M.; et al. Urine proteomics link complement activation with interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy in lupus nephritis patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2023, 63, 152263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvica, S.; Fenaroli, P.; Lee, C.-Y.; Louis, S.; Celia, A.I.; Bagnasco, S.; Yang, X.; Hodgin, J.B.; Buyon, J.; Magder, L.; et al. Inflammation in areas of fibrosis precedes loss of kidney function in lupus nephritis. bioRxiv 2024. bioRxiv: 2024.11.25.625225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broder, A.; Mowrey, W.B.; Khan, H.N.; Jovanovic, B.; Londono-Jimenez, A.; Izmirly, P.; Putterman, C. Tubulointerstitial damage predicts end stage renal disease in lupus nephritis with preserved to moderately impaired renal function—A retrospective cohort study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2018, 47, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovere, P.; Peri, G.; Fazzini, F.; Bottazzi, B.; Doni, A.; Bondanza, A.; Zimmermann, V.S.; Garlanda, C.; Fascio, U.; Sabbadini, M.G.; et al. The long pentraxin PTX3 binds to apoptotic cells and regulates their clearance by antigen-presenting dendritic cells. Blood 2000, 96, 4300–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Garlanda, C.; Doni, A.; Bottazzi, B. Pentraxins in innate immunity from C-reactive protein to the long pentraxin PTX3. J. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottazzi, B.; Vouret-Craviari, V.; Bastone, A.; De Giola, L.; Matteucci, C.; Peri, G.; Spreafico, F.; Pausa, M.; D’Ettorre, C.; Gianazza, E.; et al. Multimer formation and ligand recognition by the long pentraxin PTX3. Similarities and differences with the short pentraxins C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 32817–32823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breviario, F.; d’Aniello, E.M.; Golay, J.; Peri, G.; Bottazzi, B.; Bairoch, A.; Saccone, S.; Marzella, R.; Predazzi, V.; Rocchi, M.; et al. Interleukin-1-inducible genes in endothelial cells. Cloning of a new gene related to C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 22190–22197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.W.; Lee, T.H.; Vilcek, J. TSG-14, a tumor necrosis factor- and IL-1-inducible protein, is a novel member of the pentraxin family of acute phase proteins. J. Immunol. 1993, 150, 1804–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Hernandez, O.-D.; Bassi, N.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Anaya, J.-M. The long pentraxin 3 and its role in autoimmunity. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 39, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yu, F.; Zhao, M.H. Pentraxin 3 is closely associated with tubulointerstitial injury in lupus nephritis: A large multicenter cross-sectional study. Medicine 2016, 95, e2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, G.; Cafiero, C.; Divella, C.; Sallustio, F.; Gigante, M.; Pontrelli, P.; De Palma, G.; Rossini, M.; Grandaliano, G.; Gesualdo, L. Local synthesis of interferon-alpha in lupus nephritis is associated with type I interferons signature and LMP7 induction in renal tubular epithelial cells. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, M.; Liu, Y.-J. Regulation of TLR7/9 signaling in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Protein Cell. 2013, 4, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitraki, E.D.; Tzardi, M.; Bertsias, G.; Sotsiou, E.; Boumpas, D.T. Glomerular expression of toll-like receptor-9 in lupus nephritis but not in normal kidneys: Implications for the amplification of the inflammatory response. Lupus 2009, 18, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoyab, M.; McDonald, V.L.; Byles, C.; Todaro, G.J.; Plowman, G.D. Epithelin 1 and 2—Isolation and characterization of two cysteine-rich growth-modulating proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 7912–7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A.; Belcourt, D.; Bennett, H.; Lazure, C.; Solomon, S. Ganulins, a novel class of peptide from leukocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 173, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Banerjee, R.; Thomas, B.; Zhou, P.; Qian, L.; Jia, T.; Ma, X.; Ma, Y.; Iadecola, C.; Beal, M.F.; et al. Exaggerated inflammation, impaired host defense, and neuropathology in progranulin-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Buti, L.; Lee, S.; Matsuwaki, T.; Spooner, E.; Brinkmann, M.M.; Nishihara, M.; Ploegh, H.L. Granulin is a soluble cofactor for toll-like receptor 9 signaling. Immunity 2011, 34, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Dai, Y.; Geng, Z.; He, H.; Hong, F. Granulin in renal tubular epithelia is associated with interstitial inflammation and activates the TLR9-IFN-α pathway in lupus nephritis. Lupus 2024, 33, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, P.W., III.; Chung-Park, M.; Vacca, C.V.; London, M.; Crowley, A.Q. The renal handling of beta 2-microglobulin in the dog. Kidney Int. 1982, 22, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portman, R.J.; Kissane, J.M.; Robson, A.M.; Richardson, A. Use of ß2 microglobulin to diagnose tubulointerstitial renal lesions in children. Kidney Int. 1986, 30, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, J.R.; Resnick, J.S.; Michael, A.F.; Vernier, R.L. Ontogeny of Tamm-Horsfall urinary glycoprotein. Lab. Investig. 1974, 30, 756–761. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Muchmore, A. Tamm-Horsfall protein: Uromodulin (1950–1990). Kidney Int. 1990, 37, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Wu, T.-H.; Yu, C.-L.; Lu, J.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-Y. Increased excretions of β2-microglobulin, IL-6, and IL-8 and decreased excretion of Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein in urine of patients with active lupus nephritis. Nephron 2000, 85, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedair, R.N.; Ismail, M.M.A.; Gaber, E.W.; Mahmoud, R.A.K.; Mowafy, M.N. Study of the relationship between urinary level of uromodulin, renal involvement and disease activity in patients with system lupus erythematosus. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2020, 31, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thielemans, R.; Speeckaert, R.; Delrue, C.; de Bruyne, S.; Oyaert, M.; Speeckaert, M.M. Unveiling the hidden power of uromodulin—A promising potential biomarker for kidney diseases. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, B.-L.; Ivan, G.-N.J.; Emilio, P.-G.E.; Daniela, M.-S.J.; Betsabe, C.-H.; Luisa, V.-V.M.; Selene, F.-R.N.; Guadalupe, A.-C.E.A.; Miriam, S.-C.A.; Alfredo, C.; et al. Low serum uromodulin levels and their association with lupus flares. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caster, D.J.; Powell, D.W. Utilization of biomarkers in lupus nephritis. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019, 26, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Gao, B.; Shih, F.; Ranger, A.; Dearth, A.; Mischak, H.; Siwy, J.; Wisniacki, N.; Petri, M.; Burkly, L.C. Alterations in urinary collagen peptides in lupus nephritis subjects correlate with renal dysfunction and renal histopathology. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, F.; Akhgar, A.; Lim, S.S.; Farris, A.B.; Battle, M.; Cobb, J.; Sinibaldi, D.; Karsdal, M.A.; White, W.I. Collagen type III and VI remodeling biomarkers are associated with kidney fibrosis in lupus nephritis. Kidney360 2021, 2, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucala, R.; Spiegel, L.A.; Chesney, J.; Hogan, M.; Cerami, A. Circulating fibrocytes define a new leukocyte subpopulation that mediates tissue repair. Mol. Med. 1994, 1, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilkoff, R.A.; Bucala, R.; Herzog, E.L. Fibrocytes: Emerging effector cells in chronic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesney, J.; Metz, C.; Stavitsky, A.B.; Bacher, M.; Bucala, R. Regulated production of type 1 collagen and inflammatory cytokines by peripheral blood fibrocytes. J. Immunol. 1988, 160, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Go, H.; Lim, J.S.; Oh, J.S.; Ahn, S.M.; Kim, Y.-G.; Lee, C.-K.; Yoo, B.; Hong, S. Circulating and renal fibrocytes are associated with interstitial fibrosis in lupus nephritis. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frostegård, J.; Svenungsson, E.; Wu, R.; Gunnarsson, I.; Lundberg, I.E.; Klareskog, L.; Hörkkö, S.; Witztum, J.L. Lipid peroxidation is enhanced in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and is associated with arterial and renal disease manifestations. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lin, Z.; Feng, J.; Liang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, G.; Chen, R.; Fu, R. Identification of ferroptosis-related molecular markers in glomeruli and tubulointerstitium of lupus nephritis. Lupus 2022, 31, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alli, A.A.; Desai, D.; Elshika, A.; Conrad, M.; Proneth, B.; Clapp, W.; Atkinson, C.; Segal, M.; Searcy, L.A.; Denslow, N.D.; et al. Kidney tubular epithelial cell ferroptosis links glomerular injury to tubulointerstitial pathology in lupus nephritis. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 248, 109213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathcock, K.S.; Hirano, H.; Murakami, S.; Hodes, R.J. CD44 expression on activated B cells. Differential capacity for CD44-dependent binding to hyaluronic acid. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 6712–6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesley, J.; Howes, N.; Perschl, A.; Hyman, R. Hyaluronan binding function of CD44 is transiently activated on T cells during an in vitro immune response. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy-Chaudhury, P.; Khong, T.F.; Williams, J.H.; Haites, N.E.; Wu, B.; Simpson, J.G.; Power, D.A. CD44 in glomerulonephritis: Expression in human renal biopsies, the Thy1.1 model, and by cultured mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1996, 50, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benz, P.S.; Fan, X.; Wüthrich, R.P. Enhanced tubular epithelial CD44 expression in MRL-lpr lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 1996, 50, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Florquin, S.; Nunziata, R.; Claessen, N.; van den Berg, F.M.; Pals, S.T.; Weening, J.J. CD44 expression in IgA nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 39, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.C.Y.; Gao, L.Y.; Xu, Y.; Chau, M.K.M.; Zhang, D.; Yap, D.Y.H.; Ying, S.K.Y.; Lee, C.K.; Yung, S.; Chan, T.M. Cluster of differentiation-44 as a novel biomarker of lupus nephritis and its role in kidney inflammation and fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1443153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weening, J.J.; D’Agati, V.D.; Schwartz, M.M.; Seshan, S.V.; Alpers, C.E.; Appel, G.B.; Balow, J.E.; Bruijn, J.A.; Cook, T.; Ferrario, F.; et al. The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esdaile, J.M.; Levinton, C.; Federgreen, W.; Hayslett, J.P.; Kashgarian, M. The clinical and renal biopsy predictors of long-term outcome in lupus nephritis: A study of 87 patients and review of the literature. QJM 1989, 72, 779–833. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras, G.; Pardo, V.; Cely, C.; Borja, E.; Hurtado, A.; De La Cuesta, C.; Iqbal, K.; Lenz, O.; Asif, A.; Nahar, N.; et al. Factors associated with poor outcomes in patients with lupus nephritis. Lupus 2005, 14, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.M.; Fennell, J.S.; Lewis, E.J. Pathologic changes in the renal tubule in systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum. Pathol. 1982, 13, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsuwaida, A.O. Interstitial inflammation and long-term renal outcomes in lupus nephritis. Lupus 2013, 22, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.C.; Kashgarian, M.; Moeckel, G. Interstitial inflammation and interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy predict renal survival in lupus nephritis. Clin. Kidney J. 2018, 11, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.F.; Mardones, C.; Xipell, M.; Blasco, M.; Solé, M.; Espinosa, G.; García-Herrera, A.; Cervera, R.; Quintana, L.F. The extent of tubulointerstitial inflammation is an independent predictor of renal survival in lupus nephritis. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajema, I.M.; Wilhelmus, S.; Alpers, C.E.; Bruijn, J.A.; Colvin, R.B.; Cook, H.T.; D’Agati, V.D.; Ferrario, F.; Haas, M.; Jennette, J.C.; et al. Revision of the International Society of Nephrology/Renal Pathology Society classification for lupus nephritis: Clarification of definitions, and modified National Institutes of Health activity and chronicity indices. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Nam, E.J.; Han, M.H.; Kim, Y.J. Interstitial inflammation in the ISN/RPS 2018 classification of lupus nephritis predicts renal outcomes and is associated with Bcl-2 expression. J. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 29, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, M.D.; Wang, S.; Schwartz, D.; Mowrey, W.B.; Broder, A.; Goilav, B. Total cortical interstitial inflammation predicts chronic kidney disease progression in patients with lupus nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J. The proteasome—A suitable antineoplastic target. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubert, K.; Meister, S.; Moser, K.; Weisel, F.; Maseda, D.; Amann, K.; Wiethe, C.; Winkler, T.H.; Kalden, J.R.; Manz, R.A.; et al. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib depletes plasma cells and protects mice with lupus-like disease from nephritis. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainz, N.; Thomas, S.; Neubert, K.; Meister, S.; Benz, K.; Rauh, M.; Daniel, C.; Wiesener, M.; Voll, R.E.; Amann, K. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib prevents lupus nephritis in the NZB/W F1 mouse model by preservation of glomerular and tubulointerstitial architecture. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 2012, 120, e47–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.; Wang, J.; Perper, S.; Jiang, Y.; Yanez, D.; Kaverina, N.; Ai, J.; Liarski, V.M.; Chang, A.; Peng, Y.; et al. Bcl-2 as a therapeutic target in human tubulointerstitial inflammation. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2740–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Miyajima, A. Oncostatin M, a multifunctional cytokine. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 149, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robak, E.; Sysa-Jedrzejowska, A.; Stepień, H.; Robak, T. Circulating interleukin-6 type cytokines in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 1997, 8, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale, J.; Patel, S.; Suzuki, N.; Buxton, R.; Takagi, K.-I.; Suzuki, J.; Sumi, Y.; Imaizumi, A.; Mason, R.M.; Zhang, Z. Oncostatin M, a cytokine released by activated mononuclear cells, induces epithelial cell-myofibroblast transdifferentiation via Jak/Stat pathway activation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollack, V.; Sarközi, R.; Banki, Z.; Feifel, E.; Wehn, S.; Gstraunthaler, G.; Stoiber, H.; Mayer, G.; Montesano, R.; Strutz, F.; et al. Oncostatin M-induced effects on EMT in human proximal tubular cells: Differential role of ERK signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2007, 293, F1714–F1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Du, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, W.; Feng, X.; Hao, J.; Li, H.; Liu, S. Anti-OSM antibody inhibits tubulointerstitial lesion in a murine model of lupus nephritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 3038514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, S.; Feng, X.; Gao, F.; Liu, Q. S3I-201 ameliorates tubulointerstitial lesion of the kidneys in MRL/lpr mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; He, F.; Kyttaris, V.C. T cell specific STAT3 deficiency abrogates lupus nephritis. Lupus 2019, 28, 1468–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lv, Y.; Chen, T. STAT3 inhibition ameliorates renal interstitial inflammation in MRL/lpr mice with diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2358187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-T.; Fan, S.; Li, X.-Y.; Hou, R.; Hu, X.-W.; Wang, J.-N.; Shan, R.-R.; Dong, Z.-H.; Xie, M.-M.; Dong, Y.-H.; et al. Novel insights into STAT3 in renal diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.S.; Kang, Y.; Lee, N.; Wahl, E.R.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, K.S.; Lazova, R.; Kang, I. Self double-stranded (ds)DNA induces IL-1β production from human monocytes by activating NLRP3 inflammasome in the presence of anti-dsDNA antibodies. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinon, F.; Burns, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasome: A molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mod. Cell. 2002, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ruan, J.; Pan, Y.; Magupalli, V.G.; Wu, H.; Lieberman, J. Inflammasome-activated gasdermin D causes pyroptosis by forming membrane pores. Nature 2016, 535, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlenberg, J.M.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Smith, C.K.; Kaplan, M.J. Neutrophil extracellular trap-associated protein activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome is enhanced in lupus macrophages. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, G.; Darisipudi, M.N.; Anders, H.-J. Canonical and non-canonical effects of the NLRP3 inflammasome in kidney inflammation and fibrosis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.B.; Lima, C.A.D.; Vajgel, G.; Sandrin-Garcia, P. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in lupus nephritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, R.C.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Chae, J.J.; Higgins, S.C.; Munoz-Planillo, R.; Inserra, M.C.; Vetter, I.; Dungan, L.S.; Monks, B.G.; Stutz, A.; et al. A small molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome is a potential therapeutic for inflammatory diseases. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, J.; Wu, J.; Yang, X. Therapeutic potential of MCC950, a specific inhibitor of NLRP3 inflammasome in systemic lupus erythematosus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 172, 116261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orme, J.; Mohan, C. Macrophage subpopulations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Discov. Med. 2012, 13, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer, L.; Bethunaickan, R.; Ramanujam, M.; Huang, W.; Schiffer, M.; Tao, H.; Madaio, M.P.; Bottinger, E.P.; Davidson, A. Activated renal macrophages are markers of disease onset and disease remission in lupus nephritis. J. Immnol. 2008, 180, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horuluoglu, B.; Bayik, D.; Kayraklioglu, N.; Goguet, E.; Kaplan, M.J.; Klinman, D.M. PAM3 supports the generation of M2-like macrophages from lupus patient monocytes and improves disease outcome in murine lupus. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 99, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwant, L.E.; Vegting, Y.; Tsang-A-Sjoe, M.W.P.; Kwakernaak, A.J.; Vogt, L.; Voskuyl, A.E.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; de Winther, M.P.J.; Bemelman, F.J.; Anders, H.-J.; et al. Macrophages in lupus nephritis: Exploring a potential new therapeutic avenue. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Tang, S.; Chen, F.; Ren, X.; Han, X.; Zhou, X. Regulation of macrophage polarization by targeted metabolic reprogramming for the treatment of lupus nephritis. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
| Agents | Actions and Effectiveness |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, C.-Y.; Wu, T.-H.; Ou, S.-M.; Lee, H.-T.; Shen, C.-Y.; Lu, C.-H.; Tsai, W.-H.; Yu, C.-L. The Pathogenesis, Potential Biomarkers and Novel Therapeutic Strategies for Tubulointerstitial Nephritis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus—A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210903
Tsai C-Y, Wu T-H, Ou S-M, Lee H-T, Shen C-Y, Lu C-H, Tsai W-H, Yu C-L. The Pathogenesis, Potential Biomarkers and Novel Therapeutic Strategies for Tubulointerstitial Nephritis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus—A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):10903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210903
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Chang-Youh, Tsai-Hung Wu, Shuo-Ming Ou, Hui-Ting Lee, Chieh-Yu Shen, Cheng-Hsun Lu, Wan-Hao Tsai, and Chia-Li Yu. 2025. "The Pathogenesis, Potential Biomarkers and Novel Therapeutic Strategies for Tubulointerstitial Nephritis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus—A Narrative Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 10903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210903
APA StyleTsai, C.-Y., Wu, T.-H., Ou, S.-M., Lee, H.-T., Shen, C.-Y., Lu, C.-H., Tsai, W.-H., & Yu, C.-L. (2025). The Pathogenesis, Potential Biomarkers and Novel Therapeutic Strategies for Tubulointerstitial Nephritis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus—A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 10903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210903






